Comparative Genomics and Characterisation of the Role of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Respiration in the Fermentation of Chinese Steamed Bread
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Culture of Strains
2.3. Preparation of CSBs
2.4. Determination of pH and TTA
2.5. Specific Volume Evaluation
2.6. Texture Profile Analysis
2.7. Microstructural Analysis
2.8. Analysis of Volatile Compounds
2.9. Sensory Quality Analysis
2.10. Genome Re-Sequencing, Variant Calling and Comparative Genomic Analysis
2.11. Correlation Analysis and Establishment of a Scoring System
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Result and Discussion
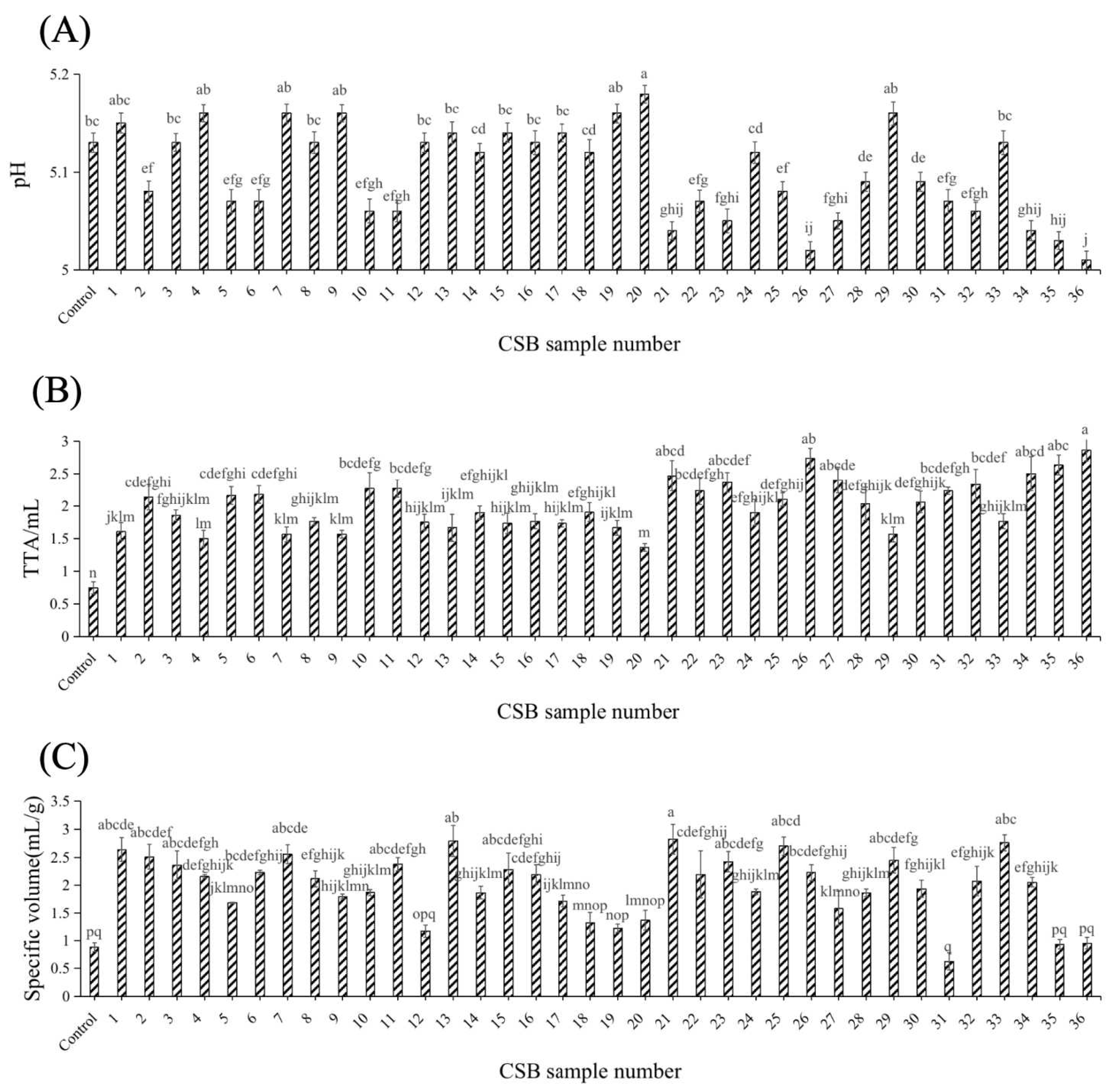
3.1. Effects of Different Yeast Strains on pH, TTA and the Specific Volume of CSBs
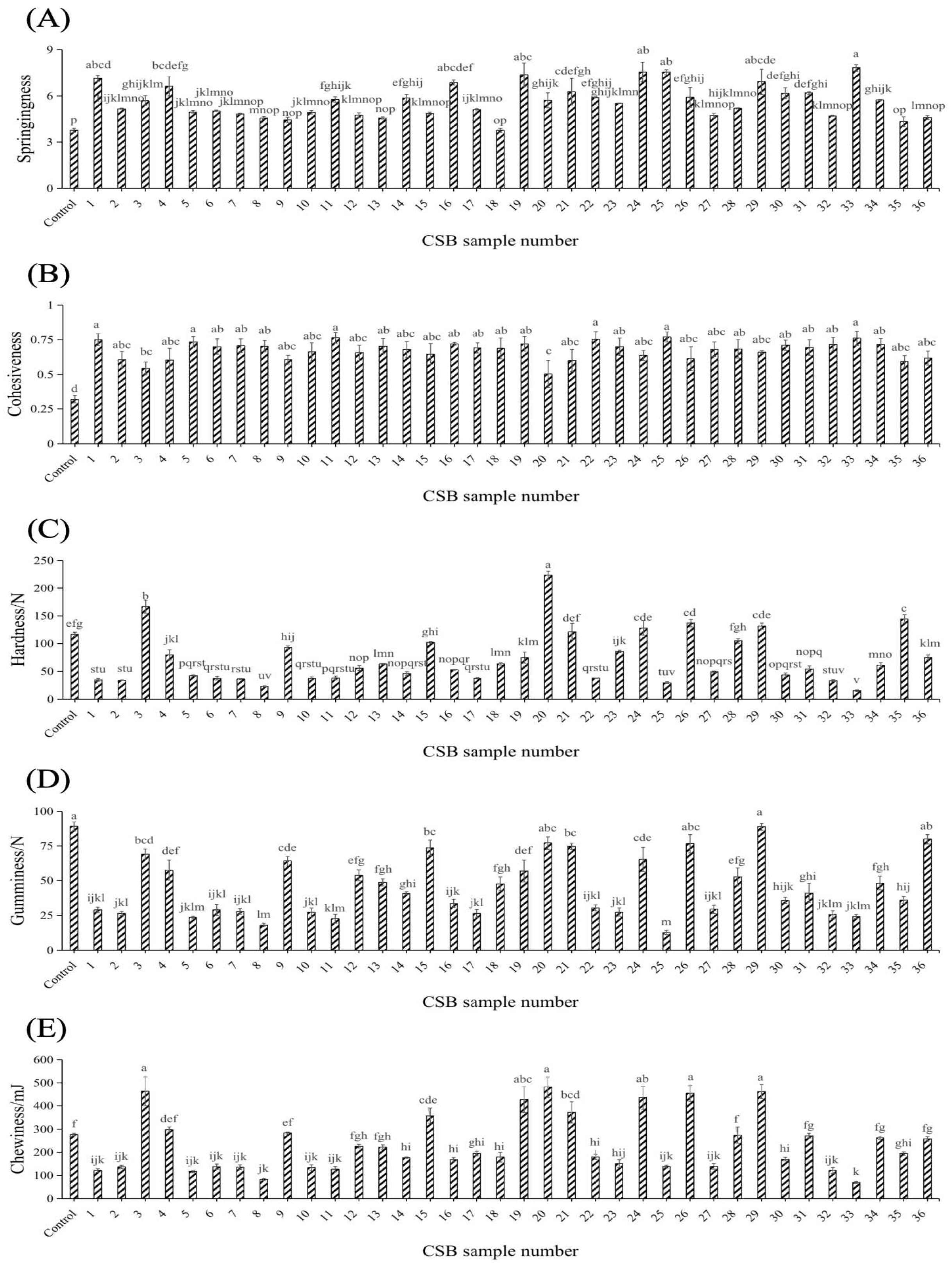
3.2. Effects of Different Yeasts on the Textural Properties of CSBs
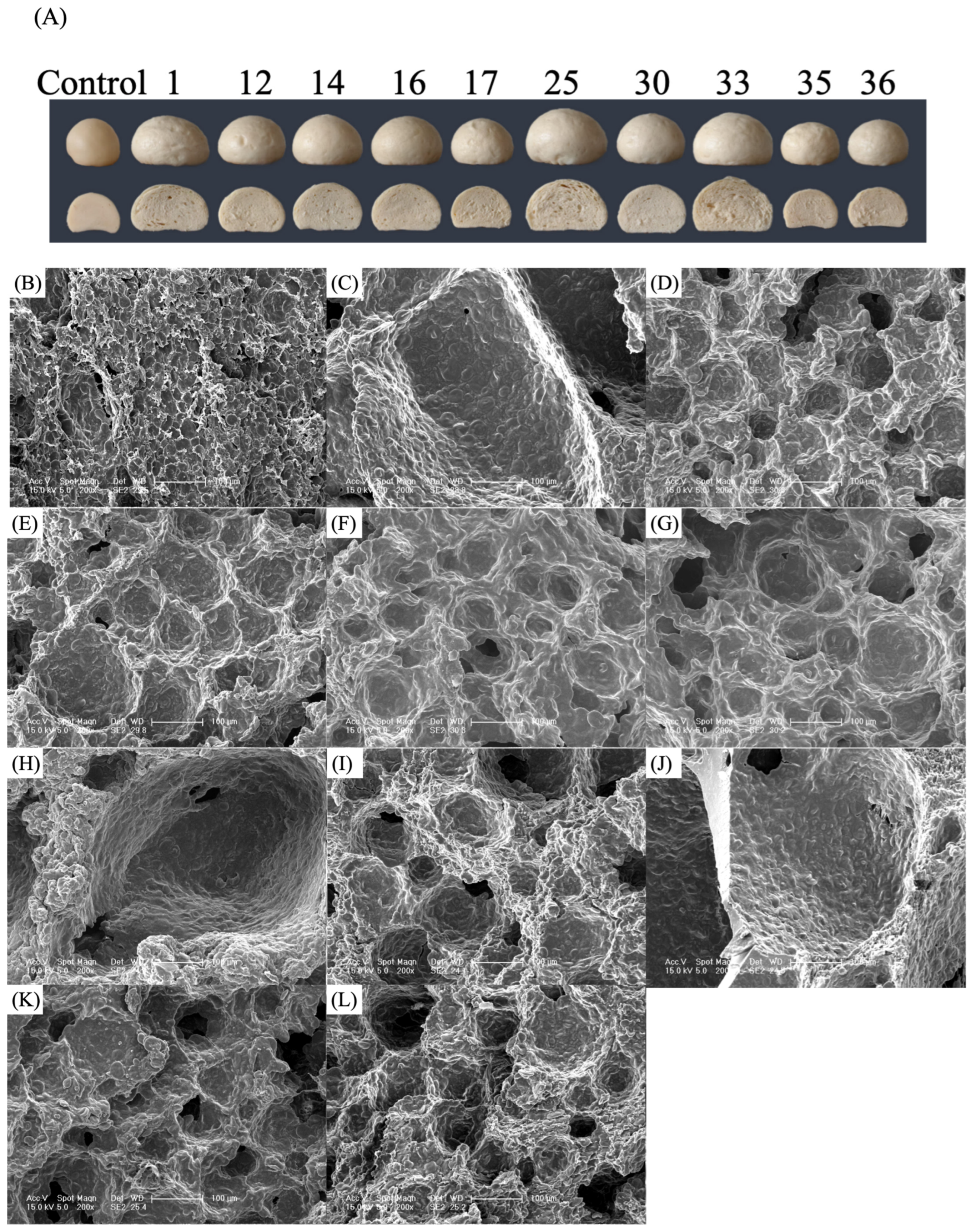
3.3. Effects of Different Yeast Strains on CSB Microstructure
3.4. Identification of Volatile Compounds in CSBs
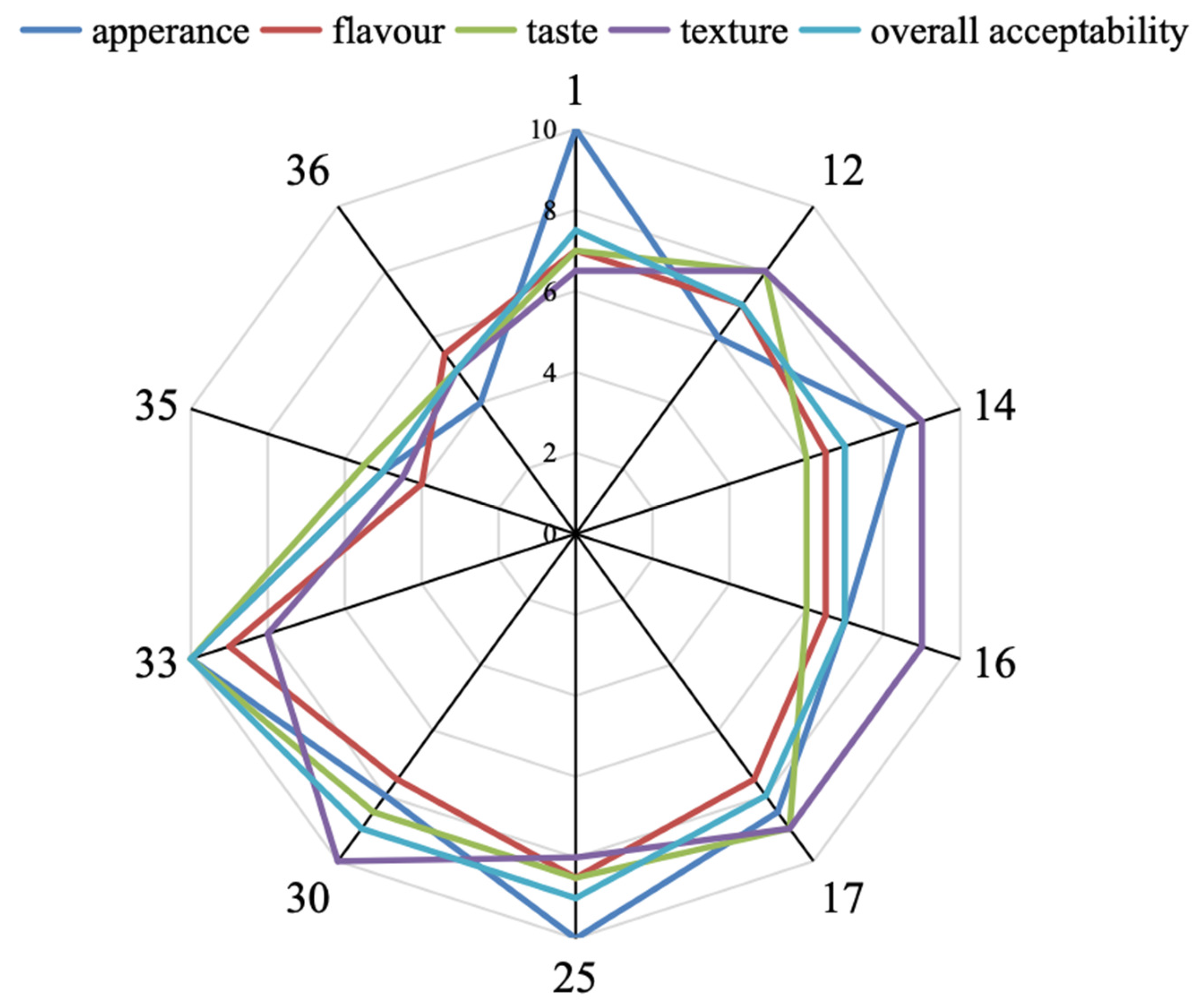
3.5. Sensory Analysis
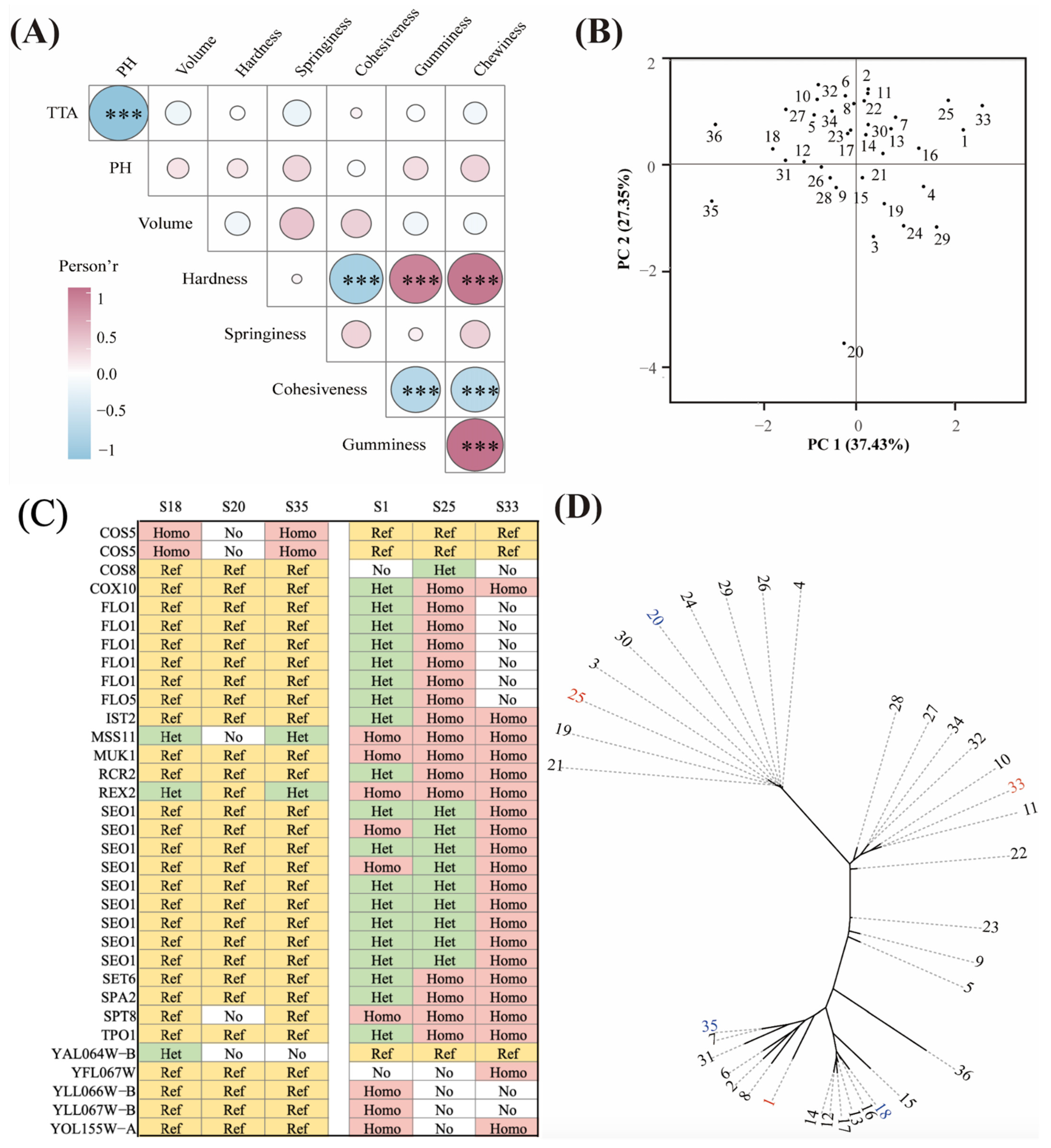
3.6. Comparative Genomic Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wei, G.M.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Zhao, F.R.; Sang, Y.X.; Regenstein, J.M.; Zhou, P. Characteristic aroma compounds during the fermentation of Chinese steamed bread fermented with different starters. Food Chem. 2024, 457, 140151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.X.; Shang, J.X.; Qin, F.P.; Guo, X.N.; Zhu, K.X.; Xing, J.J. Investigating the application of multiple-stage fermented glutinous rice procedure in dough preparation for Chinese steamed bread. Food Biosci. 2025, 63, 105601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.J.; Song, K.D.; Li, H.F.; Ma, R.C.; Cui, M.Y. Effect of mixed Saccharomyces cerevisiae Y10 and Torulaspora delbrueckii Y22 on dough fermentation for steamed bread making. Int. J. Food. Microbiol. 2019, 303, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subaşı, A.S.; Ercan, R. Technological characteristics of whole wheat bread: Efects of wheat varieties, sourdough treatments and sourdough levels. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2024, 250, 2593–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.B.; Xie, X.H.; Zhu, H.S.; Niu, B.; Liang, D.; Chen, K.; Sun, W.H.; Shi, D.F. Solid-state fermentation by S. cerevisiae with high resistance to ferulic acid improves the physicochemical properties of wheat bran and quality of bran-rich Chinese steamed bread. J. Food. Sci. 2024, 89, 954–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.T.; Ji, S.X.; Fang, J.; Li, Y.; Fan, H.P.; Li, Z. Effects of the coculture of Pediococcus pentosaceus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae with different leavening ability on the quality and volatile organic compounds of Chinese steamed bread. