Nanopore Data-Driven T2T Genome Assemblies of Colletotrichum lini Strains
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fungal Material
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. DNA Library Preparation and Sequencing on the Oxford Nanopore Technologies and Illumina Platforms
2.4. Genome Assembly and Polishing
2.5. Genome Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Virulence Level of Four C. lini Strains
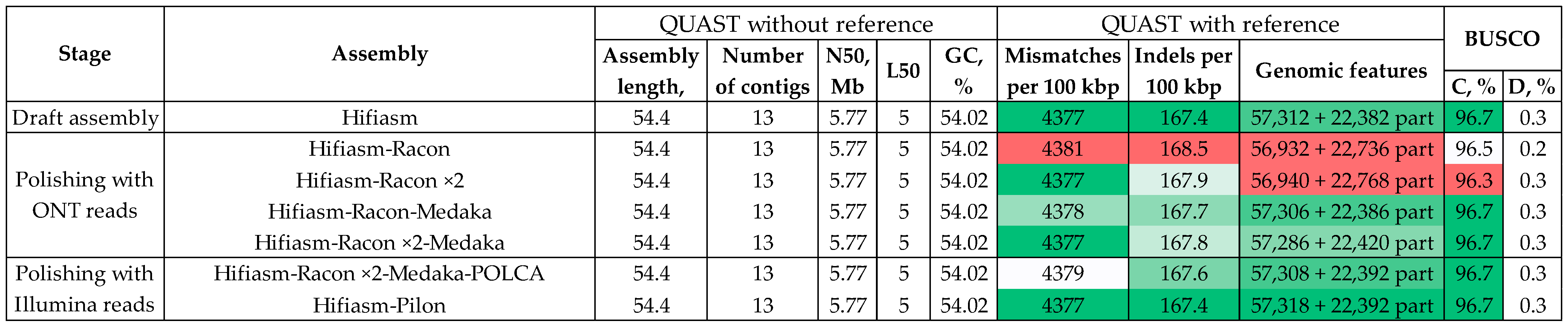
3.2. Assembly and Polishing of Four C. lini Genomes
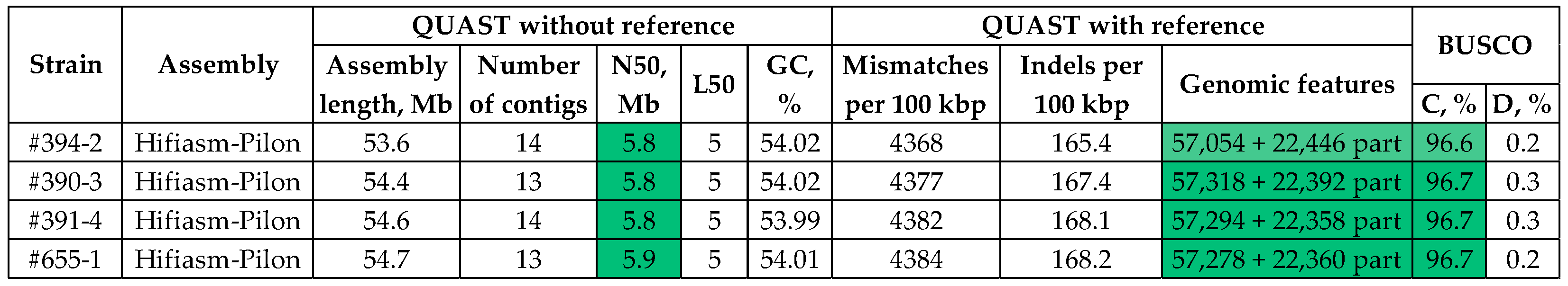
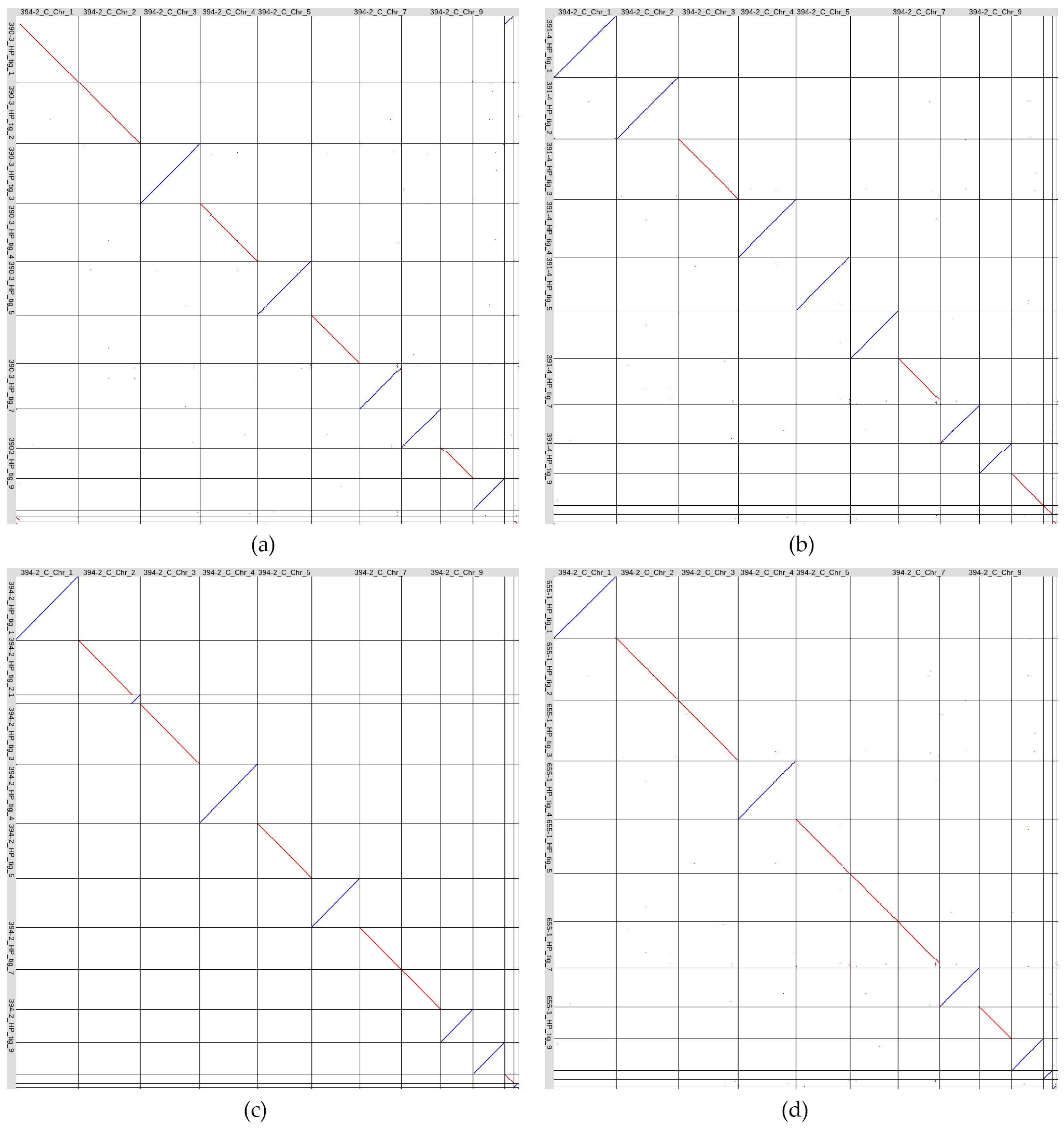
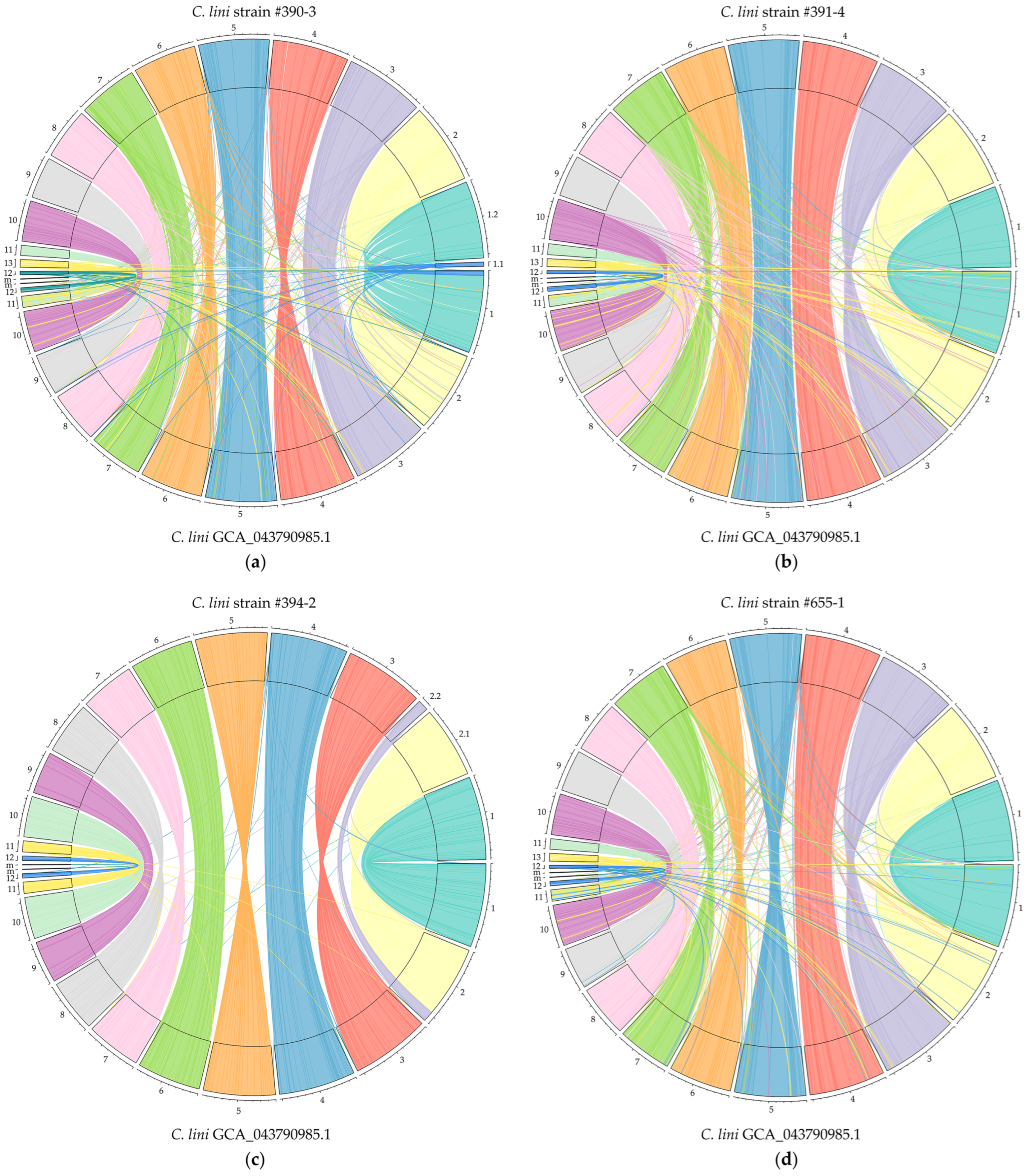
3.3. Comparative Analyses of Four C. lini Genome Assemblies
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sundström, J.F.; Albihn, A.; Boqvist, S.; Ljungvall, K.; Marstorp, H.; Martiin, C.; Nyberg, K.; Vågsholm, I.; Yuen, J.; Magnusson, U. Future threats to agricultural food production posed by environmental degradation, climate change, and animal and plant diseases—A risk analysis in three economic and climate settings. Food Secur. 2014, 6, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, L.M.; Booker, H.; Siloto, R.M.P.; Jhala, A.J.; Weselake, R.J. Chapter 6—Flax (Linum usitatissimum L.). In Industrial Oil Crops; McKeon, T.A., Hayes, D.G., Hildebrand, D.F., Weselake, R.J., Eds.; AOCS Press: Champaign, IL, USA, 2016; pp. 157–194. [Google Scholar]
- Langyan, S.; Kaur, V.; Kumar, A. Chapter 1—Overview of linseed as multipurpose-multisector crop. In Linseed: A Multipurpose-Multisector Crop of Industrial Significance; Langyan, S., Kumar, A., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Moyse, J.; Lecomte, S.; Marcou, S.; Mongelard, G.; Gutierrez, L.; Höfte, M. Overview and management of the most common eukaryotic diseases of flax (Linum usitatissimum). Plants 2023, 12, 2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, K.Y. Principal diseases of flax. In Flax: The Genus Linum; Muir, A.D., Westcott, N.D., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; pp. 92–123. [Google Scholar]
- Gruzdevienė, E.; Brazauskienė, I.; Repečkienė, J.; Lugauskas, A. The occurrence of pathogenic fungi during flax growing season in Central Lithuania. J. Plant Prot. Res. 2008, 48, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, K.D.; Cai, L.; McKenzie EH, C.; Yang, Y.L.; Zhang, J.Z.; Prihastuti, H. Colletotrichum: A catalogue of confusion. Fungal Divers. 2009, 39, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Berbee, M.L. The phylogeny of plant and animal pathogens in the Ascomycota. