Longitudinal Characterization of the Gut Bacterial and Fungal Communities in Yaks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Samples Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. 16S rDNA and ITS Genes Amplification and High-Throughput Sequencing
2.4. Bioinformatics and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. 16S rDNA and ITS Sequence Data Analysis
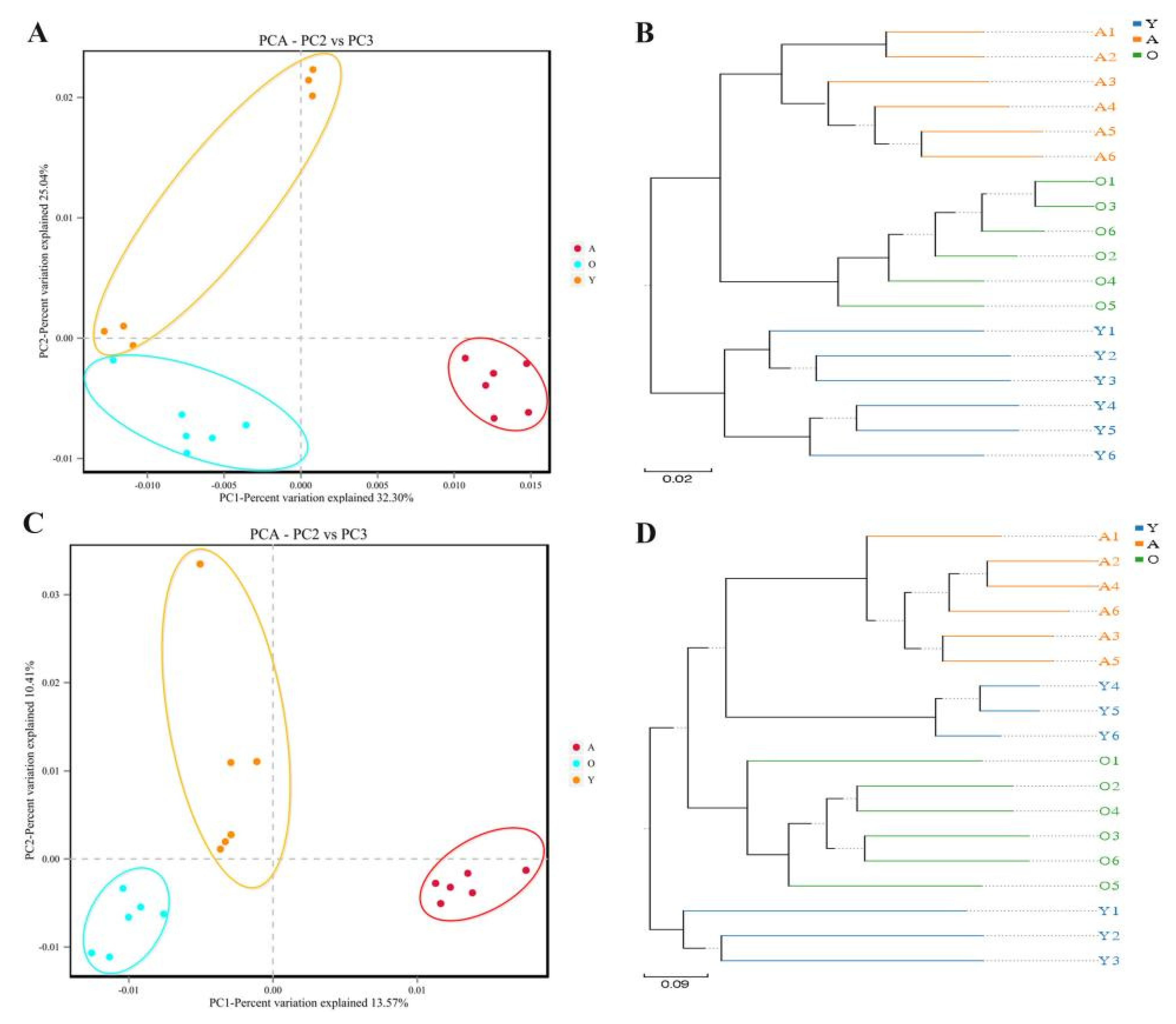
3.2. Analysis of Bacterial and Fungal Microbiome Diversity with Age
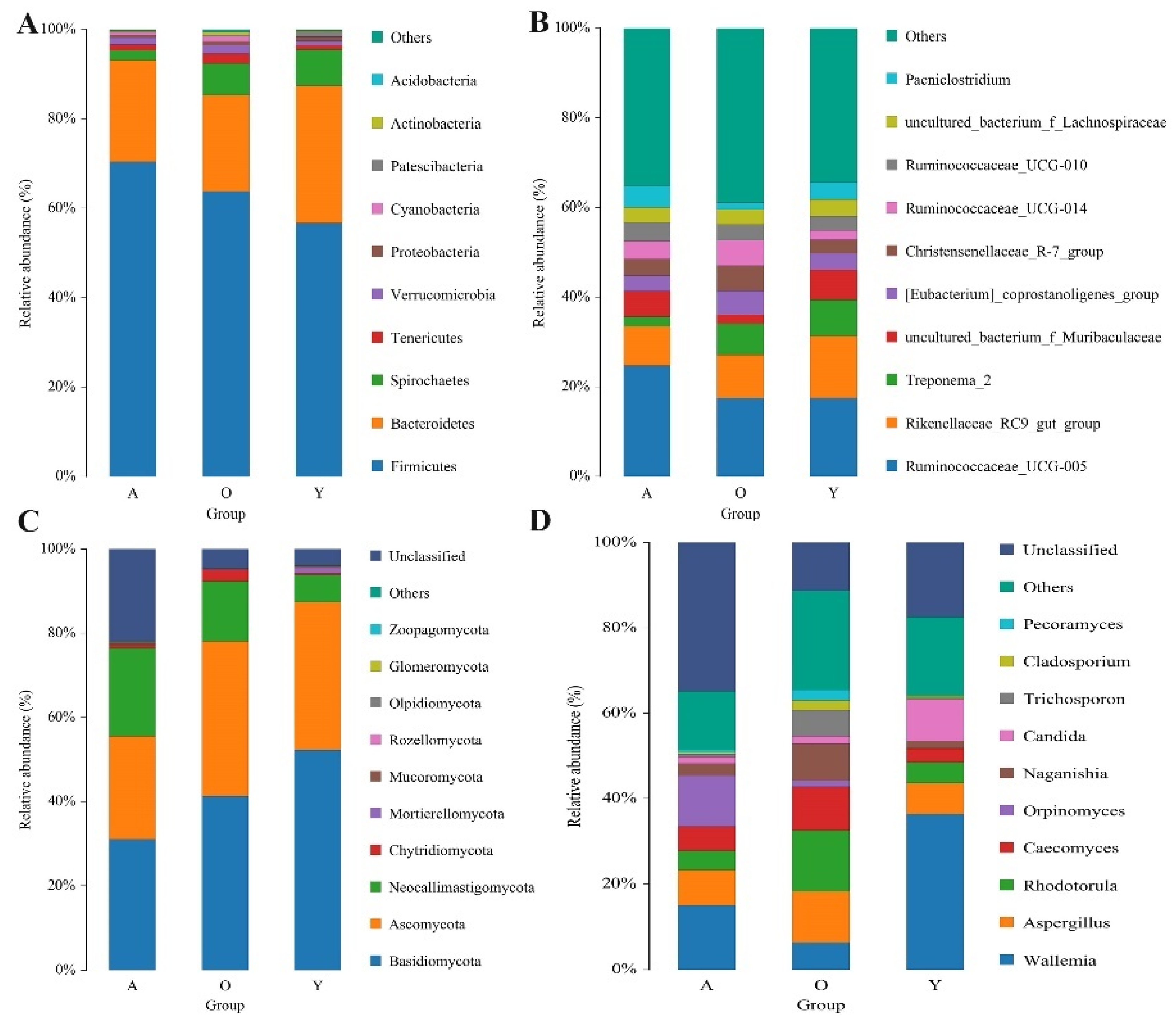
3.3. Significant Alterations in Gut Bacterial Microbiota Composition with Age
3.4. Significant Alterations in Gut Fungal-Microbiota Composition with Age
