Characterization and Fungicide Sensitivity of Phaeosphaeriopsis obtusispora That Causes Marginal Leaf Blight in Agave hybrid H.11648
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection and Isolation of Samples
2.2. Pathogenicity Determination
2.3. Morphological Observations of Pathogens
2.4. DNA Extraction and Multiple Sequence Analysis of Pathogens
2.5. Determination of the Optimal Growth Conditions of the Pathogen
2.6. Sensitivity of Mycelial Growth to Twelve Fungicides
2.7. Data Analyses
3. Results
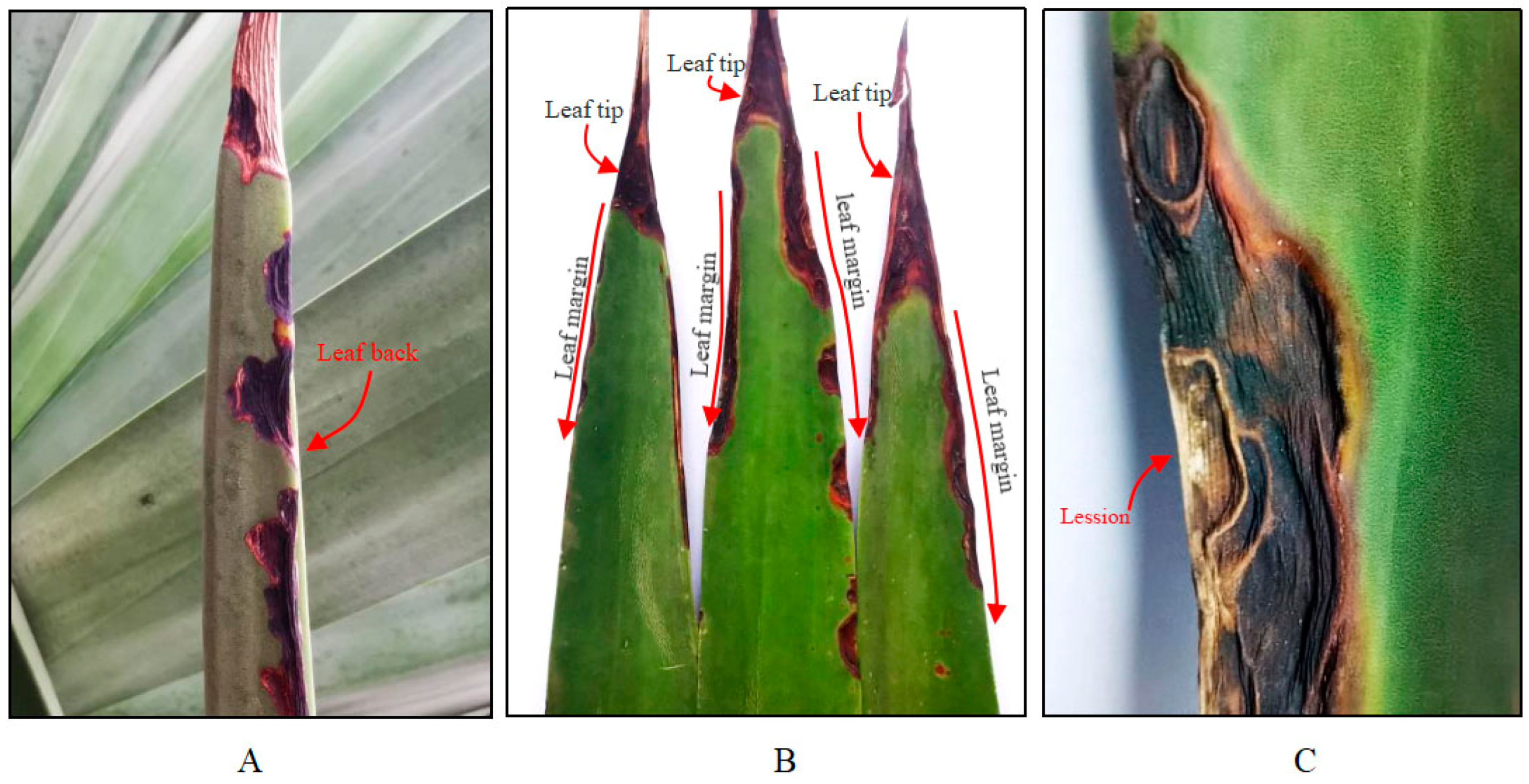
3.1. Field Symptoms
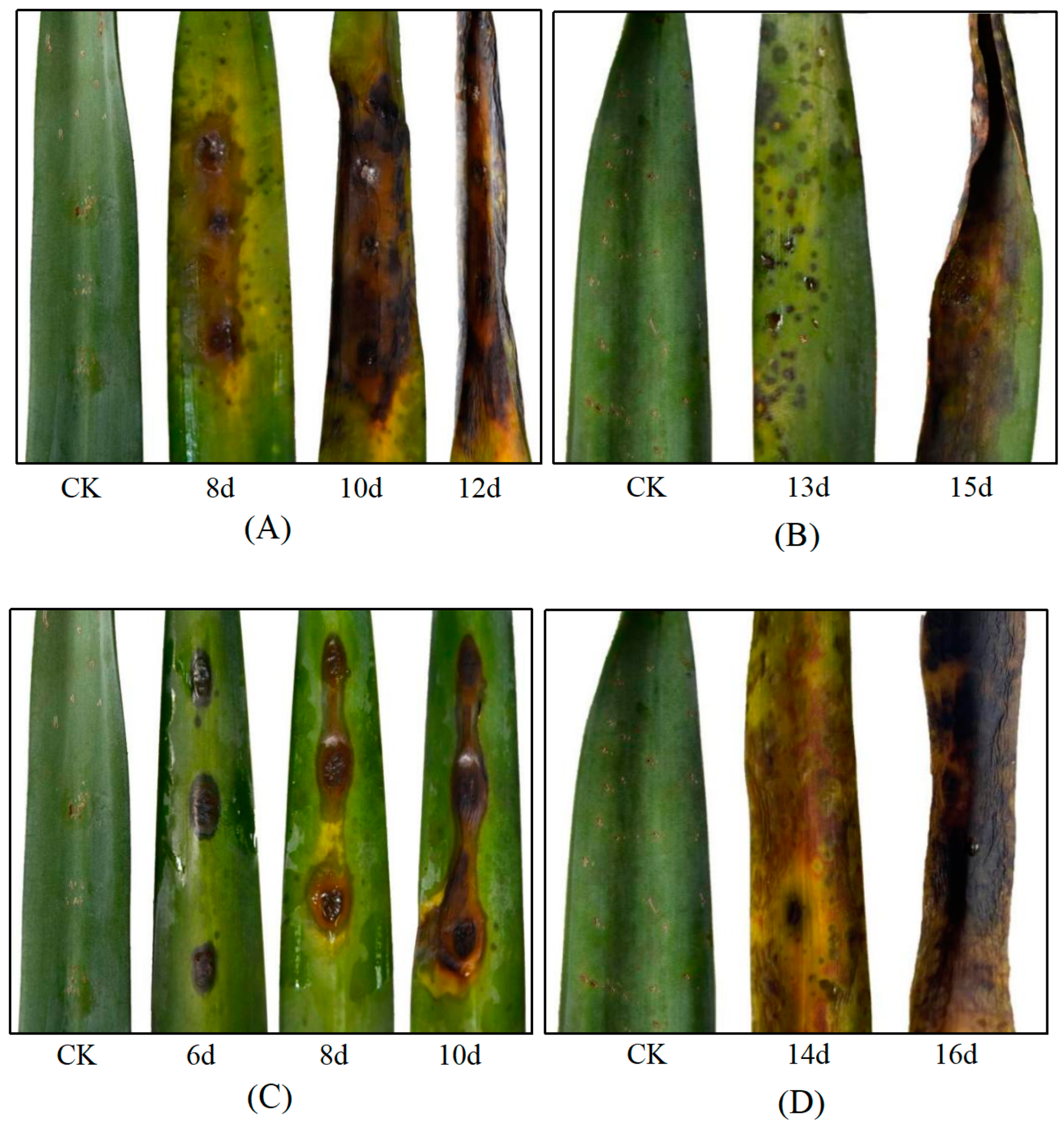
3.2. Pathogen Isolation and Pathogenicity Determination
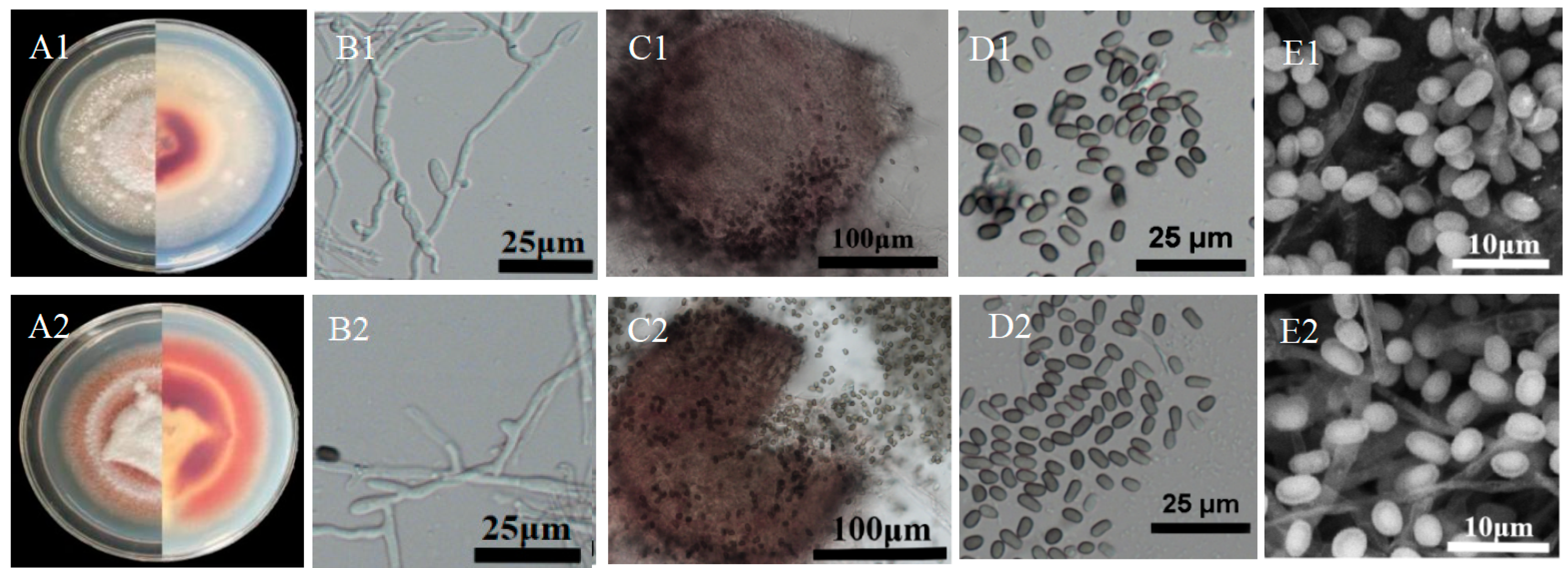
3.3. Morphologic Characteristics
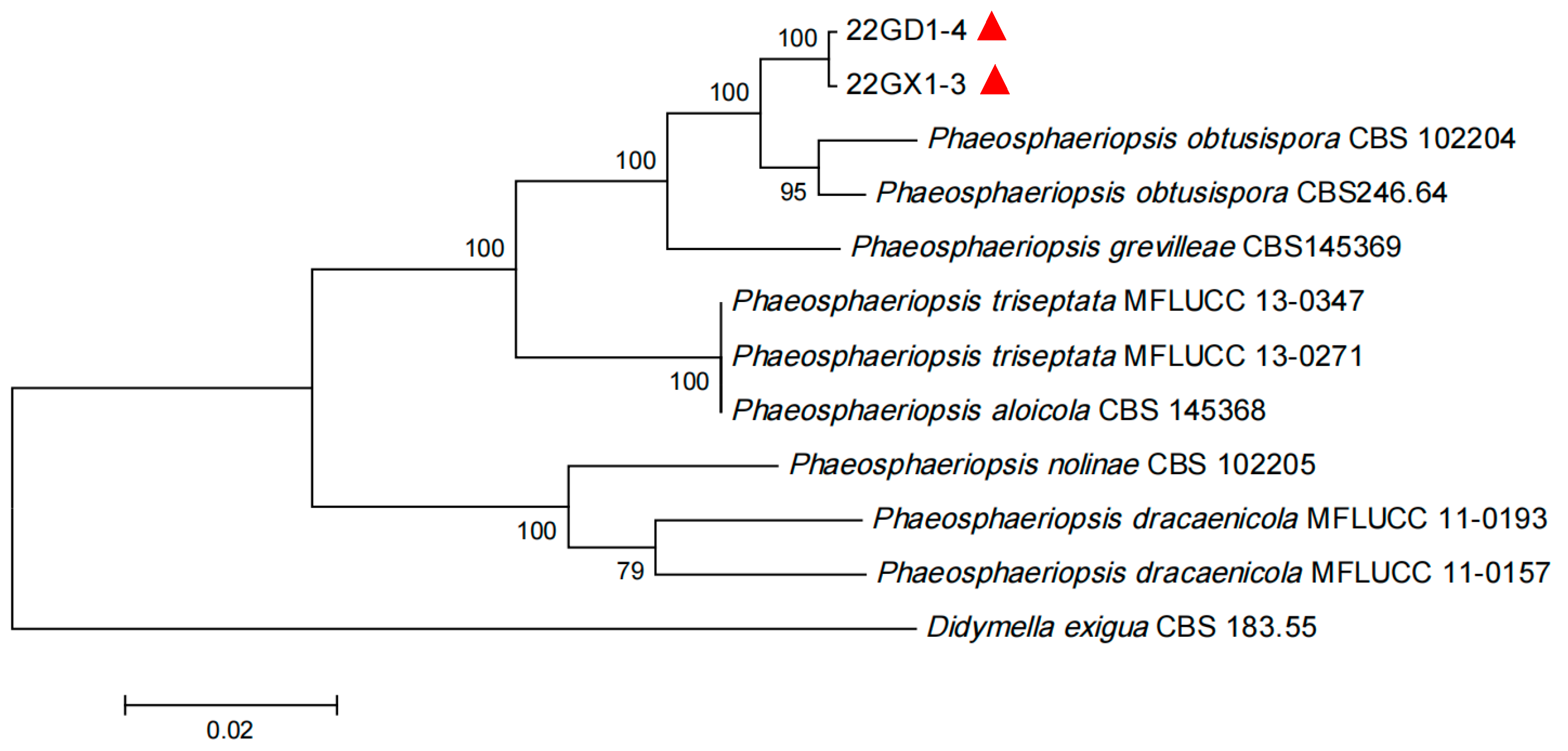
3.4. Sequence and Phylogenetic Analysis
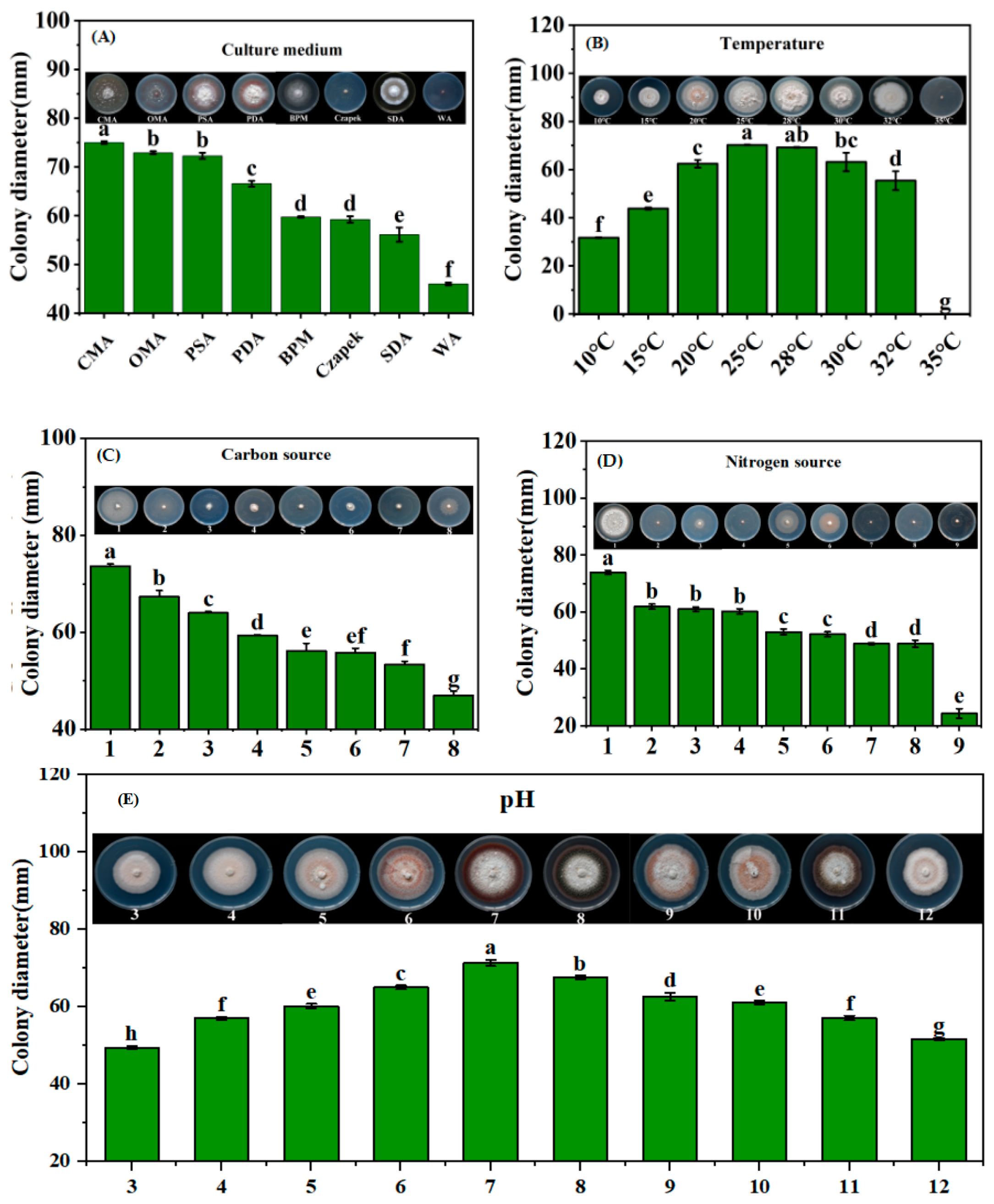
3.5. Biological Characterization of Phaeosphaeriopsis obtusispora
3.6. Sensitivity of P. obtusispora Strain to Fungicides
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duarte, E.A.A.; Damasceno, C.L.; de Oliveira, T.A.S.; Barbosa, L.O.; Martins, F.M.; de Queiroz Silva, J.R.; de Lima, T.E.F.; da Silva, R.M.; Kato, R.B.; Bortolini, D.E.; et al. Putting the mess in Order: Aspergillus welwitschiae (and Not A. niger) is the etiological agent of sisal bole rot disease in Brazil. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza, J.T.; Silva, A.C.M.; de Jesus Santos, A.F.; Santos, P.O.; Alves, P.S.; Cruz-Magalhães, V.; Marbach, P.A.S.; Loguercio, L.L. Endophytic bacteria isolated from both healthy and diseased Agave sisalana plants are able to control the bole rot disease. Biol. Control 2021, 157, 104575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raya, F.T.; Marone, M.P.; Carvalho, L.M.; Rabelo, S.C.; de Paula, M.S.; Campanari, M.F.Z.; Freschi, L.; Mayer, J.L.S.; Silva, O.; Mieczkowski, P.; et al. Extreme physiology: Biomass and transcriptional profiling of three abandoned Agave cultivars. Ind. Crop Prod. 2021, 172, 