3D Hepatic Organoid-Based Advancements in LIVER Tissue Engineering
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Physiological Microenvironment of the Liver
2.1. Liver Physiological Units
2.1.1. Liver Lobule
2.1.2. Liver Sinusoid (LSs)
2.2. Cell Types and Composition
2.2.1. Parenchymal Cells/Hepatocytes (HEPs)
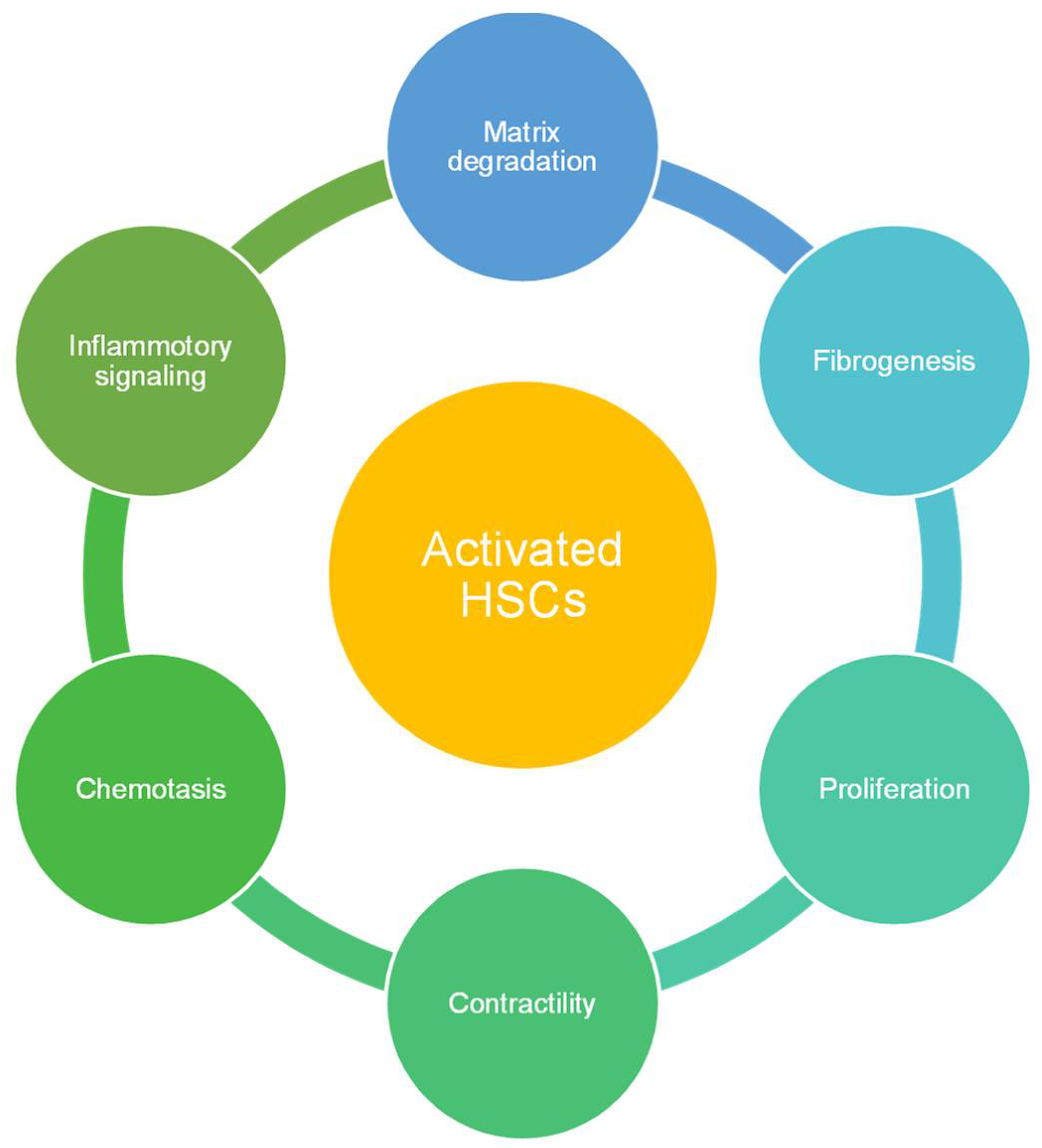
2.2.2. Hepatic Stellate Cells (HSCs)
2.2.3. Hepatic/Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells (LSECs)
2.2.4. Kupffer Cells (KCs)
2.2.5. Biliary Epithelial Cells/Cholangiocytes (BECs)
3. Development of Hepatic Tissues: Strategies and Challenges
3.1. 2D Monolayer Culture
3.2. Sandwich Culture
3.3. Scaffold Free Spheroid/Organoid Development
3.4. Liver on a Chip
4. Application of Hepatic Organoids
4.1. Drug Screening
4.2. Disease Model
4.3. Metabolism Prediction
4.4. Multi Organ-on-a-Chip
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Asrani, S.K.; Devarbhavi, H.; Eaton, J.; Kamath, P.S. Burden of liver diseases in the world. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Checa, J.C.; Bagnaninchi, P.; Ye, H.; Sancho-Bru, P.; Falcon-Perez, J.M.; Royo, F.; Garcia-Ruiz, C.; Konu, O.; Miranda, J.; Lunov, O.; et al. Advanced preclinical models for evaluation of drug-induced liver injury-consensus statement by the European Drug-Induced Liver Injury Network [PRO-EURO-DILI-NET]. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 235–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldatow, V.Y.; Lecluyse, E.L.; Griffith, L.G.; Rusyn, I. In vitro models for liver toxicity testing. Toxicol. Res. (Camb) 2013, 2, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco, V.; Shariati, S.A.; Esfandyarpour, R. Microtechnology-based methods for organoid models. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2020, 6, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Li, N.; Long, M. Chapter 6-Liver sinusoid on a chip. In Methods in Cell Biology; Doh, J., Fletcher, D., Piel, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; Volume 146, pp. 105–134. [Google Scholar]
- Usta, O.; McCarty, W.; Bale, S.; Hegde, M.; Jindal, R.; Bhushan, A.; Golberg, I.; Yarmush, M. Microengineered cell and tissue systems for drug screening and toxicology applications: Evolution of in-vitro liver technologies. Technology 2015, 3, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godoy, P.; Hewitt, N.J.; Albrecht, U.; Andersen, M.E.; Ansari, N.; Bhattacharya, S.; Bode, J.G.; Bolleyn, J.; Borner, C.; Boettger, J. Recent advances in 2D and 3D in vitro systems using primary hepatocytes, alternative hepatocyte sources and non-parenchymal liver cells and their use in investigating mechanisms of hepatotoxicity, cell signaling and ADME. Arch. Toxicol. 2013, 87, 1315–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyer, J.L.; Soroka, C.J. Bile formation and Secretion: An update. J. Hepatol. 2021, 3, 1035–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, R.J.; Schott, M.B.; Casey, C.A.; Tuma, P.L.; McNiven, M.A. The cell biology of the hepatocyte: A membrane trafficking machine. J. Cell Biol. 2019, 218, 2096–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, H.F.; Blaner, W.S.; Wennekers, H.M.; Piantedosi, R.; Brouwer, A.; de Leeuw, A.M.; Goodman, D.S.; Knook, D.L. Distributions of retinoids, retinoid-binding proteins and related parameters in different types of liver cells isolated from young and old rats. Eur. J. Biochem. 1988, 171, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, H.; Verhoofstad, W.; Brouwer, A.; De Leeuw, A.; Knook, D. Perisinusoidal fat-storing cells are the main vitamin A storage sites in rat liver. Exp. Cell Res. 1985, 160, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadori, G.; Knittel, T.; Schwögler, S.; Bieber, F.; Rieder, H.; Büschenfelde, K.