Classification of Ameloblastoma, Periapical Cyst, and Chronic Suppurative Osteomyelitis with Semi-Supervised Learning: The WaveletFusion-ViT Model Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient and Data Collection
2.2. Image Preprocessing and Augmentation
2.3. Proposed Framework
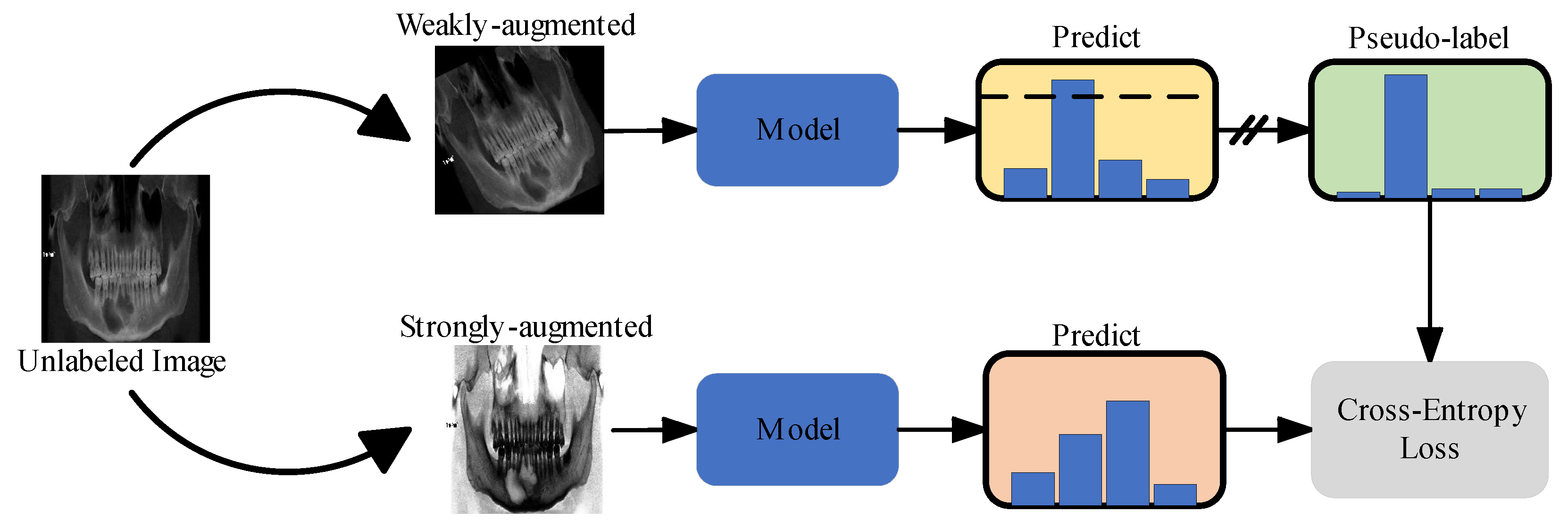
2.3.1. Semi-Supervised Learning
2.3.2. Domain Adaptation Networks
2.3.3. Wavelet Extraction and Fusion Module
2.4. Training Setup
2.5. Model Assessment
3. Results
3.1. Sample Characteristics
3.2. Model Classification Performance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mao, W.Y.; Lei, J.; Lim, L.Z.; Gao, Y.; Tyndall, D.A.; Fu, K. Comparison of radiographical characteristics and diagnostic accuracy of intraosseous jaw lesions on panoramic radiographs and CBCT. Dento Maxillo Facial Radiol. 2021, 50, 20200165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, Y.S.; Sohal, K.S.; Stoelinga, P.J.W.; Grillo, R. A meta-analysis on the presentation of Unicystic Ameloblastoma in the jaws and the consequences for their treatment. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 123, e433–e438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muraoka, H.; Kaneda, T.; Hirahara, N.; Ito, K.; Okada, S.; Kondo, T. Diagnostic Efficacy of Diffusion-weighted Imaging in Distinguishing Chronic Diffuse Sclerosing Osteomyelitis from Suppurative Osteomyelitis of the Mandible. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. MRMS Off. J. Jpn. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 2023, 22, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsesis, I.; Krepel, G.; Koren, T.; Rosen, E.; Kfir, A. Accuracy for diagnosis of periapical cystic lesions. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shear, M.; Speight, P.M. Cysts of the Oral and Maxillofacial Regions; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Koenig, L.J.; Tamimi, D.; Perschbacher, S.E. Diagnostic Imaging: Oral and Maxillofacial; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ariji, Y.; Yanashita, Y.; Kutsuna, S.; Muramatsu, C.; Fukuda, M.; Kise, Y.; Nozawa, M.; Kuwada, C.; Fujita, H.; Katsumata, A.; et al. Automatic detection and classification of radiolucent lesions in the mandible on panoramic radiographs using a deep learning object detection technique. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2019, 128, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Hu, J.; Feng, Z.; Song, M.; Zhu, H. Deep learning based diagnosis for cysts and tumors of jaw with massive healthy samples. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ver Berne, J.; Saadi, S.B.; Politis, C.; Jacobs, R. A deep learning approach for radiological detection and classification of radicular cysts and periapical granulomas. J. Dent. 2023, 135, 104581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, K.; Tao, T.; Yuan, X.; Shen, X.; Lai, W.; Long, H. An interactive dual-branch network for hard palate segmentation of the oral cavity from CBCT images. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 129, 109549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, K.F.; Yeung, A.W.K.; Bornstein, M.M.; Schwendicke, F. Personalized dental medicine, artificial intelligence, and their relevance for dentomaxillofacial imaging. Dentomaxillofacial Radiol. 