Outcomes of Atrioventricular Node Ablation and Pacing in Patients with Heart Failure and Atrial Fibrillation: From Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy to His Bundle Pacing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pace and Ablate Strategy in AF and HF Patients
3. Clinical Outcomes of AV Node Ablation
4. Survival Analysis Post AV Node Ablation
5. Deterioration of HF Post AV Node Ablation and RV Pacing
6. Sudden Death and Ventricular Arrhythmias Post AV Node Ablation
7. Risk of Permanent AF Progression Post AV Node Ablation
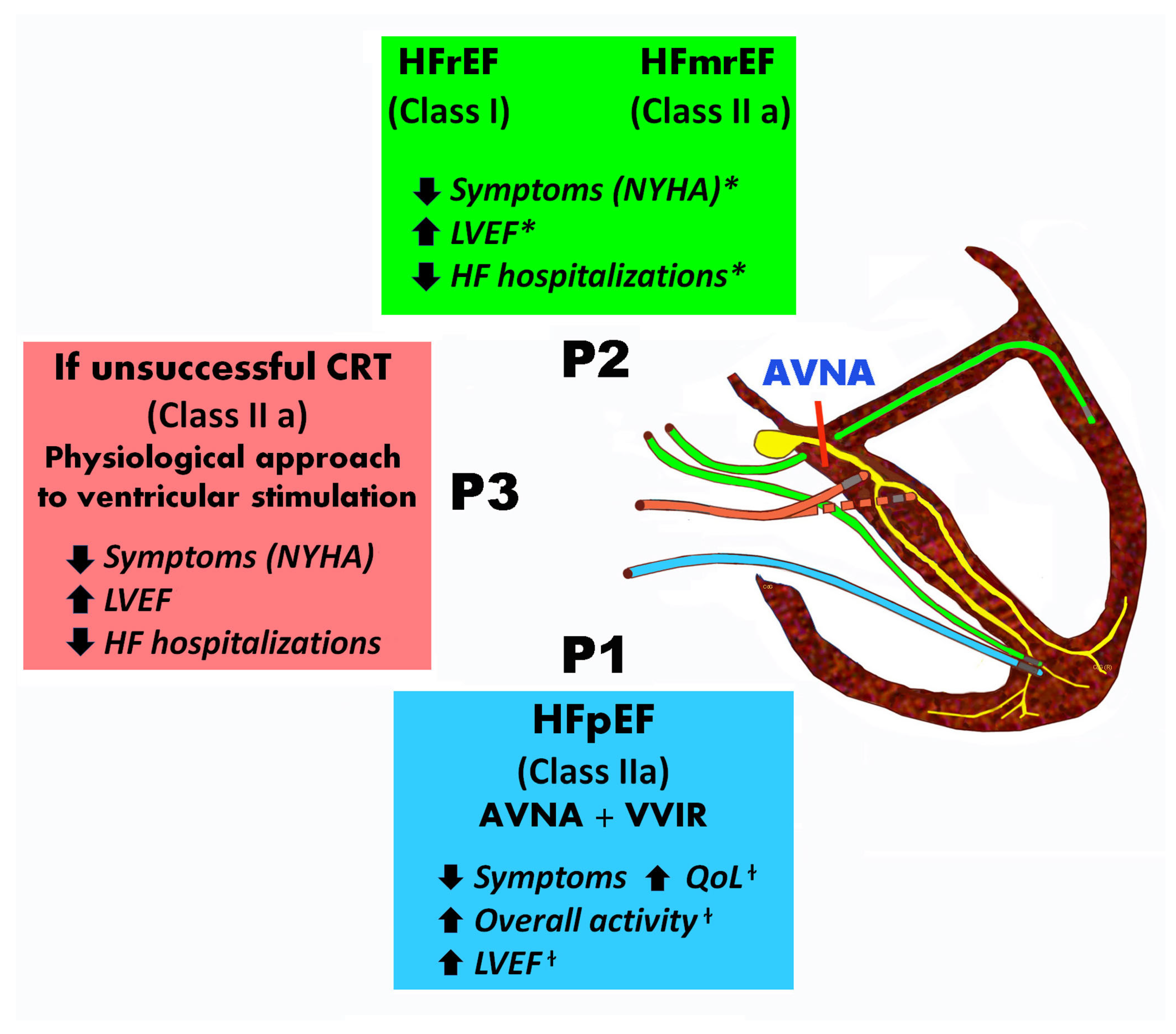
8. Biventricular Pacing in HF and AF Post AV Node Ablation
8.1. Indications of BiVPacing or CRT
8.2. His Pacing When Biventricular Pacing Fails
8.3. Left Bundle Branch Pacing (LBBP): A Promising Modality
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Chugh, S.S.; Havmoeller, R.; Narayanan, K.; Singh, D.; Rienstra, M.; Benjamin, E.J.; Gillum, R.F.; Kim, Y.H.; McAnulty, J.H., Jr.; Zheng, Z.J.; et al. Worldwide epidemiology of atrial fibrillation: A Global Burden of Disease 2010 Study. Circulation 2014, 129, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, E.J.; Muntner, P.; Alonso, A.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Carson, A.P.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Chang, A.R.; Cheng, S.; Das, S.R.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2019 Update: A Report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019, 139, e56–e528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, A.S.; Hylek, E.M.; Phillips, K.A.; Chang, Y.; Henault, L.E.; Selby, J.V.; Singer, D.E. Prevalence of diagnosed atrial fibrillation in adults: National implications for rhythm management and stroke prevention: TheAnTicoagulation and Risk Factors in Atrial Fibrillation (ATRIA) Study. JAMA 2001, 285, 2370–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyasaka, Y.; Barnes, M.E.; Gersh, B.J.; Cha, S.S.; Bailey, K.R.; Abhayaratna, W.P.; Seward, J.B.; Tsang, T.S. Secular trends in incidence of atrial fibrillation in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1980 to 2000, and implications on the projections for future prevalence. Circulation 2006, 114, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krijthe, B.P.; Kunst, A.; Benjamin, E.J.; Lip, G.Y.; Franco, O.H.; Hofman, A.; Witteman, J.C.; Stricker, B.H.; Heeringa, J. Projections on the number of individuals with atrial fibrillation in the European Union, from 2000 to 2060. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 2746–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middlekauff, H.R.; Stevenson, W.G.; Stevenson, L.W. Prognostic significance of atrial fibrillation in advanced heart failure: A study of 390 patients. Circulation 1991, 84, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, P.E.; Johnson, G.R.; Dunkman, W.B.; Fletcher, R.D.; Farrell, L.; Cohn, J.N. The influence of atrial fibrillation on prognosis in mild to moderate heart failure: The V-HeFT Studies: The V-HeFT VA Cooperative Studies Group. Circulation 1993, 87 (Suppl. S6), VI-102–VI–110. [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney, P.; Kimmel, S.; DeNofrio, D.; Wahl, P.; Loh, E. Prognostic significance of atrial fibrillation in patients at a tertiary medical center referred for heart transplantation because of severe heart failure. Am. J. Cardiol. 