Abstract
The cellulolytic filamentous fungus Trichoderma reesei has a strong capability in protein synthesis and secretion and is increasingly used as a fungal chassis for the production of heterologous proteins or secondary metabolites. However, bidirectional promoters that would significantly facilitate multiple genes’ expression have not been characterized in T. reesei. Herein, we show that a 767-bp intergenic region between two polyketide synthase encoding genes that were involved in the biosynthesis of the typical yellow pigment served as a bidirectional promoter in T. reesei. This region was shown to be able to drive the simultaneous expression of two fluorescence reporter genes when fused to each end. Quantitative RT-PCR analysis demonstrated that the driving strength of this bidirectional promoter from each direction reached about half of that of the commonly used promoter PgpdA. Moreover, the co-expression of two cellulase genes driven by this bidirectional promoter enabled T. reesei to produce cellulases on glucose and improved the total cellulase activities with cellulose Avicel as the carbon source. Our work identified the first bidirectional promoter in T. reesei, which would facilitate gene co-expression and find applications in synthetic biology using fungal systems.
1. Introduction
The filamentous fungus Trichoderma reesei has been used as an important industrial-scale cellulase producer for a long time due to its prominent capability in secreting a large quantity of cellulolytic enzymes as well as its safety and robustness in fermentation [1,2]. T. reesei is also increasingly applied as a microbial chassis for the production of heterologous enzymes and pharmaceutical proteins [2,3]. Moreover, it has been recently proved feasible to express heterologous biosynthetic gene clusters comprising multiple genes in a T. reesei strain with the inactivation of sorbicillinoid-type yellow pigment biosynthesis, which enables the fungus to convert waste biomass into secondary metabolites [3].
The production of either proteins or secondary metabolites requires promoters with appropriate strength and/or combinations for controlling gene expression in the host cells. Quite a few inducible or constitutive promoters have been identified and extensively used in T. reesei [4]. Most inducible promoters are from cellulase- or hemicellulase-encoding genes, most notably the promoter of cbh1 that encodes the major extracellular cellulase CBHI [5]. Commonly-used constitutive promoters include Aspergillus PgpdA, T. reesei Ptef1, Pcdn1, Ppdc1, and Ptcu1, which respond to exogenously added copper [6]. Nonetheless, all of these promoters are monodirectional promoters (MDPs). While sufficient for single-gene expression, MDPs become limiting when applied for the co-expression of multiple genes since they are quite time-consuming, especially in eukaryotic microbes. In addition, consecutive genetic manipulation using MDPs for gene expression is prone to cause genetic instability, which is disadvantageous to efficient genetic construction and product biosynthesis.
In contrast, the application of bidirectional promoter (BDPs) helps to facilitate genetic engineering and expand expression flexibility. Natural BDPs have been found in almost all kingdoms, ranging from bacteria to mammals [7,8]. It has been shown that BDPs are always intergenic regions regulating the flanking two genes that encode proteins relevant to the same biological process. Up to now, only a few BDPs have been identified and characterized in filamentous fungi, most of which are present in Aspergillus and Penicillium. These BDPs were discovered in the intergenic regions between two divergently oriented genes involved in penicillin production [9,10], nitrogen metabolism [10,11,12], histone proteins [13], or hemicellulases synthesis [8], and some of them have been successfully used for dual gene co-expression [13]. However, no BDPs have been characterized in T. reesei, which limits the development of the multiple gene expression system in such an important eukaryotic chassis for the efficient synthesis of recombinant proteins or secondary metabolites.
The typical yellow pigment (sorbicillinoids) secreted by T. reesei is synthesized by the sor cluster, including two polyketide synthase encoding genes sor1 and sor2 [14]. These two genes are arranged as “head-to-head” and separated by a 767-bp intergenic region. In this study, we presented evidence that the intergenic region between sor1 and sor2 served as a BDP. We also quantified the promoter strength and used this BDP for the simultaneous co-expression of two cellulase genes in T. reesei.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains and Culture Conditions
T. reesei OEypr1-Δsor1 [15] was used as the parent strain throughout this study. OEypr1-Δsor1 was previously created via the overexpression of ypr1 and the deletion of sor1 in QM9414-∆pyr4 [16], which is a derivative of T. reesei QM9414 (ATCC 26921). T. reesei cells were maintained on malt extract agar at 30℃. For the transcription and enzyme production analyses, T. reesei cells were cultured in Mandel–Andreotti (MA) medium [17] with 1% (v/v) glycerol as the carbon source for 36 h, collected, and washed thoroughly with MA medium without any carbon source. Equal mycelia were then transferred to the fresh medium with 1% (w/v) glucose or 1% (w/v) Avicel as the carbon source and cultivated for the indicated time period. Escherichia coli DH5α cells were used for routine plasmids construction. E. coli cells were cultured in lysogeny broth at 37 °C.