114043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wu, W.; Xi, J.; Chen, H.; He, C.; Li, Y.; Zheng, J.; Hu, J.S.; Yi, K. Detection and molecular identification of a 16SrI group phytoplasma associated with sisal purple leafroll disease. Plant Prot. Sci. 2023, 59, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.; Wang, G.; Wu, W.; Xi, J.; Chen, H.; Huang, X.; Tan, S.; Liang, Y.; Yi, K. Identification of Clonostachys rogersoniana as a causal agent of sisal leaf blight disease in South China. J. Phytopathol. 2023, 171, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zheng, H.Y.; Zhong, X.; Ma, C.Y. Tropical Crops Industry Development Report; China Tropical Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2019; pp. 147–156. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.M.; Luo, P.; Guo, C.M.; Li, J.Z.; Liu, Q.L.; Chen, H.L.; Zhang, S.Q.; Zheng, J.L.; Jiang, C.J.; Dai, Z.Z.; et al. AFLP analysis and zebra disease resistance identi fication of 40 sisal genotypes in China. Rep. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 39, 6379–6385. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, H.H.; Long, L.Y.; Huang, S.P.; Mao, L.Y.; Huang, Q.W.; Wang, L.P.; Li, J.X. Black spot caused by Neoscytalidium dimidiatum on sisal in Guangxi, China. Plant Dis. 2021, 105, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Wu, W.; Tan, S.; Liang, Y.; He, C.; Chen, H.; Huang, X.; Yi, K. Development of a specific nested pcr assay for the detection of 16sri group phytoplasmas associated with sisal purple leafroll disease in sisal plants and mealybugs. Plants 2022, 11, 2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, E.L. Identification of Pathogens of Two New Diseases in Sisal, Determination of Fungicide Sensitivity, and Establishment of a Duplex PCR Detection System. Master’s Thesis, Guizhou University, Guiyang, China, July 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Verrier, J.; Monod, M. Diagnosis of dermatophytosis using molecular biology. Mycopathologia 2017, 182, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clasen, B.E.; Silveira, A.D.; Baldoni, D.B.; Montagner, D.F.; Jacques, R.J.S.; Antoniolli, Z.I. Characterization of Ectomycorrhizal species through molecular biology tools and morphotyping. Sci. Agric. 