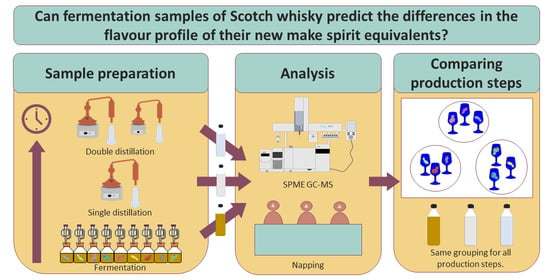
From Fermented Wash to New Make Spirit: Assessing the Evolution of Flavour Characteristics of Scotch Whisky Using Lab-Scale Process Simulations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Yeast
2.2. Wash Production
2.3. Low Wines and New Make Spirit Production
2.4. Sensory Analysis: Napping
2.4.1. Sensory Panel
2.4.2. Sample Preparation and Presentation
2.4.3. Napping
2.4.4. Data Analysis
2.5. Congener Analysis: GC–MS SPME Arrow
2.5.1. Instrumental Conditions
2.5.2. Data Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results & Discussion
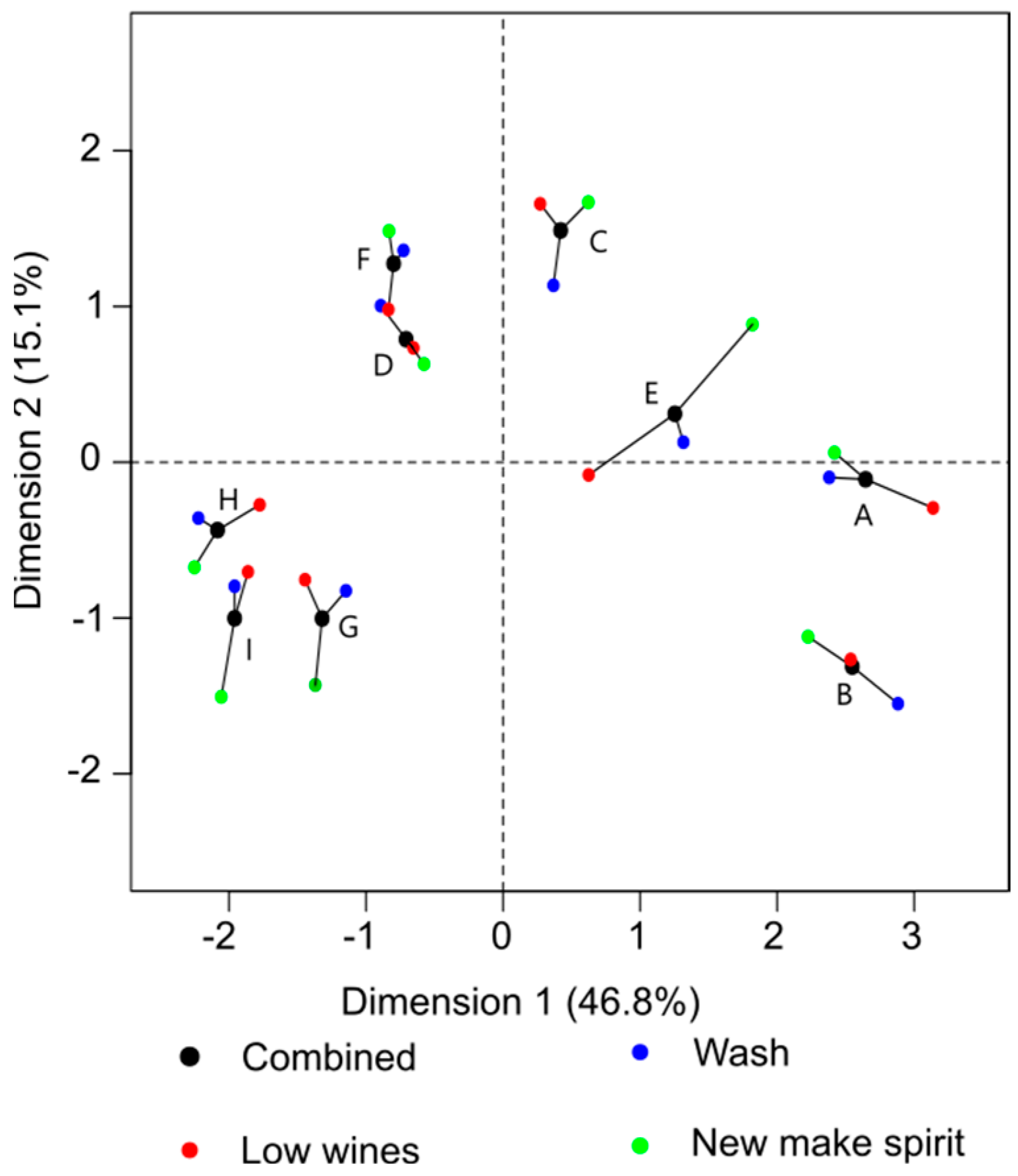
3.1. Analysis of Flavour Changes Observed by Napping
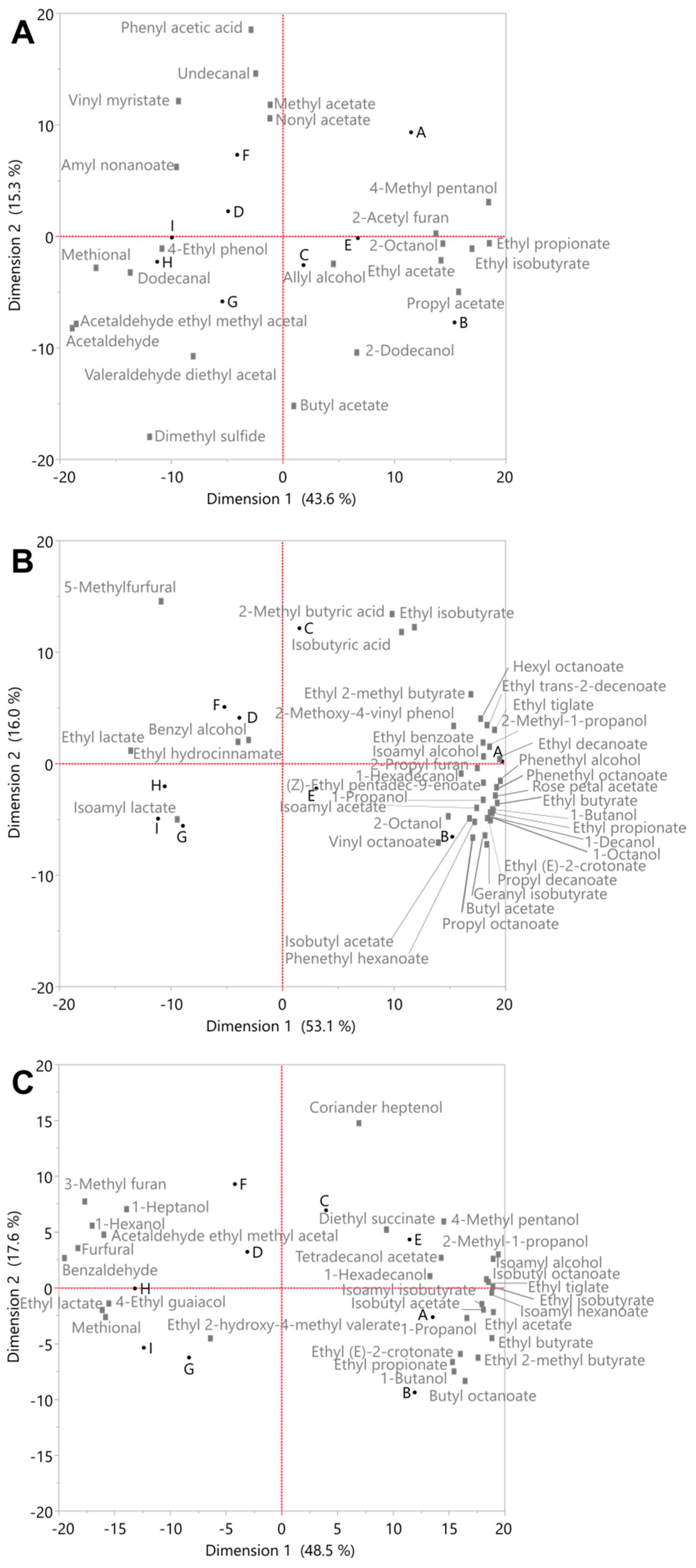
3.2. Analysis of Congeners by Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry
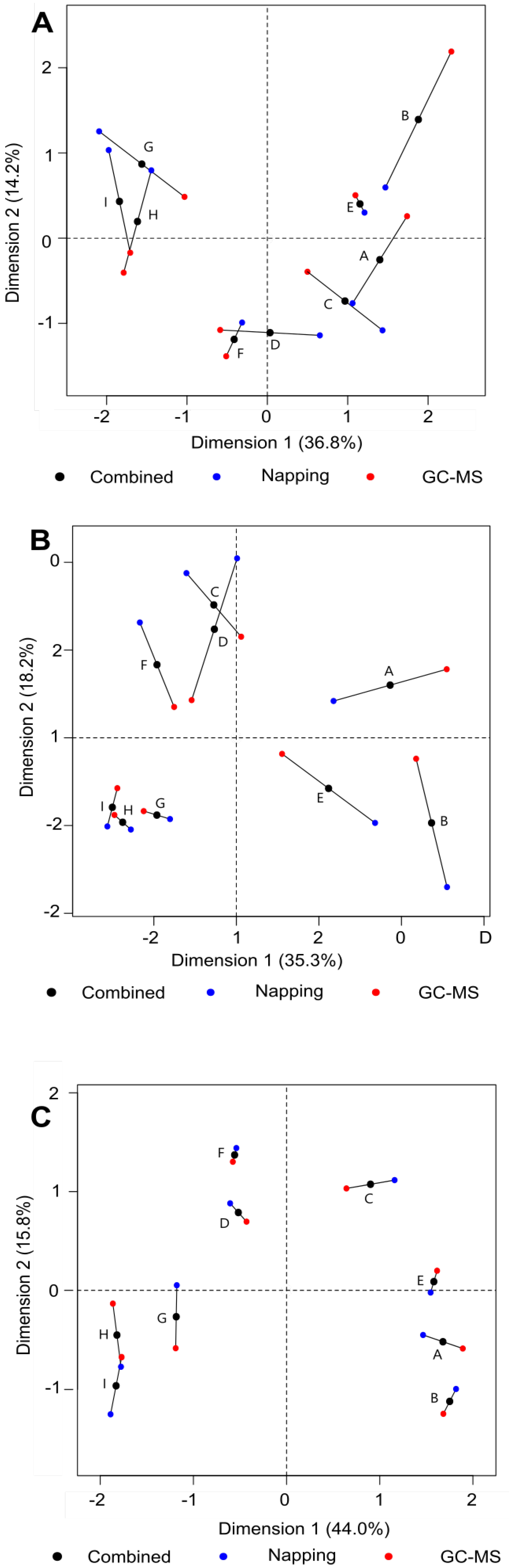
3.3. Connecting Flavour and Congener Changes through the Whisky Production Process
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Esters | Higher Alcohols | Carbonyl Compounds | Cyclic Compounds | Other | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Congener | NMS | LW | Wash | Congener | NMS | LW | Wash | Congener | NMS | LW | Wash | Congener | NMS | LW | Wash | Congener | NMS | LW | Wash |
| (Z)-Ethyl pentadec-9-enoate | x | x | 1-Butanol | x | x | 5-Methylfurfural | x | 2-Acetyl furan | x | 2-Methyl butyric acid | x | ||||||||
| Amyl nonanoate | x | 1-Decanol | x | Acetaldehyde | x | 2-Methoxy-4-vinyl phenol | x | Dimethyl sulfide | x | ||||||||||
| Butyl acetate | x | x | 1-Heptanol | x | Acetaldehyde ethyl methyl acetal | x | x | 2-Propyl furan | x | Isobutyric acid | x | ||||||||
| Butyl octanoate | x | 1-Hexadecanol | x | x | Benzaldehyde | x | 3-Methyl furan | x | Phenyl acetic acid | x | |||||||||
| Diethyl succinate | x | 1-Hexanol | x | Dodecanal | x | 4-Ethyl guaiacol | x | ||||||||||||
| Ethyl (E)-2-crotonate | x | x | 1-Octanol | x | x | Furfural | x | 4-Ethyl phenol | x | ||||||||||
| Ethyl 2-hydroxy-4-methyl valerate | x | 1-Propanol | x | x | Methional | x | x | ||||||||||||
| Ethyl 2-methyl butyrate | x | x | 2-Dodecanol | x | Undecanal | x | |||||||||||||
| Ethyl acetate | x | x | 2-Methyl-1-propanol | x | x | Valeraldehyde diethyl acetal | x | ||||||||||||
| Ethyl benzoate | x | 2-Octanol | x | ||||||||||||||||
| Ethyl butyrate | x | x | 4-Methyl pentanol | x | x | ||||||||||||||
| Ethyl decanoate | x | Allyl alcohol | x | ||||||||||||||||
| Ethyl hydrocinnamate | x | Benzyl alcohol | x | ||||||||||||||||
| Ethyl isobutyrate | x | x | x | Coriander heptenol | x | ||||||||||||||
| Ethyl isopentyl succinate | x | Isoamyl alcohol | x | x | |||||||||||||||
