Stochastic Processes Derive Gut Fungi Community Assembly of Plateau Pikas (Ochotona curzoniae) along Altitudinal Gradients across Warm and Cold Seasons
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. DNA Extraction and High-Throughput Sequencing
2.3. Amplicon Sequence Processing and Analysis
2.4. Co-Occurrence Network
2.5. Null Model
2.6. Neutral Model
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
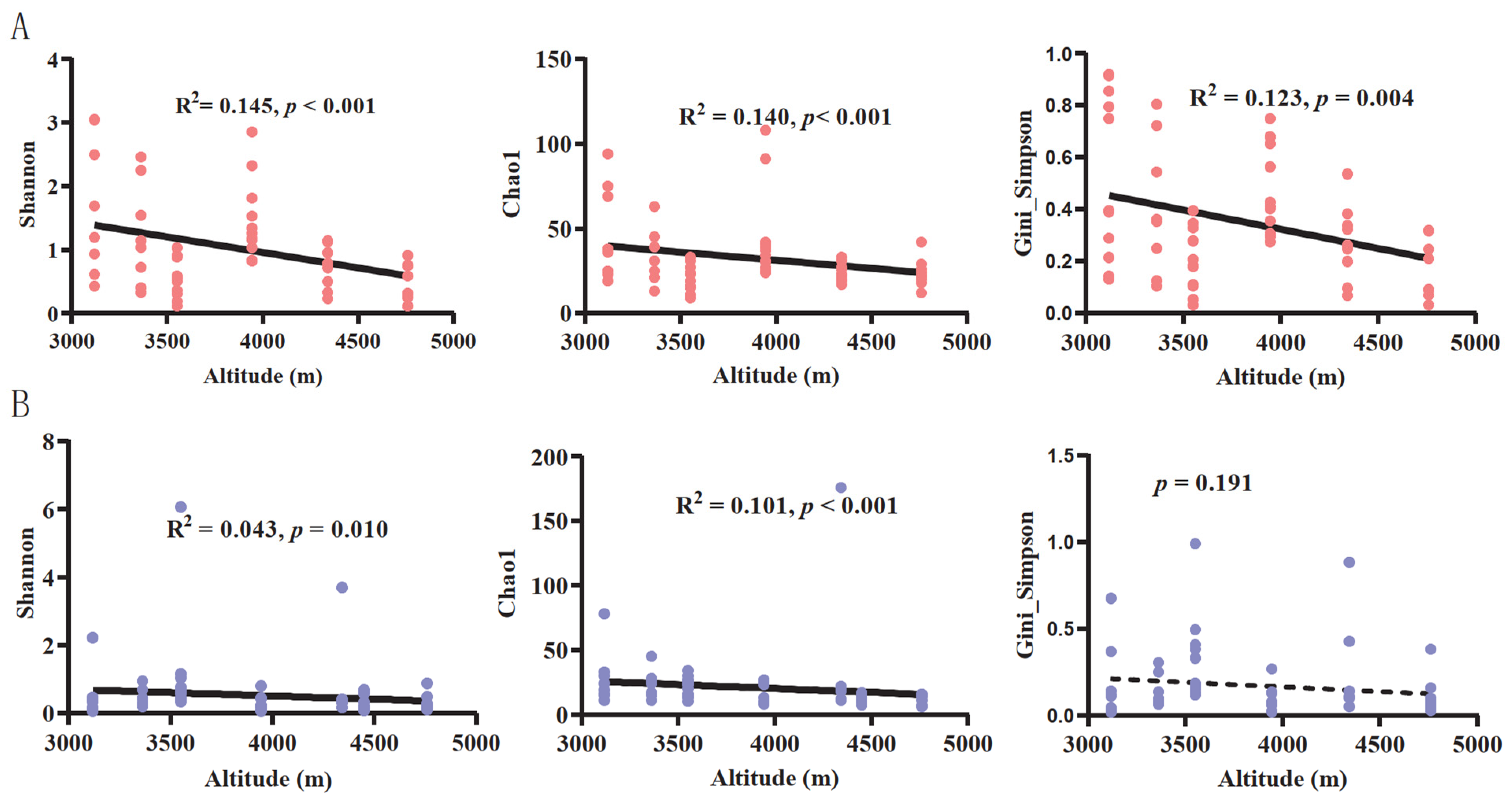
3.1. The Variation in Gut Fungal Community Composition and Alpha Diversity along Altitudinal Gradients
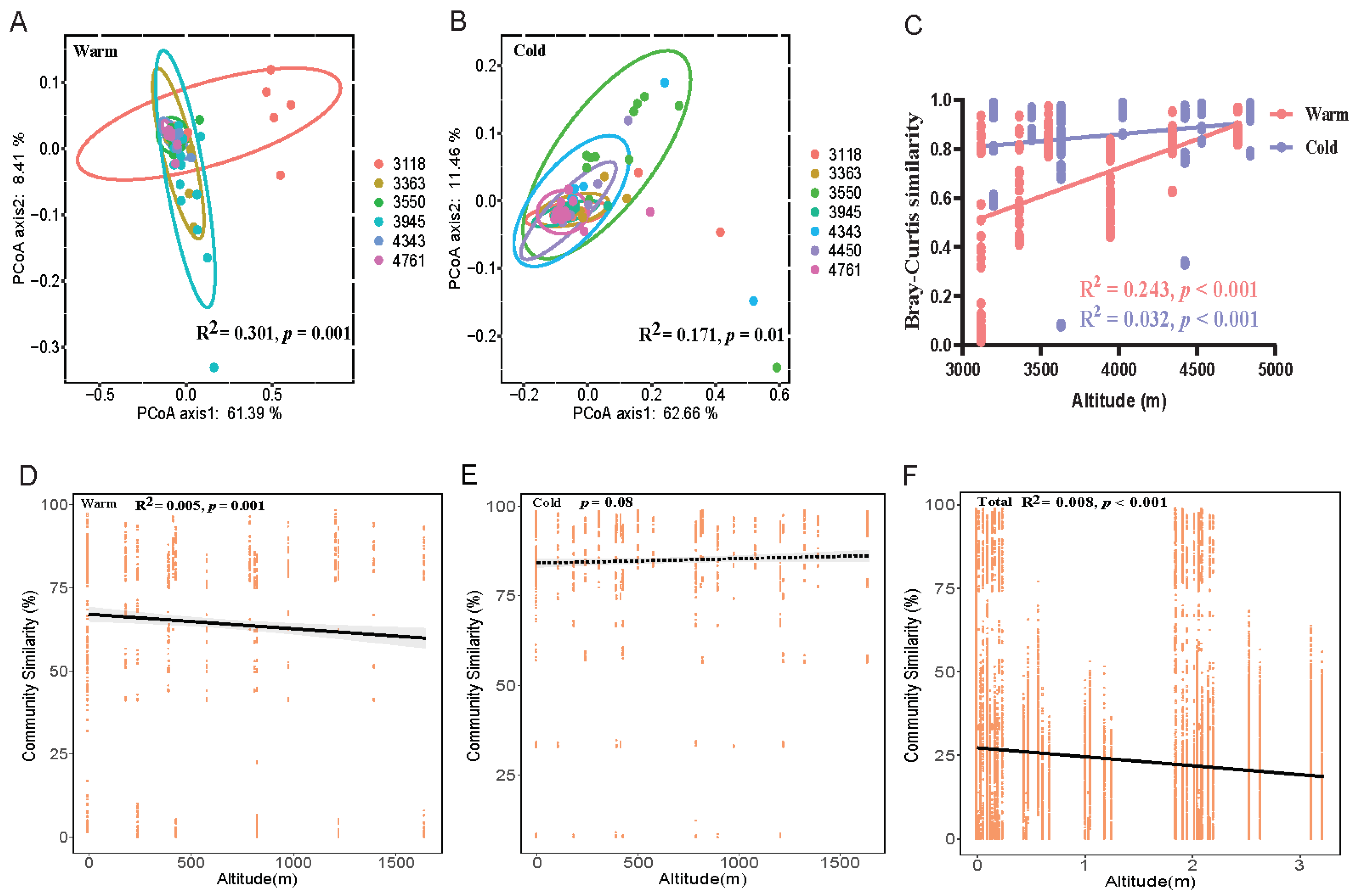
3.2. Biogeographic Analysis of Fungal Communities of Plateau Pika
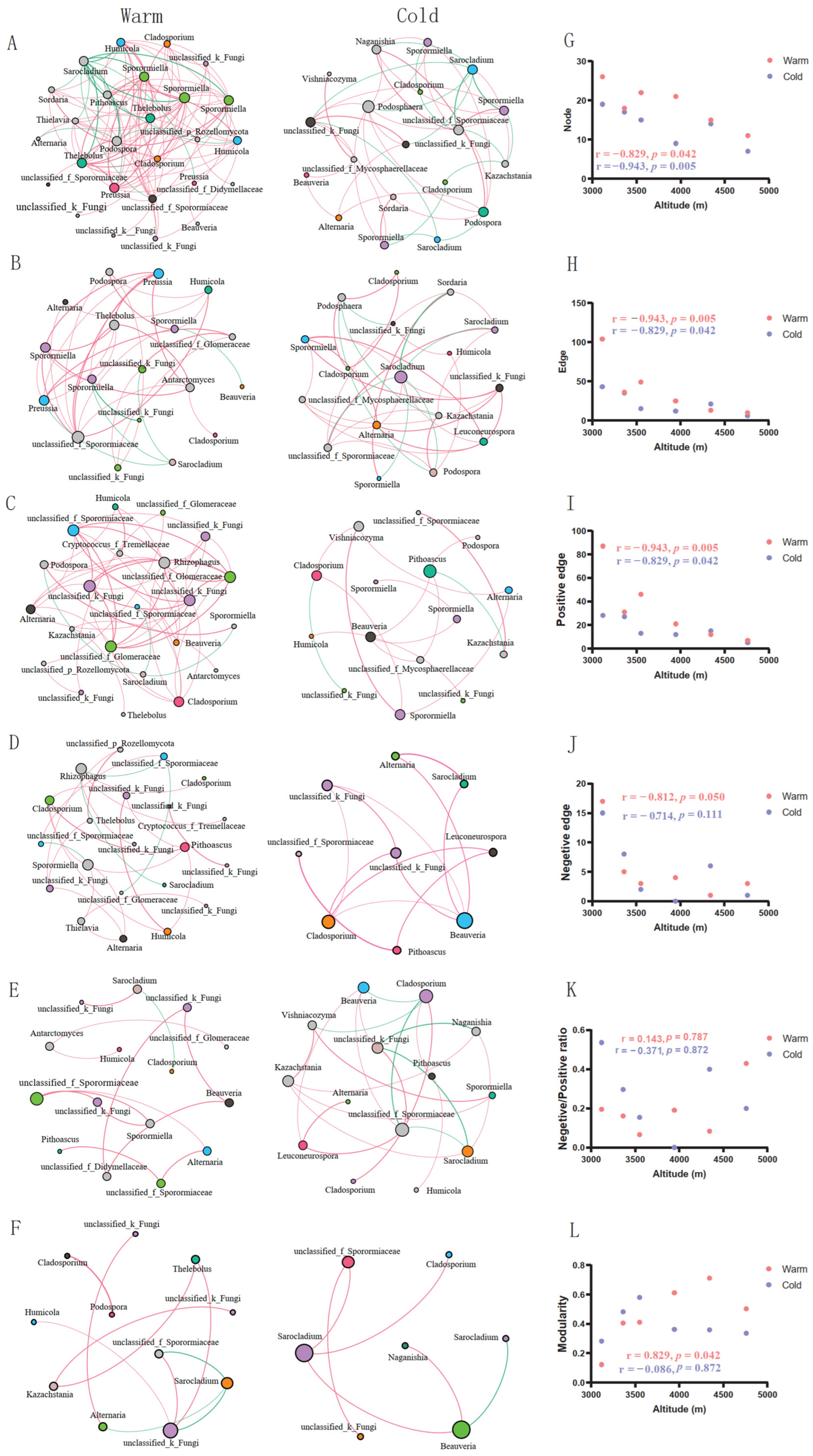
3.3. Co-Occurrence Patterns of Gut Fungal Communities along Altitudinal Gradients
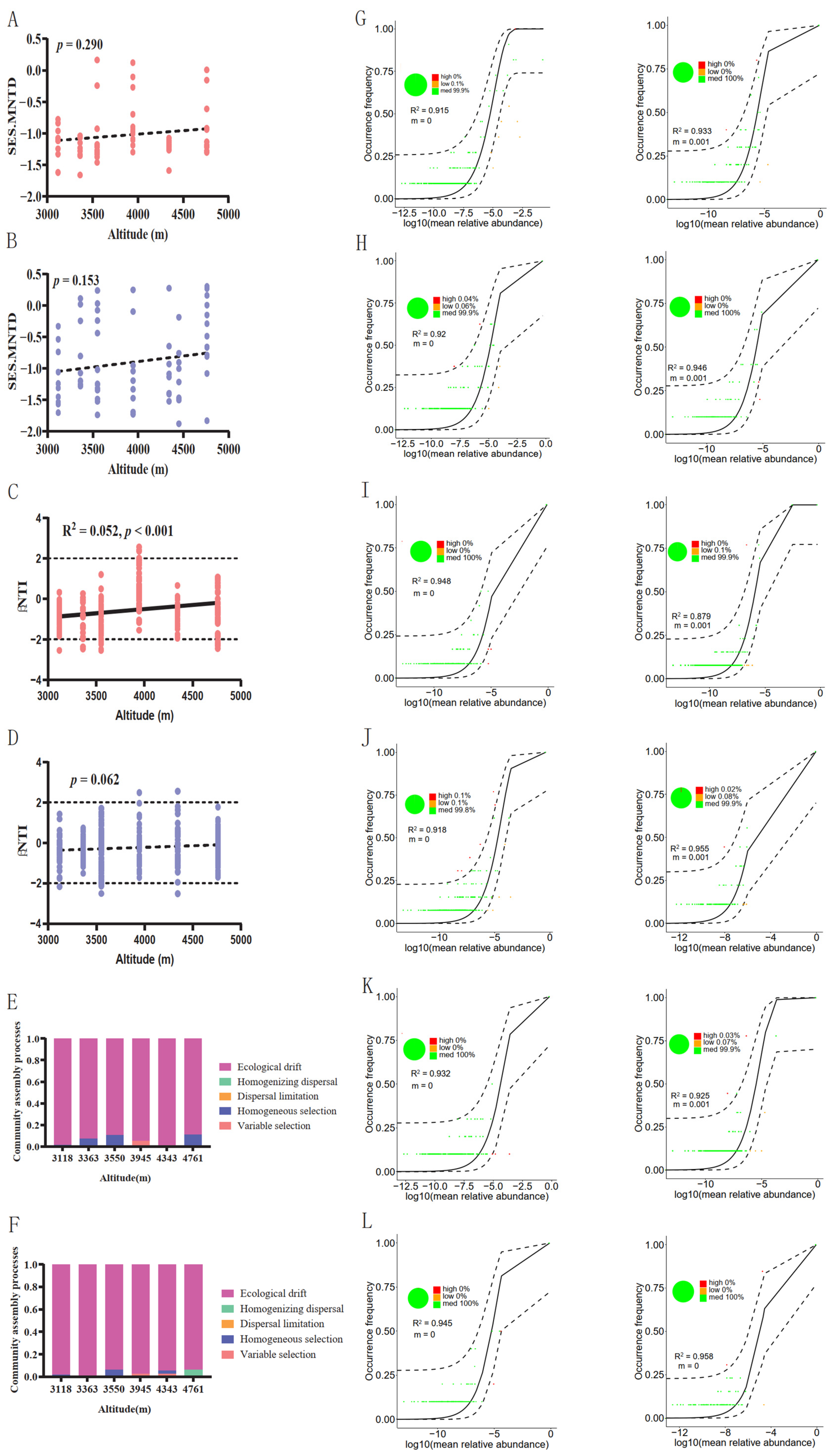
3.4. Assembly Process of Gut Fungal Communities
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qin, J.; Li, R.; Raes, J.; Arumugam, M.; Burgdorf, K.S.; Manichanh, C.; Nielsen, T.; Pons, N.; Levenez, F.; Yamada, T.; et al. A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 2010, 464, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, A.K.; Auchtung, T.A.; Wong, M.C.; Smith, D.P.; Gesell, J.R.; Ross, M.C.; Stewart, C.J.; Metcalf, G.A.; Muzny, D.M.; Gibbs, R.A.; et al. The gut mycobiome of the Human Microbiome Project healthy cohort. Microbiome 2017, 5, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderete, T.L.; Jones, R.B.; Shaffer, J.P.; Holzhausen, E.A.; Patterson, W.B.; Kazemian, E.; Chatzi, L.; Knight, R.; Plows, J.F.; Berger, P.K.; et al. Early life gut microbiota is associated with rapid infant growth in Hispanics from Southern California. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1961203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baniel, A.; Amato, K.R.; Beehner, J.C.; Bergman, T.J.; Mercer, A.; Perlman, R.F.; Petrullo, L.; Reitsema, L.; Sams, S.; Lu, A.; et al. Seasonal shifts in the gut microbiome indicate plastic responses to diet in wild geladas. Microbiome 2021, 9, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Zhang, L.; Jia, S.; Tang, X.; Fu, H.; Li, W.; Liu, C.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, Q.; Zhang, Y. Seasonal variations in the composition and functional profiles of gut microbiota reflect dietary changes in plateau pikas. Integr. Zool. 2022, 17, 379–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.; Wu, Q.; Shi, F.; Niu, J.; Zhang, T.; Degen, A.A.; Fang, Q.; Ding, L.; Shang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Seasonal dynamics of diet-gut microbiota interaction in adaptation of yaks to life at high altitude. NPJ Biofilms Microbio. 2021, 7, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Yan, L.; Jia, H.; Xiong, Y.; Ma, X.; Chu, H.; Sun, Z.; Wang, L.; Shalitanati, M.; Li, K.; et al. Gut microbial community structure and function of Przewalski’s horses varied across reintroduced sites in China. Integr. Zool. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, C.; Stojanović, O.; Colin, D.J.; Suarez-Zamorano, N.; Tarallo, V.; Veyrat-Durebex, C.; Rigo, D.; Fabbiano, S.; Stevanović, A.; Hagemann, S.; et al. Gut Microbiota Orchestrates Energy Homeostasis during Cold. Cell 2015, 163, 1360–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, L.; Li, M.; Lam, S.M.; Wang, G.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Niu, C.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; et al. Microbiota Depletion Impairs Thermogenesis of Brown Adipose Tissue and Browning of White Adipose Tissue. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 2720–2737.e2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Shi, Y.; Wang, J.; Niu, Z.; Wei, L.; Tian, H.; Yu, F.; Gao, L. The intestinal microbiota and metabolic profiles of Strauchbufo raddei underwent adaptive changes during hibernation. Integr. Zool. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Tilburg Bernardes, E.; Pettersen, V.K.; Gutierrez, M.W.; Laforest-Lapointe, I.; Jendzjowsky, N.G.; Cavin, J.B.; Vicentini, F.A.; Keenan, C.M.; Ramay, H.R.; Samara, J.; et al. Intestinal fungi are causally implicated in microbiome assembly and immune development in mice. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo, T.B.; Zhang, X.Y.; Kohl, K.D.; Wen, J.; Tian, S.J.; Wang, D.H. Coprophagy prevention alters microbiome, metabolism, neurochemistry, and cognitive behavior in a small mammal. ISME J. 2020, 14, 2625–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyte, M. Microbial endocrinology: Host-microbiota neuroendocrine interactions influencing brain and behavior. Gut Microbes 2014, 5, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heisel, T.; Montassier, E.; Johnson, A.; Al-Ghalith, G.; Lin, Y.W.; Wei, L.N.; Knights, D.; Gale, C.A. High-Fat Diet Changes Fungal Microbiomes and Interkingdom Relationships in the Murine Gut. mSphere 2017, 2, e00351-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiers, W.D.; Leonardi, I.; Iliev, I.D. From Birth and Throughout Life: Fungal Microbiota in Nutrition and Metabolic Health. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2020, 40, 323–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D. Human gut microbiome: Hopes, threats and promises. Gut 2018, 67, 1716–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Sun, L.; Wang, K.; Qiao, S.; Zhao, X.; Hu, X.; Chen, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Dai, H.; et al. The gut commensal fungus, Candida parapsilosis, promotes high fat-diet induced obesity in mice. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, C.; Dollive, S.; Grunberg, S.; Chen, J.; Li, H.; Wu, G.D.; Lewis, J.D.; Bushman, F.D. Archaea and fungi of the human gut microbiome: Correlations with diet and bacterial residents. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, M.; Fu, Y.; Zhong, H.L.; Gou, W.; Jiang, Z.; Liang, Y.; Miao, Z.; Xu, J.J.; Huynh, T.; Wahlqvist, M.L.; et al. Mapping the human gut mycobiome in middle-aged and elderly adults: Multiomics insights and implications for host metabolic health. Gut 2022, 71, 1812–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatoum, R.; Labrie, S.; Fliss, I. Antimicrobial and probiotic properties of yeasts: From fundamental to novel applications. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokol, H.; Leducq, V.; Aschard, H.; Pham, H.P.; Jegou, S.; Landman, C.; Cohen, D.; Liguori, G.; Bourrier, A.; Nion-Larmurier, I.; et al. Fungal microbiota dysbiosis in IBD. Gut 2017, 66, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pareek, S.; Kurakawa, T.; Das, B.; Motooka, D.; Nakaya, S.; Rongsen-Chandola, T.; Goyal, N.; Kayama, H.; Dodd, D.; Okumura, R.; et al. Comparison of Japanese and Indian intestinal microbiota shows diet-dependent interaction between bacteria and fungi. NPJ Biofilms Microbio. 2019, 5, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Z.; Xiang, X. Significant differences in intestinal fungal community of hooded cranes along the wintering periods. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 991998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahtab, N.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, F.; Wang, W. Seasonal Variations in the Gut Fungal Communities of Hooded Crane (Grus monacha) at Wintering and Stopover Sites in China. Animals 2021, 11, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrman, J.A.; Steele, J.A.; Hewson, I.; Schwalbach, M.S.; Brown, M.V.; Green, J.L.; Brown, J.H. A latitudinal diversity gradient in planktonic marine bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 7774–7778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhou, R.; Zhu, J.; Huang, X.; Qu, J. Environmental filtering increases with elevation for the assembly of gut microbiota in wild pikas. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 976–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.A.; Martins, F.M.; Nachman, M.W. Altitudinal variation of the gut microbiota in wild house mice. Mol. Ecol. 2019, 28, 2378–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.A.; Martins, F.M.; Phifer-Rixey, M.; Nachman, M.W. The gut microbiota and Bergmann’s rule in wild house mice. Mol. Ecol. 2020, 29, 2300–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, T.J.; Whittaker, R.J. Neutral theory and the species abundance distribution: Recent developments and prospects for unifying niche and neutral perspectives. Ecol. Evol. 2014, 4, 2263–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locey, K.J.; Lennon, J.T. Scaling laws predict global microbial diversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 5970–5975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, Q.; Deng, Y.; Yan, Q.; Shen, L.; Lin, L.; He, Z.; Wu, L.; Van Nostrand, J.D.; Buzzard, V.; Michaletz, S.T.; et al. Biogeographic patterns of soil diazotrophic communities across six forests in North America. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 2937–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeller, A.H.; Suzuki, T.A.; Lin, D.; Lacey, E.A.; Wasser, S.K.; Nachman, M.W. Dispersal limitation promotes the diversification of the mammalian gut microbiota. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 13768–13773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smits, S.A.; Leach, J.; Sonnenburg, E.D.; Gonzalez, C.G.; Lichtman, J.S.; Reid, G.; Knight, R.; Manjurano, A.; Changalucha, J.; Elias, J.E.; et al. Seasonal cycling in the gut microbiome of the Hadza hunter-gatherers of Tanzania. Science 2017, 357, 802–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, E.P.; Adler, P.B.; Lauenroth, W.K.; Gill, R.A.; Greenberg, D.; Kaufman, D.M.; Rassweiler, A.; Rusak, J.A.; Smith, M.D.; Steinbeck, J.R. A comparison of the species-time relationship across ecosystems and taxonomic groups. Oikos 2006, 112, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.P.; Wang, P.; Chen, Y.; Wilson, M.C.; Yang, X.; Ma, C.; Lu, J.; Chen, X.Y.; Wu, J.; Shu, W.S.; et al. Island biogeography of soil bacteria and fungi: Similar patterns, but different mechanisms. ISME J. 2020, 14, 1886–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, K.; Yang, Q.; Stewart, S.; Whitmore, M.A.; Zhang, G. Biogeography, succession, and origin of the chicken intestinal mycobiome. Microbiome 2022, 10, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.A.; Worobey, M. Geographical variation of human gut microbial composition. Biol. Lett. 2014, 10, 20131037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mims, T.S.; Abdallah, Q.A.; Stewart, J.D.; Watts, S.P.; White, C.T.; Rousselle, T.V.; Gosain, A.; Bajwa, A.; Han, J.C.; Willis, K.A.; et al. The gut mycobiome of healthy mice is shaped by the environment and correlates with metabolic outcomes in response to diet. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, M.L.; Sokol, H. The gut mycobiota: Insights into analysis, environmental interactions and role in gastrointestinal diseases. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, J.M.; Myers, J.A. Disentangling the importance of ecological niches from stochastic processes across scales. Philos. Trans. R Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2011, 366, 2351–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofiteru, I.D.; Lunn, M.; Curtis, T.P.; Wells, G.F.; Criddle, C.S.; Francis, C.A.; Sloan, W.T. Combined niche and neutral effects in a microbial wastewater treatment community. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 15345–15350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegen, J.C.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Wilkins, M.J.; Konopka, A.E.; Nelson, W.C.; Arntzen, E.V.; Chrisler, W.B.; Chu, R.K.; Danczak, R.E.; Fansler, S.J.; et al. Groundwater-surface water mixing shifts ecological assembly processes and stimulates organic carbon turnover. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellend, M. Conceptual synthesis in community ecology. Q. Rev. Biol. 2010, 85, 183–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Chen, X.; Kennedy, D.W.; Murray, C.J.; Rockhold, M.L.; Konopka, A. Quantifying community assembly processes and identifying features that impose them. ISME J. 2013, 7, 2069–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macarthur, R.H.; Wilson, E.O. The Theory of Island Biogeography; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, J. The Unified Neutral Theory of Biodiversity and Biogeography: By Stephen P. Hubbell, Monographs in Population Biology 32, Princeton University Press (2001), 375 pp.; ISBN 0-691-02128-7. Ecol. Econ. 2002, 32, 497–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouquet, N.; Loreau, M. Community patterns in source-sink metacommunities. Am. Nat. 2003, 162, 544–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leibold, M.A.; Holyoak, M.; Mouquet, N.; Amarasekare, P.; Chase, J.M.; Hoopes, M.F.; Holt, R.D.; Shurin, J.B.; Law, R.; Tilman, D. The Metacommunity Concept: A Framework for Multi-Scale Community Ecology. Ecol. Lett. 2004, 7, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chave, J. Neutral theory and community ecology. Ecol. Lett. 2004, 7, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speakman, J.R.; Chi, Q.; Ołdakowski, Ł.; Fu, H.; Fletcher, Q.E.; Hambly, C.; Togo, J.; Liu, X.; Piertney, S.B.; Wang, X.; et al. Surviving winter on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau: Pikas suppress energy demands and exploit yak feces to survive winter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2100707118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Tian, H.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, H.; Li, W.; Sang, D.; Lin, K.; Cui, Y.; Liao, M.; Xu, Z.; et al. A highland-adaptation mutation of the Epas1 protein increases its stability and disrupts the circadian clock in the plateau pika. Cell Rep. 2022, 39, 110816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Qu, J.; Li, K.; Li, W.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Y. Genetic diversity and sex-bias dispersal of plateau pika in Tibetan plateau. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 7708–7718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, J.P.; Zhang, X.; Shi, K.; Riordan, P. The pikas of China: A review of current research priorities and challenges for conservation. Integr. Zool. 2023, 18, 110–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Qu, J.; Li, T.; Wirth, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, X. Diet simplification selects for high gut microbial diversity and strong fermenting ability in high-altitude pikas. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 6739–6751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, H.; Zhang, L.; Fan, C.; Liu, C.; Li, W.; Cheng, Q.; Zhao, X.; Jia, S.; Zhang, Y. Environment and host species identity shape gut microbiota diversity in sympatric herbivorous mammals. Microb. Biotechnol. 2021, 14, 1300–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Su, J.; Li, H.; Xiong, J.; Fu, K.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, X.; Shi, Z.; Miao, X.; et al. Altitude-dependent metabolite biomarkers reveal the mechanism of plateau pika adaptation to high altitudes. Integr. Zool. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, C.; Zhang, L.; Fu, H.; Liu, C.; Li, W.; Cheng, Q.; Zhang, H.; Jia, S.; Zhang, Y. Enterotypes of the Gut Microbial Community and Their Response to Plant Secondary Compounds in Plateau Pikas. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Fan, C.; Zhang, L.; Tang, X.; Fu, H.; Liu, C.; Jia, S.; Zhang, Y. The plant secondary compound swainsonine reshapes gut microbiota in plateau pikas (Ochotona curzoniae). Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 6419–6433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zuo, T.; Cheung, C.P.; Gu, W.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, F.; Chen, N.; Zhan, H.; Yeoh, Y.K.; Niu, J.; et al. Population-Level Configurations of Gut Mycobiome Across 6 Ethnicities in Urban and Rural China. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 272–286.e211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tsai, T.; Deng, F.; Wei, X.; Chai, J.; Knapp, J.; Apple, J.; Maxwell, C.V.; Lee, J.A.; Li, Y.; et al. Longitudinal investigation of the swine gut microbiome from birth to market reveals stage and growth performance associated bacteria. Microbiome 2019, 7, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, D.; Ke, W.; Liang, D.; Hu, X.; Chen, F. Resveratrol-induced gut microbiota reduces obesity in high-fat diet-fed mice. Int. J. Obes. 2020, 44, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.; Konopka, A.E.; Fredrickson, J.K. Stochastic and deterministic assembly processes in subsurface microbial communities. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1653–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Konopka, A.E. Estimating and mapping ecological processes influencing microbial community assembly. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, W.T.; Lunn, M.; Woodcock, S.; Head, I.M.; Nee, S.; Curtis, T.P. Quantifying the roles of immigration and chance in shaping prokaryote community structure. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksanen, J.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; O’Hara, B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; Henry, M.; Stevens, H.; Wagner, H. Vegan: Community Ecology Package, R Package, Version 1.15-1. 2009. Available online: http://vegan.r-forge.r-project.org/(accessed on 4 January 2013).