2.2. Construction of Plasmids and T. reesei Mutant Strains
To construct the expression cassette for egfp and mCherry under the control of Psor, their encoding regions were amplified from the plasmid Ptcu1-clp1-gfp-TtrpC [18] and Ptcu1-mCherry-h2b [18], respectively. Three fragments, including Psor (767 bp) and two terminators TtrpC (759 bp) and Tcbh2 (1 kb), were then amplified from the genomic DNA isolated from QM9414, respectively. The above five fragments were fused together via several rounds of overlap-extension PCR [19] to generate the expression cassette TtrpC-egfp-Psor-mCherry-Tcbh2. This cassette was subsequently inserted into the pUC19-pyr4-sur plasmid that contains two DNA fragments corresponding to approximately 2.3 kb and 2.3 kb of pyr4 up- and downstream noncoding regions for pyr4 locus integration and an expression cassette of sur that encodes an acetolactate synthase for resistance against sulfonylurea [20]. The resultant plasmid pUC19-egfp-Psor-mCherry was linearized and used to transform OEypr1-Δsor1 to generate the recombinant strain egfp-Psor-mCherry. To construct the PgpdA-driven expression cassette for egfp, three DNA fragments, including PgpdA, egfp, and TtrpC, were fused together and then ligated into pUC19-pyr4-sur to create pUC19-PgpdA-egfp. Similarly, to construct the expression cassette for mCherry under the control of PgpdA, three DNA fragments including PgpdA, mCherry, and Tcbh2 were fused together, followed by ligation into pUC19-pyr4-sur to create pUC19-PgpdA-mCherry. The plasmids pUC19-PgpdA-egfp and pUC19-PgpdA-mCherry were, respectively, linearized and transformed into OEypr1-Δsor1 to generate the recombinant strain PgpdA-egfp and PgpdA-mCherry. To construct the expression cassette for two cellulase genes driven by Psor, the cDNA sequence of ctcbh1 (GenBank Accession No. AM711862.1) was synthesized by the staff in GENEWIZ, Inc., and the full coding sequence of eg1 together with its native terminator corresponding to downstream ~1 kb sequence (eg1-Teg1) were amplified from the genomic DNA of QM9414. Four fragments, including TtrpC, egfp, Psor, and eg1-Teg1, were fused together and inserted into pUC19-pyr4-sur to create the expression plasmid pUC19-ctcbh1-Psor-eg1, which was subsequently linearized and transformed into OEypr1-Δsor1 to yield the recombinant transformant ctcbh1-Psor-eg1. The transformation of T. reesei was performed as previously described [21]. Transformants were selected on a minimal medium for resistance to sulfonylurea (4 μg/mL). Anchored PCR was used to verify the correct integration events.
2.3. Fluorescence Microscopic Analysis
T. reesei spores were inoculated into minimal medium containing 1% (w/v) glucose and were cultured for 16 h at 30 °C in a shaking incubator. The fluorescence of mCherry and the GFP of the collected mycelia were detected using a research grade inverted NIKON TI-E fluorescence microscope (Nikon, Tokyo, Japan).
2.4. Enzyme Activity and Protein Analyses
Extracellular cellobiohydrolase activity was analyzed with 4-Nitrophenyl β-D-cellobioside (pNPC; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) as a substrate by measuring the released p-nitrophenyl amount. The reaction was performed in 160 μL of reaction mixture with 80 μL of 50 mM sodium acetate buffer (pH4.8), 40 μL of substrate, and 40 μL of diluted culture supernatant. The mixture was then incubated at 50℃ for 30 min, and the reaction was stopped by the addition of 40 μL of 10% Na2CO3 (w/v). The amount of p-nitrophenyl is determined by measuring the absorbance at 420 nm. One unit (U) of pNPC activity is defined as the amount of enzyme releasing 1 μmol of p-nitrophenyl per minute. For endoglucanase activity, measurement was carried out in a 120 μL-reaction mixture containing 60 μL of culture supernatant and 60 μL of 0.5% carboxymethylcellulose sodium salt (CMC, Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) dissolved in 50 mM sodium acetate buffer (pH 4.8) and was incubated at 50 °C for 30 min. With glucose as standard, the release of reducing sugar in the mixture was determined using the DNS method [22]. One unit of enzyme activity was defined as the amount of enzyme capable of releasing 1 μmol of glucose per minute. For protein identification, the target bands were excised from the SDS-PAGE gel and subjected to in-gel digestion with trypsin followed by liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS–MS) on a MicrOTOF-Q II mass spectrometer (Bruker Daltonic, Billerica, MA, USA) connected to a prominence nano 2D (SHIMADZU, Kyoto, Japan) chromatography system. The MS raw data for each sample were combined and searched against the NCBI T. reesei protein sequence database using Mascot search engine version 2.3.01 software. LC–MS–MS and data analyses were performed by professional staff of Beijing Protein Innovation Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China).
2.5. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
T. reesei mycelia were quickly frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80 °C. Total RNA was extracted using TRIzol reagent (Sange Biotechnology, Shanghai, China), and gDNA was removed using TURBO DNA-free kit (Ambion, Austin, TX, USA) according to the instructions. The PrimeScript RT kit (Takara Bio, Kusatsu, Japan) was used for reverse transcription according to the instructions. Quantitative PCR was performed by the bio-RAD myIQ2 thermal cyclometer (BIO-RAD, Hercules, CA, USA). Data were analyzed using relative quantitative/comparative CT (ΔΔ CT) and normalized to the endogenous control (actin). Three biological replicates were performed for each analysis and for the results. Statistical analysis was performed by the student’s t-test.
