Discovery of Three New Mucor Species Associated with Cricket Insects in Korea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Isolation
2.2. Morphological Studies
2.3. DNA Extraction, PCR, Cloning, and Sequencing
2.4. Phylogenetic Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Phylogenetic Analysis
3.2. Taxonomy
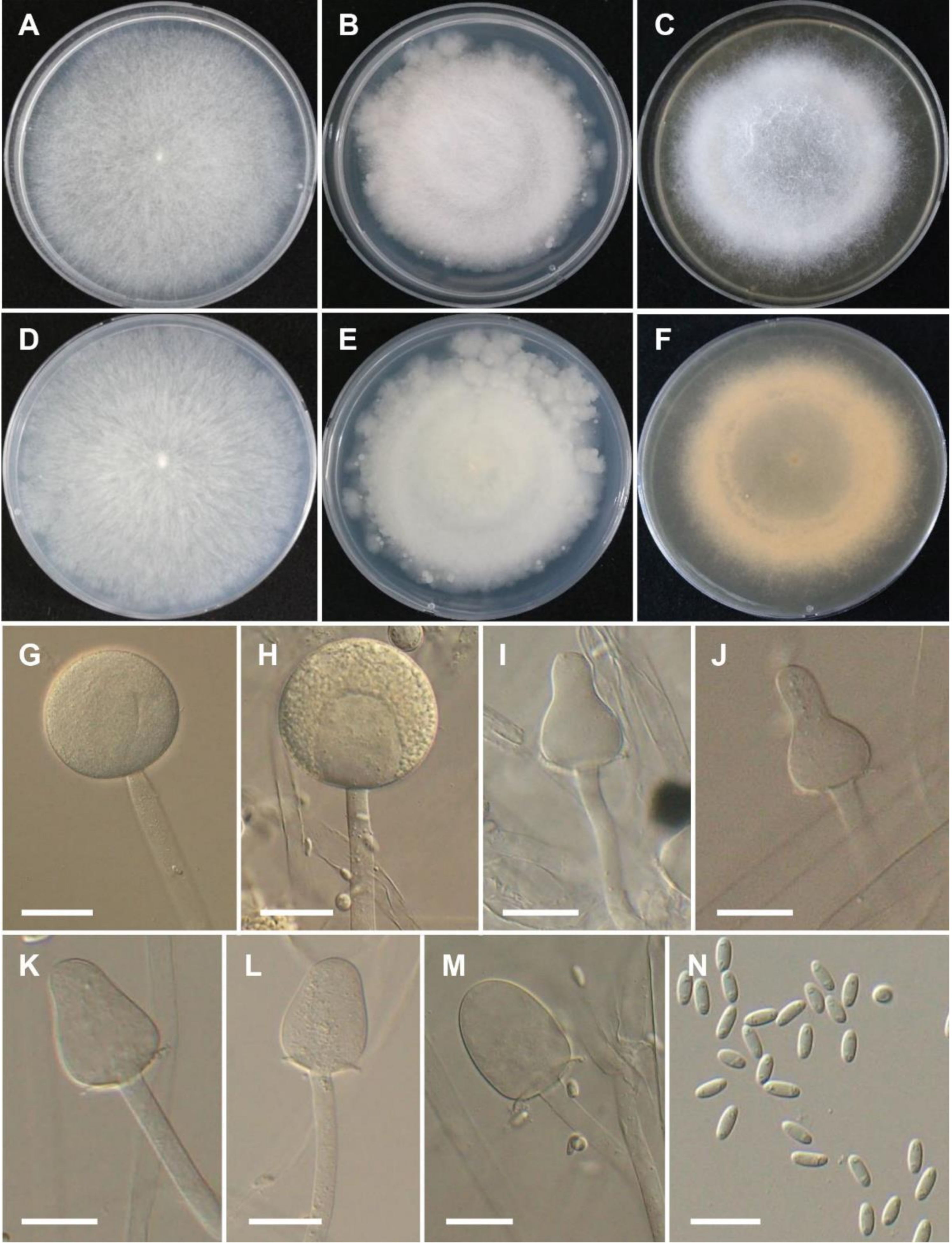
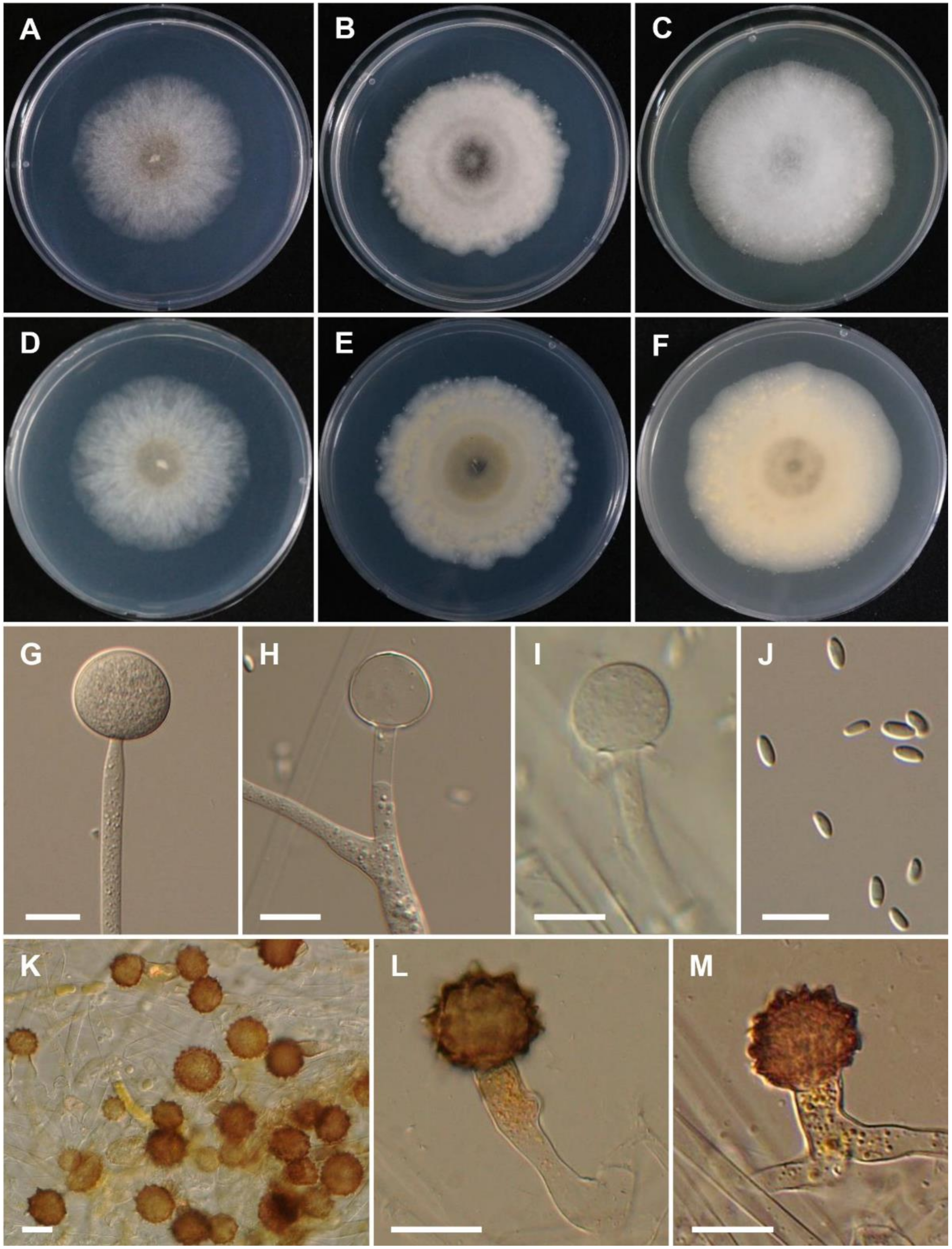
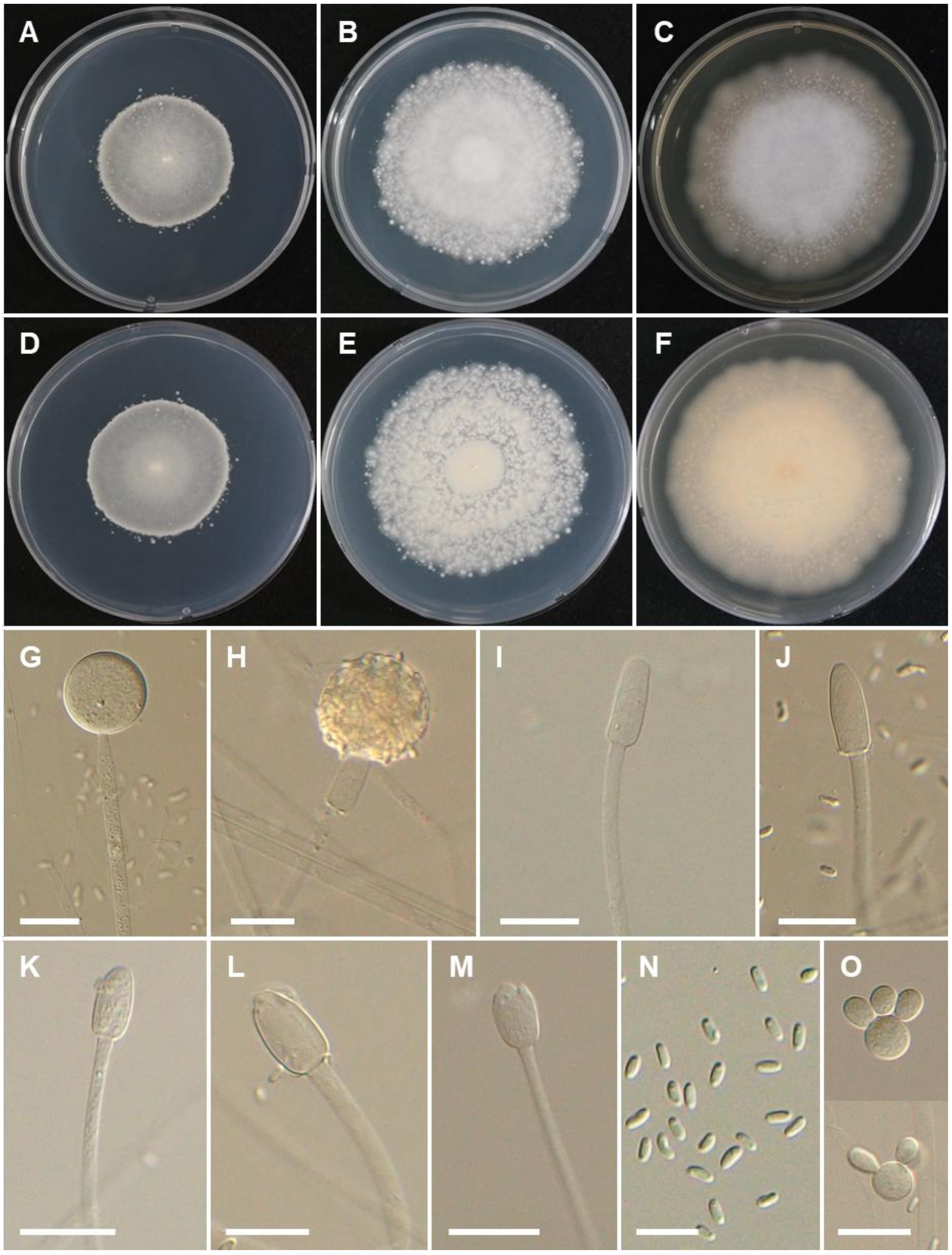
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fresenius, G. Beiträge zur Mykologie; Bei Heinrich Ludwig Brönner: Frankfurt, Germany, 1850; pp. 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Voigt, V.; James, T.Y.; Kirk, P.M.; Santiago, A.L.C.M.; Waldman, B.; Griffith, G.W.; Fu, M.; Radek, R.; Strassert, J.F.H.; Wurzbacher, C.; et al. Early-diverging fungal phyla: Taxonomy, species concept, ecology, distribution, anthropogenic impact, and novel phylogenetic proposals. Fungal Divers. 2021, 109, 59–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walther, G.; Wagner, L.; Kurzai, O. Updates on the taxonomy of Mucorales with an emphasis on clinically important taxa. J. Fungi 2019, 5, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wagner, L.; Stielow, J.B.; de Hoog, G.S.; Bensch, K.; Schwartze, V.U.; Voigt, K.; Alastruey-Izquierdo, A.; Kurzai, O.; Walther, G. A new species concept for the clinically relevant Mucor circinelloides complex. Persoonia 2020, 44, 67–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurdeal, V.G.; Gentekaki, E.; Hyde, K.D.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Lee, H.B. Novel Mucor species (Mucoromycetes, Mucoraceae) from northern Thailand. Mycokeys 2021, 84, 57–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonmee, S.; Wanasinghe, D.N.; Calabon, M.S.; Huanraluek, N.; Chandrasiri, S.K.; Jones, G.E.; Rossi, W.; Leonardi, M.; Singh, S.K.; Rana, S.; et al. Fungal diversity notes 1387–1511: Taxonomic and phylogenetic contributions on genera and species of fungal taxa. Fungal Divers. 2021, 111, 1–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, F.; Yao, S.; Cai, C.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W.; Ma, B.; Rong, C.; Cheng, C. Mucor rongii sp. nov., a new cold-tolerant species from China. Curr. Microbiol. 