BLE-GSpeed: A New BLE-Based Dataset to Estimate User Gait Speed
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
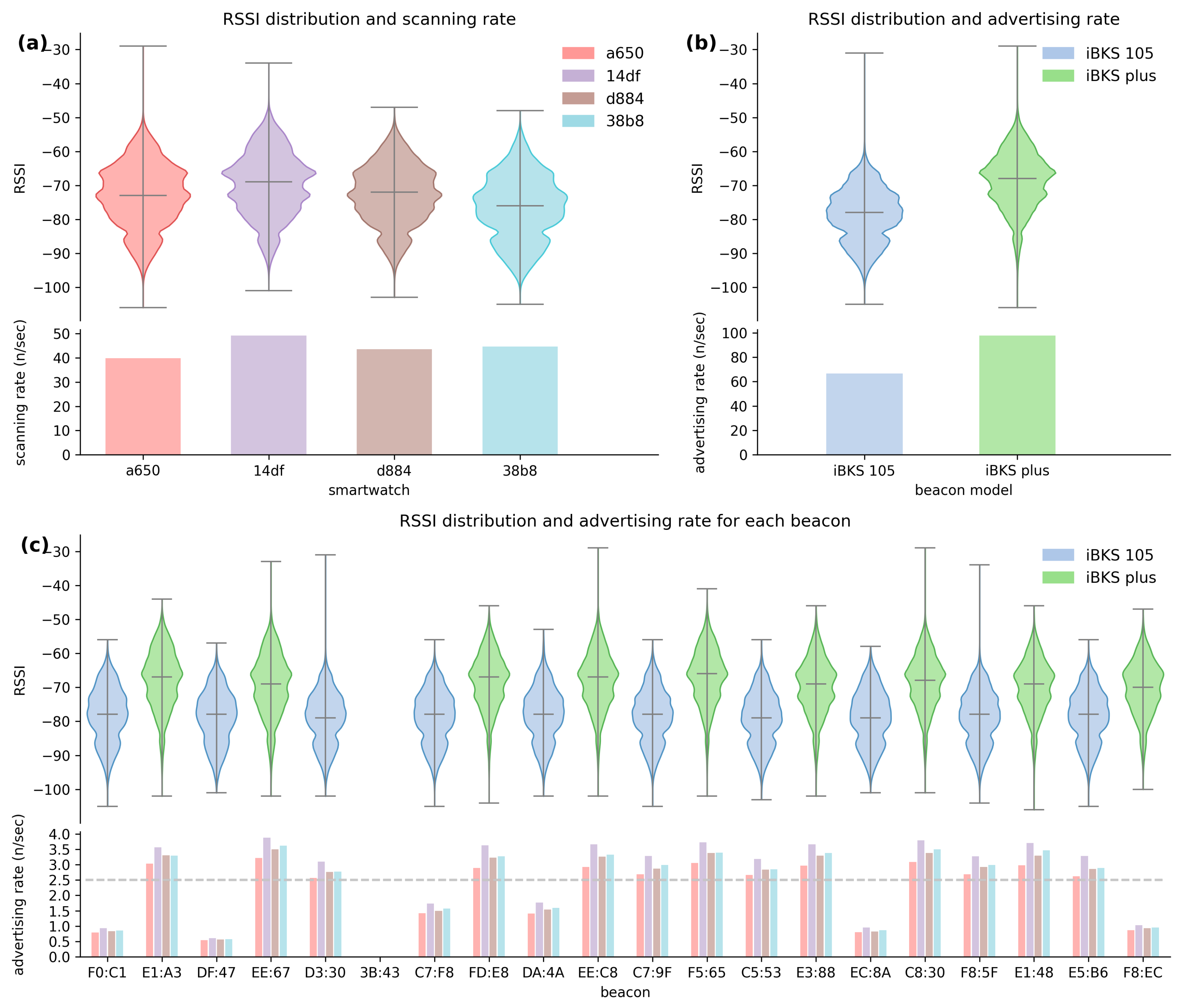
3. Data
- mac. The MAC address of the detected beacon.
- rssi. The RSSI value obtained for the beacon.
- device. A four-character descriptor for the smartwatch that performed the scan.
- timestamp. The timestamp at which the scan was received.
- user. The id of the user that was performing the experiment.
- direction. A number (0 or 1) indicating the direction of the walk.
- walk_id. A number that identifies each walk.
- speed. The actual speed of the user, in m/s.
