Functional Expression of the Recombinant Spike Receptor Binding Domain of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron in the Periplasm of Escherichia coli
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plasmid Construction
2.2. Recombinant Proteins Expressed in Mammalian Cells
2.3. Expression and Purification of Omicron RBDs in E. coli
2.4. MBP Cleavage of MBP-Fused Omicron RBD by Thrombin
2.5. Bio-Layer Interferometry (BLI) Analysis
2.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorben Assay (ELISA)
3. Results
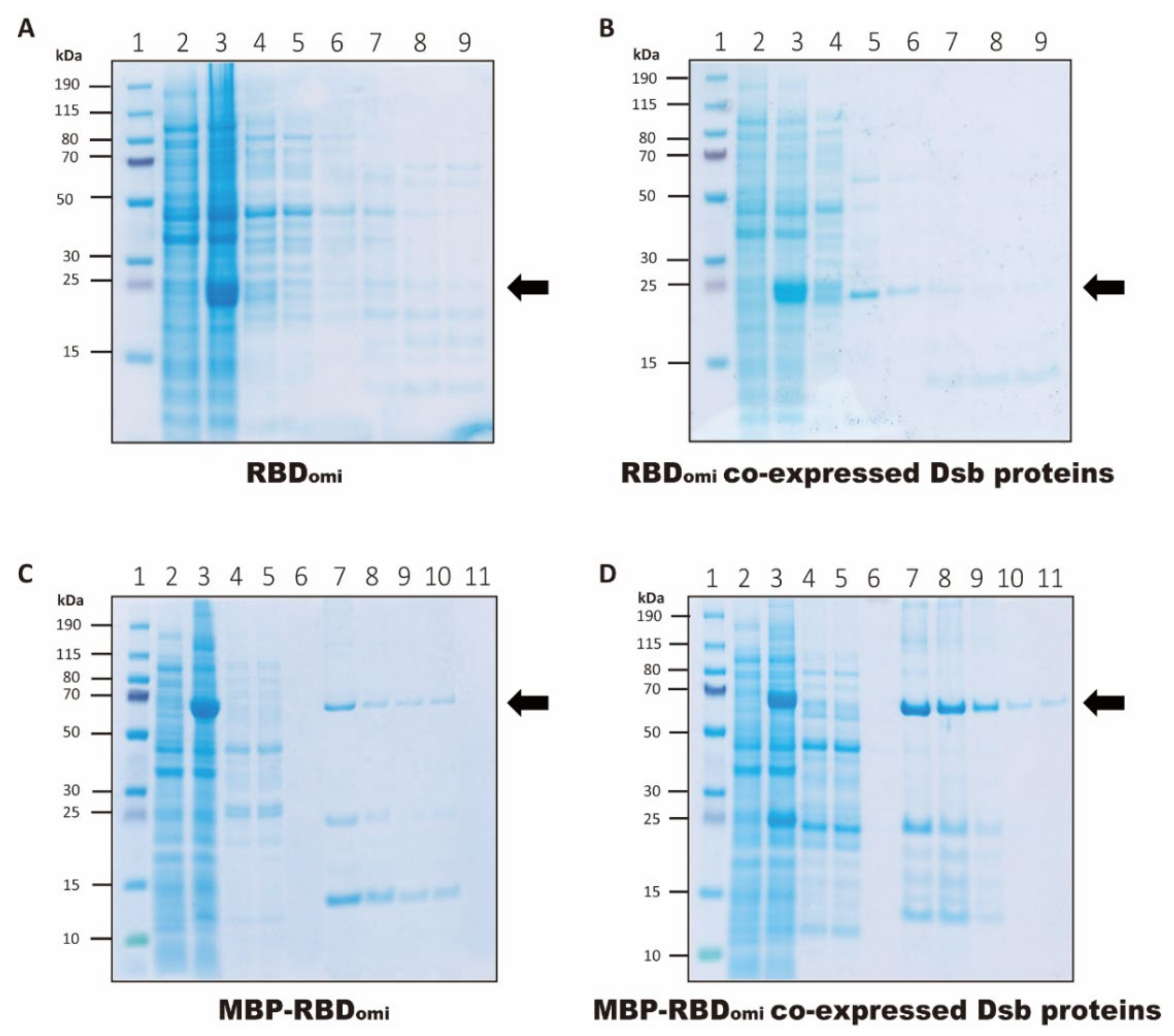
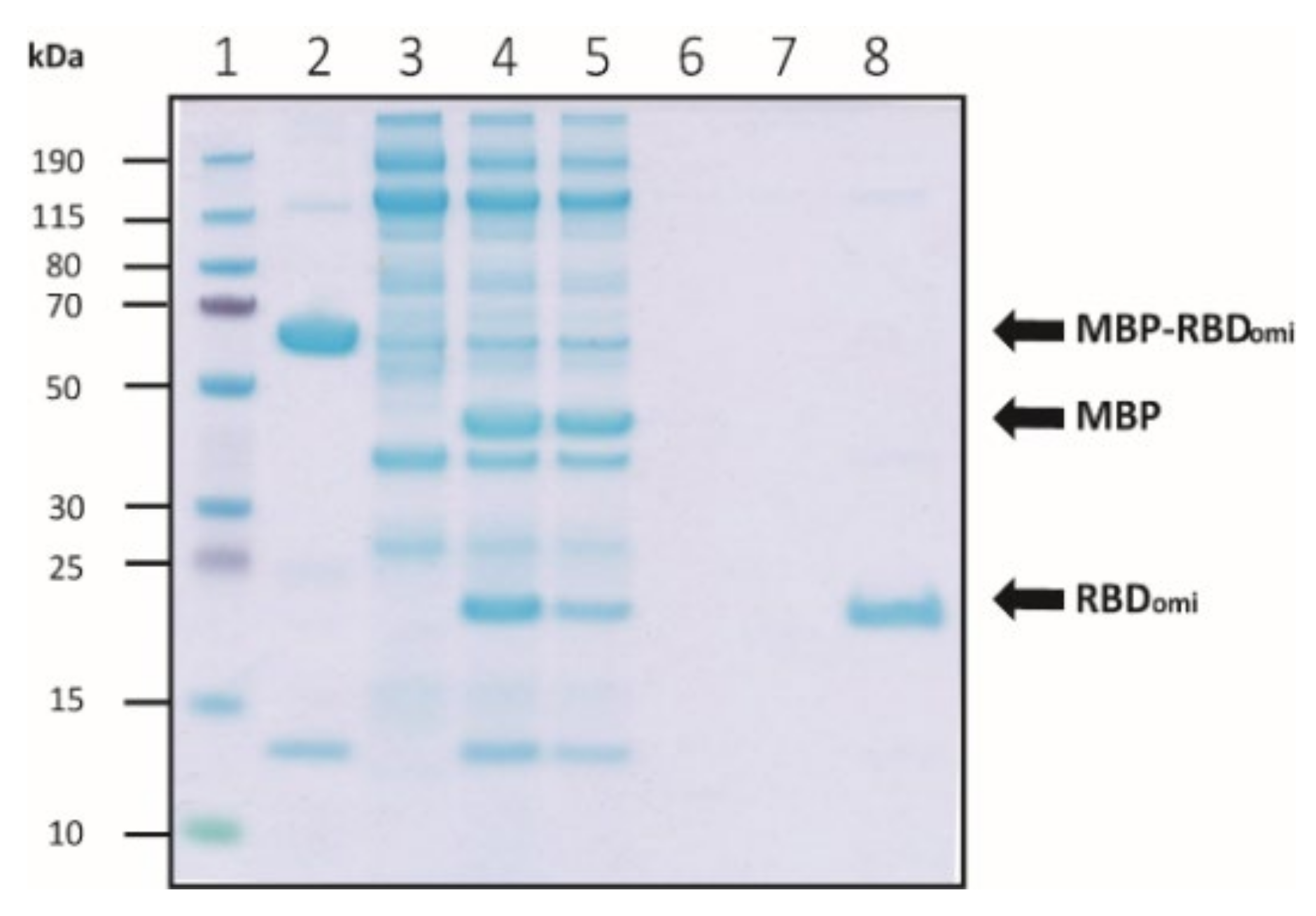
3.1. Expression and Purification of Soluble Omicron RBDs
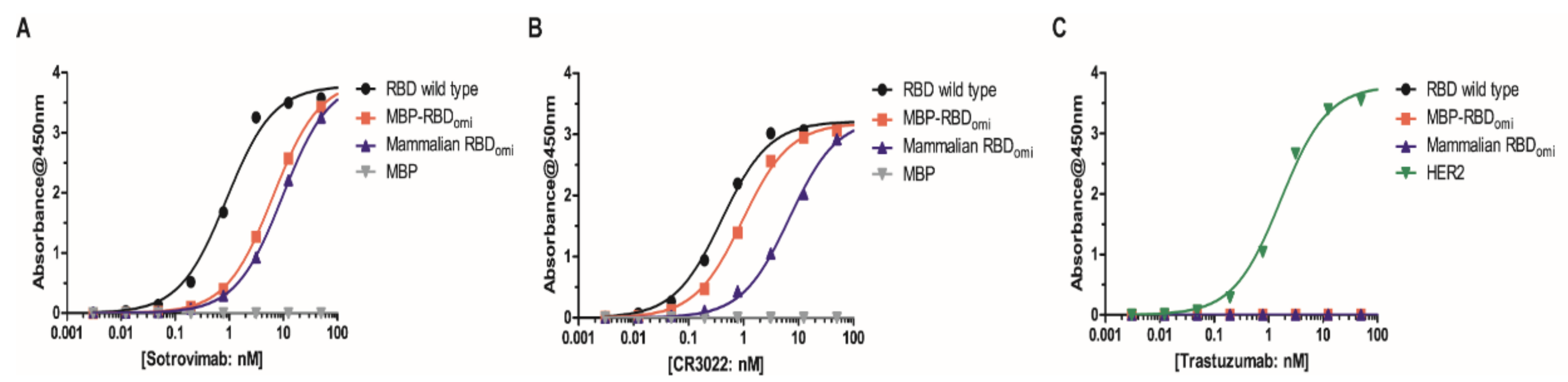
3.2. E. coli-Expresed MBP-RBDomicron Exhibits Selevtive Binding to Sotrovimab, CR3022, and Human ACE2
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lithander, F.E.; Neumann, S.; Tenison, E.; Lloyd, K.; Welsh, T.J.; Rodrigues, J.C.L.