Integrating Multi-Organ Imaging-Derived Phenotypes and Genomic Information for Predicting the Occurrence of Common Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Baseline Examination and Sample Collection
2.3. PRS Calculation
2.4. Prediction Model
2.5. Validation Cohort
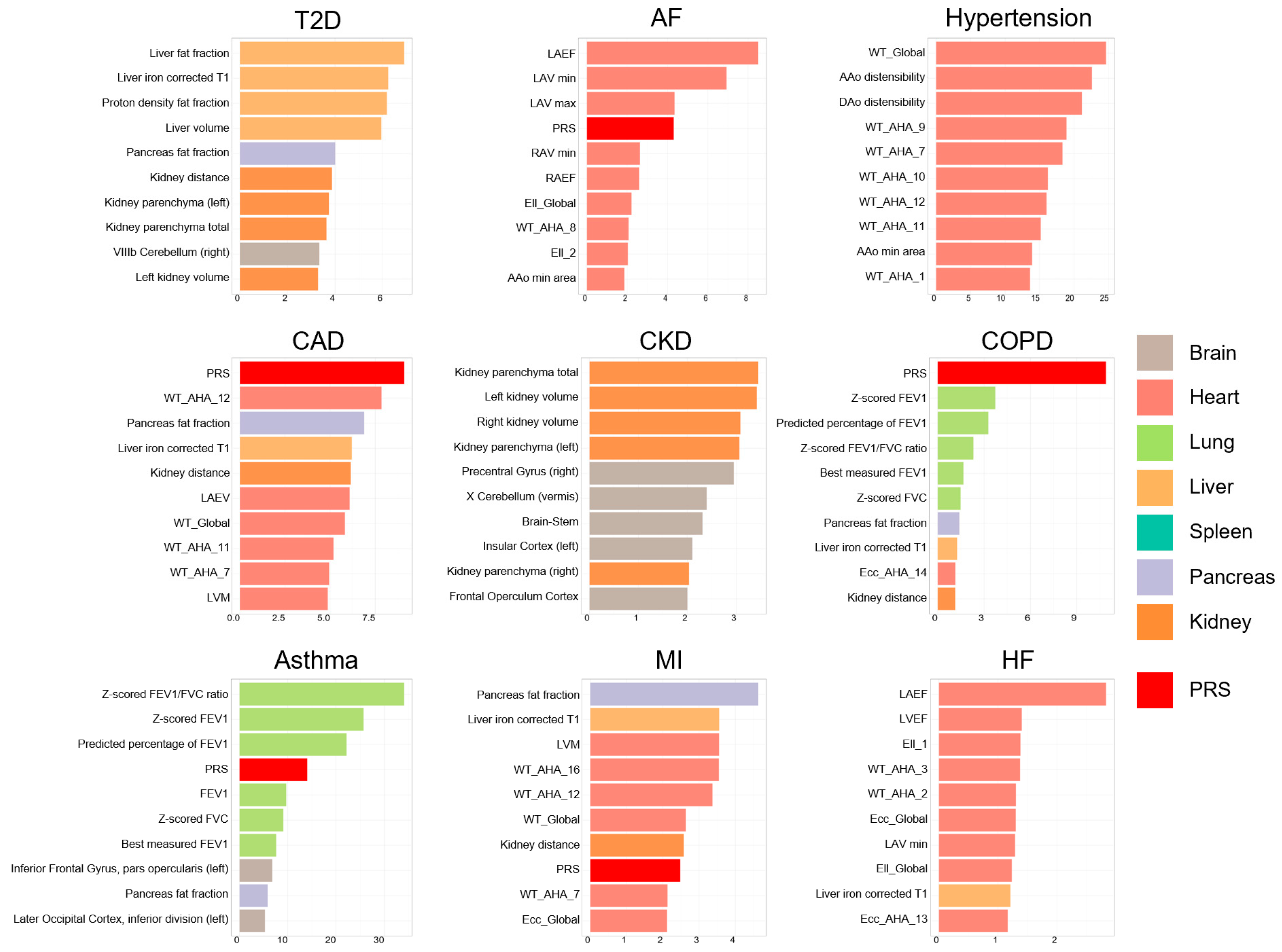
2.6. Feature Ranking
3. Results
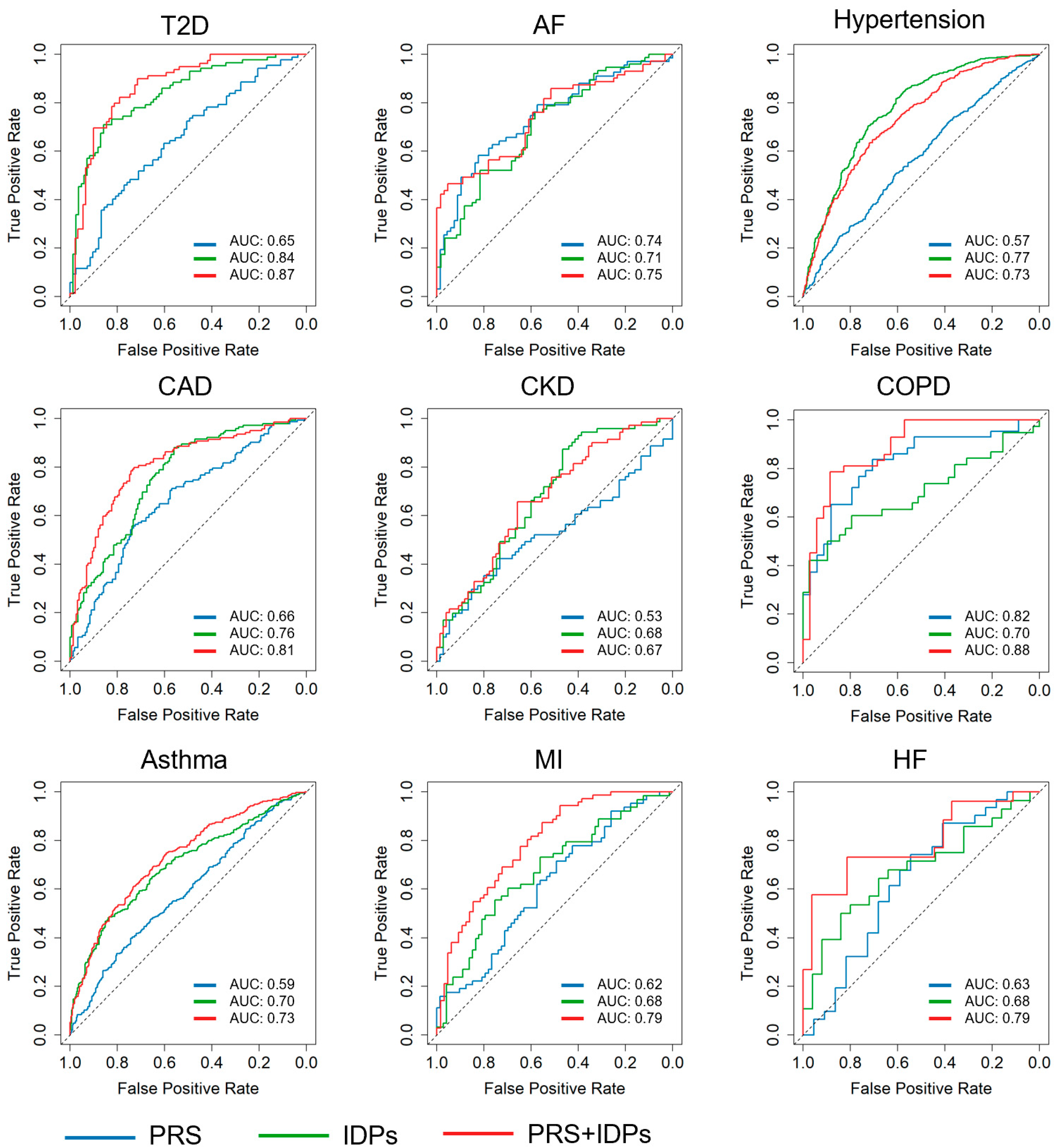
3.1. Prediction Results
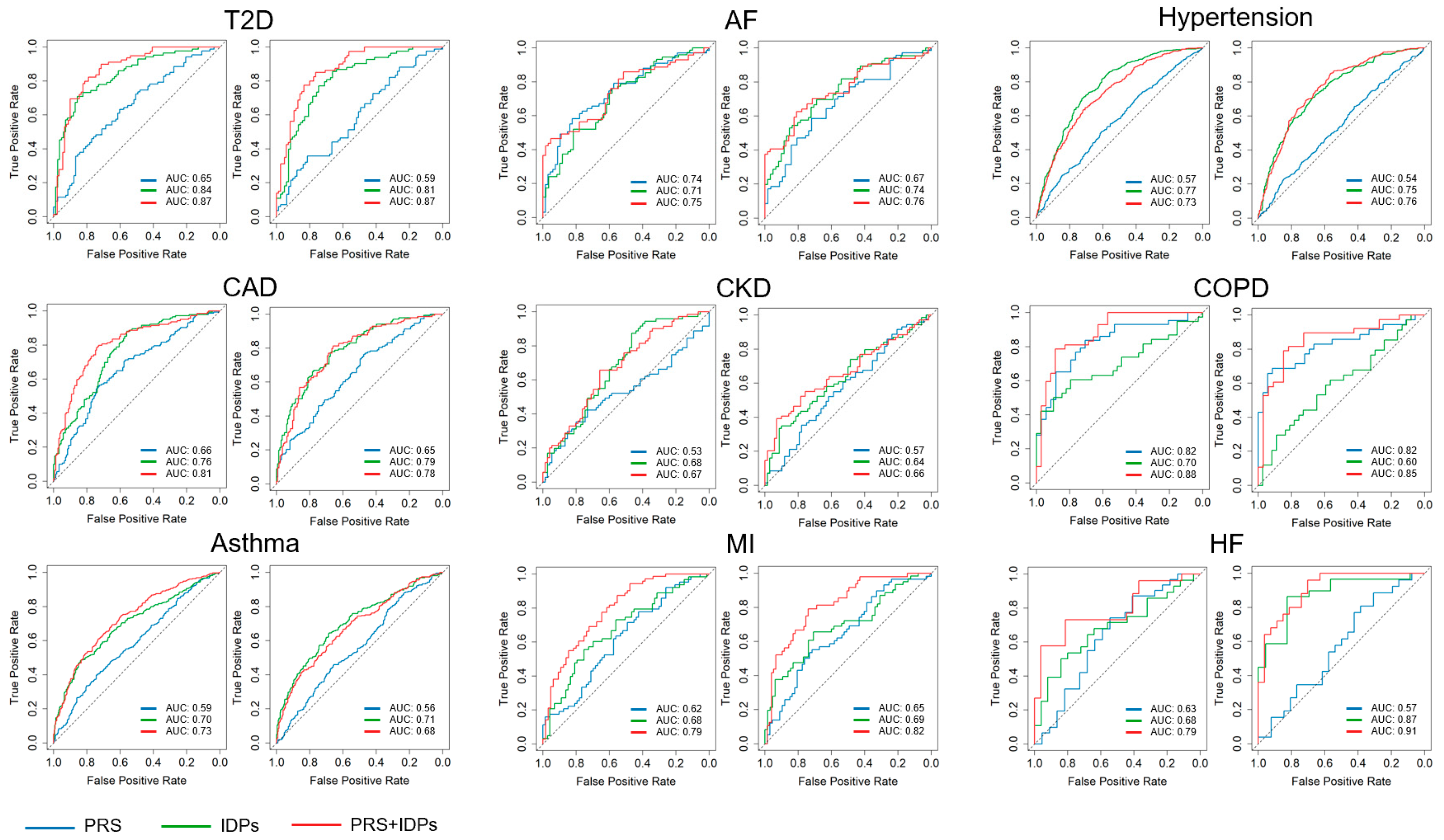
3.2. Validation
3.3. Feature Ranking
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cui, C.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Asad, Z.; Coburn, L.A.; Wilson, K.T.; Landman, B.A.; Huo, Y. Deep Multimodal Fusion of Image and Non-Image Data in Disease Diagnosis and Prognosis: A Review. Prog. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 5, 022001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, S.C.; Lambert, S.A.; Arnold, M.; Teo, S.M.; Lim, S.; Scepanovic, P.; Marten, J.; Zahid, S.; Chaffin, M.; Liu, Y.; et al. Integrative Analysis of the Plasma Proteome and Polygenic Risk of Cardiometabolic Diseases. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 1476–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wigger, L.; Barovic, M.; Brunner, A.-D.; Marzetta, F.; Schöniger, E.; Mehl, F.; Kipke, N.; Friedland, D.; Burdet, F.; Kessler, C.; et al. Multi-Omics Profiling of Living Human Pancreatic Islet Donors Reveals Heterogeneous Beta Cell Trajectories towards Type 2 Diabetes. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 1017–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Méric, G.; Havulinna, A.S.; Teo, S.M.; Åberg, F.; Ruuskanen, M.; Sanders, J.; Zhu, Q.; Tripathi, A.; Verspoor, K.; et al. Early Prediction of Incident Liver Disease Using Conventional Risk Factors and Gut-Microbiome-Augmented Gradient Boosting. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 719–730.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Li, T.; Fan, Z.; Yang, Y.; Shu, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, X.; Luo, T.; Tang, J.; Xiong, D.; et al. Heart-Brain Connections: Phenotypic and Genetic Insights from Magnetic Resonance Images. Science 2023, 380, abn6598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Littlejohns, T.J.; Holliday, J.; Gibson, L.M.; Garratt, S.; Oesingmann, N.; Alfaro-Almagro, F.; Bell, J.D.; Boultwood, C.; Collins, R.; Conroy, M.C.; et al. The UK Biobank Imaging Enhancement of 100,000 Participants: Rationale, Data Collection, Management and Future Directions. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.; Imran, M.; Ahsan, H. Biomarkers as Biomedical Bioindicators: Approaches and Techniques for the Detection, Analysis, and Validation of Novel Biomarkers of Diseases. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, J.W.; Ashley, E.A.; Elliott, P.M. Polygenic Risk Scores for the Prediction of Cardiometabolic Disease. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, C.M.; Vassos, E. Polygenic Risk Scores: From Research Tools to Clinical Instruments. Genome Med. 2020, 12, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.A. Polygenic Risk Scores. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2024, 64, 152330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usher-Smith, J.A.; Harshfield, A.; Saunders, C.L.; Sharp, S.J.; Emery, J.; Walter, F.M.; Muir, K.; Griffin, S.J. External Validation of Risk Prediction Models for Incident Colorectal Cancer Using UK Biobank. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 118, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briggs, S.E.W.; Law, P.; East, J.E.; Wordsworth, S.; Dunlop, M.; Houlston, R.; Hippisley-Cox, J.; Tomlinson, I. Integrating Genome-Wide Polygenic Risk Scores and Non-Genetic Risk to Predict Colorectal Cancer Diagnosis Using UK Biobank Data: Population Based Cohort Study. BMJ 2022, 379, e071707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Hu, K.; Fan, L.; Yan, H.; Li, P.; Jiang, T.; Liu, B. Predicting Treatment Response in Schizophrenia With Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Polygenic Risk Score. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 848205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bycroft, C.; Freeman, C.; Petkova, D.; Band, G.; Elliott, L.T.; Sharp, K.; Motyer, A.; Vukcevic, D.; Delaneau, O.; O’Connell, J.; et al. The UK Biobank Resource with Deep Phenotyping and Genomic Data. Nature 2018, 562, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langner, T.; Östling, A.; Maldonis, L.; Karlsson, A.; Olmo, D.; Lindgren, D.; Wallin, A.; Lundin, L.; Strand, R.; Ahlström, H.; et al. Kidney Segmentation in Neck-to-Knee Body MRI of 40,000 UK Biobank Participants. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Ibrahim, J.G.; Li, Y.; Li, T.; Wang, Y.; Shan, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, J.; Huang, C.; et al. Heritability of Regional Brain Volumes in Large-Scale Neuroimaging and Genetic Studies. Cereb. Cortex 2019, 29, 2904–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mojtahed, A.; Kelly, C.J.; Herlihy, A.H.; Kin, S.; Wilman, H.R.; McKay, A.; Kelly, M.; Milanesi, M.; Neubauer, S.; Thomas, E.L.; et al. Reference Range of Liver Corrected T1 Values in a Population at Low Risk for Fatty Liver Disease—A UK Biobank Sub-Study, with an Appendix of Interesting Cases. Abdom. Radiol. 2019, 44, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Basty, N.; Whitcher, B.; Bell, J.D.; Sorokin, E.P.; van Bruggen, N.; Thomas, E.L.; Cule, M. Genetic Architecture of 11 Organ Traits Derived from Abdominal MRI Using Deep Learning. eLife 2021, 10, e65554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.; Suzuki, H.; Huang, J.; Francis, C.; Wang, S.; Tarroni, G.; Guitton, F.; Aung, N.; Fung, K.; Petersen, S.E.; et al. A Population-Based Phenome-Wide Association Study of Cardiac and Aortic Structure and Function. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1654–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.R.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; De Bakker, P.I.W.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A Tool Set for Whole-Genome Association and Population-Based Linkage Analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairley, S.; Lowy-Gallego, E.; Perry, E.; Flicek, P. The International Genome Sample Resource (IGSR) Collection of Open Human Genomic Variation Resources. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D941–D947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Band, G.; Marchini, J. BGEN: A Binary File Format for Imputed Genotype and Haplotype Data. bioArxiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigginton, J.E.; Cutler, D.J.; Abecasis, G.R. A Note on Exact Tests of Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2005, 76, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolci, G.; Rahaman, M.A.; Chen, J.; Duan, K.; Fu, Z.; Abrol, A.; Menegaz, G.; Calhoun, V.D. A Deep Generative Multimodal Imaging Genomics Framework for Alzheimer’s Disease Prediction. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 22nd International Conference on Bioinformatics and Bioengineering (BIBE), Taichung, Taiwan, 7–9 November2022; pp. 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Vanguri, R.S.; Luo, J.; Aukerman, A.T.; Egger, J.V.; Fong, C.J.; Horvat, N.; Pagano, A.; Araujo-Filho, J.D.A.B.; Geneslaw, L.; Rizvi, H.; et al. Multimodal Integration of Radiology, Pathology and Genomics for Prediction of Response to PD-(L)1 Blockade in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Nat. Cancer 2022, 3, 1151–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauffal, V.; Di Achille, P.; Klarqvist, M.D.R.; Cunningham, J.W.; Hill, M.C.; Pirruccello, J.P.; Weng, L.-C.; Morrill, V.N.; Choi, S.H.; Khurshid, S.; et al. Genetics of Myocardial Interstitial Fibrosis in the Human Heart and Association with Disease. Nat. Genet. 2023, 55, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, K.L.; Alfaro-Almagro, F.; Bangerter, N.K.; Thomas, D.L.; Yacoub, E.; Xu, J.; Bartsch, A.J.; Jbabdi, S.; Sotiropoulos, S.N.; Andersson, J.L.R.; et al. Multimodal Population Brain Imaging in the UK Biobank Prospective Epidemiological Study. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 1523–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.B.; Chiou, J.; Traylor, M.; Benner, C.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Richardson, T.G.; Surendran, P.; Mahajan, A.; Robins, C.; Vasquez-Grinnell, S.G.; et al. Plasma Proteomic Associations with Genetics and Health in the UK Biobank. Nature 2023, 622, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, Z.; von Scheidt, M.; Li, S.; Steiner, A.; Güldener, U.; Koplev, S.; Ma, A.; Hao, K.; Pan, C.; et al. Transcriptome-Wide Association Study of Coronary Artery Disease Identifies Novel Susceptibility Genes. Basic. Res. Cardiol. 2022, 117, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, P.-C.; Lee, T.-H.; Kuo, K.-C.; Su, F.-Y.; Lee, T.