New Immunological Markers in Chromoblastomycosis—The Importance of PD-1 and PD-L1 Molecules in Human Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Dilutions
2.2. Patients, Skin Samples, and Ethical Aspects
2.3. Evaluation of the In Situ Inflammatory Response
2.4. Immunostaining for Cytokines, iNOS Enzyme, CD4, CD8 and Immunological Factors Related to Cell Exhaustion
2.5. Quantitative Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Inflammatory Infiltrate and Muriform Cells
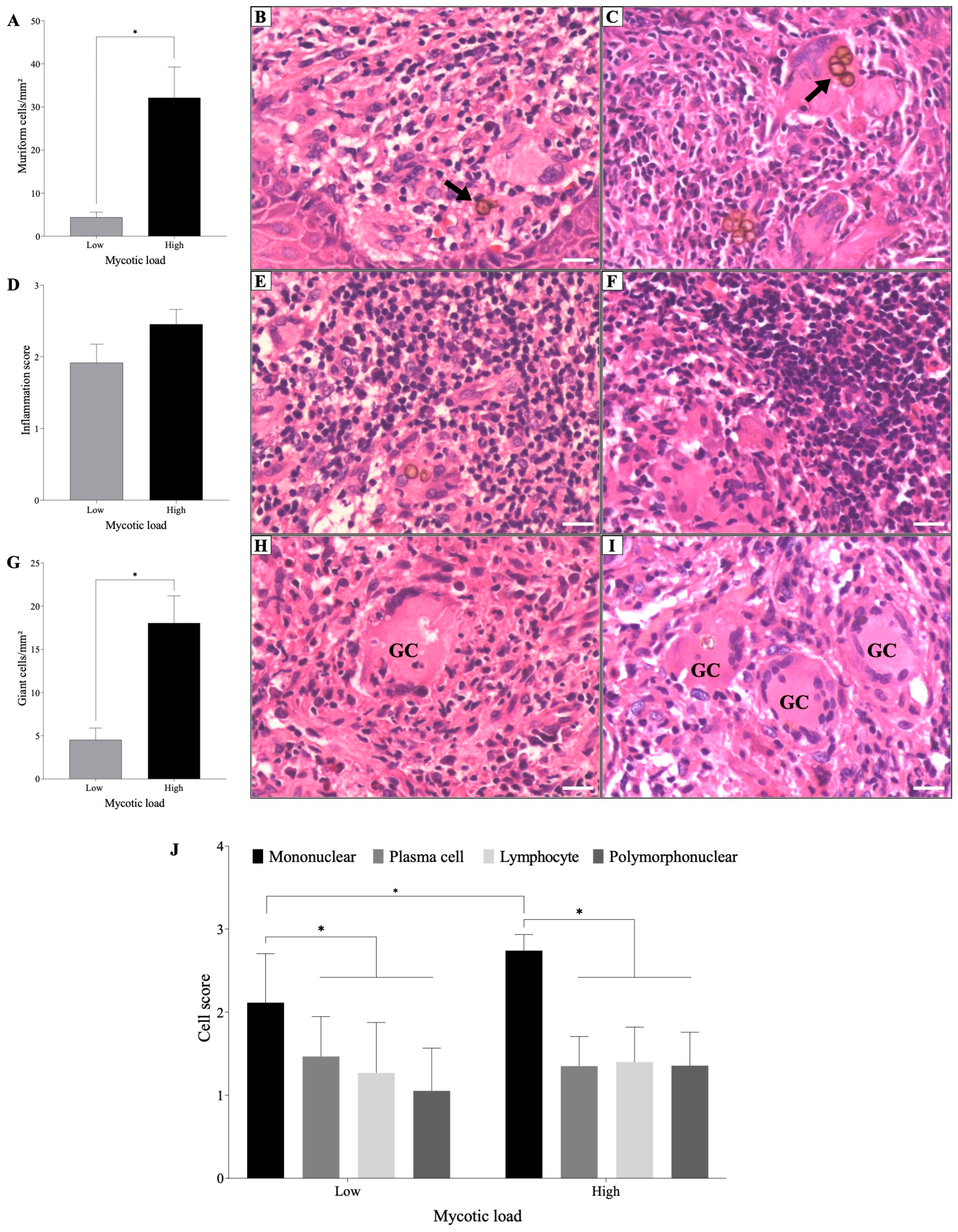
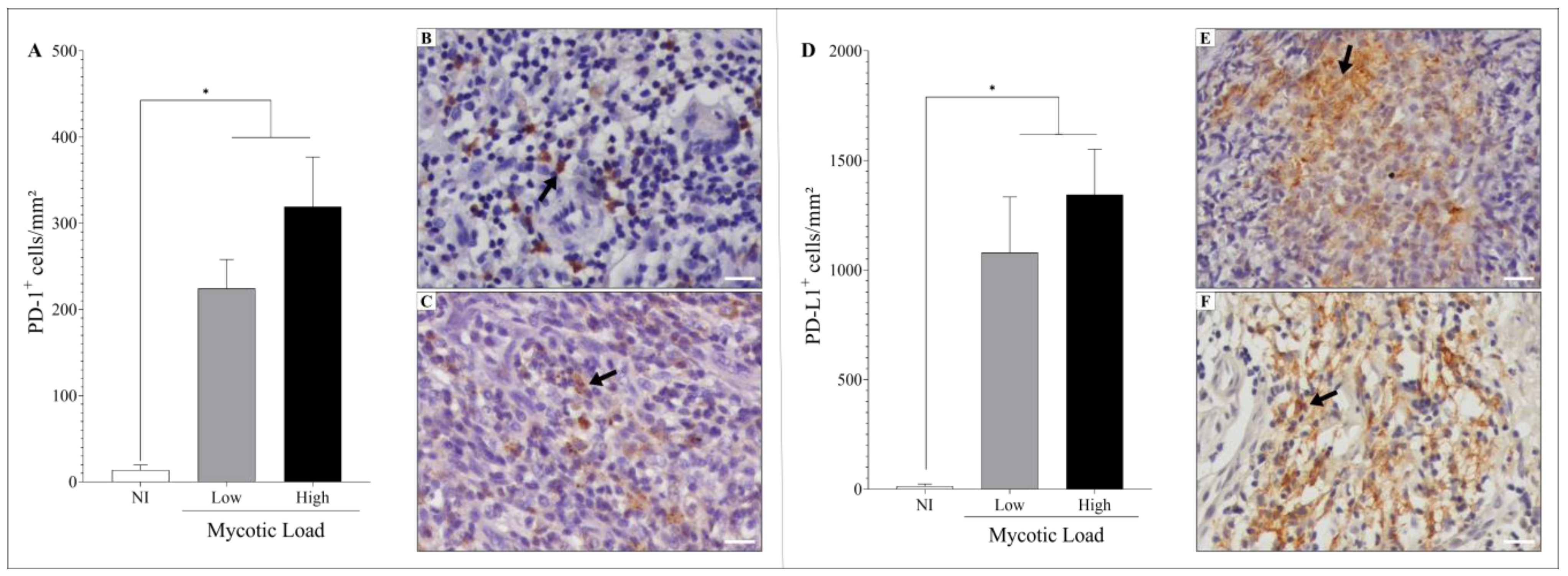
3.2. Evaluation of the Cellular Immune Response (In Situ)
3.3. Immunostaining of the Cell Exhaustion Markers
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Global Report on Neglected Tropical Diseases 2023; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, Y.; Lu, S.; Zhang, J. Retinoid Combined with Photodynamic Therapy against Hyperkeratotic Chromoblastomycosis: A Case Report and Literature Review. Mycoses 2021, 64, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queiroz-Telles, F.; Esterre, P.; Perez-Blanco, M.; Vitale, R.G.; Salgado, C.G.; Bonifaz, A. Chromoblastomycosis: An Overview of Clinical Manifestations, Diagnosis and Treatment. Med. Mycol. 2009, 47, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passero, L.F.D.; Cavallone, I.N.; Belda, W. Reviewing the Etiologic Agents, Microbe-Host Relationship, Immune Response, Diagnosis, and Treatment in Chromoblastomycosis. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 9742832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzyściak, P.M.; Pindycka-Piaszczyńska, M.; Piaszczyński, M. Chromoblastomycosis. Adv. Dermatol. Allergol. 2014, 5, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queiroz-Telles, F.; de C L Santos, D.W. Challenges in the Therapy of Chromoblastomycosis. Mycopathologia 2013, 175, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, A.N.; Biancalana, A.; Biancalana, F.S.C. Ocorrência de Fungos Demáceos Em Farpas de Portões de Madeira, No Municípuo de Soure, Pará. Rev. Ouricuri 2019, 9, 011–024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López Martínez, R.; Méndez Tovar, L.J. Chromoblastomycosis. Clin. Dermatol. 2007, 25, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozental, S.; Alviano, C.S.; de Souza, W. The in Vitro Susceptibility of Fonsecaea Pedrosoi to Activated Macrophages. Mycopathologia 1994, 126, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, P.; Garin, Y.; Richard-Lenoble, D. Chromoblastomycosis. Virchows Arch. A Pathol. Anat. Histol. 1982, 397, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe-J, F.; Zuluaga, A.I.; Leon, W.; Restrepo, A. Histopathology of Chromoblastomycosis. Mycopathologia 1989, 105, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa Garcia Pires d’Ávila, S.; Pagliari, C.; Seixas Duarte, M.I. The Cell-Mediated Immune Reaction in the Cutaneous Lesion of Chromoblastomycosis and Their Correlation with Different Clinical Forms of the Disease. Mycopathologia 2002, 156, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazo Fávero Gimenes, V.; Da Glória de Souza, M.; Ferreira, K.S.; Marques, S.G.; Gonçalves, A.G.; Vagner de Castro Lima Santos, D.; Pedroso e Silva, C.d.M.; Almeida, S.R. Cytokines and Lymphocyte Proliferation in Patients with Different Clinical Forms of Chromoblastomycosis. Microbes Infect. 2005, 7, 708–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viola, A.; Munari, F.