Comprehensive Characterization (Chromatography, Spectroscopy, Isotopic, and Digital Color Image) of Tequila 100% Agave Cristalino as Evidence of the Preservation of the Characteristics of Its Aging Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Physicochemical Characterization
2.2.1. Gas and Liquid Chromatography
2.2.2. Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry (IRMS)
2.2.3. Image Analysis by Artificial Vision
2.2.4. UV-Vis Spectroscopy
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
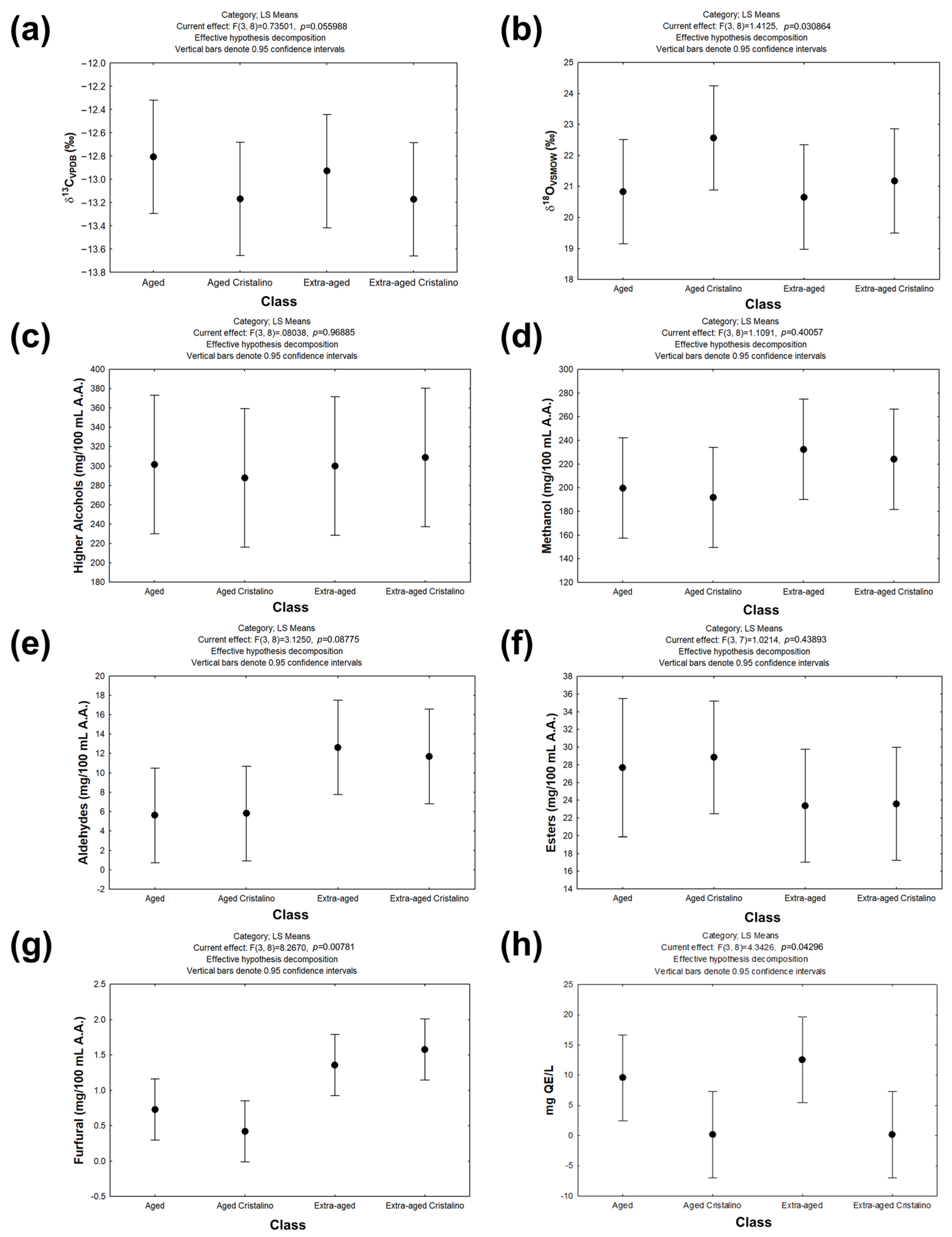
3.1. Comparison of the Chromatographic and Isotopic Profiles of the Beverage
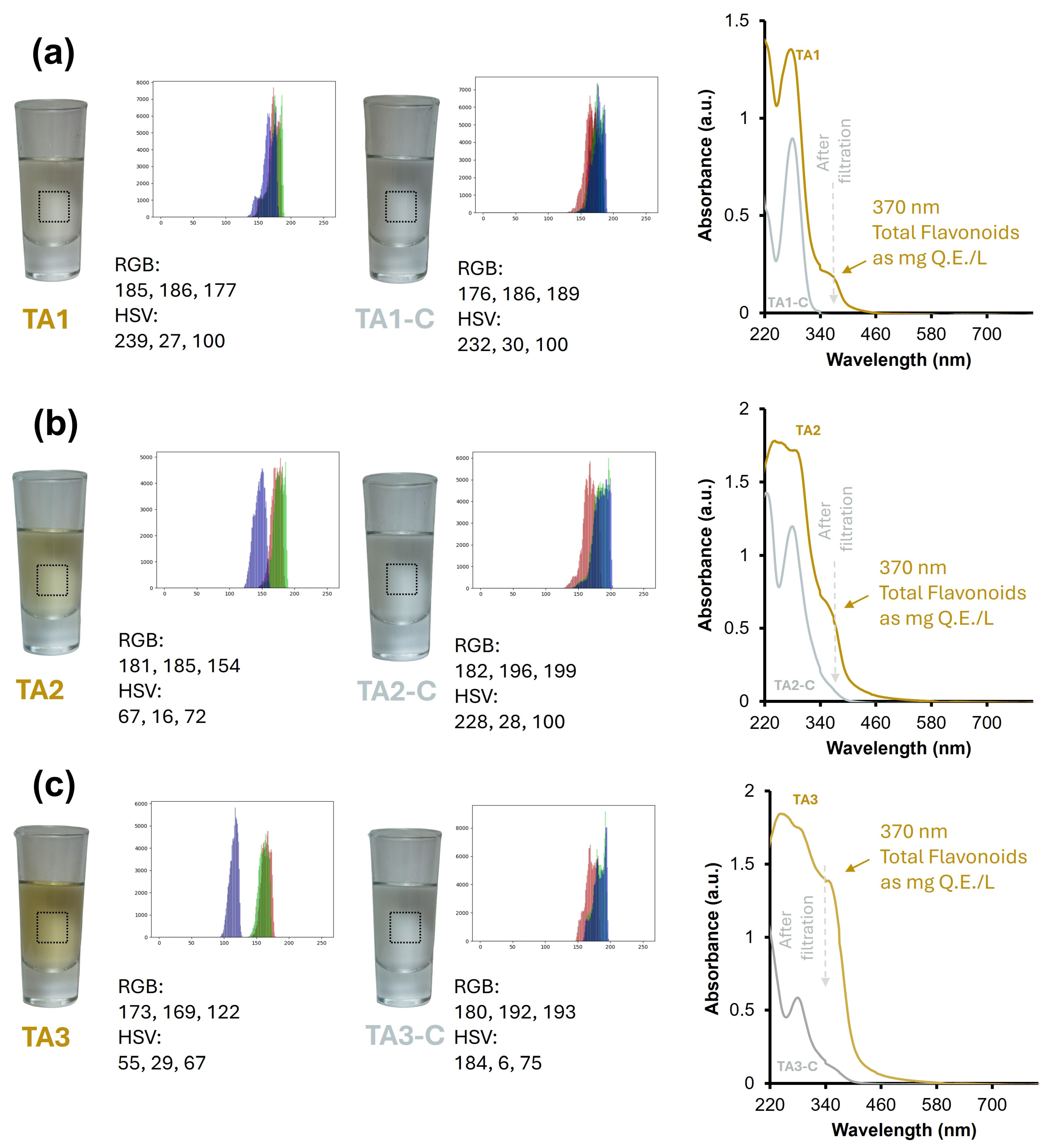
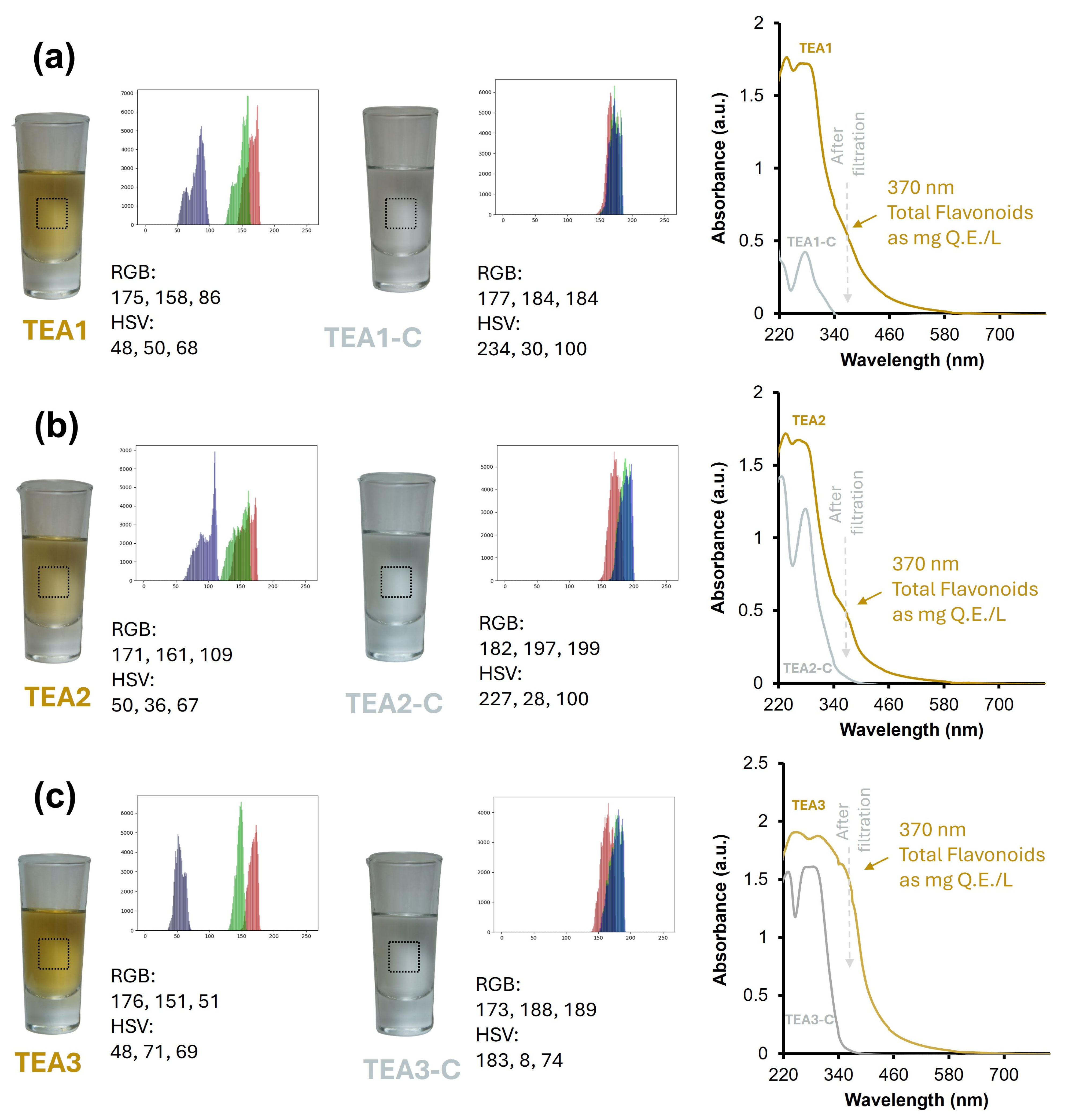
3.2. Color Perception Comparison: Tequila 100% Agave Aged vs. Tequila 100% Agave Cristalino Using Artificial Vision and UV-Vis Spectroscopy
3.3. Integrated Comparison of Chromatographic, Spectroscopic, and Isotopic Characteristics of Aged and Extra-Aged Tequilas 100% Agave and Their Corresponding Cristalino Versions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Terán-Bustamante, A.; Martínez-Velasco, A.; Castillo-Girón, V.M.; Ayala-Ramírez, S. Innovation and Technological Management Model in the Tequila Sector in Mexico. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benn, S.M.; Peppard, T.L. Characterization of Tequila Flavor by Instrumental and Sensory Analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, M.G. Tequila Aroma. In Flavor Chemistry of Ethnic Foods; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1999; pp. 211–217. [Google Scholar]
- Vallejo-Cordoba, B.; González-Córdova, A.F.; del Carmen Estrada-Montoya, M. Tequila Volatile Characterization and Ethyl Ester Determination by Solid Phase Microextraction Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry Analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 5567–5571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachenmeier, D.W.; Sohnius, E.-M.; Attig, R.; López, M.G. Quantification of Selected Volatile Constituents and Anions in Mexican Agave Spirits (Tequila, Mezcal, Sotol, Bacanora). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 3911–3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Muñoz, A.C.; Grenier, A.C.; Gutiérrez-Pulido, H.; Cervantes-Martínez, J. Development and Validation of a High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Diode Array Detection Method for the Determination of Aging Markers in Tequila. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1213, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De León Rodríguez, A.; Escalante Minakata, M.D.P.; Jiménez García, M.I.; Ordoñez Acevedo, L.G.; Flores Flores, J.L.; Barba de la Rosa, A.P. Characterization of Volatile Compounds from Ethnic Agave Alcoholic Beverages by Gas Chromatographymass Spectrometry. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2008, 46, 448–455. [Google Scholar]