4. Experiments
4.1. Gait Speed Determination
- is the received signal strength at a distance d from the beacon.
- is the received signal strength at the reference distance (1 m) from the beacon.
- d is the distance between the receiver and the beacon.
- is the reference distance (1 m)
- is a random variable with zero mean, reflecting the attenuation (in decibel) caused by fading, multipath effect, etc.
- is the path loss exponent, whose value is normally in the range of 2 to 6. The actual value depends on environmental characteristics.
- 1
- For each walk, smartwatch and mac (beacon), we find the timestamp at which the maximum RSSI value has been detected. We do so in two different ways; by looking at the raw data and applying a 13 point moving average and finding the maximum point in the smoothed version of the RSSI data. We tried different values for the window length, in the range between 3 and 25, obtaining the best results for a window length of 13 measurements.
- 2
- For two given beacons i, j, separated by a distance , and with , being the estimated timestamps at which the user walked below them, the speed of the receiver can be estimated as follows:
- 3
- In the general case, when there are more than two beacons installed, the speed can be estimated as the average of the values obtained for each pair. Given a set of k beacons, the speed of the device is calculated as follows:where , , and .
- 4
- The speed estimation obtained for each pair is only taken into account when it is comprised in the interval . This is not just because we want to consider only results that correspond to a feasible user speed, but also because the low scanning rate of the smartwatches may produce insufficient data to achieve a good estimation, and can generate artifact results that may not represent a proper approximation of the actual speed of the user.
4.2. Results
5. Conclusions
6. Reproducibility
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BLE | Bluetooth Low Energy |
| GS | Gait Speed |
| RSSI | Received Signal Strength Indicator |
| PIR | Passive Infrared Sensors |
| NTP | Network Time Protocol |
References
- Bloom, D.E.; Chatterji, S.; Kowal, P.; Lloyd-Sherlock, P.; McKee, M.; Rechel, B.; Rosenberg, L.; Smith, J.P. Macroeconomic implications of population ageing and selected policy responses. Lancet 2015, 385, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peel, N.M.; Kuys, S.S.; Klein, K. Gait speed as a measure in geriatric assessment in clinical settings: A systematic review. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2013, 68, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferre, X.; Villalba-Mora, E.; Caballero-Mora, M.A.; Sanchez, A.; Aguilera, W.; Garcia-Grossocordon, N.; Nuñez-Jimenez, L.; Rodríguez-Mañas, L.; Liu, Q.; del Pozo-Guerrero, F. Gait speed measurement for elderly patients with risk of frailty. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2017, 2017, 1310345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.Y.; Liu, Y.; Kabelac, Z.; Hristov, R.; Katabi, D.; Liu, C. Extracting gait velocity and stride length from surrounding radio signals. In Proceedings of the 2017 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Denver, CO, USA, 6–11 May 2017; pp. 2116–2126. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, K.; Wu, C.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Jamieson, K. Widar: Decimeter-level passive tracking via velocity monitoring with commodity Wi-Fi. In Proceedings of the 18th ACM International Symposium on Mobile Ad Hoc Networking and Computing, Chennai, India, 10–14 July 2017; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, C.; Wang, B.; Liu, K.R. WiSpeed: A statistical electromagnetic approach for device-free indoor speed estimation. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 2163–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cesari, M.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Penninx, B.W.; Nicklas, B.J.; Simonsick, E.M.; Newman, A.B.; Tylavsky, F.A.; Brach, J.S.; Satterfield, S.; Bauer, D.C.; et al. Prognostic value of usual gait speed in well-functioning older people—Results from the Health, Aging and Body Composition Study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2005, 53, 1675–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hackett, R.A.; Davies-Kershaw, H.; Cadar, D.; Orrell, M.; Steptoe, A. Walking speed, cognitive function, and dementia risk in the English longitudinal study of ageing. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2018, 66, 1670–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guralnik, J.M.; Ferrucci, L.; Pieper, C.F.; Leveille, S.G.; Markides, K.S.; Ostir, G.V.; Studenski, S.; Berkman, L.F.; Wallace, R.B. Lower extremity function and subsequent disability: Consistency across studies, predictive models, and value of gait speed alone compared with the short physical performance battery. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med Sci. 2000, 55, M221–M231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Studenski, S.; Perera, S.; Patel, K.; Rosano, C.; Faulkner, K.; Inzitari, M.; Brach, J.; Chandler, J.; Cawthon, P.; Connor, E.B.; et al. Gait speed and survival in older adults. JAMA 2011, 305, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sayers, S.P.; Jette, A.M.; Haley, S.M.; Heeren, T.C.; Guralnik, J.M.; Fielding, R.A. Validation of the late-life function and disability instrument. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2004, 52, 1554–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Mehrotra, S. Patient walk detection in hospital room using Microsoft Kinect V2. In Proceedings of the 2016 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016; Volume 2016, pp. 4395–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Songra, R.; Lockhart, T. Agreement in Gait Speed from Smartphone and Stopwatch for Five Meter Walk in Laboratory and Clinical Environments. Biomed. Sci. Instrum. 2014, 50, 254–264. [Google Scholar]
- Stuck, A.K.; Bachmann, M.; Füllemann, P.; Josephson, K.R.; Stuck, A.E. Effect of testing procedures on gait speed measurement: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weir, R.; Childress, D. A new method of characterising gait using a portable, real-time, ultrasound ranging device. In Proceedings of the 19th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. ’Magnificent Milestones and Emerging Opportunities in Medical Engineering’ (Cat. No.97CH36136), Chicago, IL, USA, 30 October–2 November 1997; Volume 4, pp. 1810–1812. [Google Scholar]
- Pinson, S.; Holland, C.W. Relative velocity measurement from the spectral phase of a match-filtered linear frequency modulated pulse. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2016, 140, EL191–EL196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hagler, S.; Austin, D.; Hayes, T.L.; Kaye, J.; Pavel, M. Unobtrusive and ubiquitous in-home monitoring: A methodology for continuous assessment of gait velocity in elders. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2009, 57, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Liu, A.; Shahzad, M. Gait recognition using wifi signals. In Proceedings of the UbiComp ’16: Proceedings of the 2016 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous, Heidelberg, Germany, 12–14 September 2016; pp. 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keppler, A.M.; Nuritidinow, T.; Mueller, A.; Hoefling, H.; Schieker, M.; Clay, I.; Böcker, W.; Fürmetz, J. Validity of accelerometry in step detection and gait speed measurement in orthogeriatric patients. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, Y.; Herman, T.; Brozgol, M.; Giladi, N.; Mirelman, A.; Hausdorff, J. SPARC: A new approach to quantifying gait smoothness in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2018, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansano-Sansano, E.; Aranda, F.J.; Montoliu, R.; Álvarez, F.J. GSPEED—BLE-Based Gait Speed Dataset. 2020. Available online: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4261381 (accessed on 6 December 2020). [CrossRef]
- Shubina, V.; Holcer, S.; Gould, M.; Lohan, E.S. Survey of Decentralized Solutions with Mobile Devices for User Location Tracking, Proximity Detection, and Contact Tracing in the COVID-19 Era. Data 2020, 5, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaggle: Your Machine Learning and Data Science Community. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/ (accessed on 3 November 2020).
- Sikeridis, D.; Papapanagiotou, I.; Devetsikiotis, M. BLEBeacon: A Real-Subject Trial Dataset from Mobile Bluetooth Low Energy Beacons. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.08782. [Google Scholar]
- Tóth, Z.; Tamás, J. Miskolc IIS hybrid IPS: Dataset for hybrid indoor positioning. In Proceedings of the 2016 26th International Conference Radioelektronika (RADIOELEKTRONIKA), Kosice, Slovakia, 19–20 April 2016; pp. 408–412. [Google Scholar]
- Byrne, D.; Kozlowski, M. Residential Wearable RSSI and Accelerometer Measurements with Detailed Annotations. Sci. Data 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, Z.; Luo, D.; Henry, P.; Kazemifar, S.; Rozario, T.; Yan, Y.; Westover, K.; Lu, W.; Nguyen, D.; Long, T.; et al. Accurate real time localization tracking in a clinical environment using Bluetooth Low Energy and deep learning. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Byrne, D.; Kozlowski, M. Residential Wearable RSSI and Accelerometer Measurements with Detailed Annotations. 2018. Available online: https://figshare.com/articles/Residential_Wearable_RSSI_and_Accelerometer_Measurements_with_Detailed_Annotations/6051794 (accessed on 9 July 2020). [CrossRef]