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, R.; Scolaro, T.; Castegna, A. The Metabolic Signature of Macrophage Responses. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapouri-Moghaddam, A.; Mohammadian, S.; Vazini, H.; Taghadosi, M.; Esmaeili, S.; Mardani, F.; Seifi, B.; Mohammadi, A.; Afshari, J.T.; Sahebkar, A. Macrophage Plasticity, Polarization, and Function in Health and Disease. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 233, 6425–6440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauken, K.E.; Wherry, E.J. Overcoming T Cell Exhaustion in Infection and Cancer. Trends Immunol. 2015, 36, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wherry, E.J.; Kurachi, M. Molecular and Cellular Insights into T Cell Exhaustion. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 486–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, T.; Honjo, T. The PD-1–PD-L Pathway in Immunological Tolerance. Trends Immunol. 2006, 27, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wherry, E.J. T Cell Exhaustion. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Gu, J. Defects in Macrophage Reprogramming in Cancer Therapy: The Negative Impact of PD-L1/PD-1. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 690869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, G.P.; Chow, L.; Ammons, D.T.; Wheat, W.H.; Dow, S.W. Programmed Cell Death Ligand 1 (PD-L1) Signaling Regulates Macrophage Proliferation and Activation. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2018, 6, 1260–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, Z.; Muleme, H.M.; Liu, D.; Jia, P.; Okwor, I.B.; Kuriakose, S.M.; Beverley, S.M.; Uzonna, J.E. Parasite-Derived Arginase Influences Secondary Anti- Leishmania Immunity by Regulating Programmed Cell Death-1–Mediated CD4+ T Cell Exhaustion. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 3380–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, G.; Li, S.; Wu, W.; Tan, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z. PD-1 Upregulation Is Associated with HBV-Specific T Cell Dysfunction in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira Silva, K.L.; Marin Chiku, V.; Luvizotto Venturin, G.; Correa Leal, A.A.; de Almeida, B.F.; De Rezende Eugenio, F.; Dos Santos, P.S.P.; Fabrino Machado, G.; De Lima, V.M.F. PD-1 and PD-L1 Regulate Cellular Immunity in Canine Visceral Leishmaniasis. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 62, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridley, D.S.; Ridley, M.J. The Evolution of the Lesion in Cutaneous Leishmaniasis. J. Pathol. 1983, 141, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuelgaray, E.; Boccara, D.; Ly Ka So, S.; Boismal, F.; Mimoun, M.; Bagot, M.; Bensussan, A.; Bouaziz, J.-D.; Michel, L. Increased Expression of PD1 and CD39 on CD3+ CD4+ Skin T Cells in the Elderly. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 28, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belda, W.; Casolato, A.T.S.; Luppi, J.B.; Passero, L.F.D. Managing Chromoblastomycosis with Acitretin plus Imiquimod: A Case Report on the Improvement of Cutaneous Lesions and Reduction of the Treatment Time. J. Dermatol. 