- Pérez-Cantero, A.; Guarro, J. Sarocladium and Acremonium infections: New faces of an old opportunistic fungus. Mycoses 2020, 63, 1203–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarayre, C.; Bauwens, J.; Brasseur, C.; Mattéotti, C.; Millet, C.; Guiot, P.A.; Destain, J.; Vandenbol, M.; Portetelle, D.; De Pauw, E.; et al. Isolation and cultivation of xylanolytic and cellulolytic Sarocladium kiliense and Trichoderma virens from the gut of the termite Reticulitermes santonensis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 4369–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Mehmood, K.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, X.; Shahzad, M.; Dong, X.; Li, J. Characterization of fungus microbial diversity in healthy and diarrheal yaks in Gannan region of Tibet Autonomous Prefecture. Acta Trop. 2018, 182, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zeng, T.; Deligios, M.; Milanesi, L.; Langille, M.G.I.; Zinellu, A.; Rubino, S.; Carru, C.; Kelvin, D.J. Age-Related Variation of Bacterial and Fungal Communities in Different Body Habitats across the Young, Elderly, and Centenarians in Sardinia. mSphere 2020, 5, e00558-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geel, B.V.; Guthrie, R.D.; Altmann, J.G.; Broekens, P.; Bull, I.D.; Gill, F.L.; Jansen, B.; Nieman, A.M.; Gravendeel, B. Mycological evidence of coprophagy from the feces of an Alaskan Late Glacial mammoth. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2011, 30, 2289–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couturier, M.; Tangthirasunun, N.; Ning, X.; Brun, S.; Gautier, V.; Bennati-Granier, C.; Silar, P.; Berrin, J.G. Plant biomass degrading ability of the coprophilic ascomycete fungus Podospora anserina. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 976–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarrocco, S. Dung-inhabiting fungi: A potential reservoir of novel secondary metabolites for the control of plant pathogens. Pest Manag. Sci. 2016, 72, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poidevin, L.; Berrin, J.G.; Bennati-Granier, C.; Levasseur, A.; Herpoël-Gimbert, I.; Chevret, D.; Coutinho, P.M.; Henrissat, B.; Heiss-Blanquet, S.; Record, E. Comparative analyses of Podospora anserina secretomes reveal a large array of lignocellulose-active enzymes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 7457–7469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippucci, S.; Tasselli, G.; Scardua, A.; Di Mauro, S.; Cramarossa, M.R.; Perini, D.; Turchetti, B.; Onofri, A.; Forti, L.; Buzzini, P. Study of Holtermanniella wattica, Leucosporidium creatinivorum, Naganishia adeliensis, Solicoccozyma aeria, and Solicoccozyma terricola for their lipogenic aptitude from different carbon sources. Biotechnol. Biofuels. 2016, 9, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasselli, G.; Filippucci, S.; Borsella, E.; D’Antonio, S.; Gelosia, M.; Cavalaglio, G.; Turchetti, B.; Sannino, C.; Onofri, A.; Mastrolitti, S.; et al. Yeast lipids from cardoon stalks, stranded driftwood and olive tree pruning residues as possible extra sources of oils for producing biofuels and biochemicals. Biotechnol. Biofuels. 2018, 11, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, K.; Wu, K.; Zheng, T.; Yue, J.; Wang, W.; Luo, R.; You, L.; He, X.; Li, J.; Hong, Z.; et al. Comparative Study of Oral Bacteria and Fungi Microbiota in Tibetan and Chinese Han Living at Different Altitude. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2021, 254, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starke, R.; Mondéjar, R.L.; Human, Z.R.; Navrátilová, D.; Štursová, M.; Větrovský, T.; Olson, H.M.; Orton, D.J.; Callister, S.J.; Lipton, M.S.; et al. Niche differentiation of bacteria and fungi in carbon and nitrogen cycling of different habitats in a temperate coniferous forest: A metaproteomic approach. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 155, 108170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.; Lu, Y. Abundant fungi adapt to broader environmental gradients than rare fungi in agricultural fields. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 4506–4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yu, Z.; Wang, B.; Ndayisenga, F. Gut region induces gastrointestinal microbiota community shift in Ujimqin sheep (Ovis aries): From a multi-domain perspective. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 7603–7616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, J.; Moora, M.; Semchenko, M.; Adenan, S.B.; Ahmed, T.; Akhmetzhanova, A.A.; Alatalo, J.M.; Al-Quraishy, S.; Andriyanova, E.; Anslan, S.; et al. Temperature and pH define the realised niche space of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. New Phytol. 2021, 231, 763–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burr, R.; Espenshade, P.J. Oxygen-responsive transcriptional regulation of lipid homeostasis in fungi: Implications for anti-fungal drug development. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 81, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Ci, H.; Zhang, T.; Su, J. Conformity to Bergmann’s Rule in the Plateau Pika (Ochotona curzoniae Hodgson, 1857) on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Acta Zool. Acad. Sci. Hung. 2008, 54, 411–418. [Google Scholar]
