A New Approach for the Treatment of Recurrent Vulvovaginal Candidiasis with a Combination of Pea Protein, Grape Seed Extract, and Lactic Acid Assessed In Vivo
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Microorganisms and Growth Conditions
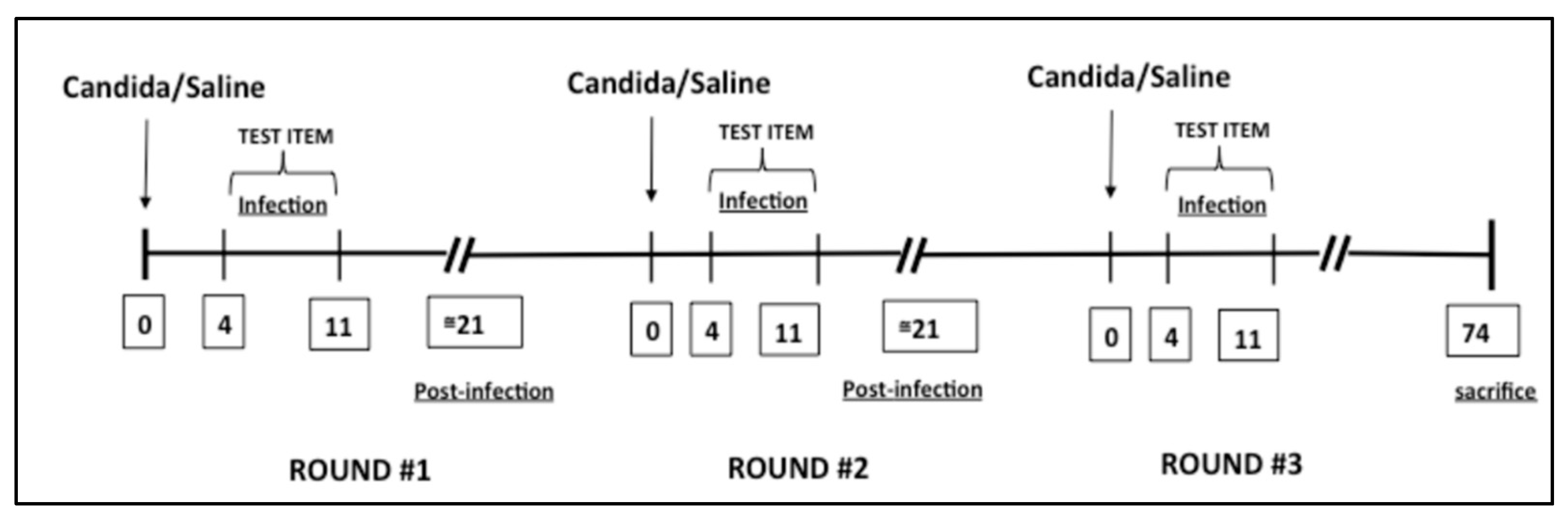
2.3. Candida albicans-Induced Vaginitis Model
2.4. Experimental Groups
- Control animal: mice received inoculations of saline (no infections);
- Control + clotrimazole: mice received inoculations of clotrimazole (no infections);
- Control + therapeutic: mice received inoculations from the therapeutic group (no infections);
- RVVC: mice received three separate vulvovaginal infections with 5 × 104 C. albicans;
- RVVC + clotrimazole: mice received three separate vulvovaginal infections with 5 × 104 C. albicans; after each C. albicans inoculation, mice were treated with clotrimazole alone (for 3 days) + saline (7 days);
- RVVC + clotrimazole + therapeutic: mice received three separate vulvovaginal infections with 5 × 104 C. albicans; after each C. albicans inoculation, mice were treated with clotrimazole alone (for 3 days) + therapeutic alone (for 7 days);
- RVVC + therapeutic: mice received three separate vulvovaginal infections with 5 × 104 C. albicans; after each C. albicans inoculation, mice were treated with the therapeutic alone (for 7 days) in each round.