2021, 48, 1612–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queiroz-Telles, F.; de Hoog, S.; Santos, D.W.C.L.; Salgado, C.G.; Vicente, V.A.; Bonifaz, A.; Roilides, E.; Xi, L.; Azevedo, C.D.M.P.E.S.; da Silva, M.B.; et al. Chromoblastomycosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 30, 233–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyedmousavi, S.; Netea, M.G.; Mouton, J.W.; Melchers, W.J.G.; Verweij, P.E.; de Hoog, G.S. Black Yeasts and Their Filamentous Relatives: Principles of Pathogenesis and Host Defense. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 527–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avelar-Pires, C.; Simoes-Quaresma, J.A.; Moraes-de Macedo, G.M.; Brasil-Xavier, M.; Cardoso-de Brito, A. Revisiting the Clinical and Histopathological Aspects of Patients with Chromoblastomycosis from the Brazilian Amazon Region. Arch. Med. Res. 2013, 44, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Tong, Z.; Li, R.; Chen, S.C.-A.; Liu, W.; Liu, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Duan, Y.; Li, D.; et al. Transformation of Fonsecaea Pedrosoi into Sclerotic Cells Links to the Refractoriness of Experimental Chromoblastomycosis in BALB/c Mice via a Mechanism Involving a Chitin-Induced Impairment of IFN-γ Production. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.M. Multinucleated Giant Cells. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2000, 7, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murch, A.R.; Grounds, M.D.; Marshall, C.A.; Papadimitriou, J.M. Direct Evidence That Inflammatory Multinucleate Giant Cells Form by Fusion. J. Pathol. 1982, 137, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Z.; Yang, X.; Yu, J.; Zhang, J.; Ran, Y. Chromoblastomycosis Caused by Fonsecaea Nubica: First Report in Northern China and Literature Review. Mycopathologia 2019, 184, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.-Y.; Yang, Y.-P.; Sheng, P.; Li, W.; Huang, W.-M.; Fan, Y.-M. Cutaneous Chromoblastomycosis Caused by Veronaea Botryosa in a Patient with Pemphigus Vulgaris and Review of Published Reports. Mycopathologia 2015, 180, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logan, C.; Singh, M.; Fox, N.; Brown, G.; Krishna, S.; Gordon, K.; Macallan, D.; Bicanic, T. Chromoblastomycosis Treated with Posaconazole and Adjunctive Imiquimod: Lending Innate Immunity a Helping Hand. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2023, 10, ofad124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhar, S.; Gupta, D.; Malakar, R.; Dhar, S. A Rare Case of Chromoblastomycosis Presenting as a Primary Ulcer. Indian J. Dermatol. 2022, 67, 560–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assefa, W.; Sinatayehu, R.; Sendeku, M.A.; Dires, M. Chromoblastomycosis: Delayed Diagnosis with Extensive Cutaneous Lesions. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2023, 131, 50–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Fang, J.; Yu, J.; Zhang, W.; He, Z.; Ye, L.; Wang, H. The Role of CD4+ T Cells in Tumor and Chronic Viral Immune Responses. MedComm 2023, 4, e390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, Y.; Setoyama, A.; Sakuragi, Y.; Saito-Sasaki, N.; Yoshioka, H.; Nakamura, M. The Role of IL-17-Producing Cells in Cutaneous Fungal Infections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bär, E.; Whitney, P.G.; Moor, K.; Reis e Sousa, C.; LeibundGut-Landmann, S. IL-17 Regulates Systemic Fungal Immunity by Controlling the Functional Competence of NK Cells. Immunity 2014, 40, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huangfu, L.; Li, R.; Huang, Y.; Wang, S. The IL-17 Family in Diseases: From Bench to Bedside. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, J.; Mudalagiriyappa, S.; Nanjappa, S.G. T Cell Responses to Control Fungal Infection in an Immunological Memory Lens. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 905867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Veerdonk, F.L.; Netea, M.G. T-Cell Subsets and Antifungal Host Defenses. Curr. Fungal Infect. Rep. 2010, 4, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deepe, G.S.; Buesing, W.R.; Ostroff, G.R.; Abraham, A.; Specht, C.A.; Huang, H.; Levitz, S.M. Vaccination with an Alkaline Extract of Histoplasma Capsulatum Packaged in Glucan Particles Confers Protective Immunity in Mice. Vaccine 2018, 36, 3359–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Rua, N.M.; Samuelson, D.R.; Charles, T.P.; Welsh, D.A.; Shellito, J.E. CD4+ T-Cell-Independent Secondary Immune Responses to Pneumocystis Pneumonia. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozza, S.; Zelante, T.; Moretti, S.; Bonifazi, P.; DeLuca, A.; D’Angelo, C.; Giovannini, G.; Garlanda, C.; Boon, L.; Bistoni, F.; et al. Lack of Toll IL-1R8 Exacerbates Th17 Cell Responses in Fungal Infection. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 4022–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.J.; Ashkar, A.A. The Dual Nature of Type I and Type II Interferons. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, S.; Jeon, R.; Vuckovic, I.; Jiang, X.; Lerman, A.; Folmes, C.D.; Dzeja, P.D.; Herrmann, J. Interferon Gamma Induces Reversible Metabolic Reprogramming of M1 Macrophages to Sustain Cell Viability and Pro-Inflammatory Activity. EBioMedicine 2018, 30, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Xi, L.; Huang, H.; Hu, Y.; Li, X.; Huang, X.; Lu, S.; Sun, J. Melanin in a Meristematic Mutant of Fonsecaea Monophora Inhibits the Production of Nitric Oxide and Th1 Cytokines of Murine Macrophages. Mycopathologia 2013, 175, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opal, S.M.; DePalo, V.A. Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines. Chest 2000, 117, 1162–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hultgren, O.; Kopf, M.; Tarkowski, A. Staphylococcus aureus-Induced Septic Arthritis and Septic Death Is Decreased in IL-4-Deficient Mice: Role of IL-4 as Promoter for Bacterial Growth. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 5082–5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cenci, E.; Romani, L.; Mencacci, A.; Spaccapelo, R.; Schiaffella, E.; Puccetti, P.; Bistoni, F. Interleukin-4 and Interleukin-10 Inhibit Nitric Oxide-Dependent Macrophage Killing OfCandida Albicans. Eur. J. Immunol. 1993, 23, 1034–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cenci, E.; Mencacci, A.; Fè d’Ostiani, C.; Del Sero, G.; Mosci, P.; Montagnoli, C.; Bacci, A.; Romani, L. Cytokine- and T Helper–Dependent Lung Mucosal Immunity in Mice with Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis. J. Infect. Dis. 1998, 178, 1750–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, R.; Tiwary, B.N. Th1 and Th2 Cytokines in a Self-Healing Primary Pulmonary Aspergillus Flavus Infection in BALB/c Mice. Cytokine 2010, 52, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto-Domínguez, A.; González-Castillo, J.A.; Castillo-Velázquez, U.; Rodriguez-Tovar, L.E.; Méndez-Zamora, G.; Zamora-Avila, D.E.; Nevárez-Garza, A.M. Distribution of M1 and M2 Macrophages in Cerebral Granulomas Caused by Encephalitozoon Cuniculi. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2022, 252, 110481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darling, A.R.; Freyschmidt, E.-J.; Burton, O.T.; Koleoglou, K.J.; Oyoshi, M.K.; Oettgen, H.C. IL-10 Suppresses IL-17-Mediated Dermal Inflammation and Reduces the Systemic Burden of Vaccinia Virus in a Mouse Model of Eczema Vaccinatum. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 150, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquis, M.; Lewandowski, D.; Dugas, V.; Aumont, F.; Sénéchal, S.; Jolicoeur, P.; Hanna, Z.; de Repentigny, L. CD8+ T Cells but Not Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes Are Required to Limit Chronic Oral Carriage of Candida Albicans in Transgenic Mice Expressing Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 2382–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindell, D.M.; Moore, T.A.; McDonald, R.A.; Toews, G.B.; Huffnagle, G.B. Generation of Antifungal Effector CD8+ T Cells in the Absence of CD4+ T Cells during Cryptococcus Neoformans Infection. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 7920–7928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mc Allister, F.; Steele, C.; Zheng, M.; Young, E.; Shellito, J.E.; Marrero, L.; Kolls, J.K. T Cytotoxic-1 CD8+ T Cells Are Effector Cells against Pneumocystis in Mice. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 1132–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jubel, J.M.; Barbati, Z.R.; Burger, C.; Wirtz, D.C.; Schildberg, F.A. The Role of PD-1 in Acute and Chronic Infection. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, R.V.; Chemnitz, J.M.; Frauwirth, K.A.; Lanfranco, A.R.; Braunstein, I.; Kobayashi, S.V.; Linsley, P.S.; Thompson, C.B.; Riley, J.L. CTLA-4 and PD-1 Receptors Inhibit T-Cell Activation by Distinct Mechanisms. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 25, 9543–9553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez, G.V.; Melucci Ganzarain, C.D.C.; Vecchione, M.B.; Trifone, C.A.; Marín Franco, J.L.; Genoula, M.; Moraña, E.J.; Balboa, L.; Quiroga, M.F. PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway Modulates Macrophage Susceptibility to Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Specific CD8+ T Cell Induced Death. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, L.-C.; Hu, B.; Zhang, S.-P. Macrophages Participate in the Immunosuppression of Condyloma Acuminatum through the PD-1/PD-L1 Signaling Pathway. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2019, 82, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, M.J.; Tsang, T.M.; Qiu, Y.; Dayrit, J.K.; Freij, J.B.; Huffnagle, G.B.; Olszewski, M.A. Macrophage M1/M2 Polarization Dynamically Adapts to Changes in Cytokine Microenvironments in Cryptococcus Neoformans Infection. mBio 2013, 4, e00264-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonam, S.R.; Chauvin, C.; Levillayer, L.; Mathew, M.J.; Sakuntabhai, A.; Bayry, J. SARS-CoV-2 Induces Cytokine Responses in Human Basophils. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 838448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esberg, A.; Isehed, C.; Holmlund, A.; Lindquist, S.; Lundberg, P. Serum Proteins Associated with Periodontitis Relapse Post-surgery: A Pilot Study. J. Periodontol. 