- Abbasi, F.; Samaei, M.R. The effect of temperature on airborne filamentous fungi in the indoor and outdoor space of a hospital. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 16868–16876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.D.; Zhao, L.; He, F.Q.; Chen, X.; Huo, L.L.; Zhao, X.Q.; Xu, S.X.; Li, Q. Analysis of nutritional components of common edible forages from different area of Sanjiangyuan alpine grassland. Gras. Turf 2021, 41, 134–142. [Google Scholar]
- Lavrinienko, A.; Scholier, T.; Bates, S.T.; Miller, A.N.; Watts, P.C. Defining gut mycobiota for wild animals: A need for caution in assigning authentic resident fungal taxa. Anim. Microbio. 2021, 3, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.; Wang, F.; Zhang, K.; Chen, Y. Diversity and distribution of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi along altitudinal gradients in Mount Taibai of the Qinling Mountains. Can. J. Microbiol. 2014, 60, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, S.; Feng, B.; Jian, S.P.; Wang, G.S.; Ge, Z.W.; Yang, Z.L. Elevation Matters More than Season in Shaping the Heterogeneity of Soil and Root Associated Ectomycorrhizal Fungal Community. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0195021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szóstak, N.; Handschuh, L.; Samelak-Czajka, A.; Tomela, K.; Schmidt, M.; Pruss, Ł.; Milanowska-Zabel, K.; Kozlowski, P.; Philips, A. Host Factors Associated with Gut Mycobiome Structure. mSystems 2023, 8, e0098622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.X.; Huo, Q.B.; Wen, T.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhao, M.Y.; Du, Y.Z. Mechanisms of fungal community assembly in wild stoneflies moderated by host characteristics and local environment. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2022, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, M.M.; Guo, X.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J. Climate warming enhances microbial network complexity and stability. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2021, 11, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, D.J.; David, A.S.; Menges, E.S.; Searcy, C.A.; Afkhami, M.E. Environmental stress destabilizes microbial networks. ISME J. 2021, 15, 1722–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Xue, C.; Tang, Q.; Li, R.W. Microbial Co-Occurrence Patterns and Keystone Species in the Gut Microbial Community of Mice in Response to Stress and Chondroitin Sulfate Disaccharide. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugas, L.R.; Bernabé, B.P.; Priyadarshini, M.; Fei, N.; Park, S.J.; Brown, L.; Plange-Rhule, J.; Nelson, D.; Toh, E.C.; Gao, X.; et al. Decreased microbial co-occurrence network stability and SCFA receptor level correlates with obesity in African-origin women. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Zhang, L.; Fan, C.; Wang, L.; Fu, H.; Ren, S.; Shen, W.; Jia, S.; Wu, G.; Zhang, Y. Dietary Fiber Influences Bacterial Community Assembly Processes in the Gut Microbiota of Durco × Bamei Crossbred Pig. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 688554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesson, P. Mechanisms of Maintenance of Species Diversity. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2000, 31, 343–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ning, D. Stochastic Community Assembly: Does It Matter in Microbial Ecology? Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2017, 81, e00002-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Q.; Li, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, J.; He, Z.; Van Nostrand, J.D.; Kempher, M.L.; Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Liao, L.; et al. Environmental filtering decreases with fish development for the assembly of gut microbiota. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 4739–4754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, X.; Zhang, L.; Ren, S.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, K.; Zhang, Y. Stochastic Processes Derive Gut Fungi Community Assembly of Plateau Pikas (Ochotona curzoniae) along Altitudinal Gradients across Warm and Cold Seasons. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 1032. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9101032
Tang X, Zhang L, Ren S, Zhao Y, Liu K, Zhang Y. Stochastic Processes Derive Gut Fungi Community Assembly of Plateau Pikas (Ochotona curzoniae) along Altitudinal Gradients across Warm and Cold Seasons. Journal of Fungi. 2023; 9(10):1032. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9101032
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Xianjiang, Liangzhi Zhang, Shien Ren, Yaqi Zhao, Kai Liu, and Yanming Zhang. 2023. "Stochastic Processes Derive Gut Fungi Community Assembly of Plateau Pikas (Ochotona curzoniae) along Altitudinal Gradients across Warm and Cold Seasons" Journal of Fungi 9, no. 10: 1032. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9101032
APA StyleTang, X., Zhang, L., Ren, S., Zhao, Y., Liu, K., & Zhang, Y. (2023). Stochastic Processes Derive Gut Fungi Community Assembly of Plateau Pikas (Ochotona curzoniae) along Altitudinal Gradients across Warm and Cold Seasons. Journal of Fungi, 9(10), 1032. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9101032