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2001, 59, 165–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Nadales, E.; Almeida Nogueira, M.F.; Baldin, C.; Castanheira, S.; El Ghalid, M.; Grund, E.; Lengeler, K.; Marchegiani, E.; Mehrotra, P.V.; Moretti, M.; et al. Fungal model systems and the elucidation of pathogenicity determinants. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2014, 70, 42–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amezrou, R.; Ducasse, A.; Compain, J.; Lapalu, N.; Pitarch, A.; Dupont, L.; Confais, J.; Goyeau, H.; Kema, G.H.J.; Croll, D.; et al. Quantitative pathogenicity and host adaptation in a fungal plant pathogen revealed by whole-genome sequencing. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercier, A.; Simon, A.; Lapalu, N.; Giraud, T.; Bardin, M.; Walker, A.-S.; Viaud, M.; Gladieux, P. Population genomics reveals molecular determinants of specialization to tomato in the polyphagous fungal pathogen Botrytis cinerea in France. Phytopathology® 2021, 111, 2355–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.; Nandineni, M.R. Genome sequencing and comparative genomics reveal a repertoire of putative pathogenicity genes in chilli anthracnose fungus Colletotrichum truncatum. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witte, T.E.; Villeneuve, N.; Boddy, C.N.; Overy, D.P. Accessory chromosome-acquired secondary metabolism in plant pathogenic fungi: The evolution of biotrophs into host-specific pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 664276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertazzoni, S.; Williams, A.H.; Jones, D.A.; Syme, R.A.; Tan, K.-C.; Hane, J.K. Accessories make the outfit: Accessory chromosomes and other dispensable DNA regions in plant-pathogenic fungi. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact.® 2018, 31, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Huang, R.; Ren, J.; Tang, L.; Huang, S.; Chen, X.; Fan, J.; Li, B.; Wang, Q.; Hsiang, T.; et al. The evolution of mini-chromosomes in the fungal genus Colletotrichum. mBio 2023, 14, e0062923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aylward, J.; Steenkamp, E.T.; Dreyer, L.L.; Roets, F.; Wingfield, B.D.; Wingfield, M.J. A plant pathology perspective of fungal genome sequencing. IMA Fungus 2017, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Meng, Z.; Xu, X.; Wang, L.; Zhao, K.; Zhu, X.; Qiao, Q.; Ge, Y.; Mao, L.; Cui, L. Systematic benchmarking of nanopore Q20+ kit in SARS-CoV-2 whole genome sequencing. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 973367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Li, H.; Jiang, M.; Hou, H.; Gao, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, J.; Peng, K.; Liu, Y.-X. Nanopore sequencing: Flourishing in its teenage years. J. Genet. Genom. 2024, 51, 1361–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Yang, J.; Ding, J.; Duan, C.; Zhao, W.; Peng, Y.-L.; Bhadauria, V. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated deletion of large chromosomal segments identifies a minichromosome modulating the Colletotrichum graminicola virulence on maize. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 245, 125462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhadauria, V.; MacLachlan, R.; Pozniak, C.; Cohen-Skalie, A.; Li, L.; Halliday, J.; Banniza, S. Genetic map-guided genome assembly reveals a virulence-governing minichromosome in the lentil anthracnose pathogen Colletotrichum lentis. New Phytol. 2019, 221, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaumann, P.-L.; Koch, C. The many questions about mini chromosomes in Colletotrichum spp. Plants 2020, 9, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Zhong, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Stukenbrock, E.H.; Tang, B.; Yang, N.; Baroncelli, R.; Peng, L.; Liu, Z.; et al. Loss of the accessory chromosome converts a pathogenic tree-root fungus into a mutualistic endophyte. Plant Commun. 2024, 5, 100672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsushima, A.; Gan, P.; Kumakura, N.; Narusaka, M.; Takano, Y.; Narusaka, Y.; Shirasu, K. Genomic plasticity mediated by transposable elements in the plant pathogenic fungus Colletotrichum higginsianum. Genome Biol. Evol. 2019, 11, 1487–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapalu, N.; Simon, A.; Lu, A.; Plaumann, P.-L.; Amselem, J.; Pigné, S.; Auger, A.; Koch, C.; Dallery, J.-F.; O’Connell, R.J. Complete genome of the Medicago anthracnose fungus, Colletotrichum destructivum, reveals a mini-chromosome-like region within a core chromosome. Microb. Genom. 2024, 10, 001283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Y.; Wang, L.; Cao, J.; Feng, H.; Li, K.; Wang, Y.; Dong, S.; Ye, W.; et al. Complete telomere-to-telomere genomes uncover virulence evolution conferred by chromosome fusion in oomycete plant pathogens. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrabi, R.; Bahkali, A.H.; Abd-Elsalam, K.A.; Moslem, M.; Ben M’Barek, S.; Gohari, A.M.; Jashni, M.K.; Stergiopoulos, I.; Kema, G.H.J.; de Wit, P.J.G.M. Horizontal gene and chromosome transfer in plant pathogenic fungi affecting host range. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 35, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorianinova, E.M.; Sigova, E.A.; Mollaev, T.D.; Rozhmina, T.A.; Kudryavtseva, L.P.; Novakovskiy, R.O.; Turba, A.A.; Zhernova, D.A.; Borkhert, E.V.; Pushkova, E.N.; et al. Comparative genomic analysis of Colletotrichum lini strains with different virulence on flax. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigova, E.A.; Dvorianinova, E.M.; Rozhmina, T.A.; Kudryavtseva, L.P.; Zhernova, D.A.; Kaplun, A.M.; Pavlova, V.A.; Bodrov, Y.V.; Arkhipov, A.A.; Borkhert, E.V.; et al. Complete annotated genome assembly of flax pathogen Colletotrichum lini. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigova, E.A.; Pushkova, E.N.; Rozhmina, T.A.; Kudryavtseva, L.P.; Zhuchenko, A.A.; Novakovskiy, R.O.; Zhernova, D.A.; Povkhova, L.V.; Turba, A.A.; Borkhert, E.V.; et al. Assembling quality genomes of flax fungal pathogens from Oxford Nanopore Technologies data. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krasnov, G.S.; Pushkova, E.N.; Novakovskiy, R.O.; Kudryavtseva, L.P.; Rozhmina, T.A.; Dvorianinova, E.M.; Povkhova, L.V.; Kudryavtseva, A.V.; Dmitriev, A.A.; Melnikova, N.V. High-quality genome assembly of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lini. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautiainen, M.; Nurk, S.; Walenz, B.P.; Logsdon, G.A.; Porubsky, D.; Rhie, A.; Eichler, E.E.; Phillippy, A.M.; Koren, S. Telomere-to-telomere assembly of diploid chromosomes with Verkko. Nat. Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 1474–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Jarvis, E.D.; Fedrigo, O.; Koepfli, K.-P.; Urban, L.; Gemmell, N.J.; Li, H. Haplotype-resolved assembly of diploid genomes without parental data. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 1332–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Le, S.; Li, Y.; Hu, F. SeqKit: A cross-platform and ultrafast toolkit for FASTA/Q file manipulation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanojević, D.; Lin, D.; Nurk, S.; Florez de Sessions, P.; Šikić, M. Telomere-to-telomere phased genome assembly using HERRO-corrected simplex Nanopore reads. bioRxiv 2024, 2024-05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaser, R.; Sović, I.; Nagarajan, N.; Šikić, M. Fast and accurate de novo genome assembly from long uncorrected reads. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Fan, J.; Sun, Z.; Liu, S. NextPolish: A fast and efficient genome polishing tool for long-read assembly. Bioinformatics 2019, 36, 2253–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, B.J.; Abeel, T.; Shea, T.; Priest, M.; Abouelliel, A.; Sakthikumar, S.; Cuomo, C.A.; Zeng, Q.; Wortman, J.; Young, S.K.; et al. Pilon: An integrated tool for comprehensive microbial variant detection and genome assembly improvement. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimin, A.V.; Salzberg, S.L. The genome polishing tool POLCA makes fast and accurate corrections in genome assemblies. PLOS Comput. Biol. 2020, 16, e1007981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouras, G.; Judd, L.M.; Edwards, R.A.; Vreugde, S.; Stinear, T.P.; Wick, R.R. How low can you go? Short-read polishing of Oxford Nanopore bacterial genome assemblies. Microb. Genom. 2024, 10, 001254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H. New strategies to improve minimap2 alignment accuracy. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 4572–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H. Aligning sequence reads, clone sequences and assembly contigs with BWA-MEM. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1303.3997. [Google Scholar]
- Simão, F.A.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Ioannidis, P.; Kriventseva, E.V.; Zdobnov, E.M. BUSCO: Assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness with single-copy orthologs. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3210–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, A.; Saveliev, V.; Vyahhi, N.; Tesler, G. QUAST: Quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koren, S.; Walenz, B.P.; Berlin, K.; Miller, J.R.; Bergman, N.H.; Phillippy, A.M. Canu: Scalable and accurate long-read assembly via adaptive k-mer weighting and repeat separation. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 722–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.; Gu, L.; Eils, R.; Schlesner, M.; Brors, B. Circlize implements and enhances circular visualization in R. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2811–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, B.; Zhan, Z.; Wang, Y. A chromosome-level genome assembly of Prosopocoilus inquinatus Westwood, 1848 (Coleoptera: Lucanidae). Sci. Data 2024, 11, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Yu, H.; Jia, Y.; Dong, Q.; Steinberg, C.; Alabouvette, C.; Edel-Hermann, V.; Kistler, H.C.; Ye, K.; Ma, L.