1999, 83, 1544–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senni, M.; Tribouilloy, C.M.; Rodeheffer, R.J.; Jacobsen, S.J.; Evans, J.M.; Bailey, K.R.; Redfield, M.M. Congestive heart failure in the community: A study of all incident cases in Olmsted County, Minnesota, in 1991. Circulation 1998, 98, 2282–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deedwania, P.C.; Singh, B.N.; Ellenbogen, K.; Fisher, S.; Fletcher, R.; Singh, S.N. Spontaneous conversion and maintenance of sinus rhythm by amiodarone in patients with heart failure and atrial fibrillation: Observations from the Veterans Affairs Congestive Heart Failure Survival Trial of Antiarrhythmic Therapy (CHF-STAT): The Department of Veterans Affairs CHF-STAT Investigators. Circulation 1998, 98, 2574–2579. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.J.; Larson, M.G.; Levy, D.; Vasan, R.S.; Leip, E.P.; Wolf, P.A.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Murabito, J.M.; Kannel, W.B.; Benjamin, E.J. Temporal relations of atrial fibrillation and congestive heart failure and their joint influence on mortality: The Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 2003, 107, 2920–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savelieva, I.; John Camm, A. Atrial fibrillation and heart failure: Natural history and pharmacological treatment. Europace 2004, 5 (Suppl. S1), S5–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, Y.M.; Redfield, M.M.; Shen, W.K.; Gersh, B.J. Atrial fibrillation and ventricular dysfunction: A vicious electromechanical cycle. Circulation 2004, 109, 2839–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindricks, G.; Potpara, T.; Dagres, N.; Arbelo, E.; Bax, J.J.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Boriani, G.; Castella, M.; Dan, G.A.; Dilaveris, P.E.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur. Heart J. 2020, 29, ehaa612. [Google Scholar]
- January, C.T.; Wann, L.S.; Alpert, J.S.; Calkins, H.; Cigarroa, J.E.; Cleveland, J.C., Jr.; Conti, J.B.; Ellinor, P.T.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Field, M.E.; et al. 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 64, e1–e76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, M.A.; Brown-Mahoney, C.; Kay, G.N.; Ellenbogen, K.A. Clinical outcomes after ablation and pacing therapy for atrial fibrillation: A meta-analysis. Circulation 2000, 101, 1138–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Sardar, P.; Lichstein, E.; Mukherjee, D.; Aikat, S. Pharmacologic rate versus rhythm-control strategies in atrial fibrillation: An updated comprehensive review and meta-analysis. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2013, 36, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueng, K.C.; Tsai, T.P.; Tsai, C.F.; Wu, D.J.; Lin, C.S.; Lee, S.H.; Chen, S.A. Acute and long-term effects of atrioventricular junction ablation and VVIR pacemaker in symptomatic patients with chronic lone atrial fibrillation and normal ventricular response. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2001, 12, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brignole, M.; Gianfranchi, L.; Menozzi, C.; Bottoni, N.; Bollini, R.; Lolli, G.; Oddone, D.; Gaggioli, G. Influence of atrioventricular junction radiofrequency ablation in patients with chronic atrial fibrillation and flutter on quality of life and cardiac performance. Am. J. Cardiol. 1994, 74, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brignole, M.; Gianfranchi, L.; Menozzi, C.; Alboni, P.; Musso, G.; Bongiorni, M.G.; Gasparini, M.; Raviele, A.; Lollim, G.; Paparella, N.; et al. Assessment of atrioventricular junction ablation and DDDR mode-switching pacemaker versus pharmacological treatment in patients with severely symptomatic paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: A randomized controlled study. Circulation 1997, 96, 2617–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, H.J.; Harris, Z.I.; Griffith, M.J.; Holder, R.L.; Gammage, M.D. Prospective