Abstract
Sporotrichosis is an implantation mycosis with subcutaneo-lymphatic or, more rarely, a viscerally disseminated affection; it can be acquired through traumatic percutaneous inoculation of the fungus present in soil or plant matter, or by feline scratching. Among the causative agents, Sporothrix brasiliensis is considered the most virulent species with a high prevalence in Brazil and recently in Argentina. Objective: To describe a S. brasiliensis outbreak in domestic and feral cats detected in the Magallanes region of southern Chile. Materials and Methods: Between the months of July and September 2022, three cats presented with suppurative subcutaneous lesions located mainly on the head and thoracic limbs. The cytology revealed the presence of yeasts with morphological characteristics suggestive of Sporothrix spp. The histopathology confirmed pyogranulomatous subcutaneous lesions associated with the presence of the same yeasts. The fungal culture followed by the partial gene sequence and analysis of the ITS region confirmed the diagnosis of the S. brasiliensis as the causative agent. The cats were treated with itraconazole associated in one case with potassium iodide. The evolution of the patients was favorable in all cases. Conclusions: An outbreak caused by S. brasiliensis was detected in domestic and feral cats in austral Chile. The correct identification of this fungus and antifungigram is essential for treatment decisions and for designing dissemination control and prevention programs under a one health approach that consider the health of people, animals, and the environment.
1. Introduction
Sporotrichosis is frequently a cutaneous or cutaneous-lymphatic mycosis of a zoonotic nature and of worldwide distribution [1,2,3]. Most cases result from the traumatic inoculation of propagules of Sporothrix spp. in the host cutaneous tissue. This is considered an implantation mycosis that can occur through an animal or environmental transmission route [4,5,6,7]. Sporothrix spp. is a dimorphic fungus, which, in its saprophytic phase, develops a filamentous form, mainly in soils rich in organic matter, at 25 °C; while at 37 °C, in the host tissues, it remains as yeast, generating infection; both phases of the fungus are culturable in the laboratory [8,9,10,11,12].
Currently, 53 Sporothrix species have been described [13], which are divided into two clades, one is “clinical or pathogenic”, isolated from human or animal cases; composed of S. schenckii of worldwide distribution, S. globosa is present in Argentina, Venezuela, United Kingdom, Spain, Italy, China, Japan, USA, and India [14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24]. S. luriei is present in South Africa and S. brasiliensis is restricted to South America [14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24]. The remaining species are nested in an “environmental clade”, often associated with organic substrates such as soils with decaying plant remains, wood, or insects [25,26,27,28].
Advances in research on the clinical/pathogenic species have allowed significant information to be generated in terms of morphology [29], physiology [30], genetics [31], epidemiology [32], and virulence [22,33,34,35,36], among other aspects, which has facilitated their identification.
Within the pathogenic species, S. brasiliensis is categorized as the most virulent, becoming the main etiological agent of zoonotic transmission between cats and humans [37,38]. Transmission can occur through scratches, bites, or contact with exudates from skin lesions of infected cats [39,40,41,42,43]. In addition, cats can carry the fungus in their claws, which may have an important role in the epidemiology of the disease [42,44,45].
A recently published study by Morgado et al. [46] mentions that South America is the continent with the highest animal sporotrichosis prevalence (81%), followed by Asia and Europe [47], while North America and Africa report the same proportion. In South America, most of the isolates are concentrated in Brazil [48] and then in Argentina [38] and occur mainly in cats, followed by dogs [49,50,51]. The most prevalent species on the continent is S. brasiliensis, and S. schenckii appears less frequently [46,52].
The development of the disease is related to predisposing factors such as exposure to the infectious agent, the depth of the wound, and the immune response the host [9,53,54]. The incubation period varies from 13 days to 3 months, mainly affecting the skin and lymph nodes adjacent to the lesion. In cats, the most frequent clinical signs are associated with the skin presentation, characterized by erosions, ulcers, and fistulas accompanied by serous-bloody or purulent exudate, mainly located on the head, face, neck, and in the distal part of the extremities [37,50,55,56,57,58]. The extra-cutaneous form of pulmonary, ocular, or neurological localization is seen less frequently [37,53,59,60,61,62]. The highest incidence of the disease occurs in out door non-castrated male cats in constant contact with the outside world; its habit of scratching the vegetation facilitates the spread of the fungus in the environment [6,63]. In addition, its territorial and fighting behavior with other cats allows rapid transmission between individuals of this species [57,64]. As a treatment, itraconazole alone or associated with potassium iodide continues to be the first option against this type of infection [65,66,67,68,69].
We describe an outbreak by S. brasiliensis in cats from Patagonia in the southern part of Chile, which is the first isolation report of this agent in cats in our country.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Geographic Location
The outbreak that we describe below occurred between the months of July and September 2022 in the Magallanes Region, in southern Chile. Cases 1 and 2 come from the Río Verde County (53°09′46″ S 70°54′29″ W), a small rural village with approximately 250 people. Case 3 comes from the city of Punta Arenas (52°36′28″ S 71°30′28″ W) with 143,000 inhabitants (www.bcn.cl). The distance between both points is 98 km.
2.2. Case Description
Case 1: Feline, female, domestic long hair (DLH), 1,2 years, 1.5 kg, wild behavior, lived outdoors with a group of cats in the Río Verde location and had no owner. Due to the skin lesions she had and the presumptive diagnosis of a fungal non-identified disease, the local veterinarian prescribed itraconazole (Itraskin, Drag Pharma, Santiago, Chile). After observing that her multiple wounds did not heal, she was taken to a veterinary center located in the city of Punta Arenas (Clinica Veterinaria Timaukel).