-L.M.; Marostica, E.; Ugai, T.; Zhao, M.; Lau, M.C.; Väyrynen, J.P.; et al. Histopathology Images Predict Multi-Omics Aberrations and Prognoses in Colorectal Cancer Patients. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.J.; Lu, M.Y.; Williamson, D.F.K.; Chen, T.Y.; Lipkova, J.; Noor, Z.; Shaban, M.; Shady, M.; Williams, M.; Joo, B.; et al. Pan-Cancer Integrative Histology-Genomic Analysis via Multimodal Deep Learning. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 865–878.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyed Tabib, N.S.; Madgwick, M.; Sudhakar, P.; Verstockt, B.; Korcsmaros, T.; Vermeire, S. Big Data in IBD: Big Progress for Clinical Practice. Gut 2020, 69, 1520–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

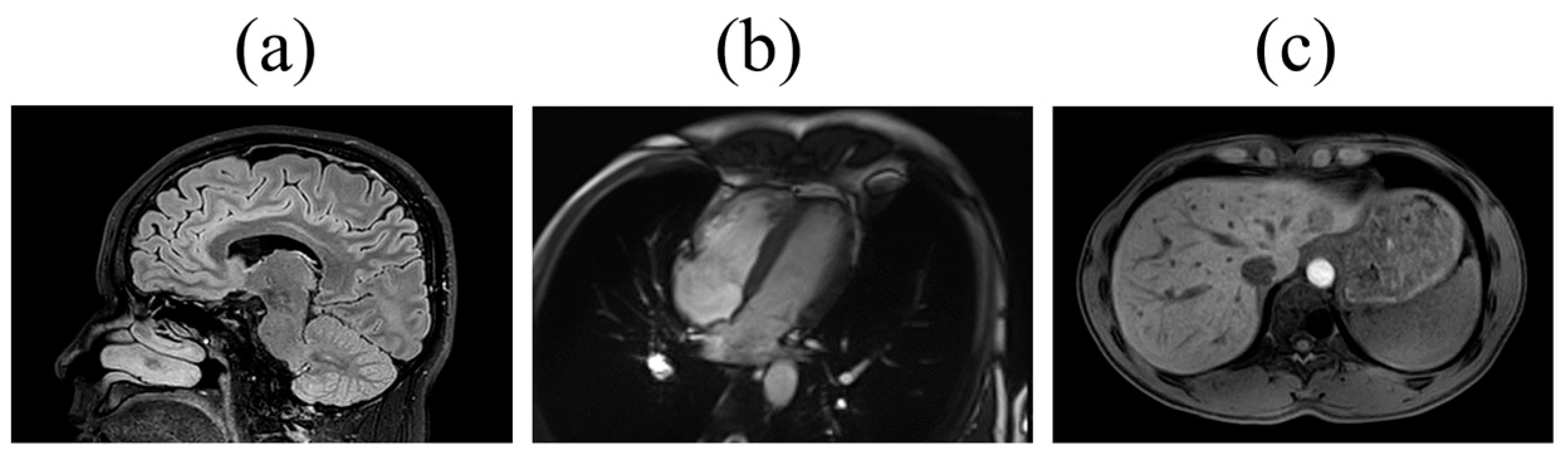
| Characteristics | All (N = 8646) | Men (N = 3808) | Women (N = 4838) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 64.2 ± 7.29 | 64.8 ± 7.4 | 63.7 ± 7.2 |
| Weight (kg) | 74.59 ± 13.82 | 82.54 ± 12.11 | 68.33 ± 11.71 |
| Height (cm) | 168.69 ± 8.99 | 175.98 ± 6.43 | 162.95 ± 6.09 |
| BMI | 26.25 ± 3.83 | 26.87 ± 3.39 | 25.77 ± 4.07 |
| Leukocytes (×109/L) | 6.53 ± 1.90 | 6.53 ± 2.23 | 6.52 ± 1.59 |
| RBC (×109/L) | 4.50 ± 0.40 | 4.75 ± 0.34 | 4.29 ± 0.32 |
| Hemoglobin (g/L) | 14.14 ± 1.22 | 15.02 ± 0.93 | 13.44 ± 0.95 |
| Blood platelets (109/L) | 251.21 ± 56.30 | 236.74 ± 51.22 | 262.64 ± 57.49 |
| ALT (U/L) | 22.46 ± 13.02 | 26.68 ± 13.09 | 19.18 ± 11.99 |
| AST (U/L) | 25.26 ± 7.98 | 27.41 ± 8.09 | 23.59 ± 7.48 |
| Dbil (μmol/L) | 1.84 ± 0.80 | 2.01 ± 0.86 | 1.69 ± 0.70 |
| Urea (mmol/L) | 5.26 ± 1.21 | 5.50 ± 1.23 | 5.08 ± 1.17 |
| C-reactive protein (mg/L) | 1.84 ± 3.08 | 1.81 ± 3.08 | 1.86 ± 3.07 |
| GGT (U/L) | 32.51 ± 34.82 | 40.61 ± 35.87 | 26.19 ± 32.62 |
| Lipoprotein (mg/L) | 43.25 ± 48.87 | 44.47 ± 49.71 | 42.30 ± 48.20 |
| TBIL (μmol/L) | 9.37 ± 4.56 | 10.54 ± 5.01 | 8.45 ± 3.39 |
| TGs (mmol/L) | 1.61 ± 0.91 | 1.89 ± 1.04 | 1.39 ± 0.71 |
| Organ | IDPs | Field ID | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brain | volume of grey matter | 25782–25920, 24360–24409 | [16] |
| Heart | cardiac and aortic structure and function | 24100–24181 | [19] |
| Lung | /volume | 3062, 3063, 3064, 20150, 20151, 20153, 20154, 20256, 20257, 20258, 21084 | [18] |