- Torres-Sospedra, J.; Montoliu, R.; Martínez-Usó, A.; Avariento, J.P.; Arnau, T.J.; Benedito-Bordonau, M.; Huerta, J. UJIIndoorLoc: A new multi-building and multi-floor database for WLAN fingerprint-based indoor localization problems. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Busan, Korea, 27–30 October 2014; pp. 261–270. [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Sospedra, J.; Jiménez, A.; Knauth, S.; Moreira, A.; Beer, Y.; Fetzer, T.; Ta, V.C.; Montoliu, R.; Seco, F.; Mendoza-Silva, G.; et al. The Smartphone-Based Offline Indoor Location Competition at IPIN 2016: Analysis and Future Work. Sensors 2017, 17, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montoliu, R.; Sansano, E.; Torres-Sospedra, J.; Belmonte, O. IndoorLoc platform: A public repository for comparing and evaluating indoor positioning systems. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Sapporo, Japan, 18–21 September 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza-Silva, G.; Matey-Sanz, M.; Torres-Sospedra, J.; Huerta, J. BLE RSS Measurements Dataset for Research on Accurate Indoor Positioning. Data 2019, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aranda, F.J.; Parralejo, F.; Álvarez, F.J.; Torres-Sospedra, J. Multi-Slot BLE Raw Database for Accurate Positioning in Mixed Indoor/Outdoor Environments. Data 2020, 5, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda, F.J.; Parralejo, F.; Álvarez, F.J.; Torres-Sospedra, J. Multi-slot BLE Raw Database for Accurate Positioning in Mixed Indoor/Outdoor Environments. Zenodo Repository. 2020. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/3927588 (accessed on 23 November 2020).
- Baronti, P.; Barsocchi, P.; Chessa, S.; Mavilia, F.; Palumbo, F. Indoor Bluetooth Low Energy Dataset for Localization, Tracking, Occupancy, and Social Interaction. Sensors 2018, 18, 4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fukuchi, C.; Fukuchi, R.; Duarte, M. A public dataset of overground and treadmill walking kinematics and kinetics in healthy individuals. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schreiber, C.; Moissenet, F. A multimodal dataset of human gait at different walking speeds established on injury-free adult participants. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voss, S.; Joyce, J.; Biskis, A.; Parulekar, M.; Armijo, N.; Zampieri, C.; Tracy, R.; Palmer, S.; Fefferman, M.; Ouyang, B.; et al. Normative database of spatiotemporal gait parameters using inertial sensors in typically developing children and young adults. Gait Posture 2020, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Coppola, S.; Dixon, P.; Li, S.; Dennerlein, J.; Hu, B. A database of human gait performance on irregular and uneven surfaces collected by wearable sensors. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapron, K.; Bouchard, K.; Gaboury, S. Real-time gait speed evaluation at home in a multi residents context. In Multimedia Tools and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lohan, E.; Torres-Sospedra, J.; Leppäkoski, H.; Richter, P.; Peng, Z.; Huerta, J. Wi-Fi Crowdsourced Fingerprinting Dataset for Indoor Positioning. Data 2017, 2, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mendoza-Silva, G.; Richter, P.; Torres-Sospedra, J.; Lohan, E.; Huerta, J. Long-Term WiFi Fingerprinting Dataset for Research on Robust Indoor Positioning. Data 2018, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tóth, Z. ILONA: Indoor Localization and Navigation System. J. Locat. Based Serv. 2016, 10, 285–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikeridis, D.; Papapanagiotou, I.; Devetsikiotis, M. CRAWDAD Dataset Unm/Blebeacon (v.2019-03-12). CRAWDAD Wireless Network Data Archive 2019. Available online: https://crawdad.org/unm/blebeacon/ (accessed on 9 July 2020).
- zoball. zoball/BLE-Tracking-with-Deep-Learning. 2020. Available online: https://github.com/zoball/BLE-Tracking-with-Deep-Learning (accessed on 9 July 2020).
- Lohan, E.; Torres-Sospedra, J.; Leppäkoski, H.; Richter, P.; Peng, Z.; Huerta, J. Wi-Fi Crowdsourced Fingerprinting Dataset for Indoor Positioning. Zenodo Repository. 2017. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/8897981 (accessed on 9 July 2020). [CrossRef]
- Lohan, E.; Torres-Sospedra, J.; Leppäkoski, H.; Richter, P.; Peng, Z.; Huerta, J. UJIIndoorLoc: A New Multi-Building and Multi-Floor Database for WLAN Fingerprint-Based Indoor Localization Problems. Indoorlocplatform. 2014. Available online: http://indoorlocplatform.uji.es/databases/all/ (accessed on 9 July 2020).