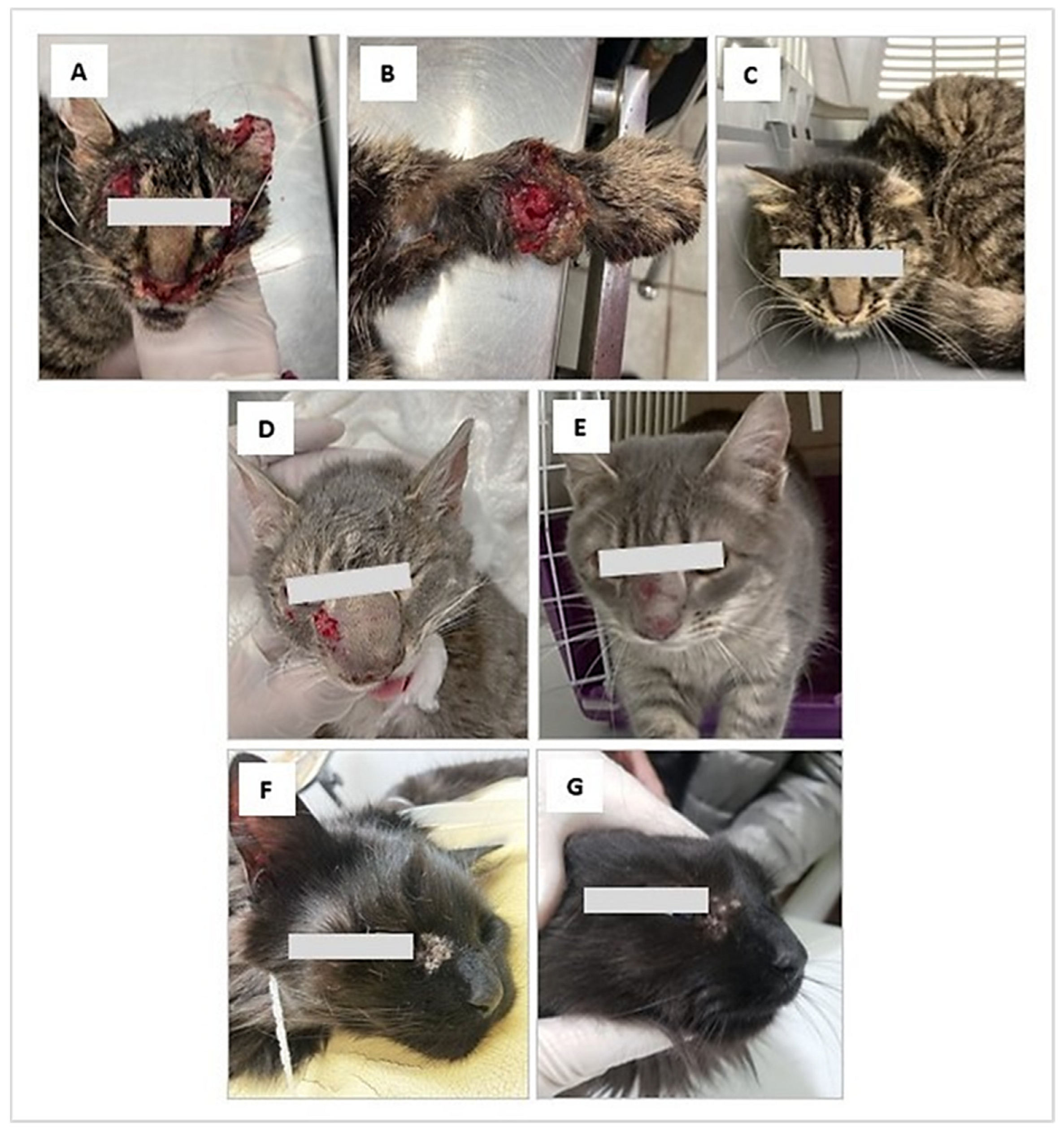
On examination, she had sero-bloody subcutaneous wounds located mainly on the face and forelimbs, with laceration of the left ear; she was also very thin and weak. A surgical cleaning procedure was performed under sedation (Figure 1A,B).
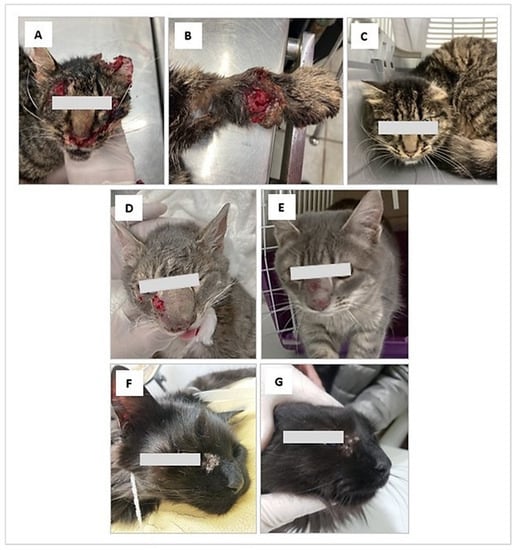

Figure 1.
Clinical aspect of feline sporotrichosis. (A,B) Ulcerated lesions in the cephalic region and forelimb, associated with laceration of the left ear. (D) Subcutaneous, sero-bloody erosions located on the face near the eye, with inflammation and deformation of the nasal septum. (F): Periocular lesion with a moist and scaly appearance. (C,G). Clinical appearance of the lesions after treatment (C) A remarkable clinical cure is observed after 5 months of treatment with itraconazole (G) The evolution of treatment it is favorable after two months with treatment with itraconazole. (E) Appearance of lesions after 2 months of treatment with itraconazole and potassium iodide.
Case 2: Feline, female, domestic short hair (DSH), 6 months, 1.2 kg, belongs to the same group of outdoor cats from Río Verde. She was taken on August 18 to the same veterinary center mentioned before.
The clinical examination showed subcutaneous, sero-bloody erosions located on the face, also associated with deformation of the nasal septum. She had not received any treatment (Figure 1D).
Case 3: Feline, female, DSH, 6 years old, 3.5 kg, indoor, from the city of Punta Arenas. On 8 September, the cat showed during clinical examination a subcutaneous mass on the right costal flank of approximately 8 cm in diameter with an ulcerated and suppurative center. In addition, a left periocular lesion with a moist and scaly appearance was observed (Figure 1F).
The owner reported that previously in another veterinary clinic, they prescribed amoxicillin; however, with this treatment, no improvement was observed.
Each patient underwent feline immunodeficiency and feline leukemia virus tests (Snap FIV/ FeLV® combo test, IDEXX, Westbrook, ME, USA), which were negative. None of these cats or their close contacts had a history of traveling to areas where the S. brasiliensis is endemic.
Due to the clinical history and the characteristics of the lesions, a skin biopsy was obtained in all cases. For the procedure, each cat was pre-medicated with Tiletamin 2.5%-Zolazepam 2.5% (Zoletil, Virbac, Santiago, Chile), anesthesia was induced with isoflurane (Baxter Latin America, Santiago, Chile) at 3%, maintaining a sedation dose of 2.5% isoflurane, with a minimum alveolar oxygen concentration of 1.2%. Two biopsies of approximately 7 mm in diameter each were obtained for histopathological and microbiological study [70]. They were later sent to the Laboratory of Anatomic Pathology and Histopathology (CITOVET) and to the Clinical Microbiology and Microbiome Laboratory, of the School of Veterinary Medicine of the Andrés Bello University, both in Santiago, Chile.
