Interactions between Aspergillus fumigatus and Pulmonary Bacteria: Current State of the Field, New Data, and Future Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Lung Microbiota in Different Clinical Situations
3. Interactions In Vitro between Lung Bacteria and A. fumigatus
3.1. Methodologies for Studying Bacterial–Fungal Interactions In Vitro
3.2. Cell–Cell Interactions
3.2.1. Fungal Adaptation to the Presence of Bacteria
3.2.2. Extracellular Soluble Molecules
3.2.3. Pf4 P. aeruginosa Phage–A. fumigatus Interaction
3.2.4. Microbial Interaction is Promoted by Volatiles
3.3. Influence of Polymicrobial Biofilms on Drug Sensitivity
3.4. Summary
4. How are Mixed Bacterial–Fungal Infections Seen by the Host Immune Response?
4.1. Fungal and Bacterial Metabolites Influence the Host Immune Response
4.2. In Vivo/Ex Vivo Models
4.3. Immune Response in Animal Model of Co-Infection
4.4. Immune Response in In Vitro and Ex Vivo Models of Co-Infection
5. Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Latgé, J.P. Aspergillus fumigatus and aspergillosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 12, 310–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosmidis, C.; Denning, D.W. The clinical spectrum of pulmonary aspergillosis. Thorax 2015, 70, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gago, S.; Denning, D.W.; Bowyer, P. Pathophysiological aspects of Aspergillus colonization in disease. Med. Mycol. 2019, 57, S219–S227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everaerts, S.; Lagrou, K.; Vermeersch, K.; Dupont, L.J.; Vanaudenaerde, B.M.; Janssens, W. Aspergillus fumigatus Detection and Risk Factors in Patients with COPD-Bronchiectasis Overlap. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jubin, V.; Ranque, S.; Stremler Le Bel, N.; Sarles, J.; Dubus, J.-C. Risk factors for Aspergillus colonization and allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in children with cystic fibrosis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2010, 45, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botterel, F.; Angebault, C.; Cabaret, O.; Stressmann, F.A.; Costa, J.-M.; Wallet, F.; Wallaert, B.; Bruce, K.; Delhaes, L. Fungal and Bacterial Diversity of Airway Microbiota in Adults with Cystic Fibrosis: Concordance Between Conventional Methods and Ultra-Deep Sequencing, and Their Practical use in the Clinical Laboratory. Mycopathologia 2018, 183, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delhaes, L.; Touati, K.; Faure-Cognet, O.; Cornet, M.; Botterel, F.; Dannaoui, E.; Morio, F.; Le Pape, P.; Grenouillet, F.; Favennec, L.; et al. Prevalence, geographic risk factor, and development of a standardized protocol for fungal isolation in cystic fibrosis: Results from the international prospective study “MFIP”. J. Cyst. Fibros. Off. J. Eur. Cyst. Fibros. Soc. 2019, 18, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pragman, A.A.; Kim, H.B.; Reilly, C.S.; Wendt, C.; Isaacson, R.E. The lung microbiome in moderate and severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolwijck, E.; van de Veerdonk, F.L. The potential impact of the pulmonary microbiome on immunopathogenesis of Aspergillus-related lung disease. Eur. J. Immunol. 2014, 44, 3156–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, E.S.; Diamond, J.M.; Bittinger, K.; Fitzgerald, A.S.; Yadav, A.; Haas, A.R.; Bushman, F.D.; Collman, R.G. Lung-enriched organisms and aberrant bacterial and fungal respiratory microbiota after lung transplant. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delhaes, L.; Monchy, S.; Fréalle, E.; Hubans, C.; Salleron, J.; Leroy, S.; Prevotat, A.; Wallet, F.; Wallaert, B.; Dei-Cas, E.; et al. The airway microbiota in cystic fibrosis: A complex fungal and bacterial community--implications for therapeutic management. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borman, A.M.; Palmer, M.D.; Delhaes, L.; Carrère, J.; Favennec, L.; Ranque, S.; Gangneux, J.-P.; Horré, R.; Bouchara, J.-P. Lack of standardization in the procedures for mycological examination of sputum samples from CF patients: A possible cause for variations in the prevalence of filamentous fungi. Med. Mycol. 2010, 48, S88–S97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, J.; Brunel, S.F.; Warris, A. Aspergillus infections in cystic fibrosis. J. Infect. 2016, 72, S50–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiteson, K.L.; Bailey, B.; Bergkessel, M.; Conrad, D.; Delhaes, L.; Felts, B.; Harris, J.K.; Hunter, R.; Lim, Y.W.; Maughan, H.; et al. The upper respiratory tract as a microbial source for pulmonary infections in cystic fibrosis. Parallels from island biogeography. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 189, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monin, L.; Mehta, S.; Elsegeiny, W.; Gopal, R.; McAleer, J.P.; Oury, T.D.; Kolls, J.; Khader, S.A. Aspergillus fumigatus Preexposure Worsens Pathology and Improves Control of Mycobacterium abscessus Pulmonary Infection in Mice. Infect. Immun. 2018, 86, e00859-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granchelli, A.M.; Adler, F.R.; Keogh, R.H.; Kartsonaki, C.; Cox, D.R.; Liou, T.G. Microbial Interactions in the Cystic Fibrosis Airway. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e00354-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huerta, A.; Soler, N.; Esperatti, M.; Guerrero, M.; Menendez, R.; Gimeno, A.; Zalacaín, R.; Mir, N.; Aguado, J.M.; Torres, A. Importance of Aspergillus spp. isolation in Acute exacerbations of severe COPD: Prevalence, factors and follow-up: The FUNGI-COPD study. Respir. Res. 2014, 15, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verweij, P.E.; Brüggemann, R.J.M.; Wauters, J.; Rijnders, B.J.A.; Chiller, T.; van de Veerdonk, F. Influenza coinfection: Be(a)ware of invasive aspergillosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2019. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penner, J.C.; Ferreira, J.A.G.; Secor, P.R.; Sweere, J.M.; Birukova, M.K.; Joubert, L.-M.; Haagensen, J.A.J.; Garcia, O.; Malkovskiy, A.V.; Kaber, G.; et al. Pf4 bacteriophage produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa inhibits Aspergillus fumigatus metabolism via iron sequestration. Microbiol. Read. Engl. 2016, 162, 1583–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özkan-Kotiloğlu, S.; Coutts, R.H.A. Multiplex Detection of Aspergillus fumigatus Mycoviruses. Viruses 2018, 10, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirazi, F.; Ferreira, J.A.G.; Stevens, D.A.; Clemons, K.V.; Kontoyiannis, D.P. Biofilm Filtrates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strains Isolated from Cystic Fibrosis Patients Inhibit Preformed Aspergillus fumigatus Biofilms via Apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraemer, R.; Deloséa, N.; Ballinari, P.; Gallati, S.; Crameri, R. Effect of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis on lung function in children with cystic fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 174, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, R.; Dupuis, A.; Aaron, S.D.; Ratjen, F. The effect of chronic infection with Aspergillus fumigatus on lung function and hospitalization in patients with cystic fibrosis. Chest 2010, 137, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yonezawa, M.; Sugiyama, H.; Kizawa, K.; Hori, R.; Mitsuyama, J.; Araki, H.; Shimakura, M.; Minami, S.; Watanabe, Y.; Yamaguchi, K. A new model of pulmonary superinfection with Aspergillus fumigatus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa in mice. J. Infect. Chemother. Off. J. Jpn. Soc. Chemother. 