| Ethyl lactate | x | x | Phenethyl alcohol | x | |||||||||||||||
| Ethyl propionate | x | x | x | ||||||||||||||||
| Ethyl tiglate | x | x | |||||||||||||||||
| Ethyl trans-2-decenoate | x | ||||||||||||||||||
| Geranyl isobutyrate | x | ||||||||||||||||||
| Hexyl octanoate | x | ||||||||||||||||||
| Isoamyl acetate | x | ||||||||||||||||||
| Isoamyl hexanoate | x | ||||||||||||||||||
| Isoamyl isobutyrate | x | ||||||||||||||||||
| Isoamyl lactate | x | ||||||||||||||||||
| Isobutyl acetate | x | ||||||||||||||||||
| Isobutyl octanoate | x | ||||||||||||||||||
| Methyl acetate | x | ||||||||||||||||||
| Nonyl acetate | x | ||||||||||||||||||
| Phenethyl hexanoate | x | ||||||||||||||||||
| Phenethyl octanoate | x | ||||||||||||||||||
| Propyl acetate | x | ||||||||||||||||||
| Propyl decanoate | x | ||||||||||||||||||
| Propyl octanoate | x | ||||||||||||||||||
| Rose petal acetate | x | ||||||||||||||||||
| Tetradecanol acetate | x | ||||||||||||||||||
| Vinyl myristate | x | ||||||||||||||||||
| Vinyl octanoate | x | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 16 | 25 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | ||||
References
- The Scotch Whisky Association. Facts & Figures. 2022. Available online: https://www.scotch-whisky.org.uk/insights/facts-figures// (accessed on 4 September 2022).
- Scottish Government. The Scotch Whisky Regulations 2009. Available online: http://www.legislation.gov.uk/uksi/2009/2890/pdfs/uksi_20092890_en.pdf (accessed on 4 September 2022).
- Bathgate, G.N. A review of malting and malt processing for whisky distillation. J. Inst. Brew. 2016, 122, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosher, M.; Trantham, K. The ‘Food’ for the Brew, Brewing Science: A Multidisciplinary Approach, 1st ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 125–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justé, A.; Malfliet, S.; Lenaerts, M.; De Cooman, L.; Aerts, G.; Willems, K.A.; Lievens, B. Microflora during malting of barley: Overview and impact on malt quality. BrewingScience 2011, 64, 22–31. [Google Scholar]
- Bringhurst, T.A.; Brosnan, J. Scotch whisky: Raw material selection and processing. In Whisky Technology, Production and Marketing, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 49–122. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, G.; Bringhurst, T.; Brosnan, J. The ideal distiller’s yeast? Brew. Distill. Int. 2011, 30–32. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, G.; Brosnan, J.; Bringhurst, T.; Jack, F. Selecting new distilling yeasts for improved fermentation and for sustainability. In Distilled Spirits—Future Challenges, New Solutions; Context Products Ltd.: Packington, UK, 2011; pp. 127–136. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, G.; Hill, A. Saccharomyces cerevisiae in the Production of Whisk(e)y. Beverages 2016, 2, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, G.; Stewart, G. Saccharomyces cerevisiae in the Production of Fermented Beverages. Beverages 2016, 2, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, I.; Stewart, G. Distilling yeast and fermentation. In Whisky Technology Production and Marketing, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 123–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, M.; Nishimura, K.-I.-C. Occurance and Formation of Damascenone, Trans-2,6,6-trimethyl-l-crotonyl-cyclohexa-1,3-diene, in Alcoholic beverages. J. Food Sci. 1980, 45, 396–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, B.; Fagnen, O.; Jack, F.; Brosnan, J. The Impact of Copper in Different Parts of Malt Whisky Pot Stills on New Make Spirit Composition and Aroma. J. Inst. Brew. 2011, 117, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicol, D.A. Batch Distillation, Whisky, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 155–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoph, N.; Bauer-Christoph, C. Flavour of Spirit Drinks: Raw Materials, Fermentation, Distillation, and Ageing, Flavours and Fragrances; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 219–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-Y.M.; Paterson, A.; Piggott, J.R.; Richardson, G.D. Origins of Flavour in Whiskies and a Revised Flavour Wheel: A Review. J. Inst. Brew. 2001, 107, 287–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franitza, L.; Granvogl, M.; Schieberle, P. Influence of the Production Process on the Key Aroma Compounds of Rum: From Molasses to the Spirit. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 9041–9053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piggott, J.R. Whisky. In Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering: Food and Beverages Industry; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conner, J. Maturation. In Whisky Technology, Production and Marketing, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 199–220. [Google Scholar]
- Reazin, G.H. Chemical Mechanisms of Whiskey Maturation. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1981, 32, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berbert de Amorim Neto, H.; Pearson, S.Y.; Walker, J.W.; Walker, G.M.; Brosnan, J. Application of novel yeast strains to the Scotch whisky fermentation process. In Distilled Spirits, Production, Technology and Innovation; Nottingham University Press: Nottingham, UK, 2008; pp. 139–143. [Google Scholar]