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Scourfield, L.; Christensen, H.; Haunton, V.J.; et al. COVID-19 in older people: A rapid clinical review. Age Ageing 2020, 49, 501–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolich-Zugich, J.; Knox, K.S.; Rios, C.T.; Natt, B.; Bhattacharya, D.; Fain, M.J. SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 in older adults: What we may expect regarding pathogenesis, immune responses, and outcomes. GeroScience 2020, 42, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Our World in Data, Coronavirus (COVID-19) Vaccinations. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/covid-vaccinations (accessed on 19 October 2022).
- Our World in Data, Coronavirus (COVID-19) Cases. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/covid-cases (accessed on 19 October 2022).
- World Health Organization COVID-19 Dashboard. Geneva. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 19 October 2022).
- Our World in Data, Coronavirus (COVID-19) Deaths. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/covid-deaths (accessed on 19 October 2022).
- Huang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Niu, Z.; Zhou, L.; Sun, Q. SARS-CoV-2 N501Y variants of concern and their potential transmission by mouse. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 2840–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohapatra, R.K.; Tiwari, R.; Sarangi, A.K.; Sharma, S.K.; Khandia, R.; Saikumar, G.; Dhama, K. Twin combination of Omicron and Delta variants triggering a tsunami wave of ever high surges in COVID-19 cases: A challenging global threat with a special focus on the Indian subcontinent. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 1761–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nextstrain, Genomic Epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 with Subsampling Focused Globally over the Past 6 Months. Available online: https://nextstrain.org/ncov/gisaid/global/6m (accessed on 19 October 2022).
