Bioengineering Liver Organoids for Diseases Modelling and Transplantation
Abstract
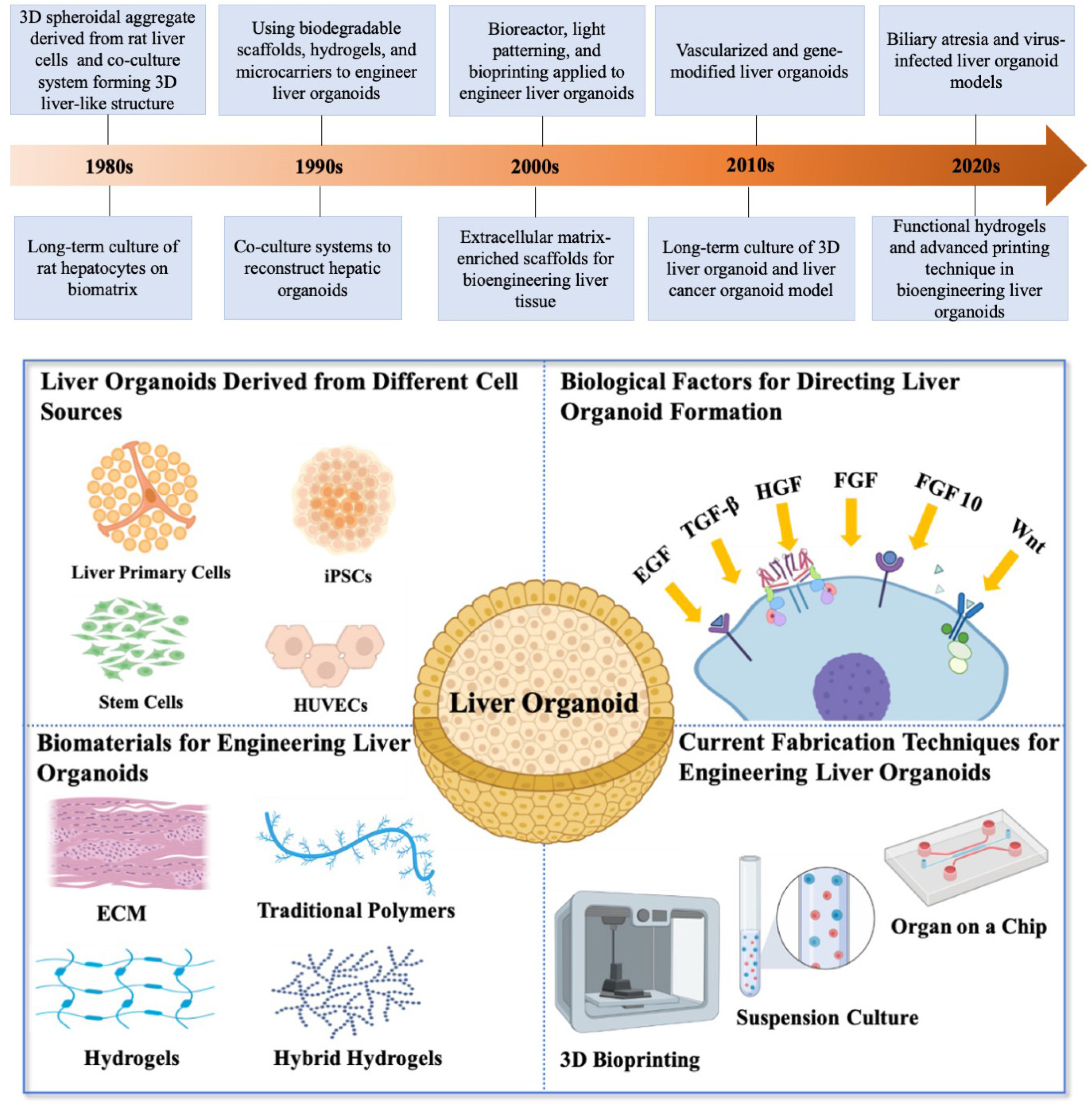
:1. Introduction
2. Bioengineering Liver Organoids
2.1. Liver Organoids Derived from Different Cell Sources
2.2. Biological Factors for Directing Liver and Biliary Organoid Formation
2.3. Biomaterials for Engineering Liver Organoids
2.4. Current Fabrication Techniques for Engineering Liver Organoid
3. Biomedical Applications of Bioengineering Liver Organoids
3.1. Liver Organoid Disease Models
3.2. Liver Organoid Cancer Models
3.3. Virus-Infected Liver Organoid Models
3.4. Limitations of the Liver Organoid Models
3.5. Transplantable Liver Organoid Tissue
4. Prospect and Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilson, H. A new method by which sponges may be artificially reared. Science 1907, 25, 912–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evans, M. Origin of mouse embryonal carcinoma cells and the possibility of their direct isolation into tissue culture. Reproduction 1981, 62, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zimmermann, B. Lung organoid culture. Differentiation 1987, 36, 86–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broutier, L.; Mastrogiovanni, G.; Verstegen, M.; Francies, H.E.; Gavarró, L.M.; Bradshaw, C.R.; Allen, G.E.; Arnes-Benito, R.; Sidorova, O.; Gaspersz, M.P. Human primary liver cancer–derived organoid cultures for disease modeling and drug screening. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1424–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lancaster, M.A.; Renner, M.; Martin, C.-A.; Wenzel, D.; Bicknell, L.S.; Hurles, M.E.; Homfray, T.; Penninger, J.M.; Jackson, A.P.; Knoblich, J.A. Cerebral organoids model human brain development and microcephaly. Nature 2013, 501, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clevers, H.; Tuveson, D.A. Organoid models for cancer research. Annu. Rev. Cancer Biol. 2019, 3, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geuens, T.; van Blitterswijk, C.A.; LaPointe, V.L. Overcoming kidney organoid challenges for regenerative medicine. NPJ Regen. Med. 2020, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, E.; Iwai, M.; Yukawa, T.; Yoshida, M.; Naomoto, Y.; Haisa, M.; Monobe, Y.; Takigawa, N.; Guo, M.; Maeda, Y. Clinical application of a lung cancer organoid (tumoroid) culture system. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2021, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakabe, K.; Takebe, T.; Asai, A. Organoid medicine in hepatology. Clin. Liver Dis. 2020, 15, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Vries, R.G.; Snippert, H.J.; Van De Wetering, M.; Barker, N.; Stange, D.E.; Van Es, J.H.; Abo, A.; Kujala, P.; Peters, P.J. Single Lgr5 stem cells build crypt-villus structures in vitro without a mesenchymal niche. Nature 2009, 459, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, D.; Mayr, U.; Boni, A.; Lukonin, I.; Rempfler, M.; Challet Meylan, L.; Stadler, M.B.; Strnad, P.; Papasaikas, P.; Vischi, D. Self-organization and symmetry breaking in intestinal organoid development. Nature 2019, 569, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taguchi, A.; Kaku, Y.; Ohmori, T.; Sharmin, S.; Ogawa, M.; Sasaki, H.; Nishinakamura, R. Redefining the in vivo origin of metanephric nephron progenitors enables generation of complex kidney structures from pluripotent stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 14, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drost, J.; Karthaus, W.R.; Gao, D.; Driehuis, E.; Sawyers, C.L.; Chen, Y.; Clevers, H. Organoid culture systems for prostate epithelial and cancer tissue. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kratochvil, M.J.; Seymour, A.J.; Li, T.L.; Paşca, S.P.; Kuo, C.J.; Heilshorn, S.C. Engineered materials for organoid systems. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2019, 4, 606–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunti, S.; Hoke, A.T.; Vu, K.P.; London Jr, N.R. Organoid and spheroid tumor models: Techniques and applications. Cancers 2021, 13, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.A.; Zhang, Y.; Rathnam, C.; Pongkulapa, T.; Lee, K.B. Bioengineering Approaches for the Advanced Organoid Research. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2007949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, D.; Baptista, P.M.; Brovold, M.; Moran, E.; Gaston, B.; Booth, C.; Samuel, M.; Atala, A.; Soker, S. Self-assembled liver organoids recapitulate hepatobiliary organogenesis in vitro. Hepatology 2018, 67, 750–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, F.; Wu, D.; Ren, Y.; Huang, Y.; Feng, B.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, T.; Chen, X.; Chen, S.; Xu, A. Generation of hepatobiliary organoids from human induced pluripotent stem cells. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 1145–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ouchi, R.; Togo, S.; Kimura, M.; Shinozawa, T.; Koido, M.; Koike, H.; Thompson, W.; Karns, R.A.; Mayhew, C.N.; McGrath, P.S. Modeling steatohepatitis in humans with pluripotent stem cell-derived organoids. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 374–384.e376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de l’Hortet, A.C.; Takeishi, K.; Guzman-Lepe, J.; Morita, K.; Achreja, A.; Popovic, B.; Wang, Y.; Handa, K.; Mittal, A.; Meurs, N. Generation of human fatty livers using custom-engineered induced pluripotent stem cells with modifiable SIRT1 metabolism. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 385–401.e389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaziotis, F.; Justin, A.W.; Tysoe, O.C.; Sawiak, S.; Godfrey, E.M.; Upponi, S.S.; Gieseck, R.L.; De Brito, M.C.; Berntsen, N.L.; Gómez-Vázquez, M.J. Reconstruction of the mouse extrahepatic biliary tree using primary human extrahepatic cholangiocyte organoids. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuciforo, S.; Heim, M.H. Organoids to model liver disease. JHEP Rep. 2021, 3, 100198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huch, M.; Gehart, H.; Van Boxtel, R.; Hamer, K.; Blokzijl, F.; Verstegen, M.M.; Ellis, E.; Van Wenum, M.; Fuchs, S.A.; de Ligt, J. Long-term culture of genome-stable bipotent stem cells from adult human liver. Cell 2015, 160, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, H.; Gehart, H.; Artegiani, B.; LÖpez-Iglesias, C.; Dekkers, F.; Basak, O.; van Es, J.; de Sousa Lopes, S.M.C.; Begthel, H.; Korving, J. Long-term expansion of functional mouse and human hepatocytes as 3D organoids. Cell 2018, 175, 1591–1606.e1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asai, A.; Aihara, E.; Watson, C.; Mourya, R.; Mizuochi, T.; Shivakumar, P.; Phelan, K.; Mayhew, C.; Helmrath, M.; Takebe, T. Paracrine signals regulate human liver organoid maturation from induced pluripotent stem cells. Development 2017, 144, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gjorevski, N.; Sachs, N.; Manfrin, A.; Giger, S.; Bragina, M.E.; Ordóñez-Morán, P.; Clevers, H.; Lutolf, M.P. Designer matrices for intestinal stem cell and organoid culture. Nature 2016, 539, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landry, J.; Bernier, D.; Ouellet, C.; Goyette, R.a.; Marceau, N. Spheroidal aggregate culture of rat liver cells: Histotypic reorganization, biomatrix deposition, and maintenance of functional activities. J. Cell Biol. 1985, 101, 914–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reid, L.M.; Gaitmaitan, Z.; Arias, I.; Ponce, P.; Rojkind, M. Long-term cultures of normal rat hepatocytes on liver biomatrix. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1980, 349, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senoo, H.; Tsukada, Y.; Sato, T.; Hata, R.-I. Co-culture of fibroblasts and hepatic parenchymal cells induces metabolic changes and formation of a three-dimensional structure. Cell Biol. Int. Rep. 1989, 13, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikos, A.G.; Sarakinos, G.; Lyman, M.D.; Ingber, D.E.; Vacanti, J.P.; Langer, R. Prevascularization of porous biodegradable polymers. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1993, 42, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takezawa, T.; Yamazaki, M.; Mori, Y.; Yonaha, T.; Yoshizato, K. Morphological and immuno-cytochemical characterization of a hetero-spheroid composed of fibroblasts and hepatocytes. J. Cell Sci. 1992, 101, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixit, V.; Piskin, E.; Arthur, M.; Denizli, A.; Tuncel, S.A.; Denkbas, E.; Gitnick, G. Hepatocyte immobilization on PHEMA microcarriers and its biologically modified forms. Cell Transplant. 1992, 1, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elçin, Y.M.; Dixit, V.; Lewin, K.; Gitnick, G. Xenotransplantation of fetal porcine hepatocytes in rats using a tissue engineering approach. Artif. Organs 1999, 23, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elçin, M.; Dixit, V.; Gitnic, G. Hepatocyte attachment on biodegradable modified chitosan membranes: In vitro evaluation for the development of liver organoids. Artif. Organs 1998, 22, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitaka, T.; Sato, F.; Mizuguchi, T.; Yokono, T.; Mochizuki, Y. Reconstruction of hepatic organoid by rat small hepatocytes and hepatic nonparenchymal cells. Hepatology 1999, 29, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M.; Matsuura, T.; Masaki, T.; Maehashi, H.; Shimizu, K.; Hataba, Y.; Iwahori, T.; Suzuki, T.; Braet, F. Reconstruction of liver organoid using a bioreactor. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahmias, Y.; Odde, D.J. Micropatterning of living cells by laser-guided direct writing: Application to fabrication of hepatic–endothelial sinusoid-like structures. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2288–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, J.; Khademhosseini, A.; Yeo, Y.; Yang, X.; Yeh, J.; Eng, G.; Blumling, J.; Wang, C.-F.; Kohane, D.S.; Langer, R. Micromolding of photocrosslinkable chitosan hydrogel for spheroid microarray and co-cultures. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 5259–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Wang, X.; Pan, Y.; Liu, H.; Cheng, J.; Xiong, Z.; Lin, F.; Wu, R.; Zhang, R.; Lu, Q. Fabrication of viable tissue-engineered constructs with 3D cell-assembly technique. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 5864–5871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavan, B.; Brun, P.; Vindigni, V.; Amadori, A.; Habeler, W.; Pontisso, P.; Montemurro, D.; Abatangelo, G.; Cortivo, R. Extracellular matrix-enriched polymeric scaffolds as a substrate for hepatocyte cultures: In vitro and in vivo studies. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 7038–7045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, P.M.; Siddiqui, M.M.; Lozier, G.; Rodriguez, S.R.; Atala, A.; Soker, S. The use of whole organ decellularization for the generation of a vascularized liver organoid. Hepatology 2011, 53, 604–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broutier, L.; Andersson-Rolf, A.; Hindley, C.J.; Boj, S.F.; Clevers, H.; Koo, B.-K.; Huch, M. Culture and establishment of self-renewing human and mouse adult liver and pancreas 3D organoids and their genetic manipulation. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 1724–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Babu, R.O.; Lui, V.C.H.; Chen, Y.; Yiu, R.S.W.; Ye, Y.; Niu, B.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, R.; Yu, M.O.N.; Chung, P.H.Y. Beta-amyloid deposition around hepatic bile ducts is a novel pathobiological and diagnostic feature of biliary atresia. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 1391–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Ni, C.; Gao, R.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L.; Wei, J.; Lv, T.; Liang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, W. Recapitulation of SARS-CoV-2 infection and cholangiocyte damage with human liver ductal organoids. Protein Cell 2020, 11, 771–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ye, S.; Boeter, J.W.; Mihajlovic, M.; van Steenbeek, F.G.; van Wolferen, M.E.; Oosterhoff, L.A.; Marsee, A.; Caiazzo, M.; van der Laan, L.J.; Penning, L.C. A chemically defined hydrogel for human liver organoid culture. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2000893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, P.N.; Bouwmeester, M.; Madrid-Wolff, J.; Falandt, M.; Florczak, S.; Rodriguez, N.G.; Li, Y.; Größbacher, G.; Samsom, R.A.; van Wolferen, M. Volumetric Bioprinting of Organoids and Optically Tuned Hydrogels to Build Liver-Like Metabolic Biofactories. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2110054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneeberger, K.; Sánchez-Romero, N.; Ye, S.; van Steenbeek, F.G.; Oosterhoff, L.A.; Pla Palacin, I.; Chen, C.; van Wolferen, M.E.; van Tienderen, G.; Lieshout, R. Large-scale production of LGR5-positive bipotential human liver stem cells. Hepatology 2020, 72, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huch, M.; Dorrell, C.; Boj, S.F.; Van Es, J.H.; Li, V.S.; Van De Wetering, M.; Sato, T.; Hamer, K.; Sasaki, N.; Finegold, M.J. In vitro expansion of single Lgr5+ liver stem cells induced by Wnt-driven regeneration. Nature 2013, 494, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kruitwagen, H.S.; Oosterhoff, L.A.; Vernooij, I.G.; Schrall, I.M.; van Wolferen, M.E.; Bannink, F.; Roesch, C.; van Uden, L.; Molenaar, M.R.; Helms, J.B. Long-term adult feline liver organoid cultures for disease modeling of hepatic steatosis. Stem Cell Rep. 2017, 8, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, R.; Bae, S.D.W.; Qiao, L.; George, J. Developing liver organoids from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs): An alternative source of organoid generation for liver cancer research. Cancer Lett. 2021, 508, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, M.; Ogawa, S.; Bear, C.E.; Ahmadi, S.; Chin, S.; Li, B.; Grompe, M.; Keller, G.; Kamath, B.M.; Ghanekar, A. Directed differentiation of cholangiocytes from human pluripotent stem cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, M.; Jiang, J.-X.; Xia, S.; Yang, D.; Ding, A.; Laselva, O.; Hernandez, M.; Cui, C.; Higuchi, Y.; Suemizu, H. Generation of functional ciliated cholangiocytes from human pluripotent stem cells. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalan-Sakrikar, N.; De Assuncao, T.M.; Navarro-Corcuera, A.; Hamdan, F.H.; Loarca, L.; Kirkeby, L.A.; Resch, Z.T.; O’Hara, S.P.; Juran, B.D.; Lazaridis, K.N. Induced pluripotent stem cells from subjects with primary sclerosing cholangitis develop a senescence phenotype following biliary differentiation. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dianat, N.; Dubois-Pot-Schneider, H.; Steichen, C.; Desterke, C.; Leclerc, P.; Raveux, A.; Combettes, L.; Weber, A.; Corlu, A.; Dubart-Kupperschmitt, A. Generation of functional cholangiocyte-like cells from human pluripotent stem cells and HepaRG cells. Hepatology 2014, 60, 700–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wörsdörfer, P.; Dalda, N.; Kern, A.; Krüger, S.; Wagner, N.; Kwok, C.K.; Henke, E.; Ergün, S. Generation of complex human organoid models including vascular networks by incorporation of mesodermal progenitor cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takayama, K.; Mitani, S.; Nagamoto, Y.; Sakurai, F.; Tachibana, M.; Taniguchi, Y.; Sekiguchi, K.; Mizuguchi, H. Laminin 411 and 511 promote the cholangiocyte differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 474, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampaziotis, F.; Cardoso de Brito, M.; Madrigal, P.; Bertero, A.; Saeb-Parsy, K.; Soares, F.A.; Schrumpf, E.; Melum, E.; Karlsen, T.H.; Bradley, J.A. Cholangiocytes derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells for disease modeling and drug validation. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takebe, T.; Zhang, R.-R.; Koike, H.; Kimura, M.; Yoshizawa, E.; Enomura, M.; Koike, N.; Sekine, K.; Taniguchi, H. Generation of a vascularized and functional human liver from an iPSC-derived organ bud transplant. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 396–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratajczak, M.; Kucia, M.; Jadczyk, T.; Greco, N.; Wojakowski, W.; Tendera, M.; Ratajczak, J. Pivotal role of paracrine effects in stem cell therapies in regenerative medicine: Can we translate stem cell-secreted paracrine factors and microvesicles into better therapeutic strategies? Leukemia 2012, 26, 1166–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guan, Y.; Xu, D.; Garfin, P.M.; Ehmer, U.; Hurwitz, M.; Enns, G.; Michie, S.; Wu, M.; Zheng, M.; Nishimura, T. Human hepatic organoids for the analysis of human genetic diseases. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e94954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaret, K.S. Genetic programming of liver and pancreas progenitors: Lessons for stem-cell differentiation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lancaster, M.A.; Huch, M. Disease modelling in human organoids. Dis. Model. Mech. 2019, 12, dmm039347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marastoni, S.; Ligresti, G.; Lorenzon, E.; Colombatti, A.; Mongiat, M. Extracellular matrix: A matter of life and death. Connect. Tissue Res. 2008, 49, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owens, T.; Valentijn, A.; Upton, J.; Keeble, J.; Zhang, L.; Lindsay, J.; Zouq, N.; Gilmore, A. Apoptosis commitment and activation of mitochondrial Bax during anoikis is regulated by p38MAPK. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 1551–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Charras, G.; Sahai, E. Physical influences of the extracellular environment on cell migration. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphrey, J.D.; Dufresne, E.R.; Schwartz, M.A. Mechanotransduction and extracellular matrix homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Huang, D.; Yu, H.; Cheng, Y.; Ren, H.; Zhao, Y. Developing tissue engineering strategies for liver regeneration. Eng. Regen. 2022, 3, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Tripathi, D.M.; Venugopal, J.R.; Ramakrishna, S. Advances in biomaterials for hepatic tissue engineering. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 13, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Richardson, B.M.; Anseth, K.S. Dynamic covalent hydrogels as biomaterials to mimic the viscoelasticity of soft tissues. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2021, 120, 100738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, H.; Wang, M. Phase inversion-based technique for fabricating bijels and bijels-derived structures with tunable microstructures. Langmuir 2020, 36, 14644–14655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H.; Chen, W.; Qin, J. One-step synthesis of composite hydrogel capsules to support liver organoid generation from hiPSCs. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 5476–5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvir-Ginzberg, M.; Elkayam, T.; Cohen, S. Induced differentiation and maturation of newborn liver cells into functional hepatic tissue in macroporous alginate scaffolds. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 1440–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Sun, X.; Wang, Z.; Guo, S.; Yu, G.; Yang, H. Synthesis and properties of gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) hydrogels and their recent applications in load-bearing tissue. Polymers 2018, 10, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Devarasetty, M.; Wang, E.; Soker, S.; Skardal, A. Mesenchymal stem cells support growth and organization of host-liver colorectal-tumor organoids and possibly resistance to chemotherapy. Biofabrication 2017, 9, 021002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skardal, A.; Devarasetty, M.; Rodman, C.; Atala, A.; Soker, S. Liver-tumor hybrid organoids for modeling tumor growth and drug response in vitro. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 43, 2361–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamai, M.; Adachi, E.; Tagawa, Y.-I. Characterization of a liver organoid tissue composed of hepatocytes and fibroblasts in dense collagen fibrils. Tissue Eng. Part A 2013, 19, 2527–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gessner, R.C.; Hanson, A.D.; Feingold, S.; Cashion, A.T.; Corcimaru, A.; Wu, B.T.; Mullins, C.R.; Aylward, S.R.; Reid, L.M.; Dayton, P.A. Functional ultrasound imaging for assessment of extracellular matrix scaffolds used for liver organoid formation. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 9341–9351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, Y.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.S.; Min, S.; Kim, S.; Ahn, D.H.; Kim, Y.G.; Cho, S.W. Vascularized liver organoids generated using induced hepatic tissue and dynamic liver-specific microenvironment as a drug testing platform. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1801954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saheli, M.; Sepantafar, M.; Pournasr, B.; Farzaneh, Z.; Vosough, M.; Piryaei, A.; Baharvand, H. Three-dimensional liver-derived extracellular matrix hydrogel promotes liver organoids function. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 4320–4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinman, H.K.; Martin, G.R. Matrigel: Basement membrane matrix with biological activity. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2005, 15, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Lavrijsen, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Verstegen, M.M.; Wang, Y.; Li, T.-C. Recapitulating hepatitis E virus–host interactions and facilitating antiviral drug discovery in human liver–derived organoids. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabj5908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, S.; Kaur, I.; Rawal, P.; Tripathi, D.M.; Vasudevan, A. Non-matrigel scaffolds for organoid cultures. Cancer Lett. 2021, 504, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ma, J. Biomimetic synthesis of Mg-substituted hydroxyapatite nanocomposites and three-dimensional printing of composite scaffolds for bone regeneration. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2019, 107, 2512–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ma, J. Evaluation of BMP-2 and VEGF loaded 3D printed hydroxyapatite composite scaffolds with enhanced osteogenic capacity in vitro and in vivo. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 112, 110893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Yang, X.; Ma, Z.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Yang, H.; Qiang, L.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Y. Developments and opportunities for 3D bioprinted organoids. Int. J. Bioprinting 2021, 7, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwmeester, M.C.; Bernal, P.N.; Oosterhoff, L.A.; van Wolferen, M.E.; Lehmann, V.; Vermaas, M.; Buchholz, M.B.; Peiffer, Q.C.; Malda, J.; van der Laan, L.J. Bioprinting of Human Liver-Derived Epithelial Organoids for Toxicity Studies. Macromol. Biosci. 2021, 21, 2100327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettinato, G.; Perelman, L.T.; Fisher, R.A. Development of a Scalable Three-Dimensional Culture of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells-Derived Liver Organoids. In Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 131–147. [Google Scholar]
- Altmaier, S.; Meiser, I.; Lemesre, E.; Chanrion, B.; Steeg, R.; Leonte, L.E.; Holst, B.; Nielsen, B.S.; Clausen, C.; Schmidt, K. Human iPSC-derived hepatocytes in 2D and 3D suspension culture for cryopreservation and in vitro toxicity studies. Reprod. Toxicol. 2022, 111, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodanov, L.; Jindal, R.; Bale, S.S.; Hegde, M.; McCarty, W.J.; Golberg, I.; Bhushan, A.; Yarmush, M.L.; Usta, O.B. Long-term maintenance of a microfluidic 3D human liver sinusoid. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2016, 113, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Z.; Tao, T.; Chen, W.; Yu, H.; Qin, J. HiPSC-derived multi-organoids-on-chip system for safety assessment of antidepressant drugs. Lab A Chip 2021, 21, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, P.K.; Chung, P.H.; St Peter, S.D.; Gayer, C.P.; Ford, H.R.; Tam, G.C.; Wong, K.K.; Pakarinen, M.P.; Davenport, M. Advances in paediatric gastroenterology. Lancet 2017, 390, 1072–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lendahl, U.; Lui, V.C.; Chung, P.H.; Tam, P.K. Biliary Atresia–emerging diagnostic and therapy opportunities. EBioMedicine 2021, 74, 103689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, P.H.; Wong, K.K.; Tam, P.K. Standard management protocol to improve the short-term outcome of biliary atresia. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2020, 56, 1774–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amarachintha, S.P.; Mourya, R.; Ayabe, H.; Yang, L.; Luo, Z.; Li, X.; Thanekar, U.; Shivakumar, P.; Bezerra, J.A. Biliary organoids uncover delayed epithelial development and barrier function in biliary atresia. Hepatology 2022, 75, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridgewater, J.; Galle, P.R.; Khan, S.A.; Llovet, J.M.; Park, J.-W.; Patel, T.; Pawlik, T.M.; Gores, G.J. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 1268–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bosch, F.X.; Ribes, J.; Díaz, M.; Cléries, R. Primary liver cancer: Worldwide incidence and trends. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, S5–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.-R.; Shi, X.-D.; Zhang, F.-P.; Zhu, K.; Zhang, R.; Yu, X.-H.; Qin, Y.-F.; He, S.-P.; Fu, H.-W.; Zhang, L. Activation of the Notch1-c-myc-VCAM1 signalling axis initiates liver progenitor cell-driven hepatocarcinogenesis and pulmonary metastasis. Oncogene 2022, 41, 2340–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-P.; Liu, C.-R.; Lee, C.-N.; Chan, T.-S.; Liu, H.E. Targeting c-Myc as a novel approach for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Hepatol. 2010, 2, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Cubero, F.J.; Nevzorova, Y.A. c-MYC—Making liver sick: Role of c-MYC in hepatic cell function, homeostasis and disease. Genes 2017, 8, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, L.; Wang, Y.; Cen, J.; Ma, X.; Cui, L.; Qiu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H.; Yang, R.