A Review of the Methods of Non-Invasive Assessment of Intracranial Pressure through Ocular Measurement
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Non-Invasive ICP Measurement
2.1. Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter (ONSD)
2.2. Flash Visual Evoked Potentials (FVEPs)
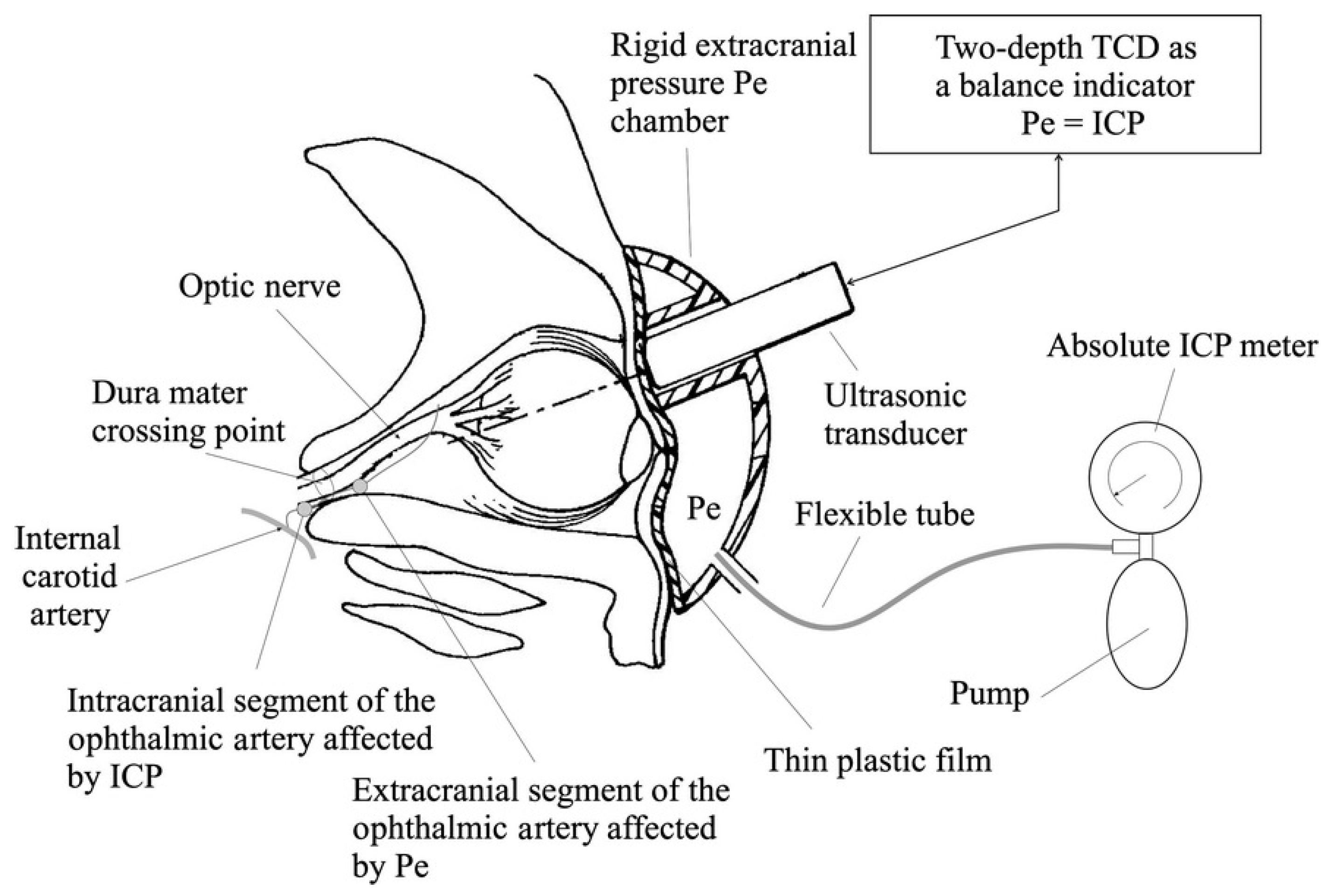
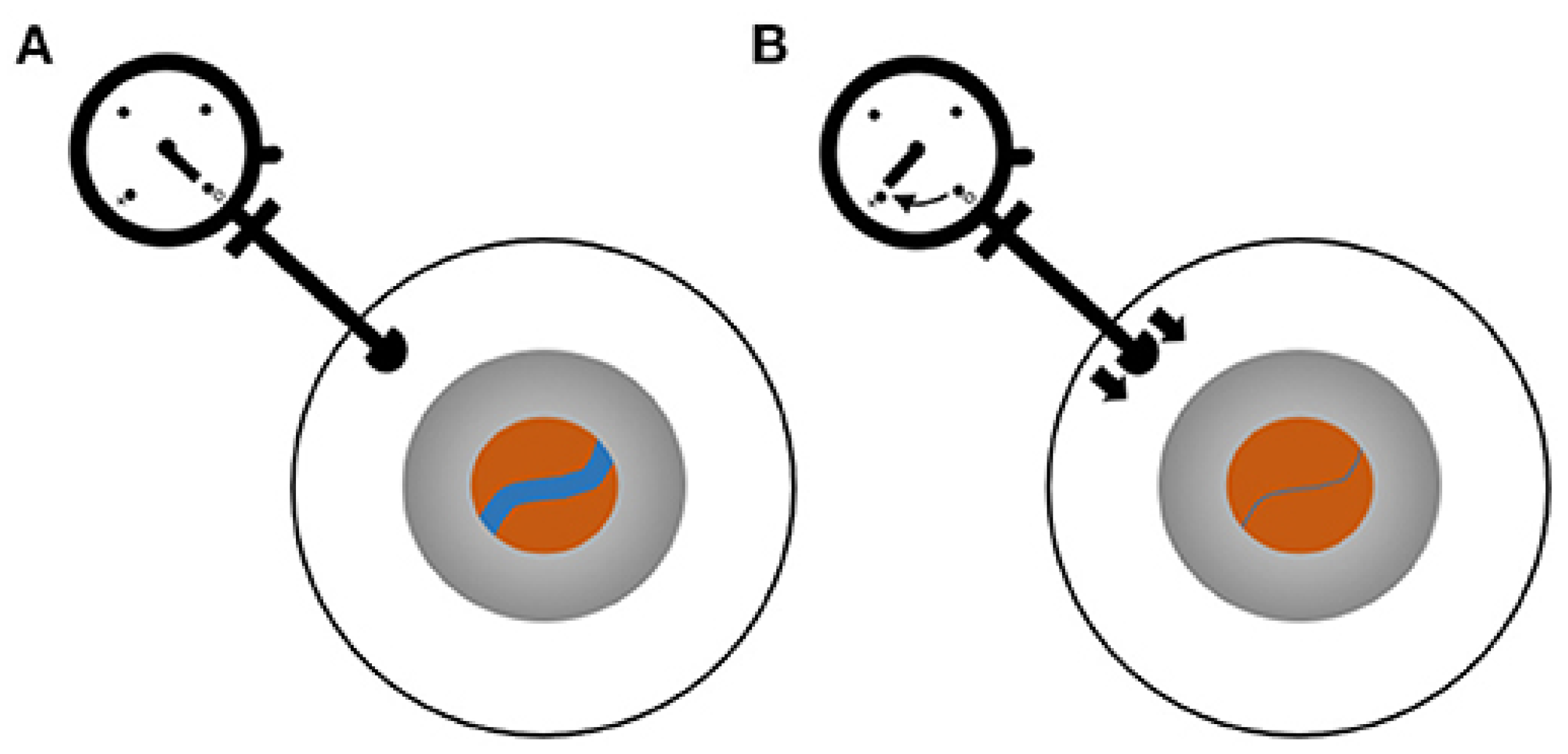
2.3. Two-Depth Transorbital Doppler (TDTD) Ultrasonography
2.4. Central Retinal Venous Pressure (CRVP)
2.5. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
2.6. Pupillometry
2.7. IOP Measurement
2.8. Retinal Arteriole and Venule Diameter Ratio (A/V Ratio)
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dhar, R.; Sandler, R.; Manwaring, K.; Mansy, H. Spectral Analysis of Tympanic Membrane Pulse Signal: An Approach for Noninvasive Detection of Elevated Intracranial Pressure. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Signal Processing in Medicine and Biology Symposium (SPMB), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 5 December 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokri, B. The Monro-Kellie hypothesis: Applications in CSF volume depletion. Neurology 2001, 56, 1746–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Voorhees, A.P.; Sigal, I.A. Cerebrospinal Fluid Pressure: Revisiting Factors Influencing Optic Nerve Head Biomechanics. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siaudvytyte, L.; Januleviciene, I.; Daveckaite, A.; Ragauskas, A.; Siesky, B.; Harris, A. Neuroretinal rim area and ocular haemodynamic parameters in patients with normal-tension glaucoma with differing intracranial pressures. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 100, 1134–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, N. Continuous recording and control of ventricular fluid pressure in neurosurgical practice. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. Suppl. 1960, 36, 1–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, N.; Flyax, S.; Kurz, W.; Jakobi, M.; Tasoglu, S.; Koch, A.W.; Yetisen, A.K. Intracranial Sensors for Continuous Monitoring of Neurophysiology. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 6, 2100339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evensen, K.B.; Eide, P.K. Measuring intracranial pressure by invasive, less invasive or non-invasive means: Limitations and avenues for improvement. Fluids Barriers CNS 2020, 17, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Medow, J.E.; Iskandar, B.J.; Wang, F.; Shokoueinejad, M.; Koueik, J.; Webster, J.G. Invasive and noninvasive means of measuring intracranial pressure: A review. Physiol. Meas. 2017, 38, R143–R182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokoohi, H.; Pyle, M.; Kuhl, E.; Loesche, M.A.; Goyal, A.; LeSaux, M.A.; Boniface, K.S.; Taheri, M.R. Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter Measured by Point-of-Care Ultrasound and MRI. J. Neuroimaging 2020, 30, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayreh, S.S. Pathogenesis of oedema of the optic disc. Doc. Ophthalmol. 1968, 24, 289–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galetta, S.; Byrne, S.F.; Smith, J.L. Echographic correlation of optic nerve sheath size and cerebrospinal fluid pressure. J. Clin. Neuroophthalmol. 1989, 9, 79–82. [Google Scholar]