- Berbert de Amorim Neto, H.; Yohannan, B.K.; Bringhurst, T.A.; Brosnan, J.M.; Pearson, S.Y.; Walker, J.W.; Walker, G.M. Evaluation of a Brazilian fuel alcohol yeast strain for Scotch whisky fermentations. J. Inst. Brew. 2009, 115, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, C.; Speers, R.A.; Hill, A. Investigating the Birthplace of Scotch Whisky: Microbiological Survey of Lindores Abbey. In Distilled Spirits. Future Challenges, New Solutions; Context Products Ltd.: Packington, UK, 2015; pp. 249–256. [Google Scholar]
- Burke, J.C.; Speers, R.A.; Hill, A.E. The types and properties of yeasts and bacteria isolated during a microbiological survey of Lindores Abbey. In Proceedings of the 2014 Brewing Summit, Edinburgh, UK, 4–7 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Miles, J. Different yeast strains achieve different new-make spirit flavours. In Distilled Spirits—Future Challenges, New Solutions; Context Products Ltd.: Packington, UK, 2015; pp. 203–208. [Google Scholar]
- Ekins, A.; Chabot, F.; Doucette, M.; D’Aoust, F. Congener profiles of selected Lallemand yeast strains. In Distilled Spirits—Local Roots; Global Reach; Context Products Ltd.: Packington, UK, 2018; pp. 85–88. [Google Scholar]
- Waymark, C.; Hill, A.E. The influence of yeast strain on whisky new make spirit aroma. Fermentation 2021, 7, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruner, J.; Fox, G. Novel Non-Cerevisiae Saccharomyces Yeast Species Used in Beer and Alcoholic Beverage Fermentations. Fermentation 2020, 6, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, M.; Meier-Dörnberg, T.; Jacob, F.; Methner, F.J.; Wagner, R.S.; Hutzler, M. Review: Pure non-Saccharomyces starter cultures for beer fermentation with a focus on secondary metabolites and practical applications. J. Inst. Brew. 2016, 122, 569–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, D.W.K.; Chua, J.Y.; Lu, Y.; Liu, S.Q. Evaluation of the potential of commercial non-Saccharomyces yeast strains of Torulaspora delbrueckii and Lachancea thermotolerans in beer fermentation. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 2049–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daute, M. Exploiting Yeast Diversity in Whisky Fermentations for Biocatalysis of Desirable Flavour Compounds. Ph.D. Thesis, Abertay University, Dundee, Scotland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Marčiulionytė, R.; Johnston, C.; Maskell, D.L.; Mayo, J.; Robertson, D.; Griggs, D.; Holmes, C.P. Roasted Malt for Distilling: Impact on Malt Whisky New Make Spirit Production and Aroma Volatile Development. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2022, 80, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, F. Sensory analysis. In Whisky Technology, Production, and Marketing, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daute, M.; Jack, F.; Baxter, I.; Harrison, B.; Grigor, J.; Walker, G. Comparison of Three Approaches to Assess the Flavour Characteristics of Scotch Whisky Spirit. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, L.; Symoneaux, R.; Maître, I.; Asselin, C.; Jourjon, F.; Pagès, J. Comparison of three sensory methods for use with the Napping® procedure: Case of ten wines from Loire valley. Food Qual. Prefer. 2008, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louw, L.; Malherbe, S.; Naes, T.; Lambrechts, M.; van Rensburg, P.; Nieuwoudt, H. Validation of two Napping® techniques as rapid sensory screening tools for high alcohol products. Food Qual. Prefer. 2013, 30, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, H.; Williams, L.J.; Valentin, D. Multiple factor analysis: Principal component analysis for multitable and multiblock data sets. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2013, 5, 149–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josse, J.; Pagès, J.; Husson, F. Testing the significance of the RV coefficient. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2008, 53, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehlholm, C.; Brockhoff, P.B.; Meinert, L.; Aaslyng, M.D.; Bredie, W.L.P. Rapid descriptive sensory methods—Comparison of Free Multiple Sorting, Partial Napping, Napping, Flash Profiling and conventional profiling. Food Qual. Prefer. 2012, 26, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baert, J.J.; De Clippeleer, J.; Hughes, P.S.; De Cooman, L.; Aerts, G. On the origin of free and bound staling aldehydes in beer. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 11449–11472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Iersel, M.F.M.; Brouwer-Post, E.; Rombouts, F.M.; Abee, T. Influence of yeast immobilization on fermentation and aldehyde reduction during the production of alcohol-free beer. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2000, 26, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstrepen, K.J.; Derdelinckx, G.; Dufour, J.; Winderickx, J.; Thevelein, J.M.; Pretorius, I.S.; Delvaux, F.R.; Box, P.O.; Osmond, G.; Sa, A. Flavor-active esters adding fruitiness to beer. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2003, 96, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Code | Yeast Strain | Origin |
|---|---|---|
| A | Saccharomyces cerevisiae—M-type | Lallemand Inc. (Montreal, QC, Canada) |