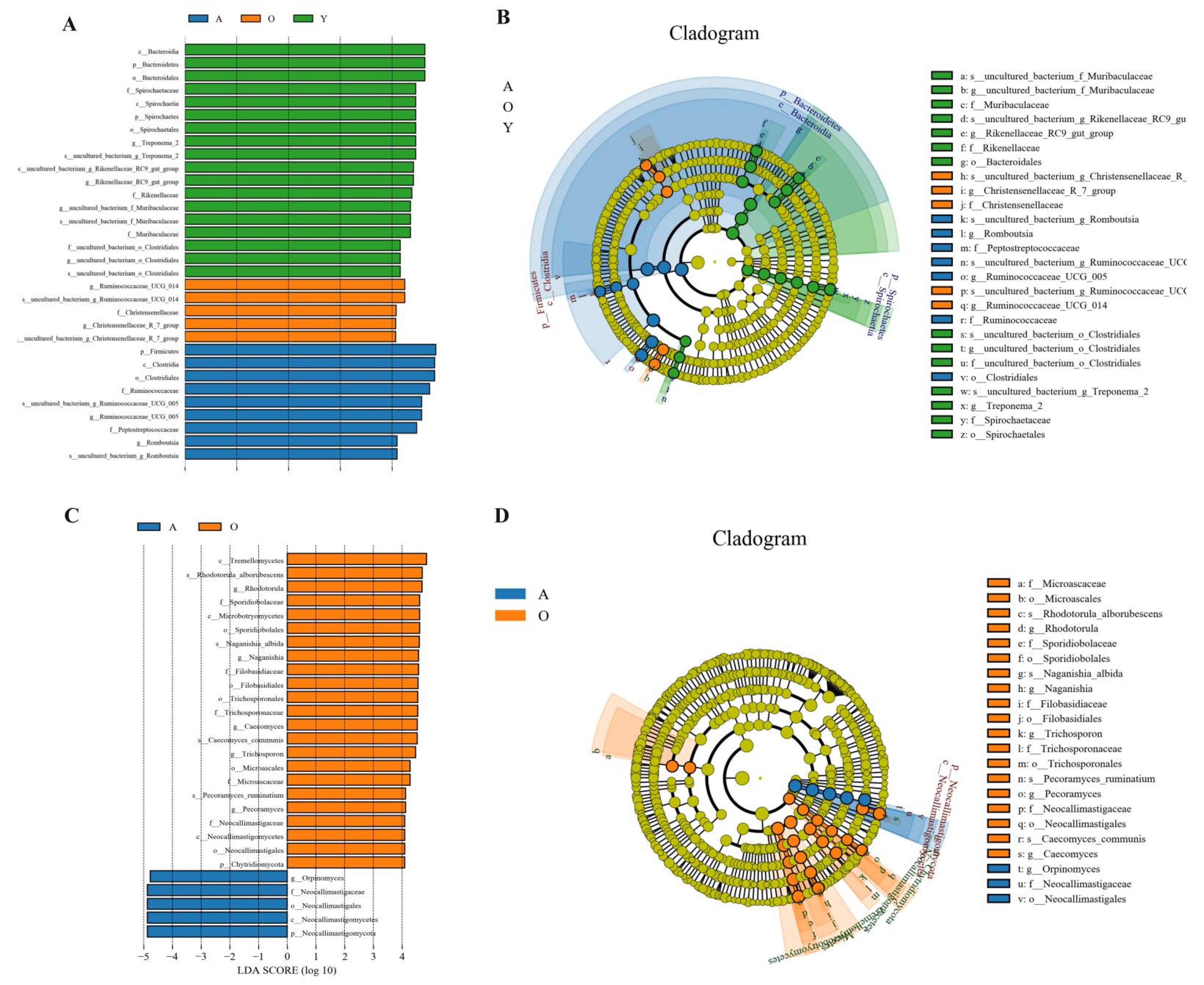
3.5. LEfSe Analysis of Samples between Groups
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qiu, Q.; Wang, L.; Wang, K.; Yang, Y.; Ma, T.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Ni, Z.; Hou, F.; Long, R.; et al. Yak whole-genome resequencing reveals domestication signatures and prehistoric population expansions. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 10283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, Q.; Zhang, G.; Ma, T.; Qian, W.; Wang, J.; Ye, Z.; Cao, C.; Hu, Q.; Kim, J.; Larkin, D.M.; et al. The yak genome and adaptation to life at high altitude. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 946–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.-J.; Wu, E. The role of gut microbiota in immune homeostasis and autoimmunity. Gut Microbes 2012, 3, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pérez, W.; Lima, M.; Clauss, M. Gross Anatomy of the Intestine in the Giraffe (Giraffa camelopardalis). Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2009, 38, 432–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomina Anatomica Veterinaria. International Committee on Veterinary Gross Anatomical Nomenclature (I.C.V.G.A.N.), 5th ed. 2005. Available online: http://www.wavaamav.org/Downloads/nav_2005.pdf (accessed on 28 May 2009).
