Mechanically Derived Tissue Stromal Vascular Fraction Acts Anti-inflammatory on TNF Alpha-Stimulated Chondrocytes In Vitro
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Lipoharvesting and the FAT Procedure
2.2. Enzymatic Dissociation of tSVF
2.3. Flow Cytometry to Determine Cell Composition of tSVF
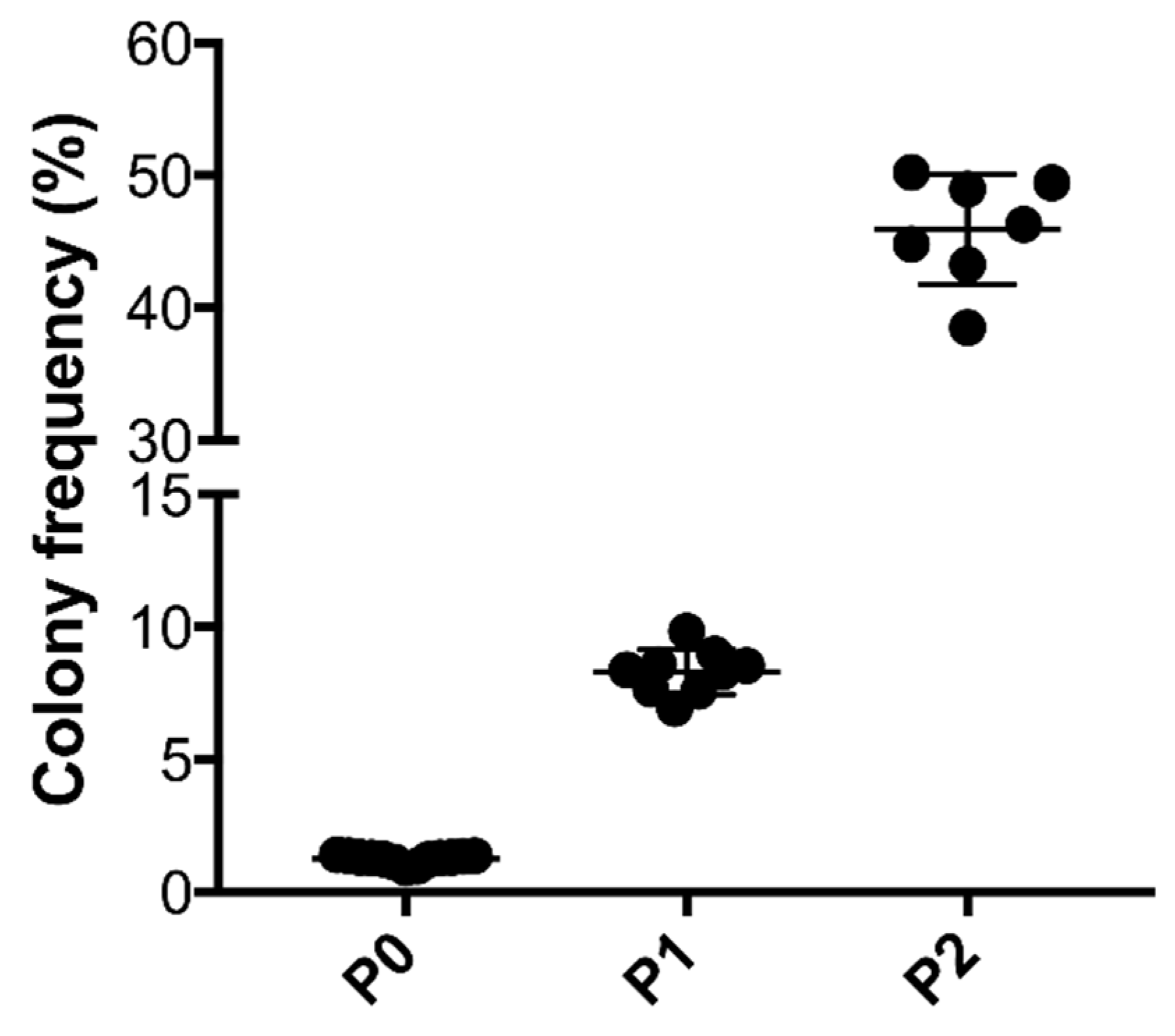
2.4. Colony Formation Unit Capacity of ASCs
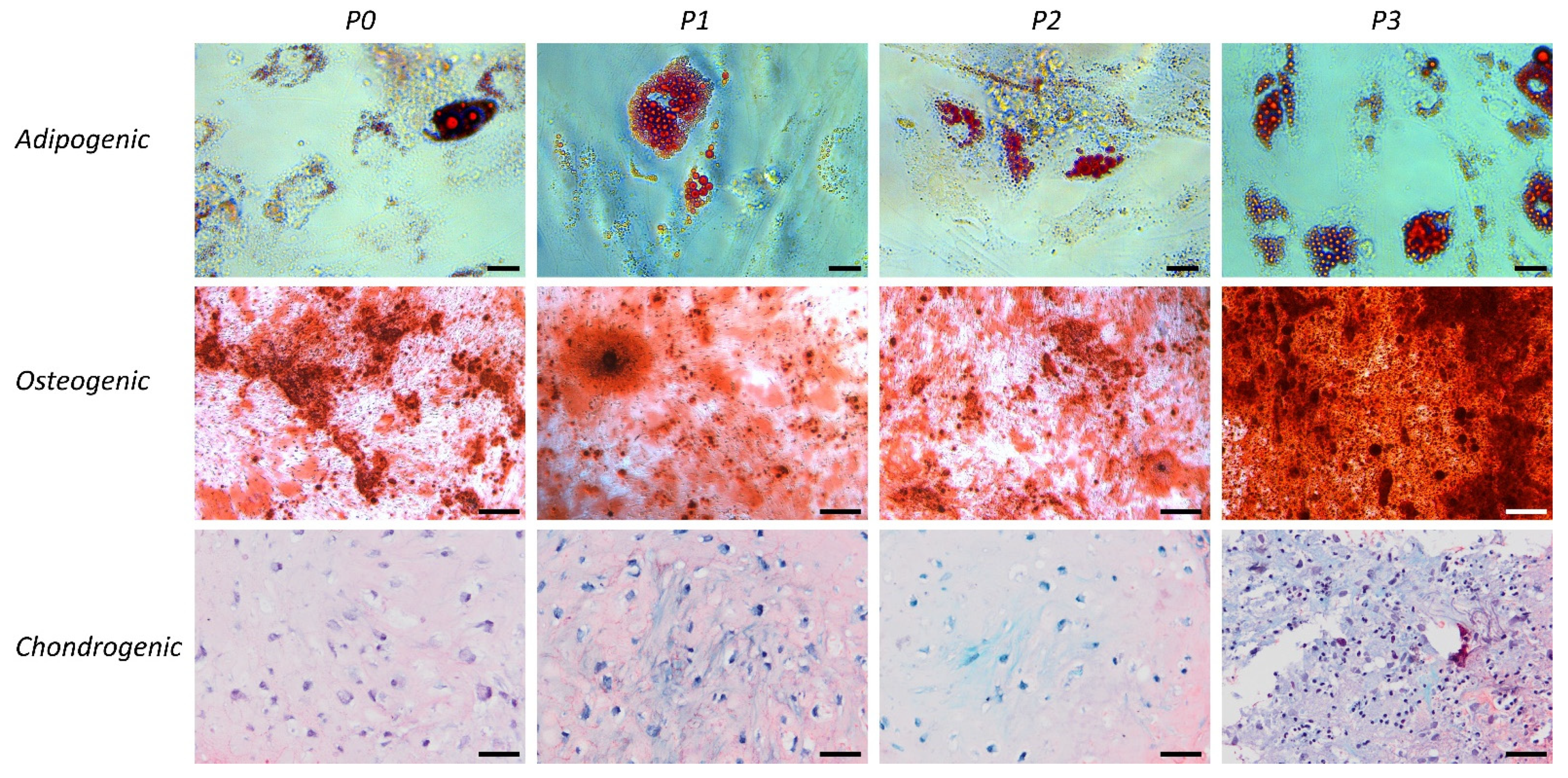
2.5. Differentiation Capacity of tSVF and ASCs
2.6. Enzymatic Isolation of Chondrocytes
2.7. Functional Analysis of Co-culture of tSVF-Derived Cells and Chondrocytes
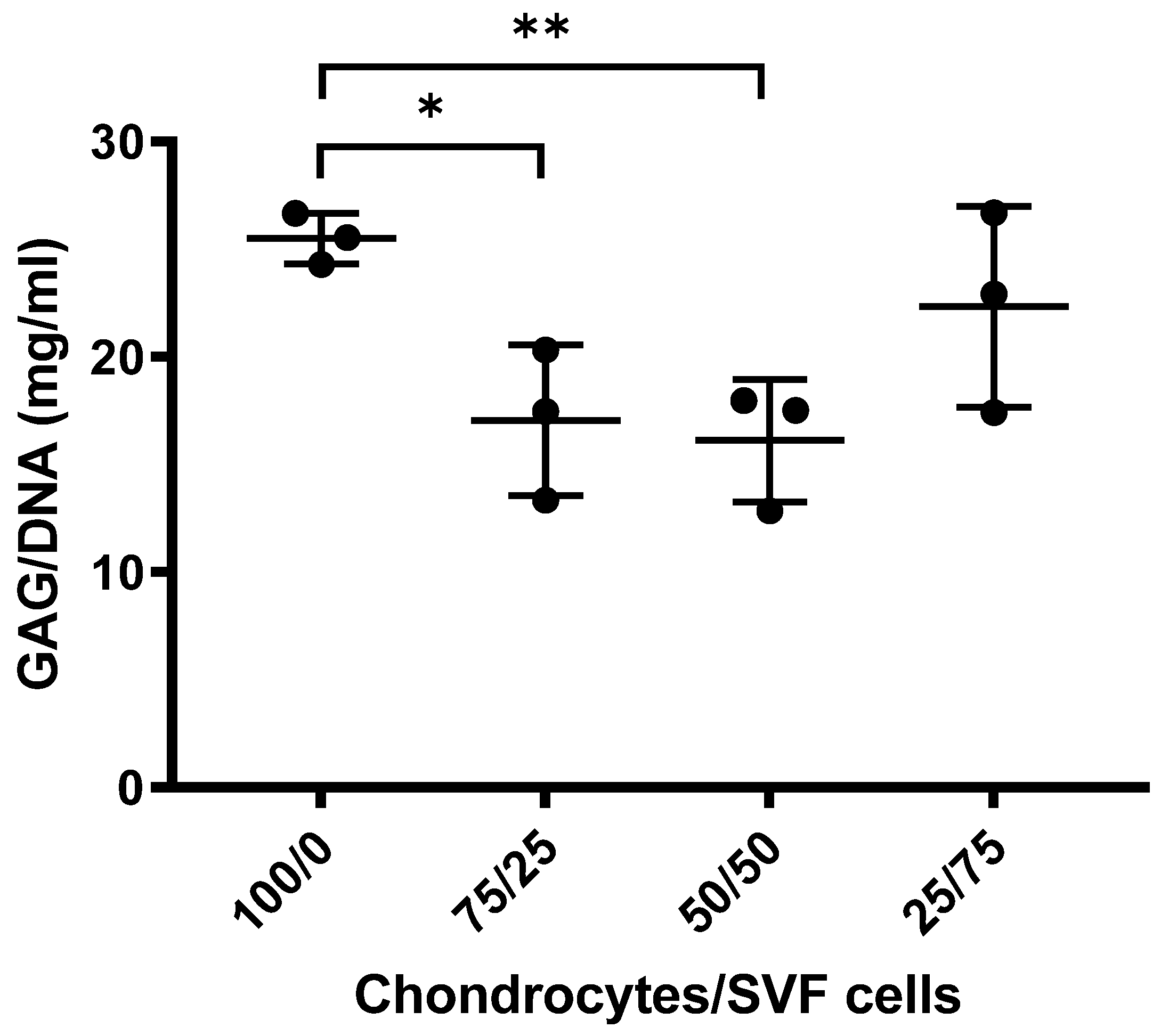
2.7.1. Cell Ratio Analysis of Chondrocytes and tSVF-Derived Cells Co-cultures
2.7.2. Sulphated Glycosaminoglycans Analysis
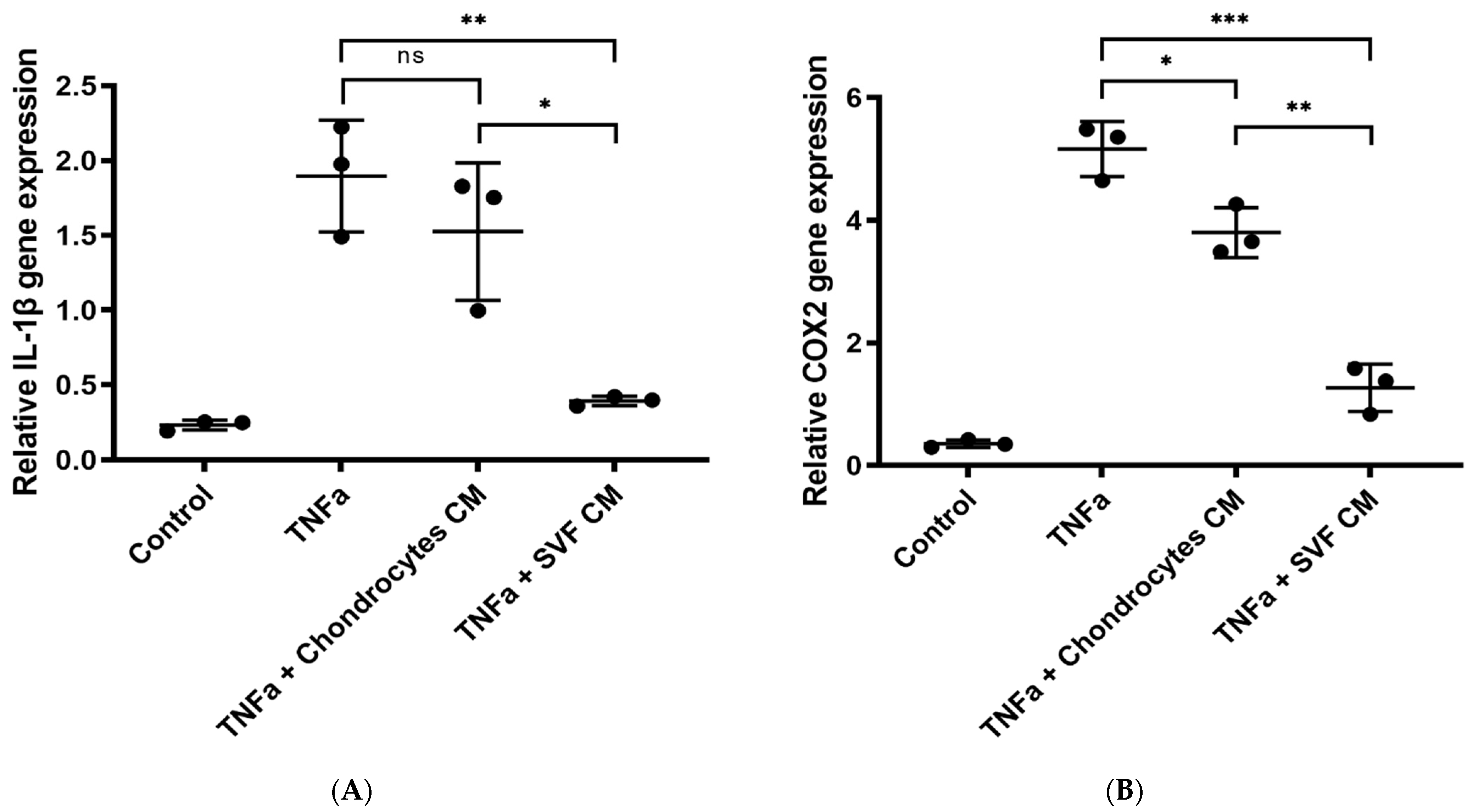
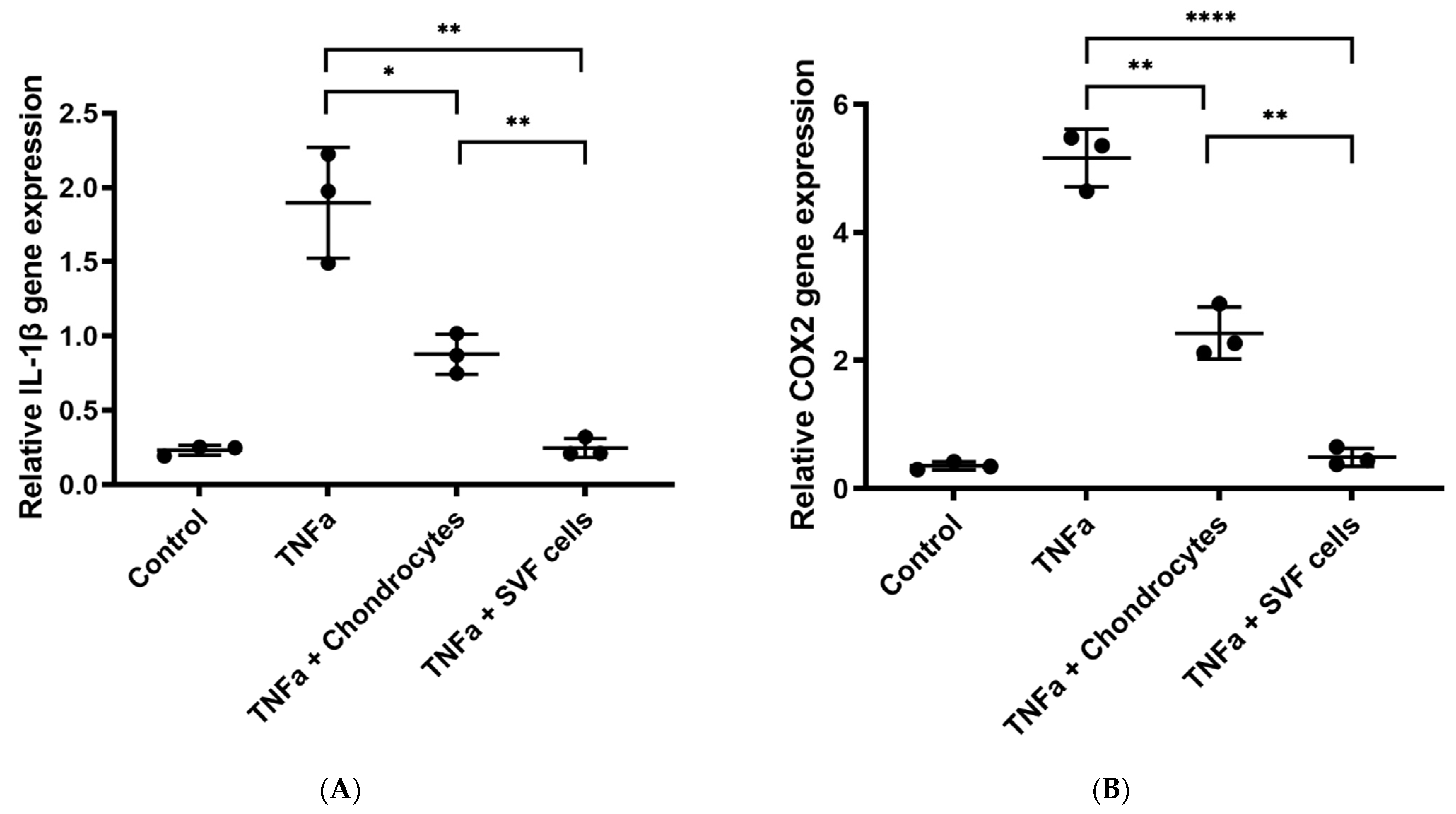
2.7.3. In Vitro Inflammation Assay
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
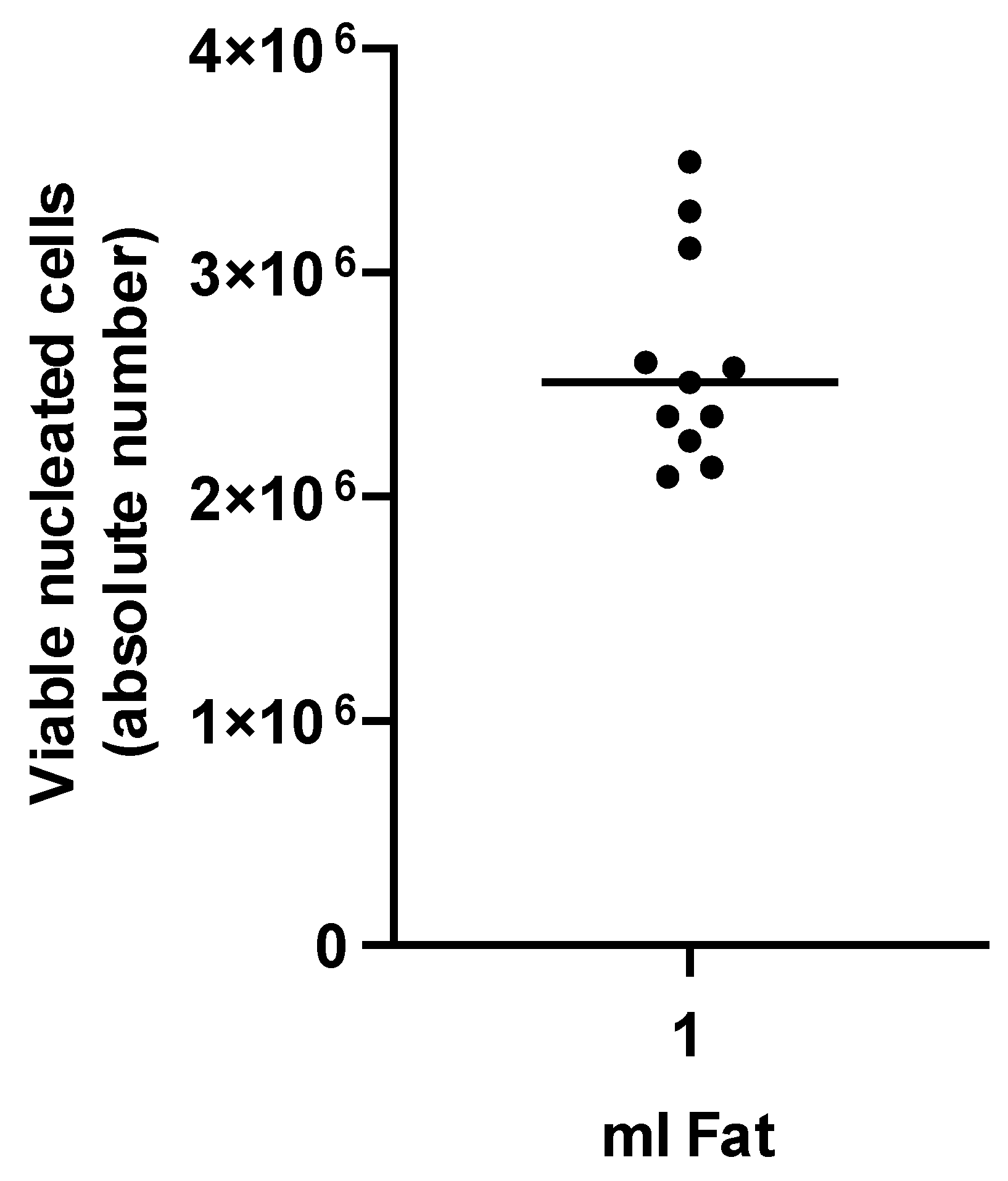
3.1. Characterization of tSVF
3.1.1. Cell Ratio Analysis of Chondrocytes and tSVF-Derived Cells in Co-Culture
3.1.2. Sulphated GAGs Analysis
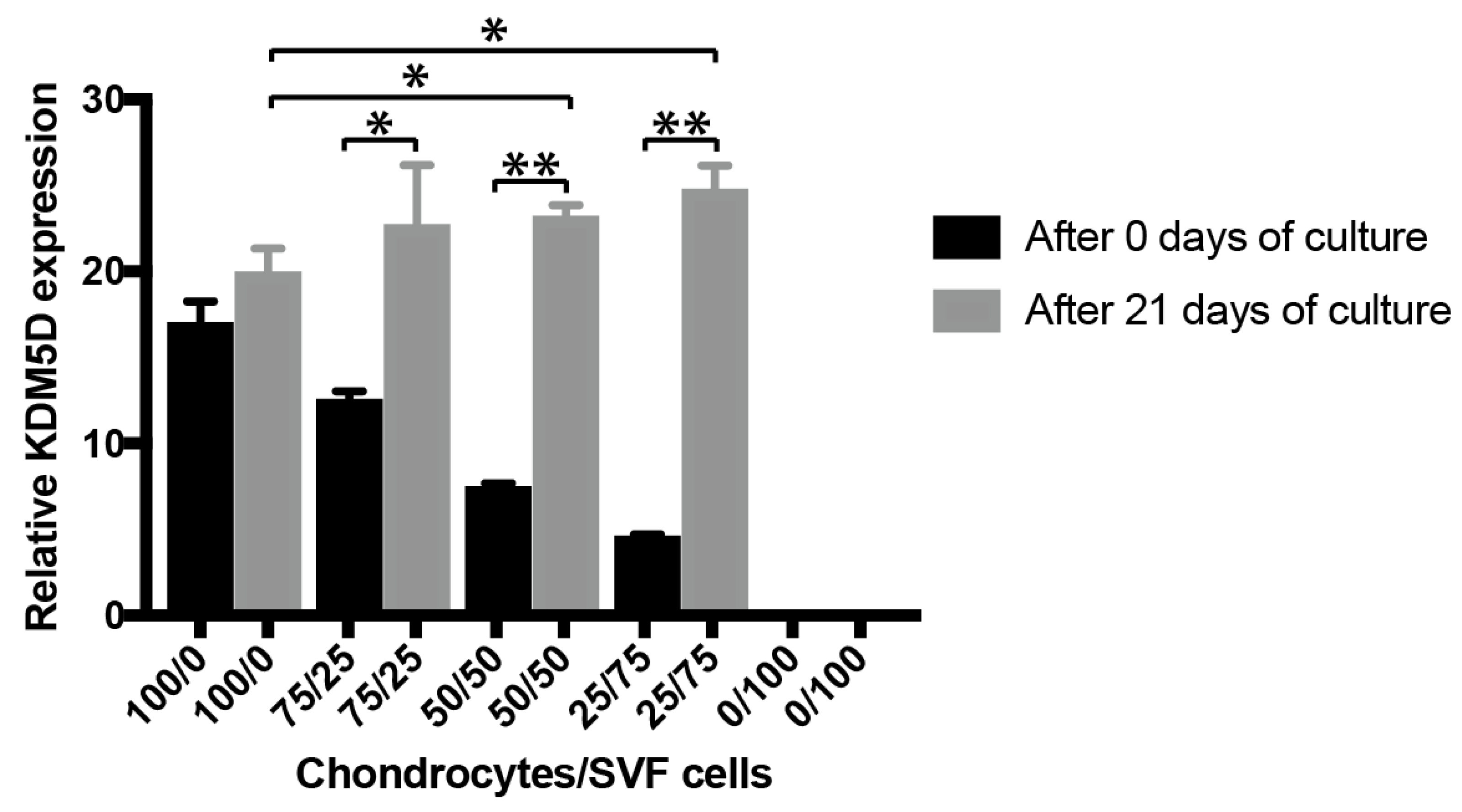
3.1.3. In Vitro Inflammation Assay
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Brongo, S.; Nicoletti, G.F.; La Padula, S.; Mele, C.M.; D’Andrea, F. Use of lipofilling for the treatment of severe burn outcomes. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2012, 130, 374e–376e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaspers, M.E.; Brouwer, K.M.; van Trier, A.J.; Groot, M.L.; Middelkoop, E.; van Zuijlen, P.P. Effectiveness of Autologous Fat Grafting in Adherent Scars: Results Obtained by a Comprehensive Scar Evaluation Protocol. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2017, 139, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Largo, R.D.; Tchang, L.A.; Mele, V.; Scherberich, A.; Harder, Y.; Wettstein, R.; Schaefer, D.J. Efficacy, safety and complications of autologous fat grafting to healthy breast tissue: A systematic review. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. JPRAS 2014, 67, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallua, N.; Baroncini, A.; Alharbi, Z.; Stromps, J.P. Improvement of facial scar appearance and microcirculation by autologous lipofilling. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. JPRAS 2014, 67, 1033–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchal, J.; Malanga, G.; Sheinkop, M. Safety and Efficacy of Percutaneous Injection of Lipogems Micro-Fractured Adipose Tissue for Osteoarthritic Knees. Am. J. Orthop. (Belle Mead N.J.) 2018, 47, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philandrianos, C.; Serrero, M.; Grimaud, F.; Magalon, J.; Visee, C.; Velier, M.; Francois, P.; Orsoni, P.; Magalon, G.; Grimaud, J.C.; et al. First clinical case report of local microinjection of autologous fat and adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction for perianal fistula in Crohn’s disease. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourin, P.; Bunnell, B.A.; Casteilla, L.; Dominici, M.; Katz, A.J.; March, K.L.; Redl, H.; Rubin, J.P.; Yoshimura, K.; Gimble, J.M. Stromal cells from the adipose tissue-derived stromal vascular fraction and culture expanded adipose tissue-derived stromal/stem cells: A joint statement of the International Federation for Adipose Therapeutics and Science (IFATS) and the International Society for Cellular Therapy (ISCT). Cytotherapy 2013, 15, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Dongen, J.A.; Tuin, A.J.; Spiekman, M.; Jansma, J.; van der Lei, B.; Harmsen, M.C. Comparison of intraoperative procedures for isolation of clinical grade stromal vascular fraction for regenerative purposes: A systematic review. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2018, 12, e261–e274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Corselli, M.; Chen, C.W.; Sun, B.; Yap, S.; Rubin, J.P.; Peault, B. The tunica adventitia of human arteries and veins as a source of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2012, 21, 1299–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, G.; Garcia, M.; Ning, H.; Banie, L.; Guo, Y.L.; Lue, T.F.; Lin, C.S. Defining stem and progenitor cells within adipose tissue. Stem Cells Dev. 2008, 17, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacFarlane, R.J.; Graham, S.M.; Davies, P.S.; Korres, N.; Tsouchnica, H.; Heliotis, M.; Mantalaris, A.; Tsiridis, E. Anti-inflammatory role and immunomodulation of mesenchymal stem cells in systemic joint diseases: Potential for treatment. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2013, 17, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiekman, M.; van Dongen, J.A.; Willemsen, J.C.; Hoppe, D.L.; van der Lei, B.; Harmsen, M.C. The power of fat and its adipose-derived stromal cells: Emerging concepts for fibrotic scar treatment. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2017, 11, 3220–3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suga, H.; Glotzbach, J.P.; Sorkin, M.; Longaker, M.T.; Gurtner, G.C. Paracrine mechanism of angiogenesis in adipose-derived stem cell transplantation. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2014, 72, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuk, P.A.; Zhu, M.; Ashjian, P.; De Ugarte, D.A.; Huang, J.I.; Mizuno, H.; Alfonso, Z.C.; Fraser, J.K.; Benhaim, P.; Hedrick, M.H. Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 4279–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dongen, J.A.; Getova, V.; Brouwer, L.A.; Liguori, G.R.; Sharma, P.K.; Stevens, H.P.; van der Lei, B.; Harmsen, M.C. Adipose tissue-derived extracellular matrix hydrogels as a release platform for secreted paracrine factors. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2019, 13, 973–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van Dongen, J.A.; Stevens, H.P.; Parvizi, M.; van der Lei, B.; Harmsen, M.C. The fractionation of adipose tissue procedure to obtain stromal vascular fractions for regenerative purposes. Wound Repair Regen. Off. Publ. Wound Health Soc. Eur. Tissue Repair Soc. 2016, 24, 994–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, T.M.; Chen, Y.H.; Sun, H.S.; Tsai, S.J. Fibroblast growth factors: Potential novel targets for regenerative therapy of osteoarthritis. Chin. J. Physiol. 2019, 62, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnson, K.W.; Chi, Y.; Bou-Gharios, G.; Leask, A.; Philip, A. TGF-b signaling in cartilage homeostasis and osteoarthritis. Front. Biosci. (Schol. Ed.) 2012, 4, 251–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhao, L.; Chen, D. Growth factor signalling in osteoarthritis. Growth Factors (Chur Switz.) 2018, 36, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, M.; Smith, E.; Hoy, D.; Nolte, S.; Ackerman, I.; Fransen, M.; Bridgett, L.; Williams, S.; Guillemin, F.; Hill, C.L.; et al. The global burden of hip and knee osteoarthritis: Estimates from the global burden of disease 2010 study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, K.; Kabata, T.; Hayashi, K.; Maeda, T.; Kajino, Y.; Iwai, S.; Fujita, K.; Hasegawa, K.; Inoue, D.; Sugimoto, N.; et al. The paracrine effect of adipose-derived stem cells inhibits osteoarthritis progression. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2015, 16, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spiekman, M.; Przybyt, E.; Plantinga, J.A.; Gibbs, S.; van der Lei, B.; Harmsen, M.C. Adipose tissue-derived stromal cells inhibit TGF-beta1-induced differentiation of human dermal fibroblasts and keloid scar-derived fibroblasts in a paracrine fashion. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2014, 134, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mancuso, P.; Raman, S.; Glynn, A.; Barry, F.; Murphy, J.M. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Osteoarthritis: The Critical Role of the Cell Secretome. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koh, Y.G.; Choi, Y.J.; Kwon, S.K.; Kim, Y.S.; Yeo, J.E. Clinical results and second-look arthroscopic findings after treatment with adipose-derived stem cells for knee osteoarthritis. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. Off. J. ESSKA 2015, 23, 1308–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, P.D.; Tran, T.D.; Nguyen, H.T.; Vu, H.T.; Le, P.T.; Phan, N.L.; Vu, N.B.; Phan, N.K.; Van Pham, P. Comparative Clinical Observation of Arthroscopic Microfracture in the Presence and Absence of a Stromal Vascular Fraction Injection for Osteoarthritis. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pak, J.; Lee, J.H.; Park, K.S.; Jeong, B.C.; Lee, S.H. Regeneration of Cartilage in Human Knee Osteoarthritis with Autologous Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells and Autologous Extracellular Matrix. Biores. Open Access 2016, 5, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Pham, P.; Hong-Thien Bui, K.; Quoc Ngo, D.; Tan Khuat, L.; Kim Phan, N. Transplantation of Nonexpanded Adipose Stromal Vascular Fraction and Platelet-Rich Plasma for Articular Cartilage Injury Treatment in Mice Model. J. Med. Eng. 2013, 2013, 832396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, H.P.; van Boxtel, J.; van Dijck, R.; van Dongen, J.A. Platelet Rich STROMA, the Combination of PRP and tSVF and Its Potential Effect on Osteoarthritis of the Knee. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attur, M.; Dave, M.; Abramson, S.B.; Amin, A. Activation of diverse eicosanoid pathways in osteoarthritic cartilage: A lipidomic and genomic analysis. Bull. NYU Hosp. Jt. Dis. 2012, 70, 99–108. [Google Scholar]