- Cardeal, Z.L.; Marriott, P.J. Comprehensive Two-Dimensional Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Analysis and Comparison of Volatile Organic Compounds in Brazilian Cachaça and Selected Spirits. Food Chem. 2009, 112, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceballos-Magaña, S.G.; de Pablos, F.; Jurado, J.M.; Martín, M.J.; Alcázar, Á.; Muñiz-Valencia, R.; Gonzalo-Lumbreras, R.; Izquierdo-Hornillos, R. Characterisation of Tequila According to Their Major Volatile Composition Using Multilayer Perceptron Neural Networks. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magana, A.A.; Wrobel, K.; Elguera, J.C.T.; Escobosa, A.R.C.; Wrobel, K. Determination of Small Phenolic Compounds in Tequila by Liquid Chromatography with Ion Trap Mass Spectrometry Detection. Food Anal. Methods 2015, 8, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yin, Z.; Zhao, D.; Sun, B.; Zheng, F. Qualitative and Quantitative Research of Propyl Lactate in Brewed Alcoholic Beverages. Int. J. Food Prop. 2018, 21, 1351–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejia Diaz, L.F.; Wrobel, K.; Corrales Escobosa, A.R.; Aguilera Ojeda, D.A.; Wrobel, K. Identification of Potential Indicators of Time-Dependent Tequila Maturation and Their Determination by Selected Ion Monitoring Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry, Using Salting-out Liquid–Liquid Extraction. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charapitsa, S.; Sytova, S.; Kavalenka, A.; Sobolenko, L.; Kostyuk, N.; Egorov, V.; Leschev, S.; Vetokhin, S.; Zayats, N. The Study of the Matrix Effect on the Method of Direct Determination of Volatile Compounds in a Wide Range of Alcoholic Beverages. Food Control 2021, 120, 107528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charapitsa, S.; Sytova, S.; Kavalenka, A.; Sabalenka, L.; Zayats, M.; Egorov, V.; Leschev, S.; Melsitova, I.; Vetokhin, S.; Zayats, N. Intelligent Use of Ethanol for the Direct Quantitative Determination of Methanol in Alcoholic Beverages. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 114, 104772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejia Diaz, L.F.; Wrobel, K.; Corrales Escobosa, A.R.; Yanez Barrientos, E.; Serrano Torres, O.; Wrobel, K. Characterization of Tequila by High Performance Liquid Chromatography—High Resolution Mass Spectrometry (HPLC-HRMS) and Partial Least Squares Regression (PLS). Anal. Lett. 2023, 56, 1701–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Cisneros, B.O.; López, M.G.; Richling, E.; Heckel, F.; Schreier, P. Tequila Authenticity Assessment by Headspace SPME-HRGC-IRMS Analysis of 13C/12C and 18O/16O Ratios of Ethanol. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 7520–7523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer-Christoph, C.; Christoph, N.; Aguilar-Cisneros, B.O.; Lopez, M.G.; Richling, E.; Rossmann, A.; Schreier, P. Authentication of Tequila by Gas Chromatography and Stable Isotope Ratio Analyses. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2003, 217, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, F.; Randet, C.; Gilbert, A.; Silvestre, V.; Jamin, E.; Akoka, S.; Remaud, G.; Segebarth, N.; Guillou, C. Improved Characterization of the Botanical Origin of Sugar by Carbon-13 SNIF-NMR Applied to Ethanol. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 11580–11585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kächele, M.; Monakhova, Y.B.; Kuballa, T.; Lachenmeier, D.W. NMR Investigation of Acrolein Stability in Hydroalcoholic Solution as a Foundation for the Valid HS-SPME/GC–MS Quantification of the Unsaturated Aldehyde in Beverages. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 820, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca-Aguiñaga, R.; Gómez-Ruiz, H.; Miguel-Cruz, F.; Romero-Cano, L.A. Analytical Characterization of Tequila (Silver Class) Using Stable Isotope Analyses of C, O and Atomic Absorption as Additional Criteria to Determine Authenticity of Beverage. Food Control 2020, 112, 107161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portaluri, V.; Thomas, F.; Jamin, E.; Akoka, S.; Remaud, G.S. Authentication of Agave Products through Isotopic Intramolecular 13C Content of Ethanol: Optimization and Validation of 13C Quantitative NMR Methodology. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 1, 1316–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren-Vega, W.M.; Fonseca-Aguiñaga, R.; González-Gutiérrez, L.V.; Carrasco-Marín, F.; Zárate-Guzmán, A.I.; Romero-Cano, L.A. Chemical Characterization of Tequila Maturation Process and Their Connection with the Physicochemical Properties of the Cask. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 98, 103804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca-Aguiñaga, R.; Warren-Vega, W.M.; Miguel-Cruz, F.; Romero-Cano, L.A. Isotopic Characterization of 100% Agave Tequila (Silver, Aged and Extra-Aged Class) for Its Use as an Additional Parameter in the Determination of the Authenticity of the Beverage Maturation Time. Molecules 2021, 26, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta-Salazar, E.; Fonseca-Aguinaga, R.; Warren-Vega, W.M.; Ana, I.Z. Effect of Age of Agave Tequilana Weber Blue Variety on Quality and Authenticity Parameters for the Tequila 100% Agave Silver Class: Evaluation at the Industrial Scale Level. Food 2021, 10, 3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca-Aguiñaga, R.; Warren-Vega, W.M.; Muñoz-Sánchez, M.; Romero-Cano, L.A. Isotopic Differences between Tequila and Tequila 100% Agave Silver Class: Effect of Sugar Enrichment on the Δ13CVPDB on the Beverage Congeners. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 129, 106134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachenmeier, D.W.; Richling, E.; López, M.G.; Frank, W.; Schreier, P. Multivariate Analysis of FTIR and Ion Chromatographic Data for the Quality Control of Tequila. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 2151–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frausto-Reyes, C.; Medina-Gutiérrez, C.; Sato-Berrú, R.; Sahagún, L.R. Qualitative Study of Ethanol Content in Tequilas by Raman Spectroscopy and Principal Component Analysis. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2005, 61, 2657–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, C.R.; Figueroa, J.A.L.; Wrobel, K.; Wrobel, K. ICP-MS Multi-Element Profiles and HPLC Determination of Furanic Compounds in Commercial Tequila. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2009, 228, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceballos-Magaña, S.G.; Jurado, J.M.; Martín, M.J.; Pablos, F. Quantitation of Twelve Metals in Tequila and Mezcal Spirits as Authenticity Parameters. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 1372–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Muñoz, A.C.; Pichardo-Molina, J.L.; Ramos-Ortíz, G.; Barbosa-García, O.; Maldonado, J.L.; Meneses-Nava, M.A.; Ornelas-Soto, N.E.; Escobedo, A.; López-de-Alba, P.L. Identification and Quantification of Furanic Compounds in Tequila and Mezcal Using Spectroscopy and Chemometric Methods. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2010, 21, 1077–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, U.; Barbosa-García, O.; Pichardo-Molina, J.L.; Ramos-Ortíz, G.; Maldonado, J.L.; Meneses-Nava, M.A.; Ornelas-Soto, N.E.; López-de-Alba, P.L. Screening Method for Identification of Adulterate and Fake Tequilas by Using UV–VIS Spectroscopy and Chemometrics. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 2356–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Rosa Vázquez, J.M.; Fabila-Bustos, D.A.; Quintanar-Hernández, L.F.d.J.; Valor, A.; Stolik, S. Detection of Counterfeit Tequila by Fluorescence Spectroscopy. J. Spectrosc. 2015, 2015, 403160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Caballero, G.; Andrade, J.M.; Olmos, P.; Molina, Y.; Jiménez, I.; Durán, J.J.; Fernandez-Lozano, C.; Miguel-Cruz, F. Authentication of Tequilas Using Pattern Recognition and Supervised Classification. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 94, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, J.M.; Ballabio, D.; Gómez-Carracedo, M.P.; Pérez-Caballero, G. Nonlinear Classification of Commercial Mexican Tequilas. J. Chemom. 2017, 31, e2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.M.; Wrobel, K.; Barrientos, E.Y.; Escobosa, A.R.C.; Serrano, O.; Donis, I.E.; Wrobel, K. Determination of Copper and Lead in Tequila by Conventional Matrix-assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-flight Mass Spectrometry and Partial Least Squares Regression. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2018, 32, 2174–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Vega, L.I.; Belio-Manzano, A.; Mercado-Ornelas, C.A.; Cortes-Mestizo, I.E.; Mendez-Garcia, V.H. Aging Spectral Markers of Tequila Observed by Raman Spectroscopy. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, Y.; Shao, F.; Lu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Xu, X. Geographical Origin Identification of Tequila Based on Multielement and Stable Isotopes. J. Food Qual. 2021, 2021, 6615264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Beltrán, C.H.; Pérez–Caballero, G.; Andrade, J.M.; Cuadros-Rodríguez, L.; Jiménez-Carvelo, A.M. Non-Targeted Spatially Offset Raman Spectroscopy-Based Vanguard Analytical Method to Authenticate Spirits: White Tequilas as a Case Study. Microchem. J. 2022, 183, 