3. Results
3.1. Histopathological Study
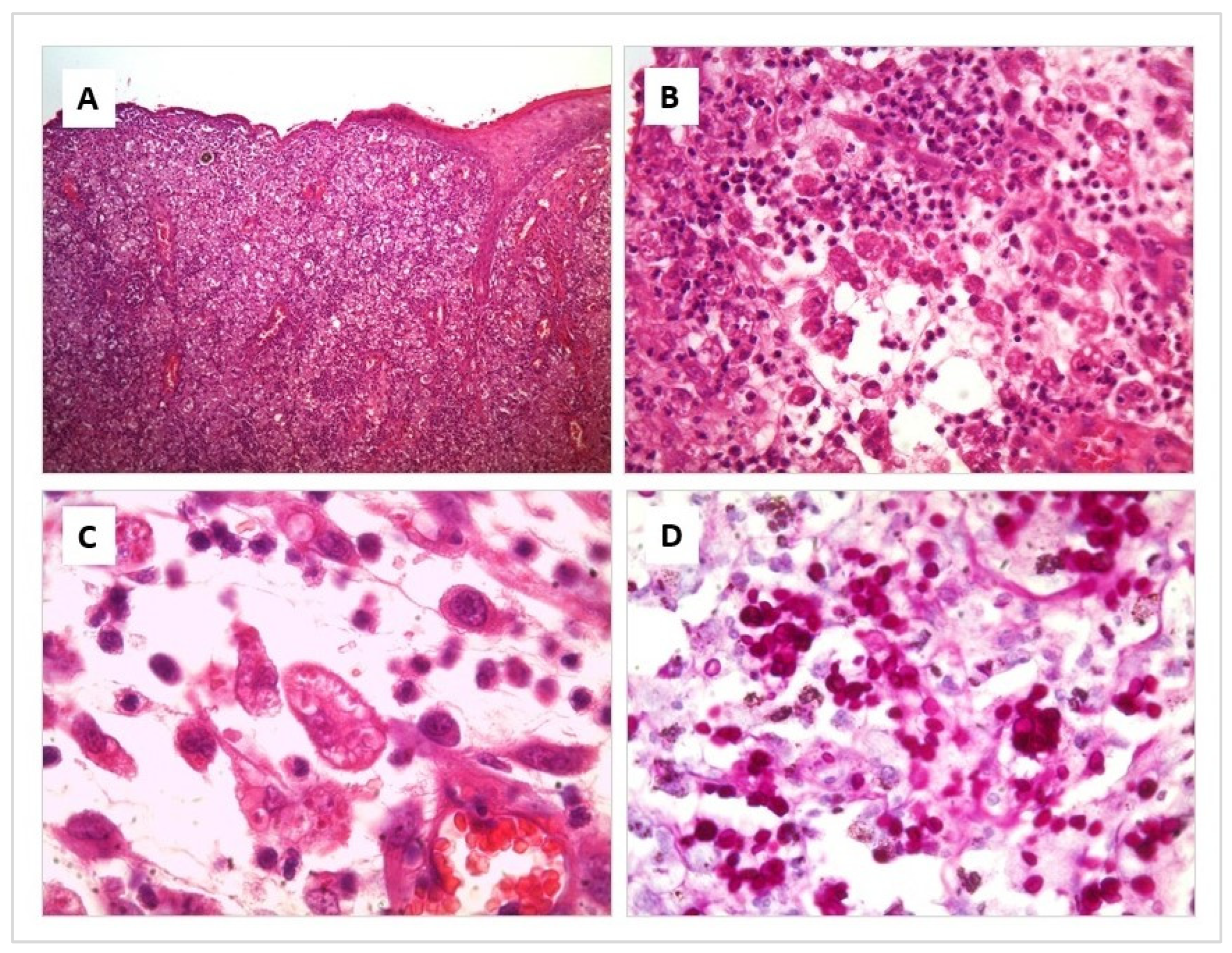
The affected areas show an acanthotic to ulcerated epidermis, with variable degrees of exudation and crusting. Throughout the superficial and deep dermis and subcutaneous tissue, there is intense diffuse pyogranulomatous inflammation. There are multiple foci of necrosis surrounded by neutrophil clusters. Prominent blood vessels have proliferation within the leucocyte infiltrate where numerous macrophages are intermingled with neutrophils. Round to elongated yeasts 2 to 3 μm in diameter are present in profusion, both free and within the cytoplasm of macrophages. They are so numerous that they are not difficult to appreciate even by Hematoxylin–Eosin (H/E) Staining. However, their morphological features, corresponding to Sporothrix spp., are more prominent and easier to appreciate by Periodic acid-Shiff (PAS) and Grocott stains, where yeasts with frequent budding figures can be seen (Figure 2).
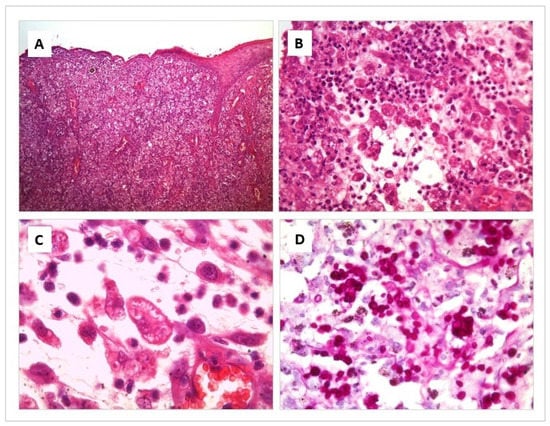
Figure 2.
Histological section of a skin lesion from a cat with Sporotrichosis. Hematoxylin-eosin (A–C) and Periodic acid-Shiff (D) stain. (A) Diffuse pyogranulomatous inflammation is present throughout the skin layers. (B) Multiple foci of necrosis are surrounded by numerous macrophages, intermingled with neutrophils. (C) Round to elongated yeasts 2 to 3 μm in diameter are present in profusion, both free and within the cytoplasm of macrophages. (D) Numerous yeasts with frequent budding figures can be seen, corresponding to Sporothrix spp.
3.2. Mycological Study
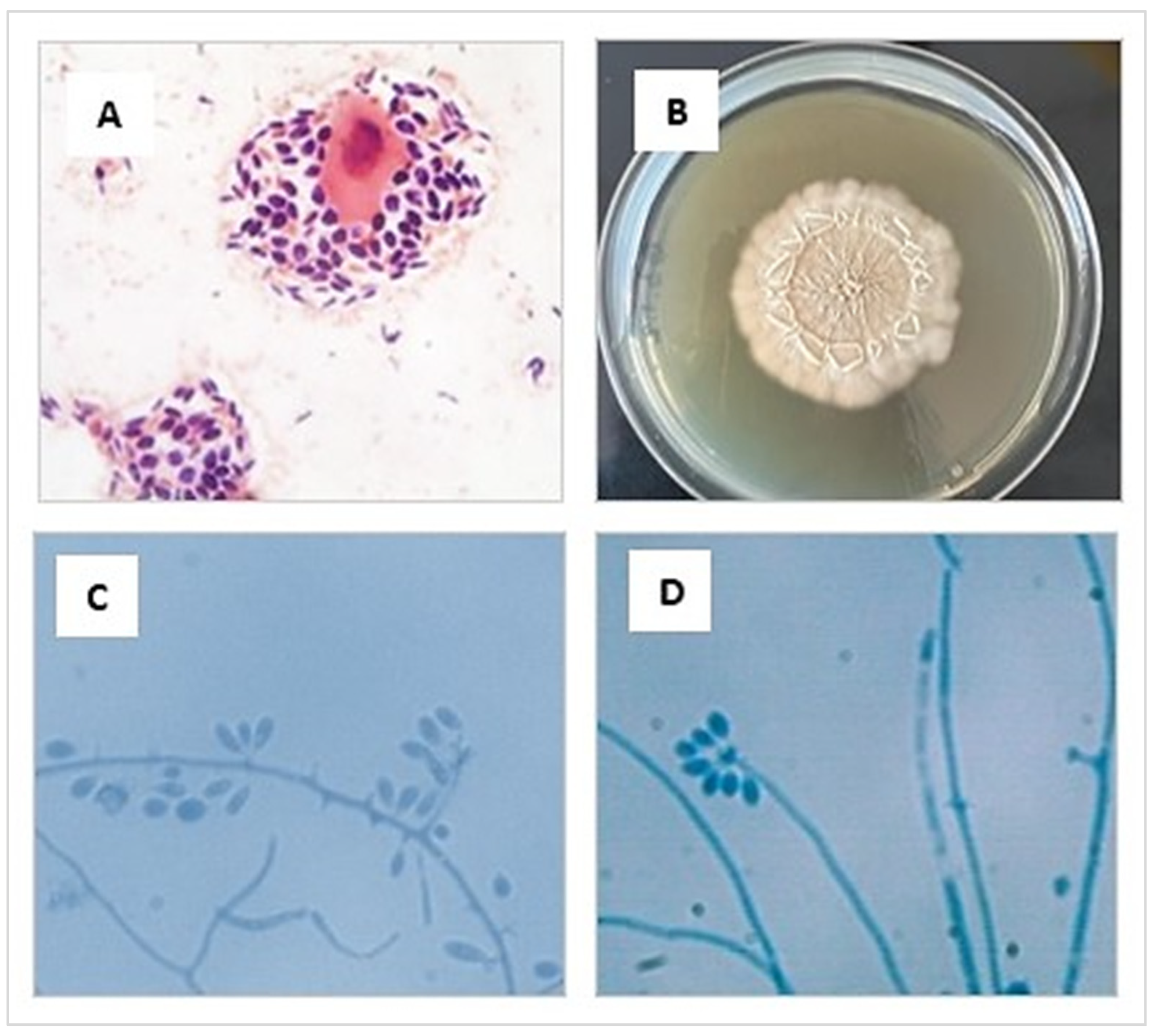
The phenotypic study was carried out in a BSL-2 biosafety cabinet and based on characteristics of the isolates. Initially, a direct microscopic examination of the sample with Gram staining was performed, where abundant blastoconidia were observed, some of them with single budding (Figure 3A). Then, the tissue sample was minced and seeded on Sabouraud agar glucose (SGA) containing chloramphenicol (0.05 g/L) and cycloheximide (0.4 g/L) (Merk, Rahway, NJ, USA), and incubated at 25 °C and 37 °C for 10 days (Figure 3B). The macro- and micromorphological characteristics of the colony [71,72,73] allowed the presumptive identification of Sporothrix spp. (Figure 3C,D).