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 104216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gianvito, P.; Tesnière, C.; Suzzi, G.; Blondin, B.; Tofalo, R. FLO5 gene controls flocculation phenotype and adhesive properties in a Saccharomyces cerevisiae sparkling wine strain. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willaert, R.G.; Kayacan, Y.; Devreese, B. The Flo Adhesin Family. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.J.; Jeon, M.S.; Moon, H.Y.; Kang, J.; Jeong, D.M.; Lee, D.W.; Kim, J.H.; Lim, J.Y.; Seo, J.A.; Jin, J.H.; et al. Integrated genomics and phenotype microarray analysis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae industrial strains for rice wine fermentation and recombinant protein production. Microb. Biotechnol. 2023, 16, 2161–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, G.; de Godoy, V.R.; Dário, M.G.; Duval, E.H.; Alves-Jr, S.L.; Bücker, A.; Rosa, C.A.; Dunn, B.; Sherlock, G.; Stambuk, B.U. Improved Sugarcane-Based Fermentation Processes by an Industrial Fuel-Ethanol Yeast Strain. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Li, C.; Li, Y.; Peng, H. Metabolic Engineering Strategies for Improved Lipid Production and Cellular Physiological Responses in Yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Jiang, S.; Jiang, S.; Lu, S.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, J.; Wu, W.; Jiang, S. CRISPR-Cas9 Approach Constructed Engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae with the Deletion of GPD2, FPS1, and ADH2 to Enhance the Production of Ethanol. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parapouli, M.; Vasileiadis, A.; Afendra, A.S.; Hatziloukas, E. Saccharomyces cerevisiae and its industrial applications. AIMS Microbiol. 2020, 6, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.L.; Wan, J.W.; Wang, Z.L.; Sun, M.; Feng, T.; Ho, C.T.; Song, S.Q. Variation of Volatile Compounds and Corresponding Aroma Profiles in Chinese Steamed Bread by Various Yeast Species Fermented at Different Times. J Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 3795–3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, E.; Garofalo, G.; Barbera, M.; Piazzese, D.; Palmieri, D.; Di Giorgi, S.; Alfonzo, A.; Gaglio, R.; Settanni, L. Effects of Various Inocula Combinations of Leuconostoc mesenteroides, Papiliotrema terrestris, and Saccharomyces cerevisiae on Dough Fermentation and Final Bread Characteristics. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 11581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiva, R.; Celador-Lera, L.; Uña, J.A.; Jiménez-López, A.; Espinosa-Alcantud, M.; Mateos-Horganero, E.; Vega, S.; Santos, M.Á.; Velázquez, E.; Tamame, M. Yeast Biodiversity in Fermented Doughs and Raw Cereal Matrices and the Study of Technological Traits of Selected Strains Isolated in Spain. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shui, W.Q.; Xiong, Y.; Xiao, W.D.; Qi, X.N.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Y.P.; Guo, Y.F.; Zhang, Z.D.; Wang, Q.H.; Ma, Y.H. Understanding the Mechanism of Thermotolerance Distinct from Heat Shock Response Through Proteomic Analysis of Industrial Strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2015, 14, 1885–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.P.; Zheng, X.L.; Ai, Z.L.; Liu, C.; Li, R.; Bian, K. Analysis of volatile aroma components from Mantou fermented by different starters. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2018, 42, e13627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekri, A.; Torbati, M.; Khosrowshahi, A.Y.; Shamloo, H.B.; Azadmard-Damirchi, S. Functional effects of phytate-degrading, probiotic lactic acid bacteria and yeast strains isolated from Iranian traditional sourdough on the technological and nutritional properties of whole wheat bread. Food Chem. 2020, 306, 125620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.F.; Jiang, L.J.; Suo, W.J.; Deng, Y.X.; Zhang, M.; Dong, S.; Guo, P.; Chen, S.F.; Li, H.J. Influence of emulsifiers and enzymes on dough rheological properties and quality characteristics of steamed bread enriched with potato pulp. Food Chem. 2021, 360, 130015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.J.; Zhou, M.M.; Cui, M.Y.; Wang, Y.H.; Li, H.F. Improvement of whole wheat dough fermentation for steamed bread making using selected phytate-degrading Wickerhamomyces anomalus P4. J. Cereal Sci. 2021, 100, 103261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, A.; Villanueva, M.; Caballero, P.A.; Lazaridou, A.; Biliaderis, C.G.; Ronda, F. Microwave treatment enhances the physical and sensory quality of quinoa-enriched gluten-free bread. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 155, 110244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Li, F.; Sanchez, B.J.; Zhu, Z.; Li, G.; Domenzain, I.; Marcisauskas, S.; Anton, P.M.; Lappa, D.; Lieven, C.; et al. A consensus S. cerevisiae metabolic model Yeast8 and its ecosystem for comprehensively probing cellular metabolism. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, P.; Yang, K.S.; Shen, J.; Lu, Z.X.; Lv, F.X.; Wang, P. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Revealing the Enhanced Volatiles of Cofermentation of Yeast and Lactic Acid Bacteria on Whole Wheat Steamed Bread Dough. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2023, 71, 19129–19141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Sadiq, F.A.; Cai, Y.; Fan, D.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, J.; Chen, W. Identification of Key Aroma Compounds in Type I Sourdough-Based Chinese Steamed Bread: Application of Untargeted Metabolomics Analysisp. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihaly Cozmuta, L.; Nicula, C.; Peter, A.; Apjok, R.; Jastrzębska, A.; Mihaly Cozmuta, A. Insights into the fermentation process of fresh and frozen dough bread made with alginate-immobilized S. cerevisiae yeast cells. J. Cereal Sci. 2022, 107, 103516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.Q.; Pan, C.W.; Chen, J. Comparative Analysis of Bread Quality Using Yeast Strains from Alcoholic Beverage Production. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, V.; Venturi, M.; Pini, N.; Guerrini, S.; Marti, A.; Bresciani, A.; Montanari, C.; Tabanelli, G.; Granchi, L. Influence of Pepper and Blueberry Purees Fermented by an Autochthonous Microbial Consortium on the Aroma and Technological Properties of Bread. Food. Bioprocess Technol. 2024; 1–15, prepublish. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Yin, Y.; Ali, B.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.N.; Xu, X.M. Isolation of yeast strains from Chinese liquor Daqu and its use in the wheat sourdough bread making. Food Biosci. 2019, 31, 100443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.W.; Kim, S.M.; Zhang, D.J.; Li, Z.J. Effects of different starter cultures on the quality characteristics and shelf-life of fermented rice cake. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 29, 1483–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.W.; Han, P.C.; Zhang, P.P.; Li, Y.K. Influence of Yeast Concentrations and Fermentation Durations on the Physical Properties of White Bread. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 195, 116063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, K.; Marvin Santiago, D.; Noda, T.; Tsuboi, K.; Sakura Kawakami, S.; Yamauchi, H. The Bread Making Qualities of Bread Dough Supplemented with Whole Wheat Flour and Treated with Enzymes. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2017, 23, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.H.; Zhao, W.; Li, P.L.; Min, G.; Zhang, A.X.; Zhang, J.L.; Liu, Y.Y.; Liu, J.K. Effects of different cultivars and particle sizes of non-degermed millet flour fractions on the physical and texture properties of Chinese steamed bread. Cereal Chem. 2020, 97, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pico, J.; Bernal, J.; Gómez, M. Wheat bread aroma compounds in crumb and crust: A review. Food Res. Int. 2015, 75, 200–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.J.; Li, Y.; Sadiq, F.A.; Yang, H.Y.; Gu, J.S.; Yuan, L.; Lee, Y.K.; He, G.Q. Predominant yeasts in Chinese traditional sourdough and their influence on aroma formation in Chinese steamed bread. Food Chem. 2018, 242, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.Z.; Xu, D.; Wu, F.F.; Jin, Z.Y.; Yin, Y.; Xu, X.M. The aroma compounds of Chinese steamed bread fermented with sourdough and instant dry yeast. Food Biosci. 2020, 38, 100775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsiou, K.; Palassaros, G.; Irakli, M.; Biliaderis, C.G.; Lazaridou, A. Effect of Pretreated Yellow Split Pea Flour Supplementation on Dough Rheology, Texture, Volatile Profile, and Sensory Attributes of Wheat Flour–Based Breads. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2024; 1–17, prepublish. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, B.; Nie, W.J.; Wang, Y.X.; Ma, J.Y.; Xing, X.L.; Huang, Z.M.; Xu, C.; Li, Z.; Ai, Z.L. Microbial diversity of fermented dough and volatile compounds in steamed bread prepared with traditional Chinese starters. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 126, 109350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.Z.; Zhao, Q.Y.; Xu, D.; Jin, Y.M.; Wu, F.F.; Jin, Z.Y.; Xu, X.M. Volatile compounds in Chinese steamed bread influenced by fermentation time, yeast level and steaming time. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 141, 110861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhang, H.; Xi, J.Z.; Jin, Y.M.; Chen, Y.S.; Guo, L.N.; Jin, Z.Y.; Xu, X.M. Improving bread aroma using low-temperature sourdough fermentation. Food Biosci. 2020, 37, 100704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, D.D.; Zhang, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Sun, B.G.; Ren, F.Z.; Chen, H.T.; He, J.N. Characterization of the aroma release and perception of white bread during oral processing by gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry and temporal dominance of sensations analysis. Food Res. Int. 2019, 123, 612–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, J.Z.; Xu, D.; Wu, F.F.; Jin, Z.Y.; Xu, X.M. Effect of Na2CO3 on quality and volatile compounds of steamed bread T fermented with yeast or sourdough. Food Chem. 2020, 324, 126786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, G.; Regenstein, J.M. Microbiota structure of traditional starters from around the Tai-hang mountains and their influence on the fermentation properties, aroma profile and quality of Chinese steamed bread. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 5116–5125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, A.N.; Petersen, M.A.; Hansen, Å.S. The aroma profile of wheat bread crumb influenced by yeast concentration and fermentation temperature. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 50, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.Y.; Tao, Y.; Han, Y.B.; Wang, P.; Li, D.D. Effect of static magnetic field treatment on γ-aminobutyric acid content and sensory characteristics of germinated brown rice cake. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marr, R.A.; Moore, J.; Formby, S.; Martiniuk, J.T.; Hamilton, J.; Ralli, S.; Konwar, K.; Rajasundaram, N.; Hahn, A.; Measday, V. Whole Genome Sequencing of Canadian Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains isolated from spontaneous wine fermentations reveals a new Pacific West Coast Wine Clade. G3 2023, 13, jkad130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivett, E.D.; Addis, H.G.; Dietz, J.V.; Carroll-Deaton, J.A.; Gupta, S.; Foreman, K.L.; Dang, M.A.; Fox, J.L.; Khalimonchuk, O.; Hegg, E.L. Evidence that the catalytic mechanism of heme a synthase involves the formation of a carbocation stabilized by a conserved glutamate. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2023, 744, 109665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.; Zhang, X. Effects of Selenium Enrichment on Dough Fermentation Characteristics of Baker’s Yeast. Foods 2023, 12, 2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Lee, S.B.; Kang, H.S.; Oh, G.T.; Kim, T. Two distinct domains of Flo8 activator mediates its role in transcriptional activation and the physical interaction with Mss11. Biochem. Biophy. Res. Commun. 2014, 449, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaumik, S.R.; Green, M. R, Differential requirement of SAGA components for recruitment of TATA-box-binding protein to promoters in vivo. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 7365–7371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobus, A.P.; Stephens, T.G.; Youssef, P.; González-Pech, R.; Ciccotosto-Camp, M.M.; Dougan, K.E.; Chen, Y.; Basso, L.C.; Frazzon, J.; Chan, C.X.; et al. Comparative Genomics Supports That Brazilian Bioethanol Saccharomyces cerevisiae Comprise a Unified Group of Domesticated Strains Related to Cachaça Spirit Yeasts. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 644089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gronchi, N.; De Bernardini, N.; Cripwell, R.A.; Treu, L.; Campanaro, S.; Basaglia, M.; Foulquié-Moreno, M.R.; Thevelein, J.M.; Van Zyl, W.H.; Favaro, L.; et al. Natural Saccharomyces cerevisiae Strain Reveals Peculiar Genomic Traits for Starch-to-Bioethanol Production: The Design of an Amylolytic Consolidated Bioprocessing Yeast. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 768562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Strain ID (S) | TTA | Volume | Hardness | Springiness | Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | −1.7331 | −1.1101 | −3.2478 | 0.0645 | −130.0260 |
| 35 | 1.6519 | −1.8862 | −1.5551 | −1.2485 | −78.8627 |
| 18 | −0.2989 | −1.2108 | 0.1840 | −1.8004 | −68.8262 |
| 9 | −1.1986 | −0.3400 | −0.4485 | −1.1439 | −64.0432 |
| 12 | −0.7086 | −1.4656 | 0.3489 | −0.8521 | −57.9189 |
| 3 | −0.4236 | 0.6494 | −2.0242 | 0.0391 | −37.3833 |
| 15 | −0.7532 | 0.5190 | −0.6427 | −0.7443 | −31.4819 |
| 28 | 0.0481 | −0.2215 | −0.7005 | −0.4271 | −29.7159 |
| 31 | 0.5830 | −2.4312 | 0.3796 | 0.5244 | −28.1468 |
| 36 | 2.2666 | −1.8506 | −0.0587 | −0.9916 | −27.4244 |
| 17 | −0.7532 | −0.4822 | 0.7423 | −0.5064 | −18.6429 |
| 19 | −0.9314 | −1.3767 | −0.0523 | 1.6503 | −15.0142 |
| 27 | 1.0284 | −0.7251 | 0.4910 | −0.8711 | −6.8956 |
| 5 | 0.3870 | −0.5414 | 0.6374 | −0.6491 | −5.5825 |
| 29 | −1.1986 | 0.8093 | −1.2760 | 1.2221 | −4.4979 |
| 8 | −0.6641 | 0.2228 | 1.0457 | −1.0138 | −4.1362 |
| 4 | −1.3768 | 0.2939 | −0.1594 | 0.9335 | −0.6060 |
| 13 | −0.9314 | 1.4195 | 0.1940 | −1.0234 | 0.1765 |
| 24 | −0.3078 | −0.1860 | −1.2074 | 1.8215 | 1.6870 |
| 7 | −1.1986 | 0.9989 | 0.7666 | −0.7696 | 3.9897 |
| 14 | −0.3078 | −0.2215 | 0.5645 | 0.2231 | 7.0370 |
| 10 | 0.6721 | −0.2156 | 0.7452 | −0.6777 | 9.0823 |
| 26 | 1.9192 | 0.4183 | −1.39233 | 0.248439 | 17.06984 |
| 32 | 0.8502 | 0.1517 | 0.832254 | −0.89015 | 18.43684 |
| 6 | 0.4315 | 0.4242 | 0.740158 | −0.573 | 22.36366 |
| 30 | 0.1198 | −0.0971 | 0.610938 | 0.502165 | 24.57858 |
| 23 | 0.9393 | 0.7619 | −0.29574 | −0.12263 | 25.30741 |
| 16 | −0.6641 | 0.3531 | 0.408185 | 1.165022 | 31.2823 |
| 34 | 1.2956 | 0.1162 | 0.228276 | 0.080346 | 32.42902 |
| 2 | 0.3157 | 0.9219 | 0.817261 | −0.45248 | 36.63929 |
| 22 | 0.5830 | 0.3591 | 0.735874 | 0.242096 | 40.89846 |
| 21 | 1.2065 | 1.4787 | −1.05178 | 0.597312 | 45.35632 |
| 11 | 0.6810 | 0.6849 | 0.724452 | 0.112062 | 47.37149 |
| 1 | −1.0917 | 1.1470 | 0.800841 | 1.421919 | 57.37611 |
| 33 | −0.6641 | 1.3662 | 1.209204 | 2.087948 | 93.81723 |
| 25 | 0.2267 | 1.2655 | 0.905788 | 1.821536 | 94.30497 |
| GO Biological Process Complete | Fold Enrichment | p-Value | FDR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electron transport coupled proton transport (GO:0015990) | 53.07 | 7.34 × 10−6 | 2.32 × 10−3 |
| Mitochondrial mRNA processing (GO:0090615) | 23.59 | 6.98 × 10−5 | 1.68 × 10−2 |
