Arabidopsis Toxicos en Levadura 12 (ATL12): A Gene Involved in Chitin-Induced, Hormone-Related and NADPH Oxidase-Mediated Defense Responses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biological Materials
2.2. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.3. Generation of Transgenic Plants and Constructs
2.4. Subcellular Localization of ATL12 Protein
2.5. Disease Assessment
2.6. Histochemical Staining Assay
2.7. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Detection via DAB Staining Assay
2.8. Quantitative RT-PCR and RT-PCR
3. Results
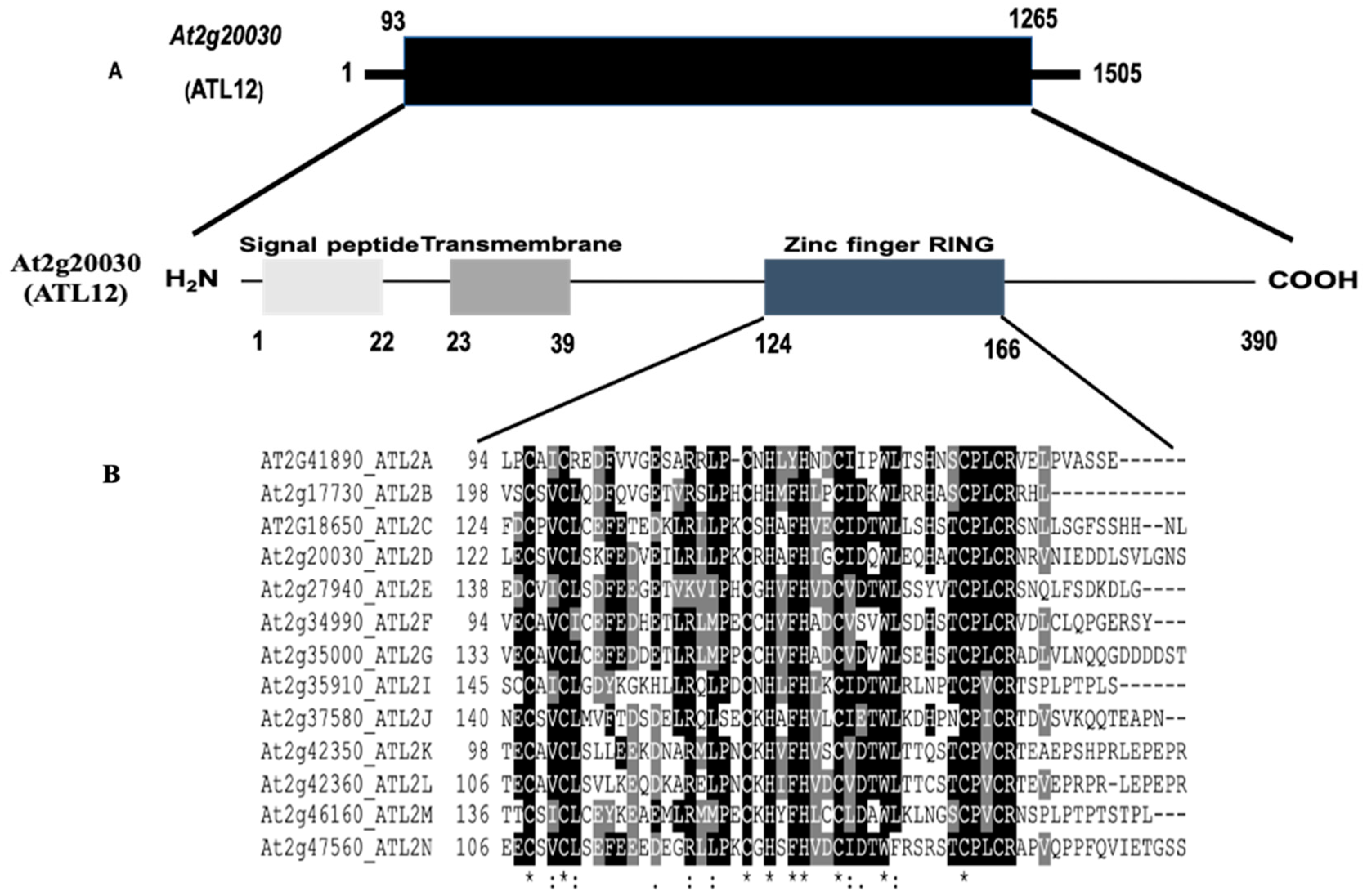
3.1. Sequence Analysis of the Arabidopsis thaliana ATL12 Gene
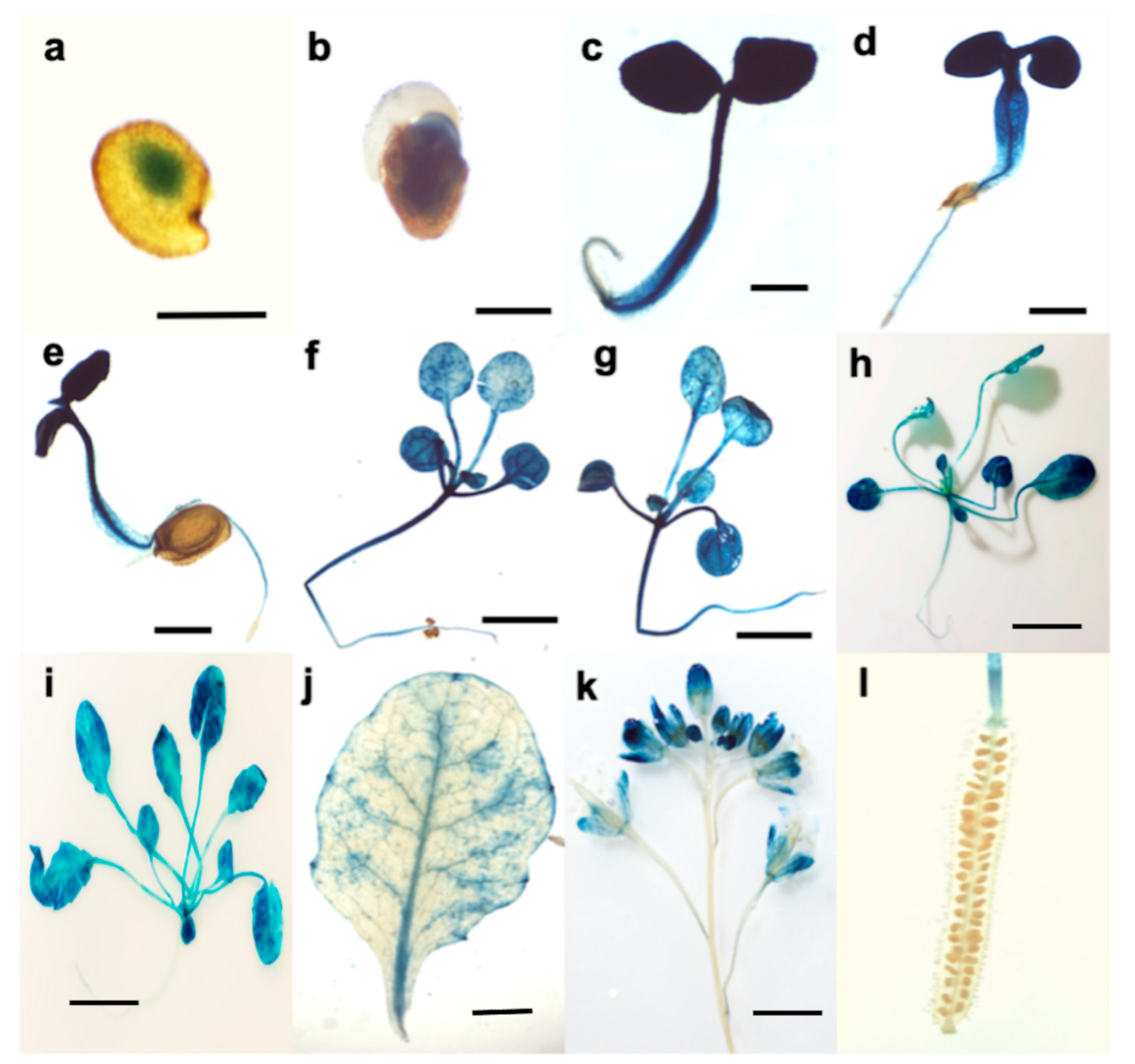
3.2. Tissue Expression Pattern of ATL12
3.3. ATL12 Localizes to the Plasma Membrane
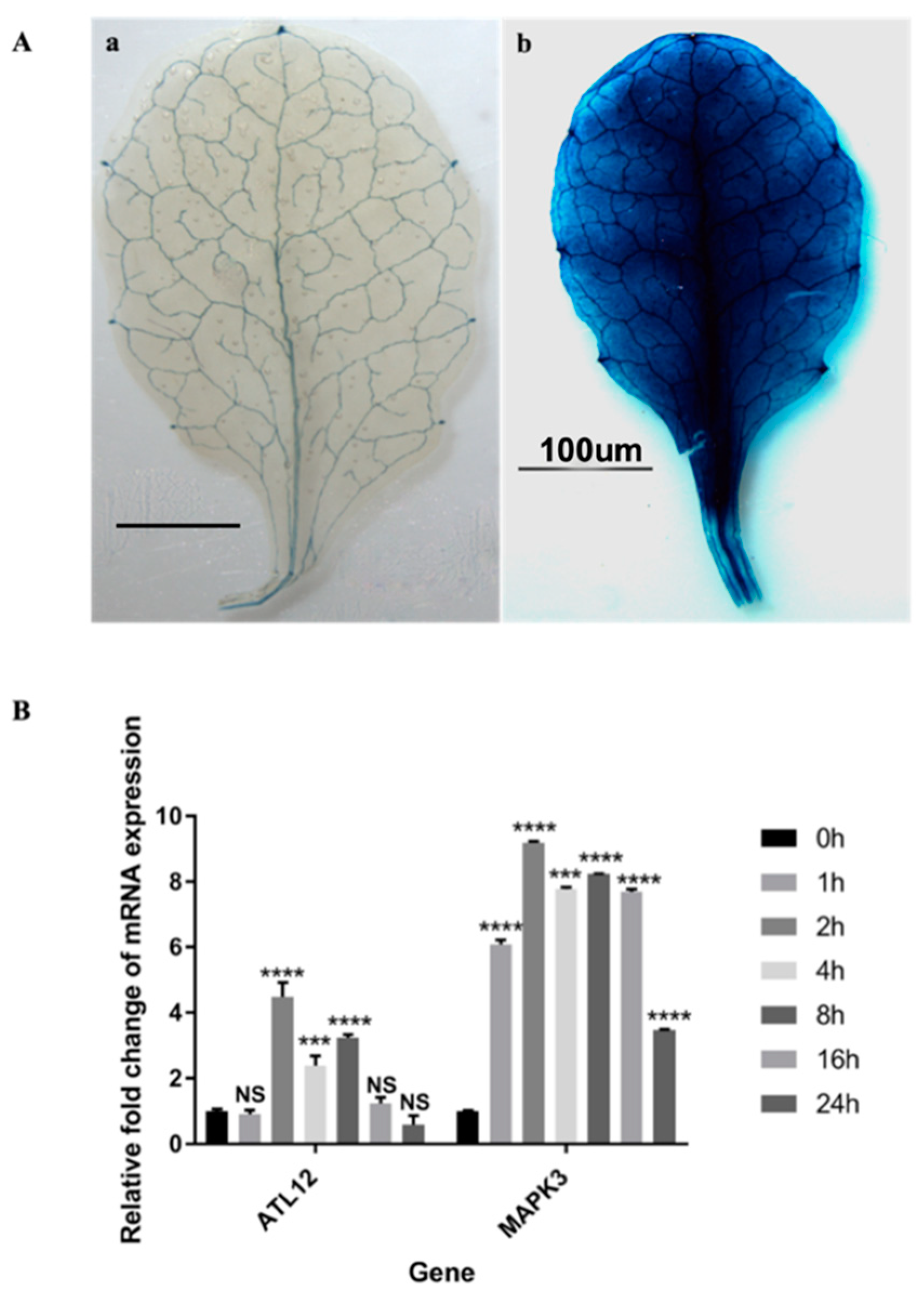
3.4. ATL12 Expression Is Induced by Chitin Treatment
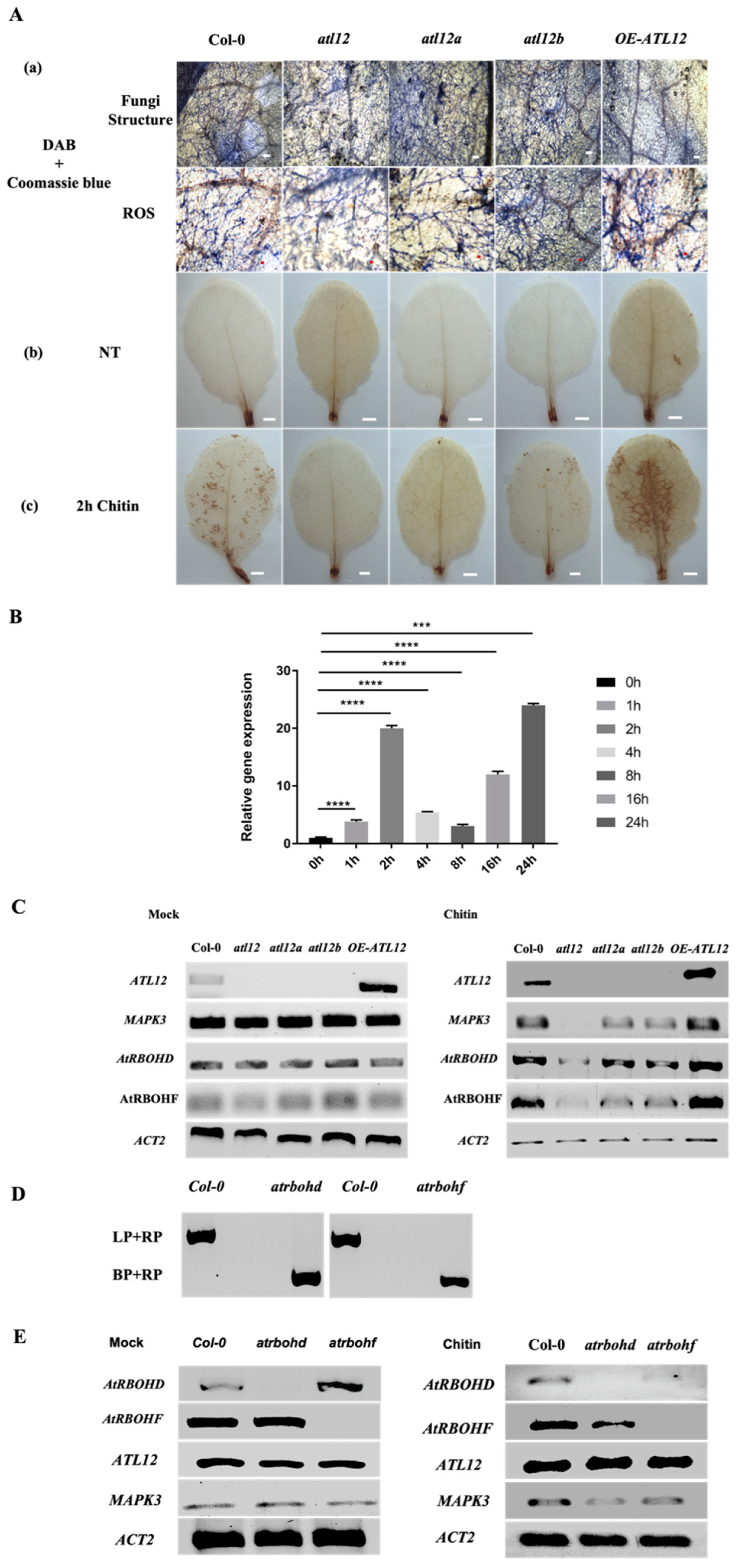
3.5. Mutants of atl12 Are More Susceptible to Golovinomyces Cichoracearum Infection
3.6. Chitin-Induced ATL12 Expression Is Linked to NADPH Oxidase AtRBOHD/F-Driven ROS Production
3.7. ATL12 May Act Downstream of Chitin-Mediated MAP Kinase 3 (MAPK3) Signaling
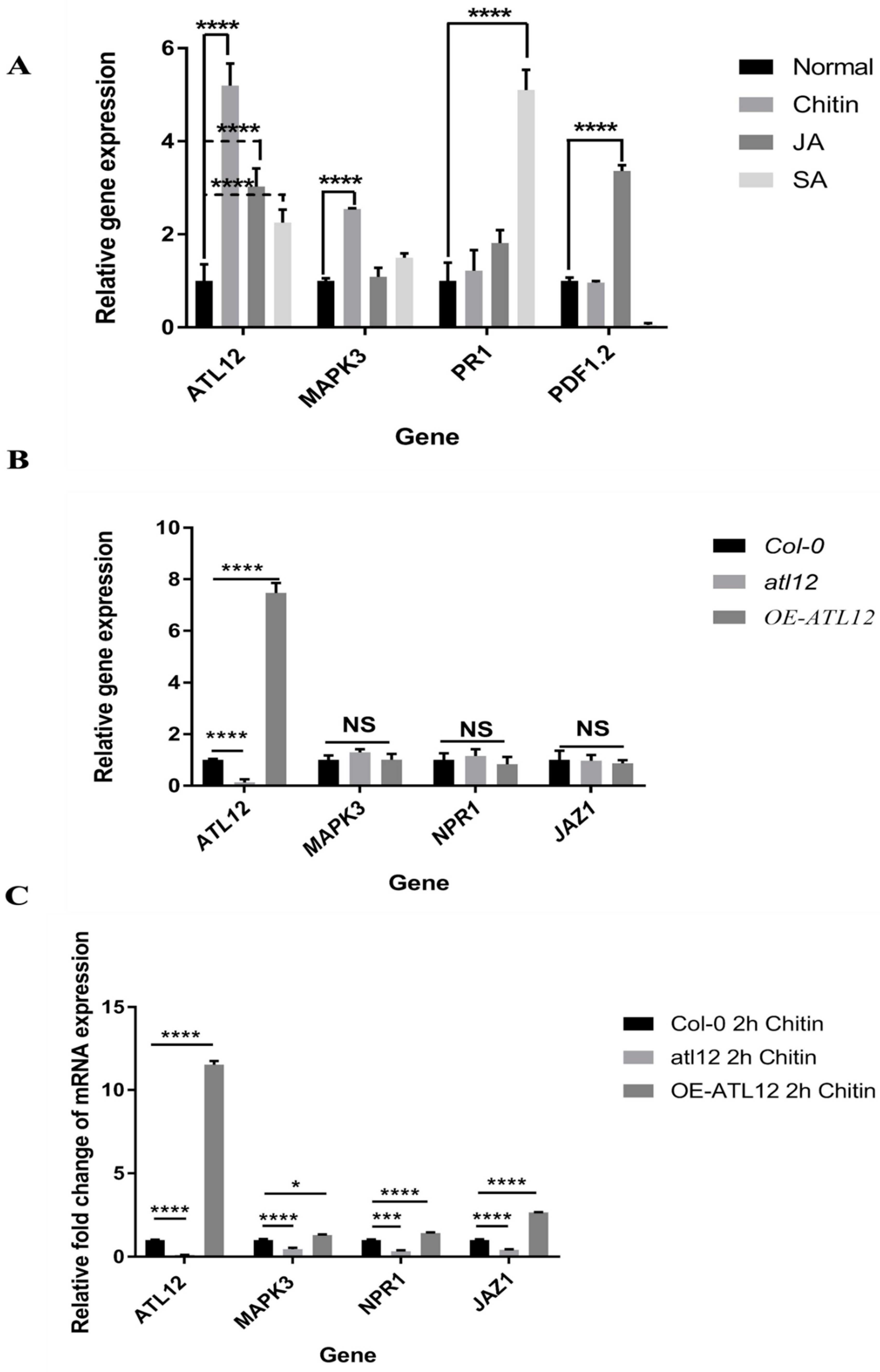
3.8. Influence of SA-, JA- and Chitin-Mediated Pathways on ATL12 Expression
4. Discussion
4.1. ATL12 Is a Putative E3 Ubiquitin Ligase That Is Involved in Defense Responses against Fungal Pathogens
4.2. ATL12 Is Involved in Both NADPH Oxidase-Mediated and Chitin Mediated Defense Responses