2000, 6, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.A.G.; Penner, J.C.; Moss, R.B.; Haagensen, J.A.J.; Clemons, K.V.; Spormann, A.M.; Nazik, H.; Cohen, K.; Banaei, N.; Carolino, E.; et al. Inhibition of Aspergillus fumigatus and Its Biofilm by Pseudomonas aeruginosa Is Dependent on the Source, Phenotype and Growth Conditions of the Bacterium. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melloul, E.; Luiggi, S.; Anaïs, L.; Arné, P.; Costa, J.-M.; Fihman, V.; Briard, B.; Dannaoui, E.; Guillot, J.; Decousser, J.-W.; et al. Characteristics of Aspergillus fumigatus in Association with Stenotrophomonas maltophilia in an In Vitro Model of Mixed Biofilm. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, F.-M.C.; Seidler, M. Characteristics of pathogenic fungi and antifungal therapy in cystic fibrosis. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2010, 8, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez Granillo, A.; Canales, M.G.M.; Espíndola, M.E.S.; Martínez Rivera, M.A.; de Lucio, V.M.B.; Tovar, A.V.R. Antibiosis interaction of Staphylococccus aureus on Aspergillus fumigatus assessed in vitro by mixed biofilm formation. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goers, L.; Freemont, P.; Polizzi, K.M. Co-culture systems and technologies: Taking synthetic biology to the next level. J. R. Soc. Interface 2014, 11, 20140065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manavathu, E.K.; Vager, D.L.; Vazquez, J.A. Development and antimicrobial susceptibility studies of in vitro monomicrobial and polymicrobial biofilm models with Aspergillus fumigatus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briard, B.; Rasoldier, V.; Bomme, P.; ElAouad, N.; Guerreiro, C.; Chassagne, P.; Muszkieta, L.; Latgé, J.-P.; Mulard, L.; Beauvais, A. Dirhamnolipids secreted from Pseudomonas aeruginosa modify antifungal susceptibility of Aspergillus fumigatus by inhibiting β1,3 glucan synthase activity. ISME J. 2017, 11, 1578–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loussert, C.; Schmitt, C.; Prevost, M.-C.; Balloy, V.; Fadel, E.; Philippe, B.; Kauffmann-Lacroix, C.; Latgé, J.P.; Beauvais, A. In vivo biofilm composition of Aspergillus fumigatus. Cell. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akoumianaki, T.; Kyrmizi, I.; Valsecchi, I.; Gresnigt, M.S.; Samonis, G.; Drakos, E.; Boumpas, D.; Muszkieta, L.; Prevost, M.-C.; Kontoyiannis, D.P.; et al. Aspergillus Cell Wall Melanin Blocks LC3-Associated Phagocytosis to Promote Pathogenicity. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valiante, V.; Jain, R.; Heinekamp, T.; Brakhage, A.A. The MpkA MAP kinase module regulates cell wall integrity signaling and pyomelanin formation in Aspergillus fumigatus. Fungal Genet. Biol. FG B 2009, 46, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakobi, M.; Winkelmann, G.; Kaiser, D.; Kempler, C.; Jung, G.; Berg, G.; Bahl, H. Maltophilin: A new antifungal compound produced by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia R3089. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 1996, 49, 1101–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Calvo, A.M.; Yuen, G.Y.; Du, L.; Harris, S.D. Induction of cell wall thickening by the antifungal compound dihydromaltophilin disrupts fungal growth and is mediated by sphingolipid biosynthesis. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2009, 56, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gennip, M.; Christensen, L.D.; Alhede, M.; Phipps, R.; Jensen, P.Ø.; Christophersen, L.; Pamp, S.J.; Moser, C.; Mikkelsen, P.J.; Koh, A.Y.; et al. Inactivation of the rhlA gene in Pseudomonas aeruginosa prevents rhamnolipid production, disabling the protection against polymorphonuclear leukocytes. APMIS Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Immunol. Scand. 2009, 117, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abalos, A.; Pinazo, A.; Infante, M.R.; Casals, M.; Garcia, F.; Manresa, A. Physicochemical and antimicrobial properties of new rhamnolipids produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa AT10 from soybean oil refinery wastes. Langmuir 2001, 17, 1367–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, R.; Jiang, L.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, G.; Song, Z. Producing cell-free culture broth of rhamnolipids as a cost-effective fungicide against plant pathogens. J. Basic Microbiol. 2012, 52, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotirova, A.; Avramova, T.; Stoitsova, S.; Lazarkevich, I.; Lubenets, V.; Karpenko, E.; Galabova, D. The importance of rhamnolipid-biosurfactant-induced changes in bacterial membrane lipids of Bacillus subtilis for the antimicrobial activity of thiosulfonates. Curr. Microbiol. 2012, 65, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Pemmaraju, S.C.; Pruthi, P.A.; Cameotra, S.S.; Pruthi, V. Candida biofilm disrupting ability of di-rhamnolipid (RL-2) produced from Pseudomonas aeruginosa DSVP20. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 169, 2374–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perlin, D.S. Current perspectives on echinocandin class drugs. Future Microbiol. 2011, 6, 441–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, R.; Sykes, D.A.; Watson, D.; Rutman, A.; Taylor, G.W.; Cole, P.J. Measurement of Pseudomonas aeruginosa phenazine pigments in sputum and assessment of their contribution to sputum sol toxicity for respiratory epithelium. Infect. Immun. 1988, 56, 2515–2517. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kownatzki, R.; Tümmler, B.; Döring, G. Rhamnolipid of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in sputum of cystic fibrosis patients. Lancet Lond. Engl. 1987, 1, 1026–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, C.E.; Visser, M.B.; Schwab, U.; Sokol, P.A. Identification of N-acylhomoserine lactones in mucopurulent respiratory secretions from cystic fibrosis patients. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 244, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhamgaye, S.; Qu, Y.; Peleg, A.Y. Polymicrobial infections involving clinically relevant Gram-negative bacteria and fungi. Cell. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1716–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowat, E.; Rajendran, R.; Williams, C.; McCulloch, E.; Jones, B.; Lang, S.; Ramage, G. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and their small diffusible extracellular molecules inhibit Aspergillus fumigatus biofilm formation. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2010, 313, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reen, F.J.; Phelan, J.P.; Woods, D.F.; Shanahan, R.; Cano, R.; Clarke, S.; McGlacken, G.P.; O’Gara, F. Harnessing Bacterial Signals for Suppression of Biofilm Formation in the Nosocomial Fungal Pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briard, B.; Bomme, P.; Lechner, B.E.; Mislin, G.L.A.; Lair, V.; Prévost, M.