Application of Sygen® in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathies—A Review of Biological Interactions
Abstract
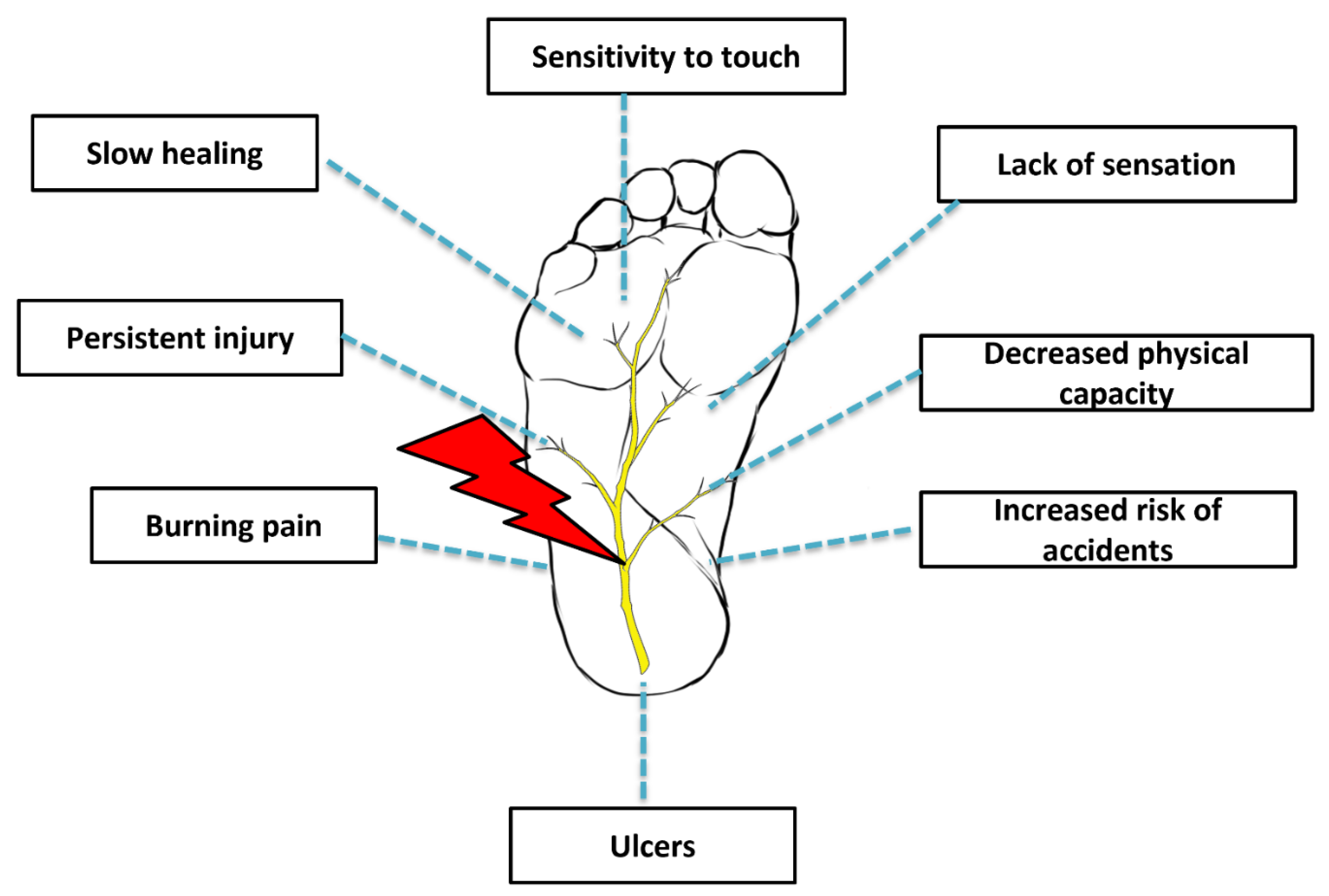
:1. Introduction
2. Etiopathogenesis
3. Conventional Management of Peripheral Neuropathy
4. Biological Properties
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Misra, U.K.; Kalita, J.; Nair, P.P. Diagnostic approach to peripheral neuropathy. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2008, 11, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesfaye, S.; Boulton, A.J.M.; Dyck, P.J.; Freeman, R.; Horowitz, M.; Kempler, P.; Lauria, G.; Malik, R.A.; Spallone, V.; Vinik, A.; et al. Diabetic Neuropathies: Update on Definitions, Diagnostic Criteria, Estimation of Severity, and Treatments. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 2285–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Terkelsen, A.J.; Karlsson, P.; Lauria, G.; Freeman, R.; Finnerup, N.; Jensen, T.S. The diagnostic challenge of small fibre neuropathy: Clinical presentations, evaluations, and causes. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 934–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulton, A.J.; Vinik, A.I.; Arezzo, J.C.; Bril, V.; Feldman, E.L.; Freeman, R.; Malik, R.A.; Maser, R.E.; Sosenko, J.M.; Ziegler, D. Diabetic Neuropathies: A statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hicks, C.W.; Selvin, E. Epidemiology of Peripheral Neuropathy and Lower Extremity Disease in Diabetes. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2019, 19, 1–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolis, D.J.; Jeffcoate, W. Epidemiology of Foot Ulceration and Amputation: Can Global Variation be Explained? Med. Clin. North Am. 2013, 97, 791–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vileikyte, L.; Leventhal, H.; Gonzalez, J.S.; Peyrot, M.; Rubin, R.R.; Ulbrecht, J.S.; Garrow, A.; Waterman, C.; Cavanagh, P.R.; Boulton, A.J. Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy and Depressive Symptoms: The association revisited. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 2378–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pop-Busui, R.; Boulton, A.J.M.; Feldman, E.L.; Bril, V.; Freeman, R.; Malik, R.A.; Sosenko, J.M.; Ziegler, D. Diabetic Neuropathy: A Position Statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2016, 40, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aureli, M.; Mauri, L.; Ciampa, M.G.; Prinetti, A.; Toffano, G.; Secchieri, C.; Sonnino, S. GM1 Ganglioside: Past Studies and Future Potential. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 53, 1824–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipione, S.; Monyror, J.; Galleguillos, D.; Steinberg, N.; Kadam, V. Gangliosides in the Brain: Physiology, Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Applications. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 572965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganglioside GM1 in acute ischemic stroke. SASS Trial. Stroke 1994, 25, 1141–1148. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneider, J.S.; Roeltgen, D.P.; Mancall, E.L.; Chapas-Crilly, J.; Rothblat, D.S.; Tatarian, G.T. Parkinson’s disease Improved function with GMl ganglioside treatment in a randomized placebo-controlled study. Neurology 1998, 50, 1630–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzini, G.O.M.; Santos, G.S.; Visoni, S.B.C.; Azzini, V.O.M.; dos Santos, R.G.; Huber, S.C.; Lana, J.F. Metabolic syndrome and subchondral bone alterations: The rise of osteoarthritis—A review. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2020, 11, S849–S855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajic, M. Mitochondrial Dynamics in Peripheral Neuropathies. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 21, 601–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, E.L.; Nave, K.-A.; Jensen, T.S.; Bennett, D.L.H. New Horizons in Diabetic Neuropathy: Mechanisms, Bioenergetics, and Pain. Neuron 2017, 93, 1296–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schreiber, A.K. Diabetic neuropathic pain: Physiopathology and treatment. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 432–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setti, T.; Arab, M.G.L.; Santos, G.S.; Alkass, N.; Andrade, M.A.P.; Lana, J.F.S.D. The protective role of glutathione in osteoarthritis. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2020, 15, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, A.Q.; Krishnan, S.; Finucane, F.M.; Rayman, G. Altered C-Fiber Function as an Indicator of Early Peripheral Neuropathy in Individuals with Impaired Glucose Tolerance. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 174–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malik, R.A.; Veves, A.; Walker, D.; Siddique, I.; Lye, R.H.; Schady, W.; Boulton, A.J.M. Sural nerve fibre pathology in diabetic patients with mild neuropathy: Relationship to pain, quantitative sensory testing and peripheral nerve electrophysiology. Acta Neuropathol. 2001, 101, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiero, R.; Ricciardi, D.; Pafundi, P.C.; Todisco, V.; Tedeschi, G.; Cirillo, G.; Sasso, F.C. Whole plantar nerve conduction study: A new tool for early diagnosis of peripheral diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pr. 2021, 176, 108856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfaye, S.; Chaturvedi, N.; Eaton, S.E.; Ward, J.D.; Manes, C.; Ionescu-Tirgoviste, C.; Witte, D.; Fuller, J.H. Vascular Risk Factors and Diabetic Neuropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pinto, A.; Tuttolomondo, A.; Di Raimondo, D.; Fernandez, P.; La Placa, S.; Di Gati, M.; Licata, G. Cardiovascular risk profile and morbidity in subjects affected by type 2 diabetes mellitus with and without diabetic foot. Metabolism 2008, 57, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doupis, J.; Lyons, T.E.; Wu, S.; Gnardellis, C.; Dinh, T.; Veves, A. Microvascular Reactivity and Inflammatory Cytokines in Painful and Painless Peripheral Diabetic Neuropathy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 2157–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quattrini, C.; Harris, N.D.; Malik, R.A.; Tesfaye, S. Impaired Skin Microvascular Reactivity in Painful Diabetic Neuropathy. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 655–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jin, H.Y.; Lee, K.A.; Song, S.K.; Liu, W.J.; Choi, J.H.; Song, C.H.; Baek, H.S.; Park, T.S. Sulodexide prevents peripheral nerve damage in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 674, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavy-LeTraon, A.P.-L.; Fontaine, S.; Tap, G.; Guidolin, B.; Senard, J.-M.; Hanaire, H. Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy and other complications in type 1 diabetes. Clin. Auton. Res. 2010, 20, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, D.; Birklein, F.; Reeh, P.W.; Sauer, S.K. Sensitized peripheral nociception in experimental diabetes of the rat. Pain 2010, 151, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, G.; Baudoin, D.; Toyooka, K. Sensory loss, pains, motor deficit and axonal regeneration in length-dependent diabetic polyneuropathy. J. Neurol. 