2018, 75, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Tian, M.; Peng, Y.; Qin, N.; Lü, H.; Ren, L.; Zhao, X. First Report on Choanephora cucurbitarum Causing Choanephora Rot in Chenopodium Plants and Its Sensitivity to Fungicide. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Yang, C.; Jin, M.; Wei, L.; Yang, L.; Zhou, J. Identification and biological characterization of a new pathogen that causes potato scab in Gansu Province, China. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 161, 105276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, P.A.; Lipps, P.E.; Hershman, D.E.; McMullen, M.P.; Draper, M.A.; Madden, L.V. Efficacy of triazole- based fungicides for fusarium head blight and deoxynivalenol control in wheat: A multivariate meta-analysis. Phytopathology 2008, 98, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juliatti, F.C.; Polloni, L.C.; de Morais, T.P.; Zacarias, N.R.S.; Silva, E.A.; Juliatti, B.C.M. Sensitivity of Phakopsora pachyrhizi populations to dithiocarbamate, chloronitrile, triazole, strobilurin, and carboxamide fungi-cides. Biosci. J. 2017, 33, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.X.; Gao, B.B.; He, Z.Z.; Li, L.S.; Zhang, Q.; Kaziem, A.E.; Wang, M.H. Stereoselective bioactivity of the chiral triazole fungicide prothioconazole and its metabolite. Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 2019, 160, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.Y.; Hou, Y.P.; Wang, J.X.; Yang, G.F.; Liang, X.Y.; Zhou, M.G. Activity of a novel strobilurin fungicide benzothiostrobin against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 2014, 115, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.C.; Zhu, J.M.; He, L.M.; Cui, K.D.; Mu, W.; Liu, F. Baseline sensitivity of Phytophthora capsici to the strobilurin fungicide benzothiostrobin and the efficacy of this fungicide. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2018, 152, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.H.; Abd El-Aty, A.M.; Choi, J.H.; Kang, C.A. Determination of field-incurred pyrimethanil residues in persimmon (Diospyros kaki Linn) by liquid chromatography. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2007, 21, 1279–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.; Zhou, J.; Lv, H.; Qin, N.; Chang, F.J.; Zhao, X. Identification, pathogenicity, and fungicide sensitivity of Ascochyta caulina (Teleomorph: Neocamarosporium calvescens) associated with black stem on quinoa in China. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 2585–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, F.; Lee, S.H.; Taylor, L.; Shawetaylor, J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Vilgalys, R.; Hester, M. Rapid genetic identification and mapping of enzymatically amplified ribosomal DNA from several cryptococcus species. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 4238–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Whelen, S.; Hall, B.D. Phylogenetic relationships among ascomycetes: Evidence from an RNA polymerse II subunit. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 1799–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capella-Gutierrez, S.; Silla-Martinez, J.M.; Gabaldon, T. trimAl: A tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1972–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.B.; Kyung, M.K.; Hack, S.J. Paraphaeosphaeria recurvifoliae, a new species causing leaf spots and necrosis on Yucca recurvifolia. Fungal Divers. 2005, 20, 71–81. [Google Scholar]
- Phookamsak, R.; Liu, J.K.; McKenzie, E.H.; Manamgoda, D.S.; Ariyawansa, H.; Thambugala, K.M.; Dai, D.Q.; Camporesi, E.; Chukeatirote, E.; Wijayawardene, N.N.; et al. Revision of phaeosphaeriaceae. Fungal Divers. 2014, 68, 159–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talhinhas, P.; Sreenivasaprasad, S.; Neves-Martins, J.; Oliveira, H. Genetic and morphological characterization of Colletotrichum acutatum causing anthracnose of lupins. Phytopathology 2002, 92, 986–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Câmara, M.P.S.; Ramaley, A.W.; Castlebury, L.A.; Palm, M.E. Neophaeosphaeria and Phaeosphaeriopsis segregates of Paraphaeosphaeria. Mycol. Res. 2003, 107, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golzar, H.; Wang, C. First report of Phaeosphaeriopsis glaucopunctata as the cause of leaf spot and necrosis on Ruscus aculeatus in Australia. Australas. Plant Dis. 2012, 7, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzanlou, M.; Crous, P.W. Phaeosphaeriopsis musae. Fungal Planet 9; CBSKNAW Fungal Biodiversity Centre: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Tennakoon, D.S.; Thambugala, K.M.; Wanasinghe, D.N.; Gentekaki, E.; Promputtha, I.; Kuo, C.H.; Hyde, K.D. Additions to Phaeosphaeriaceae (Pleosporales): Elongaticollum gen. nov., Ophiosphaerella taiwanensis sp. nov., Phaeosphaeriopsis beaucarneae sp. nov. and a new host record of Neosetophoma poaceicola from Musaceae. MycoKeys 2020, 70, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thambugala, K.M.; Camporesi, E.; Ariyawansa, H.A.; Phookamsak, R.; Liu, Z.Y.; Hyde, K.D. Phylogeny and morphology of Phaeosphaeriopsis triseptata sp. nov., and Phaeosphaeriopsis glaucopunctata. Phytotaxa 2014, 176, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.F.; Fu, M.Y.; Xiao, M.; Zhang, M.; Chen, M.C.; Zeng, X.P. Identification and biology characteristic determination on pathogen of sisal canker disease. Mol. Plant Breed. 2021, 19, 4429–4436. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.X.; Stevenson, K.L.; Brewer, M.T. Differences in sensitivity to a triazole fungicide among Stagonosporopsis species causing gummy stem blight of cucurbits. Plant Dis. 2016, 100, 2106–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Choi, J.; Kim, J.W. Triazole fungicides sensitivity of Sclerotinia homoeocarpa in Korean golf courses. Plant Pathol. J. 2017, 33, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatem, A.; Karpova, N.; Yaderets, V.; Glagoleva, E.; Petrova, K.; Shibaeva, A.; Ovchinnikov, A.; Dzhavakhiya, V. Inhibition of the growth and development of potato early blight pathogen (Alternaria solani) by combining Penicillium chrysogenum VKM F-4876D with some strobilurin-, triazole-, and phenylpyrrole-based fungicides. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuntini, B.; Alvarez, R.d.C.F.; Theodoro, G.d.F.; Zuffo, A.M. Effect of adding fungicide to mixtures of triazoles and strobilurins in the control of downy mildew and Asian soybean rust. Pesqui. Agropecuária Trop. 2019, 49, e53688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Yao, K.C.; Wang, K.Y.; Xiao, C.; Li, K.; Khan, B.; Zhao, S.S.; Yan, W.; Ye, Y.H. Bioactive-guided structural optimization of 1,2,3-triazole phenylhydrazones as potential fungicides against Fusarium graminearum. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2020, 164, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóthová, M.; Hudec, K.; Tóth, P. Sensitivity of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum to strobilurin fungicides in Slovakia. Plant Prot. Sci. 2020, 56, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, S.E.; Brannen, P.M.; Scherm, H.; Eason, N.; MacAllister, C. Efficacy of fungicide treatments for Plasmopara viticola control and occurrence of strobilurin field resistance in vineyards in Georgia, USA. Crop Prot. 2021, 139, 105371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteve-Turrillas, F.A.; Abad-Somovilla, A.; Quinones-Reyes, G.; Agullo, C.; Mercader, J.V.; Abad-Fuentes, A. Monoclonal antibody-based immunoassays for cyprodinil residue analysis in QuEChERS-based fruit extracts. Food Chem. 2015, 187, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteve-Turrillas, F.A.; Mercader, J.V.; Agullo, C.; Abad-Somovilla, A.; Abad-Fuentes, A. Site-heterologous haptens and competitive monoclonal antibody-based immunoassays for pyrimethanil residue analysis in food-stuffs. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 63, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Fungicides | Manufacturer | Concentration Gradient (µg/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| Hymexazol (99.16% a.i.) | Jiangsu Heye Agrochemical Co., Ltd., Yancheng, China | 80, 60, 40, 20, 10 |
| Iprodione (98% a.i.) | Hubei Wanye Medicine Co., Ltd., Wuhan, China | 10, 5, 1, 0.5, 0.05 |
| Myclobutanil (96% a.i.) | Hubei Supuer Chemical Co., Ltd., Wuhan, China | 15, 7.5, 1, 0.5, 0.1 |
| Pyraclostrobin (97% a.i.) | Nanjing Gaozheng Agricultural Chemical Co., Ltd., Nanjing, China | 15, 10, 1, 0.5, 0.05 |
| Triazolone (97% a.i.) | Jiangsu Arrow Agrochemical Co., Ltd., Yancheng, China | 80, 60, 40, 20, 10 |
| Thiophanate-Methyl (95% a.i.) | Shanghai Yuanye Biology Science and Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China | 10, 8, 1, 0.8, 0.4 |
| Difenoconazole (96% a.i.) | Beijing Green Nonghua Plant Protection Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China | 10, 1, 0.1, 0.01, 0.001 |
| Azoxystrobin (96% a.i.) | Shang Hai De Mo Hua Xue Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China | 15, 10, 1, 0.1, 0.01 |
| Fludioxonil (95% a.i.) | Hebei Xingbai Agriculture Technology Co., Ltd., Shijiazhuang, China | 20, 10, 1, 0.5, 0.1 |
| Tebuconazole (97.1% a.i.) | Jiangsu Fengdeng Crop Protection Co., Ltd., Changzhou, China | 5, 1.5, 0.5, 0.3, 0.15 |
| Pyrimethanil (97% a.i.) | Jiangxi Zhongxun Agrochemical Co., Ltd., Nanchang, China | 50, 25, 10, 1, 0.5 |
| Trifloxystrobin (97% a.i.) | Bayer (China) Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China | 20, 10, 1, 0.5, 0.1, 0.05 |
| Fungicide | Regression Equation | Correlation Coefficient (r) | EC50 a/µg/mL |
|---|---|---|---|
| Difenoconazole | y = 0.5929x + 5.1596 | 0.9483 | 0.5380 |
| Tebuconazole | y = 1.8915x + 4.5722 | 0.9886 | 1.6835 |