2.6. Sequence Analysis
T. reesei nucleotide sequences were retrieved from the JGI database (https://mycocosm.jgi.doe.gov/Trire2/Trire2.home.html (accessed on 1 Sepetember 2019)). The presence of CpG island was predicted using online CpGFinder and CpGplot services available at websites of (http://www.softberry.com/ (accessed on 1 January 2021)) and (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/emboss/ (accessed on 1 January 2021)), respectively.
3. Results
3.1. The Intergenic Region between sor1 and sor2 Functions as a Bidirectional Promoter in T. reesei
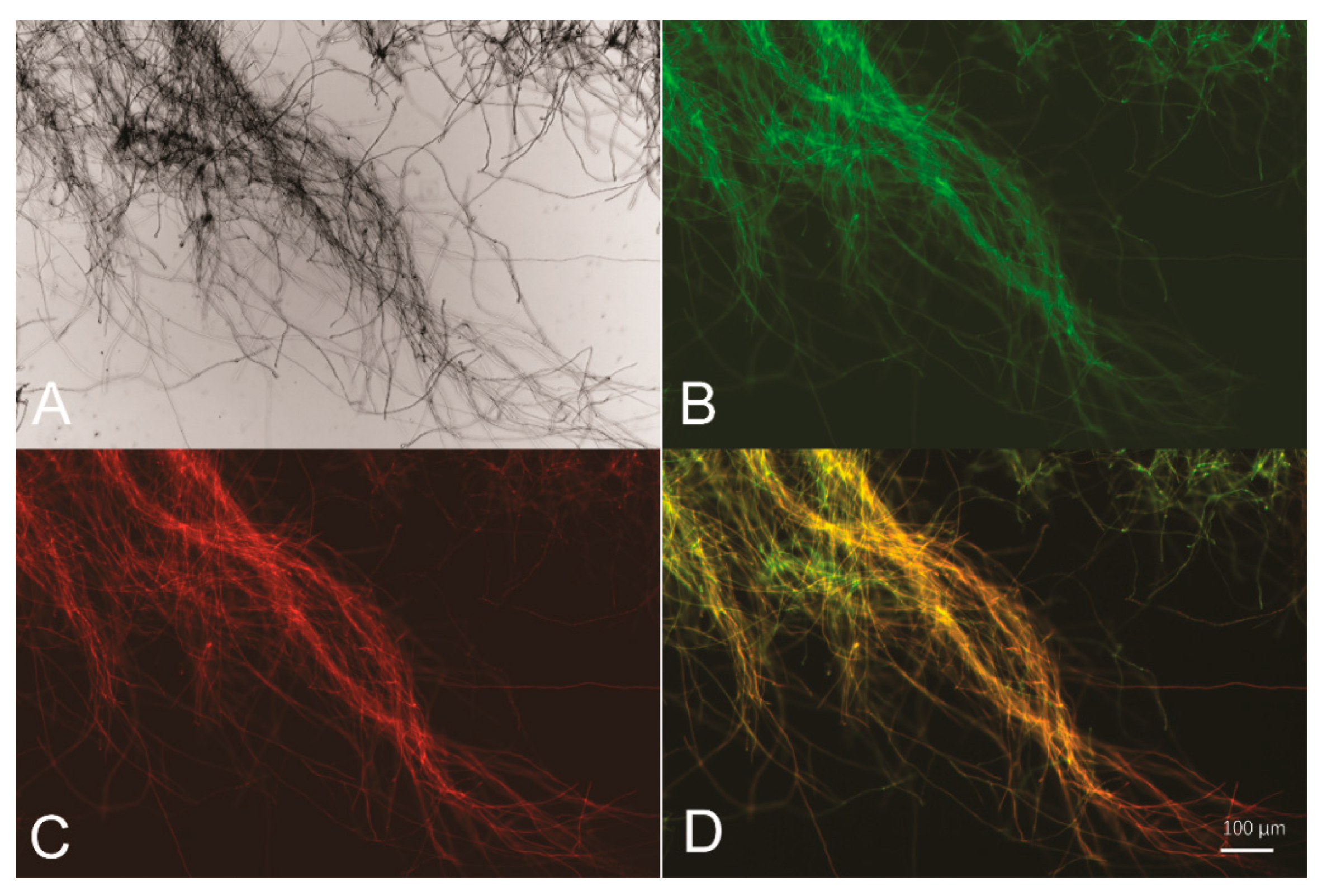
To test whether the 767-bp intergenic region between sor1 and sor2 functions as a BDP, two reporter genes encoding a red fluorescence protein (mCherry) and a green fluorescence protein (GFP) were fused to either end of the intergenic sequence (hereafter named Psor), followed by transcription terminators Tcbh2 and Ttrpc1, respectively (Figure 1). The final expression cassette was integrated into the pyr4 locus of the parental T. reesei strain via homologous recombination, and the resulting recombinant strain egfp-Psor-mCherry was cultured and subjected to fluorescence microscopic analyses. Based on the observations presented in Figure 2, Psor is able to simultaneously drive the expression of two reporter genes from both ends, indicating that Psor serves as a bidirectional promoter in T. reesei.