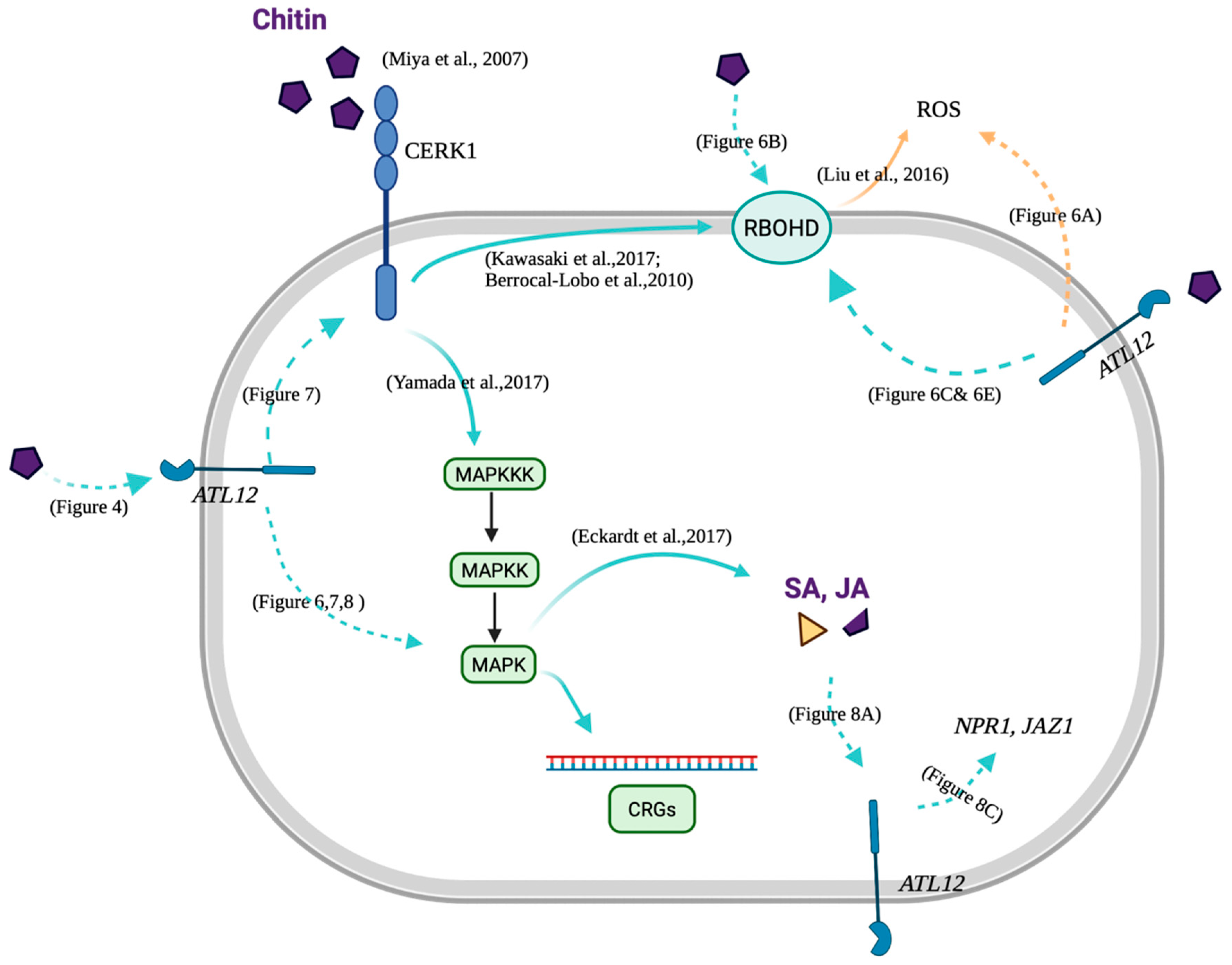
4.3. Possible Role of ATL12 in Hormone, NADPH Oxidase-Mediated and Chitin- Mediated Defense
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bigeard, J.; Colcombet, J.; Hirt, H. Signaling Mechanisms in Pattern-Triggered Immunity (PTI). Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 521–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fones, H.N.; Bebber, D.P.; Chaloner, T.M.; Kay, W.T.; Steinberg, G.; Gurr, S.J. Threats to global food security from emerging fungal and oomycete crop pathogens. Nat. Food 2020, 1, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micali, C.; Göllner, K.; Humphry, M.; Consonni, C.; Panstruga, R. The Powdery Mildew Disease of Arabidopsis: A Paradigm for the Interaction between Plants and Biotrophic Fungi. Arab. Book 2008, 6, e0115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petutschnig, E.K.; Jones, A.M.; Serazetdinova, L.; Lipka, U.; Lipka, V. The Lysin Motif Receptor-like Kinase (LysM-RLK) CERK1 Is a Major Chitin-binding Protein in Arabidopsis thaliana and Subject to Chitin-induced Phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 28902–28911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.D.G.; Dangl, J.L. The plant immune system. Nature 2006, 444, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.K.; Sharma, K.; Misra, R.S. Elicitor recognition, signal transduction and induced resistance in plants. J. Plant Interact. 