-C.; Latgé, J.-P.; Haas, H.; Beauvais, A. Pseudomonas aeruginosa manipulates redox and iron homeostasis of its microbiota partner Aspergillus fumigatus via phenazines. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sass, G.; Nazik, H.; Penner, J.; Shah, H.; Ansari, S.R.; Clemons, K.V.; Groleau, M.-C.; Dietl, A.-M.; Visca, P.; Haas, H.; et al. Studies of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Mutants Indicate Pyoverdine as the Central Factor in Inhibition of Aspergillus fumigatus Biofilm. J. Bacteriol. 2018, 200. [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis, P.; Dingemans, J. Pseudomonas aeruginosa adapts its iron uptake strategies in function of the type of infections. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2013, 3, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kravchenko, V.V.; Kaufmann, G.F.; Mathison, J.C.; Scott, D.A.; Katz, A.Z.; Grauer, D.C.; Lehmann, M.; Meijler, M.M.; Janda, K.D.; Ulevitch, R.J. Modulation of gene expression via disruption of NF-kappaB signaling by a bacterial small molecule. Science 2008, 321, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogan, D.A.; Vik, A.; Kolter, R. A Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing molecule influences Candida albicans morphology. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 1212–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cugini, C.; Calfee, M.W.; Farrow, J.M.; Morales, D.K.; Pesci, E.C.; Hogan, D.A. Farnesol, a common sesquiterpene, inhibits PQS production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 65, 896–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey-Klett, P.; Burlinson, P.; Deveau, A.; Barret, M.; Tarkka, M.; Sarniguet, A. Bacterial-fungal interactions: Hyphens between agricultural, clinical, environmental, and food microbiologists. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. MMBR 2011, 75, 583–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez, P.N.; Koch, G.; Thompson, J.A.; Xavier, K.B.; Cool, R.H.; Quax, W.J. The multiple signaling systems regulating virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. MMBR 2012, 76, 46–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Kim, J.; Liew, M.; Yan, J.K.; Herrera, O.; Bok, J.W.; Kelleher, N.L.; Keller, N.P.; Wang, Y. Redox metabolites signal polymicrobial biofilm development via the NapA oxidative stress cascade in Aspergillus. Curr. Biol. CB 2015, 25, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, M. Pyocyanin induces oxidative stress in human endothelial cells and modulates the glutathione redox cycle. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2002, 33, 1527–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, D.K.; Grahl, N.; Okegbe, C.; Dietrich, L.E.P.; Jacobs, N.J.; Hogan, D.A. Control of Candida albicans metabolism and biofilm formation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa phenazines. mBio 2013, 4, e00526-00512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moree, W.J.; Phelan, V.V.; Wu, C.-H.; Bandeira, N.; Cornett, D.S.; Duggan, B.M.; Dorrestein, P.C. Interkingdom metabolic transformations captured by microbial imaging mass spectrometry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 13811–13816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandel, J.; Humbert, N.; Elhabiri, M.; Schalk, I.J.; Mislin, G.L.A.; Albrecht-Gary, A.