| Myclobutanil | y = 1.1636x + 4.6198 | 0.9939 | 2.1218 |
| Pyraclostrobin | y = 0.6366x + 4.2386 | 0.9864 | 15.7005 |
| Thiophanate-Methyl | y = 0.8889x + 3.8021 | 0.9759 | 22.2619 |
| Iprodione | y = 0.4872x + 4.2368 | 0.9869 | 36.8578 |
| Triazolone | y = 1.1520x + 3.1337 | 0.9856 | 41.6926 |
| Fludioxonil | y = 0.3898x + 4.3256 | 0.9742 | 53.7377 |
| Hymexazol | y = 1.3385x + 2.2064 | 0.9839 | 122.2286 |
| Trifloxystrobin | y = 0.3823x + 4.1771 | 0.9838 | 142.1241 |
| Pyrimethanil | y = 0.7482x + 3.2913 | 0.9770 | 192.2392 |
| Azoxystrobin | y = 0.3002x + 4.1523 | 0.9800 | 667.5094 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, W.; Wang, G.; Li, E.; Tan, S.; Xu, G.; Huang, X.; Chen, H.; Liang, Y.; Li, R.; Qin, J.; et al. Characterization and Fungicide Sensitivity of Phaeosphaeriopsis obtusispora That Causes Marginal Leaf Blight in Agave hybrid H.11648. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10070486
Wu W, Wang G, Li E, Tan S, Xu G, Huang X, Chen H, Liang Y, Li R, Qin J, et al. Characterization and Fungicide Sensitivity of Phaeosphaeriopsis obtusispora That Causes Marginal Leaf Blight in Agave hybrid H.11648. Journal of Fungi. 2024; 10(7):486. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10070486
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Weihuai, Guihua Wang, Erli Li, Shibei Tan, Gang Xu, Xing Huang, Helong Chen, Yanqiong Liang, Rui Li, Jianfeng Qin, and et al. 2024. "Characterization and Fungicide Sensitivity of Phaeosphaeriopsis obtusispora That Causes Marginal Leaf Blight in Agave hybrid H.11648" Journal of Fungi 10, no. 7: 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10070486
APA StyleWu, W., Wang, G., Li, E., Tan, S., Xu, G., Huang, X., Chen, H., Liang, Y., Li, R., Qin, J., & Yi, K. (2024). Characterization and Fungicide Sensitivity of Phaeosphaeriopsis obtusispora That Causes Marginal Leaf Blight in Agave hybrid H.11648. Journal of Fungi, 10(7), 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10070486