2.5. Histological Evaluation
2.6. Myeloperoxidase Assay
2.7. ELISA Assay
2.8. Materials
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
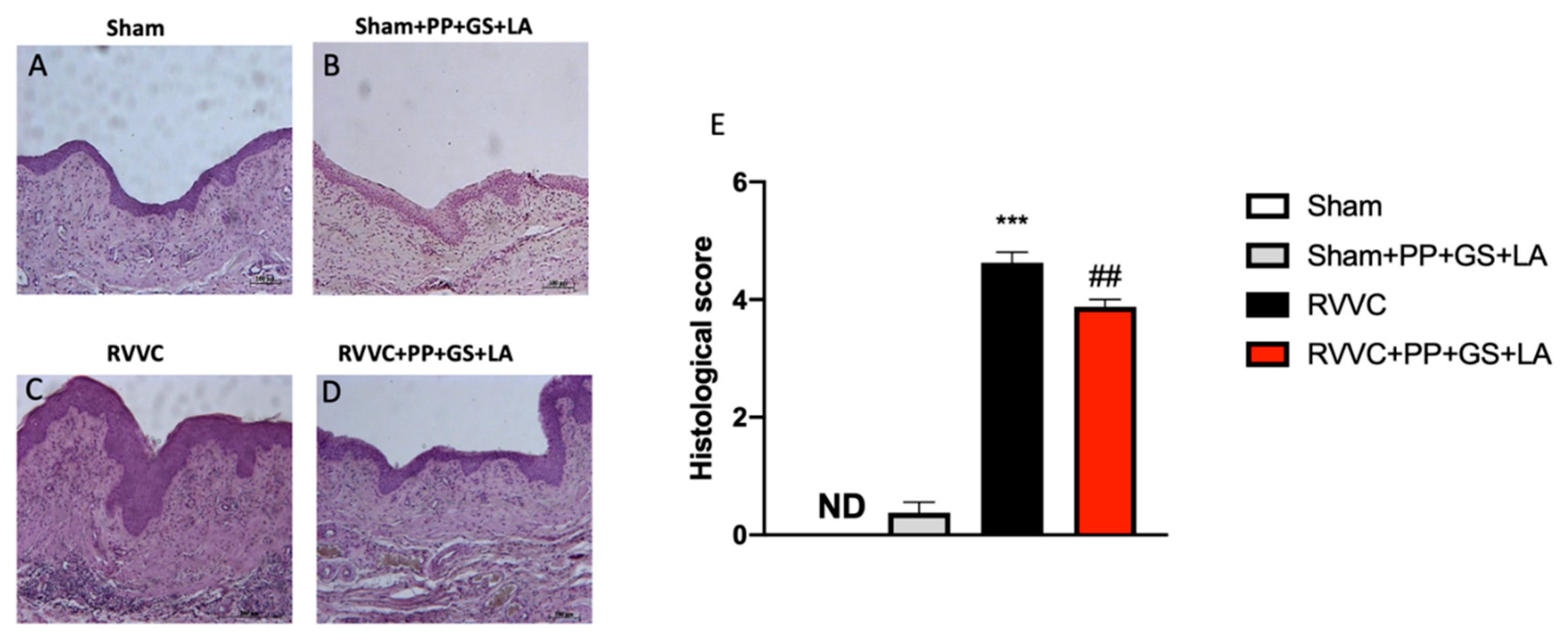
3.1. Histological Evaluation of the Therapeutic’s Efficacy in RVVC
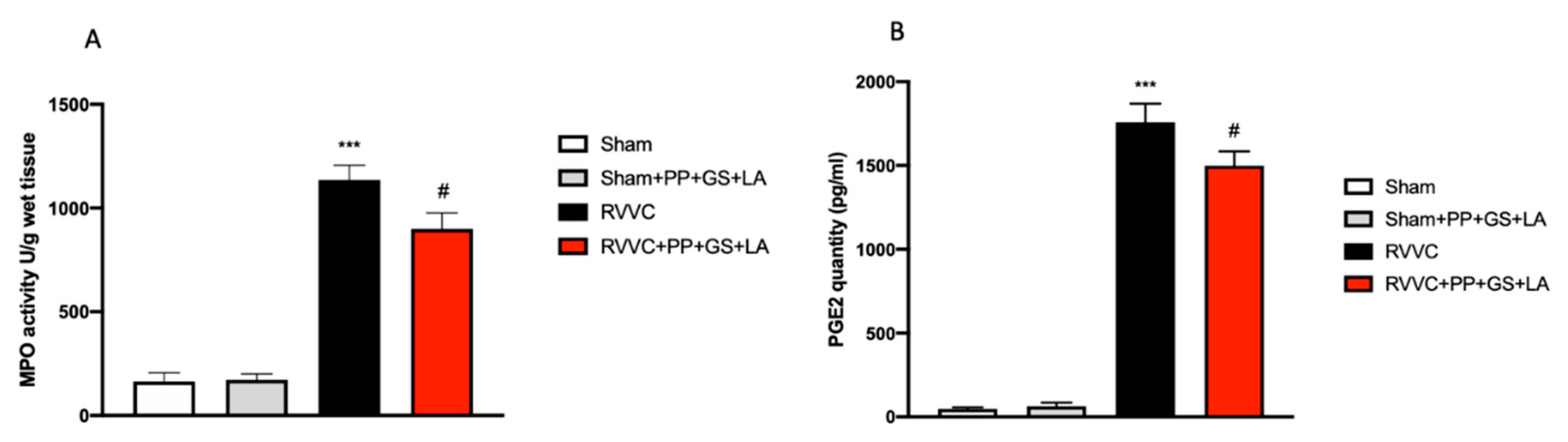
3.2. Protective Effects of the Therapeutic to Prevent Vaginal Inflammation Related to RVVC
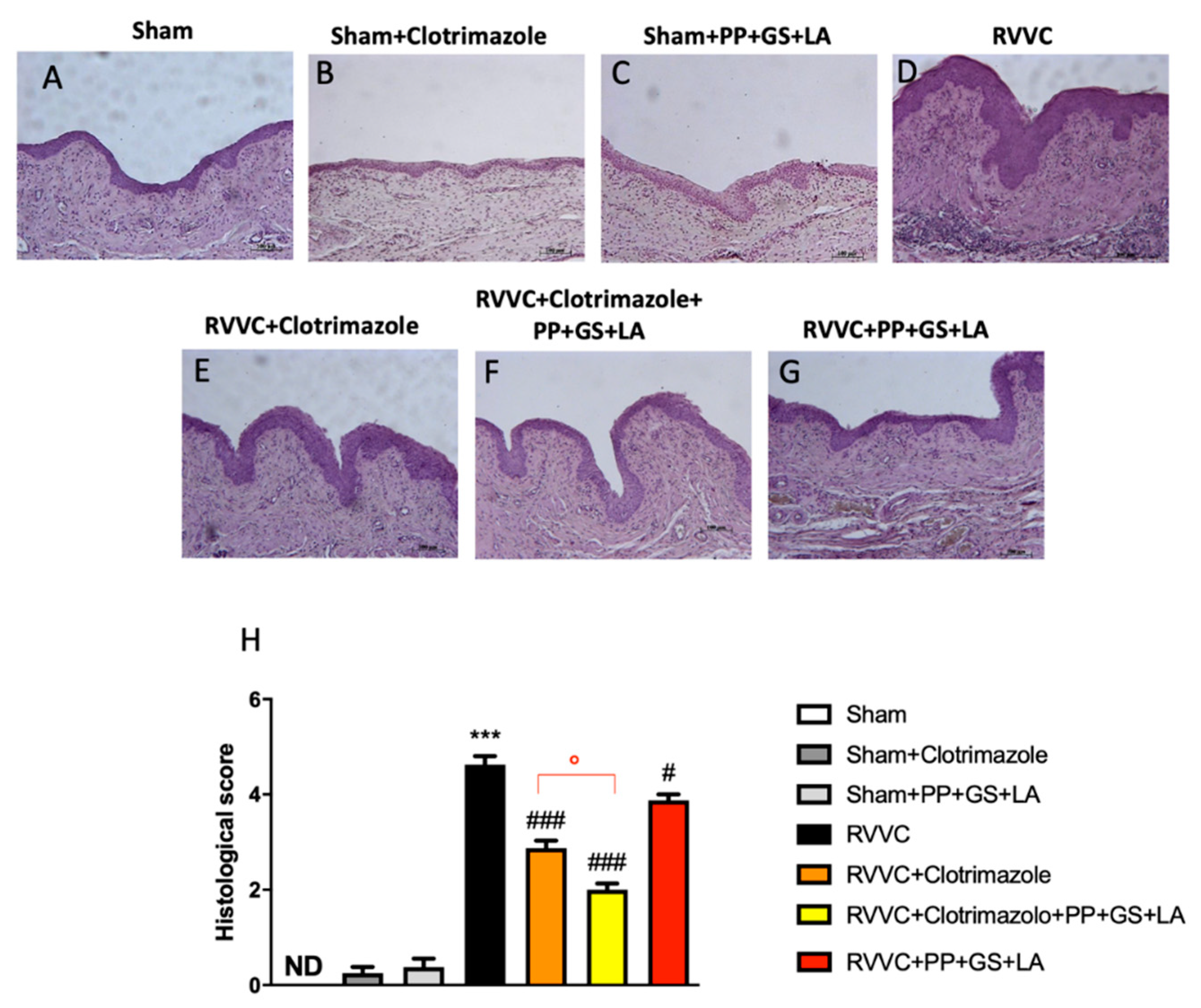
3.3. Role of the Therapeutic in Enhancing the Efficacy of Clotrimazole in RVVC-Related Histological Damage
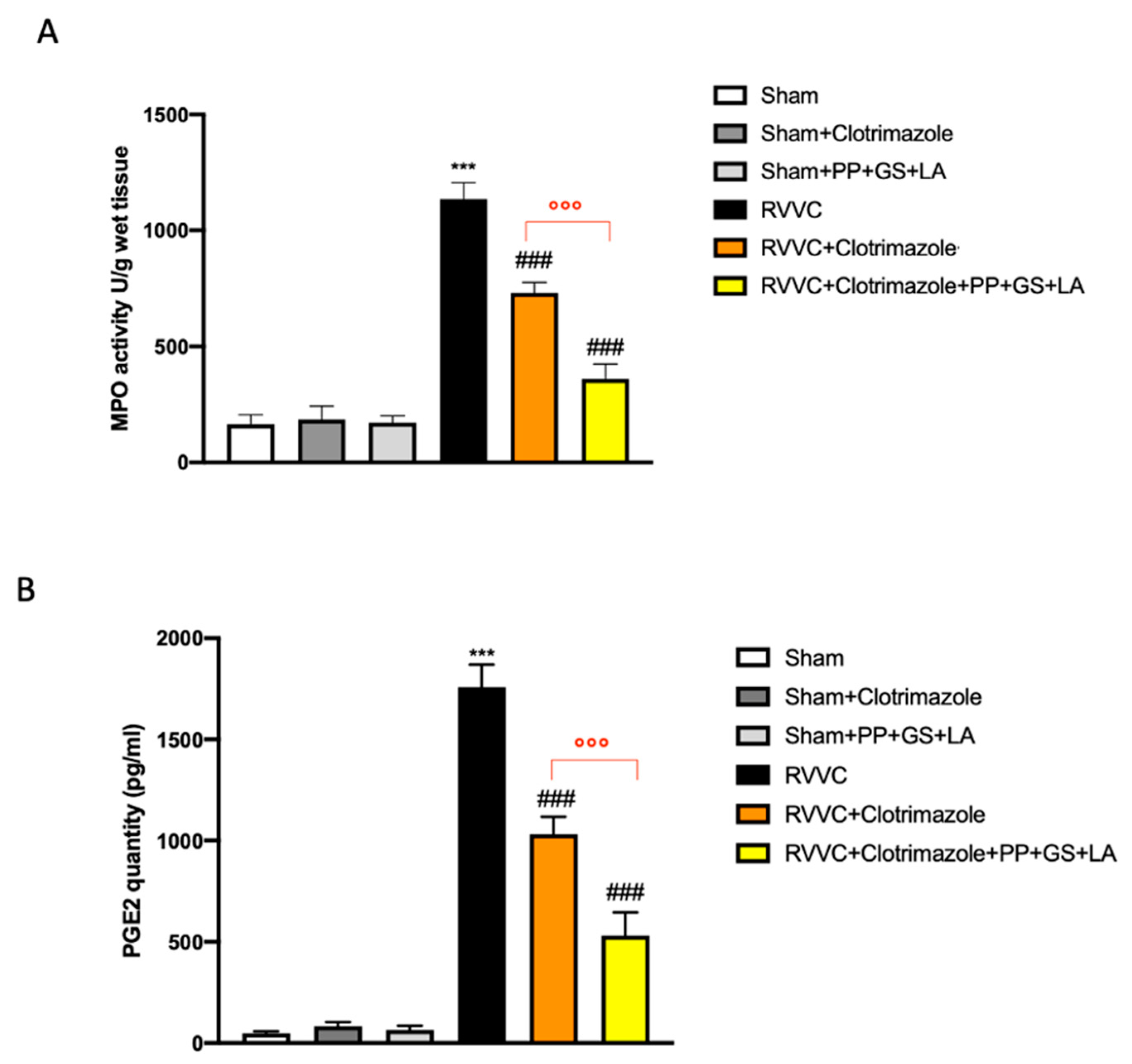
3.4. Role of the Therapeutic in Enhancing the Efficacy of Clotrimazole in RVVC-Related Vaginal Inflammation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Denning, D.W.; Kneale, M.; Sobel, J.D.; Rautemaa-Richardson, R. Global burden of recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis: A systematic review. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, e339–e347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matheson, A.; Mazza, D. Recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis: A review of guideline recommendations. Aust. N. Z. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2017, 57, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achkar, J.M.; Fries, B.C. Candida infections of the genitourinary tract. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 253–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talapko, J.; Juzbasic, M.; Matijevic, T.; Pustijanac, E.; Bekic, S.; Kotris, I.; Škrlec, I. Candida albicans-The Virulence Factors and Clinical Manifestations of Infection. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleury, F.J. Recurrent Candida vulvovaginitis. Chemotherapy 1982, 28 (Suppl. S1), 48–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willems, H.M.E.; Ahmed, S.S.; Liu, J.; Xu, Z.; Peters, B.M. Vulvovaginal Candidiasis: A Current Understanding and Burning Questions. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshfeghy, Z.; Tahari, S.; Janghorban, R.; Najib, F.S.; Mani, A.; Sayadi, M. Association of sexual function and psychological symptoms including depression, anxiety and stress in women with recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis. J. Turk. Ger. Gynecol. Assoc. 2020, 21, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, P.G.; Kauffman, C.A.; Andes, D.R.; Clancy, C.J.; Marr, K.A.; Ostrosky-Zeichner, L.; Reboli, A.C.; Schuster, M.G.; Vazquez, J.A.; Walsh, T.J.