- Hanafi, M.G.; Verki, M.M.; Parei, S.N. Ultrasonic Assessment of Optic Nerve Sheath to Detect Increased Intracranial Pressure. J. Med. Ultrasound. 2019, 27, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amini, A.; Kariman, H.; Arhami Dolatabadi, A.; Hatamabadi, H.R.; Derakhshanfar, H.; Mansouri, B.; Safari, S.; Eqtesadi, R. Use of the sonographic diameter of optic nerve sheath to estimate intracranial pressure. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2013, 31, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebraheim, A.M.; Mourad, H.S.; Kishk, N.A.; Eldin, N.B.; Saad, A.A. Sonographic assessment of optic nerve and ophthalmic vessels in patients with idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Neurol. Res. 2018, 40, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- del Saz-Saucedo, P.; Redondo-Gonzalez, O.; Mateu-Mateu, A.; Huertas-Arroyo, R.; Garcia-Ruiz, R.; Botia-Paniagua, E. Sonographic assessment of the optic nerve sheath diameter in the diagnosis of idiopathic intracranial hypertension. J. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 361, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.E.; Hong, E.P.; Kim, H.C.; Lee, S.U.; Jeon, J.P. Ultrasonographic optic nerve sheath diameter to detect increased intracranial pressure in adults: A meta-analysis. Acta Radiol. 2019, 60, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koziarz, A.; Nath, S.; Almenawer, S.A. Bedside Optic Nerve Ultrasonography for Diagnosing Increased Intracranial Pressure. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 171, 869–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishk, N.A.; Ebraheim, A.M.; Ashour, A.S.; Badr, N.M.; Eshra, M.A. Optic nerve sonographic examination to predict raised intracranial pressure in idiopathic intracranial hypertension: The cut-off points. Neuroradiol. J. 2018, 31, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimberly, H.H.; Noble, V.E. Using MRI of the optic nerve sheath to detect elevated intracranial pressure. Crit Care 2008, 12, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, A.; Kinouchi, H.; Horikoshi, T.; Uchida, M.; Ishigame, K. Effect of intracranial pressure on the diameter of the optic nerve sheath. J. Neurosurg. 2008, 109, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geeraerts, T.; Newcombe, V.F.; Coles, J.P.; Abate, M.G.; Perkes, I.E.; Hutchinson, P.J.; Outtrim, J.G.; Chatfield, D.A.; Menon, D.K. Use of T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of the optic nerve sheath to detect raised intracranial pressure. Crit Care 2008, 12, R114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Hong, D.Y.; Sung, B.Y.; Lee, S.; Paik, J.H.; Jung, H.M. Comparison of ultrasonography and computed tomography for measuring optic nerve sheath diameter for the detection of elevated intracranial pressure. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2021, 204, 106609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekhon, M.S.; Griesdale, D.E.; Robba, C.; McGlashan, N.; Needham, E.; Walland, K.; Shook, A.C.; Smielewski, P.; Czosnyka, M.; Gupta, A.K.; et al. Optic nerve sheath diameter on computed tomography is correlated with simultaneously measured intracranial pressure in patients with severe traumatic brain injury. Intensive Care Med. 2014, 40, 1267–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazurek, M.H.; Cahn, B.A.; Yuen, M.M.; Prabhat, A.M.; Chavva, I.R.; Shah, J.T.; Crawford, A.L.; Welch, E.B.; Rothberg, J.; Sacolick, L.; et al. Portable, bedside, low-field magnetic resonance imaging for evaluation of intracerebral hemorrhage. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koziarz, A.; Sne, N.; Kegel, F.; Nath, S.; Badhiwala, J.H.; Nassiri, F.; Mansouri, A.; Yang, K.; Zhou, Q.; Rice, T.; et al. Bedside Optic Nerve Ultrasonography for Diagnosing Increased Intracranial Pressure: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 171, 896–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, W.D.; Hollman, A.S.; Dutton, G.N.; Carachi, R. Measurement of optic nerve sheath diameter by ultrasound: A means of detecting acute raised intracranial pressure in hydrocephalus. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2002, 86, 1109–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soliman, I.; Johnson, G.; Gillman, L.M.; Zeiler, F.A.; Faqihi, F.; Aletreby, W.T.; Balhamar, A.; Mahmood, N.N.; Ahmad Mumtaz, S.; Alharthy, A.; et al. New Optic Nerve Sonography Quality Criteria in the Diagnostic Evaluation of Traumatic Brain Injury. Crit. Care Res. Pract. 2018, 2018, 3589762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zoerle, T.; Caccioppola, A.; D’Angelo, E.; Carbonara, M.; Conte, G.; Avignone, S.; Zanier, E.R.; Birg, T.; Ortolano, F.; Triulzi, F.; et al. Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter is not Related to Intracranial Pressure in Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Patients. Neurocrit. Care 2020, 33, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardim, D.; Czosnyka, M.; Chandrapatham, K.; Badenes, R.; Bertuccio, A.; Noto, A.D.; Donnelly, J.; Pelosi, P.; Ball, L.; Hutchinson, P.J.; et al. Effects of Age and Sex on Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter in Healthy Volunteers and Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Rumpel, H.; Lim, W.E.; Baskaran, M.; Perera, S.A.; Nongpiur, M.E.; Aung, T.; Milea, D.; Girard, M.J. Finite Element Analysis Predicts Large Optic Nerve Head Strains During Horizontal Eye Movements. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 2452–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, D.H.; Pulliam, M.W.; Rosenfeld, J.G.; Watts, C. Relationship between visual evoked potentials and intracranial pressure. J. Neurosurg. 1981, 55, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.L.; Zhou, J.Y.; Zhu, G.H. Clinical experience with the noninvasive ICP monitoring system. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2005, 95, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.I.; Li, Y.; Minhui, X.; Yihua, Z. Realization of a comprehensive non-invasive detection of intracranial pressure analyzer based upon FVEP and TCD. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2012, 114, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Luan, X.; Wu, Y. Clinical Application of Intracranial Pressure Monitoring Based on Flash Visual Evoked Potential in Treatment of Patients with Hypertensive Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Res. Sq. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, D.I.; Jacobson, D.M. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension. J. Neuroophthalmol. 2004, 24, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaslid, R.; Markwalder, T.M.; Nornes, H. Noninvasive transcranial Doppler ultrasound recording of flow velocity in basal cerebral arteries. J. Neurosurg. 