2008, 255, 1693–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickenson, A.H.; Matthews, E.A.; Suzuki, R. Neurobiology of neuropathic pain: Mode of action of anticonvulsants. Eur. J. Pain 2002, 6, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, K.E.; Liu, J.; Sima, A.A.F.; Wiley, J.W. Impaired inhibitory G-protein function contributes to increased calcium currents in rats with diabetic neuropathy. J. Neurophysiol. 2001, 86, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mika, J.; Zychowska, M.; Popiolek-Barczyk, K.; Rojewska, E.; Przewlocka, B. Importance of glial activation in neuropathic pain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 716, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vydyanathan, A.; Wu, Z.-Z.; Chen, S.-R.; Pan, H.-L. A-Type Voltage-Gated K+ Currents Influence Firing Properties of Isolectin B4-Positive but Not Isolectin B4-Negative Primary Sensory Neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 2005, 93, 3401–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Greenhalgh, D.G. Wound healing and diabetes mellitus. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2003, 30, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamaisi, M.; Balanson, S. Dysregulation of wound healing mechanisms in diabetes and the importance of negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT). Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2017, 33, e2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsalamandris, S.; Antonopoulos, A.S.; Oikonomou, E.; Papamikroulis, G.-A.; Vogiatzi, G.; Papaioannou, S.; Deftereos, S.; Tousoulis, D. The Role of Inflammation in Diabetes: Current Concepts and Future Perspectives. Eur. Cardiol. Rev. 2019, 14, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boulton, A.J.M.; Kempler, P.; Ametov, A.; Ziegler, D. Whither pathogenetic treatments for diabetic polyneuropathy? Patho-genetic Treatments for DSPN. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2013, 29, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaghan, B.C.; A Little, A.; Feldman, E.; Hughes, R.A.C. Enhanced glucose control for preventing and treating diabetic neuropathy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 6, CD007543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didangelos, T.; Karlafti, E.; Kotzakioulafi, E.; Kontoninas, Z.; Margaritidis, C.; Giannoulaki, P.; Kantartzis, K. Efficacy and Safety of the Combination of Superoxide Dismutase, Alpha Lipoic Acid, Vitamin B12, and Carnitine for 12 Months in Patients with Diabetic Neuropathy. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.G.; Russell, J.; Feldman, E.L.; Goldstein, J.; Peltier, A.; Smith, S.; Hamwi, J.; Pollari, D.; Bixby, B.; Howard, J.; et al. Lifestyle Intervention for Pre-Diabetic Neuropathy. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 1294–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bril, V.; England, J.; Franklin, G.M.; Backonja, M.; Cohen, J.; Del Toro, D.; Feldman, E.; Iverson, D.J.; Perkins, B.; Russell, J.W.; et al. Evidence-based guideline: Treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy: Report of the American Academy of Neurology, the American Association of Neuromuscular and Electrodiagnostic Medicine, and the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. Neurology 2011, 76, 1758–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boomershine, C.S.; Ormseth, M.J.; A Scholz, B. Duloxetine in the management of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain. Patient Prefer. Adherence 2011, 5, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Højsted, J.; Sjøgren, P. Addiction to opioids in chronic pain patients: A literature review. Eur. J. Pain 2007, 11, 490–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiricozzi, E.; Lunghi, G.; Di Biase, E.; Fazzari, M.; Sonnino, S.; Mauri, L. GM1 Ganglioside Is a Key Factor in Maintaining the Mammalian Neuronal Functions Avoiding Neurodegeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Svennerholm, L. Ganglioside Designation. In Structure and Function of Gangliosides; Svennerholm, L., Mandel, P., Dreyfus, H., Urban, P.-F., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1980; p. 11. [Google Scholar]