- Mi, J.; Zhou, J.; Huang, X.; Long, R. Lower Methane Emissions from Yak Compared with Cattle in Rusitec Fermenters. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boguhn, J.; Zuber, T.; Rodehutscord, M. Effect of donor animals and their diet onin vitronutrient degradation and microbial protein synthesis using grass and corn silages. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2012, 97, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, W.K.; Medina, L.A.; Koch, H.; Sing, K.-W.; Soh, E.J.Y.; Ascher, J.S.; Jaffé, R.; Moran, N.A. Dynamic microbiome evolution in social bees. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1600513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zepeda, M.M.; Xiong, Z.; Escalera-Zamudio, M.; Runge, A.K.; Theze, J.; Streicker, D.; Frank, H.K.; Loza-Rubio, E.; Liu, S.; Ryder, O.A.; et al. Hologenomic adaptations underlying the evolution of sanguivory in the common vampire bat. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brooks, A.W.; Kohl, K.D.; Brucker, R.M.; van Opstal, E.J.; Bordenstein, S.R. Phylosymbiosis: Relationships and functional effects of microbial communities across host evolutionary history. PLoS Biol. 2016, 15, e1002587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aagaard, K.; Ma, J.; Antony, K.M.; Ganu, R.; Petrosino, J.; Versalovic, J. The Placenta Harbors a Unique Microbiome. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 237ra65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; Costello, E.K.; Contreras, M.; Magris, M.; Hidalgo, G.; Fierer, N.; Knight, R. Delivery mode shapes the acquisition and structure of the initial microbiota across multiple body habitats in newborns. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 11971–11975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- La Rosa, P.S.; Warner, B.B.; Zhou, Y.; Weinstock, G.; Sodergren, E.; Hall-Moore, C.M.; Stevens, H.J.; Bennett, W.E.; Shaikh, N.; Linneman, L.A.; et al. Patterned progression of bacterial populations in the premature infant gut. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 12522–12527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koenig, J.E.; Spor, A.; Scalfone, N.; Fricker, A.D.; Stombaugh, J.; Knight, R.; Angenent, L.T.; Ley, R.E. Succession of microbial consortia in the developing infant gut microbiome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4578–4585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Integrative, H.M.P.; Proctor, L.M.; Creasy, H.H.; Fettweis, J.M.; Lloyd-Price, J.; Mahurkar, A.; Huttenhower, C. The integrative human microbiome project. Nature 2019, 569, 641–648. [Google Scholar]
- Haiser, H.J.; Gootenberg, D.B.; Chatman, K.; Sirasani, G.; Balskus, E.P.; Turnbaugh, P.J. Predicting and Manipulating Cardiac Drug Inactivation by the Human Gut Bacterium Eggerthella lenta. Science 2013, 341, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russell, J.B.; Rychlik, J.L. Factors that alter rumen microbial ecology. Science 2001, 292, 1119–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giron, F.; Quigley, E.M.M. Pharmabiotic Manipulation of the Microbiota in Gastrointestinal Disorders: A Clinical Perspective. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 24, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- David, L.A.; Materna, A.C.; Friedman, J.; Campos-Baptista, M.I.; Blackburn, M.C.; Perrotta, A.; Erdman, S.E.; Alm, E.J. Host lifestyle affects human microbiota on daily timescales. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Huang, J.; Zhai, Z.; Zhengxiao, Z.; Ding, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Fan, W.; et al. The Dynamic Distribution of Porcine Microbiota across Different Ages and Gastrointestinal Tract Segments. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jami, E.; Israel, A.; Kotser, A.; Mizrahi, I. Exploring the bovine rumen bacterial community from birth to adulthood. ISME J. 2013, 7, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.; Liu, G.; Shafer, A.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, J.; Lin, S.; Wu, H.; Zhou, M.; Hu, D.; Liu, S. Comparative Analysis of the Gut Microbial Communities in Forest and Alpine Musk Deer Using High-Throughput Sequencing. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujimura, K.E.; Sitarik, A.R.; Havstad, S.; Lin, D.L.; LeVan, S.; Fadrosh, D.; Panzer, A.R.; LaMere, B.; Rackaityte, E.; Lukacs, N.W.; et al. Neonatal gut microbiota associates with childhood multisensitized atopy and T cell differentiation. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 1187–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arrieta, M.C.; Arévalo, A.; Stiemsma, L.; Dimitriu, P.; Chico, M.E.; Loor, S.; Finlay, B. Associations between infant fungal and bacterial dysbiosis and childhood atopic wheeze in a nonindustrialized setting. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 142, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iliev, I.D.; Funari, V.A.; Taylor, K.D.; Nguyen, Q.; Reyes, C.N.; Strom, S.; Brown, J.; Becker, C.A.; Fleshner, P.R.; Dubinsky, M.; et al. Interactions Between Commensal Fungi and the C-Type Lectin Receptor Dectin-1 Influence Colitis. Science 2012, 336, 1314–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liggenstoffer, A.S.; Youssef, N.H.; Couger, M.B.; Elshahed, M.S. Phylogenetic diversity and community structure of anaerobic gut fungi (phylum Neocallimastigomycota) in ruminant and non-ruminant herbivores. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1225–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Mehmood, K.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, X.; Shahzad, M.; Dong, X.; Li, J. Characterization of fungus microbial diversity in healthy and diarrheal yaks in Gannan region of Tibet Autonomous Prefecture. Acta Trop. 2018, 182, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willing, B.P.; Dicksved, J.; Halfvarson, J.; Andersson, A.F.; Lucio, M.; Zheng, Z.; Järnerot, G.; Tysk, C.; Jansson, J.K.; Engstrand, L. A Pyrosequencing Study in Twins Shows That Gastrointestinal Microbial Profiles Vary with Inflammatory Bowel Disease Phenotypes. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 1844–1854.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijay-Kumar, M.; Aitken, J.D.; Carvalho, F.A.; Cullender, T.C.; Mwangi, S.; Srinivasan, S.; Sitaraman, S.V.; Knight, R.; Ley, R.; Gewirtz, A.T. Metabolic Syndrome and Altered Gut Microbiota in Mice Lacking Toll-Like Receptor 5. Science 2010, 328, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.; Nie, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Fan, Q.; Yan, X. Gradual Changes of Gut Microbiota in Weaned Miniature Piglets. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, J.; Xue, Z.; Zhang, M.; Pang, X.; Zhao, L. Modulation of gut microbiota by berberine and metformin during the treatment of high-fat diet-induced obesity in rats. Sci. Rep. 2015, 23, 14405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, T.; Richards, E.M.; Pepine, C.J.; Raizada, M.K. The gut microbiota and the brain–gut–kidney axis in hypertension and chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 442–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, L.; Xu, Y.; Liu, N.; Sun, X.; Hu, L.; Huang, H.; Wei, K.; Zhu, R. Dynamic Distribution of Gut Microbiota in Goats at Different Ages and Health States. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badman, J.; Daly, K.; Kelly, J.; Moran, A.W.; Cameron, J.; Watson, I.; Newbold, J.; Shirazi-Beechey, S. The Effect of Milk Replacer Composition on the Intestinal Microbiota of Pre-ruminant Dairy Calves. Front. Veter. Sci. 2019, 6, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, A.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, H.; Mehmood, K.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, J.; Waqas, M.; Iqbal, M.; Li, J. Probiotic Potential of Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides and Lactobacillus Strains Isolated from Yaks. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langó, Z. Who has first observed Planctomyces. Acta. Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 2005, 52, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, S.; Jogler, M.; Jogler, C. On the maverick Planctomycetes. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 42, 739–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niu, Q.; Li, P.; Hao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Kim, S.W.; Li, H.; Ma, X.; Gao, S.; He, L.; Wu, W.; et al. Dynamic distribution of the gut microbiota and the relationship with apparent crude fiber digestibility and growth stages in pigs. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DiBaise, J.K.; Zhang, H.; Crowell, M.D.; Krajmalnik-Brown, R.; Decker, G.A.; Rittmann, B.E. Gut Microbiota and Its Possible Relationship with Obesity. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glávits, R.; Ivanics, É.; Thuma, Á.; Kaszanyitzky, É.; Samu, P.; Ursu, K.; Dencsö, L.; Dán, Á. Typhlocolitis associated with spirochaetes in duck flocks. Avian Pathol. 2011, 40, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thoetkiattikul, H.; Mhuantong, W.; Laothanachareon, T.; Tangphatsornruang, S.; Pattarajinda, V.; Eurwilaichitr, L.; Champreda, V. Comparative Analysis of Microbial Profiles in Cow Rumen Fed with Different Dietary Fiber by Tagged 16S rRNA Gene Pyrosequencing. Curr. Microbiol. 2013, 67, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Malmuthuge, N.; Steele, M.A.; Guan, L.L. Shift of hindgut microbiota and microbial short chain fatty acids profiles in dairy calves from birth to pre-weaning. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constable, P.D. Antimicrobial Use in the Treatment of Calf Diarrhea. J. Veter. Intern. Med. 2004, 18, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubin, K.; Callahan, M.K.; Ren, B.; Khanin, R.; Viale, A.; Ling, L.; Wolchok, J.D. Intestinal microbiome analyses identify melanoma patients at risk for checkpoint-blockade-induced colitis. Nat. Commun. 2016, 2, 10391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Downes, J.; Dewhirst, F.E.; Tanner, A.C.R.; Wade, W.G. Description of Alloprevotella rava gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from the human oral cavity, and reclassification of Prevotella tannerae Moore et al. 1994 as Alloprevotella tannerae gen. nov., comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 1214–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, T.N.; Bazzano, L.A.; Ajami, N.J.; He, H.; Zhao, J.; Petrosino, J.F.; Correa, A.; He, J. Gut Microbiome Associates with Lifetime Cardiovascular Disease Risk Profile Among Bogalusa Heart Study Participants. Circ. Res. 2016, 119, 956–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bengelsdorf, F.R.; Poehlein, A.; Schiel-Bengelsdorf, B.; Daniel, R.; Dürre, P. Genome Sequence of the Acetogenic Bacterium Oxobacter pfennigii DSM 3222 T. Genome Announc. 2015, 3, e01408-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhuang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Shou, Q.; Li, H.; Zhu, Y.E.; He, L.; Jiao, J. Eicosapentaenoic and Docosahexaenoic Acids Differentially Alter Gut Microbiome and Reverse High-Fat Diet–Induced Insulin Resistance. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2020, 64, e1900946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskar, M.; Awata, T.; Kasai, T.; Katayama, A. Anaerobic dechlorination by a humin-dependent pentachlorophenol-dechlorinating consortium under autotrophic conditions induced by homoacetogenesis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamauchi, K.E.; Snel, J. Transmission electron microscopic demonstration of phagocytosis and intracellular processing of segmented filamentous bacteria by intestinal epithelial cells of the chick ileum. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 6496–6504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slifierz, M.J.; Friendship, R.M.; Weese, J.S. Longitudinal study of the early-life fecal and nasal microbiotas of the domestic pig. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopetuso, L.R.; Scaldaferri, F.; Petito, V.; Gasbarrini, A. Commensal clostridia: Leading players in the maintenance of gut homeostasis. Gut Pathog. 2013, 5, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerritsen, J.; Umanets, A.; Staneva, I.; Hornung, B.; Ritari, J.; Paulin, L.; Rijkers, G.T.; De Vos, W.M.; Smidt, H. Romboutsia hominis sp. nov., the first human gut-derived representative of the genus Romboutsia, isolated from ileostoma effluent. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 3479–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bretin, A.; Lucas, C.; Larabi, A.; Dalmasso, G.; Billard, E.; Barnich, N.; Bonnet, R.; Nguyen, H.T.T. AIEC infection triggers modification of gut microbiota composition in genetically predisposed mice, contributing to intestinal inflammation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filippo, C.; Cavalieri, D.; Di Paola, M.; Ramazzotti, M.; Poullet, J.B.; Massart, S.; Lionetti, P. Impact of diet in shaping gut microbiota revealed by a comparative study in children from Europe and rural Africa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14691–14696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shang, Q.; Shan, X.; Cai, C.; Hao, J.; Li, G.; Yu, G. Correction: Dietary fucoidan modulates the gut microbiota in mice by increasing the abundance of Lactobacillus and Ruminococcaceae. Food Funct. 2017, 9, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Li, X.H.; Chen, Y.X.; Cheng, Z.H.; Duan, Q.H.; Meng, Q.H.; Tao, X.P.; Shang, B.; Dong, H.M. Age-Related Response of Rumen Microbiota to Mineral Salt and Effects of Their Interactions on Enteric Methane Emissions in Cattle. Microb. Ecol. 2017, 73, 590–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, A.; Zhang, L.; Waqas, M.; Mehmood, K.; Iqbal, M.; Muyou, C.; Li, Z.; Lian, Y.; Sizhu, S.; et al. Probiotic potential of Lactobacillus on the intestinal microflora against Escherichia coli induced mice model through high-throughput sequencing. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 137, 103760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Siles, M.; Duncan, S.H.; Garcia-Gil, L.J.; Martinez-Medina, M. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii: From microbiology to diagnostics and prognostics. ISME J. 2017, 11, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Long, W.; Zhang, C.; Liu, S.; Zhao, L.; Hamaker, B.R. Fiber-utilizing capacity varies in Prevotella- versus Bacteroides-dominated gut microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouattara, A.S.; Traore, A.S.; Garcia, J.L. Characterization of Anaerovibrio burkinabensis sp. nov., a lactate fermenting bacterium isolated from rice field soils. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1992, 42, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.-J.; Lee, J.; Shin, N.-R.; Kim, M.-S.; Hyun, D.-W.; Yun, J.-H.; Kim, P.S.; Whon, T.W.; Bae, J.-W. Chronic Repression of mTOR Complex 2 Induces Changes in the Gut Microbiota of Diet-induced Obese Mice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sundberg, C.W.; Prost, R.W.; Fitts, R.H.; Hunter, S.K. Bioenergetic basis for the increased fatigability with ageing. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 4943–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalt, F.; Schulthess, B.; Sidler, F.; Herren, S.; Fucentese, S.F.; Zingg, P.O.; Berli, M.; Zinkernagel, A.S.; Zbinden, R.; Achermann, Y. Corynebacterium Species Rarely Cause Orthopedic Infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeffery, I.; Lynch, D.B.; O’Toole, P.W. Composition and temporal stability of the gut microbiota in older persons. ISME J. 2016, 10, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maynard, C.; Weinkove, D. The Gut Microbiota and Ageing. Biochem. Cell Biol. Ageing 2018, 90, 351–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagi, E.; Rampelli, S.; Turroni, S.; Quercia, S.; Candela, M.; Brigidi, P. The gut microbiota of centenarians: Signatures of longevity in the gut microbiota profile. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2017, 165, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruninger, R.J.; Puniya, A.K.; Callaghan, T.M.; Edwards, J.E.; Youssef, N.; Dagar, S.S.; Fliegerova, K.; Griffith, G.W.; Forster, R.; Tsang, A.; et al. Anaerobic fungi (phylumNeocallimastigomycota): Advances in understanding their taxonomy, life cycle, ecology, role and biotechnological potential. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 90, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wheeler, M.L.; Limon, J.J.; Underhill, D.M. Immunity to Commensal Fungi: Detente and Disease. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2017, 12, 359–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, R.R.; Pedezzi, R.; Souto, T.B. Exploring the bioprospecting and biotechnological potential of white-rot and anaerobic Neocallimastigomycota fungi: Peptidases, esterases, and lignocellulolytic enzymes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 3089–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanafy, R.A.; Lanjekar, V.B.; Dhakephalkar, P.K.; Callaghan, T.M.; Dagar, S.S.; Griffith, G.W.; Youssef, N.H. Seven new Neocallimastigomycota genera from wild, zoo-housed, and domesticated herbivores greatly expand the taxonomic diversity of the phylum. Mycologia 2020, 112, 1212–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanafy, R.A.; Elshahed, M.S.; Liggenstoffer, A.S.; Griffith, G.W.; Youssef, N.H. Pecoramyces ruminantium, gen. nov., sp. nov., an anaerobic gut fungus from the feces of cattle and sheep. Mycologia 2017, 109, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Garcia, A.; Pellon, A.; Rementeria, A.; Buldain, I.; Barreto-Bergter, E.; Rollin-Pinheiro, R.; De Meirelles, J.V.; Xisto, M.I.D.S.; Ranque, S.; Havlicek, V.; et al. Scedosporium and Lomentospora: An updated overview of underrated opportunists. Med. Mycol. 2018, 56, S102–S125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couturier, M.; Tangthirasunun, N.; Ning, X.; Brun, S.; Gautier, V.; Bennati-Granier, C.; Silar, P.; Berrin, J.-G. Plant biomass degrading ability of the coprophilic ascomycete fungus Podospora anserina. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 976–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.; Zhang, F.; Yang, X.; Wu, N.; Jiang, W.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. Changes in the composition of intestinal fungi and their role in mice with dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 27, 10416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajc, J.; Gunde-Cimerman, N. The Genus Wallemia—From Contamination of Food to Health Threat. Microorganisms 2018, 6, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Theodorou, M.K.; Mennim, G.; Davies, D.R.; Zhu, W.-Y.; Trinci, A.P.J.; Brookman, J.L. Anaerobic fungi in the digestive tract of mammalian herbivores and their potential for exploitation. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 1996, 55, 913–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ljungdahl, L.G. The Cellulase/Hemicellulase System of the Anaerobic FungusOrpinomycesPC-2 and Aspects of Its Applied Use. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1125, 308–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmore, S.P.; Henske, J.K.; O’Malley, M.A. Driving biomass breakdown through engineered cellulosomes. Bioengineered 2015, 6, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hooker, C.A.; Lee, K.Z.; Solomon, K.V. Leveraging anaerobic fungi for biotechnology. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2019, 59, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Tilburg Bernardes, E.; Pettersen, V.K.; Gutierrez, M.W.; Laforest-Lapointe, I.; Jendzjowsky, N.G.; Cavin, J.B.; Arrieta, M.C. Contribution of fungal microbiome to intestinal physiology, early-life immune development and mucosal inflammation in mice. bioRxiv 2019, 819979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Fu, Y.; He, Y.; Kulyar, M.F.-e.-A.; Iqbal, M.; Li, K.; Liu, J. Longitudinal Characterization of the Gut Bacterial and Fungal Communities in Yaks. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7070559
Wang Y, Fu Y, He Y, Kulyar MF-e-A, Iqbal M, Li K, Liu J. Longitudinal Characterization of the Gut Bacterial and Fungal Communities in Yaks. Journal of Fungi. 2021; 7(7):559. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7070559
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yaping, Yuhang Fu, Yuanyuan He, Muhammad Fakhar-e-Alam Kulyar, Mudassar Iqbal, Kun Li, and Jiaguo Liu. 2021. "Longitudinal Characterization of the Gut Bacterial and Fungal Communities in Yaks" Journal of Fungi 7, no. 7: 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7070559
APA StyleWang, Y., Fu, Y., He, Y., Kulyar, M. F. -e. -A., Iqbal, M., Li, K., & Liu, J. (2021). Longitudinal Characterization of the Gut Bacterial and Fungal Communities in Yaks. Journal of Fungi, 7(7), 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7070559