-J.; et al. Chromosome-scale genome assembly of Fusarium oxysporum strain Fo47, a fungal endophyte and biocontrol agent. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2020, 33, 1108–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Zheng, X.; Kang, Z.; Lu, P.; Zhang, J.; Cao, P.; Chen, Q.; Liu, X. A chromosome-level haplotype-resolved genome assembly of oriental tobacco budworm (Helicoverpa assulta). Sci. Data 2024, 11, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Xue, Y.; Liu, X.; Ding, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, J.; Sun, C.; Tang, J.; et al. A near-complete chromosome-level genome assembly of looseleaf lettuce (Lactuca sativa var. crispa). Sci. Data 2024, 11, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Concepcion, G.T.; Feng, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, H. Haplotype-resolved de novo assembly using phased assembly graphs with hifiasm. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Chu, Y.; Guo, S.; Hu, J.; Li, R.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, X.; Du, Z.; Zhao, L.; Yu, W.; et al. T2T-YAO: A telomere-to-telomere assembled diploid reference genome for Han Chinese. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2023, 21, 1085–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguinkal, J.A.; Zoclanclounon, Y.A.B.; Brunner, R.M.; Chen, Y.; Goldammer, T. Haplotype-resolved and near-T2T genome assembly of the African catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Sci. Data 2024, 11, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holley, G.; Beyter, D.; Ingimundardottir, H.; Møller, P.L.; Kristmundsdottir, S.; Eggertsson, H.P.; Halldorsson, B.V. Ratatosk: Hybrid error correction of long reads enables accurate variant calling and assembly. Genome Biol. 2021, 22, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmela, L.; Rivals, E. LoRDEC: Accurate and efficient long read error correction. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3506–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorianinova, E.M.; Pushkova, E.N.; Bolsheva, N.L.; Borkhert, E.V.; Rozhmina, T.A.; Zhernova, D.A.; Novakovskiy, R.O.; Turba, A.A.; Sigova, E.A.; Melnikova, N.V.; et al. Genome of Linum usitatissimum convar. crepitans expands the view on the section Linum. Front Genet 2023, 14, 1269837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhadauria, V.; Zhang, M.; Ma, W.; Yang, J.; Zhao, W.; Peng, Y.