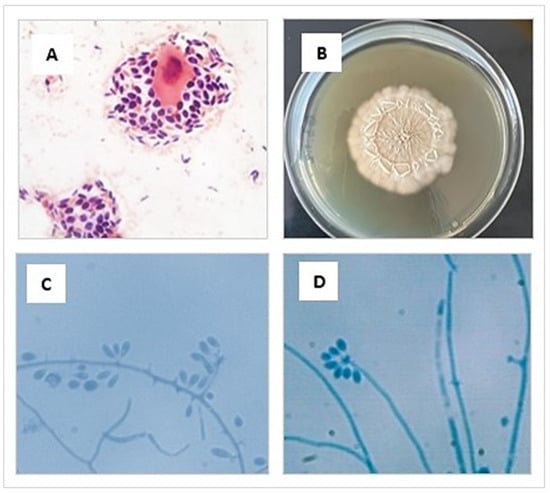
Figure 3.
(A) Cytologic preparation collected from an ulcerated lesion of the cat’s skin showing an intermediate epithelial cell surrounded by many yeasts, stained using the Gram and observed at 1000× magnification. (B) Macromorphology of the colonies of S. brasiliensis cultivated in SGA medium for 10 days at 25 °C (C,D) Preparation made from a microculture of a colony of S. brasiliensis grown in SGA. Septate hyaline hyphae are seen, and conidiogenous cells arise from undifferentiated hyphae, forming conidia in groups on small, clustered denticles, stained using the lactophenol cotton blue observed at 1000× magnification.
The genotypic study of the 3 isolated colony included DNA extraction performed with the Quick-DNA Fungal/Bacterial kit (Zimo Research, Irvine, CA, USA), following the manufacturer’s instructions. PCR amplification was performed using universal primers ITS5 and ITS4 [52,74,75,76,77]. The sequences obtained were edited, assembled, and analyzed by comparing the nucleotide similarity using the BLASTn tool of the National Centre for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). The sequences of isolates were successfully confirmed as S. brasiliensis (accession number OX416764, OX416765, and OX416766), presenting 100% genetic identity with this species.
In vitro antifungal susceptibility test: The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) was determined by broth microdilution, according to document M38-A2. from the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) [78]. Each microplate was loaded with RPMI 1640 medium buffered to pH 7.0 with 0.165 mol/L of morpholinopropanesulfonic acid (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA).
From the different antifungals obtained in pure powder, concentrations that fluctuated between 0.125 and 64 mg/L were prepared. The drugs tested were amphotericin B (AMB), fluconazole (FLC), itraconazole (ITR), ketoconazole (KET), posaconazole (POS), voriconazole (VRC), and terbinafine (TRB) (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA).
Inoculum of each strain of 1–5 × 104 conidia/mL were prepared in sterile saline solution, including Candida parapsilosis ATCC 22019 and C. krusei ATCC 6258 as reference strains. MICs were determined by visual inspection after 48-72 h of incubation at 35 °C. For AMB, ITR, VRC, and POS, the MICs were the lowest concentrations that 100% inhibited the growth of the fungus. For FLC, KET, and TRB, the MIC was the lowest concentration that resulted in a 50% and 80% reduction in growth, respectively, relative to that of the growth control [78].
The results obtained demonstrated good activity in the most antifungals used against tested tree strains of S. brasiliensis. The azoles showing an MIC range of 0.25–1 μg/mL, with the exception that fluconazole showed MIC > 64 μg/mL in all strains. AMB and TRB showed MIC values between 0.5 and 1 μg/mL. The MICs for the control strains were within the expected range, as described by the CLSI guidelines [78].
3.3. Treatment and Clinical Evolution
Initial treatment began with itraconazole 10 mg/kg per day for each patient. Once the causative agent was diagnosed, a dose adjustment of 100 mg/kg/day was made. The owners were educated about the zoonotic potential and prognosis for the disease.
Both feral cats (cases 1 and 2) were adopted and are still being treated with itraconazole. In both cases, it has been observed that the dermatological lesions have slowly improved but not completely yet. A noticeable improvement has also been observed in their general condition and body weight. Case 1 is currently still undergoing treatment, until completing 5 months of treatment.
In clinical case 3, a fluctuating behavior on the clinical evolution has been observed. The patient has presented some systemic episodes with fever and loss of body weight. During the antifungal treatment, small new skin lesions have appeared on the face with a tendency to deform the nasal septum. For this reason, potassium iodide (2.5 mg/kg) was also recently indicated, but their effect has not yet been possible to evaluate.
This corresponds to the first report that identifies S. brasiliensis in felines from Chile, in this case, from the Magallanes Region.
4. Discussion
The epidemiological characteristic of the clinical cases considered in this study correspond to the description of an outbreak that, according to histopathology, microbiology, and molecular analysis, identifies as S. brasiliensis.
The first description of S. brasiliensis was made in 2007 in Brazil, and it is currently responsible for more than 90% of the cases of sporotrichosis in humans and felines in that country, where it is considered an endemic mycosis [1,56,76,79,80,81]. Typically, this fungus has been associated with temperate and humid climates; however, this has changed in recent years, as S. brasiliensis has been detected in different climatic regions, such as Argentina, where it has also been identified in humans and felines [82].
Among the risk factors associated with feline sporotrichosis, the previously reported research results include cats that live or roam outdoors or have free access to the street, uncastrated males, and territorial behaviors with fights that lead to scratches or bites [6,57,63,64], information that is consistent with the data observed in these cases.
Nodules and subcutaneous ulcers were the more frequently observed lesions in the cases under study; this agrees with previous reports [37,50,55,56,57,58,83].
The presumptive identification of the agent was carried out by means of the phenotypic characteristics and the confirmation of the identity, by means of molecular techniques. Currently, the phenotypic characteristic alone is not sufficient to identify species of the genus Sporothrix spp., due to the uncertainty of the tests involved. Thus, the use of molecular methodologies is required [37,46,55,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,83,84]; among them, the sequencing of the ITS region of the rDNA is one of the most used [19,72].
The treatment choice in the three cases was itraconazole indicated for 4–6 months. Itraconazole remains the drug of choice for the treatment of feline sporotrichosis and its efficacy in monotherapy has been previously documented [37,55,66,67,83,85,86]. Its in vitro activity against S. brasiliensis strains isolated from cats [65,66,87] has also been reported. However, the correlation between in vitro antifungal susceptibility testing and in vivo therapeutic response is not always positive. In this regard, other authors report unsuccessful therapies with this antifungal [67,88,89], which has been associated with the virulence of the species and the spreading of the lesions [33,90].