-M. Pyochelin, a siderophore of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Physicochemical characterization of the iron(III), copper(II) and zinc(II) complexes. Dalton Trans. Camb. Engl. 2003 2012, 41, 2820–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumas, Z.; Ross-Gillespie, A.; Kümmerli, R. Switching between apparently redundant iron-uptake mechanisms benefits bacteria in changeable environments. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2013, 280, 20131055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Medina, E.; Fan, D.; Coughlin, L.A.; Ho, E.X.; Lamont, I.L.; Reimmann, C.; Hooper, L.V.; Koh, A.Y. Candida albicans Inhibits Pseudomonas aeruginosa Virulence through Suppression of Pyochelin and Pyoverdine Biosynthesis. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, C.D.; Graham, R. Isolation of an iron-binding compound from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 1979, 137, 357–364. [Google Scholar]
- Adler, C.; Corbalán, N.S.; Seyedsayamdost, M.R.; Pomares, M.F.; de Cristóbal, R.E.; Clardy, J.; Kolter, R.; Vincent, P.A. Catecholate siderophores protect bacteria from pyochelin toxicity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braud, A.; Hannauer, M.; Mislin, G.L.A.; Schalk, I.J. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa pyochelin-iron uptake pathway and its metal specificity. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 3517–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
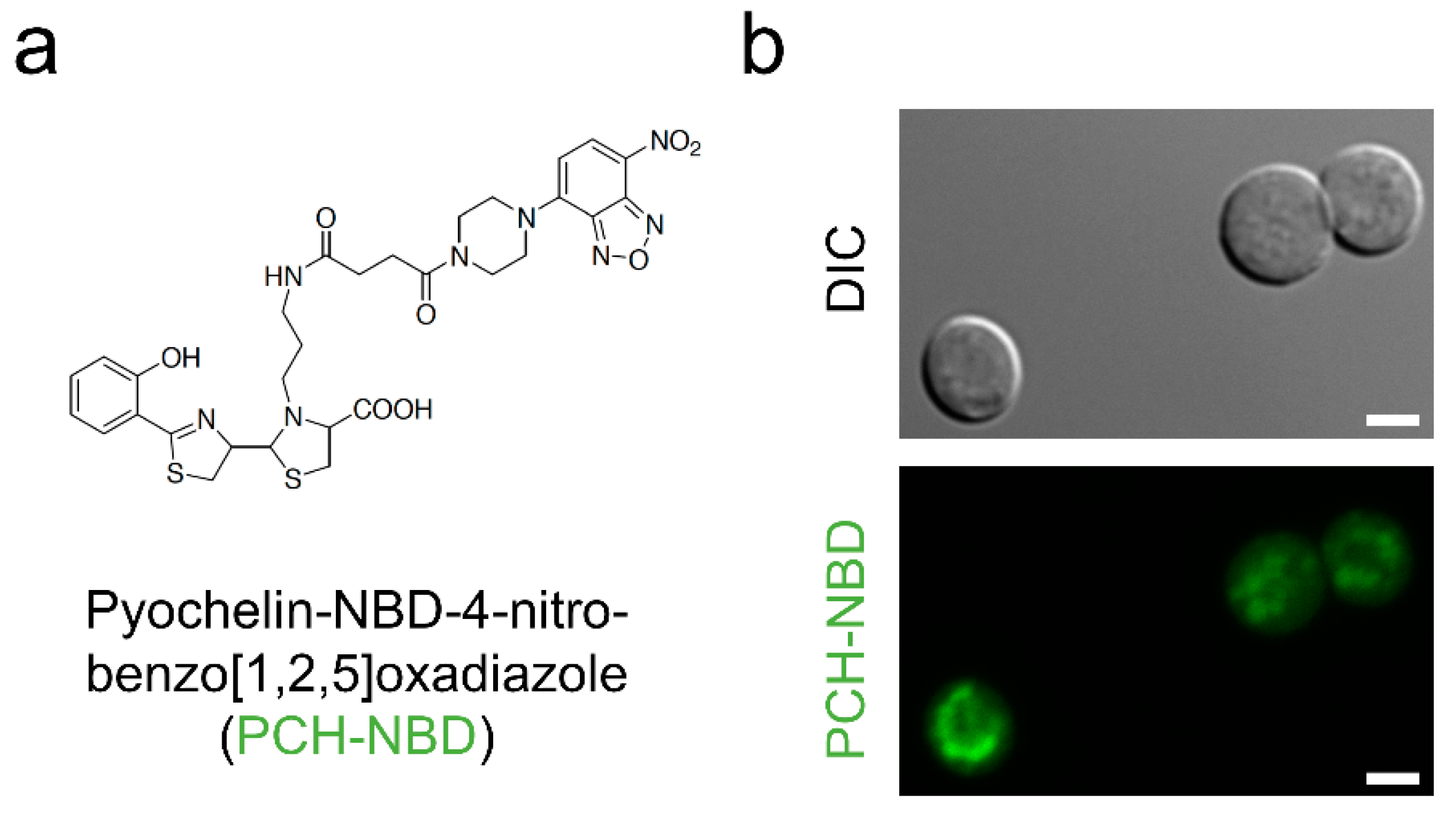
- Noël, S.; Guillon, L.; Schalk, I.J.; Mislin, G.L.A. Synthesis of fluorescent probes based on the pyochelin siderophore scaffold. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 844–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeWitte, J.J.; Cox, C.D.; Rasmussen, G.T.; Britigan, B.E. Assessment of structural features of the pseudomonas siderophore pyochelin required for its ability to promote oxidant-mediated endothelial cell injury. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2001, 393, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, R.; Clemons, K.V.; Stevens, D.A. Effect of Anaerobiasis or Hypoxia on Pseudomonas aeruginosa Inhibition of Aspergillus fumigatus Biofilm. Arch. Microbiol. 2017, 199, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briard, B.; Heddergott, C.; Latgé, J.-P. Volatile Compounds Emitted by Pseudomonas aeruginosa Stimulate Growth of the Fungal Pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus. mBio 2016, 7, e00219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heddergott, C.; Calvo, A.M.; Latgé, J.P. The volatome of Aspergillus fumigatus. Eukaryot. Cell 2014, 13, 1014–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, E.F.; Tsui, C.; Kucharíková, S.; Andes, D.; Van Dijck, P.; Jabra-Rizk, M.A. Commensal Protection of Staphylococcus aureus against Antimicrobials by Candida albicans Biofilm Matrix. mBio 2016, 7, e01365-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nett, J.E.; Sanchez, H.; Cain, M.T.; Andes, D.R. Genetic basis of Candida biofilm resistance due to drug-sequestering matrix glucan. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, R.C.; Klepac-Ceraj, V.; Lorenzi, M.M.; Grotzinger, H.; Martin, T.R.; Newman, D.K. Phenazine content in the cystic fibrosis respiratory tract negatively correlates with lung function and microbial complexity. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 47, 738–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allard, J.B.; Rinaldi, L.; Wargo, M.J.; Allen, G.; Akira, S.; Uematsu, S.; Poynter, M.E.; Hogan, D.A.; Rincon, M.; Whittaker, L.A. Th2 allergic immune response to inhaled fungal antigens is modulated by TLR-4-independent bacterial products. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009, 39, 776–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britigan, B.E.; Rasmussen, G.T.; Cox, C.D. Augmentation of oxidant injury to human pulmonary epithelial cells by the Pseudomonas aeruginosa siderophore pyochelin. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar]