-H.M.Z. Dexamethasone modulates α2-macroglobulin and apolipoprotein E gene expression in cultured rat liver fat-storing (Ito) cells. Hepatology 1991, 14, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitkopf, K.; Godoy, P.; Ciuclan, L.; Singer, M.; Dooley, S. TGF-β/Smad signaling in the injured liver. Z. für Gastroenterol. 2006, 44, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, Y.H.; Schwabe, R.F.; Bataller, R.; Russo, M.P.; Jobin, C.; Brenner, D.A. Toll-like receptor 4 mediates inflammatory signaling by bacterial lipopolysaccharide in human hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology 2003, 37, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fimmel, C.J.; Brown, K.E.; O’Neill, R.; Kladney, R.D. Complement C4 protein expression by rat hepatic stellate cells. J. Immunol. 1996, 157, 2601–2609. [Google Scholar]
- Marra, F.; Pinzani, M. Role of hepatic stellate cells in the pathogenesis of portal hypertension. Nefrologia 2002, 22, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Bonacchi, A.; Petrai, I.; Defranco, R.M.; Lazzeri, E.; Annunziato, F.; Efsen, E.; Cosmi, L.; Romagnani, P.; Milani, S.; Failli, P. The chemokine CCL21 modulates lymphocyte recruitment and fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 1060–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, P.; Castagliuolo, I.; Pinzani, M.; Palù, G.; Martines, D. Exposure to bacterial cell wall products triggers an inflammatory phenotype in hepatic stellate cells. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2005, 289, G571–G578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchida, T.; Friedman, S.L. Mechanisms of hepatic stellate cell activation. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskin, D.L. Nonparenchymal cells and hepatotoxicity. Semin. Liver Dis. 1990, 10, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokomori, H.; Oda, M.; Ogi, M.; Sakai, K.; Ishii, H. Enhanced expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase and caveolin-1 in human cirrhosis. Liver 2002, 22, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracia-Sancho, J.; Caparrós, E.; Fernández-Iglesias, A.; Francés, R. Role of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in liver diseases. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 411–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poisson, J.; Lemoinne, S.; Boulanger, C.; Durand, F.; Moreau, R.; Valla, D.; Rautou, P.-E. Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells: Physiology and role in liver diseases. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLeve, L.D. Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in hepatic fibrosis. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1740–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, A.L.; Qurashi, M.; Shetty, S. The Role of Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells in the Axis of Inflammation and Cancer Within the Liver. Front. Physiol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, L.J.; Barnes, M.; Tang, H.; Pritchard, M.T.; Nagy, L.E. Kupffer cells in the liver. Compr. Physiol. 2013, 3, 785. [Google Scholar]