2021, 78, 2464–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijayawardene, N.N.; Hyde, K.D.; Al-Ani, L.K.T.; Dai, D.Q.; Sánchez-García, M. Outline of fungi and fungus-like taxa—2021. Mycosphere 2022, 13, 53–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benny, G.L. The methods used by Dr. R. K. Benjamin, and other mycologists, to isolate Zygomycetes. Aliso 2008, 26, 37–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, G.; Pawlowska, J.; Alastruey-Izquierdo, A.; Wrzosek, M.; Rodriguez-Tudela, J.L.; Dolatabadi, S.; Chakrabarti, A.; de Hoog, G.S. DNA barcoding in Mucorales: An inventory of biodiversity. Persoonia 2013, 30, 11–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wanasinghe, D.N.; Phukhamsakda, C.; Hyde, K.D.; Jeewon, R.; Lee, H.B.; Jones, E.G.; Tibpromma, S.; Tennakoon, D.S.; Dissanayake, A.J.; Jayasiri, S.C. Fungal diversity notes 709–839: Taxonomic and phylogenetic contributions to fungal taxa with an emphasis on fungi on Rosaceae. Fungal Divers. 2018, 89, 1–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.T.; Jeon, Y.J.; Mun, H.Y.; Goh, J.; Chung, N.; Lee, H.B. Isolation and characterization of four unrecorded Mucor species in Korea. Mycobiology 2020, 48, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, T.T.T.; Lee, H.B. Mucor cheongyangensis, a new species isolated from the surface of Lycorma delicatula in Korea. Phytotaxa 2020, 446, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, D.X.; Barreto, R.W.; Lee, H.B.; Cordeiro, T.R.L.; de Souza, C.A.F.; de Oliveira, R.J.V.; Santiago, A.L.C.M. Novel Mucoralean fungus from a repugnant substrate: Mucor merdophylus sp. nov., isolated from dog excrement. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 2642–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, W.; Keighley, C.; Wolfe, R.; Lee, W.; Slavin, M.A.; Kong, D.C.M.; Chen, C.A. The epidemiology and clinical manifestations of mucormycosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of case reports. Clin. Microbiol. Inf. 2019, 25, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagner, L.; de Hoog, S.; Alastruey-Izquierdo, A.; Voigt, K.; Kurzai, O.; Walther, G. A revised species concept for opportunistic Mucor species reveals species-specific antifungal susceptibility profiles. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e00653-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karimi, K.; Zamani, A. Mucor indicus: Biology and industrial application perspectives: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 466–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, P.M.; Bittencourt, M.L.A.; Caprara, C.C.; Freitas, M.; Almeida, R.P.C.; Silveira, D.; Fonseca, Y.M.; Filho, E.X.F.; Junior, A.P.; Magalhães, P.O. A biotechnology perspective of fungal proteases. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2015, 46, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alves, M.H.; Campos-Takaki, G.M.C.; Okada, K.; Pessoa, I.H.F.; Milanez, A.I. Detection of extracellular protease in Mucor species. Rev. Iberoam. Micol. 2005, 22, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roopesh, K.; Ramachandran, S.; Nampoothiri, K.M.; Szakacs, G.; Pandey, A. Comparison of phytase production on wheat bran and oilcakes in solid-state fermentation by Mucor racemosus. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, K.; Wolf, T.; Ochsenreiter, K.; Nagy, G.; Kaerger, K.; Shelest, E.; Papp, T. 15 Genetic and metabolic aspects of primary and secondary metabolism of the Zygomycetes. In Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 3rd ed.; Hoffmeister, D., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2016; Volume III, pp. 361–385. [Google Scholar]
- Yazdi, M.T.; Zarrini, G.; Mohit, E.; Faramarzi, M.A.; Setayesh, N.; Sedighi, N.; Mohseni, F.A. Mucor hiemalis: A new source for uricase production. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 22, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.K.F.; Faria, E.L.P.; Rivaldi, J.D.; Andrade, G.S.S.; de Oliveira, P.C.; de Castro, H.F. Performance of whole-cells lipase derived from Mucor circinelloides as a catalyst in the ethanolysis of non-edible vegetable oils under batch and continuous run conditions. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 67, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, L.R.; Millner, P.D. Some Asian fermented foods and beverages. Mycologia 1974, 66, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nout, M.J.R.; Aidoo, K.E. Asian fungal fermented food. In Industrial Applications; Hofrichter, M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 29–58. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.J.; Hyde, K.D.; Zhao, R.L.; Hongsanan, S.; Abdel-Aziz, F.A.; Abdel-Wahab, M.A.; Alvarado, P.; Alves-Silva, G.; Ammirati, J.F.; Ariyawansa, H.A.; et al. Fungal diversity notes 253–366: Taxonomic and phylogenetic contributions to fungal taxa. Fungal Divers. 