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Candidiasis: 2016 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 62, e1–e50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobel, J.D.; Wiesenfeld, H.C.; Martens, M.; Danna, P.; Hooton, T.M.; Rompalo, A.; Sperling, M.; Livengood, C., III; Horowitz, B.; von Thron, J.; et al. Maintenance fluconazole therapy for recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 876–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauters, T.G.; Dhont, M.A.; Temmerman, M.I.; Nelis, H.J. Prevalence of vulvovaginal candidiasis and susceptibility to fluconazole in women. Am. J. Obstet Gynecol. 2002, 187, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lirio, J.; Giraldo, P.C.; Amaral, R.L.; Sarmento, A.C.A.; Costa, A.P.F.; Goncalves, A.K. Antifungal (oral and vaginal) therapy for recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis: A systematic review protocol. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e027489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farr, A.; Effendy, I.; Frey Tirri, B.; Hof, H.; Mayser, P.; Petricevic, L.; Ruhnke, M.; Schaller, M.; Schaefer, A.P.; Sustr, V.; et al. Guideline: Vulvovaginal candidosis (AWMF 015/072, level S2k). Mycoses 2021, 64, 583–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliman, S.; Alnajdy, D.; El-Keblawy, A.A.; Mosa, K.A.; Khoder, G.; Noreddin, A.M. Plants’ Natural Products as Alternative Promising Anti-Candida Drugs. Pharm. Rev. 2017, 11, 104–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaleiro, C.; Salgueiro, L.; Goncalves, M.J.; Hrimpeng, K.; Pinto, J.; Pinto, E. Antifungal activity of the essential oil of Angelica major against Candida, Cryptococcus, Aspergillus and dermatophyte species. J. Nat. Med. 2015, 69, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonetti, G.; Santamaria, A.R.; D’Auria, F.D.; Mulinacci, N.; Innocenti, M.; Cecchini, F.; Pericolini, E.; Gabrielli, E.; Panella, S.; Antonacci, D.; et al. Evaluation of anti-Candida activity of Vitis vinifera L. seed extracts obtained from wine and table cultivars. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 127021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campolo, M.; Casili, G.; Paterniti, I.; Filippone, A.; Lanza, M.; Ardizzone, A.; Scuderi, S.A.