Enhancing Trauma Care: A Machine Learning Approach with XGBoost for Predicting Urgent Hemorrhage Interventions Using NTDB Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
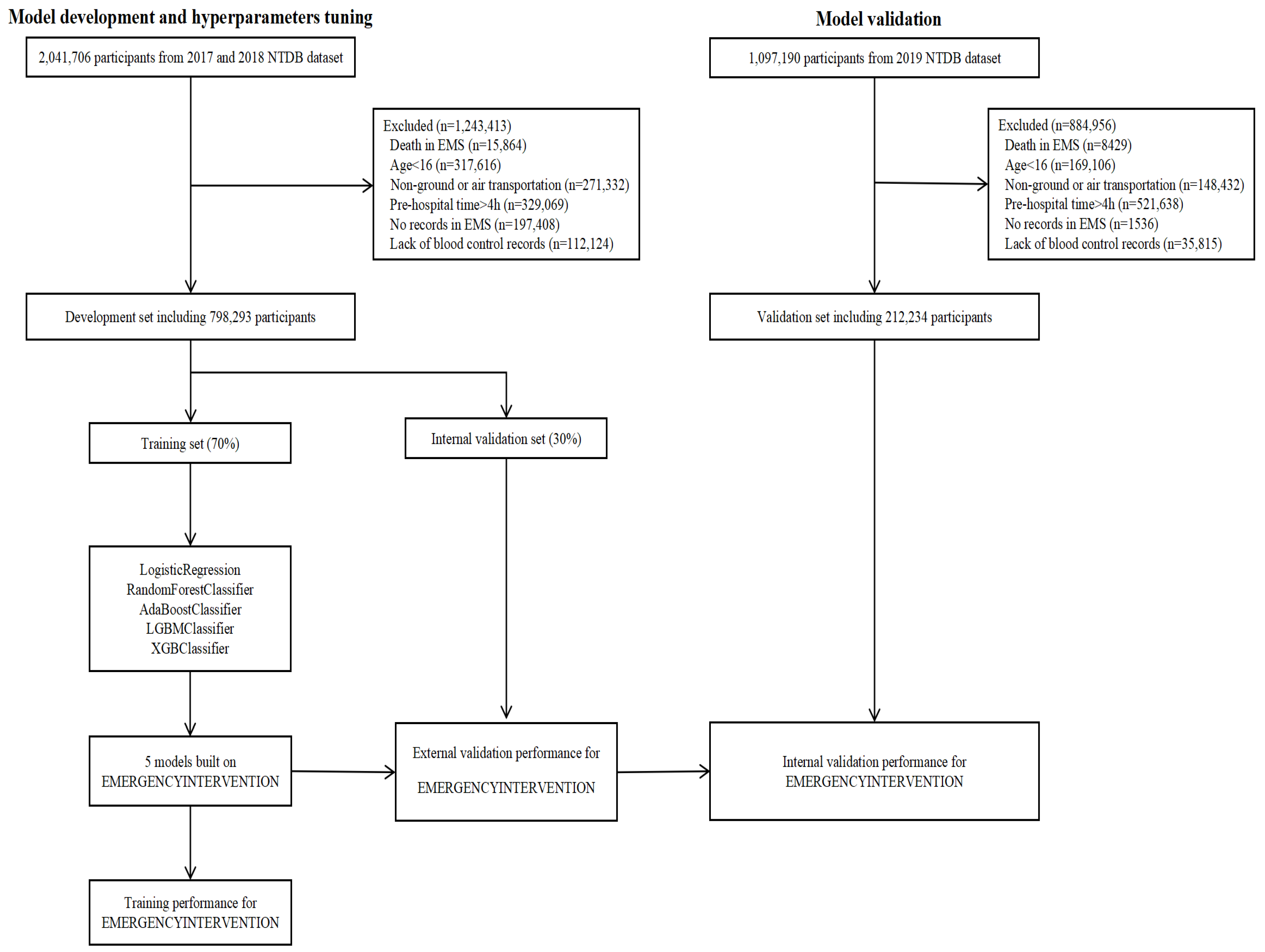
2.1. Dataset
2.2. Dataset Preprocessing
2.3. Model Development
2.4. Statistical Analysis Methods
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Model Performance
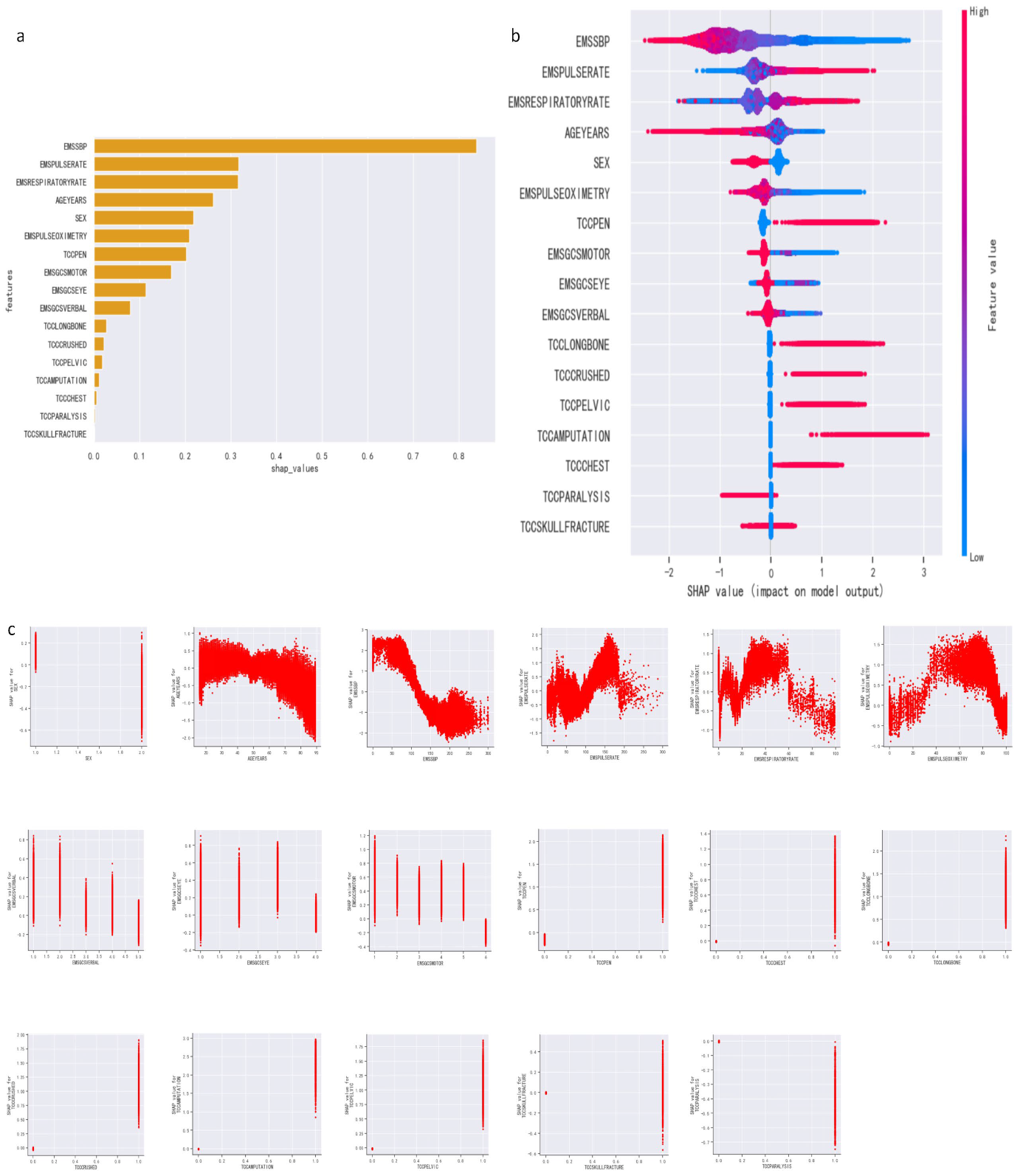
3.3. Feature Importance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Atwan, Y.; Schemitsch, E.H. Economic Aspects of Trauma Care. In Textbook of Polytrauma Management: A Multidisciplinary Approach; Pape, H.-C., Borrelli, J., Jr., Moore, E.E., Pfeifer, R., Stahel, P.F., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 11–16. ISBN 978-3-030-95906-7. [Google Scholar]
- Kauvar, D.S.; Wade, C.E. The epidemiology and modern management of traumatic hemorrhage: US and international perspectives. Crit. Care 2005, 9, S1–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spahn, D.R.; Rossaint, R. Coagulopathy and blood component transfusion in trauma. Br. J. Anaesth. 2005, 95, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vulliamy, P.; Thaventhiran, A.J.; Davenport, R.A. What’s new for trauma haemorrhage management? Br. J. Hosp. Med. 2019, 80, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latif, R.K.; Clifford, S.P.; Baker, J.A.; Lenhardt, R.; Haq, M.Z.; Huang, J.; Farah, I.; Businger, J.R. Traumatic hemorrhage and chain of survival. Scand. J. Trauma Resusc. Emerg. Med. 2023, 31, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spahn, D.R.; Bouillon, B.; Cerny, V.; Coats, T.J.; Duranteau, J.; Fernández-Mondéjar, E.; Filipescu, D.; Hunt, B.J.; Komadina, R.; Nardi, G.; et al. Management of bleeding and coagulopathy following major trauma: An updated European guideline. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eren, F.; Yildogan, A.T.; Demir, A.; Ozguncu, C.; Yilmaz, S.E. Delayed cerebral ischemia and therapeutic approaches after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Explor. Neuroprot. Ther. 2022, 2, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curry, N.S.; Davenport, R. Transfusion strategies for major haemorrhage in trauma. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 184, 508–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, J.W.; Khan, M.A.; Raja, A.S.; Cohen, M.J.; Como, J.J.; Cotton, B.A.; Dubose, J.J.; Fox, E.E.; Inaba, K.; Rodriguez, C.J.; et al. Damage control resuscitation in patients with severe traumatic hemorrhage: A practice management guideline from the Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2017, 82, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, E.; Weaver, A.; Gall, L.; West, A.; Nevin, D.; Tallach, R.; O’Neill, B.; Lahiri, S.; Allard, S.; Tai, N.; et al. A Decade of Damage Control Resuscitation: New Transfusion Practice, New Survivors, New Directions. Ann. Surg. 2021, 273, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaski, I.A.; Naess, P.A.; Baksaas-Aasen, K.; Skaga, N.O.; Gaarder, C. Achieving balanced transfusion early in critically bleeding trauma patients: An observational study exploring the effect of attending trauma surgical presence during resuscitation. Trauma Surg. Acute Care Open 2023, 8, e001160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, R.A.; Sabir, S.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Avery, R.K.; Zhang, Y.S.; Khademhosseini, A.; Oklu, R. Endovascular Embolization by Transcatheter Delivery of Particles: Past, Present, and Future. J. Funct. Biomater. 2017, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behravesh, S.; Yakes, W.; Gupta, N.; Naidu, S.; Chong, B.W.; Khademhosseini, A.; Oklu, R. Venous malformations: Clinical diagnosis and treatment. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2016, 6, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, L.-G.; Ljungdahl, M.; Sundbom, M.; Nyman, R. Transcatheter Arterial Embolization versus Surgery in the Treatment of Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding after Therapeutic Endoscopy Failure. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2008, 19, 1413–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loffroy, R.; Guiu, B.; D’Athis, P.; Mezzetta, L.; Gagnaire, A.; Jouve, J.-L.; Ortega-Deballon, P.; Cheynel, N.; Cercueil, J.-P.; Krausé, D. Arterial embolotherapy for endoscopically unmanageable acute gastroduodenal hemorrhage: Predictors of early rebleeding. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Off. Clin. Pract. J. Am. Gastroenterol. Assoc. 2009, 7, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamb, C.M.; MacGoey, P.; Navarro, A.P.; Brooks, A.J. Damage control surgery in the era of damage control resuscitation. Br. J. Anaesth. 2014, 113, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, C.Y.; Scalea, T.M. Damage control surgery: Old concepts and new indications. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2023, 29, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handelman, G.S.; Kok, H.K.; Chandra, R.V.; Razavi, A.H.; Lee, M.J.; Asadi, H. eDoctor: Machine learning and the future of medicine. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 284, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achuta Rao, S.V.; Kondaiah, K.; Rajesh Chandra, G.; Kiran Kumar, K. A Survey on Machine Learning: Concept, Algorithms and Applications. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Innovative Research in Computer and Communication Engineering, Bengaluru, India, 24–25 February 2017; pp. 1301–1309. [Google Scholar]
- Haider, A.H. Improving the quality of science arising from the NTDB: We can do this! J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2013, 74, 352–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikouline, A.; Feng, J.; Rudzicz, F.; Nathens, A.; Nolan, B. Machine learning in the prediction of massive transfusion in trauma: A retrospective analysis as a proof-of-concept. Eur. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2024, 50, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierrie, S.N.; Seymour, R.B.; Wally, M.K.; Studnek, J.; Infinger, A.; Hsu, J.R.; Evidence-based Musculoskeletal Injury and Trauma Collaborative (EMIT). Pilot randomized trial of pre-hospital advanced therapies for the control of hemorrhage (PATCH) using pelvic binders. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 42, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhammoud, A.; Moghamis, I.; Abdelrahman, H.; Ghouri, S.I.; Asim, M.; Babikir, E.; Al-Thani, H.; El-Menyar, A. Clinical characteristics, injury pattern and management of pediatric pelvic fracture: An observational retrospective study from a level I trauma center. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.; Park, C.; Lee, J.; Yoon, D. Machine Learning Model for the Prediction of Hemorrhage in Intensive Care Units. Healthc. Inform. Res. 2022, 28, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Shen, W.; Wang, G. Early Prediction of Sepsis Based on Machine Learning Algorithm. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2021, 2021, 6522633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, C.; Li, M.; Huang, T.; Li, F. Stroke Risk Assessment Decision-Making Using a Machine Learning Model: Logistic-AdaBoost. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2023, 139, 699–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhaneswaran, B.; Ifham, M.; Kumara, B. Boosting Ensemble Machine Learning Approach for Covid-19 Death Prediction. Sri Lanka J. Soc. Sci. Humanit. 2023, 3, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Ji, H.; Ma, X.; Wu, J.; Huang, Y.; Wang, X.; Gui, R.; Zhao, Q.; et al. Machine Learning for the Prediction of Complications in Patients After Mitral Valve Surgery. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 771246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagassou, M.; Mwangi, R.W.; Nyarige, E. A Hybrid Ensemble Learning Approach Utilizing Light Gradient Boosting Machine and Category Boosting Model for Lifestyle-Based Prediction of Type-II Diabetes Mellitus. J. Data Anal. Inf. Process. 2023, 11, 480–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duhayyim, M.; Abbas, S.; Hejaili, A.; Kryvinska, N.; Almadhor, A.; Mohammad, U. An Ensemble Machine Learning Technique for Stroke Prognosis. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 2023, 47, 413–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, S. Comparative Analysis of Classification Accuracy for XGBoost, LightGBM, CatBoost, H2O, and Classifium. Master’s Thesis, Østfold University College, Halden, Norway, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, S.; Akhlaq, F.; Imran, A.S.; Kastrati, Z.; Daudpota, S.M.; Moosa, M. The enlightening role of explainable artificial intelligence in medical & healthcare domains: A systematic literature review. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 166, 107555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H. A Machine Learning-Based Prediction Model for Acute Kidney Injury in Patients With Congestive Heart Failure. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 842873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kang, W.S.; Kim, D.W.; Seo, S.H.; Kim, J.; Jeong, S.T.; Yon, D.K.; Lee, J. An Artificial Intelligence Model for Predicting Trauma Mortality Among Emergency Department Patients in South Korea: Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2023, 25, e49283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, V.V.; Chadaga, K.; Sampathila, N.; Prabhu, S.; Rajagopala Chadaga, P. A machine learning and explainable artificial intelligence triage-prediction system for COVID-19. Decis. Anal. J. 2023, 7, 100246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.E.; Baldock, T.; Wei, N.; Walshaw, T.; Walker, R.; Trompeter, A.; Scott, S.; Eardley, W.G.P.; Stevenson, I.; Yoong, A.; et al. Lack of regional pathways impact on surgical delay: Analysis of the Orthopaedic Trauma Hospital Outcomes–Patient Operative Delays (ORTHOPOD) study. Injury 2023, 54, 111007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.