- Grassi, S.; Chiricozzi, E.; Mauri, L.; Sonnino, S.; Prinetti, A. Sphingolipids and neuronal degeneration in lysosomal storage disorders. J. Neurochem. 2019, 148, 600–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonnino, S.; Cantù, L.; Corti, M.; Acquotti, D.; Venerando, B. Aggregative properties of gangliosides in solution. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1994, 71, 21–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saqr, H.E.; Pearl, D.K.; Yates, A.J. A Review and Predictive Models of Gang ioside Uptake by Biological Membranes. J. Neurochem. 2006, 61, 395–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roisen, F.J.; Bartfeld, H.; Nagele, R.; Yorke, G. Ganglioside Stimulation of Axonal Sprouting in Vitro. Science 1981, 214, 577–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledeen, R.W. Biology of gangliosides: Neuritogenic and neuronotrophic properties. J. Neurosci. Res. 1984, 12, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisler, F.H.; Coleman, W.P.; Grieco, G.; Poonian, D. The Sygen® Multicenter Acute Spinal Cord Injury Study. Spine 2001, 26, S87–S98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledeen, R.W.; Wu, G. The multi-tasked life of GM1 ganglioside, a true factotum of nature. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2015, 40, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiricozzi, E.; Pomè, D.Y.; Maggioni, M.; DI Biase, E.; Parravicini, C.; Palazzolo, L.; Loberto, N.; Eberini, I.; Sonnino, S. Role of the GM1 ganglioside oligosaccharide portion in the TrkA-dependent neurite sprouting in neuroblastoma cells. J. Neurochem. 2017, 143, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Magistretti, P.J.; Geisler, F.H.; Schneider, J.S.; Li, P.A.; Fiumelli, H.; Sipione, S. Gangliosides: Treatment Avenues in Neurodegenerative. Dis. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galleguillos, D.; Wang, Q.; Steinberg, N.; Shrivastava, G.; Dhami, K.; Rubinstein, K.; Giuliani, F.; Churchward, M.; Power, C.; Todd, K.; et al. Anti-inflammatory role of GM1 and modulatory effects of gangliosides on microglia functions. J Neuroinflammation. 2022, 19, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavaillon, J.-M.; Fitting, C.; Hauttecoeur, B.; Haeffner-Cavaillon, N. Inhibition by gangliosides of the specific binding of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to human monocytes prevents LPS-induced interleukin-1 production. Cell. Immunol. 1987, 106, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeng, K.-C.G.; Chen, T.-L.; Lan, J.-L. Gangliosides suppression of murine lymphoproliferation and interleukin 1 production. Immunol. Lett. 1988, 19, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trang, T.; Beggs, S.; Salter, M.W. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor from microglia: A molecular substrate for neuropathic pain. Neuron Glia Biol. 2011, 7, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrini, F.; De Koninck, Y. Microglia Control Neuronal Network Excitability via BDNF Signalling. Neural Plast. 2013, 2013, 429815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimmerjahn, A.; Kirchhoff, F.; Helmchen, F. Resting Microglial Cells Are Highly Dynamic Surveillants of Brain Parenchyma in Vivo. Science 2005, 308, 1314–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosales, C.; Uribe-Querol, E. Phagocytosis: A Fundamental Process in Immunity. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 9042851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Da Silva, J.S.; Hasegawa, T.; Miyagi, T.; Dotti, C.G.; Abad-Rodriguez, J. Asymmetric membrane ganglioside sialidase activity specifies axonal fate. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturgill, E.R.; Aoki, K.; Lopez, P.H.; Colacurcio, D.; Vajn, K.; Lorenzini, I.; Majić, S.; Yang, W.H.; Heffer, M.; Tiemeyer, M.; et al. Biosynthesis of the major brain gangliosides GD1a and GT1b. Glycobiology 2012, 22, 1289–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quarles, R.H. Myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG): Past, present and beyond. J. Neurochem. 2007, 100, 1431–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, N.R.; Nguyen, T.; Bullen, J.J.W.; Griffin, J.W.; Schnaar, R.L. Myelin-Associated Glycoprotein (MAG) Protects Neurons from Acute Toxicity Using a Ganglioside-Dependent Mechanism. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2009, 1, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, J.; Goshima, Y.; Ohshima, T. CRMP4 mediates MAG-induced inhibition of axonal outgrowth and protection against Vincristine-induced axonal degeneration. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 519, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, P.H.H.; Báez, B.B. Gangliosides in Axon Stability and Regeneration. In Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 383–412. [Google Scholar]
- Kappagantula, S.; Andrews, M.; Cheah, M.; Abad-Rodriguez, J.; Dotti, C.G.; Fawcett, J.W. Neu3 Sialidase-Mediated Ganglioside Conversion Is Necessary for Axon Regeneration and Is Blocked in CNS Axons. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 2477–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Facci, L.; Leon, A.; Toffano, G.; Sonnino, S.; Ghidoni, R.; Tettamanti, G. Promotion of Neuritogenesis in Mouse Neuroblastoma Cells by Exogenous Gangliosides. Relationship Between the Effect and the Cell Association of Ganglioside GM1. J. Neurochem. 1984, 42, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaper, S.D.; Katoh-Semba, R.; Varon, S. GM1 ganglioside accelerates neurite outgrowth from primary peripheral and central neurons under selected culture conditions. Dev. Brain Res. 1985, 23, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susuki, K.; Baba, H.; Tohyama, K.; Kanai, K.; Kuwabara, S.; Hirata, K.; Furukawa, K.; Furukawa, K.; Rasband, M.; Yuki, N. Gangliosides contribute to stability of paranodal junctions and ion channel clusters in myelinated nerve fibers. Glia 2007, 55, 746–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Fromholt, S.E.; Hess, E.J.; Crawford, T.O.; Griffin, J.W.; Sheikh, K.A.; Schnaar, R.L. Myelin-associated glycoprotein and complementary axonal ligands, gangliosides, mediate axon stability in the CNS and PNS: Neuropathology and behavioral deficits in single- and double-null mice. Exp. Neurol. 2005, 195, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trinchera, M.; Parini, R.; Indellicato, R.; Domenighini, R.; Dall’Olio, F. Diseases of ganglioside biosynthesis: An expanding group of congenital disorders of glycosylation. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2018, 124, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roda, R.H.; FitzGibbon, E.J.; Boucekkine, H.; Schindler, A.B.; Blackstone, C. Neurologic syndrome associated with homozygous mutation at MAG sialic acid binding site. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2016, 3, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinecke, S.; Richert, S.; De Hoz, L.; Brügger, B.; Kungl, T.; Asadollahi, E.; Quintes, S.; Blanz, J.; McGonigal, R.; Naseri, K.; et al. Peroxisomal dysfunctions cause lysosomal storage and axonal Kv1 channel redistribution in peripheral neuropathy. eLife 2017, 6, e23332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Susuki, K. Node of Ranvier Disruption as a Cause of Neurological Diseases. ASN Neuro 2013, 5, e00118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otani, Y.; Yermakov, L.M.; Dupree, J.L.; Susuki, K. Chronic peripheral nerve compression disrupts paranodal axoglial junctions. Muscle Nerve 2016, 55, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Classification | Definition |
