Assessment and Management of Dysphagia in Acute Stroke: An Initial Service Review of International Practice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Assessment and management techniques were dichotomised, resulting in two categories: (a) Frequently/More (for those who utilised Frequently (for 11–50% patients ) and for Most (>50% patients )) and (b) Less than Frequently (for techniques used for less than 11% patients) and were subject to Chi Square analysis.
- Only management techniques utilised by over 50% of the respondents Frequently/More (defined as techniques utilised Frequently (for 11–50% patients) and for Most (>50% patients)) were subject to further analyses. This allowed for a comparison of the key techniques that were utilised and comparisons between countries. This also enabled us to subject the data to Chi Square analysis.
- The timing of the assessment(s) and management data between countries were considered and were subject to descriptive statistics and analysis using the Kruskal Wallis test.
- Any relationships between assessment techniques and management techniques, as defined in 2. (above), were explored
3. Results
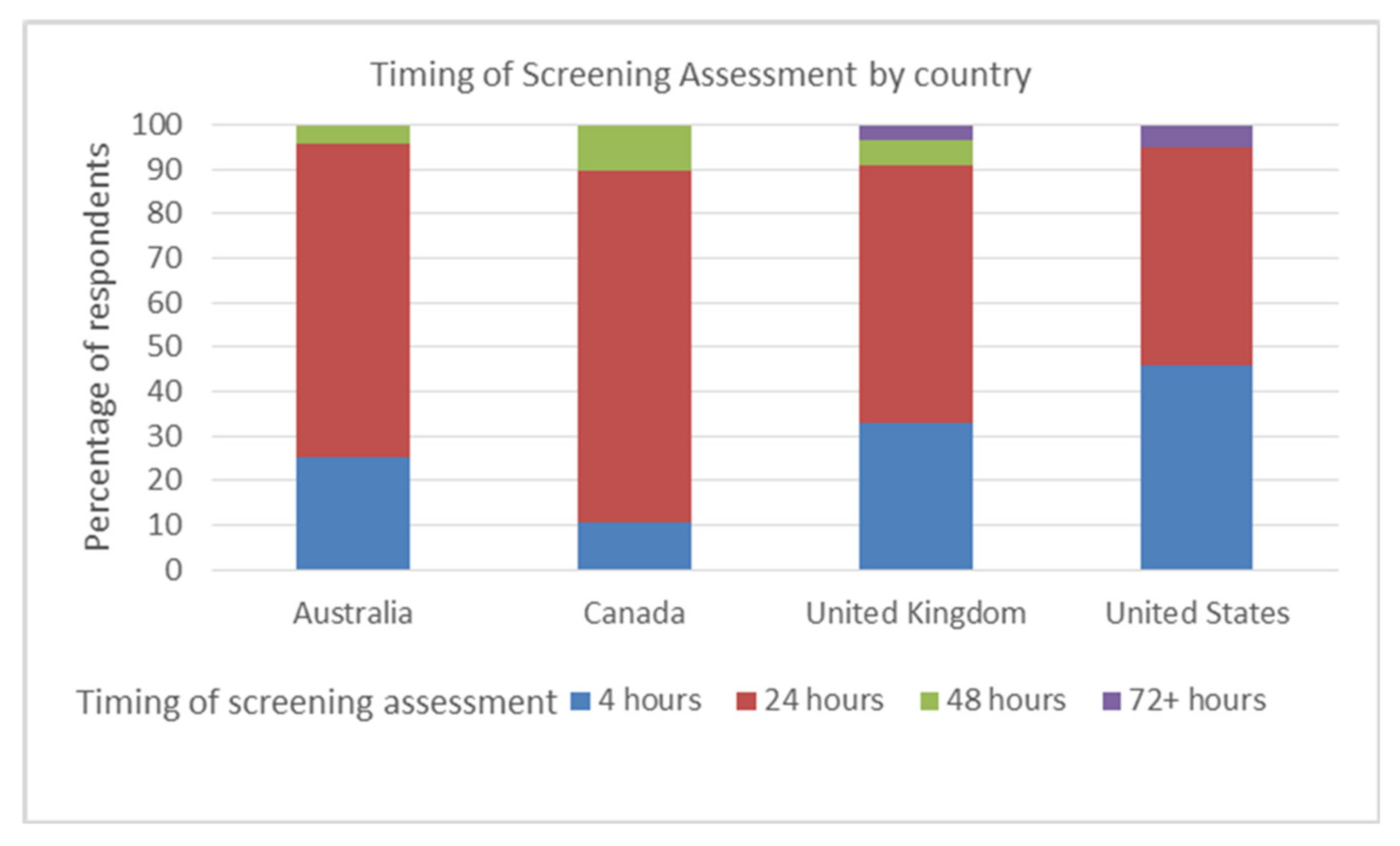
3.1. Screening Assessments and Cervical Auscultation
3.2. Instrumental Assessment: VFS and Fees
3.2.1. Videofluoroscopy (VFS)
3.2.2. Fibreoptic Endoscopic Evaluation of Swallowing (FEES)
3.3. Swallow Management and Rehabilitation
3.3.1. Modification Food/Fluid
3.3.2. Postural/Compensatory Techniques.
3.3.3. Sensory Stimulation
3.3.4. Relationship between Assessment and Management
4. Discussion
Clinical Management
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smithard, D.G.; O’Neill, P.A.; Parks, C.; Morris, J. Complications and outcome after acute stroke. Does dysphagia matter? Stroke A J. Cereb. Circ. 1996, 27, 1200–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, G.; Hankey, G.J. Initial clinical and demographic predictors of swallowing impairment following acute stroke. Dysphagia 2001, 16, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smithard, D.G.; Smeeton, N.C.; Wolfe, C.D. Long-term outcome after stroke: Does dysphagia matter? Age Ageing 2007, 36, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogus-Pulia, N.; Robbins, J. Approaches to the Rehabilitation of Dysphagia in Acute Poststroke Patients. Semin Speech Lang. 2013, 34, 154–169. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, Y.J.; Na, Y.J.; Han, S.H. Swallowing apraxia in a patient with recurrent ischemic strokes: A case report. Medicine 2019, 98, e17056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, D.L.; Roffe, C.; Beavan, J.; Blackett, B.; Fairfield, C.A.; Hamdy, S.; Havard, D.; McFarlane, M.; McLauglin, C.; Randall, M.; et al. Post-stroke dysphagia: A review and design considerations for future trials. Int. J. Stroke 2016, 11, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intercollegiate Stroke Working Party. National Clinical Guideline for Stroke, 4th ed.; Royal College of Physicians: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- National Stroke Foundation. Concise Clinical Guidelines for Stroke Management; National Stroke Foundation: Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- The Management of Stroke Working Group. VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Stroke Rehabilitation; Office of Quality and Performance: Washington, VA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Casaubon, L.K.; Boulanger, J.-M.; Glasser, E.; Blacquiere, D.; Boucher, S.; Brown, K.; Goddard, T.; Gordon, J.; Horton, M.; Lalonde, J.; et al. Canadian Stroke Best Practice Recommendations: Acute Inpatient Stroke Care Guidelines, Update 2015. Int. J. Stroke 2016, 11, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odderson, I.R.; Keaton, J.C.; McKenna, B.S. Swallow management in patients on an acute stroke pathway: Quality is cost effective. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1995, 76, 1130–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinchey, J.A.; Shephard, T.; Furie, K.; Smith, D.; Wang, D.; Tonn, S. Formal dysphagia screening protocols prevent pneumonia. Stroke A J. Cereb. Circ. 2005, 36, 1972–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, C.; Leslie, P.; Drinnan, M.J. Adult dysphagia assessment in the UK and Ireland: Are SLTs assessing the same factors? Dysphagia 2007, 22, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baijens, L.W.; Clave, P.; Cras, P.; Ekberg, O.; Forster, A.; Kolb, G.F.; Leners, J.C.; Masiero, S.; Mateos-Nozal, J.; Ortega, O.; et al. European Society for Swallowing Disorders—European Union Geriatric Medicine Society white paper: Oropharyngeal dysphagia as a geriatric syndrome. Clin. Interv Aging 2016, 11, 1403–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archer, S.K.; Wellwood, I.; Smith, C.H.; Newham, D.J. Dysphagia therapy in stroke: A survey of speech and language therapists. Int. J. Lang. Commun. Disord. /R. Coll. Speech Lang. 2013, 48, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smithard, D.G. Dysphagia Management and Stroke Units. Curr. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Rep. 2016, 4, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathers-Schmidt, B.A.; Kurlinski, M. Dysphagia evaluation practices: Inconsistencies in clinical assessment and instrumental examination decision-making. Dysphagia 2003, 18, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettigrew, C.M.; O’Toole, C. Dysphagia evaluation practices of speech and language therapists in Ireland: Clinical assessment and instrumental examination decision-making. Dysphagia 2007, 22, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Rumbach, A.; Coombes, C.; Doeltgen, S. A Survey of Australian Dysphagia Practice Patterns. Dysphagia 2018, 33, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martino, R.; Pron, G.; Diamant, N.E. Oropharyngeal dysphagia: Surveying practice patterns of the speech-language pathologist. Dysphagia 2004, 19, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepp, S.K.; Tirschwell, D.L.; Miller, R.M.; Longstreth, W.T., Jr. Swallowing screens after acute stroke: A systematic review. Stroke A J. Cereb. Circ. 2012, 43, 869–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speyer, R.; Baijens, L.; Heijnen, M.; Zwijnenberg, I. Effects of therapy in oropharyngeal dysphagia by speech and language therapists: A systematic review. Dysphagia 2010, 25, 40–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milazzo, M.; Panepinto, A.; Sabatini, A.M.; Danti, S. Tongue Rehabilitation Device for Dysphagic Patients. Sensors 2019, 19, 4657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, J.; Gangnon, R.E.; Theis, S.M.; Kays, S.A.; Hewitt, A.L.; Hind, J.A. The Effects of Lingual Exercise on Swallowing in Older Adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2005, 53, 1483–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rattray, J.; Jones, M.C. Essential elements of questionnaire design and development. J. Clin. Nurs. 2007, 16, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallant, J. SPSS Survival Manual; McGraw-Hill Education: Berkshire, UK; OUP: Oxford, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, T.A.T.; Wiles, C.M. Clinical measurement of swallowing in health and in neurogenic dysphagia. Qjm. Int. J. Med. 1996, 89, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suiter, D.M.; Leder, S.B. Clinical utility of the 3-ounce water swallow test. Dysphagia 2008, 23, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulow, M.; Olsson, R.; Ekberg, O. Videomanometric analysis of supraglottic swallow, effortful swallow, and chin tuck in patients with pharyngeal dysfunction. Dysphagia 2001, 16, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lise, S.; Sue, P.; Pam, E.; Jenny, F. Combined electrical stimulation and exercise for swallow rehabilitation post-stroke: A pilot randomized control trial. Int. J. Lang. Commun. Disord. 2018, 53, 405–417. [Google Scholar]