| Liver | volume/fat fraction/iron/ corrected T1 | 21080, 21088, 21089, 40060, 40061, 40062 | [17,18] |
| Spleen | volume/fat fraction/iron | 21083, 21170, 21173 | [18] |
| Pancreas | volume/fat fraction/iron | 21087, 21090, 21091 | [18] |
| Kidney | volume/kidney distance | 21081, 21082, 21160–21163 | [15] |
| Disease | ICD10 Code and Field ID | Number |
|---|---|---|
| HF | I110, I130, I132, Z941, T862, I500, I501, I509 | 89 |
| MI | I252, I210, I211, I212, I213, I214, I219, I21X, I220, I221 | 226 |
| AF | I480, I481, I482, I483, I484, I489 | 225 |
| CAD | Z955, I252, Z951, I240, I241, I248, I249, I250, I251, I253, I254, I255, I256, I258, I259, I210, I211, I212, I213, I214, I219, I21X, I220, I221, I228, I229, I230, I231, I232, I233, I234, I235, I236, I238 | 497 |
| T2D | E110, E111, E112, E113, E114, E115, E116, E117, E118, E119 | 284 |
| Hypertension | I10, I110, I119, I120, I129, I130, I131, I132, I139, I150, I151, I152, I158, I159, O100, O101, O102, O103, O104, O109 | 1637 |
| COPD | 42016 | 128 |
| Asthma | 42014 | 1093 |
| CKD | 132032 | 244 |
| Disease | Model | Cor | AUC | Interval | Sen | Spec | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CKD | PRS | −0.06 | 0.53 | 0.43~0.63 | 0.42 | 0.73 | 0.42 |
| IDP | 0.34 | 0.68 | 0.59~0.76 | 0.87 | 0.47 | 0.66 | |
| PRS + IDP | 0.31 | 0.67 | 0.58~0.76 | 0.66 | 0.66 | 0.66 | |
| Asthma | PRS | 0.16 | 0.59 | 0.54~0.63 | 0.40 | 0.74 | 0.56 |
| IDP | 0.34 | 0.70 | 0.66~0.74 | 0.48 | 0.84 | 0.66 | |
| PRS + IDP | 0.40 | 0.73 * | 0.69~0.77 | 0.61 | 0.73 | 0.67 | |
| COPD | PRS | 0.54 | 0.82 | 0.73~0.92 | 0.84 | 0.71 | 0.78 |
| IDP | 0.38 | 0.70 | 0.58~0.82 | 0.61 | 0.79 | 0.70 | |
| PRS + IDP | 0.66 | 0.88 | 0.81~0.96 | 0.79 | 0.89 | 0.83 | |
| AF | PRS | 0.40 | 0.74 | 0.66~0.82 | 0.58 | 0.82 | 0.70 |
| IDP | 0.37 | 0.71 | 0.62~0.79 | 0.76 | 0.58 | 0.68 | |
| PRS + IDP | 0.43 | 0.75 | 0.66~0.83 | 0.46 | 0.95 | 0.70 | |
| CAD | PRS | 0.27 | 0.66 | 0.60~0.72 | 0.56 | 0.72 | 0.65 |
| IDPs | 0.44 | 0.76 | 0.71~0.81 | 0.88 | 0.56 | 0.71 | |
| PRS + IDP | 0.50 | 0.81* | 0.75~0.86 | 0.80 | 0.73 | 0.76 | |
| HF | PRS | 0.22 | 0.63 | 0.47~0.79 | 0.74 | 0.55 | 0.66 |
| IDP | 0.32 | 0.68 | 0.53~0.83 | 0.50 | 0.84 | 0.66 | |
| PRS + IDP | 0.50 | 0.79 | 0.66~0.91 | 0.73 | 0.81 | 0.77 | |