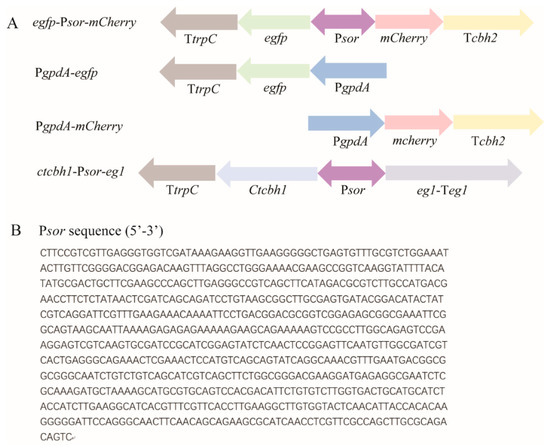
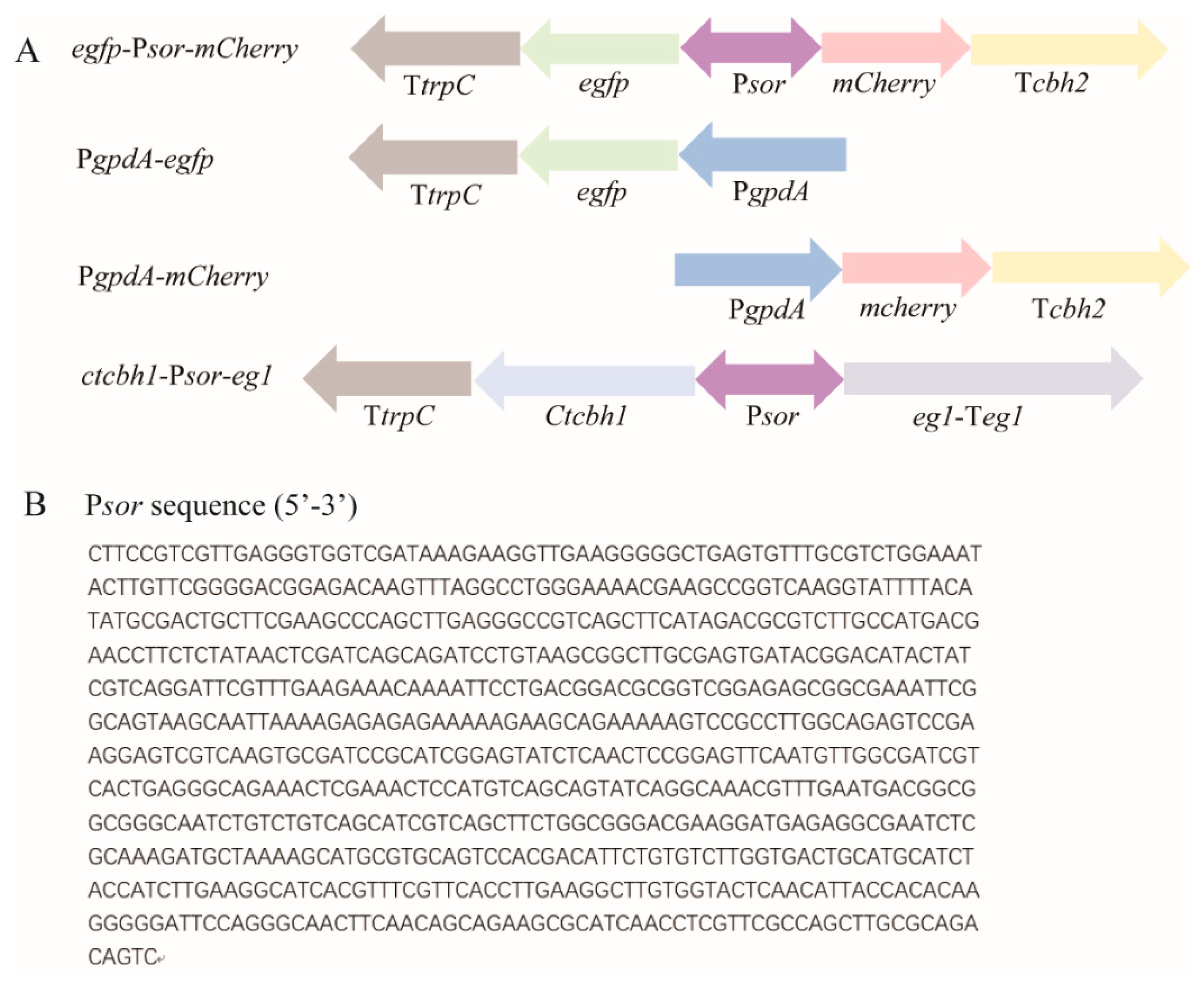
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of the expression cassettes incorporated into the indicated recombinant T. reesei strains, including egfp-Psor-mCherry, PgpdA-egfp, PgpdA-mCherry, and ctcbh1-Psor-eg1 (A), and nucleotide sequence of Psor (B). The expression cassettes were, respectively, integrated into the pyr4 locus of parental T. reesei strain. Psor: the 767 bp-intergenic region between sor1 and sor2; PgpdA: the commonly used gpdA promoter from Aspergillus; TtrpC: trpC terminator; and Tcbh2: cbh2 terminator. The sequence of Psor was retrieved from JGI database (https://mycocosm.jgi.doe.gov/Trire2/Trire2.home.html (accessed on 1 Sepetember 2019)).