2012, 7, 95–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, G.S.; Reddy, A. PAMP-triggered immunity: Early events in the activation of FLAGELLIN SENSITIVE2. Plant Signal. Behav. 2008, 3, 423–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyin, H.; Edu, Y.; Edong, Z. Chitin Oligosaccharide and Chitosan Oligosaccharide: Two Similar but Different Plant Elicitors. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.-H.; Yan, H.-Z.; Liou, R.-F. A novel elicitor protein from Phytophthora parasitica induces plant basal immunity and systemic acquired resistance. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2015, 16, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, J.A.; Daudi, A.; Butt, V.S.; Bolwell, G.P. Reactive oxygen species and their role in plant defence and cell wall metabolism. Planta 2012, 236, 765–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrocal-Lobo, M.; Stone, S.; Yang, X.; Antico, J.; Callis, J.; Ramonell, K.M.; Somerville, S. ATL9, a RING Zinc Finger Protein with E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Activity Implicated in Chitin- and NADPH Oxidase-Mediated Defense Responses. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takenaka, Y.; Nakano, S.; Tamoi, M.; Sakuda, S.; Fukamizo, T. Chitinase Gene Expression in Response to Environmental Stresses in Arabidopsis thaliana: Chitinase Inhibitor Allosamidin Enhances Stress Tolerance. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2009, 73, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miya, A.; Albert, P.; Shinya, T.; Desaki, Y.; Ichimura, K.; Shirasu, K.; Narusaka, Y.; Kawakami, N.; Kaku, H.; Shibuya, N. CERK1, a LysM receptor kinase, is essential for chitin elicitor signaling in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19613–19618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Yoshimura, S.; Terauchi, A.; Kawasaki, T. Conservation of Chitin-Induced MAPK Signaling Pathways in Rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2017, 58, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, T.; Yamada, K.; Yoshimura, S.; Yamaguchi, K. Chitin receptor-mediated activation of MAP kinases and ROS production in rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Signal. Behav. 2017, 12, e1361076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, J.; Zhang, X.-C.; Neece, D.; Ramonell, K.M.; Clough, S.; Kim, S.-Y.; Stacey, M.G.; Stacey, G. A LysM Receptor-Like Kinase Plays a Critical Role in Chitin Signaling and Fungal Resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, A.; Ewan, R.; Mesmar, J.; Gudipati, V.; Sadanandom, A. E3 ubiquitin ligases and plant innate immunity. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dielen, A.-S.; Badaoui, S.; Candresse, T.; German-Retana, S. The ubiquitin/26S proteasome system in plant-pathogen interactions: A never-ending hide-and-seek game. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2010, 11, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadanandom, A.; Bailey, M.; Ewan, R.; Lee, J.; Nelis, S. The ubiquitin–proteasome system: Central modifier of plant signalling. New Phytol. 