| Mitochondrial electron transport, cytochrome c to oxygen (GO:0006123) | 15.61 | 4.06 × 10−5 | 1.03 × 10−2 |
| Mitochondrial ATP synthesis coupled electron transport (GO:0042775) | 12.25 | 1.69 × 10−7 | 2.13 × 10−4 |
| ATP synthesis coupled electron transport (GO:0042773) | 12.25 | 1.69 × 10−7 | 1.71 × 10−4 |
| Aerobic electron transport chain (GO:0019646) | 12.25 | 1.69 × 10−7 | 1.42 × 10−4 |
| Respiratory electron transport chain (GO:0022904) | 11.11 | 3.48 × 10−7 | 2.20 × 10−4 |
| Oxidative phosphorylation (GO:0006119) | 10.61 | 4.88 × 10−7 | 2.74 × 10−4 |
| Electron transport chain (GO:0022900) | 10.41 | 1.29 × 10−7 | 2.17 × 10−4 |
| Proton transmembrane transport (GO:1902600) | 7.24 | 2.40 × 10−7 | 1.73 × 10−4 |
| Aerobic respiration (GO:0009060) | 5.9 | 4.89 × 10−6 | 1.65 × 10−3 |
| Cellular respiration (GO:0045333) | 5.56 | 8.21 × 10−6 | 2.30 × 10−3 |
| Inorganic ion transmembrane transport (GO:0098660) | 5.21 | 5.41 × 10−8 | 2.73 × 10−4 |
| Inorganic cation transmembrane transport (GO:0098662) | 4.82 | 2.12 × 10−6 | 9.75 × 10−4 |
| Cation transmembrane transport (GO:0098655) | 4.31 | 1.51 × 10−6 | 7.63 × 10−4 |
| Ion transmembrane transport (GO:0034220) | 4.25 | 7.86 × 10−8 | 1.99 × 10−4 |
| Energy derivation by oxidation of organic compounds (GO:0015980) | 3.97 | 1.46 × 10−4 | 3.08 × 10−2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Pang, J.; Liu, M.; Yuan, T.; Wang, Q.; Liu, J. Comparative Genomics and Characterisation of the Role of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Respiration in the Fermentation of Chinese Steamed Bread. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11020114
Gao Y, Guo Y, Pang J, Liu M, Yuan T, Wang Q, Liu J. Comparative Genomics and Characterisation of the Role of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Respiration in the Fermentation of Chinese Steamed Bread. Journal of Fungi. 2025; 11(2):114. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11020114
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Yawen, Yufeng Guo, Jianing Pang, Mingkai Liu, Tengdan Yuan, Qinhong Wang, and Jingsheng Liu. 2025. "Comparative Genomics and Characterisation of the Role of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Respiration in the Fermentation of Chinese Steamed Bread" Journal of Fungi 11, no. 2: 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11020114
APA StyleGao, Y., Guo, Y., Pang, J., Liu, M., Yuan, T., Wang, Q., & Liu, J. (2025). Comparative Genomics and Characterisation of the Role of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Respiration in the Fermentation of Chinese Steamed Bread. Journal of Fungi, 11(2), 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11020114