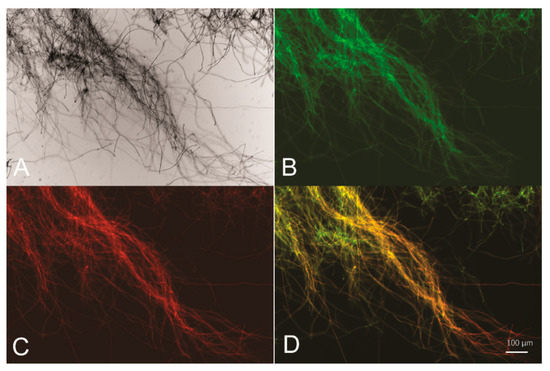
Figure 2.
Psor is able to drive simultaneous expression of two reporter genes egfp and mCherry. Bright-field (A), green fluorescence (B), red fluorescence (C), and merged fluorescence image (D) of T. reesei egfp-Psor-mCherry mycelia collected from glucose-containing cultures for 16 h.
Sequence analyses showed that Psor shared some similarities with most reported BDPs in mammals [23], including a lack of the key core promoter element TATA box and the presence of a CpG island, which greatly contributed to the total high GC content (52%). In contrast to the obvious presence of a CpG island, poor information regarding the conserved binding motifs of transcriptional factors was predicted from Psor sequence.
3.2. Quantitative Determination of Promoter Strength of Psor
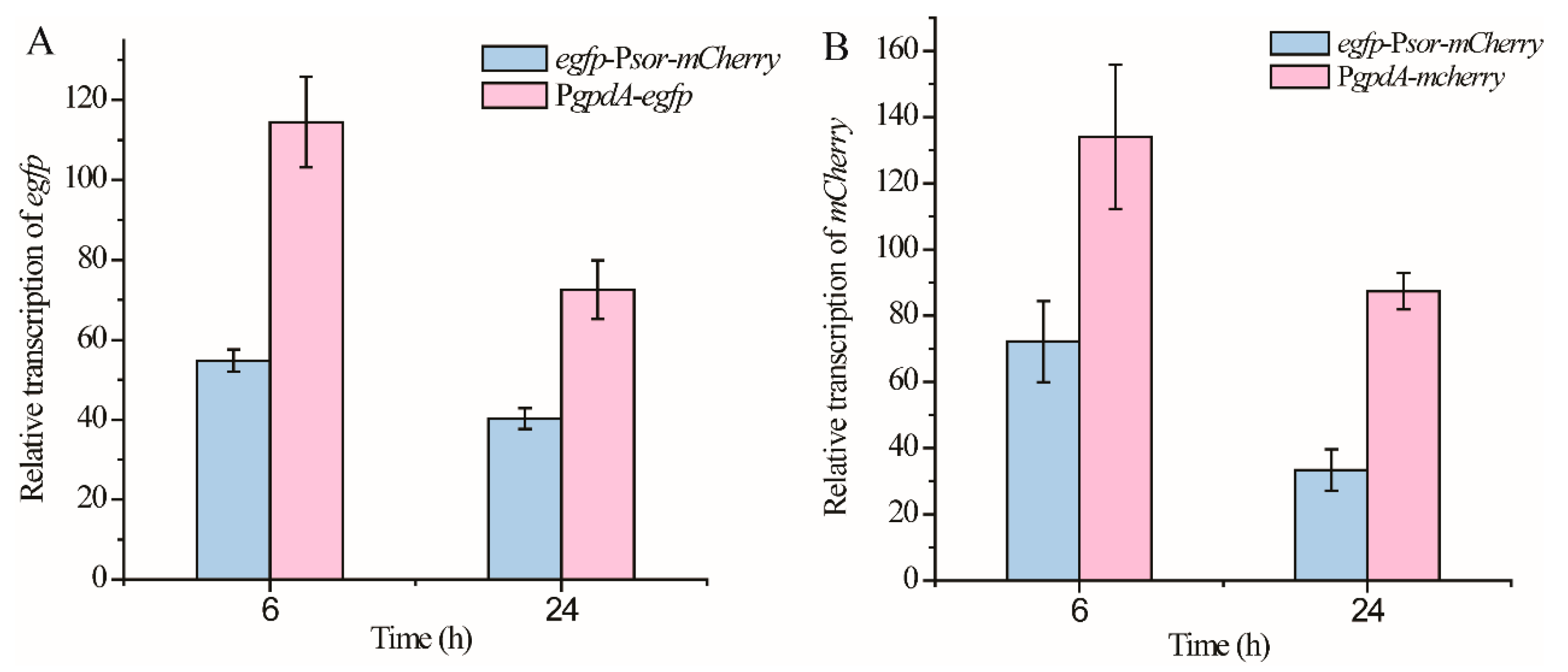
Next, we compared the promoter strength from each direction of Psor with that of PgpdA, which is originally from Aspergillus and commonly used in T. reesei as a constitutive promoter. The respective expression cassette of egfp and mCherry driven by PgpdA was integrated into the pyr4 locus of the parental T. reesei strain, to construct the reference strain PgpdA-egfp and PgpdA-mCherry, respectively (Figure 1). Whereas egfp-Psor-mCherry cells exhibited a similar signal strength of GFP or mCherry fluorescence with that observed from PgpdA-egfp or PgpdA-mCherry, their relative transcriptional levels of egfp or mCherry were further determined and compared using quantitative RT-PCR analyses. As shown in Figure 3A, the relative transcriptional level of egfp driven by Psor in the antisense direction reached up to ~50% of that driven by PgpdA during the early cultivation phase (6 h) and increased to ~62% when the cultivation time was extended to 24 h. Similar to egfp, the relative expression level of mCherry driven by Psor in the sense direction reached up to 53% and 38% of that driven by PgpdA after mycelial cultivation of 6 h or 24 h (Figure 3B). These results indicated that the driving strength of Psor from each end can come up to about half of that of PgpdA.