randomized study of ablation and pacing versus medical therapy for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: Effects of pacing mode and mode-switch algorithm. Circulation 1999, 99, 1587–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brignole, M.; Menozzi, C.; Gianfranchi, L.; Musso, G.; Mureddu, R.; Bottoni, N.; Lolli, G. Assessment of atrioventricular junction ablation and VVIR pacemaker versus pharmacological treatment in patients with heart failure and chronic atrial fibrillation: A randomized, controlled study. Circulation 1998, 98, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weerasooriya, R.; Davis, M.; Powell, A.; Szili-Torok, T.; Shah, C.; Whalley, D.; Kanagaratnam, L.; Heddle, W.; Leitch, J.; Perks, A.; et al. The Australian Intervention Randomized Control of Rate in Atrial Fibrillation Trial (AIRCRAFT). J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003, 41, 1697–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, C.; Jahangir, A.; Friedman, P.A.; Patel, P.J.; Munger, T.M.; Rea, R.F.; Lloyd, M.A.; Packer, D.L.; Hodge, D.O.; Gersh, B.J.; et al. Long-term survival after ablation of the atrioventricular node and implantation of a permanent pacemaker in patients with atrial fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung-Lai-Wah, J.A.; Qi, A.; Uzun, O.; Humphries, K.; Humphries, K.; Kerr, C.R. Long-term survival following radiofrequency catheter ablation of atrioventricular junction for atrial fibrillation: Clinical and ablation determinants of mortality. J. Interv. Card Electrophysiol. 2002, 6, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darpo, B.; Walfridsson, H.; Aunes, M.; Bergfeldt, L.; Edvardsson, N.; Linde, C.; Lurje, L.; van der Linden, M.; Rosenqvist, M. Incidence of sudden death after radiofrequency ablation of the atrioventricular junction for atrial fibrillation. Am. J. Cardiol. 1997, 80, 1174–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brignole, M.; Pentimalli, F.; Palmisano, P.; Landolina, M.; Quartieri, F.; Occhetta, E.; Calò, L.; Mascia, G.; Mont, L.; Vernooy, K.; et al. AV junction ablation and cardiac resynchronization for patients with permanent atrial fibrillation and narrow QRS: The APAF-CRT mortality trial. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 4731–4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healey, J.S.; Yee, R.; Tang, A. Right ventricular apical pacing: A necessary evil? Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2007, 22, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tops, L.F.; Schalij, M.J.; Bax, J.J. The effects of right ventricular apical pacing on ventricular function and dyssynchrony implications for therapy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 54, 764–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderheyden, M.; Goethals, M.; Anguera, I.; Nellens, P.; Andries, E.; Brugada, J.; Brugada, P. Hemodynamic deterioration following radiofrequency ablation of the atrioventricular conduction system. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 1997, 20 Pt 1, 2422–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twidale, N.; McDonald, T.; Nave, K.; Seal, A. Comparison of the effects of AV nodal ablation versus AV nodal modification in patients with congestive heart failure and uncontrolled atrial fibrillation. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 1998, 21 Pt 1, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björkenheim, A.; Brandes, A.; Andersson, T.; Magnuson, A.; Edvardssonl, N.; Wandt, B.; Pedersen, H.S.; Poçi, D. Predictors of hospitalization for heart failure and of all-cause mortality after atrioventricular nodal ablation and right ventricular pacing for atrial fibrillation. Europace 2014, 16, 1772–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, R.H.; Wever, E.F.; Hauer, R.N.; Wittkampf, F.H.; Robles de Medina, E.O. Bradycardia dependent QT prolongation and ventricular fibrillation following catheter ablation of the atrioventricular junction with radiofrequency energy. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 1994, 17, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geelen, P.; Brugada, J.; Andries, E.; Brugada, P. Ventricular fibrillation and sudden death after radiofrequency catheter ablation of the atrioventricular junction. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 1997, 20, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, S.M.; Bergfeldt, L.; Rosenqvist, M. Long-term follow-up of patients treated by radiofrequency ablation of the atrioventricular junction. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 1995, 18, 1609–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.X.; Lee, H.C.; Hodge, D.O.; Cha, Y.M.; Friedman, P.A.; Rea, R.F.; Munger, T.M.; Jahangir, A.; Srivathsan, K.; Shen, W.K. Effect of pacing method on risk of sudden death after atrioventricular node ablation and pacemaker implantation in patients with atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm 2013, 10, 696–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cellarier, G.; Deharo, J.C.; Chalvidan, T.; Gouvernet, J.; Peyre, J.P.; Savon, N.; Djiane, P. Prolonged QT interval and altered QT/RR relation early after radiofrequency ablation of the atrioventricular junction. Am. J. Cardiol. 1999, 83, 1671–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, S.R.; Gillis, A.M.; Mitchell, B.; Wyse, D.G.; Sheldon, R.S.; ExnerM, D.V.; Morck, M.; Duff, H.J. Paced QT dispersion and QT morphology after radiofrequency atrioventricular junction ablation: Impact of left ventricular function. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2003, 26, 662–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdan, M.H.; Page, R.L.; Sheehan, C.J.; Zagrodzky, J.D.; Wasmund, S.L.; Ramaswamy, K.; Joglar, J.A.; Smith, M.L. Increased sympathetic activity after atrioventricular junction ablation in patients with chronic atrial fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2000, 36, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroga, A.; Marshall, H.J.; Clune, M.; Gammage, M.D. Ablate and pace revisited: Long-term survival and predictors of permanent atrial fibrillation. Heart 2003, 89, 1035–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianfranchi, L.; Brignole, M.; Menozzi, C.; Lolli, G.; Bottoni, N. Progression of permanent atrial fibrillation after atrioventricular junction ablation and dual-chamber pacemaker implantation in patients with paroxysmal atrial tachyarrhythmias. Am. J. Cardiol. 1998, 81, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gribbin, G.M.; Bourke, J.P.; McComb, J.M. Predictors of atrial rhythm after atrioventricular node ablation for the treatment of paroxysmal atrial arrhythmias. Heart 1998, 79, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, M.O.; Hellkamp, A.S.