108126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Hernández, P.A.; Gómez-Navarro, C.S.; Warren-Vega, W.M.; Gutiérrez, L.V.G.; Zárate-Guzmán, A.I.; Romero-Cano, L.A. Comprehension of the Adsorption Mechanism in the Selective Color Removal of Extra-Aged Tequila to Produce Cristalino Tequila Using Tailored Carbon Materials. Food Chem. Adv. 2023, 2, 100174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreon-Alvarez, A.; Casillas, N.; Ibanez, J.G.; Hernandez, F.; Prado-Ramírez, R.; Barcena-Soto, M.; Go’mez-Salazar, S. Determination of Cu in Tequila by Anodic Stripping Voltammetry. Anal. Lett. 2008, 41, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna-Moreno, D.; Monzón-Hernández, D.; Noé-Arias, E.; Regalado, L.E. Determination of Quality and Adulteration of Tequila through the Use of Surface Plasmon Resonance. Appl. Opt. 2012, 51, 5161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Pérez, A.; Pérez-Castañeda, J.I.; Castañeda-Guzmán, R.; Pérez-Ruiz, S.J. Determination of Tequila Quality by Photoacoustic Analysis. Int. J. Thermophys. 2013, 34, 1695–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, P.R.; Lamy-Mendes, A.C.; Rezende, E.I.P.; Mangrich, A.S.; Marcolino, L.H., Jr.; Bergamini, M.F. Electrochemical Determination of Copper Ions in Spirit Drinks Using Carbon Paste Electrode Modified with Biochar. Food Chem. 2015, 171, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carreon-Alvarez, A.; Suárez-Gómez, A.; Zurita, F.; Gómez-Salazar, S.; Soltero, J.F.A.; Barcena-Soto, M.; Casillas, N.; Porfirio-Gutierrez; Moreno-Medrano, E.D. Assessment of Physicochemical Properties of Tequila Brands: Authentication and Quality. J. Chem. 2016, 2016, 6254942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataria, T.K.; Sosa-Morales, M.E.; Olvera-Cervantes, J.L.; Corona-Chavez, A. Dielectric Properties of Tequila in the Microwave Frequency Range (0.5–20 GHz) Using Coaxial Probe. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, S377–S384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acuña-Avila, P.; Calavia, R.; Vigueras-Santiago, E.; Llobet, E. Identification of Tequila with an Array of ZnO Thin Films: A Simple and Cost-Effective Method. Sensors 2017, 17, 2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Pérez, R.; Sevilla, J.M.; Pineda, T.; Blázquez, M.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, J. Electrocatalytic Performance Enhanced of the Electrooxidation of Gamma-Hydroxybutyric Acid (GHB) and Ethanol on Platinum Nanoparticles Surface. A Contribution to the Analytical Determination of GHB in the Presence of Ethanol. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 256, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Necochea-Chamorro, J.I.; Carrillo-Torres, R.C.; Sánchez-Zeferino, R.; Álvarez-Ramos, M.E. Fiber Optic Sensor Using ZnO for Detection of Adulterated Tequila with Methanol. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2019, 52, 101982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado-Arriola, J.A.; Sánchez-Zeferino, R.; Álvarez-Ramos, M.E. Photoluminescent Properties of ZnO Nanorods Films Used to Detect Methanol Contamination in Tequila. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 312, 112142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, M.D.O.K.; Castro, G.A.D.; Vilanculo, C.; Fernandes, S.A.; Suarez, W.T. A Color Reaction for the Determination of Cu2+ in Distilled Beverages Employing Digital Imaging. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1177, 338844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, A.; Bueno, D.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Electronic Eye Based on RGB Analysis for the Identification of Tequilas. Biosensors 2021, 11, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren-Vega, W.M.; Fonseca-Aguiñaga, R.; González-Gutiérrez, L.V.; Romero-Cano, L.A. Use of Electrochemical Color Index as Emerging Analytical Method for Evaluating the Quality of Tequila 100% Agave. Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 103300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes-Peña, K.D.; Fonseca-Aguiñaga, R.; Warren-Vega, W.M.; Romero-Cano, L.A. Decoding of the Isotopic Fingerprint of Tequila 100% Agave Silver Class and Image Analysis to Evaluate Differences between Spirits. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez, A.; Bueno, D.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Electronic Eye for Identification of Tequila Samples. In Proceedings of the 1st International Electronic Conference on Biosensors, Basel, Switzerland, 2 November 2020; p. 44. [Google Scholar]
- Heil, J.; Marschner, B.; Stumpe, B. Digital Photography as a Tool for Microscale Mapping of Soil Organic Carbon and Iron Oxides. Catena 2020, 193, 104610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granados-Vega, B.V.; Maldonado-Flores, C.; Gómez-Navarro, C.S.; Warren-Vega, W.M.; Campos-Rodríguez, A.; Romero-Cano, L.A. Development of a Low-Cost Artificial Vision System as an Alternative for the Automatic Classification of Persian Lemon: Prototype Test Simulation. Foods 2023, 12, 3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortoletto, A.M.; Alcarde, A.R. Congeners in Sugar Cane Spirits Aged in Casks of Different Woods. Food Chem. 2013, 139, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Ramírez, J.E.; Martín-del-Campo, S.T.; Escalona-Buendía, H.; García-Fajardo, J.A.; Estarrón-Espinosa, M. Physicochemical Quality of Tequila during Barrel Maturation. A Preliminary Study. CyTA J. Food 2013, 11, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Heras, M.; González-Sanjosé, M.L.; González-Huerta, C. Consideration of the Influence of Aging Process, Type of Wine and Oenological Classic Parameters on the Levels of Wood Volatile Compounds Present in Red Wines. Food Chem. 2007, 103, 1434–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren-Vega, W.M.; Contreras-Atrisco, Z.A.; Ramírez-Quezada, M.F.; Romero-Cano, L.A. A Novel Approach of Artificial Intelligence for the Study of the Relation of Physicochemical Profile and Color Acquired by Tequila 100% Agave in Its Maturation Process. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 123, 105533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glories, Y. La Couleur Des Vins Rouges. 