- Article
Study of Possible Alternatives to Sulphur Dioxide for Inhibiting Tyrosinase and Protecting Grape Must from Browning
- Aitor García-Roldán,
- Antoni Canalda-Sabaté and
- Joan Miquel Canals
- + 6 authors
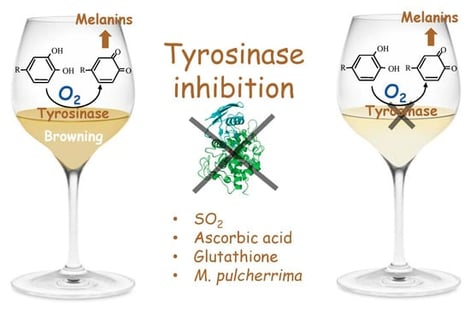
Winemakers have to deal with enzymatic browning caused by a grape polyphenol oxidase called tyrosinase. Due to the problems related to sulphur dioxide and its use in winemaking, oenologists need alternative and effective treatments for inhibiting enzymatic browning. This research studies ascorbic acid, glutathione (pure and in the form of a specific inactivated dry yeast rich in glutathione), and bioprotection by a selected strain of Metschnikowia pulcherrima as alternatives to SO2 for preventing enzymatic browning, following a methodology developed in previous works. All the studied treatments resulted in a significant reduction in enzymatic browning. More specifically, all treatments significantly reduced the Vmax of the apparent tyrosinase activity, indicating their potential to protect against enzymatic browning and thus allowing for a reduction in the doses of SO2 added to the wine.
6 February 2026