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Esposito, E. Effect of a Product Containing Xyloglucan and Pea Protein on a Murine Model of Atopic Dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.S.; Cabral, K.M.; Zingali, R.B.; Kurtenbach, E. Characterization of two novel defense peptides from pea (Pisum sativum) seeds. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2000, 378, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.X.; Ng, T.B. An antifungal protein from the pea Pisum sativum var. arvense Poir. Peptides 2006, 27, 1732–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonetti, G.; Brasili, E.; Pasqua, G. Antifungal Activity of Phenolic and Polyphenolic Compounds from Different Matrices of Vitis vinifera L. against Human Pathogens. Molecules 2020, 25, 3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Dey, S.; Marbaniang, D.; Pal, P.; Ray, S.; Mazumder, B. Grape seed extract: Having a potential health benefits. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 1205–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, K.; Maltese, F.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R. Metabolic constituents of grapevine and grape-derived products. Phytochem. Rev. 2010, 9, 357–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Veer, C.; Bruisten, S.M.; van Houdt, R.; Matser, A.A.; Tachedjian, G.; van de Wijgert, J.H.H.M.; de Vries, H.J.C.; van der Helm, J.J. Effects of an over-the-counter lactic-acid containing intra-vaginal douching product on the vaginal microbiota. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Er, S.; Istanbullu Tosun, A.; Arik, G.; Kivanc, M. Anticandidal activities of lactic acid bacteria isolated from the vagina. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 49, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pike, I.H.; Evans, E.G.; Carney, J.A. Mannan estimation as a measure of the growth of Candida albicans. J. Med. Vet. Mycol. 1991, 29, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, A.S.; Luo, G.; Gebremariam, T.; Lee, H.; Schmidt, C.S.; Hennessey, J.P., Jr.; French, S.W.; Yeaman, M.R.; Filler, S.G.; Edwards, J.E., Jr. NDV-3 protects mice from vulvovaginal candidiasis through T- and B-cell immune response. Vaccine 2013, 31, 5549–5556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruschetta, G.; Impellizzeri, D.; Campolo, M.; Casili, G.; Di Paola, R.; Paterniti, I.; Esposito, E.; Cuzzocrea, S. FeTPPS Reduces Secondary Damage and Improves Neurobehavioral Functions after Traumatic Brain Injury. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swidsinski, A.; Guschin, A.; Tang, Q.; Dorffel, Y.; Verstraelen, H.; Tertychnyy, A.; Khayrullina, G.; Luo, X.; Sobel, J.D.; Jiang, X. Vulvovaginal candidiasis: Histologic lesions are primarily polymicrobial and invasive and do not contain biofilms. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2019, 220, 91.e1–91.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paredes, J.M.; Weiss, S.J. Human neutrophils transform prostaglandins by a myeloperoxidase-dependent mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 2738–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, C.L.; Davies, M.J. Role of myeloperoxidase and oxidant formation in the extracellular environment in inflammation-induced tissue damage. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 172, 633–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, T.; Narumiya, S. Prostaglandins and chronic inflammation. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 33, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasper, L.; Miramon, P.; Jablonowski, N.; Wisgott, S.; Wilson, D.; Brunke, S.; Hube, B. Antifungal activity of clotrimazole against Candida albicans depends on carbon sources, growth phase and morphology. J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 64, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, J.; Lilly, E.; Barousse, M.; Fidel, P.L., Jr. Epithelial cell-derived S100 calcium-binding proteins as key mediators in the hallmark acute neutrophil response during Candida vaginitis. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 5126–5137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, H.L.; Moots, R.J.; Bucknall, R.C.; Edwards, S.W. Neutrophil function in inflammation and inflammatory diseases. Rheumatology 2010, 49, 1618–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arastehfar, A.; Kargar, M.L.; Mohammadi, S.R.; Roudbary, M.; Ghods, N.; Haghighi, L.; Daneshnia, F.; Tavakoli, M.; Jafarzadeh, J.; Hedayati, M.T.; et al. A High Rate of Recurrent Vulvovaginal Candidiasis and Therapeutic Failure of Azole Derivatives Among Iranian Women. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 655069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfim, A.P.; Sakita, K.M.; Faria, D.R.; Arita, G.S.; Vendramini, F.; Capoci, I.R.G.; Braga, A.G.; Dos Santos, R.S.; Bruschi, M.L.; Becker, T.C.A.; et al. Preclinical approaches in vulvovaginal candidiasis treatment with mucoadhesive thermoresponsive systems containing propolis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quindos, G.; Gil-Alonso, S.; Marcos-Arias, C.; Sevillano, E.; Mateo, E.; Jauregizar, N.; Eraso, E. Therapeutic tools for oral candidiasis: Current and new antifungal drugs. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2019, 24, e172–e180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaller, M.A.; Diekema, D.J. Rare and emerging opportunistic fungal pathogens: Concern for resistance beyond Candida albicans and Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 4419–4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, E.; Campolo, M.; Casili, G.; Lanza, M.; Filippone, A.; Peritore, A.F.; Cuzzocrea, S. Effect of pea protein plus grape seed dry extract on a murine model of Candida albicans induced vaginitis. Future Microbiol. 2018, 13, 1375–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachedjian, G.; Aldunate, M.; Bradshaw, C.S.; Cone, R.A. The role of lactic acid production by probiotic Lactobacillus species in vaginal health. Res. Microbiol. 2017, 168, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeise, K.D.; Woods, R.J.; Huffnagle, G.B. Interplay between Candida albicans and Lactic Acid Bacteria in the Gastrointestinal Tract: Impact on Colonization Resistance, Microbial Carriage, Opportunistic Infection, and Host Immunity. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 34, e0032320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassone, A.; Sobel, J.D. Experimental Models of Vaginal Candidiasis and Their Relevance to Human Candidiasis. Infect. Immun. 2016, 84, 1255–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKloud, E.; Delaney, C.; Sherry, L.; Kean, R.; Williams, S.; Metcalfe, R.; Thomas, R.; Richardson, R.; Gerasimidis, K.; Nile, C.J.; et al. Recurrent Vulvovaginal Candidiasis: A Dynamic Interkingdom Biofilm Disease of Candida and Lactobacillus. Msystems 2021, 6, e0062221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, J.; Peters, B.M.; Noverr, M.C.; Fidel, P.L., Jr. Novel Mechanism behind the Immunopathogenesis of Vulvovaginal Candidiasis: “Neutrophil Anergy”. Infect. Immun. 