- Manferdini, C.; Maumus, M.; Gabusi, E.; Piacentini, A.; Filardo, G.; Peyrafitte, J.A.; Jorgensen, C.; Bourin, P.; Fleury-Cappellesso, S.; Facchini, A.; et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells exert antiinflammatory effects on chondrocytes and synoviocytes from osteoarthritis patients through prostaglandin E2. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 1271–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; He, C. Pro-inflammatory cytokines: The link between obesity and osteoarthritis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2018, 44, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bingham, S.; Beswick, P.J.; Blum, D.E.; Gray, N.M.; Chessell, I.P. The role of the cylooxygenase pathway in nociception and pain. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2006, 17, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer, M.D.; Busquets-Cortés, C.; Capó, X.; Tejada, S.; Tur, J.A.; Pons, A.; Sureda, A. Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibitors as a Therapeutic Target in Inflammatory Diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 3225–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojdasiewicz, P.; Poniatowski Ł, A.; Szukiewicz, D. The role of inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 561459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sophia Fox, A.J.; Bedi, A.; Rodeo, S.A. The basic science of articular cartilage: Structure, composition, and function. Sports Health 2009, 6, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andia, I.; Maffulli, N. Platelet-rich plasma for managing pain and inflammation in osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2013, 9, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Leijten, J.C.; Georgi, N.; Post, J.N.; van Blitterswijk, C.A.; Karperien, M. Trophic effects of mesenchymal stem cells increase chondrocyte proliferation and matrix formation. Tissue Eng. Part A 2011, 17, 1425–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Prins, H.J.; Helder, M.N.; van Blitterswijk, C.A.; Karperien, M. Trophic effects of mesenchymal stem cells in chondrocyte co-cultures are independent of culture conditions and cell sources. Tissue