- Wang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Iketani, S.; Nair, M.S.; Li, Z.; Mohri, H.; Wang, M.; Yu, J.; Bowen, A.D.; Chang, J.Y.; et al. Antibody evasion by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariants BA.2.12.1, BA.4 and BA.5. Nature 2022, 608, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, N.; Stowe, J.; Kirsebom, F.; Toffa, S.; Rickeard, T.; Gallagher, E.; Gower, C.; Kall, M.; Groves, N.; O’Connell, A.-M.; et al. Covid-19 Vaccine Effectiveness against the Omicron (B.1.1.529) Variant. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1532–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özüdoğru, O.; Bahçe, Y.G.; Acer, Ö. SARS CoV-2 reinfection rate is higher in the Omicron variant than in the Alpha and Delta variants. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 17, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashita, E.; Yamayoshi, S.; Simon, V.; van Bakel, H.; Sordillo, E.M.; Pekosz, A.; Fukushi, S.; Suzuki, T.; Maeda, K.; Halfmann, P.; et al. Efficacy of Antibodies and Antiviral Drugs against Omicron BA.2.12.1, BA.4, and BA.5 Subvariants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 468–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Jian, F.; Xiao, T.; Song, W.; Yisimayi, A.; Huang, W.; Li, Q.; Wang, P.; An, R.; et al. Omicron escapes the majority of existing SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies. Nature 2022, 602, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanBlargan, L.A.; Errico, J.M.; Halfmann, P.J.; Zost, S.J.; Crowe, J.E.; Purcell, L.A.; Kawaoka, Y.; Corti, D.; Fremont, D.H.; Diamond, M.S. An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by therapeutic monoclonal antibodies. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, L.; Sun, Q. Antibodies and Vaccines Target RBD of SARS-CoV-2. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, N.B.; Ahmed, M.A.-H.; Roop, S.B.; Mohamed, M.M.A.; Hassan, A.I.R.; Kulvinder, S.S.; Nabih, A.B.; Elrashdy, M.R. Production of Biopharmaceuticals in E. coli: Current Scenario and Future Perspectives. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 25, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.; Ge, J.; Yu, J.; Shan, S.; Zhou, H.; Fan, S.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; et al. Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor. Nature 2020, 581, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Peng, S.; Mei, S.; Liang, K.; Khan, M.S.I.; Vong, E.G.; Zhan, J. Expression and functional identification of recombinant SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain (RBD) from E. coli system. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 52, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellone, M.L.; Puglisi, A.; Dal Piaz, F.; Hochkoeppler, A. Production in Escherichia coli of recombinant COVID-19 spike protein fragments fused to CRM197. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 558, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, G.A.; Komarov, A.; Kaznadzey, A.; Mazo, I.; Kireeva, M.L. Expression of SARS-CoV-2 surface glycoprotein fragment 319–640 in E. coli., and its refolding and purification. Protein Expr. Purif. 2021, 183, 105861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maffei, M.; Montemiglio, L.C.; Vitagliano, G.; Fedele, L.; Sellathurai, S.; Bucci, F.; Compagnone, M.; Chiarini, V.; Exertier, C.; Muzi, A.; et al. The Nuts and Bolts of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor-Binding Domain Heterologous Expression. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tantiwiwat, T.; Thaiprayoon, A.; Siriatcharanon, A.-k.; Tachaapaikoon, C.; Plongthongkum, N.; Waraho-Zhmayev, D. Utilization of Receptor-Binding Domain of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Expressed in Escherichia coli for the Development of Neutralizing Antibody Assay. Mol. Biotechnol. 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prahlad, J.; Struble, L.R.; Lutz, W.E.; Wallin, S.A.; Khurana, S.; Schnaubelt, A.; Broadhurst, M.J.; Bayles, K.W.; Borgstahl, G.E.O. CyDisCo production of functional recombinant SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor binding domain. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 1983–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaciarz, A.; Veijola, J.; Uchida, Y.; Saaranen, M.J.; Wang, C.; Hörkkö, S.; Ruddock, L.W. Systematic screening of soluble expression ofantibody fragments in the cytoplasm of E. coli. Microb. Cell Factories 2016, 15, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, R.; Tsumoto, K. Addition of arginine hydrochloride and proline to the culture medium enhances recombinant protein expression in Brevibacillus choshinensis: The case of RBD of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and its antibody. Protein Expr. Purif. 2022, 194, 106075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkmen, M. Production of disulfide-bonded proteins in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr. Purif. 2012, 82, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurokawa, Y.; Yanagi, H.; Yura, T. Overexpression of Protein Disulfide Isomerase DsbC Stabilizes Multiple-Disulfide-Bonded Recombinant Protein Produced and Transported to the Periplasm in Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 3960–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurokawa, Y.; Yanagi, H.; Yura, T. Overproduction of Bacterial Protein Disulfide Isomerase (DsbC) and Its Modulator (DsbD) Markedly Enhances Periplasmic Production of Human Nerve Growth Factor in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 14393–14399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoover, D.M.; Lubkowski, J. DNAWorks: An automated method for designing oligonucleotides for PCR-based gene synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.T.; Reddy, S.T.; Kang, T.H.; Borrok, M.J.; Sandlie, I.; Tucker, P.W.; Georgiou, G. Aglycosylated IgG variants expressed in bacteria that selectively bind FcγRI potentiate tumor cell killing by monocyte-dendritic cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Xie, X.; Gao, L.; Jin, J. Designed variants of ACE2-Fc that decouple anti-SARS-CoV-2 activities from unwanted cardiovascular effects. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 1626–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, M.; Kwon, H.S.; Lee, K.-H.; Lee, J.C.; Jung, S.T. Engineered aglycosylated full-length IgG Fc variants exhibiting improved FcγRIIIa binding and tumor cell clearance. mAbs 2018, 10, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wen, A.; Yuan, X.; Yu, C.; Yang, J.; He, B.; Cao, Y.; Lu, G. Characterization of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron spike RBD reveals significantly decreased stability, severe evasion of neutralizing-antibody recognition but unaffected engagement by decoy ACE2 modified for enhanced RBD binding. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iketani, S.; Liu, L.; Guo, Y.; Liu, L.; Chan, J.F.W.; Huang, Y.; Wang, M.; Luo, Y.; Yu, J.; Chu, H.; et al. Antibody evasion properties of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron sublineages. Nature 2022, 604, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mader, A.