2a. Partie Mesure, Origine et Interpretarion. J. Int. Sci. Vigne Vin. 1984, 18, 253–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora, F. Elaboración y Crianza Del Vino Tinto: Aspectos Científicos y Prácticos, 1st ed.; Mundiprensa: Madrid, Spain, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Andrés-Lacueva, C.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M.; Buxaderas, S.; De La Torre-Boronat, M.D.C. Influence of Variety and Aging on Foaming Properties of Cava (Sparkling Wine). 2. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 2520–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto-Delgado, C.; Terrones, M.; Rangel-Mendez, J.R. Development of Highly Microporous Activated Carbon from the Alcoholic Beverage Industry Organic By-Products. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Méndez, O.; López-Álvarez, J.A.; Díaz-Pérez, A.L.; Altamirano, J.; Reyes De la Cruz, H.; Rutiaga-Quiñones, J.G.; Campos-García, J. Volatile Compound Profile Conferred to Tequila Beverage by Maturation in Recycled and Regenerated White Oak Barrels from Quercus Alba. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2017, 243, 2073–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, C.M.; Berry, D.R. Effect of Temperature and PH on the Formation of Higher Alcohols, Fatty Acids and Esters in the Malt Whisky Fermentation. Food Microbiol. 1984, 1, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Cadwallader, K.R. Chapter: A Critical Review of the Flavor Chemistry of Tequila. In Chemistry of Alcoholic Beverages; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2023; pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar]

| Year | Analytical Technique | Matrix | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1996 | GC-SCD, GC-FID, GC-MS | T100% silver class (SC) | [2] |
| 1999 | GC-MS | T100% (SC, AC, EC) | [3] |
| 2004 | SPME, GC-MS | T100% (SC, AC, EC) | [4] |
| 2006 | GC, IC | T, T100% (SC) | [5] |
| 2008 | HPLC-DAD | T, T100%, (SC, AC, EC) | [6] |
| 2008 | HS-SPME-GC-MS | T (SC) | [7] |
| 2009 | GCxGC/TOFMS | T (SC) | [8] |
| 2013 | HS-SPME-GC-MS, HPLC-DAD | T100% (SC, AC, EC) | [9] |
| 2015 | HPLC-ESI-ITMS | T100% (SC, AC, EC) | [10] |
| 2018 | SPME, LLE, GC-MS | T (SC) | [11] |
| 2019 | GC-MS-SIM | T (SC, AC, EC, UC) | [12] |
| 2021 | GC-FID | T | [13] |
| 2022 | GC-FID | T | [14] |
| 2022 | HPLC-HRMS | T (SC, AC, EC, UC) | [15] |
| Year | Analytical Technique | Matrix | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2002 | SPME-HRGC-IRMS | T, T100% (SC) | [16] |
| 2003 | GC-IRMS | T, T100% (SC) | [17] |
| 2010 | SNIF-NMR | T100% (SC) | [18] |
| 2014 | HS-SPME/GC-MS | T, T100% (SC) | [19] |
| 2020 | GC-IRMS | T, T100% (SC) | [20] |
| 2021 | SNIF-NMR | T (SC) | [21] |
| 2021 | GC-IRMS | T100% (SC, AC, EC) | [22] |
| 2021 | GC-IRMS | T100% (SC, AC, EC) | [23] |
| 2021 | GC-IRMS | T100% (SC) | [24] |
| 2024 | GC-IRMS | T, T100% (SC) | [25] |
| Year | Analytical Technique | Matrix | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2005 | FTIR | T100%, T (SC) | [26] |
| 2005 | Raman | T (SC, AC) | [27] |
