Eumycetoma Caused by Madurella pseudomycetomatis in a Captive Tiger (Panthera tigris)
Abstract
1. Introduction
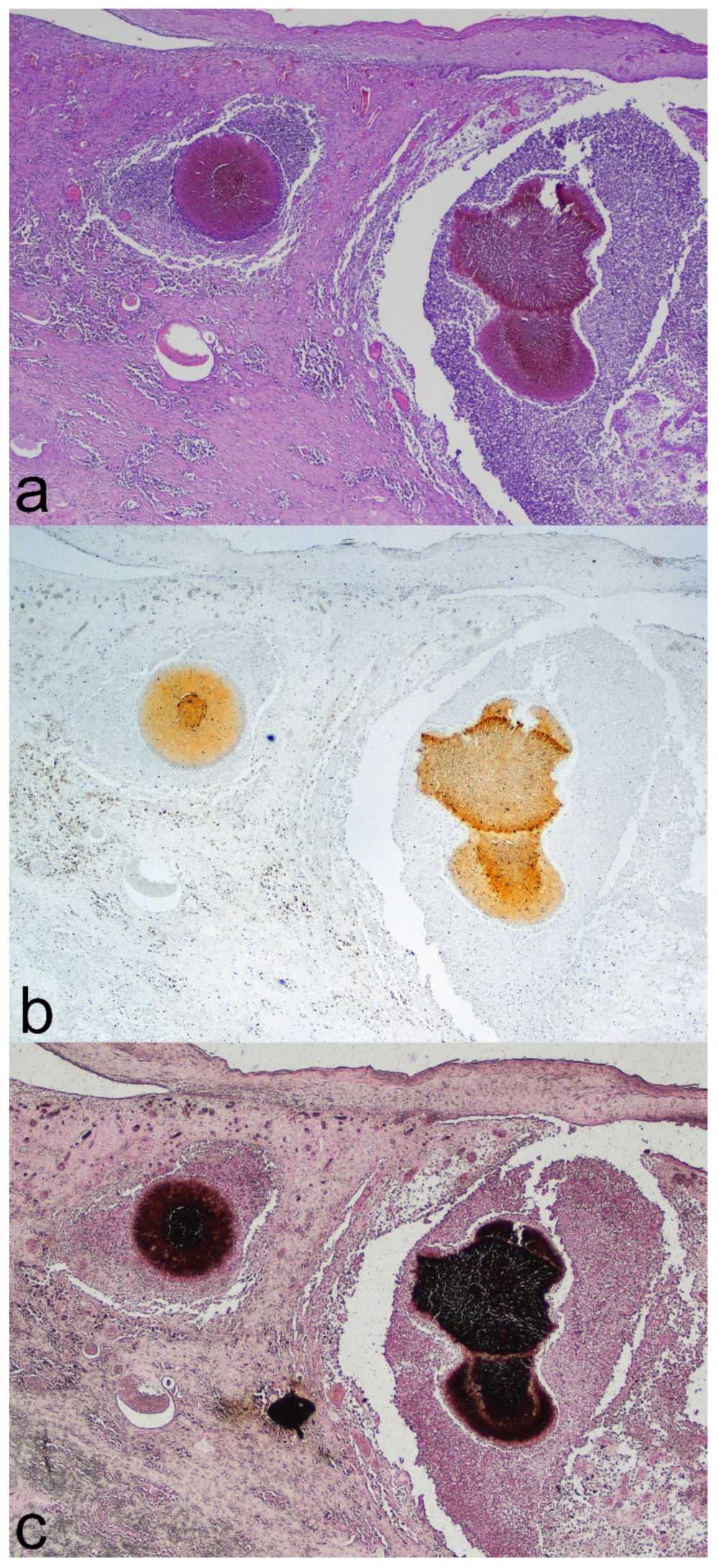
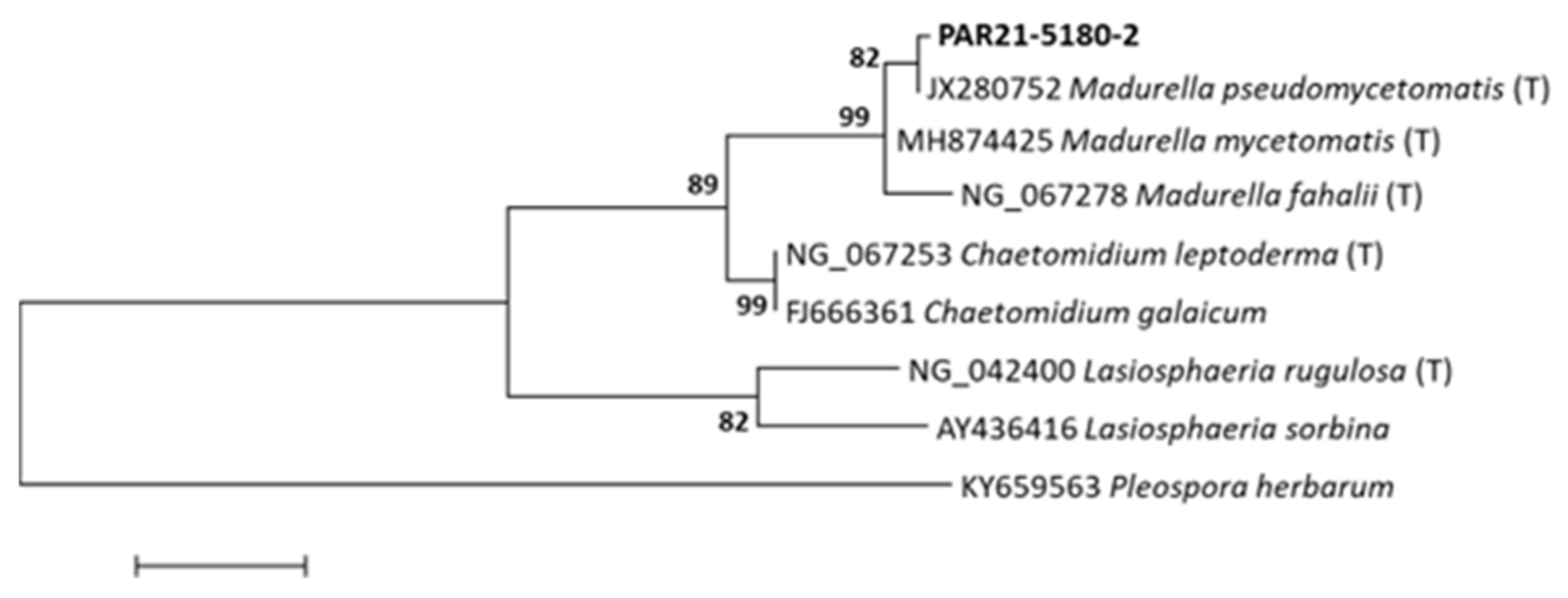
2. Detailed Case Description
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grooters, A.M.; Foil, C.S. Miscellaneous fungal infections. In Infectious Diseases of the Dog and the Cat; Saunders: St Louis, MO, USA, 2012; pp. 685–688. [Google Scholar]
- Guarner, J.; Brandt, M.E. Histopathologic Diagnosis of Fungal Infections in the 21st Century. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 24, 247–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenman, H.C.; Greer, E.M.; McGrail, C.W. The Role of Melanins in Melanotic Fungi for Pathogenesis and Environmental Survival. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 4247–4257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyedmousavi, S.; Guillot, J.; de Hoog, G.S. Phaeohyphomycoses, Emerging Opportunistic Diseases in Animals. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramo, F.; Bastelli, F.; Nardoni, S.; Mancianti, F. Feline Cutaneous Phaeohyphomycosis Due to Cladophyalophora Bantiana. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2002, 4, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liatis, T.; Theochari, F.; Kalogianni, L.; Soubasis, N.; Oikonomidis, I.L.; Velegraki, A.; Psalla, D.; Triantafyllou, E.; Patsikas, M.; Polizopoulou, Z. Brainstem Phaeohyphomycosis Due to Curvularia Lunata (Cochliobolus Lunatus) in a Cat. Aust. Vet. J. 2021, 99, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaid, D.M.; Bakheet, O.E.; Ahmed, E.S.; Abdalati, F.; Mhmoud, N.A.; Mohamed, E.S.W.; Bakhiet, S.M.; Siddig, E.E.; Fahal, A.H. Multiple Extensive Madurella Mycetomatis Eumycetoma Lesions: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2021, 115, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akritidis, N. Parasitic, Fungal and Prion Zoonoses: An Expanding Universe of Candidates for Human Disease. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedmousavi, S.; Guillot, J.; Tolooe, A.; Verweij, P.E.; de Hoog, G.S. Neglected Fungal Zoonoses: Hidden Threats to Man and Animals. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, N.; Gunew, M.; Marshall, R.; Martin, P.; Barrs, V. Focal Pulmonary Granuloma Caused by Cladophialophora Bantiana in a Domestic Short Haired Cat. Med. Mycol. 2011, 49, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janovsky, M.; Gröne, A.; Ciardo, D.; Völlm, J.; Burnens, A.; Fatzer, R.; Bacciarini, L.N. Phaeohyphomycosis in a Snow Leopard (Uncia Uncia) Due to Cladophialophora Bantiana. J. Comp. Pathol. 2006, 134, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, P.R.D.; Dutra, V.; Maruyama, F.H.; Garcia, S.D.; Duarte, R.P.; de Azevedo, E.Z.; Nazakato, L.; Machado, G.F. Cerebral Phaeohyphomycosis Due to Cladosporium Spp. in a Lion (Panthera Leo). J. Comp. Pathol. 2017, 156, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaff, A.R.; Ferguson, S.; Phair, K.; Ferris, R.; Goe, A. Eumycetoma and Disseminated Phaeohyphomycosis in a Sumatran Tiger. J. Vet. Diagnostic Investig. 2021, 33, 1197–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ZIMS. Species360 Zoological Information Management System. Available online: https://www.species360.org/ (accessed on 8 November 2022).
- Danesi, P.; Falcaro, C.; Schmertmann, L.J.; de Miranda, L.H.M.; Krockenberger, M.; Malik, R. Cryptococcus in Wildlife and Free-Living Mammals. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddig, E.E.; Mhmoud, N.A.; Bakhiet, S.M.; Abdallah, O.B.; Mekki, S.O.; El Dawi, N.I.; Van De Sande, W.; Fahal, A.H. The Accuracy of Histopathological and Cytopathological Techniques in the Identification of the Mycetoma Causative Agents. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Meng, X.; Mo, C.; Wei, X.; Ma, A. Melanin of Fungi: From Classification to Application. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 38, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Nimse, S.B.; Mathew, D.E.; Dhimmar, A.; Sahastrabudhe, H.; Gajjar, A.; Ghadge, V.A.; Kumar, P.; Shinde, P.B. Microbial Melanin: Recent Advances in Biosynthesis, Extraction, Characterization, and Applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2021, 53, 107773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcobello, J.T.; Revankar, S.G. Phaeohyphomycosis. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 41, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, K.L.; Proia, A.D.; Puri, P.K. Fontana-Masson Stain in Fungal Infections. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 77, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, R.A.; Kamat, N.M.; Nadkarni, V.S. Purification and Characterisation of a Sulphur Rich Melanin from Edible Mushroom Termitomyces Albuminosus Heim. Mycology 2018, 9, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.; Konings, M.; Parel, F.; Eadie, K.; Strepis, N.; Fahal, A.; Verbon, A.; van de Sande, W.W.J. Inhibiting DHN- and DOPA-Melanin Biosynthesis Pathway Increased the Therapeutic Value of Itraconazole in Madurella Mycetomatis Infected Galleria Mellonella. Med. Mycol. 2022, 60, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Cunha, K.C.; Sutton, D.A.; Fothergill, A.W.; Gené, J.; Cano, J.; Madrid, H.; de Hoog, S.; Crous, P.W.; Guarro, J. In Vitro Antifungal Susceptibility and Molecular Identity of 99 Clinical Isolates of the Opportunistic Fungal Genus Curvularia. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 76, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Deng, J.; Zhou, C.J.; Zhong, B.Y.; Hao, F. Phenotypic and Molecular Characterization of Madurella pseudomycetomatis sp. Nov., a Novel Opportunistic Fungus Possibly Causing Black-Grain Mycetoma. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borjian Boroujeni, Z.; Hashemi, S.J.; Daie Ghazvini, R.; Khodavaisy, S.; Zareei, M.; Hosseinpour, L.; Ardi, P.; Shokri, M. Recurrent Eumycetoma Caused by Novel Species Madurella pseudomycetomatis: A Case Report. Med. Mycol. Case Rep. 2019, 26, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyuykonge, B.; Klaassen, C.; Zandijk, W.; de Hoog, G.; Ahmed, S.; Desnos-Ollivier, M.; Verbon, A.; Bonifaz, A.; Sande, W. Diagnostic implications of mycetoma derived from Madurella pseudomycetomatis isolates from Mexico. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, 1828–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albanese, F.; Muscatello, L.V.; Michelutti, A.; Falcaro, C.; Bellentani, L.; Danesi, P. Canine Eumycetoma Caused by Madurella pseudomycetomatis. Med. Mycol. Case Rep. 2022, 35, 51–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hospenthal, D. Agents of mycetoma. In Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s Principles and Practices of Infectious Diseases; Bennett, J.E., Dolin, R., Blaser, M.J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 3141–3145. ISBN 9780323482554. [Google Scholar]