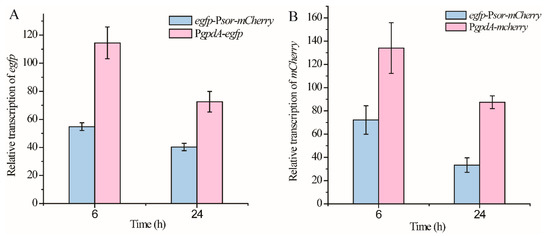
Figure 3.
Comparison of the promoter strength from each direction of Psor with that of PgpdA. Transcriptional analyses of egfp (A) from strains egfp-Psor-mCherry and PgpdA-gfp and transcriptional analyses of mCherry (B) from strains egfp-Psor-mCherry and PgpdA-mCherry. T. reesei cells were cultured in MA medium with 1% glucose as the carbon source. Values in this figure are the mean of three biological replicates. Error bars are the SD from these replicates.
3.3. Co-Expression of Two Cellulase Genes Using Psor
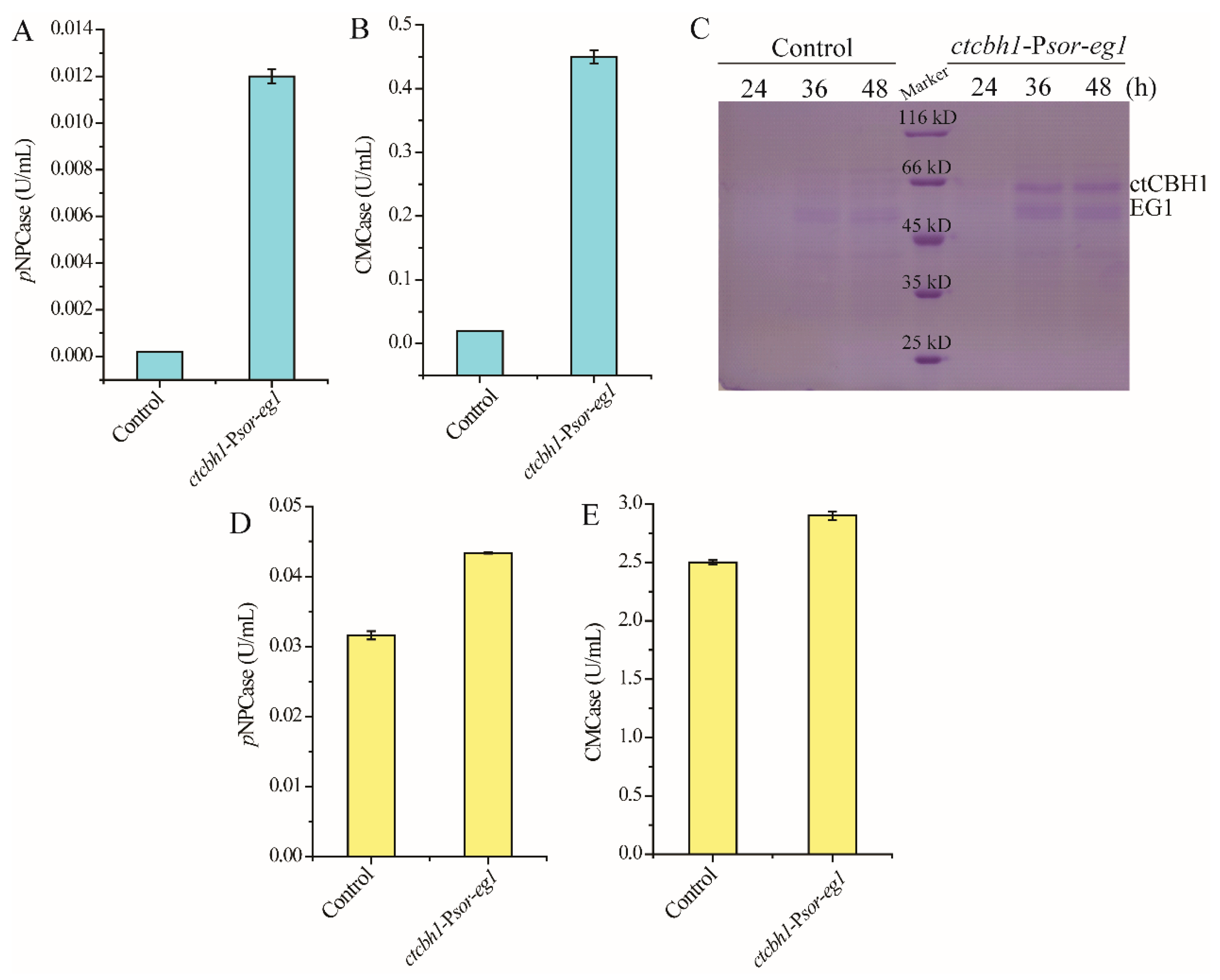
Psor was further used for the co-expression of two cellulase genes: the major endoglucanase encoding gene eg1 from T. reesei, and the gene encoding cellobiohydrolase I from another cellulolytic fungus Chaetomium thermophilum (ctcbh1) that has been shown to have higher catalytic activity than T. reesei cellobiohydrolase I [24]. In contrast with the parental strain, which did not produce any cellulase during cultivation on glucose, the strain ctcbh1-Psor-eg1 displayed significant endoglucanase and cellobiohydrolase activities in the culture supernatant (Figure 4A,B), indicating that Psor simultaneously initiated the expression of ctcbh1 and eg1. SDS-PAGE combined with mass spectrometric analysis verified the presence of ctCBHI and EGI in the culture supernatant (Figure 4C). Moreover, when ctcbh1-Psor-eg1 was cultivated for 120 h with cellulose Avicel as the carbon source, the cellobiohydrolase and endoglucanase activities within the culture supernatant increased by 37% and 17%, respectively, as compared with the parental strain, demonstrating that the co-expression of two celluase genes driven by Psor contributes to improving total cellulase production (Figure 4D,E).