2016, 78, 1–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, C.L.F.; Lima, D.X.; De Souza, C.A.; De Oliveira, R.J.; Cavalcanti, I.B.; Gurgel, L.; Santiago, A.L.C.M.A. Description of Mucor pernambucoensis (Mucorales, mucoromycota), a new species isolated from the Brazilian upland rainforest. Phytotaxa 2018, 350, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.T.; Voigt, K.; Santiago, A.L.S.; Kirk, P.M.; Lee, H.B. Discovery of novel Backusella (Backusellaceae, Mucorales) isolated from invertebrates and toads in Cheongyang, Korea. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols; Innis, M.A., Gelfand, D.H., Sninsky, J.J., White, T.J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1990; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Vilgalys, R.; Hester, M. Rapid genetic identification and mapping of enzymatically amplified ribosomal DNA from several species of Cryptococus. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 4238–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sayers, E.W.; Cavanaugh, M.; Clark, K.; Pruitt, K.D.; Schoch, C.L.; Stephen, T.; Sherry, S.T.; Karsch-Mizrachi, I. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D161–D164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Rozewicki, J.; Yamada, K.D. MAFFT online service: Multiple sequence alignment, interactive sequence choice and visualization. Brief. Bioinform. 2017, 20, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capella-Gutiérrez, S.; Silla-Martínez, J.M.; Gabaldón, T. TrimAl: A tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1972–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guindon, S.; Gascuel, O. A simple, fast and accurate method to estimate large phylogenies by maximum-likelihood. Syst. Biol. 2003, 52, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Treschew. Mucor odoratus. Bot. Tidskr. 1941, 45, 148. [Google Scholar]
- Pidoplichko, N.M.; Mil’ko, A.A. Atlas Mukoral’nykh Gribov [Atlas of the Mucorales]. Izdat; Naukova Dumka: Kiev, Ukraine, 1971; p. 115. [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin, R.K.; Mehrotra, B.S. Obligate azygospore formation in two species of Mucor (Mucorales). Aliso 1963, 5, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schipper, M.A.A.A. On certain species of Mucor with a key to all accepted species. Stud. Mycol. 1978, 17, l–53. [Google Scholar]