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; Greenspon, A.J.; Freedman, R.A.; Lee, K.L.; Lamas, G.A.; MOde Selection Trial Investigators. Adverse effect of ventricular pacing on heart failure and atrial fibrillation among patients with normal baseline QRS duration in a clinical trial of pacemaker therapy for sinus node dysfunction. Circulation 2003, 107, 2932–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brignole, M.; Menozzi, C.; Gasparini, M.; Bongiorni, M.G.; Botto, G.L.; Ometto, R.; Alboni, P.; Bruna, C.; Vincenti, A.; Verlato, R.; et al. An evaluation of the strategy of maintenance of sinus rhythm by antiarrhythmic drug therapy after ablation and pacing therapy in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Eur. Heart J. 2002, 23, 892–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkoff, B.L.; Cook, J.R.; Epstein, A.E.; Greene, H.L.; Hallstrom, A.P.; Hsia, H.; Kutalek, S.P.; Sharma, A.; Dual Chamber and VVI Implantable Defibrillator Trial Investigators. Dual-chamber pacing or ventricular backup pacing in patients with an implantable defibrillator: The Dual Chamber and VVI Implantable Defibrillator (DAVID) Trial. JAMA 2002, 288, 3115–3123. [Google Scholar]
- Puggioni, E.; Brignole, M.; Gammage, M.; Soldati, E.; Bongiorni, M.G.; Simantirakis, E.N.; Vardas, P.; Gadler, F.; Bergfeldt, L.; Tomasi, C.; et al. Acute comparative effect of right and left ventricular pacing in patients with permanent atrial fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 43, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simantirakis, E.N.; Vardakis, K.E.; Kochiadakis, G.E.; Manios, E.G.; Igoumenidis, N.E.; Brignole, M.; Vardas, P.E. Left ventricular mechanics during right ventricular apical or left ventricular-based pacing in patients with chronic atrial fibrillation after atrioventricular junction ablation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 43, 1013–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, A.R.; Greenberg, J.M.; Kanuru, N.; Kanuru, N.; Baker, C.M.; Mera, F.V.; Smith, A.L.; Langberg, J.J.; DeLurgio, D.B. Cardiac resynchronization in patients with congestive heart failure and chronic atrial fibrillation: Effect of upgrading to biventricular pacing after chronic right ventricular pacing. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2002, 39, 1258–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doshi, R.N.; Daoud, E.G.; Fellows, C.; Turk, K.; Duran, A.; Hamdan, M.H.; Pires, L.A.; PAVE Study Group. Left ventricular-based cardiac stimulation post AV nodal ablation evaluation (the PAVE study). J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2005, 16, 1160–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavrakis, S.; Garabelli, P.; Reynolds, D.W. Cardiac resynchronization therapy after atrioventricular junction ablation for symptomatic atrial fibrillation: A meta-analysis. Europace 2012, 14, 1490–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3599–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glikson, M.; Nielsen, J.C.; Kronborg, M.B.; Michowitz, Y.; Auricchio, A.; Barbash, I.M.; Barrabés, J.A.; Boriani, G.; Braunschweig, F.; Brignole, M.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines on cardiac pacing and cardiac resynchronization therapy. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3427–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.S.; Dandamudi, G.; Herweg, B.; Wilson, D.; Singh, R.; Naperkowski, A.; Koneru, J.N.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; Vijayaraman, P. Permanent His-bundle pacing as an alternative to biventricular pacing for cardiac resynchronization therapy: A multicenter experience. Heart Rhythm 2018, 15, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, P.; Casavant, D.A.; Romanyshyn, M.; Anderson, K. Permanent, direct His-bundle pacing: A novel approach to cardiac pacing in patients with normal His-Purkinje activation. Circulation 2000, 101, 869–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Su, L.; Wu, S.; Xu, L.; Xiao, F.; Zhou, X.; Ellenbogen, K.A. Benefits of permanent His bundle pacing combined with atrioventricular node ablation in atrial fibrillation patients with heart failure with both preserved and reduced left ventricular ejection fraction. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e005309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Cai, M.; Wu, S.; Wang, S.; Xu, T.; Wang, S.; Xu, T.; Vijayaraman, P.; Huang, W. Long-term performance and risk factors analysis after permanent His-bundle pacing and atrioventricular node ablation in patients with atrial fibrillation and heart failure. Europace 2020, 22 (Suppl. S2), ii19–ii26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wang, S.; Su, L.; Fu, G.; Su, Y.; Chen, K.; Zou, J.; Han, H.; Wu, S.; Sheng, X.; et al. His-bundle pacing vs biventricular pacing following atrioventricular nodal ablation in patients with atrial fibrillation and reduced ejection fraction: A multicenter, randomized, crossover study-The ALTERNATIVE-AF trial. Heart Rhythm. 2022, 19, 1948–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraman, P.; Ponnusamy, S.; Cano, Ó.; Sharma, P.S.; Naperkowski, A.; Subsposh, F.A.; Moskal, P.; Bednarek, A.; Dal Forno, A.R.; Young, W.; et al. Left Bundle Branch Area Pacing for Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy: Results From the International LBBAP Collaborative Study Group. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2021, 7, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, M.; Shi, R.; Kramer, D.B.; Riad, O.; Hunnybun, D.; Jarman, J.W.E.; Foran, J.; Cantor, E.; Markides, V.; Wong, T. Conduction system pacing learning curve: Left bundle pacing compared to His bundle pacing. Int. J. Cardiol. Heart Vasc. 2023, 44, 101171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanovski, M.; Mrak, M.; Mežnar, A.Z. Žižek, D. Biventricular versus Conduction System Pacing after Atrioventricular Node Ablation in Heart Failure Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2022, 9, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| First Author | Year of Publication | Design | Number of Patients | Highlights |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wood et al. [16] | 2000 | Meta-analysis | 1181 | ↑ QOL ↑ Exercise duration ↓ Symptoms ↓ Healthcare use ↑ Cardiac function |
| Chatarjee et al. [17] | 2013 | Meta-analysis | 7867 | ↑ QOL ↓ Symptoms ↑ LVEF |
| Ueng et al. [18] | 2001 | AVNA + VVIR pacing vs drug therapy | 50 | ↑ QOL ↑ Overall activity ↓ Overall symptoms ↑ LVEF |
| Brignole et al. [19] | 1994 | AVNA + pacing vs pacing | 23 | ↓ Symptoms ↑ QOL ↑ LV function |
| Brignole et al. [20] | 1997 | AVNA + DDDR pacemaker vs pharmaceutical drugs | 43 | ↓ Palpitations ↓ Effort dyspnea ↓ Exercise intolerance ↓ Easy fatigue |
| Marshall et al. [21] | 1999 | AVNA + DDDR/MS pacing vs drug therapy | 56 | ↓ Overall Symptoms ↓ Palpitations ↓ Dyspnea ↑ Psychological general well-being |
| Brignole et al. [22] | 1998 | AVNA + VVIR pacing vs drug therapy | 66 | ↓ Palpitations ↓ Exercise intolerance ↓ Effort dyspnea ↓ Chest discomfort ↓ Easy fatigue |
| Weerasooriya et al. [23] | 2003 | AVNA + pacing vs medication | 99 | ↓ Peak ventricular rate during exercise and daily activity ↓ Symptoms ↑ QOL |
| First Author | Year of Publication | Number of Patients | Design | Highlights |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Puggioni et al. [46] | 2004 | 44 | LV pacing vs. RV pacing + AVNA | ↑ LVEF ↓ MR |
| Simantirakis et al. [47] | 2004 | 12 | LV-based pacing vs. RV pacing + AVNA | ↑ LV contractility |
| Leon et al. [48] | 2002 | 20 | BiV pacing vs. RV pacing + AVNA | ↑ LVEF ↓ LV diastolic diameter ↓ End-systolic diameter ↓ Number of hospitalizations NYHA class improved |
| Doshi et al. [49] | 2005 | 184 | BiV pacing vs. RV pacing + AVNA | ↑ 6-min walk distance ↑ LVEF |