- National Institute for Excellence in Health and Care. Transcutaneous neuromuscular electrical stimulation for oropharyngeal dysphagia in adults. In Interventional Procedure Guidance IPG634; National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE): London, UK, 2018; Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg634 (accessed on 13 September 2019).
- Donovan, N.J.; Daniels, S.K.; Edmiaston, J.; Weinhardt, J.; Summers, D.; Mitchell, P.H. Dysphagia screening: State of the art: Invitational conference proceeding from the State-of-the-Art Nursing Symposium, International Stroke Conference 2012. Stroke A J. Cereb. Circ. 2013, 44, e24–e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, G. The Mann Assessment of Swallowing Ability; Singular Publishing: Clifton Park, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- OHJ, C.; Nicole, R.P.; Lisbeth, G.A.; JoAnne, R.; Nasia, S. Bedside diagnosis of dysphagia: A systematic review. J. Hosp. Med. 2015, 10, 256–265. [Google Scholar]
- Speyer, R. Oropharyngeal Dysphagia: Screening and Assessment. Otolaryngol. Clin. North. Am. 2013, 46, 989–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intercollegiate Stroke Working Party. National Clinical Guideline for Stroke, 5th ed.; Royal College of Physicians: London UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Teasell, R.W.; McRae, M.; Heitzner, J.; Bhardwaj, A.; Finestone, H. Frequency of videofluoroscopic modified barium swallow studies and pneumonia in stroke rehabilitation patients: A comparative study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1999, 80, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, A.M.D.; Michael, J.; Leslie, P. Assessing Penetration and Aspiration: How Do Videofluoroscopy and Fiberoptic Endoscopic Evaluation of Swallowing Compare? Laryngoscope 2007, 117, 1723–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, P.; Drinnan, M.J.; Finn, P.; Ford, G.A.; Wilson, J.A. Reliability and validity of cervical auscultation: A controlled comparison using videofluoroscopy. Dysphagia 2004, 19, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clave, P.; de Kraa, M.; Arreola, V.; Girvent, M.; Farre, R.; Palomera, E.; Serra-Prat, M. The effect of bolus viscosity on swallowing function in neurogenic dysphagia. Aliment. Pharm. 2006, 24, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payne, C.; Methven, L.; Fairfield, C.; Gosney, M.; Bell, A.E. Variability of starch-based thickened drinks for patients with dysphagia in the hospital setting. J. Texture Stud. 2012, 43, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Keeffe, S.T. Use of modified diets to prevent aspiration in oropharyngeal dysphagia: Is current practice justified? Bmc Geriatr. 2018, 18, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cichero, J.A.; Steele, C.; Duivestein, J.; Clave, P.; Chen, J.; Kayashita, J.; Dantas, R.; Lecko, C.; Speyer, R.; Lam, P.; et al. The Need for International Terminology and Definitions for Texture-Modified Foods and Thickened Liquids Used in Dysphagia Management: Foundations of a Global Initiative. Curr. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Rep. 2013, 1, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, R.; Vilardell, N.; Clavé, P.; Speyer, R. Effect of Bolus Viscosity on the Safety and Efficacy of Swallowing and the Kinematics of the Swallow Response in Patients with Oropharyngeal Dysphagia: White Paper by the European Society for Swallowing Disorders (ESSD). Dysphagia 2016, 31, 232–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crary, M.A.; Carnaby, G.D.; Shabbir, Y.; Miller, L.; Silliman, S. Clinical Variables Associated with Hydration Status in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients with Dysphagia. Dysphagia 2016, 31, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rofes, L.; Arreola, V.; Almirall, J.; Cabre, M.; Campins, L.; Garcia-Peris, P.; Speyer, R.; Clave, P. Diagnosis and management of oropharyngeal Dysphagia and its nutritional and respiratory complications in the elderly. Gastroenterol. Res. Pr. 2011, 2011, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnaby, G.D.; Harenberg, L. What is “Usual Care” in Dysphagia Rehabilitation: A survey of USA dysphagia practice patterns. Dysphagia 2013, 28, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valerie, A.; Bernice, M.; Surinder, B.; Cathy, L.; Robin, C. A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Measurementsof Tongue and Hand Strength and Endurance Using the IowaOral Performance Instrument (IOPI). Dysphagia 2013, 28, 350–369. [Google Scholar]
- McKenna, V.S.; Zhang, B.; Haines, M.B.; Kelchner, L.N. A Systematic Review of Isometric Lingual Strength-Training Programs in Adults with and Without Dysphagia. Am. J. Speech-Lang. Pathol. 2017, 26, 524–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organisation. International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health: ICF; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001. [Google Scholar]


| Yes/No Use of Screen | Nurse/Other Screening (n = 170) | 3 Oz Water Swallow (n = 145) | Timed Test of Swallowing (n = 141) | Cervical Auscultation (n = 145) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes-% use screen (n) | 91 (154) | 32 (46) | 18 (26) | 43 (63) |
| No-% don’t use screen (n) | 9 (16) | 68 (99) | 82 (115) | 57 (82) |
| Frequency of Use– % of Patients | VFS (n = 169) | FEES (n = 150) |
|---|---|---|
| Not at all | 4.2% | 51% |
| Rarely (0–10%) | 34.3% | 34% |
| Frequently (11–50%) | 50.3% | 13.3% |
| In most patients (>50%) | 11.2% | 2.0% |
| Management Technique (n) | None (0%) | Rarely (0–10%) | Frequently (11–50%) | Most (>50%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Food Modification (170) | 0 | 0.6 | 38.2 | 61.2 |
| Thickened liquid (170) | 0 | 9.4 | 50 | 40.6 |
| Frazier Free Water (167) | 41.9 | 37.1 | 18 | 3 |
| Ice Cool bolus (163) | 20.9 | 48.5 | 23.9 | 6.7 |
| Carbonation (163) | 46.6 | 41.1 | 11 | 1.2 |
| Sour bolus (164) | 50 | 35.4 | 11.6 | 3 |
| Effortful swallow(169) | 1.8 | 29.6 | 60.4 | 8.3 |
| Chin tuck (166) | 0.6 | 31.3 | 60.8 | 7.2 |
| Tongue Exercises (165) | 7.3 | 24.2 | 49.7 | 18.8 |
| Transcutaneous electrical stimulation (160) | 80.6 | 13.1 | 6.3 | 0 |
| Faucial Stimulation (163) | 58.3 | 35 | 6.1 | 0.6 |
| VFS and Technique | Association between Assessment and Management |
|---|---|
| VFS/compensatory techniques ** | p < 0.001 χ2 (1,n = 169) = 19.022, phi = .35 |
| VFS/postural techniques | p > 0.05 n = 169 p = 0.90 |
| VFS/Chin tuck | p > 0.05 n = 163 p = 0.121 |
| VFS/Effortful swallow ** | p < 0.001 χ2 (1,n = 166) = 22.876, phi = .38 |
| VFS/tongue exercises ** | p < 0.001 χ2 (1, n = 1162) = 11.252, phi = .27 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fairfield, C.A.; G. Smithard, D. Assessment and Management of Dysphagia in Acute Stroke: An Initial Service Review of International Practice. Geriatrics 2020, 5, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics5010004
Fairfield CA, G. Smithard D. Assessment and Management of Dysphagia in Acute Stroke: An Initial Service Review of International Practice. Geriatrics. 2020; 5(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics5010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleFairfield, Carol A., and David G. Smithard. 2020. "Assessment and Management of Dysphagia in Acute Stroke: An Initial Service Review of International Practice" Geriatrics 5, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics5010004
APA StyleFairfield, C. A., & G. Smithard, D. (2020). Assessment and Management of Dysphagia in Acute Stroke: An Initial Service Review of International Practice. Geriatrics, 5(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics5010004






