An Alpha-Glucan from Lomentospora prolificans Mediates Fungal–Host Interaction Signaling through Dectin-1 and Mincle
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microorganisms and Growth Conditions
2.2. Extraction and Purification of α-Glucan
2.3. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (NMR)
2.4. Production of Rabbit Immune Serum
2.5. Mice
2.6. Cytotoxicity of α-Glucan
2.7. α-Amyloglucosidase Treatment
2.8. ELISA
2.9. Flow Cytometer Analysis
2.10. Phagocytic Assay
2.11. Quantification of Nitric Oxide and Superoxide
2.12. Cytokines Assays
2.13. C-Type Lectin Receptors (CLRs) Reporter Assay
2.14. TLR2 and TLR4 Reporter Assay
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
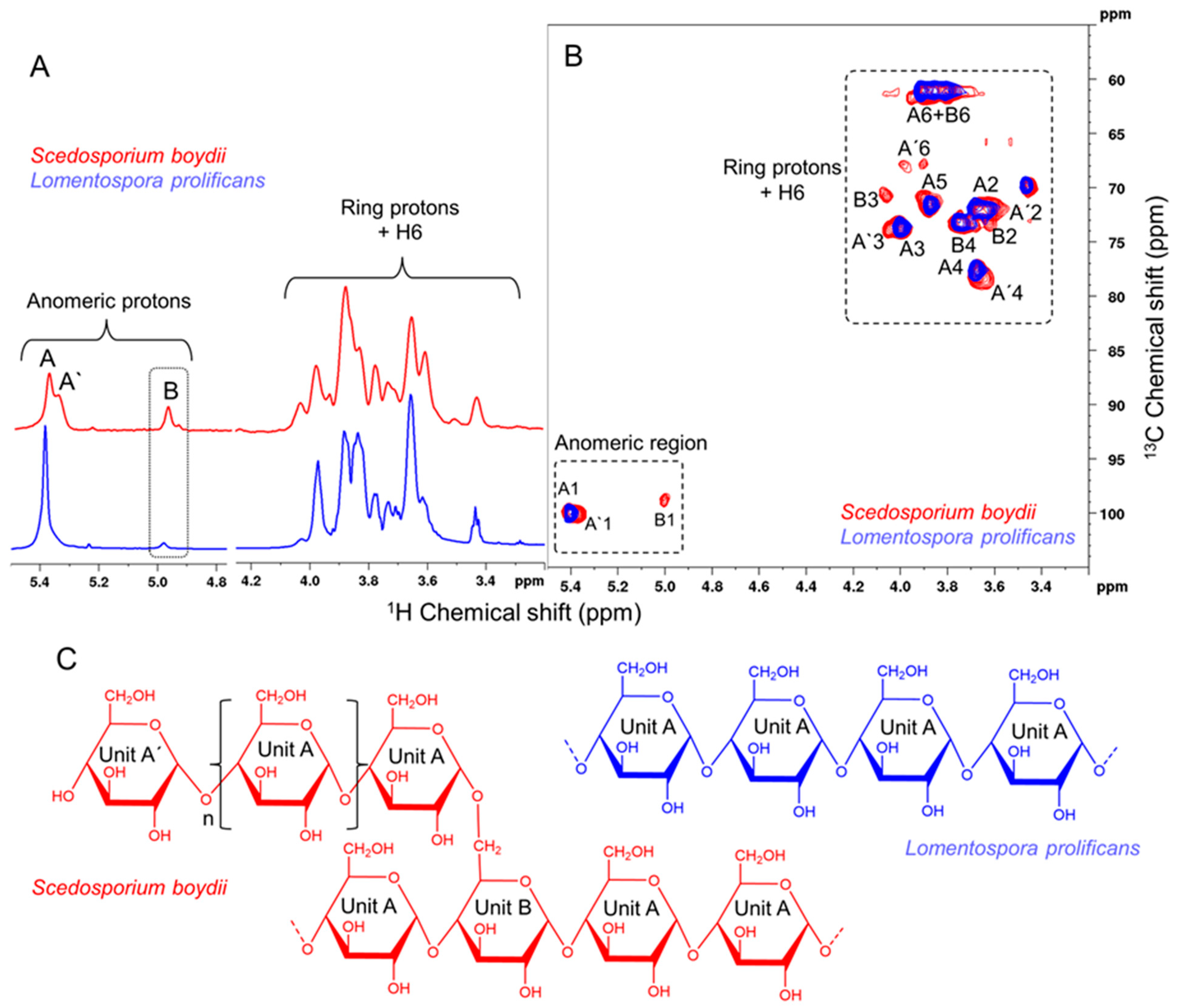
3.1. Isolation and Characterization of L. prolificans α-Glucan
3.2. α-Glucan Is Detected on the Surface of L. prolificans Conidia
3.3. α-Glucan Plays a Role in the Phagocytosis of L. prolificans by Macrophages
3.4. α-Glucan Induces Nitric Oxide and Superoxide Release by Macrophages
3.5. L. prolificans α-Glucan Is Unable to Induce TNF-α Production
3.6. L. prolificans α-Glucan Is Recognized by TLR2
3.7. L. prolificans α-Glucan Is Recognized by Dectin-1 and Mincle
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cortez, K.J.; Roilides, E.; Quiroz-Telles, F.; Meletiadis, J.; Antachopoulos, C.; Knudsen, T.; Buchanan, W.; Milanovich, J.; Sutton, D.A.; Fothergill, A.; et al. Infections caused by Scedosporium spp. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 21, 157–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lackner, M.; de Hoog, G.S.; Yang, L.; Ferreira Moreno, L.; Ahmed, S.A.; Andreas, F.; Kaltseis, J.; Nagl, M.; Lass-Flörl, C.; Risslegger, B.; et al. Proposed nomenclature for Pseudallescheria, Scedosporium and related genera. Fungal Divers. 2014, 67, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilgado, F.; Cano, J.; Gené, J.; Serena, C.; Guarro, J. Different virulence of the species of the Pseudallescheria boydii complex. Med. Mycol. 2009, 47, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harun, A.; Gilgado, F.; Chen, S.C.; Meyer, W. Abundance of Pseudallescheria/Scedosporium species in the Australian urban environment suggests a possible source for scedosporiosis including the colonization of airways in cystic fibrosis. Med. Mycol. 2010, 48 (Suppl. S1), S70–S76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buldain, I.; Martin-Souto, L.; Antoran, A.; Areitio, M.; Aparicio-Fernandez, L.; Rementeria, A.; Hernando, F.L.; Ramirez-Garcia, A. The Host Immune Response to Scedosporium/Lomentospora. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreto-Bergter, E.; Figueiredo, R.T. Fungal glycans and the innate immune recognition. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2014, 4, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bittencourt, V.C.; Figueiredo, R.T.; da Silva, R.B.; Mourão-Sá, D.S.; Fernandez, P.L.; Sassaki, G.L.; Mulloy, B.; Bozza, M.T.; Barreto-Bergter, E. An alpha-glucan of Pseudallescheria boydii is involved in fungal phagocytosis and Toll-like receptor activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 22614–22623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. A colorimetric method for the determination of sugars. Nature 1951, 168, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.S.; Vilela-Silva, A.C.; Valente, A.P.; Mourão, P.A. A 2-sulfated, 3-linked alpha-L-galactan is an anticoagulant polysaccharide. Carbohydr. Res. 