-Z.; Wang, C. Modelling liver cancer initiation with organoids derived from directly reprogrammed human hepatocytes. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Feng, G.; Zheng, K.I.; Yan, Q.-Q.; Rios, R.S.; Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; Van Poucke, S.; Liu, W.-Y.; Zheng, M.-H. COVID-19 and liver dysfunction: Current insights and emergent therapeutic strategies. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2020, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramani, S.; Crawford, S.E.; Blutt, S.E.; Estes, M.K. Human organoid cultures: Transformative new tools for human virus studies. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2018, 29, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lui, V.C.-H.; Hui, K.P.-Y.; Babu, R.O.; Yue, H.; Chung, P.H.-Y.; Tam, P.K.-H.; Chan, M.C.-W.; Wong, K.K.-Y. Human liver organoid derived intra-hepatic bile duct cells support SARS-CoV-2 infection and replication. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emerson, S.U.; Purcell, R.H. Hepatitis E virus. Rev. Med. Virol. 2003, 13, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, Y.-Z.; Zheng, Y.-W.; Miyakawa, K.; Murata, S.; Zhang, R.-R.; Sekine, K.; Ueno, Y.; Takebe, T.; Wakita, T.; Ryo, A. Recapitulation of hepatitis B virus–host interactions in liver organoids from human induced pluripotent stem cells. EBioMedicine 2018, 35, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Natarajan, V.; Simoneau, C.R.; Erickson, A.L.; Meyers, N.L.; Baron, J.L.; Cooper, S.; McDevitt, T.C.; Ott, M. Modelling T-cell immunity against hepatitis C virus with liver organoids in a microfluidic coculture system. Open Biol. 2022, 12, 210320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tang, L.; Yi, Q. Engineering the Vasculature of Stem-Cell-Derived Liver Organoids. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettinato, G.; Coughlan, M.F.; Zhang, X.; Chen, L.; Khan, U.; Glyavina, M.; Sheil, C.J.; Upputuri, P.K.; Zakharov, Y.N.; Vitkin, E. Spectroscopic label-free microscopy of changes in live cell chromatin and biochemical composition in transplantable organoids. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabj2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchida, T.; Murata, S.; Hasegawa, S.; Mikami, S.; Enosawa, S.; Hsu, H.-C.; Fukuda, A.; Okamoto, S.; Mori, A.; Matsuo, M. Investigation of clinical safety of human iPS cell-derived liver organoid transplantation to infantile patients in porcine model. Cell Transplant. 2020, 29, 0963689720964384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Chu, J.; Lui, V.C.H.; Chen, S.; Chen, Y.; Tam, P.K.H. Bioengineering Liver Organoids for Diseases Modelling and Transplantation. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 796. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9120796
Li J, Chu J, Lui VCH, Chen S, Chen Y, Tam PKH. Bioengineering Liver Organoids for Diseases Modelling and Transplantation. Bioengineering. 2022; 9(12):796. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9120796
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Junzhi, Jing Chu, Vincent Chi Hang Lui, Shangsi Chen, Yan Chen, and Paul Kwong Hang Tam. 2022. "Bioengineering Liver Organoids for Diseases Modelling and Transplantation" Bioengineering 9, no. 12: 796. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9120796
APA StyleLi, J., Chu, J., Lui, V. C. H., Chen, S., Chen, Y., & Tam, P. K. H. (2022). Bioengineering Liver Organoids for Diseases Modelling and Transplantation. Bioengineering, 9(12), 796. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9120796