Some reports recommend itraconazole associated with potassium iodide, for deeper lesions located in the nasal region, which invade the cartilage beneath [58,90]. The general condition of the cat, the presence or absence of respiratory signs, as well as the number, extension, and location of the lesions are factors that can influence the prognosis [9,54,86].
Based on the description of this outbreak, we generate guidelines that provide practical information that can help veterinarians in diagnosing sporotrichosis opportunely and accurately in our country. In addition, programs with a one health focus that include education, responsible pet ownership, and waste containment are required to avoid dissemination into the environment [6,91], thus promoting awareness of the zoonotic potential of this species and the importance for human, animal, and environmental health. For this reason, as soon as the causal agent was identified, the veterinarians working in the area were contacted and invited to a seminar where the problem was exposed and discussed. In addition, a meeting was held with representatives from the Ministry of Health of Magallanes (MINSAL), the Regional Ministerial Secretariat (SEREMI), the Livestock Agricultural Service (SAG), local veterinary services, and human hospitals. As a result, an alert was generated in the region with a distribution of educational material and recommendations for dissemination control actions.
Further ongoing studies will include the search for S. brasiliensis in the claws of diseased and clinically healthy animals and from the soil and plants, to help reveal transmission routes.
5. Recommendations
Considering that the lesions present on the skin of cats contain a considerable fungal burden, it is essential to use personal protection elements, such as disposable gloves and aprons, when attending to or having contact with these cases. In cats with continuous secretions and/or multiple skin lesions, the use of an N95 or PFF2 face mask and safety glasses are also recommended [92,93].
Author Contributions
The individual contributions of the authors are mentioned below. Conceptualization, P.T. and C.G.; methodology, P.T., C.G., O.B., V.R., C.d.R. and S.S.; validation, formal analysis, P.T. and C.G.; research, P.T., C.G., O.B., V.R., P.P. and C.d.R.; resources, P.T. and C.G.; writing—original draft preparation, P.T.; writing—review and editing, P.T., C.G., O.B. and V.R.; project management, funding acquisition, P.T. and C.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by ANID. PAI Project 77190079 and The APC was financed by the Universidad Andrés Bello.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from the patients’ owners to publish this article.
Acknowledgments
We would like to give a special mention for the valuable support given by José Márquez, T.M., from the Agostini Laboratory, Punta Arenas, for guiding us into the right path; to Carolina Valdebenito and Eduardo Rice, from Río Verde, who cared for the group of sick cats and adopted some of them to carry out their treatment; Esther Barrera, M.V. and Maria Olga Gamin M.V. for their technical support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chakrabarti, A.; Bonifaz, A.; Gutierrez-Galhardo, M.C.; Mochizuki, T.; Li, S. Global epidemiology of sporotrichosis. Med. Mycol. 2015, 53, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PAHO. Sporothrix brasiliensis, an Emerging Fungal Pathogen, Notable for Its Zoonotic Transmission and Epidemic Potential for Human and Animal Health in the Americas. Available online: https://www.someve.com.ar/images/noticias/2019/S-brasiliensis_lasAmericas_30082019_ES.pdf (accessed on 15 November 2022).
- Sizar, O.; Talati, R. Sporotrichosis; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Fichman, V.; Freitas, D.F.S.; Valle, A.C.F.D.; de Souza, R.V.; Curi, A.L.L.; Valete-Rosalino, C.M.; de Macedo, P.M.; Varon, A.G.; Figueiredo-Carvalho, M.H.G.; Almeida-Silva, F.; et al. Severe Sporotrichosis Treated with Amphotericin B: A 20-Year Cohort Study in an Endemic Area of Zoonotic Transmission. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Criseo, G.; Romeo, O. Ribosomal DNA Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis of Environmental Sporothrix schenckii Strains: Comparison with Clinical Isolates. Mycopathologia 2010, 169, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira Bento, A.; de Sena Costa, A.S.; Lima, S.L.; do Monte Alves, M.; de Azevedo Melo, A.S.; Rodrigues, A.M.; da Silva-Rocha, W.P.; Milan, E.P.; Chaves, G.M. The spread of cat-transmitted sporotrichosis due to Sporothrix brasiliensis in Brazil towards the Northeast region. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Montes, H.M. Special Issue “Sporothrix and Sporotrichosis 2.0”. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes-Bezerra, L.M.; Walker, L.A.; Nino-Vega, G.; Mora-Montes, H.M.; Neves, G.W.P.; Villalobos-Duno, H.; Barreto, L.; Garcia, K.; Franco, B.; Martínez-Álvarez, J.A.; et al. Cell walls of the dimorphic fungal pathogens Sporothrix schenckii and Sporothrix brasiliensis exhibit bilaminate structures and sloughing of extensive and intact layers. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, G.W.P.; Wong, S.S.W.; Aimanianda, V.; Simenel, C.; Guijarro, J.I.; Walls, C.; Willment, J.A.; Gow, N.A.R.; Munro, C.A.; Brown, G.D.; et al. Complement-Mediated Differential Immune Response of Human Macrophages to Sporothrix Species Through Interaction with Their Cell Wall Peptidorhamnomannans. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 749074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalobos-Duno, H.L.; Barreto, L.A.; Alvarez-Aular, A.; Mora-Montes, H.M.; Lozoya-Pérez, N.E.; Franco, B.; Lopes-Bezerra, L.M.; Niño-Vega, G.A. Comparison of Cell Wall Polysaccharide Composition and Structure Between Strains of Sporothrix schenckii and Sporothrix brasiliensis. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 726958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gow, N.A.R.; Lenardon, M.D. Architecture of the dynamic fungal cell wall. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2022. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabello, V.B.S.; Almeida-Silva, F.; Scramignon-Costa, B.D.S.; Motta, B.D.S.; de Macedo, P.M.; Teixeira, M.D.M.; Almeida-Paes, R.; Irinyi, L.; Meyer, W.; Zancopé-Oliveira, R.M. Environmental Isolation of Sporothrix brasiliensis in an Area with Recurrent Feline Sporotrichosis Cases. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 894297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.M.; Hagen, F.; de Camargo, Z.P. A Spotlight on Sporothrix and Sporotrichosis. Mycopathologia 2022, 187, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris-Jones, R. Sporotrichosis. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2002, 27, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, E.; León-Navarro, I.; Rodríguez-Brito, S.; Mendoza, M.; Niño-Vega, G.A. Molecular epidemiology of human sporotrichosis in Venezuela reveals high frequency of Sporothrix globosa. BMC Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, M.M.; de Almeida-Paes, R.; de Medeiros Muniz, M.; de Lima Barros, M.B.; Galhardo, M.C.; Zancope-Oliveira, R.M. Sporotrichosis caused by Sporothrix globosa in Rio De Janeiro, Brazil: Case report. Mycopathologia 2010, 169, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brilhante, R.S.N.; de Aguiar, F.R.M.; da Silva, M.L.Q.; de Oliveira, J.S.; de Camargo, Z.P.