- Baijal, U.; Mehrotra, B.S. Species of Mucor from India-II. Sydowia 1965, 19, 204–212. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, C.; Liu, W.; Cheng, H.; Hui, F. Mucor chuxiongensis sp. nov., a novel fungal species isolated from rotten wood. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 1881–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadson, M.M.G.; Philippov, G. Une nouvelle Mucorinée. Mucor guilliermondii nov. sp. et ses forms-levures. Rev. Gén. Bot. 1925, 37, 450–463. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.-Q.; Zheng, R.-Y. A new species of Mucor with giant spores. Acta. Mycol. Sin. Suppl. I. 1986, 1, 57–60. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, P.J.; Clark-Walker, G.D.; Stewart, P.R. Effects of oxygen and glucose on energy metabolism and dimorphism of Mucor genevensis grown in continuous culture: Reversibility of yeast-mycelium conversion. J. Bacteriol. 1974, 119, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orlowski, M. Mucor dimorphism. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1991, 55, 234–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifia, M.; Karimi, K.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Production of ethanol by filamentous and yeast-like forms of Mucor indicus from fructose, glucose, sucrose, and molasses. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 35, 1253–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifyazs, S.; Karimi, K. Effects of fermentation conditions on valuable products of ethanolic fungus Mucor indicus. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 30, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Taxon Name | Strain Number | GenBank Accession Number | Host/Substrate | Country | Citation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITS | LSU | |||||
| Blakeslea trispora | CBS 564.91 | - | JN206515 | soil | China | [10] |
| Choanephora cucurbitarum | CBS 674.93 | - | JN206514 | n.a | China | [10] |
| C. infundibulifera | CBS 153.51 | - | JN206513 | n.a | n.a | [10] |
| Ellisomyces anomalus | CBS 243.57 (T) | JN205992 | JN206423 | dung of lizard | USA | [10] |
| Gilbertella persicaria | CBS 532.77 | - | JN206517 | dung of mouse | India | [10] |
| G. persicaria | CBS 190.32 | - | HM849691 | Prunus persica; fruit | USA | [10] |
