Isoliquiritigenin Nanoemulsion Preparation by Combined Sonication and Phase-Inversion Composition Method: In Vitro Anticancer Activities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
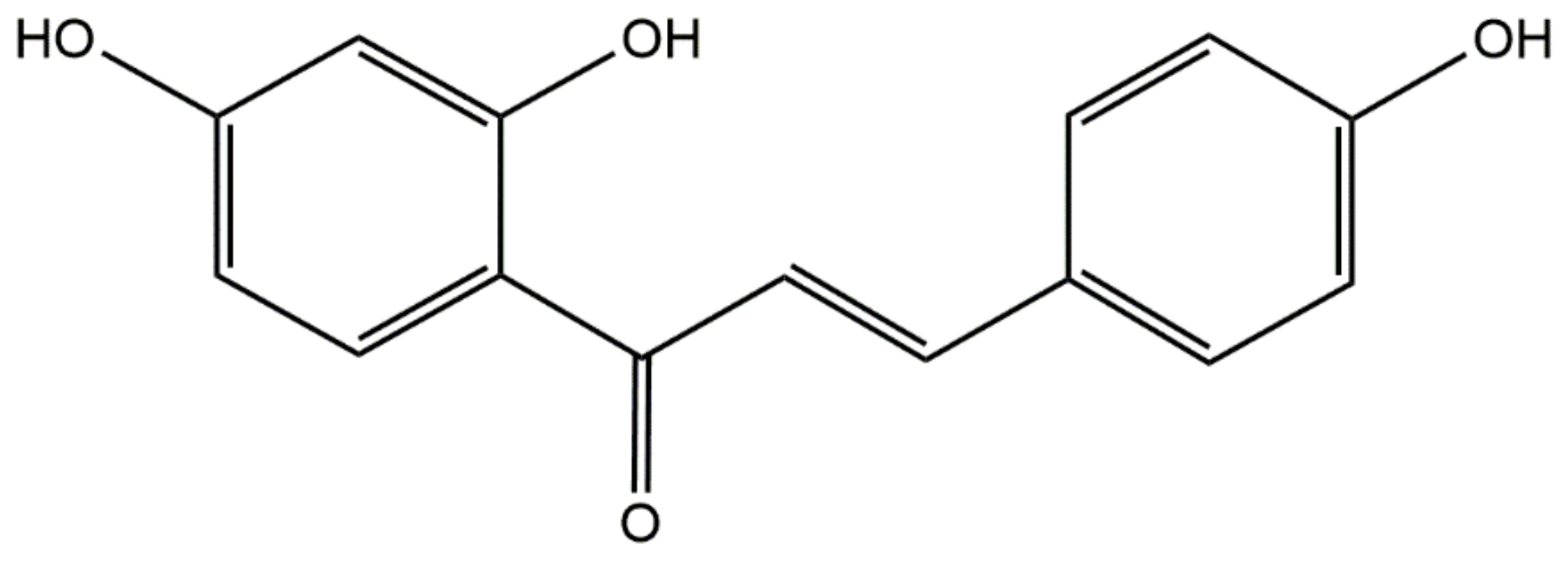
2.2. Solubility Studies
2.3. Optimization of Nanoemulsion Preparation Process
2.3.1. Stirring Speed
2.3.2. Bath Sonication Water Height
2.3.3. Bath Sonication Time
2.3.4. ILQ Concentration
2.4. The Optimized ILQ Nanoemulsion (ILQ-NE) Preparation
2.5. Droplet Size Measurements, Loading Capacity, UV-Visible Light Absorption Spectrum and Fluorescence Spectrum
2.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.7. Physical Stability of ILQ-NE
2.8. Chemical Stability of ILQ-NE
2.9. In Vitro Release Study
2.10. Cell Culture and Cytotoxicity Test
2.11. Cellular Uptake Test
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Solubility Studies
3.2. Optimization of ILQ-NE Preparation
3.2.1. Effect of Stirring Speed on the Appearance, Droplet Size and Storage Stability
3.2.2. Effect of Ultrasonic Depth on the Droplet Size, Appearance and Storage Stability
3.2.3. Effect of Sonication Time on the Droplet Size, Appearance and Storage Stability
3.2.4. Effect of ILQ Concentration on the Droplet Size, Appearance and Storage Stability
3.3. Physicochemical Properties of ILQ-NE
3.4. Physical Stability of ILQ-NE
3.4.1. Physical Stability of ILQ-NE in Physiological Environment
3.4.2. Physical Stability of ILQ-NE during Long-Term Storage at 4 °C
3.5. Chemical Stability of ILQ-NE
3.5.1. Chemical Stability of ILQ-NE in Comparison with Free ILQ
3.5.2. Chemical Stability of ILQ-NE during Long-Term Storage at 4 °C
3.6. Drug Release Profile In Vitro
3.7. Assessment of Cytotoxicity
3.8. Cellular Uptake Test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, K.L.; Yu, Y.C.; Hsia, S.M. Perspectives on the role of isoliquiritigenin in cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Tsai, H.Y.; Chen, C.L.; Chen, J.L.; Lu, C.C.; Fang, Y.P.; Wu, D.C.; Huang, Y.B.; Lin, M.W. Isoliquiritigenin inhibits gastric cancer stemness, modulates tumor microenvironment, and suppresses tumor growth through glucose-regulated protein 78 downregulation. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Zhan, M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.M.; Miao, M. Development of an orally bioavailable isoliquiritigenin self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system to effectively treat ovalbumin-induced asthma. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 8945–8961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Q.; Wang, J.; Cui, W.; Zhou, Y.; Xing, X.; Che, R.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Bello-Onaghise, G.; Dong, C.; et al. In vitro activity and in vivo efficacy of isoliquiritigenin against staphylococcus xylosus ATCC 700404 by IGPD target. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qiao, F.; Zhao, Y.; Mai, Y.; Guo, J.; Dong, L.; Zhang, W.; Yang, J. Isoliquiritigenin nanosuspension enhances cytostatic effects in A549 lung cancer cells. Planta Med. 2020, 86, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.J.; Wang, Q.L.; Adu-Frimpong, M.; Liu, J.; Zhang, K.Y.; Xu, X.M.; Yu, J.N. Preparation and evaluation of isoliquiritigenin-loaded F127/P123 polymeric micelles. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2019, 45, 1224–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Q.; Adu-Frimpong, M.; Wei, Q.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, K.; Wei, C.; Weng, W.; Ji, H.; Toreniyazov, E.; et al. Preparation, in vitro and in vivo evaluation of isoliquiritigenin-loaded TPGS modified proliposomes. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 563, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, G.Y.; Suh, J.Y.; Park, S.N. Ceramide-based nanostructured lipid carriers for transdermal delivery of isoliquiritigenin: Development, physicochemical characterization, and in vitro skin permeation studies. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 34, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Zhang, J.; Fu, C.; Xie, X.; Peng, F.; You, J.; Tang, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, P.; Chen, J. iRGD-modified lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles loaded with isoliquiritigenin to enhance anti-breast cancer effect and tumor-targeting ability. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 4147–4162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, B.; Zhu, S.; Zhu, L.; Peng, B. Licorice isoliquiritigenin-encapsulated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for osteoclast inhibition and bone loss prevention. Theranostics 2019, 9, 5183–5199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, L.; Zhang, J.; Geng, J.; Qu, J.; Liu, L. Development of a hydrogen peroxide-responsive and oxygen-carrying nanoemulsion for photodynamic therapy against hypoxic tumors using phase inversion composition method. J. Innov. Opt. Health Sci. 2021, 14, 2150003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, J.; McClements, D.J. Formation of flavor oil microemulsions, nanoemulsions and emulsions: Influence of composition and preparation method. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 5026–5035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiner, T.B.; Santamaria-Echart, A.; Ribeiro, A.; Peres, A.M.; Dias, M.M.; Pinho, S.P.; Barreiro, M.F. Formulation and optimization of nanoemulsions using the natural surfactant saponin from quillaja bark. Molecules 2020, 25, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mayer, S.; Weiss, J.; Mcclements, D.J. Vitamin E-enriched nanoemulsions formed by emulsion phase inversion: Factors influencing droplet size and stability. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 402, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawin-Mikołajewicz, A.; Nartowski, K.P.; Dyba, A.J.; Gołkowska, A.M.; Malec, K.; Karolewicz, B. Ophthalmic nanoemulsions: From composition to technological processes and quality control. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 3719–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.L.; Zhao, F.F.; Zhang, J.Y.; Yu, L.; Zhang, G.J.; Liu, C.Y.; Wang, N.; Xu, B.C. Development of polyglycerol fatty acid ester-based low-energy nanoemulsion for the improvement of curcumin stability. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2022, 43, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Guan, X.; Zheng, C.; Wang, N.; Lu, H.; Huang, Z. New low-energy method for nanoemulsion formation: pH regulation based on fatty acid/amine complexes. Langmuir 2020, 36, 10082–10090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; McClements, D.J. Development of microfluidization methods for efficient production of concentrated nanoemulsions: Comparison of single- and dual-channel microfluidizers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 466, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.M.; He, Y.; Bhandari, B. Optimization of nano-emulsions production by microfluidization. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2007, 225, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadinezhad, S.; Khodaiyan, F.; Salami, M.; Hosseini, H.; Ghanbarzadeh, B. Effect of different parameters on orange oil nanoemulsion particle size: Combination of low energy and high energy methods. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2019, 13, 2501–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, Q.-H.; Thuy, T.T.-H.; Nguyen, T.T.-T. Fabrication of a narrow size nano curcuminoid emulsion by combining phase inversion temperature and ultrasonication: Preparation and bioactivity. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 9658–9667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, K.; Kumar, R.; Mehta, S.K. Nanoemulsion: A new medium to study the interactions and stability of curcumin with bovine serum albumin. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 209, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Yang, J.; Luo, Q.; Shi, J.; Xu, H.; Zhang, J. Preparation and in vitro and in vivo evaluation of an isoliquiritigenin-loaded ophthalmic nanoemulsion for the treatment of corneal neovascularization. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 2217–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saberi, A.H.; Fang, Y.; McClements, D.J. Fabrication of vitamin E-enriched nanoemulsions: Factors affecting particle size using spontaneous emulsification. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 391, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinsuebpol, C.; Changsan, N. Effects of ultrasonic operating parameters and emulsifier system on sacha inchi oil nanoemulsion characteristics. J. Oleo Sci. 2020, 69, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, L.; Zhou, C.L.; Chen, F.P.; Han, D.; Wang, C.Y.; Li, J.X.; Chi, Z.; Liu, C.G. Development of a carboxymethyl chitosan functionalized nanoemulsion formulation for increasing aqueous solubility, stability and skin permeability of astaxanthin using low-energy method. J. Microencapsul. 