-P.; Zhao, Q.-Y.; Wu, J.; Luo, Y.-W.; Dong, H.; Chen, Z.-W.; Gui, R.; Wang, Y.J. Machine Learning for the Prediction of Red Blood Cell Transfusion in Patients During or After Liver Transplantation Surgery. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 632210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chee, M.L.; Chee, M.L.; Huang, H.; Mazzochi, K.; Taylor, K.; Wang, H.; Feng, M.; Ho, A.F.W.; Siddiqui, F.J.; Ong, M.E.H.; et al. Artificial intelligence and machine learning in prehospital emergency care: A scoping review. iScience 2023, 26, 107407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alamoodi, A.H.; Zaidan, B.B.; Albahri, O.S.; Garfan, S.; Ahmaro, I.Y.Y.; Mohammed, R.T.; Zaidan, A.A.; Ismail, A.R.; Albahri, A.S.; Momani, F.; et al. Systematic review of MCDM approach applied to the medical case studies of COVID-19: Trends, bibliographic analysis, challenges, motivations, recommendations, and future directions. Complex Intell. Syst. 2023, 9, 4705–4731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, C. Trends in using deep learning algorithms in biomedical prediction systems. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1256351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Yang, M.; Kozar, R.; Zhang, L. Integrating transportation data with emergency medical service records to improve triage decision of high-risk trauma patients. J. Transp. Health 2021, 22, 101106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Candidate Variables | Variable in NTDB * |
|---|---|
| Gender | SEX |
| Age | AGEYEARS |
| Initial EMS Systolic Blood Pressure | EMSSBP |
| Initial EMS Pulse Rate | EMSPULSERATE |
| Initial EMS Respiratory Rate | EMSRESPIRATORYRATE |
| EMS Oxygen Saturation | EMSPULSEOXIMETRY |
| EMS GCS—Eye | EMSGCSEYE |
| EMS GCS—Verbal | EMSGCSVERBAL |
| EMS GCS—Motor | EMSGCSMOTOR |
| Trauma Center Critera: All penetrating injuries to head, neck, torso, and extremities proximal to elbow or knee | TCCPEN |
| Trauma Center Critera: Chest wall instability or deformity (e.g., flail chest) | TCCCHEST |
| Trauma Center Critera: Two or more proximal long-bone fractures | TCCLONGBONE |