| Stavrakis et al. [50] | 2012 | 68 | CRT vs. RV pacing + AVNA (Meta-analysis) | ↓ HF hospitalizations ↑ LVEF |
| Class | Level | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Class I | A | CRT rather than RV pacing is recommended for patients with HFrEF (EF < 40%) irrespective of NYHA class or QRS width, who are candidates for ventricular pacing for high degree AV block. Patients with AF are also included in this recommendation. |
| B | CRT is recommended in patients withHFrEF, symptomatic AFand uncontrolled heart rate who are eligible for AVJ ablation. | |
| Class IIa | B | AVJ ablation should be added in patients with HF and permanent AF who are eligible for CRT, in case of incomplete biventricular pacing (<90–95%) because of conducted AF. |
| B | RV pacing should be considered in patients with HFpEF, symptomatic AF and uncontrolled heart rate who are going to undergo AVJ ablation. | |
| Β | Upgrading from RV pacing to CRT should be considered in patients with conventional pacemaker or ICD who develop HF with LVEF ≤ 35% despite the optimal medical treatment and have a significant proportion of RV pacing. | |
| C | CRT rather than standard RV pacing should be considered in patients with HFmrEF, symptomatic AF and uncontrolled heart rate who are candidates for AVJ ablation. | |
| C | CRT should be considered for patients with HF and LVEF ≤ 35% who remain in NYHA class III/IV despite the optimal medical treatment and have AF with inherent QRS ≥ 130 ms. | |
| Class IIb | B | CRT may be considered in patients with HFpEF, symptomatic AF and uncontrolled heart rate who are candidates for AVJ ablation. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koniari, I.; Gerakaris, A.; Kounis, N.; Velissaris, D.; Rao, A.; Ainslie, M.; Adlan, A.; Plotas, P.; Ikonomidis, I.; Mplani, V.; et al. Outcomes of Atrioventricular Node Ablation and Pacing in Patients with Heart Failure and Atrial Fibrillation: From Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy to His Bundle Pacing. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2023, 10, 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd10070272
Koniari I, Gerakaris A, Kounis N, Velissaris D, Rao A, Ainslie M, Adlan A, Plotas P, Ikonomidis I, Mplani V, et al. Outcomes of Atrioventricular Node Ablation and Pacing in Patients with Heart Failure and Atrial Fibrillation: From Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy to His Bundle Pacing. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease. 2023; 10(7):272. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd10070272
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoniari, Ioanna, Andreas Gerakaris, Nicholas Kounis, Dimitrios Velissaris, Archana Rao, Mark Ainslie, Ahmed Adlan, Panagiotis Plotas, Ignatios Ikonomidis, Virginia Mplani, and et al. 2023. "Outcomes of Atrioventricular Node Ablation and Pacing in Patients with Heart Failure and Atrial Fibrillation: From Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy to His Bundle Pacing" Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 10, no. 7: 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd10070272
APA StyleKoniari, I., Gerakaris, A., Kounis, N., Velissaris, D., Rao, A., Ainslie, M., Adlan, A., Plotas, P., Ikonomidis, I., Mplani, V., Hung, M.-Y., de Gregorio, C., Kolettis, T., & Gupta, D. (2023). Outcomes of Atrioventricular Node Ablation and Pacing in Patients with Heart Failure and Atrial Fibrillation: From Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy to His Bundle Pacing. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease, 10(7), 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd10070272