- Kolios, G.; Valatas, V.; Kouroumalis, E. Role of Kupffer cells in the pathogenesis of liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2006, 12, 7413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilzer, M.; Roggel, F.; Gerbes, A.L. Role of Kupffer cells in host defense and liver disease. Liver Int. 2006, 26, 1175–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirica, A.E.; Mathis, G.A.; Sano, N.; Elmore, L.W. Isolation, culture, and transplantation of intrahepatic biliary epithelial cells and oval cells. Pathobiology 1990, 58, 44–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alison, M.R.; Golding, M.; Sarraf, C.E.; Edwards, R.J.; Lalani, E.-N. Liver damage in the rat induces hepatocyte stem cells from biliary epithelial cells. Gastroenterology 1996, 110, 1182–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.; Luo, Y.; Lu, Y.; Liu, T.; Wu, Z.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, W.; Lin, B. A cell lines derived microfluidic liver model for investigation of hepatotoxicity induced by drug-drug interaction. Biomicrofluidics 2019, 13, 024101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milner, E.; Ainsworth, M.; McDonough, M.; Stevens, B.; Buehrer, J.; Delzell, R.; Wilson, C.; Barnhill, J. Emerging Three-Dimensional Hepatic Models in Relation to Traditional Two-Dimensional In Vitro Assays for Evaluating Drug Metabolism and Hepatoxicity. Med. Drug Discov. 2020, 8, 100060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aday, S.; Hasirci, N.; Deliloglu Gurhan, I. A cost-effective and simple culture method for primary hepatocytes. Anim. Cells Syst. 2011, 15, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Chan, W.C.; Badylak, S.F.; Bhatia, S.N. Assessing porcine liver-derived biomatrix for hepatic tissue engineering. Tissue Eng. 2004, 10, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, V.; Berglund, E.J.; Chen, D.X.; Kidambi, S. Substrate stiffness regulates primary hepatocyte functions. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 80956–80966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foucher, J.; Chanteloup, E.; Vergniol, J.; Castéra, L.; Le Bail, B.; Adhoute, X.; Bertet, J.; Couzigou, P.; de Lédinghen, V. Diagnosis of cirrhosis by transient elastography (FibroScan): A prospective study. Gut 2006, 55, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takebe, T.; Sekine, K.; Enomura, M.; Koike, H.; Kimura, M.; Ogaeri, T.; Zhang, R.-R.; Ueno, Y.; Zheng, Y.-W.; Koike, N. Vascularized and functional human liver from an iPSC-derived organ bud transplant. Nature 2013, 499, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, J.C.Y.; Yarmush, M.L.; Koebe, H.G.; Tompkins, R.G. Hepatocyte function and extracellular matrix geometry: Long-term culture in a sandwich configuration. FASEB J. 1989, 3, 174–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keemink, J.; Oorts, M.; Annaert, P. Primary hepatocytes in sandwich culture. In Protocols in In Vitro Hepatocyte Research; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 175–188. [Google Scholar]
- Treijtel, N.; Barendregt, A.; Freidig, A.P.; Blaauboer, B.J.; van Eijkeren, J.C. Modeling the in vitro intrinsic clearance of the slowly metabolized compound tolbutamide determined in sandwich-cultured rat hepatocytes. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2004, 32, 884–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeigerer, A.; Wuttke, A.; Marsico, G.; Seifert, S.; Kalaidzidis, Y.; Zerial, M. Functional properties of hepatocytes in vitro are correlated with cell polarity maintenance. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 350, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turncliff, R.Z.; Tian, X.; Brouwer, K.L.R. Effect of culture conditions on the expression and function of Bsep, Mrp2, and Mdr1a/b in sandwich-cultured rat hepatocytes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006, 71, 1520–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swift*, B.; Pfeifer*, N.D.; Brouwer, K.L.R. Sandwich-cultured hepatocytes: An in vitro model to evaluate hepatobiliary transporter-based drug interactions and hepatotoxicity. Drug Metab. Rev. 2010, 42, 446–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Toprakhisar, B.; Van Haele, M.; Antoranz, A.; Boon, R.; Chesnais, F.; De Smedt, J.; Tricot, T.; Idoype, T.I.; Canella, M. A fully defined matrix to support a pluripotent stem cell derived multi-cell-liver steatohepatitis and fibrosis model. Biomaterials 2021, 276, 121006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.