2023, 52, 20220335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, D.H.; Jeong, S.N. Diagnosis of cystic lesions using panoramic and cone beam computed tomographic images based on deep learning neural network. Oral Dis. 2020, 26, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsumata, A. Deep learning and artificial intelligence in dental diagnostic imaging. Jpn. Dent. Sci. Rev. 2023, 59, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, K.F.; Ai, Q.Y.H.; Wong, L.M.; Yeung, A.W.K.; Li, D.T.S.; Leung, Y.Y. Current Applications of Deep Learning and Radiomics on CT and CBCT for Maxillofacial Diseases. Diagnostics 2022, 13, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, Z.K.; Mao, L.; Chen, H.; Sun, T.G.; Shen, X.M.; Liu, J.; Sun, Z.J. Improved Diagnostic Accuracy of Ameloblastoma and Odontogenic Keratocyst on Cone-Beam CT by Artificial Intelligence. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 793417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bispo, M.S.; Pierre Júnior, M.; Apolinário, A.L., Jr.; Dos Santos, J.N.; Junior, B.C.; Neves, F.S.; Crusoé-Rebello, I. Computer tomographic differential diagnosis of ameloblastoma and odontogenic keratocyst: Classification using a convolutional neural network. Dento Maxillo Facial Radiol. 2021, 50, 20210002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endres, M.G.; Hillen, F.; Salloumis, M.; Sedaghat, A.R.; Niehues, S.M.; Quatela, O.; Hanken, H.; Smeets, R.; Beck-Broichsitter, B.; Rendenbach, C. Development of a deep learning algorithm for periapical disease detection in dental radiographs. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, T.; Choi, D.I.; Hwang, J.; Lee, T.; Lee, I.; Cho, S. Panoramic dental tomosynthesis imaging by use of CBCT projection data. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, Z.; Yang, S.; Huang, E.; Zhao, L.; Yang, W.; Feng, Q. Automatic reconstruction method for high-contrast panoramic image from dental cone-beam CT data. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2019, 175, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, L.; Tang, M.; Liang, B.; Mo, S.; Kang, N.; Song, S.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, X. Automated sagittal skeletal classification of children based on deep learning. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Nayak, D.R.; Balabantaray, B.K.; Tanveer, M.; Nayak, R. A survey on cancer detection via convolutional neural networks: Current challenges and future directions. Neural Netw. 2024, 169, 637–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, Q.; Zhou, H.; Guo, N.; Niu, B. A survey of class-imbalanced semi-supervised learning. Mach. Learn. 2023, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Wang, L. FocalMix: Semi-Supervised Learning for 3D Medical Image Detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; Volume 2020, pp. 3950–3959. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.; Zeng, X.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, P.; Wu, X.; Ren, H.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Y. Semi-supervised medical image segmentation via hard positives oriented contrastive learning. Pattern Recognit. 2024, 146, 110020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Li, S.; Hu, Y.; Tao, H.; Zhang, L. Semi-XctNet: Volumetric images reconstruction network from a single projection image via semi-supervised learning. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 155, 106663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berenguer, A.D.; Kvasnytsia, M.; Bossa, M.N.; Mukherjee, T.; Deligiannis, N.; Sahli, H. Semi-supervised medical image classification via distance correlation minimization and graph attention regularization. Med. Image Anal. 2024, 94, 103107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Song, D.; Wang, W.; Rao, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, M. Self-supervised learning and semi-supervised learning for multi-sequence medical image classification. Neurocomputing 2022, 513, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Heng, Q.; Hou, W.; Fan, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wang, J.; Savvides, M.; Shinozaki, T.; Raj, B.; et al. FreeMatch: Self-adaptive Thresholding for Semi-supervised Learning. In Proceedings of the The Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations: 2023, Kigali, Rwanda, 1–5 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, L.A.M.; Torres, R.D. Semi-supervised transfer subspace for domain adaptation. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 75, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Liu, M. Domain adaptation for medical image analysis: A survey. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 69, 1173–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Chen, X.; Xie, S.; Li, Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Masked autoencoders are scalable vision learners. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition: 2022, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 16000–16009. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, G.N.M.; da Silva, H.E.C.; Ossege, F.E.L.; Figueiredo, P.T.D.; Melo, N.D.; Stefani, C.M.; Leite, A.F. Radiomics in bone pathology of the jaws. Dentomaxillofacial Radiol. 2023, 52, 20220225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S. An image is worth 16 × 16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:11929.2020. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-cam: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision: 2017, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Jo, E.; Kim, H.J.; Cha, I.-H.; Jung, Y.-S.; Nam, W.; Kim, J.-Y.; Kim, J.-K.; Kim, Y.H.; Oh, T.G.; et al. Deep learning for automated detection of cyst and tumors of the jaw in panoramic radiographs. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, X.; Yang, X. Refined tooth and pulp segmentation using U-Net in CBCT image. Dentomaxillofacial Radiol. 2021, 50, 20200251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullmer, J.M.; Scarfe, W.C.; Kushner, G.M.; Alpert, B.; Farman, A.G. Cone beam computed tomographic findings in refractory chronic suppurative osteomyelitis of the mandible. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2007, 45, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Meent, M.M.; Pichardo, S.E.; Rodrigues, M.F.; Verbist, B.M.; van Merkesteyn, J.R. Radiographic characteristics of chronic diffuse sclerosing osteomyelitis/tendoperiostitis of the mandible: A comparison with chronic suppurative osteomyelitis and osteoradionecrosis. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 46, 1631–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yfanti, Z.; Tetradis, S.; Nikitakis, N.G.; Alexiou, K.E.; Makris, N.; Angelopoulos, C.; Tsiklakis, K. Radiologic findings of osteonecrosis, osteoradionecrosis, osteomyelitis and jaw metastatic disease with cone beam CT. Eur. J. Radiol. 2023, 165, 110916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Velden, B.H.; Kuijf, H.J.; Gilhuijs, K.G.; Viergever, M.A. Explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) in deep learning-based medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 2022, 79, 102470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Characteristics | AME (n = 181) | CSOJ (n = 102) | PC (n = 102) | Healthy (n = 154) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | <0.001 | |||||
| Male | 114 (63%) | 58 (56.9%) | 38 (37.3%) | 35 (22.7%) | ||
| Female | 67 (37%) | 44 (43.1%) | 64 (62.7%) | 119 (77.3%) | ||
| Age | 33.81 ± 15.82 | 44.23 ± 21.98 | 34.92 ± 16.05 | 28.20 ± 10.97 | <0.001 | |
| Location | <0.001 | |||||
| Maxilla | 8 (4.4%) | 13 (12.7%) | 62 (60.8%) | / | ||
| Mandible | 173 (95.6%) | 89 (87.3%) | 40 (39.2%) | / | ||
| Method Type | Method | Category | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fully- Supervised | Densenet-121 | Healthy | 98.06 ± 3.87 | 80.52 ± 9.03 | 85.52 ± 5.52 |
| AM | 81.22 ± 3.67 | 94.42 ± 1.95 | 89.98 ± 0.67 | ||
| PC | 52.24 ± 16.3 | 90.40 ± 6.32 | 83.12 ± 3.36 | ||
| CSO | 36.95 ± 12.73 | 97.02 ± 2.01 | 85.72 ± 1.71 | ||
| Means | 67.12 ± 5.25 | 90.59 ± 1.39 | 86.09 ± 1.77 | ||
| ViT-B/16 | Healthy | 97.35 ± 3.88 | 87.07 ± 8.37 | 89.98 ± 5.95 | |
| AM | 90.08 ± 5.67 | 96.38 ± 3.35 | 94.25 ± 1.23 | ||
| PC | 64.76 ± 13.92 | 91.07 ± 4.56 | 86.08 ± 3.08 | ||
| CSO | 41.10 ± 8.67 | 96.33 ± 0.87 | 85.90 ± 0.59 | ||
| Means | 73.32 ± 4.35 | 92.70 ± 1.37 | 89.05 ± 2.13 | ||
| Semi- Supervised | WaveletFusion-ViT | Healthy | 98.04 ± 2.59 | 98.96 ± 1.52 | 98.70 ± 1.11 |
| AM | 90.06 ± 5.14 | 94.98 ± 3.78 | 93.32 ± 1.59 | ||
| PC | 78.33 ± 16.23 | 89.47 ± 4.90 | 87.39 ± 3.22 | ||
| CSO | 51.95 ± 7.91 | 94.51 ± 3.11 | 86.46 ± 1.60 | ||
| Means | 79.60 ± 2.74 | 94.48 ± 0.70 | 91.47 ± 1.11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, B.; Qin, H.; Nong, X.; Zhang, X. Classification of Ameloblastoma, Periapical Cyst, and Chronic Suppurative Osteomyelitis with Semi-Supervised Learning: The WaveletFusion-ViT Model Approach. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11060571
Liang B, Qin H, Nong X, Zhang X. Classification of Ameloblastoma, Periapical Cyst, and Chronic Suppurative Osteomyelitis with Semi-Supervised Learning: The WaveletFusion-ViT Model Approach. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(6):571. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11060571
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Bohui, Hongna Qin, Xiaolin Nong, and Xuejun Zhang. 2024. "Classification of Ameloblastoma, Periapical Cyst, and Chronic Suppurative Osteomyelitis with Semi-Supervised Learning: The WaveletFusion-ViT Model Approach" Bioengineering 11, no. 6: 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11060571
APA StyleLiang, B., Qin, H., Nong, X., & Zhang, X. (2024). Classification of Ameloblastoma, Periapical Cyst, and Chronic Suppurative Osteomyelitis with Semi-Supervised Learning: The WaveletFusion-ViT Model Approach. Bioengineering, 11(6), 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11060571