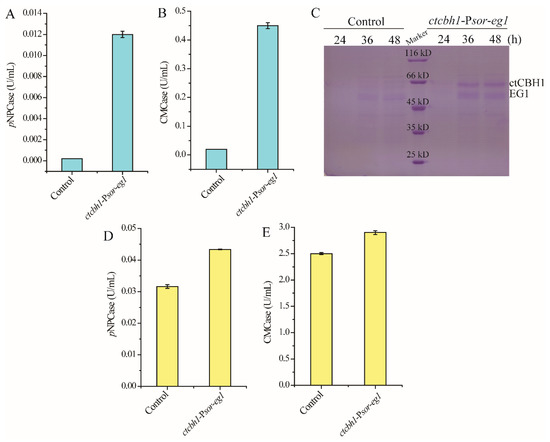
Figure 4.
Co-expression of two cellulase genes using Psor. (A,B) Extracellular cellobiase (pNPCase, A) and endoglucanase (CMCase, B) activities of the strain ctcbh1-Psor-eg1 cultured in MA medium with 1% glucose as the carbon source for 72 h. (C) SDS-PAGE analysis of extracellular supernatant of the strain ctcbh1-Psor-eg1 cultured in MA medium with 1% glucose as the carbon source for 24–48 h. (D,E) Extracellular cellobiase (pNPCase, D) and endoglucanase (CMCase, E) activities of the strain ctcbh1-Psor-eg1 cultured in MA medium with 1% Avicel as the carbon source for 120 h. The parental strain T. reesei OEypr1-Δsor1 was used as the control strain. Values in this figure are the mean of three biological replicates. Error bars are the SD from these replicates.
4. Discussion
Whereas BDPs are widespread in all kingdoms and have much application potential in the co-expression of genes, none have been identified in T. reesei, which serves as an important and robust fungal factory for the production of native or heterologous proteins or even heterologous secondary metabolites. Herein, we showed that Psor, within the sor cluster responsible for the synthesis of yellow pigment in T. reesei, functioned as a BDP and can be used for dual gene co-expression with two reporter genes and two cellulase genes as proofs of concept. Notably, the co-expression of two cellulase genes using Psor contributed to the improvement of total cellulase activities. We chose OEypr1-Δsor1 as the parental strain, in which the yellow pigment production was completely abolished as a result of sor1 deletion and therefore exhibited some preferred characters, including improved conidiation, the maintenance of cell wall integrity, and stress tolerance [15]. Particularly, the elimination of the yellow pigment from the culture supernatant greatly facilitates the downstream isolation of target products. Meanwhile, the overexpression of ypr1 encoding the main activator for sor cluster [15] was expected to enhance the driving activity of Psor. OEypr1-Δsor1 therefore served as an ideal parental strain for Psor application. Nonetheless, we also observed that even with the overexpression of ypr1, the promoter strength of Psor from each end reached only half of that as shown by the promoter PgpdA. Whereas this promoter strength may not satisfy the requirement from high-level gene expression, it is suitable for the synthesis of products whose excessive load would overburden the cellular machinery of the host, especially those with toxicity. It may also find applications in the synthesis of secondary metabolites that require the co-expression of multiple respective genes. The application of BDP would obviously facilitate genetic manipulation and therefore is helps to reduce costs.