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Pereira, V.S.; Serpa, R.; Castelo-Branco, D.; Correia, E.E.M.; et al. Antifungal susceptibility of Sporothrix schenckii complex biofilms. Med. Mycol. 2018, 56, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córdoba, S.; Isla, G.; Szusz, W.; Vivot, W.; Hevia, A.; Davel, G.; Canteros, C.E. Molecular identification and susceptibility profile of Sporothrix schenckii sensu lato isolated in Argentina. Mycoses 2018, 61, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New, D.; Beukers, A.G.; Kidd, S.E.; Merritt, A.J.; Weeks, K.; van Hal, S.J.; Arthur, I. Identification of multiple species and subpopulations among Australian clinical Sporothrix isolates using whole genome sequencing. Med. Mycol. 2019, 57, 905–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, L.; Velásquez, G.; Mendoza, M.; Camacho, E.; Goncalves, E.; Rodríguez, S.; Niño-Vega, G.A. Geographical distribution and ecological niche modeling of the etiological agents of human sporotrichosis in Venezuela. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2021, 52, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brilhante, R.S.N.; Fernandes, M.R.; Pereira, V.S.; Costa, A.d.C.; Oliveira, J.S.d.; de Aguiar, L.; Rodrigues, A.M.; de Camargo, Z.P.; Pereira-Neto, W.A.; Sidrim, J.J.C.; et al. Biofilm formation on cat claws by Sporothrix species: An ex vivo model. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 150, 104670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Carnero, L.C.; Martínez-Álvarez, J.A. Virulence Factors of Sporothrix schenckii. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Castro, R.; Pinto-Almazán, R.; Arenas, R.; Sánchez-Cárdenas, C.D.; Espinosa-Hernández, V.M.; Sierra-Maeda, K.Y.; Conde-Cuevas, E.; Juárez-Durán, E.R.; Xicohtencatl-Cortes, J.; Carrillo-Casas, E.M.; et al. Epidemiology of clinical sporotrichosis in the Americas in the last ten years. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nava-Pérez, N.; Neri-García, L.G.; Romero-González, O.E.; Terrones-Cruz, J.A.; García-Carnero, L.C.; Mora-Montes, H.M. Biological and clinical attributes of Sporothrix globosa, a causative agent of sporotrichosis. Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, 15, 2067–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Meyer, E.M.; de Beer, Z.W.; Summerbell, R.C.; Moharram, A.; de Hoog, G.S.; Vismer, H.F.; Wingfield, M.J. Taxonomy and phylogeny of new wood- and soil-inhabiting Sporothrix species in the Ophiostoma stenoceras-Sporothrix schenckii complex. Mycologia 2008, 100, 647–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Soto, M.C.; Aguilar-Ancori, E.G.; Tirado-Sánchez, A.; Bonifaz, A. Ecological Determinants of Sporotrichosis Etiological Agents. J. Fungi 2018, 4, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesseler, A.; Schauerte, N.; Geiger, C.; Kaerger, K.; Walther, G.; Kurzai, O.; Eisenberg, T. Sporothrix humicola (Ascomycota: Ophiostomatales)—A soil-borne fungus with pathogenic potential in the eastern quoll (Dasyurus viverrinus). Med. Mycol. Case Rep. 2019, 25, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.M.; Della Terra, P.P.; Gremião, I.D.; Pereira, S.A.; Orofino-Costa, R.; de Camargo, Z.P. The threat of emerging and re-emerging pathogenic Sporothrix species. Mycopathologia 2020, 185, 813–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.-D.; Zhou, X.; Liu, T.-T.; Yang, Z.-B. Morphological and physiological comparison of taxa comprising the Sporothrix schenckii complex. J. Zhejiang Univ. B 2015, 16, 940–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, G.F.; dos Santos, P.O.; Amaral, C.C.; Sasaki, A.A.; Godoy-Martinez, P.; Camargo, Z.P.D. Characteristics of 151 Brazilian Sporothrix schenckii isolates from 5 different geographic regions of Brazil: A forgotten and re-emergent pathogen. Open Mycol. J. 2009, 3, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, A.A.; Fernandes, G.F.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Lima, F.M.; Marini, M.M.; dos S. Feitosa, L.; de Melo Teixeira, M.; Felipe, M.S.S.; da Silveira, J.F.; de Camargo, Z.P. Chromosomal polymorphism in the Sporothrix schenckii complex. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.M.; de Melo Teixeira, M.; De Hoog, G.S.; Schubach, T.M.P.; Pereira, S.A.; Fernandes, G.F.; Bezerra, L.M.L.; Felipe, M.S.; De Camargo, Z.P. Phylogenetic Analysis Reveals a High Prevalence of Sporothrix brasiliensis in Feline Sporotrichosis Outbreaks. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrillaga-Moncrieff, I.; Capilla, J.; Mayayo, E.; Marimon, R.; Marine, M.; Genis, J.; Cano-Lira, J.F.; Guarro, J. Different virulence levels of the species of Sporothrix in a murine model. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2009, 15, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, G.F.; dos Santos, P.O.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Sasaki, A.A.; Burger, E.; de Camargo, Z.P. Characterization of virulence profile, protein secretion and immunogenicity of different Sporothrix schenckii sensu stricto isolates compared with S. globose and S. brasiliensis species. Virulence 2013, 4, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossato, L.; Dos Santos, S.S.; Ferreira, L.G.; De Almeida, S.R. The importance of Toll-like receptor 4 during experimental Sporothrix brasiliensis infection. Med. Mycol. 2019, 57, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa-Moreira, D.; Menezes, R.C.; Romeo, O.; Borba, C.M.; Oliveira, M.M.E. Clinical and Anatomopathological Evaluation of BALB/c Murine Models Infected with Isolates of Seven Pathogenic Sporothrix Species. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubach, T.M.P.; Schubach, A.; Okamoto, T.; Barros, M.B.L.; Figueiredo, F.B.; Cuzzi, T.; Fialho-Monteiro, P.C.; Reis, R.S.; Perez, M.A.; Wanke, B. Evaluation of an epidemic of sporotrichosis in cats: 347 cases (1998–2001). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2004, 224, 1623–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etchecopaz, A.; Toscanini, M.; Gisbert, A.; Mas, J.; Scarpa, M.; Iovannitti, C.; Bendezú, K.; Nusblat, A.; Iachini, R.; Cuestas, M. Sporothrix brasiliensis: A Review of an Emerging South American Fungal Pathogen, Its Related Disease, Presentation and Spread in Argentina. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gremião, I.D.F.; Miranda, L.H.M.; Reis, E.G.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Pereira, S.A. Zoonotic Epidemic of Sporotrichosis: Cat to Human Transmission. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanamberg, A.; Araujo, R.; Ravazzolo, A.P.; Driemeier, D.; Driemeier, R.M.S.; Ferreiro, L. Sporothrix brasiliensis on cats with skin ulcers in Southern Brazil. Med. Mycol. 2021, 59, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, S.; Arias-Rodriguez, C.; Sánchez-Cifuentes, E.A.; Santa-Vélez, C.; Larrañaga-Piñeres, I.; Gaviria-Barrera, M.E.; Vásquez-Ochoa, L.A.; Montoya, D.; Jiménez-Alzate, M.D.P. First three cases of cat-associated zoonotic cutaneous sporotrichosis in Colombia. Int. J. Dermatol. 2022, 61, 1276–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, G.M.P.; Borba-Santos, L.P.; Vila, T.; Gremião, I.D.F.; Pereira, S.A.; De Souza, W.; Rozental, S. Sporothrix spp. Biofilms Impact in the Zoonotic Transmission Route: Feline Claws Associated Biofilms, Itraconazole Tolerance, and Potential Repurposing for Miltefosine. Pathogens 2022, 11, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Andrade Galliano Daros Bastos, F.; Raimundo Cognialli, R.C.; Rodrigues de Farias, M.; Dos Santos Monti, F.; Wu, K.; Queiroz-Telles, F. Spread of Sporothrix spp. through respiratory droplets from infected cats: A potential route of transmission. Med. Mycol. 