- Baronti, P.; Barsocchi, P.; Chessa, S.; Mavilia, F.; Palumbo, F. Indoor Bluetooth Low Energy Datasetfor Localization, Tracking, Occupancy, and Social Interaction. 2018. Available online: http://wnlab.isti.cnr.it/_media/dataset.zip (accessed on 9 July 2020).
- Mendoza-Silva, G.M.; Torres-Sospedra, J.; Huerta, J.; Matey Sanz, M. BLE RSS Meaurements Database and Supporting Materials. Zenodo Repository. 2018. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/1066041 (accessed on 9 July 2020). [CrossRef]
- Fukuchi, C.; Fukuchi, R.; Duarte, M. A Public Dataset of Overground and Treadmill Walking Kinematics And Kinetics in Healthy Individual. Figshare Repository. 2018. Available online: https://figshare.com/ or https://figshare.com/articles/A_public_data_set_of_overground_and_treadmill_walking_kinematics_and_kinetics_of_healthy_individuals/5722711/2 (accessed on 3 November 2020). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voss, S.; Joyce, J.; Biskis, A.; Parulekar, M.; Armijo, N.; Zampieri, C.; Tracy, R.; Palmer, S.; Fefferman, M.; Ouyang, B.; et al. Normative Database of Spatiotemporal Gait Parameters Using Inertial Sensors in Typically Developing Children and Young Adults. ScientificDirect, Elsevier, Gait and Posture. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0966636220301600 (accessed on 23 November 2020).
- Team, S.D.C. Metadata Record for: A Database of Human Gait Performance on Irregular and Uneven Surfaces Collected by Wearable Sensors. 2020. Available online: https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.12505022.v1 (accessed on 6 December 2020). [CrossRef]
- LIARALab. Available online: https://github.com/LIARALab (accessed on 3 November 2020).
- iBKS 105 · Accent Systems. Available online: https://accent-systems.com/product/ibks-105/ (accessed on 3 November 2020).
- iBKS Plus · Accent Systems. Available online: https://accent-systems.com/product/ibks-plus/ (accessed on 3 November 2020).
- Furset, K.; Hoffman, P. High Pulse Drain Impact on CR2032 Coin Cell Battery Capacity. Nordic Semiconductor and Energizer; Technical Report, Technical Memo. 2011. Available online: https://www.dmcinfo.com/Portals/0/Blog%20Files/High%20pulse%20drain%20impact%20on%20CR2032%20coin%20cell%20battery%20capacity.pdf (accessed on 6 December 2020).
- Goldsmith, A. Wireless Communications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, CA, USA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]







| Database | People Monitoring | Wi-Fi Fingerprinting | Bluetooth Fingerprinting | GS Monitoring | GS Evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Works | [24,25,26,27] | [29,30,31,41,42] | [32,33,35] | [36,38,39] | [40] |
| Databases | [28,43,44,45] | [46,47] | [34,48,49] | [50,51,52] | [53] |
| Beacon Model | Method | Error (m) | # Beacons |
|---|---|---|---|
| iBKS 105 | raw data | 0.1935 | 4 |
| iBKS 105 | smoothed data | 0.0855 | 10 |
| iBKS plus | raw data | 0.1732 | 4 |
| iBKS plus | smoothed data | 0.1357 | 9 |
| mixed | raw data | 0.1928 | 8 |
| mixed | smoothed data | 0.2566 | 9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sansano-Sansano, E.; Aranda, F.J.; Montoliu, R.; Álvarez, F.J. BLE-GSpeed: A New BLE-Based Dataset to Estimate User Gait Speed. Data 2020, 5, 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/data5040115
Sansano-Sansano E, Aranda FJ, Montoliu R, Álvarez FJ. BLE-GSpeed: A New BLE-Based Dataset to Estimate User Gait Speed. Data. 2020; 5(4):115. https://doi.org/10.3390/data5040115
Chicago/Turabian StyleSansano-Sansano, Emilio, Fernando J. Aranda, Raúl Montoliu, and Fernando J. Álvarez. 2020. "BLE-GSpeed: A New BLE-Based Dataset to Estimate User Gait Speed" Data 5, no. 4: 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/data5040115
APA StyleSansano-Sansano, E., Aranda, F. J., Montoliu, R., & Álvarez, F. J. (2020). BLE-GSpeed: A New BLE-Based Dataset to Estimate User Gait Speed. Data, 5(4), 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/data5040115