Compared with several other reported BDPs from filamentous fungi with a length ranging from ~800 bp to 1200 bp [8,9,10,12,13], T. reesei Psor has a shorter length of 767 bp. Nonetheless, it is currently unclear whether the flanking regions of Psor (the coding sequences within sor1 or sor2) are involved in the activation of sor genes, although the 767 bp-intergenic region is competent to drive the expression of two reporter genes and two cellulase genes. We have also noted that, whereas Ypr1 and Ypr2 have been demonstrated to act as the activator and repressor for sor genes, respectively [14], their binding sites as well as other cis-regulatory elements within Psor have not been identified yet. The future clarification of these key cis-regulatory elements and the regulatory mechanism to initiate the bidirectional transcription of Psor would contribute to reinforcing the promoter strength and reducing the promoter length.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.Z. and W.L.; methodology, W.Z. and W.L.; investigation, W.Z., W.L., X.W. and F.L.; data analyses, W.Z., W.L., X.W., F.L., R.Y. and X.M.; and writing, W.Z., W.L. and X.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by grants from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFA0900500), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31770047 and 31970029), the major basic research projects of the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2019ZD19), and the Open Projects Fund from the State Key Laboratory of Microbial Technology of Shandong University (Project NO. M2021-05).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate Liu Guodong from Shandong University for kindly providing experimental materials and insightful suggestions on the data analyses.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bischof, R.H.; Ramoni, J.; Seiboth, B. Cellulases and beyond: The first 70 years of the enzyme producer Trichoderma reesei. Microb. Cell Fact. 2016, 15, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Taylor, L.E., II; Vander Wall, T.A.; Linger, J.; Himmel, M.E.; Podkaminer, K.; Adney, W.S.; Decker, S.R. Heterologous protein expression in Hypocrea jecorina: A historical perspective and new developments. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenouda, M.L.; Ambilika, M.; Skellam, E.; Cox, R.J. Heterologous Expression of Secondary Metabolite Genes in Trichoderma reesei for Waste Valorization. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitz, E.; Wanka, F.; Seiboth, B. The Promoter Toolbox for Recombinant Gene Expression in Trichoderma reesei. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2018, 6, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyyssonen, E.; Keranen, S. Multiple roles of the cellulase CBHI in enhancing production of fusion antibodies by the filamentous fungus Trichoderma reesei. Curr. Genet. 1995, 28, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.; Zheng, F.; Li, C.; Zhang, W.; Chen, G.; Liu, W. Characterization of a copper responsive promoter and its mediated overexpression of the xylanase regulator 1 results in an induction-independent production of cellulases in Trichoderma reesei. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2015, 8, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Pelechano, V.; Jarvelin, A.I.; Steinmetz, L.M. Functional consequences of bidirectional promoters. Trends Genet. 2011, 27, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, A.; Gurdaswani, V.; D’Souza, J.S.; Ghag, S.B. Functional characterization of an inducible bidirectional promoter from Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergh, K.T.; Litzka, O.; Brakhage, A.A. Identification of a major cis-acting DNA element controlling the bidirectionally transcribed penicillin biosynthesis genes acvA (pcbAB) and ipnA (pcbC) of Aspergillus nidulans. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 3908–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Martin, J.F. Molecular control of expression of penicillin biosynthesis genes in fungi: Regulatory proteins interact with a bidirectional promoter region. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 2355–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muro-Pastor, M.I.; Strauss, J.; Ramon, A.; Scazzocchio, C. A paradoxical mutant GATA factor. Eukaryot. Cell 2004, 3, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiemann, P.; Soukup, A.A.; Folz, J.S.; Wang, P.M.; Noack, A.; Keller, N.P. CoIN: Co-inducible nitrate expression system for secondary metabolites in Aspergillus nidulans. Fungal. Biol. Biotechnol. 2018, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendsvig, J.K.H.; Workman, C.T.; Hoof, J.B. Bidirectional histone-gene promoters in Aspergillus: Characterization and application for multi-gene expression. Fungal. Biol. Biotechnol. 2019, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derntl, C.; Rassinger, A.; Srebotnik, E.; Mach, R.L.; Mach-Aigner, A.R. Identification of the Main Regulator Responsible for Synthesis of the Typical Yellow Pigment Produced by Trichoderma reesei. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 6247–6257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; An, N.; Guo, J.; Wang, Z.; Meng, X.; Liu, W. Influences of genetically perturbing synthesis of the typical yellow pigment on conidiation, cell wall integrity, stress tolerance, and cellulase production in Trichoderma reesei. J. Microbiol. 2021, 59, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lv, X.; Cao, Y.; Zheng, F.; Meng, X.; Shen, Y.; Chen, G.; Liu, W.; Zhang, W. A novel transcriptional regulator RXE1 modulates the essential transactivator XYR1 and cellulase gene expression in Trichoderma reesei. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 4511–4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandels, M.; Parrish, F.W.; Reese, E.T. Sophorose as an inducer of cellulase in Trichoderma viride. J. Bacteriol. 1962, 83, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yang, R.; Cao, Y.; Zheng, F.; Meng, X.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhang, W.; Liu, W. CLP1, a Novel Plant Homeo Domain Protein, Participates in Regulating Cellulase Gene Expression in the Filamentous Fungus Trichoderma reesei. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckman, K.L.; Pease, L.R. Gene splicing and mutagenesis by PCR-driven overlap extension. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 924–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Fan, Y.; Xia, Y.X.; Keyhani, N.O. Sulfonylurea resistance as a new selectable marker for the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 87, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penttila, M.; Nevalainen, H.; Ratto, M.; Salminen, E.; Knowles, J. A versatile transformation system for the cellulolytic filamentous fungus Trichoderma reesei. Gene 1987, 61, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, M.J.; Biely, P.; Poutanen, K. Interlaboratory Testing of Methods for Assay of Xylanase Activity. J. Biotechnol. 1992, 23, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scruggs, B.S.; Gilchrist, D.A.; Nechaev, S.; Muse, G.W.; Burkholder, A.; Fargo, D.C.; Adelman, K. Bidirectional Transcription Arises from Two Distinct Hubs of Transcription Factor Binding and Active Chromatin. Mol. Cell 2015, 58, 1101–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Du, J.; He, R.; Zhang, Z.; Qi, F.; Huang, J.; Qin, L. Improved Production of Majority Cellulases in Trichoderma reesei by Integration of cbh1 Gene from Chaetomium thermophilum. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).