-L. The hidden truths of fungal virulence and adaptation on hosts: Unraveling the conditional dispensability of minichromosomes in the hemibiotrophic Colletotrichum pathogens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, A.S.; Azinheira, H.G.; Cabral, A.; Tavares, S.; Tavares, D.; Castro, M.; Várzea, V.; Silva, M.C.; Abranches, R.; Loureiro, J.; et al. Cytogenomic characterization of Colletotrichum kahawae, the causal agent of coffee berry disease, reveals diversity in minichromosome profiles and genome size expansion. Plant Pathol. 2016, 65, 968–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Strain | Basecalled Data Volume, Gb | Basecalled Data N50, kb | Coverage with Basecalled Data | Corrected Data Volume, Gb | Coverage with Corrected Data | Ultra-Long Read (>50 kb) Data Volume, Gb | Coverage with Ultra-Long Reads |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #394-2 | 2.4 | 14.1 | 45× | 1.4 | 25× | 0.09 | 1.5× |
| #390-3 | 10.0 | 13.0 | 180× | 5.4 | 100× | 0.14 | 2.5× |
| #391-4 | 4.0 | 14.0 | 75× | 2.0 | 35× | 0.15 | 2.5× |
| #655-1 | 6.9 | 16.3 | 125× | 4.1 | 75× | 0.29 | 5.0× |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sigova, E.A.; Dvorianinova, E.M.; Arkhipov, A.A.; Rozhmina, T.A.; Kudryavtseva, L.P.; Kaplun, A.M.; Bodrov, Y.V.; Pavlova, V.A.; Borkhert, E.V.; Zhernova, D.A.; et al. Nanopore Data-Driven T2T Genome Assemblies of Colletotrichum lini Strains. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10120874
Sigova EA, Dvorianinova EM, Arkhipov AA, Rozhmina TA, Kudryavtseva LP, Kaplun AM, Bodrov YV, Pavlova VA, Borkhert EV, Zhernova DA, et al. Nanopore Data-Driven T2T Genome Assemblies of Colletotrichum lini Strains. Journal of Fungi. 2024; 10(12):874. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10120874
Chicago/Turabian StyleSigova, Elizaveta A., Ekaterina M. Dvorianinova, Alexander A. Arkhipov, Tatiana A. Rozhmina, Ludmila P. Kudryavtseva, Antoniy M. Kaplun, Yakov V. Bodrov, Valeria A. Pavlova, Elena V. Borkhert, Daiana A. Zhernova, and et al. 2024. "Nanopore Data-Driven T2T Genome Assemblies of Colletotrichum lini Strains" Journal of Fungi 10, no. 12: 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10120874
APA StyleSigova, E. A., Dvorianinova, E. M., Arkhipov, A. A., Rozhmina, T. A., Kudryavtseva, L. P., Kaplun, A. M., Bodrov, Y. V., Pavlova, V. A., Borkhert, E. V., Zhernova, D. A., Pushkova, E. N., Melnikova, N. V., & Dmitriev, A. A. (2024). Nanopore Data-Driven T2T Genome Assemblies of Colletotrichum lini Strains. Journal of Fungi, 10(12), 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10120874