-L.; Kim, Y.-K.; Cho, K.-H.; Jang, Y.-C.; Choi, Y.-J.; Chung, J.-H.; Cho, C.-S. Roles of spheroid formation of hepatocytes in liver tissue engineering. Int. J. Stem Cells 2010, 3, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bell, C.C.; Hendriks, D.F.G.; Moro, S.M.L.; Ellis, E.; Walsh, J.; Renblom, A.; Fredriksson Puigvert, L.; Dankers, A.C.A.; Jacobs, F.; Snoeys, J.; et al. Characterization of primary human hepatocyte spheroids as a model system for drug-induced liver injury, liver function and disease. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, D.F.; Fredriksson Puigvert, L.; Messner, S.; Mortiz, W.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M. Hepatic 3D spheroid models for the detection and study of compounds with cholestatic liability. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Souza, A.A.; Devarajan, P.V. Asialoglycoprotein receptor mediated hepatocyte targeting-strategies and applications. J. Control. Release 2015, 203, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, A.; Kobayashi, K.; Akaike, T. Control of adhesion and detachment of parenchymal liver cells using lactose-carrying polystyrene as substratum. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 1992, 3, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobe, S.; Takei, Y.; Kobayashi, K.; Akaike, T. Receptor-mediated formation of multilayer aggregates of primary cultured adult rat hepatocytes on lactose-substituted polystyrene. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1992, 184, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shri, M.; Agrawal, H.; Rani, P.; Singh, D.; Onteru, S.K. Hanging Drop, A Best Three-Dimensional (3D) Culture Method for Primary Buffalo and Sheep Hepatocytes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.-Y.; Chiang, T.-H.; Hsieh, L.-H.; Yang, W.-Y.; Hsu, H.-H.; Yeh, C.-K.; Huang, C.-C.; Huang, J.-H. Development of a Novel Hanging Drop Platform for Engineering Controllable 3D Microenvironments. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puryear Iii, J.R.; Yoon, J.-K.; Kim, Y. Advanced Fabrication Techniques of Microengineered Physiological Systems. Micromachines 2020, 11, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhise, N.S.; Manoharan, V.; Massa, S.; Tamayol, A.; Ghaderi, M.; Miscuglio, M.; Lang, Q.; Shrike Zhang, Y.; Shin, S.R.; Calzone, G.; et al. A liver-on-a-chip platform with bioprinted hepatic spheroids. Biofabrication 2016, 8, 014101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, J.; Özkan, A.; Oh, C.; Mahajan, G.; Prantil-Baun, R.; Ingber, D.E. Simulating drug concentrations in PDMS microfluidic organ chips. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 3509–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennert, K.; Steinborn, S.; Gröger, M.; Ungerböck, B.; Jank, A.-M.; Ehgartner, J.; Nietzsche, S.; Dinger, J.; Kiehntopf, M.; Funke, H.; et al. A microfluidically perfused three dimensional human liver model. Biomaterials 2015, 71, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broutier, L.; Mastrogiovanni, G.; Verstegen, M.M.A.; Francies, H.E.; Gavarró, L.M.; Bradshaw, C.R.; Allen, G.E.; Arnes-Benito, R.; Sidorova, O.; Gaspersz, M.P.; et al. Human primary liver cancer–derived organoid cultures for disease modeling and drug screening. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1424–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartfeld, S.; Bayram, T.; van de Wetering, M.; Huch, M.; Begthel, H.; Kujala, P.; Vries, R.; Peters, P.J.; Clevers, H. In vitro expansion of human gastric epithelial stem cells and their responses to bacterial infection. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 126–136. e126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, S.H.; Chamberlain, M.D.; Mahesh, S.; Sefton, M.V.; Wheeler, A.R. Hepatic organoids for microfluidic drug screening. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 3290–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, B.; He, Y.; Bao, J. Liver Organoids: Formation Strategies and Biomedical Applications. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2021, 18, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Choi, B.; No, D.Y.; Lee, G.; Lee, S.-r.; Oh, H.; Lee, S.-H. A 3D alcoholic liver disease model on a chip. Integr. Biol. 2016, 8, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, S.N.; Underhill, G.H.; Zaret, K.S.; Fox, I.J. Cell and tissue engineering for liver disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 245sr242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.H.; Lee, J.S.; Wang, X.; Hoon Lee, S. Bottom-Up Engineering of Well-Defined 3D Microtissues Using Microplatforms and Biomedical Applications. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 56–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon No, D.; Lee, K.-H.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.-H. 3D liver models on a microplatform: Well-defined culture, engineering of liver tissue and liver-on-a-chip. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 3822–3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Tan, Z.; Su, Y.; Liu, J.; Chang, M.; Yan, F.; Chen, J.; Chen, T.; Li, C.; et al. Human ESC-derived expandable hepatic organoids enable therapeutic liver repopulation and pathophysiological modeling of alcoholic liver injury. Cell Res. 2019, 29, 1009–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, X.; Luo, Y.; Wu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhao, W.; Lin, B. A liver-chip-based alcoholic liver disease model featuring multi-non-parenchymal cells. Biomed. Microdevices 2019, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Tasnim, F.; Huang, X.; Yu, H. A scalable and sensitive steatosis chip with long-term perfusion of in situ differentiated HepaRG organoids. Biomaterials 2021, 275, 120904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbadawy, M.; Yamanaka, M.; Goto, Y.; Hayashi, K.; Tsunedomi, R.; Hazama, S.; Nagano, H.; Yoshida, T.; Shibutani, M.; Ichikawa, R. Efficacy of primary liver organoid culture from different stages of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) mouse model. Biomaterials 2020, 237, 119823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Prieto, A.M.; Skelton, J.K.; Wai, S.N.; Large, E.; Lussignol, M.; Vizcay-Barrena, G.; Hughes, D.; Fleck, R.A.; Thursz, M.; Catanese, M.T.; et al. 3D microfluidic liver cultures as a physiological preclinical tool for hepatitis B virus infection. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, R.J.; Jochemsen, R. Nonclinical pharmacokinetics and toxicokinetics. In International Pharmaceutical Product Registration; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 352–392. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, J.A.; Hyland, R.; Jones, B.C.; Smith, D.A.; Hurst, S.; Goosen, T.C.; Peterkin, V.; Koup, J.R.; Ball, S.E. Drug-drug interactions for UDP-glucuronosyltransferase substrates: A pharmacokinetic explanation for typically observed low exposure (AUCI/AUC) ratios. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2004, 32, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasinu, P.; Bouic, P.J.; Rosenkranz, B. Liver-based in vitro technologies for drug biotransformation studies-a review. Curr. Drug Metab. 2012, 13, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanioka, N.; Saito, K.; Isobe, T.; Ohkawara, S.; Jinno, H.; Tanaka-Kagawa, T. Favipiravir biotransformation in liver cytosol: Species and sex differences in humans, monkeys, rats, and mice. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2021, 42, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lu, Y.-F.; Corton, J.C.; Klaassen, C.D. Expression of cytochrome P450 isozyme transcripts and activities in human livers. Xenobiotica 2021, 51, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riede, J.; Wollmann, B.M.; Molden, E.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M. Primary Human Hepatocyte Spheroids as an In Vitro Tool for Investigating Drug Compounds with Low Hepatic Clearance. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2021, 49, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouchi, R.; Togo, S.; Kimura, M.; Shinozawa, T.; Koido, M.; Koike, H.; Thompson, W.; Karns, R.A.; Mayhew, C.N.; McGrath, P.S.; et al. Modeling Steatohepatitis in Humans with Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Organoids. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 374–384.e376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Patel, D.; Kwa, T.; Haque, A.; Matharu, Z.; Stybayeva, G.; Gao, Y.; Diehl, A.M.; Revzin, A. Liver injury-on-a-chip: Microfluidic co-cultures with integrated biosensors for monitoring liver cell signaling during injury. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 4467–4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Sung, J.H. Gut-liver on a chip toward an in vitro model of hepatic steatosis. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2018, 115, 2817–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.w.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, D.; Sung, J.H. In vitro hepatic steatosis model based on gut–liver-on-a-chip. Biotechnol. Prog. 2021, 37, e3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esch, M.B.; Mahler, G.J.; Stokol, T.; Shuler, M.L. Body-on-a-chip simulation with gastrointestinal tract and liver tissues suggests that ingested nanoparticles have the potential to cause liver injury. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 3081–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Z.; Tao, T.; Chen, W.; Yu, H.; Qin, J. HiPSC-derived multi-organoids-on-chip system for safety assessment of antidepressant drugs. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimek, K.; Frentzel, S.; Luettich, K.; Bovard, D.; Rütschle, I.; Boden, L.; Rambo, F.; Erfurth, H.; Dehne, E.-M.; Winter, A.; et al. Human multi-organ chip co-culture of bronchial lung culture and liver spheroids for substance exposure studies. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Panwar, A.; Das, P.; Tan, L.P. 3D Hepatic Organoid-Based Advancements in LIVER Tissue Engineering. Bioengineering 2021, 8, 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering8110185
Panwar A, Das P, Tan LP. 3D Hepatic Organoid-Based Advancements in LIVER Tissue Engineering. Bioengineering. 2021; 8(11):185. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering8110185
Chicago/Turabian StylePanwar, Amit, Prativa Das, and Lay Poh Tan. 2021. "3D Hepatic Organoid-Based Advancements in LIVER Tissue Engineering" Bioengineering 8, no. 11: 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering8110185
APA StylePanwar, A., Das, P., & Tan, L. P. (2021). 3D Hepatic Organoid-Based Advancements in LIVER Tissue Engineering. Bioengineering, 8(11), 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering8110185