1982, 57, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bellner, J.; Romner, B.; Reinstrup, P.; Kristiansson, K.A.; Ryding, E.; Brandt, L. Transcranial Doppler sonography pulsatility index (PI) reflects intracranial pressure (ICP). Surg. Neurol. 2004, 62, 45–51, discussion 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaloria, N.; Panda, N.B.; Bhagat, H.; Kaloria, N.; Soni, S.L.; Chauhan, R.; Chhabra, R.; Jangra, K. Pulsatility Index Reflects Intracranial Pressure Better than Resistive Index in Patients with Clinical Features of Intracranial Hypertension. J. Neurosci. Rural Pract. 2020, 11, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Behrens, A.; Lenfeldt, N.; Ambarki, K.; Malm, J.; Eklund, A.; Koskinen, L.O. Transcranial Doppler pulsatility index: Not an accurate method to assess intracranial pressure. Neurosurgery 2010, 66, 1050–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweifel, C.; Czosnyka, M.; Carrera, E.; de Riva, N.; Pickard, J.D.; Smielewski, P. Reliability of the blood flow velocity pulsatility index for assessment of intracranial and cerebral perfusion pressures in head-injured patients. Neurosurgery 2012, 71, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgalla, M.H.; Magunia, H. Noninvasive measurement of intracranial pressure via the pulsatility index on transcranial Doppler sonography: Is improvement possible? J. Clin. Ultrasound. 2016, 44, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragauskas, A.; Matijosaitis, V.; Zakelis, R.; Petrikonis, K.; Rastenyte, D.; Piper, I.; Daubaris, G. Clinical assessment of noninvasive intracranial pressure absolute value measurement method. Neurology 2012, 78, 1684–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macias, B.R.; Liu, J.H.K.; Otto, C.; Hargens, A.R. Intracranial Pressure and Its Effect on Vision in Space and on Earth: Vision Impairment in Space; World Scientific: Houston, TX, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Siaudvytyte, L.; Januleviciene, I.; Ragauskas, A.; Bartusis, L.; Siesky, B.; Harris, A. Update in intracranial pressure evaluation methods and translaminar pressure gradient role in glaucoma. Acta Ophthalmol. 2015, 93, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lucinskas, P.; Deimantavicius, M.; Bartusis, L.; Zakelis, R.; Misiulis, E.; Dziugys, A.; Hamarat, Y. Human ophthalmic artery as a sensor for non-invasive intracranial pressure monitoring: Numerical modeling and in vivo pilot study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coccius, E.A. Ueber die Anwendung des Augen-Spiegels Nebst Angabe Eines Neuen Instrumentes; Immanuel Müller: Leipzig, Germany, 1853. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, W.H.; Hazelton, M.L.; Yu, D.Y. Retinal venous pulsation: Expanding our understanding and use of this enigmatic phenomenon. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2016, 55, 82–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, B.E. The clinical significance of spontaneous pulsations of the retinal vein. Arch. Neurol. 1978, 35, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacks, A.S.; Miller, N.R. Spontaneous retinal venous pulsation: Aetiology and significance. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2003, 74, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.N.; Shallwani, H.; Khan, M.U.; Shamim, M.S. Noninvasive monitoring intracranial pressure—A review of available modalities. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2017, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios-Montenegro, E.N.; Anderson, D.R.; David, N.J. Intracranial pressure and ocular hemodynamics. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1973, 89, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer-Schwickerath, R.; Kleinwachter, T.; Firsching, R.; Papenfuss, H.D. Central retinal venous outflow pressure. Graefes Arch Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 1995, 233, 783–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firsching, R.; Schutze, M.; Motschmann, M.; Behrens-Baumann, W. Venous opthalmodynamometry: A noninvasive method for assessment of intracranial pressure. J. Neurosurg. 2000, 93, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firsching, R.; Muller, C.; Pauli, S.U.; Voellger, B.; Rohl, F.W.; Behrens-Baumann, W. Noninvasive assessment of intracranial pressure with venous ophthalmodynamometry. Clinical article. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 115, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, P.S.; Jensen, O.E.; Foss, A.J. A theoretical model to allow prediction of the CSF pressure from observations of the retinal venous pulse. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 6319–6323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moss, H.E. Retinal Vein Changes as a Biomarker to Guide Diagnosis and Management of Elevated Intracranial Pressure. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 751370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querfurth, H.W.; Arms, S.W.; Lichy, C.M.; Irwin, W.T.; Steiner, T. Prediction of intracranial pressure from noninvasive transocular venous and arterial hemodynamic measurements: A pilot study. Neurocrit. Care 2004, 1, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, W.H.; Khoo, Y.J.; Kermode, A.G.; Lind, C.R.; Hazelton, M.L.; Parsons, K.E.; Yu, D.Y. Utilisation of retinal vein photoplethysmography to measure intracranial pressure. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2020, 92, 104–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, W.H.; Vukmirovic, A.; Abdul-Rahman, A.; Khoo, Y.J.; Kermode, A.G.; Lind, C.R.; Dunuwille, J.; Yu, D.Y. Zero retinal vein pulsation amplitude extrapolated model in non-invasive intracranial pressure estimation. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skau, M.; Yri, H.; Sander, B.; Gerds, T.A.; Milea, D.; Jensen, R. Diagnostic value of optical coherence tomography for intracranial pressure in idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Graefes Arch Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2013, 251, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swanson, J.W.; Xu, W.; Ying, G.S.; Pan, W.; Lang, S.S.; Heuer, G.G.; Bartlett, S.P.; Taylor, J.A. Intracranial pressure patterns in children with craniosynostosis utilizing optical coherence tomography. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2020, 36, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupersmith, M.J.; Sibony, P.; Mandel, G.; Durbin, M.; Kardon, R.H. Optical coherence tomography of the swollen optic nerve head: Deformation of the peripapillary retinal pigment epithelium layer in papilledema. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 6558–6564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sibony, P.; Kupersmith, M.J.; Honkanen, R.; Rohlf, F.J.; Torab-Parhiz, A. Effects of lowering cerebrospinal fluid pressure on the shape of the peripapillary retina in intracranial hypertension. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 8223–8231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tun, T.A.; Wang, X.; Baskaran, M.; Nongpiur, M.E.; Tham, Y.C.; Perera, S.A.; Strouthidis, N.G.; Aung, T.; Cheng, C.Y.; Girard, M.J.A. Variation of Peripapillary Scleral Shape with Age. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2019, 60, 3275–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Tun, T.A.; Nongpiur, M.E.; Htoon, H.M.; Tham, Y.C.; Strouthidis, N.G.; Aung, T.; Cheng, C.Y.; Girard, M.J. Peripapillary sclera exhibits a v-shaped configuration that is more pronounced in glaucoma eyes. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 106, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsen, H.H.J.K.; Moe, M.C.; Petrovski, G. Non-invasive Estimation of Pulsatile and Static Intracranial Pressure by Optical Coherence Tomography. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2022, 11, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, C.; Hutch, M.; Barra, M.; Kim, A.; Zafar, S.; Smirnakis, S. Effects of Osmotic Therapy on Pupil Reactivity: Quantification Using Pupillometry in Critically Ill Neurologic Patients. Neurocrit. Care 2019, 30, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, M.D.; Singh, V. Portable infrared pupillometry in critical care. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taylor, W.R.; Chen, J.W.; Meltzer, H.; Gennarelli, T.A.; Kelbch, C.; Knowlton, S.; Richardson, J.; Lutch, M.J.; Farin, A.; Hults, K.N.; et al. Quantitative pupillometry, a new technology: Normative data and preliminary observations in patients with acute head injury. Technical note. J. Neurosurg. 2003, 98, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.W.; Gombart, Z.J.; Rogers, S.; Gardiner, S.K.; Cecil, S.; Bullock, R.M. Pupillary reactivity as an early indicator of increased intracranial pressure: The introduction of the Neurological Pupil index. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2011, 2, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McNett, M.; Moran, C.; Grimm, D.; Gianakis, A. Pupillometry Trends in the Setting of Increased Intracranial Pressure. J. Neurosci. Nurs. 2018, 50, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, A.R.; Su, Z.; Toman, E.; Belli, A.; Davies, D. Optical pupillometry in traumatic brain injury: Neurological pupil index and its relationship with intracranial pressure through significant event analysis. Brain Inj. 2019, 33, 1032–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giede-Jeppe, A.; Sprugel, M.I.; Huttner, H.B.; Borutta, M.; Kuramatsu, J.B.; Hoelter, P.; Engelhorn, T.; Schwab, S.; Koehn, J. Automated Pupillometry Identifies Absence of Intracranial Pressure Elevation in Intracerebral Hemorrhage Patients. Neurocrit. Care 2021, 35, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashutka, M.K.; Chandra, A.; Murray, H.N.; Phillips, G.S.; Hiestand, B.C. The relationship of intraocular pressure to intracranial pressure. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2004, 43, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajjadi, S.A.; Harirchian, M.H.; Sheikhbahaei, N.; Mohebbi, M.R.; Malekmadani, M.H.; Saberi, H. The relation between intracranial and intraocular pressures: Study of 50 patients. Ann. Neurol. 2006, 59, 867–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; McCulley, T.J.; Horton, J.C. No correlation between intraocular pressure and intracranial pressure. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 64, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirk, T.; Jones, K.; Miller, S.; Corbett, J. Measurement of intraocular and intracranial pressure: Is there a relationship? Ann. Neurol. 2011, 70, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayreh, S.S.; Edwards, J. Ophthalmic arterial and venous pressures. Effects of acute intracranial hypertension. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1971, 55, 649–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersen, M.S.; Pedersen, C.B.; Poulsen, F.R. A new novel method for assessing intracranial pressure using non-invasive fundus images: A pilot study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Method | Equipment | Continuous Monitoring | Quantitatively | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter (ONSD) | Ultrasonography/Computed Tomography/Magnetic Resonance Imaging | No | No | Not accurate due to differences in baseline ONSD between individuals |
| Flash Visual Evoked Potentials (FVEP) | Electroencephalo-gram | No | No | Not suitable for certain patients, such as those with frontal lobe hematoma, retinal damage, or optic neuropathy |
| Two-depth Transorbital Doppler (TDTD) | Transcranial Doppler Ultrasonography | No/Yes | Yes | Operators need professional training |
| Central Retinal Venous Pressure (CRVP) | Ophthalmodyn-amometer | No | Yes | Not suitable for patients with persistent papilledema after a rapid decrease in ICP |
| Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) | OCT | No | No | Not suitable for patients with severe papilledema |
| Pupillometry | Automatic pupillometer | No | No | Pupillary reactivity is affected by many factors |
| IOP | Tonometer | No | No | IOP is not a reliable parameter for ICP assessment |
| Retinal Arteriole and Venule Diameter Ratio | Fundus camera | No | No | Accuracy still requires further research |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, J.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Fan, Y. A Review of the Methods of Non-Invasive Assessment of Intracranial Pressure through Ocular Measurement. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9070304
Dong J, Li Q, Wang X, Fan Y. A Review of the Methods of Non-Invasive Assessment of Intracranial Pressure through Ocular Measurement. Bioengineering. 2022; 9(7):304. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9070304
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Jinhui, Qi Li, Xiaofei Wang, and Yubo Fan. 2022. "A Review of the Methods of Non-Invasive Assessment of Intracranial Pressure through Ocular Measurement" Bioengineering 9, no. 7: 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9070304
APA StyleDong, J., Li, Q., Wang, X., & Fan, Y. (2022). A Review of the Methods of Non-Invasive Assessment of Intracranial Pressure through Ocular Measurement. Bioengineering, 9(7), 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9070304