2012, 196, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ausubel, F.M. Are innate immune signaling pathways in plants and animals conserved? Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Oh, T.R.; Cho, S.K.; Yang, S.W.; Kim, W.T. Arabidopsis Tóxicos en Levadura 78 (AtATL78) mediates ABA-dependent ROS signaling in response to drought stress. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 469, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, M.; Guzmán, P. Isolation and gene expression analysis of Arabidopsis thaliana mutants with constitutive expression of ATL2, an early elicitor-response RING-H2 zinc-finger gene. Genetics 2004, 167, 919–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clough, S.J.; Bent, A.F. Floral dip: A simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 1998, 16, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Bi, G.; Liang, X.; Zhou, J.-M. Early signalling mechanisms underlying receptor kinase-mediated immunity in plants. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 374, 20180310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glazebrook, J. Contrasting Mechanisms of Defense against Biotrophic and Necrotrophic Pathogens. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2005, 43, 205–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, M.; Parra, S.; Alcaraz, L.D.; Guzmán, P. The ATL Gene Family from Arabidopsis thaliana and Oryza sativa Comprises a Large Number of Putative Ubiquitin Ligases of the RING-H2 Type. J. Mol. Evol. 2006, 62, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Nowara, D.; Schweizer, P. Protein Polyubiquitination Plays a Role in Basal Host Resistance of Barley. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 3321–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzano, C.; Abraham, Z.; López-Torrejón, G.; Del Pozo, J.C. Identification of ubiquitinated proteins in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2008, 68, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, S.L. The role of ubiquitin and the 26S proteasome in plant abiotic stress signaling. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreher, K.; Callis, J. Ubiquitin, Hormones and Biotic Stress in Plants. Ann. Bot. 2007, 99, 787–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; Guo, T.; Lefebvre, M.; Scaglione, S.; Antico, C.J.; Jing, T.; Yang, X.; Shan, W.; Ramonell, K.M. Expression and regulation of ATL9, an E3 ubiquitin ligase involved in plant defense. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Nan, N.; Shi, L.; Li, N.; Huang, S.; Zhang, A.; Liu, Y.; Guo, P.; Liu, B.; Xu, Z. Arabidopsis BRCA1 represses RRTF1-mediated ROS production and ROS-responsive gene expression under dehydration stress. New Phytol. 2020, 228, 1591–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, D.R.; Bindschedler, L.; Strickland, T.S.; Bolwell, G.P. Production of reactive oxygen species in Arabidopsis thaliana cell suspension cultures in response to an elicitor from Fusarium oxysporum: Implications for basal resistance. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 1817–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, N.H.; McAinsh, M.R.; Hetherington, A.; Knight, M. ROS perception in Arabidopsis thaliana: The ozone-induced calcium response. Plant J. 2005, 41, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukagoshi, H.; Busch, W.; Benfey, P.N. Transcriptional Regulation of ROS Controls Transition from Proliferation to Differentiation in the Root. Cell 2010, 143, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Ullah, F.; Zhou, D.-X.; Yi, M.; Zhao, Y. Mechanisms of ROS Regulation of Plant Development and Stress Responses. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derksen, H.; Rampitsch, C.; Daayf, F. Signaling cross-talk in plant disease resistance. Plant Sci. 2013, 207, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; He, C. Regulation of plant reactive oxygen species (ROS) in stress responses: Learning from AtRBOHD. Plant Cell Rep. 2016, 35, 995–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y. Arabidopsis thaliana CRK41 negatively regulates salt tolerance via H2O2 and ABA cross-linked networks. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2020, 179, 104210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, T.K.; Anderson, M.D.; Martin, B.A.; Stewart, C.R. Evidence for Chilling-Induced Oxidative Stress in Maize Seedlings and a Regulatory Role for Hydrogen Peroxide. Plant Cell 1994, 6, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Chan, Z. ROS Regulation during Abiotic