Eng. Part A 2012, 18, 1542–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Leijten, J.; van Blitterswijk, C.A.; Karperien, M. Fibroblast growth factor-1 is a mesenchymal stromal cell-secreted factor stimulating proliferation of osteoarthritic chondrocytes in co-culture. Stem Cells Dev. 2013, 22, 2356–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Windt, T.S.; Saris, D.B.; Slaper-Cortenbach, I.C.; van Rijen, M.H.; Gawlitta, D.; Creemers, L.B.; de Weger, R.A.; Dhert, W.J.; Vonk, L.A. Direct Cell-Cell Contact with Chondrocytes Is a Key Mechanism in Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Mediated Chondrogenesis. Tissue Eng. Part A 2015, 21, 2536–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Windt, T.S.; Vonk, L.A.; Slaper-Cortenbach, I.; Nizak, R.; van Rijen, M.; Saris, D. Allogeneic MSCs and Recycled Autologous Chondrons Mixed in a One-Stage Cartilage Cell Transplantion: A First-in-Man Trial in 35 Patients. Stem Cells (Dayt. Ohio) 2017, 35, 1984–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Windt, T.S.; Vonk, L.A.; Slaper-Cortenbach, I.C.; van den Broek, M.P.; Nizak, R.; van Rijen, M.H.; de Weger, R.A.; Dhert, W.J.; Saris, D.B. Allogeneic Mesenchymal Stem Cells Stimulate Cartilage Regeneration and Are Safe for Single-Stage Cartilage Repair in Humans upon Mixture with Recycled Autologous Chondrons. Stem Cells (Dayt. Ohio) 2017, 35, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekkers, J.E.; Tsuchida, A.I.; van Rijen, M.H.; Vonk, L.A.; Dhert, W.J.; Creemers, L.B.; Saris, D.B. Single-stage cell-based cartilage regeneration using a combination of chondrons and mesenchymal stromal cells: Comparison with microfracture. Am. J. Sports Med. 2013, 41, 2158–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannasi, C.; Niada, S.; Magagnotti, C.; Ragni, E.; Andolfo, A.; Brini, A.T. Comparison of two ASC-derived therapeutics in an in vitro OA model: Secretome versus extracellular vesicles. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niada, S.; Giannasi, C.; Gomarasca, M.; Stanco, D.; Casati, S.; Brini, A.T. Adipose-derived stromal cell secretome reduces TNFα-induced hypertrophy and catabolic markers in primary human articular chondrocytes. Stem Cell Res. 2019, 38, 101463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofiño-Vian, M.; Guillén, M.I.; Pérez Del Caz, M.D.; Castejón, M.A.; Alcaraz, M.J. Extracellular Vesicles from Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Downregulate Senescence Features in Osteoarthritic Osteoblasts. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 7197598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tofiño-Vian, M.; Guillén, M.I.; Pérez Del Caz, M.D.; Silvestre, A.; Alcaraz, M.J. Microvesicles from Human Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells as a New Protective Strategy in Osteoarthritic Chondrocytes. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 47, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dongen, J.A.; van Boxtel, J.; Harmsen, M.C.; Stevens, H.P. The Development of Facial Lipofilling from a Historical Point of View. Facial Plast. Surg. FPS 2019, 35, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhuri, O.; Cooper-White, J.; Janmey, P.A.; Mooney, D.J.; Shenoy, V.B. Effects of extracellular matrix viscoelasticity on cellular behaviour. Nature 2020, 584, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haltmayer, E.; Ribitsch, I.; Gabner, S.; Rosser, J.; Gueltekin, S.; Peham, J.; Giese, U.; Dolezal, M.; Egerbacher, M.; Jenner, F. Co-culture of osteochondral explants and synovial membrane as in vitro model for osteoarthritis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozito, T.P.; Alexander, P.G.; Lin, H.; Gottardi, R.; Cheng, A.W.; Tuan, R.S. Three-dimensional osteochondral microtissue to model pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2013, 4, S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aggarwal, B.B. Signalling pathways of the TNF superfamily: A double-edged sword. Nature reviews. Immunology 2003, 3, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buhrmann, C.; Shayan, P.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Shakibaei, M. Evidence that TNF-β (lymphotoxin α) can activate the inflammatory environment in human chondrocytes. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2013, 15, R202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beekhuizen, M.; Bastiaansen-Jenniskens, Y.M.; Koevoet, W.; Saris, D.B.; Dhert, W.J.; Creemers, L.B.; van Osch, G.J. Osteoarthritic synovial tissue inhibition of proteoglycan production in human osteoarthritic knee cartilage: Establishment and characterization of a long-term cartilage-synovium coculture. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 1918–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Target Gene | Primers | |