- Hashizume, H.; Taga, S.; Sakata, M.K.; Taha, M.H.M.; Siddig, E.E.; Minamoto, T.; Fahal, A.H.; Kaneko, S. Detection of Multiple Mycetoma Pathogens Using Fungal Metabarcoding Analysis of Soil DNA in an Endemic Area of Sudan. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloret, A.; Hartmann, K.; Pennisi, M.G.; Ferrer, L.; Addie, D.; Belák, S.; Boucraut-Baralon, C.; Egberink, H.; Frymus, T.; Gruffydd-Jones, T.; et al. Rare Opportunistic Mycoses in Cats: Phaeohyphomycosis and Hyalohyphomycosis: ABCD Guidelines on Prevention and Management. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2013, 15, 628–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revankar, S.G.; Sutton, D.A.; Rinaldi, M.G. Primary Central Nervous System Phaeohyphomycosis: A Review of 101 Cases. Clin Infect Dis. 2004, 38, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Orlandi, M.; Giglia, G.; Danesi, P.; Laricchiuta, P.; Abramo, F. Eumycetoma Caused by Madurella pseudomycetomatis in a Captive Tiger (Panthera tigris). J. Fungi 2022, 8, 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8121289
Orlandi M, Giglia G, Danesi P, Laricchiuta P, Abramo F. Eumycetoma Caused by Madurella pseudomycetomatis in a Captive Tiger (Panthera tigris). Journal of Fungi. 2022; 8(12):1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8121289
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrlandi, Margherita, Giuseppe Giglia, Patrizia Danesi, Piero Laricchiuta, and Francesca Abramo. 2022. "Eumycetoma Caused by Madurella pseudomycetomatis in a Captive Tiger (Panthera tigris)" Journal of Fungi 8, no. 12: 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8121289
APA StyleOrlandi, M., Giglia, G., Danesi, P., Laricchiuta, P., & Abramo, F. (2022). Eumycetoma Caused by Madurella pseudomycetomatis in a Captive Tiger (Panthera tigris). Journal of Fungi, 8(12), 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8121289