| Hyphomucor assamensis | CBS 254.85 | JN206212 | JN206440 | Burmannia | Malaysia | [10] |
| H. assamensis | CBS 415.77 (T) | JN206211 | JN206439 | n.a | India | [10] |
| Mucor amphibiorum | CBS 763.74 (T) | HM999957 | HM849688 | amphibian | Germany | [10] |
| M. amphibiorum | CBS 185.77 | JN206170 | - | diseased Dendrobates sp. | Central America | [10] |
| M. azygosporus | CBS 292.63 (T) | JN206187 | JN206497 | soil | USA | [10] |
| M. ardhlaengiktus | CBS 210.80 (ET) | JN206172 | JN206504 | garden soil | India | [10] |
| M. ardhlaengiktus | CBS 650.78 | JN206174 | JN206499 | dung of lizard | India | [10] |
| M. caatinguensis | URM 7223 | KT960375 KT960376 KT960377 | KT960369 KT960370 KT960371 | soil | Brazil | [26] |
| M. chiangraiensis | MFLUCC 21-0079 (T) | MZ433253 | MZ433250 | soil | Thailand | [5] |
| M. exponens | CBS 141.20 (NT) | JN206206 | JN206441 | n.a | Germany | [10] |
| M. falcatus | CBS 251.35 (HT) | JN206250 | JN206509 | honeycomb | Germany | [10] |
| M. falcatus | CBS 252.35 | JN206249 | - | dung of rabbit | Germany | [10] |
| M. fluvii | CNUFC-MSW21-2 | MF667991 | MF667996 | freshwater | Korea | [11] |
| M. fluvii | CNUFC-MSW21-1 (T) | MF667992 | MF667995 | freshwater | Korea | [11] |
| M. fuscus | CBS 282.78 | JN206201 | JN206442 | cheese | France | [10] |
| M.grylli | CNUFC CY102 (T) | OM868230 (c1) OM868231 (c2) | OM843127 | Gryllussp. | Korea | This study |
| M.grylli | CNUFC CY103 | - | OM843128 | Gryllussp. | Korea | This study |
| M.hyangburmii | CNUFC CY22 (T) | OM868232 (c1) OM868233 (c3) | OM843129 | Gryllussp. | Korea | This study |
| M.hyangburmii | CNUFC CY23 | - | OM843130 | Gryllussp. | Korea | This study |
| M. inaequisporus | CBS 255.36 (T) | JN206177 | JN206502 | Spondias mombin; fruit | Ghana | [10] |
| M. inaequisporus | CBS 496.66 | JN206179 | JN206501 | Diospyros kaki; immature fruit | Japan | [10] |
| M. inaequisporus | CBS 351.50 | JN206178 | JN206500 | Musa sapientum; fruit | Indonesia | [10] |
| M. indicus | CBS 226.29 (ET) | HM999956 | HM849690 | n.a | Switzerland | [10] |
| M. indicus | CBS 671.79 | JN206183 | - | n.a | Indonesia | [10] |
| M. indicus | CBS 120585 | JN206180 | - | human; muscle | India | [10] |
| M.kunryangriensis | CNUFC CY223 (T) | OM868234 (c1) OM868235 (c2) OM868236 (c3) | OM843131 | Gryllussp. | Korea | This study |