| B | Dekkera bruxellensis—CBS11269 | Abertay University (Dundee, Scotland) |
| C | Saccharomyces cerevisiae—Belle Saison | Lallemand Inc. (Montreal, QC, Canada) |
| D | Metschnikowia fructicola—Gaia | Lallemand Inc. (Montreal, QC, Canada) |
| E | Debaryomyces hansenii—NCYC 7037 | Abertay University (Dundee, Scotland) |
| F | Torulaspora delbrueckii—TD291 | Lallemand Inc. (Montreal, QC, Canada) |
| G | Candida oleophila—TMW 3.0609 | Prof. Luwig Niessen; Technical University Munich (Munich, Germany) |
| H | Zygotorulaspora florentina—LYCC8121 | Abertay University (Dundee, Scotland) |
| I | Wickerhamomyces anomalus—LYCC7025 | Abertay University (Dundee, Scotland) |
| Method | RV Score |
|---|---|
| Napping wash—Napping low wines | 0.80 |
| Napping wash—Napping new make spirit | 0.85 |
| Napping wash—GC–MS wash | 0.77 |
| Napping wash—GC–MS low wines | 0.74 |
| Napping wash—GC–MS new make spirit | 0.82 |
| Napping low wines—Napping new make spirit | 0.84 |
| Napping low wines—GC–MS wash | 0.85 |
| Napping low wines—GC–MS low wines | 0.77 |
| Napping low wines—GC–MS new make spirit | 0.81 |
| Napping new make spirit—GC–MS wash | 0.92 |
| Napping new make spirit—GC–MS low wines | 0.85 |
| Napping new make spirit—GC–MS new make spirit | 0.94 |
| GC–MS wash—GC–MS low wines | 0.93 |
| GC–MS wash—GC–MS new make spirit | 0.93 |
| GC–MS low wines—GC–MS new make spirit | 0.90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Daute, M.; Baxter, I.; Harrison, B.; Walker, G.; Jack, F. From Fermented Wash to New Make Spirit: Assessing the Evolution of Flavour Characteristics of Scotch Whisky Using Lab-Scale Process Simulations. Beverages 2023, 9, 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages9020037
Daute M, Baxter I, Harrison B, Walker G, Jack F. From Fermented Wash to New Make Spirit: Assessing the Evolution of Flavour Characteristics of Scotch Whisky Using Lab-Scale Process Simulations. Beverages. 2023; 9(2):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages9020037
Chicago/Turabian StyleDaute, Martina, Irene Baxter, Barry Harrison, Graeme Walker, and Frances Jack. 2023. "From Fermented Wash to New Make Spirit: Assessing the Evolution of Flavour Characteristics of Scotch Whisky Using Lab-Scale Process Simulations" Beverages 9, no. 2: 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages9020037
APA StyleDaute, M., Baxter, I., Harrison, B., Walker, G., & Jack, F. (2023). From Fermented Wash to New Make Spirit: Assessing the Evolution of Flavour Characteristics of Scotch Whisky Using Lab-Scale Process Simulations. Beverages, 9(2), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages9020037