-L.; Tydykov, L.; Glück, V.; Bertok, M.; Weidlich, T.; Gottwald, C.; Stefl, A.; Vogel, M.; Plentz, A.; Köstler, J.; et al. Omicron’s binding to sotrovimab, casirivimab, imdevimab, CR3022, and sera from previously infected or vaccinated individuals. iScience 2022, 25, 104076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, M.-S.; Jung, S.T. Aglycosylated full-length IgG antibodies: Steps toward next-generation immunotherapeutics. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2014, 30, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Qin, S.; Dai, L.; Tian, Z. The glycosylation in SARS-CoV-2 and its receptor ACE2. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-Y.; Liao, H.-Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, S.-W.; Cheng, C.-W.; Shahed-Al-Mahmud, M.; Liu, Y.-M.; Mohapatra, A.; Chen, T.-H.; Lo, J.M.; et al. Vaccination with SARS-CoV-2 spike protein lacking glycan shields elicits enhanced protective responses in animal models. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabm0899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Ma, Y.; Chen, M.; Wu, G.; Yan, C.; Zhang, X.-E. SARS-CoV-2 spike protein receptor-binding domain N-glycans facilitate viral internalization in respiratory epithelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 579, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Q.; Sun, P.; Wang, T.; Mi, T.; Xu, H.; Wu, J.; Liu, B. Non-glycosylated SARS-CoV-2 RBD elicited a robust neutralizing antibody response in mice. J. Immunol. Methods 2022, 506, 113279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


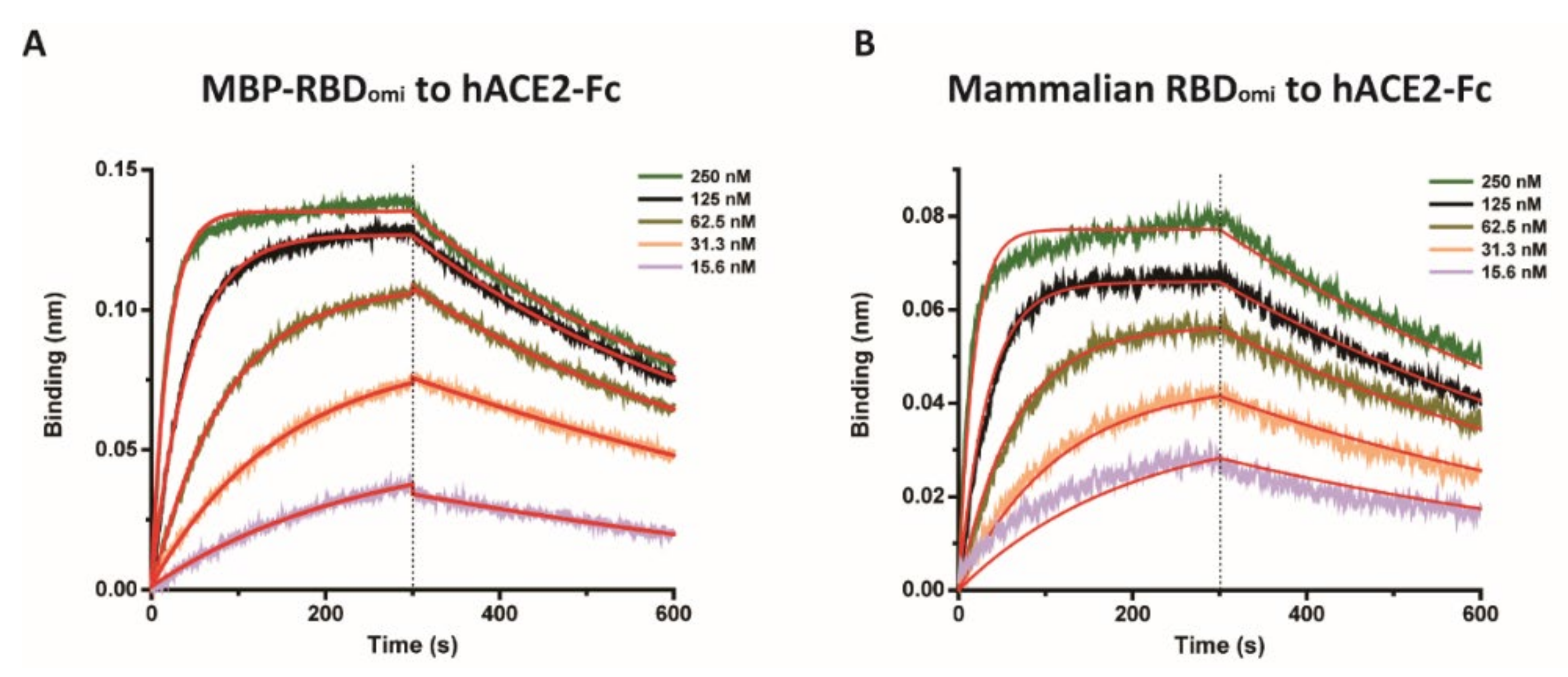
| kon (1/M · s) | koff (1/s) | KD (M) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MBP-RBDomi | 1.72 × 105 | 1.74 × 10−3 | 10.1 × 10−9 ± 0.06 × 10−9 |
| Mammalian RBDomi | 2.26 × 105 | 1.61 × 10−3 | 7.16 × 10−9 ± 0.07 × 10−9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, W.S.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.; Ka, S.Y.; Chae, H.D.; Jung, I.; Jung, S.T.; Na, J.-H. Functional Expression of the Recombinant Spike Receptor Binding Domain of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron in the Periplasm of Escherichia coli. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9110670
Kim WS, Kim JH, Lee J, Ka SY, Chae HD, Jung I, Jung ST, Na J-H. Functional Expression of the Recombinant Spike Receptor Binding Domain of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron in the Periplasm of Escherichia coli. Bioengineering. 2022; 9(11):670. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9110670
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Woo Sung, Ji Hyun Kim, Jisun Lee, Su Yeon Ka, Hee Do Chae, Inji Jung, Sang Taek Jung, and Jung-Hyun Na. 2022. "Functional Expression of the Recombinant Spike Receptor Binding Domain of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron in the Periplasm of Escherichia coli" Bioengineering 9, no. 11: 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9110670
APA StyleKim, W. S., Kim, J. H., Lee, J., Ka, S. Y., Chae, H. D., Jung, I., Jung, S. T., & Na, J.-H. (2022). Functional Expression of the Recombinant Spike Receptor Binding Domain of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron in the Periplasm of Escherichia coli. Bioengineering, 9(11), 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9110670