2022, 60, myac079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossow, J.A.; Queiroz-Telles, F.; Caceres, D.H.; Beer, K.D.; Jackson, B.R.; Pereira, J.G.; Ferreira Gremião, I.D.; Pereira, S.A. A One Health Approach to Combatting Sporothrix brasiliensis: Narrative Review of an Emerging Zoonotic Fungal Pathogen in South America. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fichman, V.; Freitas, D.F.S.; de Macedo, P.M.; Valle, A.C.F.D.; Almeida-Silva, F.; Zancopé-Oliveira, R.M.; Almeida-Paes, R.; Gutierrez-Galhardo, M.C. Sporotrichosis After Tattooing Caused by Sporothrix brasiliensis. Mycopathologia 2022, 187, 137–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgado, D.S.; Castro, R.; Ribeiro-Alves, M.; Corrêa-Moreira, D.; Castro-Alves, J.; Pereira, S.A.; Menezes, R.C.; Oliveira, M.M.E. Global distribution of animal sporotrichosis: A systematic review of Sporothrix sp. identified using molecular tools. Curr. Res. Microb. Sci. 2022, 3, 100140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.S.; Kano, R. Feline sporotrichosis in Asia. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2021, 52, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veasey, J.V.; Carvalho, G.S.M.; Ruiz, L.R.B.; Neves Neto, M.F.; Zaitz, C. Epidemiological and geographical distribution profile of urban sporotrichosis in the city of São Paulo. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2022, 97, 228–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida-Silva, F.; Rabello, V.B.S.; Scramignon-Costa, B.S.; Zancopé-Oliveira, R.M.; de Macedo, P.M.; Almeida-Paes, R. Beyond Domestic Cats: Environmental Detection of Sporothrix brasiliensis DNA in a Hyperendemic Area of Sporotrichosis in Rio de Janeiro State, Brazil. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boechat, J.S.; Oliveira, M.M.E.; Gremião, I.D.F.; Almeida-Paes, R.; Machado, A.C.S.; Zancopé-Oliveira, R.M.; Oliveira, R.V.C.; Morgado, D.S.; Corrêa, M.L.; Figueiredo, A.B.F.; et al. Sporothrix brasiliensis and Feline Sporotrichosis in the Metropolitan Region of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil (1998–2018). J. Fungi 2022, 8, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, F.B.D.S.; Gadelha, C.L.; Lopes, I.V.; da Silva, M.B.; de Sousa, B.R.; Dulgheroff, A.C.B.; Guerra, F.Q.S.; Ferraz, C.E.; Magalhães, V.; Oliveira, M.M.E.; et al. Dog-transmitted ocular sporotrichosis. J. Mycol. Med. 2022, 33, 101335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho, J.A.; Beale, M.A.; Hagen, F.; Fisher, M.C.; Kano, R.; Bonifaz, A.; Toriello, C.; Negroni, R.; Rego, R.S.M.; Gremião, I.D.F.; et al. Trends in the molecular epidemiology and population genetics of emerging Sporothrix species. Stud. Mycol. 2021, 100, 100129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Miranda, L.H.M.; Meli, M.; Conceição-Silva, F.; Novacco, M.; Menezes, R.C.; Pereira, S.A.; Sugiarto, S.; Dos Reis, É.G.; Gremião, I.D.F.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R. Co-infection with feline retrovirus is related to changes in immunological parameters of cats with sporotrichosis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queiroz-Telles, F.; Buccheri, R.; Benard, G. Sporotrichosis in Immunocompromised Hosts. J. Fungi 2019, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gremião, I.D.; Menezes, R.C.; Schubach, T.M.; Figueiredo, A.B.; Cavalcanti, M.C.; Pereira, S.A. Feline sporotrichosis: Epidemiological and clinical aspects. Med. Mycol. 2015, 53, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boechat, J.S.; Oliveira, M.M.E.; Almeida-Paes, R.; Gremião, I.D.F.; Machado, A.C.S.; Oliveira, R.V.C.; Figueiredo, A.B.F.; Rabello, V.B.S.; Silva, K.B.L.; Zancopé-Oliveira, R.M.; et al. Feline sporotrichosis: Associations between clinical-epidemiological profiles and phenotypic-genotypic characteristics of the etiological agents in the Rio de Janeiro epizootic area. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 2018, 113, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duangkaew, L.; Yurayart, C.; Limsivilai, O.; Chen, C.; Kasorndorkbua, C. Cutaneous sporotrichosis in a stray cat from Thailand. Med. Mycol. Case Rep. 2018, 23, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonsales, F.F.; Fernandes, N.C.C.A.; Mansho, W.; Montenegro, H.; Benites, N.R. Direct PCR of lesions suggestive of sporotrichosis in felines. Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec. 2020, 72, 2002–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacerda Filho, A.M.; Cavalcante, C.M.; Da Silva, A.B.; Inácio, C.P.; de Lima-Neto, R.G.; de Andrade, M.C.L.; Magalhães, O.M.C.; Dos Santos, F.A.G.; Neves, R.P. High-Virulence Cat-Transmitted Ocular Sporotrichosis. Mycopathologia 2019, 184, 547–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinelli, T.P.; Bezerra, L.M.; de Souza, B.O.F.; Rocha, A.; Neto, J.E.; Sá, F.B. Primary conjunctival sporotrichosis in three cats from Northeastern Brazil. Vet. Ophthalmol. 2021, 24, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, H.M.; da Rocha, R.C.B.; de Farias, M.R.; Moore, B.A.; Montiani-Ferreira, F. Ocular lesions in cats diagnosed with systemic sporotrichosis. Vet. Ophthalmol. 2022. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santi, J.P.; Santos, C.R.G.R.; Dos Santos, A.S.; Souza, H.J.M. Intranasal clotrimazole spray 1% associated with oral itraconazole for nasal feline sporotrichosis: A case series. Rev. Bras. Med. Vet. 2022, 44, e004821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.M.; de Hoog, G.S.; de Camargo, Z.P. Feline Sporotrichosis. In Emerging and Epizootic Fungal Infections in Animals; Seyedmousavi, S., de Hoog, G.S., Guillot, J., Verweij, P.E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 1, pp. 199–231. ISBN 978-3-319-72093-7. [Google Scholar]
- Moreira, S.M.; Andrade, E.H.P.; Paiva, M.T.; Zibaoui, H.M.; Salvato, L.A.; Azevedo, M.I.; Oliveira, C.S.F.; Soares, D.F.M.; Keller, K.M.; Magalhães, S.L.; et al. Implementation of an Animal Sporotrichosis Surveillance and Control Program, Southeastern Brazil. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 949–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, K.; de Castro, R.A.; Borba Dos Santos, L.P.; Quintella, L.P.; Lopes-Bezerra, L.M.; Rozental, S. Amphotericin B, alone or followed by itraconazole therapy, is effective in the control of experimental disseminated sporotrichosis by Sporothrix brasiliensis. Med. Mycol. 2015, 53, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinel-Ingroff, A.; Abreu, D.P.B.; Almeida-Paes, R.; Brilhante, R.S.N.; Chakrabarti, A.; Chowdhary, A.; Hagen, F.; Córdoba, S.; Gonzalez, G.M.; Govender, N.P.; et al. Multicenter, International Study of MIC/MEC Distributions for Definition of Epidemiological Cutoff Values for Sporothrix Species Identified by Molecular Methods. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e01057-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, E.W.; Borba, C.M.; Pereira, S.A.; Gremião, I.D.F.; Langohr, I.M.; Oliveira, M.M.E.; de Oliveira, R.V.C.; da Cunha, C.R.; Zancopé-Oliveira, R.M.; de Miranda, L.H.M.; et al. Clinical features, fungal load, coinfections, histological skin changes, and itraconazole treatment response of cats with sporotrichosis caused by Sporothrix brasiliensis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maschio-Lima, T.; Marques, M.D.R.; Lemes, T.H.; Brizzotti-Mazuchi, N.S.; Caetano, M.H.; de Almeida, B.G.; Bianco, L.M.; Monteiro, R.C.; Rodrigues, A.M.; de Camargo, Z.P.; et al. Clinical and epidemiological aspects of feline sporotrichosis caused by Sporothrix brasiliensis and in vitro antifungal susceptibility. Vet. Res. Commun. 2021, 45, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gremião, I.D.F.; de Miranda, L.H.M.; Pereira-Oliveira, G.R.; Menezes, R.C.; Machado, A.C.D.S.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Pereira, S.A. Advances and challenges in the management of feline sporotrichosis. Rev. Iberoam. Micol. 2022, 39, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachman, R.; Ligaj, M.; Chinthapalli, S.; Wani, R.S. Zoonotic acquisition of cutaneous Sporothrix braziliensis infection in the UK. BMJ Case Rep. 2022, 15, e248418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas, R.; Sánchez-Cardenas, C.D.; Ramirez-Hobak, L.; Arriaga, L.F.R.; Memije, M.E.V. Sporotrichosis: From KOH to Molecular Biology. J. Fungi 2018, 4, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marimon, R.; Cano, J.; Gené, J.; Sutton, D.A.; Kawasaki, M.; Guarro, J. Sporothrix brasiliensis, S. globosa, and S. mexicana, Three New Sporothrix Species of Clinical Interest. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 3198–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreira, T.; Corrêa-Moreira, D.; Borba, C.; Moraes, A.; Oliveira, M. Molecular and phenotypic reidentification of Sporothrix schenckii clinical isolates preserved under mineral oil for 34 to 64 years in a culture collection in Brazil. Curr. Res. Microb. Sci. 2022, 3, 100128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.-T.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, X. Molecular identification of Sporothrix clinical isolates in China. J. Zhejiang Univ. B 2014, 15, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marimon, R.; Gené, J.; Cano, J.; Trilles, L.; Dos Santos Lazéra, M.; Guarro, J. Molecular Phylogeny of Sporothrix schenckii. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 3251–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Beer, Z.; Duong, T.; Wingfield, M. The divorce of Sporothrix and Ophiostoma: Solution to a problematic relationship. Stud. Mycol. 2016, 83, 165–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Carvalho, J.A.; Monteiro, R.C.; Hagen, F.; de Camargo, Z.P.; Rodrigues, A.M. Trends in Molecular Diagnostics and Genotyping Tools Applied for Emerging Sporothrix Species. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI standard M38; CLSI Reference Method for Broth Dilution Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of Filamentous Fungi 2008 Approved Standard—Second Edition. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2008; 52p.
- Oliveira, D.C.; Lopes, P.G.M.; Spader, T.B.; Mahl, C.D.; Tronco-Alves, G.R.; Lara, V.M.; Santurio, J.M.; Alves, S.H. Antifungal Susceptibilities of Sporothrix albicans, S. brasiliensis, and S. luriei of the S. schenckii Complex Identified in Brazil. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 3047–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macêdo-Sales, P.A.; Souza, L.O.P.; Della-Terra, P.P.; Lozoya-Pérez, N.E.; Machado, R.L.D.; Rocha, E.M.D.S.D.; Lopes-Bezerra, L.M.; Guimarães, A.J.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Mora-Montes, H.M.; et al. Coinfection of domestic felines by distinct Sporothrix brasiliensis in the Brazilian sporotrichosis hyperendemic area. Fungal Genet Biol. 2020, 140, 103397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenegro, H.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Dias, M.A.G.; Da Silva, E.A.; Bernardi, F.; De Camargo, Z.P. Feline sporotrichosis due to Sporothrix brasiliensis: An emerging animal infection in São Paulo, Brazil. BMC Vet. Res. 2014, 10, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gremião, I.D.F.; Oliveira, M.M.E.; De Miranda, L.H.M.; Freitas, D.F.S.; Pereira, S.A. Geographic Expansion of Sporotrichosis, Brazil. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 621–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.A.; Passos, S.R.L.; Silva, J.N.; Gremião, I.D.F.; Figueiredo, F.B.; Teixeira, J.L.; Monteiro, P.C.F.; Schubach, T.M.P. Response to azolic antifungal agents for treating feline sporotrichosis. Vet. Rec. 2010, 166, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.M.E.; Almeida-Paes, R.; Muniz, M.M.; Gutierrez-Galhardo, M.C.; Zancope-Oliveira, R.M. Phenotypic and Molecular Identification of Sporothrix Isolates from an Epidemic Area of Sporotrichosis in Brazil. Mycopathologia 2011, 172, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, C.N.; Odaguiri, J.; Larsson, C.E. Retrospective assessment of the treatment of sporotrichosis in cats and dogs using itraconazole. Acta Sci. Vet. 2013, 41, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- De Miranda, L.H.M.; Silva, J.N.; Gremião, I.D.F.; Menezes, R.C.; Almeida-Paes, R.; Dos Reis, G.; Oliveira, R.D.V.C.D.; De Araujo, D.S.D.A.; Ferreiro, L.; Pereira, S.A. Monitoring Fungal Burden and Viability of Sporothrix spp. in Skin Lesions of Cats for Predicting Antifungal Treatment Response. J. Fungi 2018, 4, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida-Paes, R.; Brito-Santos, F.; Figueiredo-Carvalho, M.H.G.; Machado, A.C.S.; Oliveira, M.M.E.; Pereira, S.A.; Gutierrez-Galhardo, M.C.; Zancopé-Oliveira, R.M. Minimal inhibitory concentration distributions and epidemiological cutoff values of five antifungal agents against Sporothrix brasiliensis. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2017, 112, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Rocha, R.F.D.B.; Schubach, T.M.P.; Pereira, S.A.; dos Reis, G.; Carvalho, B.W.; Gremião, I.D.F. Refractory feline sporotrichosis treated with itraconazole combined with potassium iodide. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2018, 59, 720–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcão, E.M.M.; de Lima Filho, J.B.; Campos, D.P.; Valle, A.C.F.D.; Bastos, F.I.; Gutierrez-Galhardo, M.C.; Freitas, D.F.S. Hospitalizações e óbitos relacionados à esporotricose no Brasil (1992–2015) [Hospitalizations and deaths related to sporotrichosis in Brazil (1992–2015)]. Cad. Saude Publica 2019, 35, e00109218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, É.G.; Schubach, T.M.; Pereira, S.A.; Silva, J.N.; Carvalho, B.W.; Quintana, M.S.; Gremião, I.D. Association of itraconazole and potassium iodide in the treatment of feline sporotrichosis: A prospective study. Med. Mycol. 2016, 54, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.M.; Gonçalves, S.S.; de Carvalho, J.A.; Borba-Santos, L.P.; Rozental, S.; de Camargo, Z.P. Current Progress on Epidemiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Sporotrichosis and Their Future Trends. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.T.; Menezes, R.C.; Gremião, I.D.; Schubach, T.M.; Boechat, J.S.; Pereira, S.A. Zoonotic sporotrichosis: Biosafety procedures. Acta Sci. Vet. 2012, 40, 1067. [Google Scholar]
- Seyedmousavi, S.; Guillot, J.; Tolooe, A.; Verweij, P.E.; de Hoog, G.S. Neglected fungal zoonoses: Hidden threats to man and animals. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).