2018, 86, e00684-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, T.G.; Lim, Y.S.; Tan, A.; Leong, R.; Pavelka, N. Fungal Symbionts Produce Prostaglandin E2 to Promote Their Intestinal Colonization. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odds, F.C.; Davidson, A.D.; Jacobsen, M.D.; Tavanti, A.; Whyte, J.A.; Kibbler, C.C.; Ellis, D.H.; Maiden, M.C.J.; Shaw, D.J.; Gow, N.A.R. Candida albicans strain maintenance, replacement, and microvariation demonstrated by multilocus sequence typing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 3647–3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrbanac, A.; Riestra, A.M.; Coady, A.; Knight, R.; Nizet, V.; Patras, K.A. The murine vaginal microbiota and its perturbation by the human pathogen group B Streptococcus. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paterniti, I.; Casili, G.; Filippone, A.; Lanza, M.; Ardizzone, A.; Capra, A.P.; Campolo, M.; Esposito, E. A New Approach for the Treatment of Recurrent Vulvovaginal Candidiasis with a Combination of Pea Protein, Grape Seed Extract, and Lactic Acid Assessed In Vivo. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 1251. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8121251
Paterniti I, Casili G, Filippone A, Lanza M, Ardizzone A, Capra AP, Campolo M, Esposito E. A New Approach for the Treatment of Recurrent Vulvovaginal Candidiasis with a Combination of Pea Protein, Grape Seed Extract, and Lactic Acid Assessed In Vivo. Journal of Fungi. 2022; 8(12):1251. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8121251
Chicago/Turabian StylePaterniti, Irene, Giovanna Casili, Alessia Filippone, Marika Lanza, Alessio Ardizzone, Anna Paola Capra, Michela Campolo, and Emanuela Esposito. 2022. "A New Approach for the Treatment of Recurrent Vulvovaginal Candidiasis with a Combination of Pea Protein, Grape Seed Extract, and Lactic Acid Assessed In Vivo" Journal of Fungi 8, no. 12: 1251. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8121251
APA StylePaterniti, I., Casili, G., Filippone, A., Lanza, M., Ardizzone, A., Capra, A. P., Campolo, M., & Esposito, E. (2022). A New Approach for the Treatment of Recurrent Vulvovaginal Candidiasis with a Combination of Pea Protein, Grape Seed Extract, and Lactic Acid Assessed In Vivo. Journal of Fungi, 8(12), 1251. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8121251











