Elastin-Collagen Based Hydrogels as Model Scaffolds to Induce Three-Dimensional Adipocyte Culture from Adipose Derived Stem Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Scaffold Formation
2.2. Scaffold Characterization
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Biochemical Characterization
2.5. Statistical Analysis
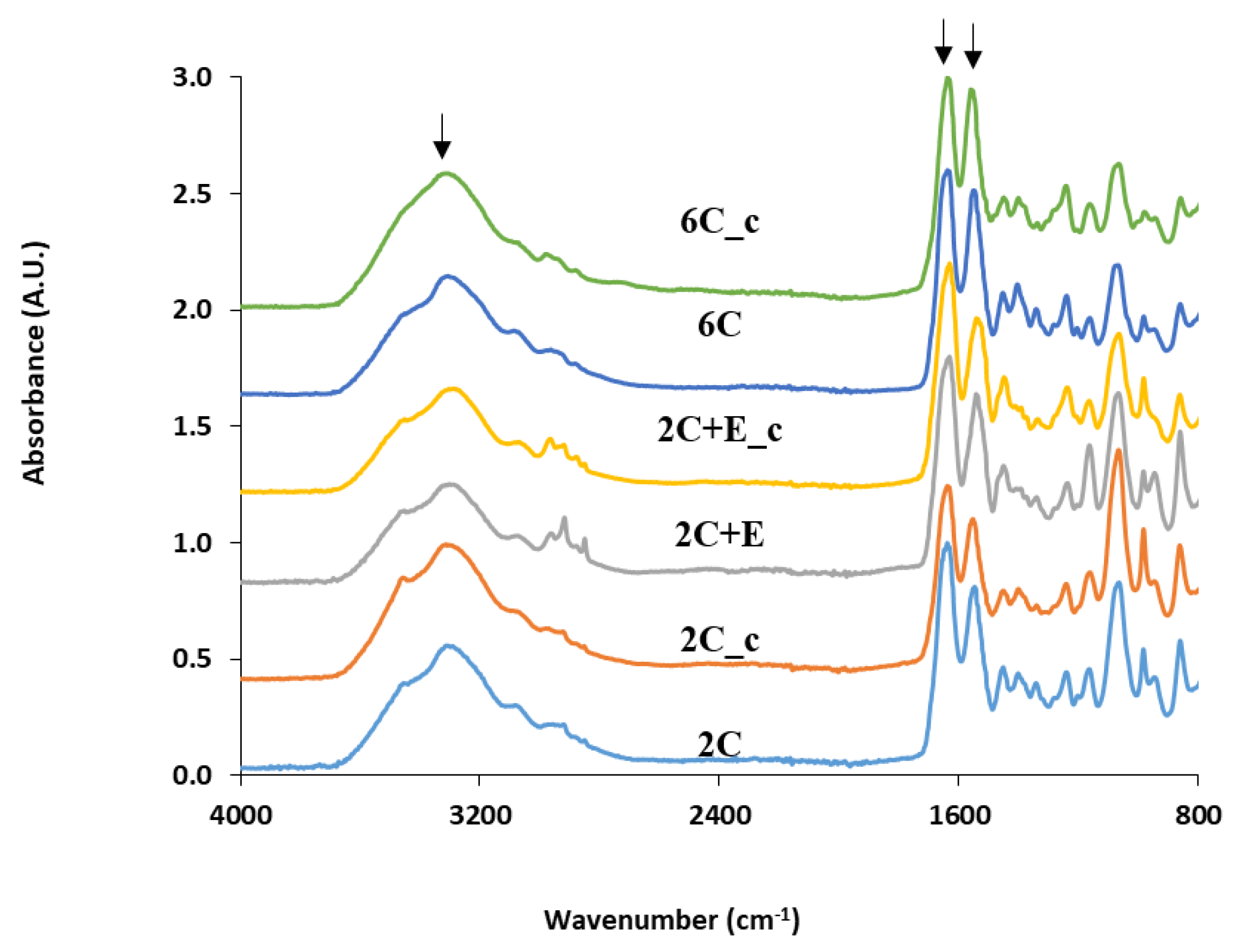
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Flegal, K.M.; Carroll, M.D.; Ogden, C.L.; Curtin, L.R. Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999–2008. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2010, 303, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pi-Sunyer, F.X. The obesity epidemic: Pathophysiology and consequences of obesity. Obes. Res. 2002, 10, 97S–104S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrick, C.W. Breast tissue engineering. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2004, 6, 109–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, A.J. Mesenchymal cell culture: Adipose tissue. In Methods of Tissue Engineering, 1st ed.; Atala, A., Lanza, R.P., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2002; pp. 277–286. [Google Scholar]
- Patrick, C.W. Adipose tissue engineering: The future of breast and soft tissue reconstruction following tumor resection. Semin. Surg. Oncol. 2000, 19, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauney, J.R.; Nguyen, T.; Gillen, K.; Kirker-Head, C.; Gimble, J.M.; Kaplan, D.L. Engineering adipose-like tissue in vitro and in vivo utilizing human bone marrow and adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells with silk fibroin 3D scaffolds. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 5280–5290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, L.; Peptan, I.; Clark, P.; Mao, J.J. Ex vivo adipose tissue engineering by human marrow stromal cell seeded gelatin sponge. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2005, 33, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höfner, C.; Muhr, C.; Horder, H.; Wiesner, M.; Wittmann, K.; Lukaszyk, D.; Radeloff, K.; Winnefeld, M.; Becker, M.; Blunk, T.; et al. Human ASC spheroids possess high adipogenic capacity and acquire an adipose tissue-like ECM pattern. Tissue Eng. Part A 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, P.A.; Weeks, C.A.; McMurphy, A.J.; Janorkar, A.V. Spheroid organization kinetics of H35 rat hepatoma model cell system on elastin-like polypeptide–polyethyleneimine copolymer substrates. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2014, 102A, 852–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, P.A.; Harris, L.M.; Purser, C.A.; Baker, R.C.; Janorkar, A.V. A surface-tethered spheroid model for functional evaluation of 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biotechol. Bioeng. 2014, 111, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teong, B.; Wu, S.C.; Chang, C.M.; Chen, J.W.; Chen, H.T.; Chen, C.H.; Chang, J.K.; Ho, M.L. The stiffness of a crosslinked hyaluronan hydrogel affects its chondro-induction activity on hADSCs. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B 2017, 106B, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomillion, C.T.; Burg, K.J.L. Stem cells and adipose tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 6052–6063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, D.; Nunalee, M.L.; Lim, D.W.; Simnick, A.J.; Chilkoti, A. Peptide-based biopolymers in biomedicine and biotechnology. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2008, 62, 125–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellmund, K.S.; Koksch, B. Self-Assembling peptides as extracellular matrix mimics to influence stem cell’s fate. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Divoux, A.; Tordjman, J.; Lacasa, D.; Veyrie, N.; Hugol, D.; Aissat, A.; Basdevant, A.; Guerre-Millo, M.; Poitou, C.; Zucker, J.D.; et al. Fibrosis in human adipose tissue: Composition, distribution, and link with lipid metabolism and fat mass loss. Diabetes 2010, 59, 2817–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zheng, C.; Luo, X.; Wang, X.; Jiang, H. Recent advances of collagen-based biomaterials: Multi-hierarchical structure, modification and biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 99, 1509–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; Zhang, D.; Macedo, M.H.; Cui, W.; Sarmento, B.; Shen, G. Advanced collagen-based biomaterials for regenerative biomedicine. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2019, 29, 1804943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parenteau-Bareil, R.; Gauvin, R.; Berthod, F. Collagen-based biomaterials for tissue engineering applications. Materials 2010, 3, 1863–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, P.; Nguyen, Q.; Hollis, A.; Marquart, M.E.; Janorkar, A.V. Drug-loaded elastin-like polypeptide-collagen hydrogels with high modulus for bone tissue engineering. Macromol. Biosci. 2019, 19, 1900142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, K.; Janorkar, A.V. Milieu for endothelial differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells. Bioengineering 2018, 5, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurumurthy, B.; Griggs, J.A.; Janorkar, A.V. Optimization of collagen-elastin-like polypeptide composite tissue engineering scaffolds using response surface methodology. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 84, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, M.; Bellingham, C.M.; Stahl, R.J.; Sitarz, E.E.; Lane, C.J.; Keeley, F.W. Sequence and structure determinants for the self-aggregation of recombinant polypeptides modeled after human elastin. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 48553–48562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srokowski, E.M.; Woodhouse, K.A. Development and characterization of novel cross-linked bio-elastomeric materials. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2008, 19, 785–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.C.; Tirrell, D.A. Cell response to RGD density in cross-linked artificial extracellular matrix protein films. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 2984–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Macosko, C.W.; Urry, D.W. Elastomeric polypentapeptides crosslinked into matrices and fibers. Biomacromolecules 2001, 2, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; McMillan, R.A.; Apkarian, R.P.; Pourdeyhimi, B.; Conticello, V.P.; Chaikof, E.L. Generation of synthetic elastin-mimetic small diameter fibers and fiber networks. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 2989–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, F.J.; Reboto, V.; Martin, S.M.; Lopez, I.; Rodríguez-Cabello, J.C. Tailored recombinant elastin-like polymers for advanced biomedical and nano(bio)technological applications. Biotechnol. Lett. 2006, 8, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, N.C.; Wang, S.; Young, T.H. The influence of spheroid formation of human adipose-derived stem cells on chitosan films on stemness and differentiation capabilities. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 1748–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurumurthy, B.; Bierdeman, P.C.; Janorkar, A.V. Spheroid model for functional osteogenic evaluation of human adipose derived stem cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2017, 105A, 1230–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, S.J.; Cobb, J.S.; Janorkar, A.V. Comparison of the formation, adipogenic maturation, and retention of human adipose-derived stem cell spheroids in scaffold-free culture techniques. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2020, 108, 3022–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.H.; Kim, T.H.; Im, G.I.; Lee, J.H. Investigation of pore size effect on chondrogenic differentiation of adipose stem cells using a pore size gradient scaffold. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 1948–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubillaga, V.; Alonso-Varona, A.; Fernandes, S.C.M.; Salaberria, A.M.; Palomares, T. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell chondrospheroids cultured in hypoxia and a 3D porous chitosan/chitin nanocrystal scaffold as a platform for cartilage tissue engineering. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, R.; Tirrell, D.A. Designing materials for biology and medicine. Nature 2004, 428, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutolf, M.; Hubbell, J.S. Synthetic biomaterials as instructive extracellular microenvironments for morphogenesis in tissue engineering. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, R.G. The role of matrix stiffness in regulating cell behavior. Hepatology 2008, 47, 1394–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cigognini, D.; Lomas, A.; Kumar, P.; Satyam, A.; English, A.; Azeem, A.; Pandit, A.; Zeugolis, D. Engineering in vitro microenvironments for cell based therapies and drug discovery. Drug. Discov. Today 2013, 18, 1099–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilak, F.; Cohen, D.M.; Estes, B.T.; Gimble, J.M.; Liedtke, W.; Chen, C.S. Control of stem cell fate by physical interactions with the extracellular matrix. Cell Stem Cell 2009, 5, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, G.C.; Engler, A.J. Intrinsic extracellular matrix properties regulate stem cell differentiation. J. Biomech. 2010, 43, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, M.K.; Xavier, J.R.; Carrow, J.K.; Desai, P.; Alge, D.; Gaharwar, A.K. Mechanically stiff nanocomposite hydrogels at ultralow nanoparticle content. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Zacarias, J.L.; Castro-Muñozledo, F.; Kuri-Harcuch, W. Quantitation of adipose conversion and triglycerides by staining intracytoplasmic lipids with Oil red O. Histochemistry 1992, 97, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.L.; Findlay, M.W.; Knight, K.R.; Penington, A.; Thompson, E.W.; Messina, A.; Morrison, W.A. Contact with existing adipose tissue is inductive for adipogenesis in Matrigel. Tissue Eng. 2006, 12, 2041–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, Y.; Ozeki, M.; Inamoto, T.; Tabata, Y. Adipose tissue engineering based on human preadipocytes combined with gelatin microspheres containing basic fibroblast growth factor. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 2513–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashi, A.V.; Abberton, K.M.; Thomas, G.P.; Morrison, W.A.; O’Connor, A.J.; Cooper-White, J.J.; Thompson, E.W. Adipose tissue engineering based on the controlled release of fibroblast growth factor-2 in a collagen matrix. Tissue Eng. 2006, 12, 3035–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torio-Padron, N.; Baerlecken, N.; Momeni, A.; Stark, G.B.; Borges, J. Engineering of adipose tissue by injection of human preadipocytes in fibrin. Aesthet. Plast. Surg. 2007, 31, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flynn, L.; Semple, J.L.; Woodhouse, K.A. Decellularized placental matrices for adipose tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2006, 79A, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohiuddin, O.A.; O’Donnell, B.T.; Poche, J.N.; Iftikhar, R.; Wise, R.M.; Motherwell, J.M.; Campbell, B.; Savkovic, S.D.; Bunnell, B.A.; Hayes, D.J.; et al. Human adipose-derived hydrogel characterization based on in vitro ASC biocompatibility and differentiation. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 2019, 9276398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemmrich, K.; von Heimburg, D.; Rendchen, R.; Di Bartolo, C.; Milella, E.; Pallua, N. Implantation of preadipocyte-loaded hyaluronic acid based scaffolds into nude mice to evaluate potential for soft tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 7025–7037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmrich, K.; Van de Sijpe, K.; Rhodes, N.P.; Hunt, J.A.; Di Bartolo, C.; Pallua, N.; Blondeel, P.; von Heimburg, D. autologous in vivo adipose tissue engineering in hyaluronan-based gels—A pilot study. J. Surg. Res. 2008, 144, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halberstadt, C.; Austin, C.; Rowley, J.; Culberson, C.; Loebsack, A.; Wyatt, S.; Coleman, S.; Blacksten, L.; Burg, K.; Mooney, D.; et al. A hydrogel material for plastic and reconstructive applications injected into the subcutaneous space of a sheep. Tissue Eng. 2002, 8, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Bellas, E.; Vunjak-Novakovic, G.; Kaplan, D.L. Adipogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells on 3D silk scaffolds. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 702, 319–330. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H.; Park, Y.; Jung, Y.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, S.H. Combinatorial therapy with three-dimensionally cultured adipose-derived stromal cells and self-assembling peptides to enhance angiogenesis and preserve cardiac function in infarcted hearts. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2017, 11, 2816–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Ren, H.; He, J.; Qiao, L.; Cui, F. Functionalized self-assembling peptide nanofiber hydrogels mimic stem cell niche to control human adipose stem cell behavior in vitro. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 6798–6805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurumurthy, B.; Pal, P.; Griggs, J.A.; Janorkar, A.V. Optimization of collagen-elastin-like polypeptide-bioglass scaffold composition for osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells. Materialia 2020, 9, 100572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhouli, N.; Mansfield, J.; Green, E.; Bell, J.; Knight, B.; Liversedge, N.; Tham, J.C.; Welbourn, R.; Shore, A.C.; Kos, K.; et al. The mechanical properties of human adipose tissues and their relationships to the structure and composition of the extracellular matrix. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 305, E1427–E1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Name | Collagen | ELP | Crosslinking with EDC/NHS * |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2C | 2 mg/mL | -- | -- |
| 2C_c | 2 mg/mL | -- | Yes |
| 2C+E | 2 mg/mL | 6 mg/mL | -- |
| 2C+E_c | 2 mg/mL | 6 mg/mL | Yes |
| 6C | 6 mg/mL | -- | -- |
| 6C_c | 6 mg/mL | -- | Yes |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Newman, K.; Clark, K.; Gurumurthy, B.; Pal, P.; Janorkar, A.V. Elastin-Collagen Based Hydrogels as Model Scaffolds to Induce Three-Dimensional Adipocyte Culture from Adipose Derived Stem Cells. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering7030110
Newman K, Clark K, Gurumurthy B, Pal P, Janorkar AV. Elastin-Collagen Based Hydrogels as Model Scaffolds to Induce Three-Dimensional Adipocyte Culture from Adipose Derived Stem Cells. Bioengineering. 2020; 7(3):110. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering7030110
Chicago/Turabian StyleNewman, Kristen, Kendra Clark, Bhuvaneswari Gurumurthy, Pallabi Pal, and Amol V. Janorkar. 2020. "Elastin-Collagen Based Hydrogels as Model Scaffolds to Induce Three-Dimensional Adipocyte Culture from Adipose Derived Stem Cells" Bioengineering 7, no. 3: 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering7030110
APA StyleNewman, K., Clark, K., Gurumurthy, B., Pal, P., & Janorkar, A. V. (2020). Elastin-Collagen Based Hydrogels as Model Scaffolds to Induce Three-Dimensional Adipocyte Culture from Adipose Derived Stem Cells. Bioengineering, 7(3), 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering7030110