| Hypertension | PRS | 0.12 | 0.57 | 0.53~0.61 | 0.50 | 0.61 | 0.56 |
| IDP | 0.45 | 0.77 | 0.74~0.80 | 0.71 | 0.72 | 0.71 | |
| PRS + IDP | 0.40 | 0.73 | 0.70~0.76 | 0.65 | 0.71 | 0.68 | |
| MI | PRS | 0.24 | 0.62 | 0.52~0.71 | 0.71 | 0.49 | 0.60 |
| IDP | 0.29 | 0.68 | 0.58~0.77 | 0.56 | 0.75 | 0.66 | |
| PRS + IDP | 0.48 | 0.79 | 0.71~0.86 | 0.87 | 0.55 | 0.72 | |
| T2D | PRS | 0.27 | 0.65 | 0.57~0.73 | 0.63 | 0.60 | 0.62 |
| IDP | 0.57 | 0.84 | 0.78~0.90 | 0.71 | 0.86 | 0.78 | |
| PRS + IDP | 0.60 | 0.87 * | 0.81~0.92 | 0.82 | 0.79 | 0.81 |
| Disease | Model | Cor | AUC | Interval | Sen | Spec | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CKD | Baseline | 0.31 | 0.67 | 0.58~0.76 | 0.66 | 0.66 | 0.66 |
| Baseline + drink | 0.36 | 0.72 | 0.62~0.82 | 0.55 | 0.82 | 0.67 | |
| Baseline + smoke | 0.37 | 0.72 | 0.62~0.82 | 0.62 | 0.76 | 0.69 | |
| Baseline + drink + smoke | 0.31 | 0.68 | 0.58~0.78 | 0.49 | 0.82 | 0.65 | |
| Asthma | Baseline | 0.35 | 0.70 | 0.66~0.74 | 0.59 | 0.70 | 0.65 |
| Baseline + drink | 0.33 | 0.69 | 0.65~0.74 | 0.78 | 0.55 | 0.67 | |
| Baseline + smoke | 0.36 | 0.71 | 0.66~0.75 | 0.70 | 0.61 | 0.65 | |
| Baseline + drink + smoke | 0.38 | 0.72 | 0.67~0.76 | 0.65 | 0.70 | 0.67 | |
| COPD | Baseline | 0.71 | 0.91 | 0.84~0.97 | 0.92 | 0.74 | 0.83 |
| Baseline + drink | 0.55 | 0.84 | 0.72~0.97 | 0.79 | 0.93 | 0.86 | |
| Baseline + smoke | 0.42 | 0.76 | 0.62~0.89 | 0.71 | 0.75 | 0.73 | |
| Baseline + drink + smoke | 0.60 | 0.85 | 0.73~0.98 | 0.88 | 0.85 | 0.86 | |
| AF | Baseline | 0.50 | 0.81 | 0.74~0.89 | 0.76 | 0.76 | 0.76 |
| Baseline + drink | 0.39 | 0.78 | 0.68~0.87 | 0.61 | 0.92 | 0.76 | |
| Baseline + smoke | 0.49 | 0.79 | 0.70~0.88 | 0.64 | 0.88 | 0.74 | |
| Baseline + drink + smoke | 0.39 | 0.75 | 0.65~0.85 | 0.68 | 0.82 | 0.78 | |
| CAD | Baseline | 0.46 | 0.77 | 0.72~0.82 | 0.66 | 0.79 | 0.73 |
| Baseline + drink | 0.51 | 0.80 | 0.75~0.86 | 0.69 | 0.84 | 0.76 | |
| Baseline + smoke | 0.44 | 0.76 | 0.70~0.83 | 0.68 | 0.74 | 0.71 | |
| Baseline + drink + smoke | 0.40 | 0.73 | 0.66~0.79 | 0.69 | 0.69 | 0.69 | |
| HF | Baseline | 0.63 | 0.87 | 0.78~0.97 | 0.85 | 0.81 | 0.83 |
| Baseline + drink | 0.56 | 0.82 | 0.69~0.95 | 0.90 | 0.65 | 0.78 | |
| Baseline + smoke | 0.37 | 0.68 | 0.51~0.86 | 0.42 | 1.00 | 0.73 | |