- Reece, E.; Doyle, S.; Greally, P.; Renwick, J.; McClean, S. Aspergillus fumigatus Inhibits Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Co-culture: Implications of a Mutually Antagonistic Relationship on Virulence and Inflammation in the CF Airway. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hraiech, S.; Brégeon, F.; Brunel, J.-M.; Rolain, J.-M.; Lepidi, H.; Andrieu, V.; Raoult, D.; Papazian, L.; Roch, A. Antibacterial efficacy of inhaled squalamine in a rat model of chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2452–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.; Thévenot, G.; Danel, S.; Chapron, J.; Tazi, A.; Macey, J.; Dusser, D.J.; Fajac, I.; Burgel, P.-R. Pseudomonas aeruginosa induces vascular endothelial growth factor synthesis in airway epithelium in vitro and in vivo. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 38, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, N.; Datta, K.; Askin, F.B.; Staab, J.F.; Marr, K.A. Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator regulates epithelial cell response to Aspergillus and resultant pulmonary inflammation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 185, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiser, N.W.; Engelhardt, J.F. New animal models of cystic fibrosis: what are they teaching us? Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2011, 17, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casaulta, C.; Schöni, M.H.; Weichel, M.; Crameri, R.; Jutel, M.; Daigle, I.; Akdis, M.; Blaser, K.; Akdis, C.A. IL-10 controls Aspergillus fumigatus- and Pseudomonas aeruginosa-specific T-cell response in cystic fibrosis. Pediatr. Res. 2003, 53, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Malcolm, K.C.; Nichols, E.M.; Caceres, S.M.; Kret, J.E.; Martiniano, S.L.; Sagel, S.D.; Chan, E.D.; Caverly, L.; Solomon, G.M.; Reynolds, P.; et al. Mycobacterium abscessus induces a limited pattern of neutrophil activation that promotes pathogen survival. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baxter, C.G.; Rautemaa, R.; Jones, A.M.; Webb, A.K.; Bull, M.; Mahenthiralingam, E.; Denning, D.W. Intravenous antibiotics reduce the presence of Aspergillus in adult cystic fibrosis sputum. Thorax 2013, 68, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, J.L.; Van Dalfsen, J.M.; Shawar, R.M.; Otto, K.L.; Garber, R.L.; Quan, J.M.; Montgomery, A.B.; Albers, G.M.; Ramsey, B.W.; Smith, A.L. Effect of chronic intermittent administration of inhaled tobramycin on respiratory microbial flora in patients with cystic fibrosis. J. Infect. Dis. 1999, 179, 1190–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barkauskas, C.E.; Chung, M.-I.; Fioret, B.; Gao, X.; Katsura, H.; Hogan, B.L.M. Lung organoids: Current uses and future promise. Dev. Camb. Engl. 2017, 144, 986–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, J.; Hamidi, F.; Leborgne, R.; Beau, R.; Castier, Y.; Mordant, P.; Boukkerou, A.; Latgé, J.P.; Pretolani, M. Penetration of the Human Pulmonary Epithelium by Aspergillus fumigatus Hyphae. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, 1306–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netzker, T.; Fischer, J.; Weber, J.; Mattern, D.J.; König, C.C.; Valiante, V.; Schroeckh, V.; Brakhage, A.A. Microbial communication leading to the activation of silent fungal secondary metabolite gene clusters. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuck, K.M.; Shipley, S.; Newman, D.J. Induced production of N-formyl alkaloids from Aspergillus fumigatus by co-culture with Streptomyces peucetius. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1653–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- König, C.C.; Scherlach, K.; Schroeckh, V.; Horn, F.; Nietzsche, S.; Brakhage, A.A.; Hertweck, C. Bacterium induces cryptic meroterpenoid pathway in the pathogenic fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. Chembiochem Eur. J. Chem. Biol. 2013, 14, 938–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAleer, J.P.; Nguyen, N.L.H.; Chen, K.; Kumar, P.; Ricks, D.M.; Binnie, M.; Armentrout, R.A.; Pociask, D.A.; Hein, A.; Yu, A.; et al. Pulmonary Th17 Antifungal Immunity Is Regulated by the Gut Microbiome. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2016, 197, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

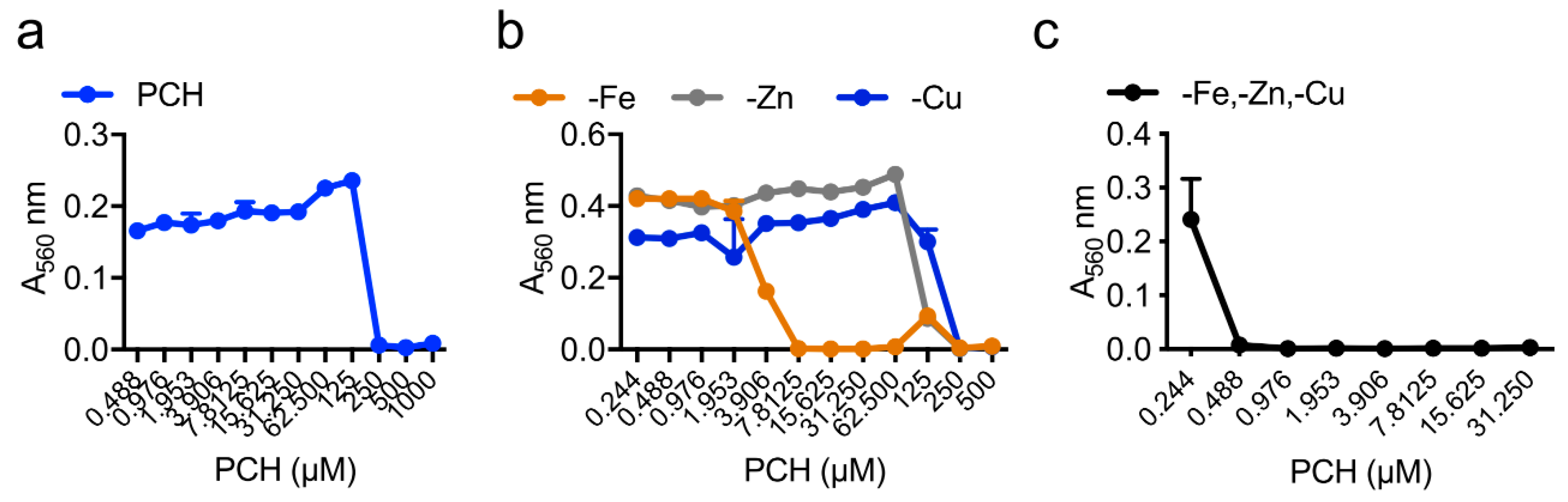
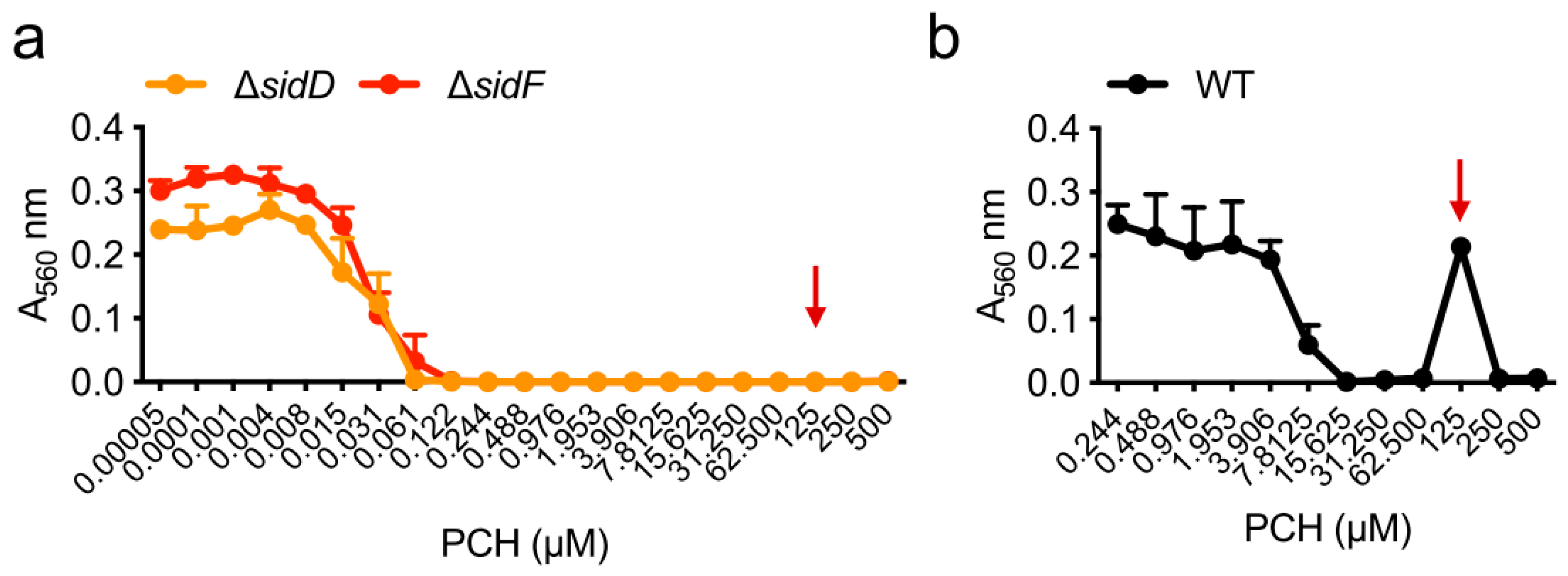



| Strain | MM | MM(-Fe) | MM(-Zn) |
|---|---|---|---|
| WT | 250 µM | 7.8 µM | 250 µM |
| ΔhapX | 250 µM | 1.9 µM | 250 µM |
| ΔsidC | 250 µM | 7.8 µM | 250 µM |
| ΔsidD | 62 µM | 0.1 µM | 0.8 µM |
| ΔsidF | 62 µM | 0.1 µM | 0.8 µM |
| P. aeruginosa | A. fumigatus | Host Immune Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Homoserine lactones | Fungal growth inhibition | Interferon-γ induction, NFκB disruption |
| Pyoverdine | Iron starvation, fungal growth inhibition | ? |
| Pyochelin | Iron starvation, ROS/RNS production, fungal killing | ROS production, cell apoptosis |
| Ferric iron provision, fungal growth stimulation | ||
| Phenazine 1HP | Iron chelation, ROS/RNS production, fungal killing | ROS production, cell apoptosis |
| Phenazines PYO, PCA, PCN (< 100 µM) | Ferric iron provision, fungal growth stimulation | ROS production, cell apoptosis |
| Dirhamnolipids | Inhibition of β1,3 glucan synthase | Polymorphonuclear leucocytes necrosis, calcium-mediated protein kinase C inhibition |
| Thick cell wall, high chitin, GAG and melanin production, persistence, resistance to caspofungin | ||
| Dimethylsulfide | Fungal growth stimulation | ? |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Briard, B.; Mislin, G.L.A.; Latgé, J.-P.; Beauvais, A. Interactions between Aspergillus fumigatus and Pulmonary Bacteria: Current State of the Field, New Data, and Future Perspective. J. Fungi 2019, 5, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof5020048
Briard B, Mislin GLA, Latgé J-P, Beauvais A. Interactions between Aspergillus fumigatus and Pulmonary Bacteria: Current State of the Field, New Data, and Future Perspective. Journal of Fungi. 2019; 5(2):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof5020048
Chicago/Turabian StyleBriard, Benoit, Gaëtan L. A. Mislin, Jean-Paul Latgé, and Anne Beauvais. 2019. "Interactions between Aspergillus fumigatus and Pulmonary Bacteria: Current State of the Field, New Data, and Future Perspective" Journal of Fungi 5, no. 2: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof5020048
APA StyleBriard, B., Mislin, G. L. A., Latgé, J.-P., & Beauvais, A. (2019). Interactions between Aspergillus fumigatus and Pulmonary Bacteria: Current State of the Field, New Data, and Future Perspective. Journal of Fungi, 5(2), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof5020048