| 2009 | ICP-MS | T, T100% (SC, AC, EC) | [28] |
| 2009 | ICP-OES | T100% (SC, AC, EC) | [29] |
| 2010 | UV-Vis | T, T100% (SC) | [30] |
| 2010 | UV-Vis | T, T100% (SC, AC) | [31] |
| 2015 | XRF | T, T100% (SC, AC, EC) | [32] |
| 2017 | UV-Vis | T (SC, AC, EC, UC) | [33] |
| 2017 | UV-Vis | T (SC, AC, EC, UC) | [34] |
| 2018 | MALDI-TOFMS & ICP-MS | T (SC, AC, EC, UC) | [35] |
| 2019 | Raman | T100% (SC, AC, EC) | [36] |
| 2021 | ICP-MS & IRMS | T (SC) | [37] |
| 2022 | SORS | T, T100% (SC) | [38] |
| 2023 | UV-Vis | T100% (EC, SC) | [39] |
| Year | Analytical Technique | Matrix | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2008 | Anodic stripping voltammetry | T (100%) | [40] |
| 2012 | Surface plasmon resonance | T (SC, AC, EC) | [41] |
| 2013 | Pulsed laser photoacoustic | T, T100% (SC, AC) | [42] |
| 2015 | Differential pulse adsorptive stripping voltammetry | T (SC) | [43] |
| 2016 | Physicochemical properties | T (SC, AC, EC) | [44] |
| 2017 | Open-ended coaxial probe | T100% (SC) | [45] |
| 2017 | ZnO thin films sensor | T (AC) | [46] |
| 2018 | Cyclic voltammetry | T (SC) | [47] |
| 2019 | Fiber optic sensor | T (SC) | [48] |
| 2020 | ZnO Nanorods films | T (AC) | [49] |
| 2021 | Digital image analysis | T (SC) | [50] |
| 2021 | Electronic eye | T100% (SC, AC, EC) | [51] |
| 2023 | Differential pulse voltammetry | T100% (SC, AC, EC, UC) | [52] |
| 2024 | Image analysis | T100% (SC) | [53] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Warren-Vega, W.M.; Fonseca-Aguiñaga, R.; Villa-González, A.; Gómez-Navarro, C.S.; Romero-Cano, L.A. Comprehensive Characterization (Chromatography, Spectroscopy, Isotopic, and Digital Color Image) of Tequila 100% Agave Cristalino as Evidence of the Preservation of the Characteristics of Its Aging Process. Beverages 2025, 11, 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages11020042
Warren-Vega WM, Fonseca-Aguiñaga R, Villa-González A, Gómez-Navarro CS, Romero-Cano LA. Comprehensive Characterization (Chromatography, Spectroscopy, Isotopic, and Digital Color Image) of Tequila 100% Agave Cristalino as Evidence of the Preservation of the Characteristics of Its Aging Process. Beverages. 2025; 11(2):42. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages11020042
Chicago/Turabian StyleWarren-Vega, Walter M., Rocío Fonseca-Aguiñaga, Arantza Villa-González, Camila S. Gómez-Navarro, and Luis A. Romero-Cano. 2025. "Comprehensive Characterization (Chromatography, Spectroscopy, Isotopic, and Digital Color Image) of Tequila 100% Agave Cristalino as Evidence of the Preservation of the Characteristics of Its Aging Process" Beverages 11, no. 2: 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages11020042
APA StyleWarren-Vega, W. M., Fonseca-Aguiñaga, R., Villa-González, A., Gómez-Navarro, C. S., & Romero-Cano, L. A. (2025). Comprehensive Characterization (Chromatography, Spectroscopy, Isotopic, and Digital Color Image) of Tequila 100% Agave Cristalino as Evidence of the Preservation of the Characteristics of Its Aging Process. Beverages, 11(2), 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages11020042