2021, 92, 1805–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groeger, S.; Jarzina, F.; Mamat, U.; Meyle, J. Induction of B7-H1 Receptor by Bacterial Cells Fractions of Porphyromonas Gingivalis on Human Oral Epithelial Cells. Immunobiology 2017, 222, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, L.; Tan, X. PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway: A Double-Edged Sword in Periodontitis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 159, 114215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Liang, Q.; Guo, R.; Zhang, L.; Han, X.; Wang, J.; Shao, L.; et al. Systemic Immune Dysregulation in Severe Tuberculosis Patients Revealed by a Single-Cell Transcriptome Atlas. J. Infect. 2023, 86, 421–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-Y.; Lin, C.-W.; Cheng, K.-S.; Lin, C.; Wang, Y.-M.; Lin, I.-T.; Chou, Y.-H.; Hsu, P.-N. Increased Programmed Death-Ligand-1 Expression in Human Gastric Epithelial Cells in Helicobacter Pylori Infection. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2010, 161, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Suarez, G.; Beswick, E.J.; Sierra, J.C.; Graham, D.Y.; Reyes, V.E. Expression of B7-H1 on Gastric Epithelial Cells: Its Potential Role in Regulating T Cells during Helicobacter Pylori Infection. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 3000–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhadra, R.; Gigley, J.P.; Weiss, L.M.; Khan, I.A. Control of Toxoplasma Reactivation by Rescue of Dysfunctional CD8 + T-Cell Response via PD-1–PDL-1 Blockade. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 9196–9201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habib, S.; El Andaloussi, A.; Elmasry, K.; Handoussa, A.; Azab, M.; Elsawey, A.; Al-Hendy, A.; Ismail, N. PDL-1 Blockade Prevents T Cell Exhaustion, Inhibits Autophagy, and Promotes Clearance of Leishmania Donovani. Infect. Immun. 2018, 86, e00019-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madureira, A.C. Programmed Cell Death-Ligand-1 Expression in Bladder Schistosomal Squamous Cell Carcinoma—There’s Room for Immune Checkpoint Blockage? Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 955000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Guan, F.; Sun, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lu, S.; Liu, W. B Cells Induced by Schistosoma Japonicum Infection Display Diverse Regulatory Phenotypes and Modulate CD4+ T Cell Response. Parasit. Vectors 2020, 13, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, P.; Walsh, C.M.; Mangan, N.E.; Fallon, R.E.; Sayers, J.R.; McKenzie, A.N.J.; Fallon, P.G. Schistosoma mansoni Worms Induce Anergy of T Cells via Selective Up-Regulation of Programmed Death Ligand 1 on Macrophages. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 1240–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karnam, A.; Bonam, S.R.; Rambabu, N.; Wong, S.S.W.; Aimanianda, V.; Bayry, J. Wnt-β-Catenin Signaling in Human Dendritic Cells Mediates Regulatory T-Cell Responses to Fungi via the PD-L1 Pathway. mBio 2021, 12, e0282421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen-Victor, E.; Karnam, A.; Fontaine, T.; Beauvais, A.; Das, M.; Hegde, P.; Prakhar, P.; Holla, S.; Balaji, K.N.; Kaveri, S.V.; et al. Aspergillus Fumigatus Cell Wall α-(1,3)-Glucan Stimulates Regulatory T-Cell Polarization by Inducing PD-L1 Expression on Human Dendritic Cells. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 216, 1281–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurster, S.; Albert, N.D.; Kontoyiannis, D.P. Candida Auris Bloodstream Infection Induces Upregulation of the PD-1/PD-L1 Immune Checkpoint Pathway in an Immunocompetent Mouse Model. mSphere 2022, 7, e0081721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.C.; Burnham, C.-A.; Compton, S.M.; Rasche, D.P.; Mazuski, R.; SMcDonough, J.; Unsinger, J.; Korman, A.J.; Green, J.M.; Hotchkiss, R.S. Blockade of the Negative Co-Stimulatory Molecules PD-1 and CTLA-4 Improves Survival in Primary and Secondary Fungal Sepsis. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lázár-Molnár, E.; Gácser, A.; Freeman, G.J.; Almo, S.C.; Nathenson, S.G.; Nosanchuk, J.D. The PD-1/PD-L Costimulatory Pathway Critically Affects Host Resistance to the Pathogenic Fungus Histoplasma capsulatum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2658–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janelle, V.; Neault, M.; Lebel, M.-È.; De Sousa, D.M.; Boulet, S.; Durrieu, L.; Carli, C.; Muzac, C.; Lemieux, S.; Labrecque, N.; et al. P16INK4a Regulates Cellular Senescence in PD-1-Expressing Human T Cells. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 698565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieren, D.K.J.; Smits, N.A.M.; van de Garde, M.D.B.; Guichelaar, T. Response Kinetics Reveal Novel Features of Ageing in Murine T Cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.-W.; Johmura, Y.; Suzuki, N.; Omori, S.; Migita, T.; Yamaguchi, K.; Hatakeyama, S.; Yamazaki, S.; Shimizu, E.; Imoto, S.; et al. Blocking PD-L1–PD-1 Improves Senescence Surveillance and Ageing Phenotypes. Nature 2022, 611, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lages, C.S.; Lewkowich, I.; Sproles, A.; Wills-Karp, M.; Chougnet, C. Partial Restoration of T-Cell Function in Aged Mice by in Vitro Blockade of the PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway. Aging Cell 2010, 9, 785–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Channappanavar, R.; Twardy, B.S.; Krishna, P.; Suvas, S. Advancing Age Leads to Predominance of Inhibitory Receptor Expressing CD4 T Cells. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2009, 130, 709–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cavallone, I.N.; Belda, W., Jr.; de Carvalho, C.H.C.; Laurenti, M.D.; Passero, L.F.D. New Immunological Markers in Chromoblastomycosis—The Importance of PD-1 and PD-L1 Molecules in Human Infection. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9121172
Cavallone IN, Belda W Jr., de Carvalho CHC, Laurenti MD, Passero LFD. New Immunological Markers in Chromoblastomycosis—The Importance of PD-1 and PD-L1 Molecules in Human Infection. Journal of Fungi. 2023; 9(12):1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9121172
Chicago/Turabian StyleCavallone, Italo N., Walter Belda, Jr., Caroline Heleno C. de Carvalho, Marcia D. Laurenti, and Luiz Felipe D. Passero. 2023. "New Immunological Markers in Chromoblastomycosis—The Importance of PD-1 and PD-L1 Molecules in Human Infection" Journal of Fungi 9, no. 12: 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9121172
APA StyleCavallone, I. N., Belda, W., Jr., de Carvalho, C. H. C., Laurenti, M. D., & Passero, L. F. D. (2023). New Immunological Markers in Chromoblastomycosis—The Importance of PD-1 and PD-L1 Molecules in Human Infection. Journal of Fungi, 9(12), 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9121172