| Trauma Center Critera: Crushed, degloved, mangled, or pulseless extremity | TCCCRUSHED |
| Trauma Center Critera: Amputation proximal to wrist or ankle | TCCAMPUTATION |
| Trauma Center Critera: Pelvic fracture | TCCPELVIC |
| Trauma Center Critera: Open or depressed skull fracture | TCCSKULLFRACTURE |
| Trauma Center Critera: Paralysis | TCCPARALYSIS |
| Characteristics | Training Set (n = 558,805) | Internal Validation Set (n = 239,488) | External Validation Set (n = 212,234) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | 0.007 | |||
| Male | 341,005 (61.02) | 145,932 (60.93) | 130,158 (61.33) | |
| Female | 217,743 (38.97) | 93,525 (39.05) | 82,038 (38.65) | |
| Transport mode | <0.001 | |||
| Ground | 516,501 (92.43) | 221,333 (92.42) | 190,546 (89.78) | |
| Helicopter | 41,677 (7.46) | 17,887 (7.47) | 21,161 (9.97) | |
| Fixed-wing | 627 (0.11) | 268 (0.11) | 527 (0.25) | |
| TCCPEN, yes | 23,213 (4.15) | 9952 (4.16) | 7334 (3.46) | <0.001 |
| TCCCHEST, yes | 1378 (0.25) | 565 (0.24) | 651 (0.31) | <0.001 |
| TCCLONGBONE, yes | 4106 (0.73) | 1732 (0.72) | 1707 (0.80) | 0.002 |
| TCCCRUSHED, yes | 2947 (0.53) | 1187 (0.50) | 1469 (0.69) | <0.001 |
| TCCAMPUTATION, yes | 573 (0.10) | 262 (0.11) | 228 (0.11) | 0.88 |
| TCCPELVIC, yes | 3088 (0.55) | 1306 (0.55) | 1368 (0.64) | <0.001 |
| TCCSKULLFRACTURE, yes | 1751 (0.31) | 793 (0.33) | 982 (0.46) | <0.001 |
| TCCPARALYSIS, yes | 2060 (0.37) | 904 (0.38) | 806 (0.38) | 0.92 |
| EMERGENCYINTERVENTION | <0.001 | |||
| MT, yes | 9265 (1.66) | 3945 (1.65) | 3658 (1.72) | |
| ANGIOEMBOLIZATION, yes | 4838 (0.87) | 1979 (0.83) | 1876 (0.88) | |
| HMRRHGCTRLSURG, yes | 13,904 (2.49) | 5875 (2.45) | 5388 (2.54) | |
| Age | 52.47 (21.79) | 52.43 (21.80) | 52.17 (21.73) | <0.001 |
| EMSSBP, mmHg | 139.25 (29.38) | 139.29 (29.50) | 139.88 (29.85) | <0.001 |
| EMSPULSERATE, n/minute | 90.65 (20.92) | 90.59 (20.85) | 90.68 (21.22) | 0.15 |
| EMSRESPIRATORYRATE, n/minute | 18.36 (4.94) | 18.37 (4.96) | 18.58 (5.11) | <0.001 |
| EMSPULSEOXIMETRY, % | 96.11 (6.68) | 96.08 (6.80) | 95.99 (6.48) | <0.001 |
| EMSGCSEYE | 3.78 (0.70) | 3.78 (0.70) | 3.78 (0.74) | <0.001 |
| EMSGCSVERBAL | 4.56 (1.01) | 4.56 (1.01) | 4.59 (1.04) | <0.001 |
| EMSGCSMOTOR | 5.69 (1.04) | 5.69 (1.05) | 5.69 (1.10) | <0.001 |
| EMSTOTALGCS | 14.04 (2.60) | 14.04 (2.60) | 14.05 (2.76) | <0.001 |
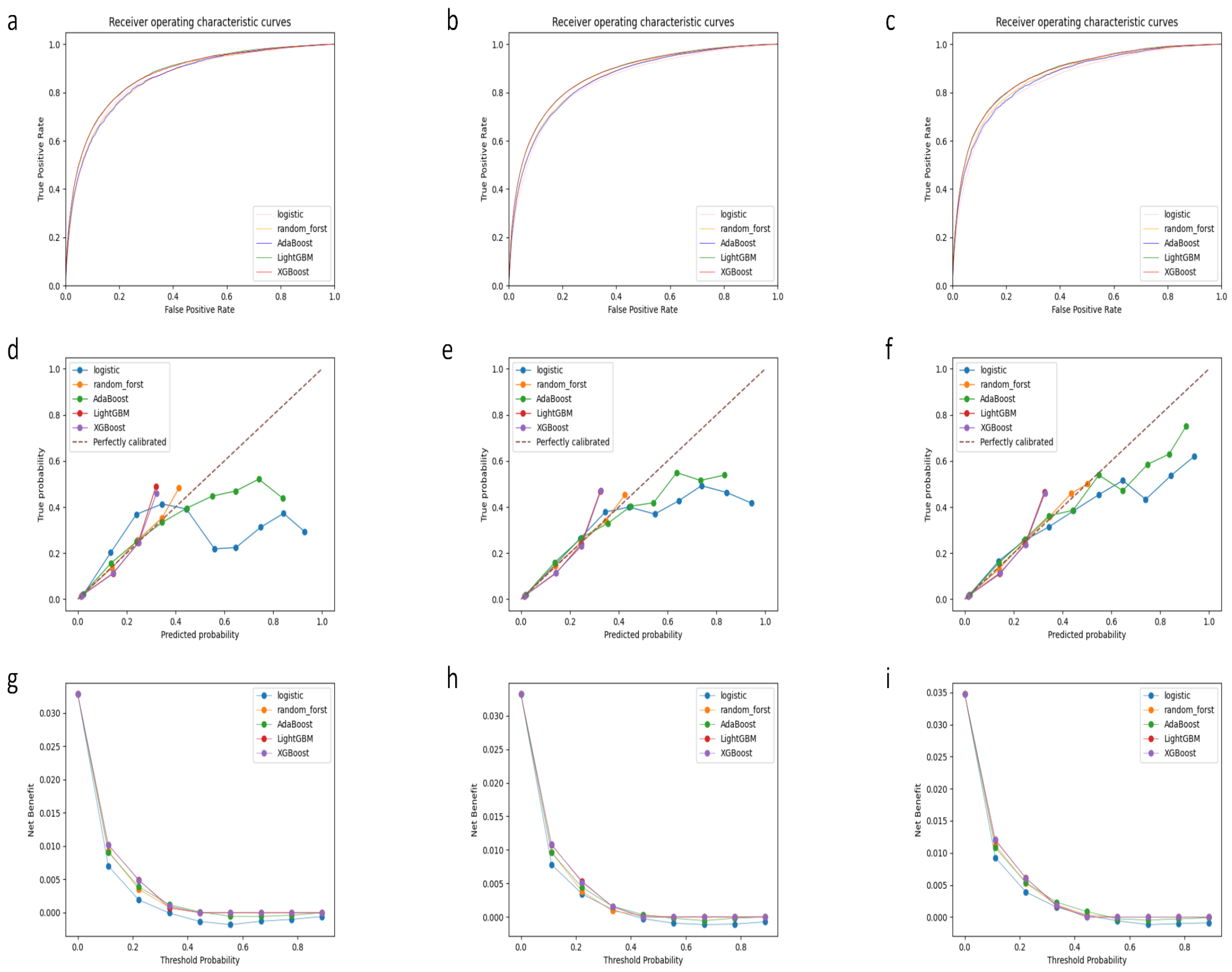