|---|---|---|
| 18S | Forward | GTAACCCGTTGAACCCCATT |
| Reversed | CCATCCAATCGGTAGTAGCG | |
| KDM5D | Forward | TAACACACACCCGTTTGACAA |
| Reversed | GCTGCTGAACTTTGAAGGCTG | |
| IL-1b | Forward | 5′-GCTGAGGAAGATGCTGGTTC-3′ |
| Reversed | 5′-TCCATATCCTGTCCCTGGAG-3′ | |
| COX2 | Forward | 5′-GCCCGACTCCCTTGGGTGTC-3′ |
| Reversed | 5′-TTGGTGAAAGCTGGCCCTCGC-3′ |
| Patient CD Markers | #1 | #2 | #3 | #4 | #5 | #6 | Cell Population |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD45−; CD90+; CD105+ | 32.90% | 44.40% | 73.70% | 36.00% | 59.90% | 28.30% | Mesenchymal stromal cell |
| CD31+; CD34+ | 55.70% | 57.50% | 88.00% | 17.00% | 10.90% | 8.20% | Endothelial cell |
| CD45+; CD34− | 3.10% | 0.70% | 0.90% | 5.80% | 1.40% | 8.60% | Leukocyte |
| CD34+/−; CD31−; CD146+ | 0.20% | 0.20% | 0.10% | 0.40% | 0.00% | 0.50% | Pericyte |
| CD45+; CD34+ | 0.50% | 0.00% | 1.00% | 0.00% | 0.10% | 0.30% | Hematopoietic stem cell-like cell |
| CD34bright; CD31−, CD146− | 20.30% | 12.50% | 2.90% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | Supra-adventitial cell |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
van Boxtel, J.; Vonk, L.A.; Stevens, H.P.; van Dongen, J.A. Mechanically Derived Tissue Stromal Vascular Fraction Acts Anti-inflammatory on TNF Alpha-Stimulated Chondrocytes In Vitro. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9080345
van Boxtel J, Vonk LA, Stevens HP, van Dongen JA. Mechanically Derived Tissue Stromal Vascular Fraction Acts Anti-inflammatory on TNF Alpha-Stimulated Chondrocytes In Vitro. Bioengineering. 2022; 9(8):345. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9080345
Chicago/Turabian Stylevan Boxtel, Joeri, Lucienne A. Vonk, Hieronymus P. Stevens, and Joris A. van Dongen. 2022. "Mechanically Derived Tissue Stromal Vascular Fraction Acts Anti-inflammatory on TNF Alpha-Stimulated Chondrocytes In Vitro" Bioengineering 9, no. 8: 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9080345
APA Stylevan Boxtel, J., Vonk, L. A., Stevens, H. P., & van Dongen, J. A. (2022). Mechanically Derived Tissue Stromal Vascular Fraction Acts Anti-inflammatory on TNF Alpha-Stimulated Chondrocytes In Vitro. Bioengineering, 9(8), 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9080345