| Baseline + drink + smoke | 0.24 | 0.58 | 0.40~0.77 | 0.64 | 0.56 | 0.60 | |
| Hypertension | Baseline | 0.47 | 0.78 | 0.75~0.81 | 0.67 | 0.76 | 0.72 |
| Baseline + drink | 0.46 | 0.77 | 0.74~0.81 | 0.77 | 0.65 | 0.71 | |
| Baseline + smoke | 0.45 | 0.77 | 0.73~0.80 | 0.86 | 0.56 | 0.71 | |
| Baseline + drink + smoke | 0.44 | 0.76 | 0.73~0.79 | 0.67 | 0.71 | 0.69 | |
| MI | Baseline | 0.49 | 0.80 | 0.73~0.88 | 0.87 | 0.63 | 0.75 |
| Baseline + drink | 0.48 | 0.78 | 0.69~0.87 | 0.83 | 0.71 | 0.77 | |
| Baseline + smoke | 0.50 | 0.79 | 0.70~0.88 | 0.79 | 0.66 | 0.73 | |
| Baseline + drink + smoke | 0.36 | 0.73 | 0.63~0.82 | 0.64 | 0.75 | 0.70 | |
| T2D | Baseline | 0.56 | 0.84 | 0.78~0.90 | 0.67 | 0.86 | 0.76 |
| Baseline + drink | 0.53 | 0.81 | 0.74~0.89 | 0.85 | 0.72 | 0.78 | |
| Baseline + smoke | 0.50 | 0.79 | 0.71~0.87 | 0.90 | 0.62 | 0.76 | |
| Baseline + drink + smoke | 0.52 | 0.80 | 0.73~0.88 | 0.85 | 0.63 | 0.73 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Sun, L.; Sun, M.; Hu, X.; Li, Q.; Yu, M.; Wang, C.; Ren, X.; Ma, J. Integrating Multi-Organ Imaging-Derived Phenotypes and Genomic Information for Predicting the Occurrence of Common Diseases. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11090872
Liu M, Li Y, Sun L, Sun M, Hu X, Li Q, Yu M, Wang C, Ren X, Ma J. Integrating Multi-Organ Imaging-Derived Phenotypes and Genomic Information for Predicting the Occurrence of Common Diseases. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(9):872. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11090872
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Meng, Yan Li, Longyu Sun, Mengting Sun, Xumei Hu, Qing Li, Mengyao Yu, Chengyan Wang, Xinping Ren, and Jinlian Ma. 2024. "Integrating Multi-Organ Imaging-Derived Phenotypes and Genomic Information for Predicting the Occurrence of Common Diseases" Bioengineering 11, no. 9: 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11090872
APA StyleLiu, M., Li, Y., Sun, L., Sun, M., Hu, X., Li, Q., Yu, M., Wang, C., Ren, X., & Ma, J. (2024). Integrating Multi-Organ Imaging-Derived Phenotypes and Genomic Information for Predicting the Occurrence of Common Diseases. Bioengineering, 11(9), 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11090872