| AUROC | Spec | Sens | PPV | NPV | Accuracy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training set | ||||||
| Logistic regression | 0.858 | 0.821 | 0.751 | 0.125 | 0.990 | 0.819 |
| Random forest | 0.857 | 0.796 | 0.762 | 0.113 | 0.990 | 0.795 |
| Ada boost | 0.858 | 0.800 | 0.763 | 0.115 | 0.990 | 0.799 |
| XGB | 0.872 | 0.826 | 0.764 | 0.130 | 0.990 | 0.824 |
| LGB | 0.873 | 0.816 | 0.775 | 0.125 | 0.991 | 0.815 |
| Internal validation set | ||||||
| Logistic regression | 0.845 | 0.821 | 0.727 | 0.123 | 0.989 | 0.818 |
| Random forest | 0.856 | 0.794 | 0.766 | 0.113 | 0.990 | 0.793 |
| Ada boost | 0.855 | 0.803 | 0.752 | 0.116 | 0.990 | 0.801 |
| XGB | 0.869 | 0.823 | 0.763 | 0.129 | 0.990 | 0.821 |
| LGB | 0.870 | 0.817 | 0.771 | 0.127 | 0.990 | 0.815 |
| External validation set | ||||||
| Logistic regression | 0.850 | 0.831 | 0.733 | 0.135 | 0.989 | 0.827 |
| Random forest | 0.865 | 0.801 | 0.778 | 0.123 | 0.990 | 0.800 |
| Ada boost | 0.861 | 0.806 | 0.763 | 0.124 | 0.990 | 0.804 |
| XGB | 0.875 | 0.821 | 0.778 | 0.135 | 0.990 | 0.819 |
| LGB | 0.877 | 0.815 | 0.786 | 0.133 | 0.991 | 0.814 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Jin, Z.; Tang, B.; Huang, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Q.; He, J. Enhancing Trauma Care: A Machine Learning Approach with XGBoost for Predicting Urgent Hemorrhage Interventions Using NTDB Data. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 768. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11080768
Zhang J, Jin Z, Tang B, Huang X, Wang Z, Chen Q, He J. Enhancing Trauma Care: A Machine Learning Approach with XGBoost for Predicting Urgent Hemorrhage Interventions Using NTDB Data. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(8):768. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11080768
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jin, Zhichao Jin, Bihan Tang, Xiangtong Huang, Zongyu Wang, Qi Chen, and Jia He. 2024. "Enhancing Trauma Care: A Machine Learning Approach with XGBoost for Predicting Urgent Hemorrhage Interventions Using NTDB Data" Bioengineering 11, no. 8: 768. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11080768
APA StyleZhang, J., Jin, Z., Tang, B., Huang, X., Wang, Z., Chen, Q., & He, J. (2024). Enhancing Trauma Care: A Machine Learning Approach with XGBoost for Predicting Urgent Hemorrhage Interventions Using NTDB Data. Bioengineering, 11(8), 768. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11080768