| M.kunryangriensis | CNUFC CY224 | - | OM843132 | Gryllussp. | Korea | This study |
| M. lanceolatus | CBS 638.74 | JN206205 | JN206443 | cheese | France | [10] |
| M. laxorrhizus | CBS 143.85 (NT) | JN206209 | JN206444 | lake mud | UK | [10] |
| M. nederlandicus | CBS 735.70 | JN206176 | JN206503 | n.a | n.a | [10] |
| M. nederlandicus | MFLU 21-0078 | MZ433254 | MZ433251 | soil | Thailand | [5] |
| M. pernambucoensis | URM 7640 (T) | MH155323 | MH155322 | soil | Brazil | [27] |
| M. prayagensis | CBS 652.78 | JN206189 (c1) JN206190 (c3) | JN206498 | dung of shrew | India | [10] |
| M. prayagensis | CBS 816.70 (T) | JN206188 | JN206496 | n.a | India | [10] |
| M. odoratus | CBS 130.41 (T) | JN206197 | JN206495 | laboratory air | Denmark | [10] |
| M. odoratus | CBS 201.71 | JN206198 | - | dung of horse | Netherlands | [10] |
| M. odoratus | CBS 120.71 | JN206195 | - | n.a | USA | [10] |
| M. ucrainicus | CBS 674.88 | JN206192 | JN206507 | soil of litter layer | Germany | [10] |
| M. ucrainicus | CBS 221.71 (T) | JN206191 | - | dung of mouse | Ukraine | [10] |
| M. zychae | CBS 416.67 (T) | JN206199 | JN206505 | manured soil | India | [10] |
| M. variisporus | CBS 837.70 (T) | JN206175 | JN206508 | n.a | India | [10] |
| Mycotypha microspora | CBS 230.32 (T) | - | JN206510 | Citrus aurantium; peel, contaminant | Netherlands | [10] |
| Mycotypha sp. | CBS 109960 | - | JN206511 | human; pus of wound | Thailand | [10] |
| Poitrasia circinans | CBS 153.58 (T) | JN206516 | soil | Trinidad and Tobago | [10] | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, T.T.T.; Lee, H.B. Discovery of Three New Mucor Species Associated with Cricket Insects in Korea. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8060601
Nguyen TTT, Lee HB. Discovery of Three New Mucor Species Associated with Cricket Insects in Korea. Journal of Fungi. 2022; 8(6):601. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8060601
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Thuong T. T., and Hyang Burm Lee. 2022. "Discovery of Three New Mucor Species Associated with Cricket Insects in Korea" Journal of Fungi 8, no. 6: 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8060601
APA StyleNguyen, T. T. T., & Lee, H. B. (2022). Discovery of Three New Mucor Species Associated with Cricket Insects in Korea. Journal of Fungi, 8(6), 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8060601