2002, 337, 2231–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomin, V.H.; Valente, A.P.; Pereira, M.S.; Mourão, P.A. Mild acid hydrolysis of sulfated fucans: A selective 2-desulfation reaction and an alternative approach for preparing tailored sulfated oligosaccharides. Glycobiology 2005, 15, 1376–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haido, R.M.T.; Silva, M.H.; Ejzemberg, R.; Leitão, E.A.; Hearn, V.M.; Evans, E.G.V.; Bergter, E.B. Analysis of peptidogalactomannans from the mycelial surface of Aspergillus fumigatus. Med. Mycol. 1998, 36, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borenfreund, E.; Puerner, J.A. Toxicity determined in vitro by morphological alterations and neutral red absorption. Toxicol. Lett. 1985, 24, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xisto, M.I.; Bittencourt, V.C.; Liporagi-Lopes, L.C.; Haido, R.M.; Mendonça, M.S.; Sassaki, G.; Figueiredo, R.T.; Romanos, M.T.; Barreto-Bergter, E. O-glycosylation in cell wall proteins in Scedosporium prolificans is critical for phagocytosis and inflammatory cytokines production by macrophages. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dake, M.S.; Jadhv, J.P.; Patil, N.B. Variations of two pools of glycogen and carbohydrate in Saccharomyces cerevisiae grown with various ethanol concentrations. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 37, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitao, E.A.; Bittencourt, V.C.; Haido, R.M.; Valente, A.P.; Peter-Katalinic, J.; Letzel, M.; de Souza, L.M.; Barreto-Bergter, E. Beta-galactofuranose-containing O-linked oligosaccharides present in the cell wall peptidogalactomannan of Aspergillus fumigatus contain immunodominant epitopes. Glycobiology 2003, 13, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Meirelles, J.V.; Xisto, M.; Rollin-Pinheiro, R.; Serrato, R.V.; Haido, R.M.T.; Barreto-Bergter, E. Peptidorhamanomannan: A surface fungal glycoconjugate from Scedosporium aurantiacum and Scedosporium minutisporum and its recognition by macrophages. Med. Mycol. 2021, 59, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xisto, M.; Santos, S.S.; Rossato, L.; Yoshikawa, F.S.Y.; Haido, R.M.T.; de Almeida, S.R.; Barreto-Bergter, E. Peptidorhamnomannan from Lomentospora prolificans modulates the inflammatory response in macrophages infected with Candida albicans. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madesh, M.; Balasubramanian, K.A. Microtiter plate assay for superoxide dismutase using MTT reduction by superoxide. Indian J. Biochem. Biophys. 1998, 35, 184–188. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; LeBert, V.; Hung, C.Y.; Galles, K.; Saijo, S.; Lin, X.; Cole, G.T.; Klein, B.S.; Wüthrich, M. C-type lectin receptors differentially induce th17 cells and vaccine immunity to the endemic mycosis of North America. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 1107–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xisto, M.; Henao, J.E.M.; Dias, L.D.S.; Santos, G.M.P.; Calixto, R.O.R.; Bernardino, M.C.; Taborda, C.P.; Barreto-Bergter, E. Glucosylceramides From Lomentospora prolificans Induce a Differential Production of Cytokines and Increases the Microbicidal Activity of Macrophages. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shiokawa, M.; Yamasaki, S.; Saijo, S. C-type lectin receptors in anti-fungal immunity. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2017, 40, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiredo, R.T.; Fernandez, P.L.; Dutra, F.F.; González, Y.; Lopes, L.C.; Bittencourt, V.C.; Sassaki, G.L.; Barreto-Bergter, E.; Bozza, M.T. TLR4 recognizes Pseudallescheria boydii conidia and purified rhamnomannans. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 40714–40723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rappleye, C.A.; Eissenberg, L.G.; Goldman, W.E. Histoplasma capsulatum alpha-(1,3)-glucan blocks innate immune recognition by the beta-glucan receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 1366–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fontaine, T.; Beauvais, A.; Loussert, C.; Thevenard, B.; Fulgsang, C.C.; Ohno, N.; Clavaud, C.; Prevost, M.C.; Latgé, J.P. Cell wall alpha1-3glucans induce the aggregation of germinating conidia of Aspergillus fumigatus. Fungal. Genet. Biol. 2010, 47, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele, C.; Rapaka, R.R.; Metz, A.; Pop, S.M.; Williams, D.L.; Gordon, S.; Kolls, J.K.; Brown, G.D. The beta-glucan receptor dectin-1 recognizes specific morphologies of Aspergillus fumigatus. PLoS Pathog. 2005, 1, e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dinadayala, P.; Sambou, T.; Daffé, M.; Lemassu, A. Comparative structural analyses of the alpha-glucan and glycogen from Mycobacterium bovis. Glycobiology 2008, 18, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smythe, C.; Villar-Palasi, C.; Cohen, P. Structural and functional studies on rabbit liver glycogenin. Eur. J. Biochem. 1989, 183, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, L. Immunity to fungal infections. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhithasri, V.; Nisha, N.; Biswas, L.; Anil Kumar, V.; Biswas, R. Innate immune recognition of microbial cell wall components and microbial strategies to evade such recognitions. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 168, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.D. Innate antifungal immunity: The key role of phagocytes. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kudeken, N.; Kawakami, K.; Saito, A. Different susceptibilities of yeasts and conidia of Penicillium marneffei to nitric oxide (NO)-mediated fungicidal activity of murine macrophages. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1998, 112, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brummer, E.; Stevens, D.A. Antifungal mechanisms of activated murine bronchoalveolar or peritoneal macrophages for Histoplasma capsulatum. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1995, 102, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Casadevall, A. Susceptibility of melanized and nonmelanized Cryptococcus neoformans to nitrogen- and oxygen-derived oxidants. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 3004–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blasi, E.; Pitzurra, L.; Puliti, M.; Chimienti, A.R.; Mazzolla, R.; Barluzzi, R.; Bistoni, F. Differential susceptibility of yeast and hyphal forms of Candida albicans to macrophage-derived nitrogen-containing compounds. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 1806–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandes, K.S.; Coelho, A.L.; Lopes Bezerra, L.M.; Barja-Fidalgo, C. Virulence of Sporothrix schenckii conidia and yeast cells, and their susceptibility to nitric oxide. Immunology 2000, 101, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latgé, J.P. Aspergillus fumigatus and aspergillosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 12, 310–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van der Graaf, C.A.; Netea, M.G.; Verschueren, I.; van der Meer, J.W.; Kullberg, B.J. Differential cytokine production and Toll-like receptor signaling pathways by Candida albicans blastoconidia and hyphae. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 7458–7464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kakutani, R.; Adachi, Y.; Takata, H.; Kuriki, T.; Ohno, N. Essential role of Toll-like receptor 2 in macrophage activation by glycogen. Glycobiology 2012, 22, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishikawa, E.; Ishikawa, T.; Morita, Y.S.; Toyonaga, K.; Yamada, H.; Takeuchi, O.; Kinoshita, T.; Akira, S.; Yoshikai, Y.; Yamasaki, S. Direct recognition of the mycobacterial glycolipid, trehalose dimycolate, by C-type lectin Mincle. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 2879–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schoenen, H.; Bodendorfer, B.; Hitchens, K.; Manzanero, S.; Werninghaus, K.; Nimmerjahn, F.; Agger, E.M.; Stenger, S.; Andersen, P.; Ruland, J.; et al. Cutting edge: Mincle is essential for recognition and adjuvanticity of the mycobacterial cord factor and its synthetic analog trehalose-dibehenate. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 2756–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kottom, T.J.; Hebrink, D.M.; Jenson, P.E.; Nandakumar, V.; Wüthrich, M.; Wang, H.; Klein, B.; Yamasaki, S.; Lepenies, B.; Limper, A.H. The Interaction of Pneumocystis with the C-Type Lectin Receptor Mincle Exerts a Significant Role in Host Defense against Infection. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 3515–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ishikawa, T.; Itoh, F.; Yoshida, S.; Saijo, S.; Matsuzawa, T.; Gonoi, T.; Saito, T.; Okawa, Y.; Shibata, N.; Miyamoto, T.; et al. Identification of distinct ligands for the C-type lectin receptors Mincle and Dectin-2 in the pathogenic fungus Malassezia. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 13, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, T.; Hosono, Y.; Shimizu, T.; Yamasaki, S.; Williams, S.J. Candida albicans steryl 6-O-acyl-α-D-mannosides agonize signalling through Mincle. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 15060–15063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, M.; Dambuza, I.M.; Asamaphan, P.; Stappers, M.; Reid, D.; Yamasaki, S.; Brown, G.D.; Gow, N.A.R.; Erwig, L.P. The pattern recognition receptors dectin-2, mincle, and FcRγ impact the dynamics of phagocytosis of Candida, Saccharomyces, Malassezia, and Mucor species. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feinberg, H.; Jégouzo, S.A.F.; Rex, M.J.; Drickamer, K.; Weis, W.I.; Taylor, M.E. Mechanism of pathogen recognition by human dectin-2. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 13402–13414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGreal, E.P.; Rosas, M.; Brown, G.D.; Zamze, S.; Wong, S.Y.; Gordon, S.; Martinez-Pomares, L.; Taylor, P.R. The carbohydrate-recognition domain of Dectin-2 is a C-type lectin with specificity for high mannose. Glycobiology 2006, 16, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masuda, Y.; Nakayama, Y.; Mukae, T.; Tanaka, A.; Naito, K.; Konishi, M. Maturation of dendritic cells by maitake α-glucan enhances anti-cancer effect of dendritic cell vaccination. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 67, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodridge, H.S.; Wolf, A.J.; Underhill, D.M. Beta-glucan recognition by the innate immune system. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 230, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa Mda, G.; Reid, D.M.; Schweighoffer, E.; Tybulewicz, V.; Ruland, J.; Langhorne, J.; Yamasaki, S.; Taylor, P.R.; Almeida, S.R.; Brown, G.D. Restoration of pattern recognition receptor costimulation to treat chromoblastomycosis, a chronic fungal infection of the skin. Cell Host Microbe 2011, 9, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wevers, B.A.; Kaptein, T.M.; Zijlstra-Willems, E.M.; Theelen, B.; Boekhout, T.; Geijtenbeek, T.B.; Gringhuis, S.I. Fungal engagement of the C-type lectin mincle suppresses dectin-1-induced antifungal immunity. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 15, 494–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Atoms | →4)-αGlc(1→ (Unit A) | αGlc(1→4) (Unit A′) | →4,6)-αGlc(1→4) (Unit B) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S. boydiia | |||
| H/C1 | 5.39/100.5 | 5.38/100.1 | 4.98/99.2 |
| H/C2 | 3.66/72.2 | 3.66/72.3 | 3.61/ND |
| H/C3 | 3.96/73.9 | 3.97/74.0 | 4.00/ND |
| H/C4 | 3.66/78.0 | 3.64/78.0 | 3.65/78.8 |
| H/C5 | 3.88/71.9 | 3.85/72.0 | 3.89/ND |
| H/C6 | 3.87/61.3 | 3.90/61.3 | ND/ND |
| S. boydiib | |||
| H/C1 | 5.38/100.1 | 5.34/100.1 | 4.97/98.9 |
| H/C2 | 3.64/71.8 | 3.60/71.8 | 3.59/73.4 |
| H/C3 | 3.97/73.5 | 4.02/73.6 | 4.03/70.6 |
| H/C4 | 3.64/77.6 | 3.62/77.0 | 3.66/73.4 |
| H/C5 | 3.85/71.7 | 3.88/70.6 | ND |
| H/C6 | 3.87–3.77/60.9 | 3.96–3.87/67.6 | 3.87–3.77/60.9 |
| L. prolificansb | |||
| H/C1 | 5.38/100.1 | ND | ND |
| H/C2 | 3.64/71.8 | ND | ND |
| H/C3 | 3.97/73.5 | ND | ND |
| H/C4 | 3.64/77.6 | ND | ND |
| H/C5 | 3.85/71.7 | ND | ND |
| H/C6 | 3.87–3.77/60.9 | ND | ND |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xisto, M.I.D.d.S.; Dias, L.d.S.; Bezerra, F.F.; Bittencourt, V.C.B.; Rollin-Pinheiro, R.; Cartágenes-Pinto, A.C.; Haido, R.M.T.; Mourão, P.A.d.S.; Barreto-Bergter, E. An Alpha-Glucan from Lomentospora prolificans Mediates Fungal–Host Interaction Signaling through Dectin-1 and Mincle. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9030291
Xisto MIDdS, Dias LdS, Bezerra FF, Bittencourt VCB, Rollin-Pinheiro R, Cartágenes-Pinto AC, Haido RMT, Mourão PAdS, Barreto-Bergter E. An Alpha-Glucan from Lomentospora prolificans Mediates Fungal–Host Interaction Signaling through Dectin-1 and Mincle. Journal of Fungi. 2023; 9(3):291. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9030291
Chicago/Turabian StyleXisto, Mariana Ingrid Dutra da Silva, Lucas dos Santos Dias, Francisco Felipe Bezerra, Vera Carolina Bordallo Bittencourt, Rodrigo Rollin-Pinheiro, Ana Carolina Cartágenes-Pinto, Rosa Maria Tavares Haido, Paulo Antônio de Souza Mourão, and Eliana Barreto-Bergter. 2023. "An Alpha-Glucan from Lomentospora prolificans Mediates Fungal–Host Interaction Signaling through Dectin-1 and Mincle" Journal of Fungi 9, no. 3: 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9030291
APA StyleXisto, M. I. D. d. S., Dias, L. d. S., Bezerra, F. F., Bittencourt, V. C. B., Rollin-Pinheiro, R., Cartágenes-Pinto, A. C., Haido, R. M. T., Mourão, P. A. d. S., & Barreto-Bergter, E. (2023). An Alpha-Glucan from Lomentospora prolificans Mediates Fungal–Host Interaction Signaling through Dectin-1 and Mincle. Journal of Fungi, 9(3), 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9030291