|---|---|
| Possible DSPN | Symptoms: decreased sensation and numbness in lower limbs; signs: symmetric decrease of distal sensation or unequivocally decreased or absent ankle reflexes |
| Probable DSPNConfirmed DSPN | Detection of multiple signs and symptoms of neuropathy: neuropathic symptoms, decreased distal sensation, or unequivocally decreased or absent ankle reflexes Detection of nerve conduction test score abnormality + signs or symptoms of DSPN |
| Subclinical DSPN | No signs or symptoms of neuropathy are confirmed with neurophysiologic tests |
| Author | Biological Properties |
|---|---|
| Svennerholm, 1980 | Large, bulky polar head group; water solubility; forms micellar aggregates; lipid-to-lipid interactions |
| Roisen et al., 1981 Ledeen, 1984 | Stimulates axonal sprouting in vitro Neuritogenic and neurotrophic roles, protecting nerves and also helping them to regrow over time |
| Geisler et al., 2001 Nimmerjahn et al., 2005 Da Silva et al., 2005 Susuki et al., 2007 | Enhanced neuritic sprouting, neurotrophism, neuroprotection, anti-apoptosis, and anti-excitotoxic activity Enhanced chemotaxis and migratory activity of microglia Myelin stability and regulation of axon structure and neurite outgrowth Organization of nodes and paranodes in myelinated fibers |
| Chiricozzi et al., 2017 | Facilitates tropomyosin-related kinase (TRK) receptor activation and downstream signaling, and induces sysnthesis and release of neurotrophins |
| Galleguillos et al., 2020 | Anti-inflammatory and modulatory roles of exogenous GM1 administration on microglia |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coelho, M.A.; Jeyaraman, M.; Jeyaraman, N.; Rajendran, R.L.; Sugano, A.A.; Mosaner, T.; Santos, G.S.; Bizinotto Lana, J.V.; Lana, A.V.S.D.; da Fonseca, L.F.; et al. Application of Sygen® in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathies—A Review of Biological Interactions. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9050217
Coelho MA, Jeyaraman M, Jeyaraman N, Rajendran RL, Sugano AA, Mosaner T, Santos GS, Bizinotto Lana JV, Lana AVSD, da Fonseca LF, et al. Application of Sygen® in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathies—A Review of Biological Interactions. Bioengineering. 2022; 9(5):217. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9050217
Chicago/Turabian StyleCoelho, Marcelo Amaral, Madhan Jeyaraman, Naveen Jeyaraman, Ramya Lakshmi Rajendran, André Atsushi Sugano, Tomas Mosaner, Gabriel Silva Santos, João Vitor Bizinotto Lana, Anna Vitória Santos Duarte Lana, Lucas Furtado da Fonseca, and et al. 2022. "Application of Sygen® in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathies—A Review of Biological Interactions" Bioengineering 9, no. 5: 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9050217
APA StyleCoelho, M. A., Jeyaraman, M., Jeyaraman, N., Rajendran, R. L., Sugano, A. A., Mosaner, T., Santos, G. S., Bizinotto Lana, J. V., Lana, A. V. S. D., da Fonseca, L. F., Domingues, R. B., Gangadaran, P., Ahn, B.-C., & Lana, J. F. S. D. (2022). Application of Sygen® in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathies—A Review of Biological Interactions. Bioengineering, 9(5), 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9050217