Stress Responses in Crop Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckardt, N.A. The Plant Cell Reviews Plant Immunity: Receptor-Like Kinases, ROS-RLK Crosstalk, Quantitative Resistance, and the Growth/Defense Trade-Off. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 601–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, F.; Guo, T.; Ramonell, K.M. Arabidopsis Toxicos en Levadura 12 (ATL12): A Gene Involved in Chitin-Induced, Hormone-Related and NADPH Oxidase-Mediated Defense Responses. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 883. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7100883
Kong F, Guo T, Ramonell KM. Arabidopsis Toxicos en Levadura 12 (ATL12): A Gene Involved in Chitin-Induced, Hormone-Related and NADPH Oxidase-Mediated Defense Responses. Journal of Fungi. 2021; 7(10):883. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7100883
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Feng, Tingwei Guo, and Katrina M. Ramonell. 2021. "Arabidopsis Toxicos en Levadura 12 (ATL12): A Gene Involved in Chitin-Induced, Hormone-Related and NADPH Oxidase-Mediated Defense Responses" Journal of Fungi 7, no. 10: 883. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7100883
APA StyleKong, F., Guo, T., & Ramonell, K. M. (2021). Arabidopsis Toxicos en Levadura 12 (ATL12): A Gene Involved in Chitin-Induced, Hormone-Related and NADPH Oxidase-Mediated Defense Responses. Journal of Fungi, 7(10), 883. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7100883