2017, 34, 707–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcclements, D.J. Emulsion design to improve the delivery of functional lipophilic components. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 1, 241–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollipara, S.; Gandhi, R.K. Pharmacokinetic aspects and in vitro-in vivo correlation potential for lipid-based formulations. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2014, 4, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, P.; Arora, K.; Gu, Y.G.; Kumar, V.; Mishra, I.M. Formation and stability of water-in-oil nano-emulsions with mixed surfactant using in situ combined condensation-dispersion method. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 97, 2039–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Qian, X.; Zhao, L.; Xu, J. A fluorescent responsive tetraphenylethene based metal–organic framework. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2019, 105, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.O.; Misran, M.; Lee, P.F.; Tan, L.P. Development of a controlled release of salicylic acid loaded stearic acid-oleic acid nanoparticles in cream for topical delivery. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 205703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piorkowski, D.T.; McClements, D.J. Beverage emulsions: Recent developments in formulation, production, and applications. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 42, 5–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.X.; Wang, L.; Liu, M.Q.; Ren, X.L.; Han, T.T.; Deng, Y.R. Study on solubilization and stabilization of eight flavonoids by 17 Chinese herbal polysaccharides. J. Chem. 2020, 2020, 6235284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, S.; Umar Aslam Khan, M.; Shamsan Al-Arjan, W.; Izwan Abd Razak, S.; Javed, A.; Rafiq Abdul Kadir, M. Nanocomposite hydrogels for melanoma skin cancer care and treatment: In vitro drug delivery, drug release kinetics and anti-cancer activities. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.U.A.; Abd Razak, S.I.; Haider, S.; Mannan, H.A.; Hussain, J.; Hasan, A. Sodium alginate-f-GO composite hydrogels for tissue regeneration and antitumor applications. Int J. Biol Macromol. 2022, 208, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.F.; Zhang, D.R.; Tian, K.L.; Lou, H.Y.; Qi, X.L.; Wang, Y.C.; Duan, C.X.; Jia, L.J.; Wang, F.H.; Liu, Y.; et al. Growth inhibition and induction of apoptosis in MCF-7 breast cancer cells by oridonin nanosuspension. Drug Deliv. 2011, 18, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]















| Excipients | Solubility (mg g−1) | Excipients | Solubility (mg g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Peanut oil Canola oil | 103.89 ± 0.0032 113.55 ± 0.0044 | Tween 85 Tween 80 | 445.33 ± 0.0068 447.72 ± 0.0019 |
| Corn oil Soybean oil | 113.98 ± 0.0031 147.12 ± 0.0044 | Tween 40 Tween 60 | 568.85 ± 0.0086 573.49 ± 0.0054 |
| Labrafil® M 1944 CS | 703.32 ± 0.0164 | Cremophor® EL | 664.33 ± 0.0065 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Guo, T.; Yue, P.; Qian, T.; Zeng, X.; Luo, Y.; Li, J.; Teng, L.; Liu, Q.; et al. Isoliquiritigenin Nanoemulsion Preparation by Combined Sonication and Phase-Inversion Composition Method: In Vitro Anticancer Activities. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9080382
Wang J, Chen H, Guo T, Yue P, Qian T, Zeng X, Luo Y, Li J, Teng L, Liu Q, et al. Isoliquiritigenin Nanoemulsion Preparation by Combined Sonication and Phase-Inversion Composition Method: In Vitro Anticancer Activities. Bioengineering. 2022; 9(8):382. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9080382
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jianman, Hongjin Chen, Tao Guo, Ping Yue, Tianbao Qian, Xiangyu Zeng, Yali Luo, Jiangmin Li, Lijing Teng, Qingyu Liu, and et al. 2022. "Isoliquiritigenin Nanoemulsion Preparation by Combined Sonication and Phase-Inversion Composition Method: In Vitro Anticancer Activities" Bioengineering 9, no. 8: 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9080382
APA StyleWang, J., Chen, H., Guo, T., Yue, P., Qian, T., Zeng, X., Luo, Y., Li, J., Teng, L., Liu, Q., Hong, L., Yu, Z., & Hu, Z. (2022). Isoliquiritigenin Nanoemulsion Preparation by Combined Sonication and Phase-Inversion Composition Method: In Vitro Anticancer Activities. Bioengineering, 9(8), 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9080382








