Fungal Aeroallergens—The Impact of Climate Change
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Allergy Epidemiology
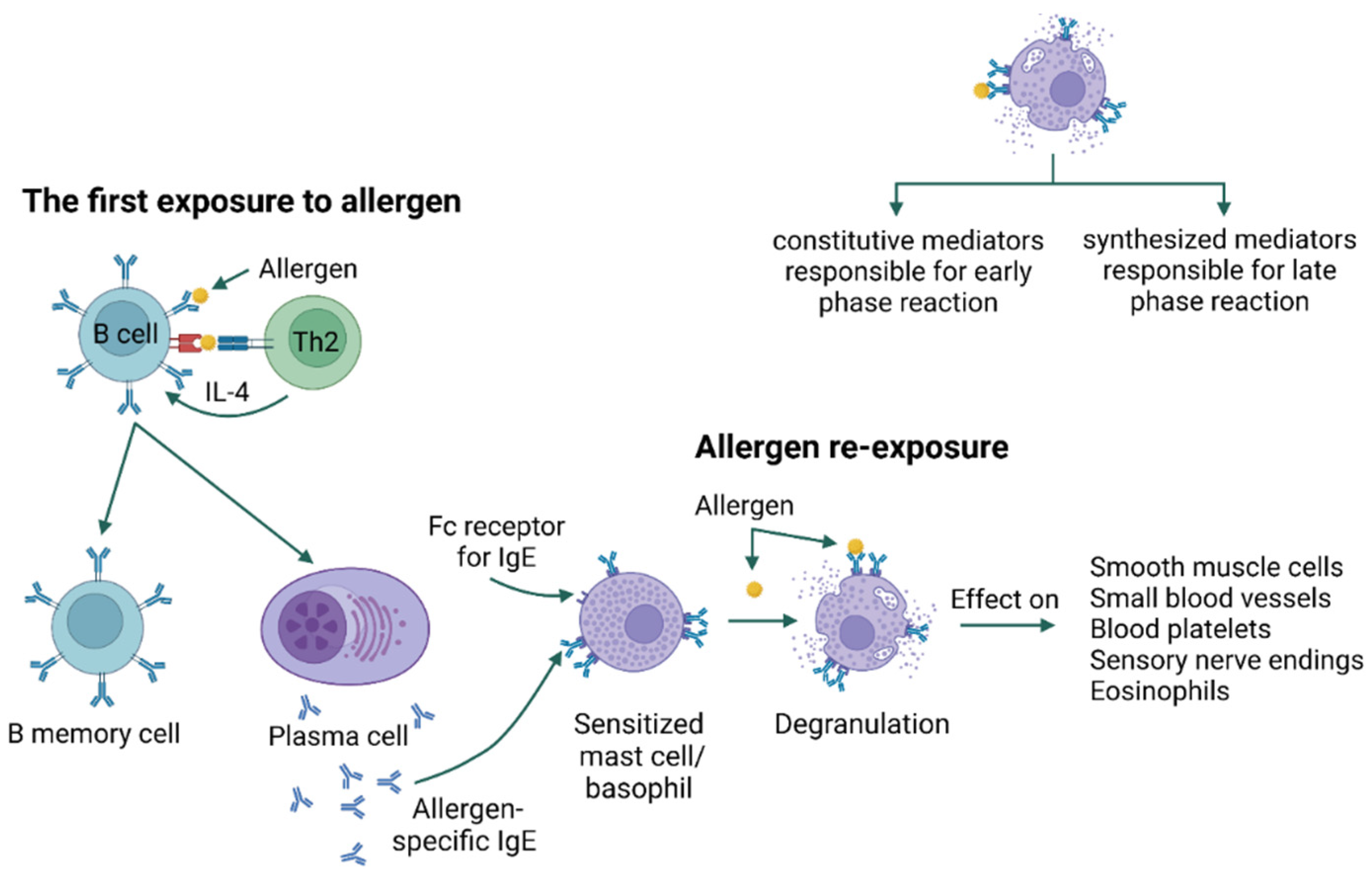
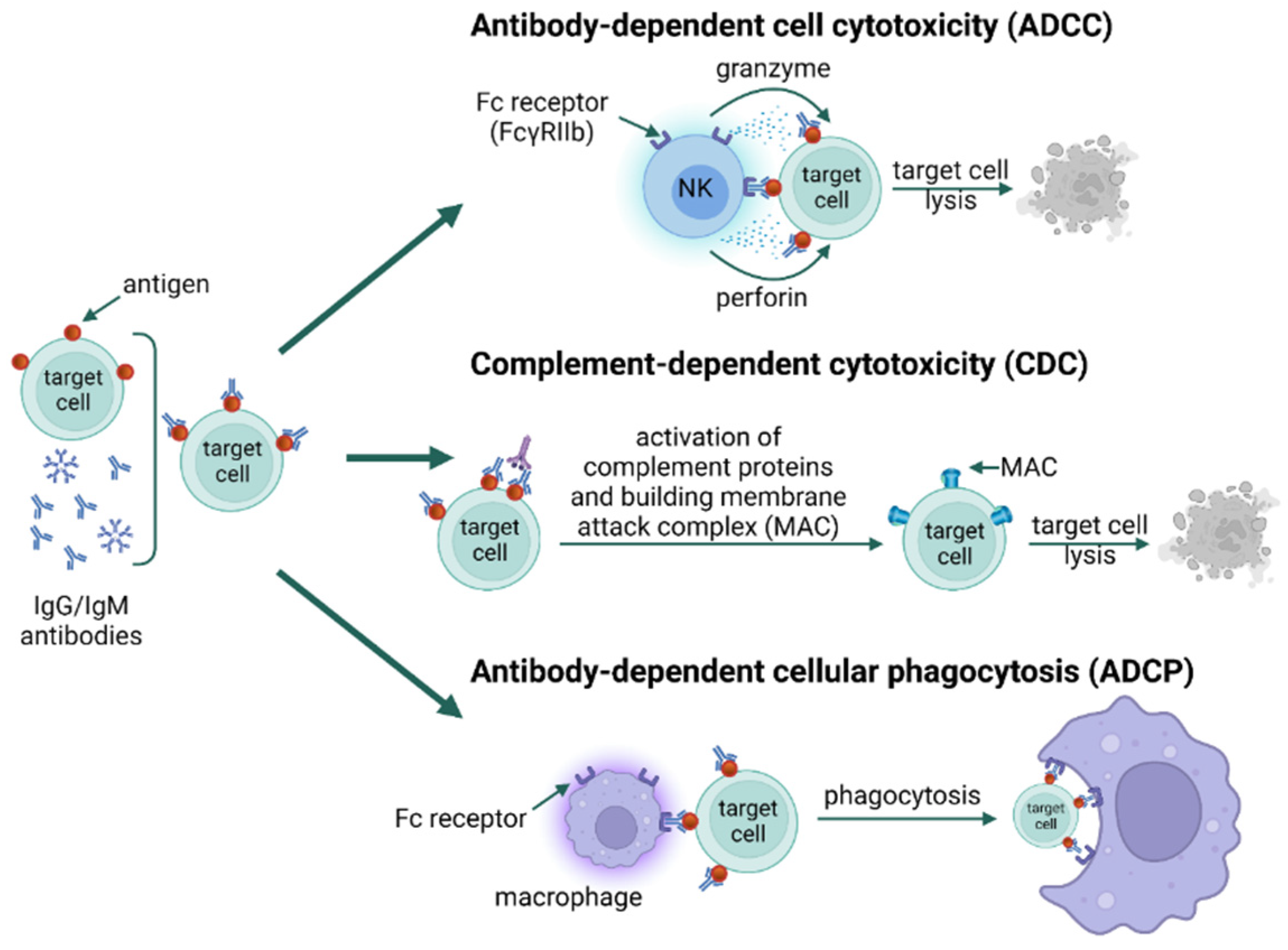
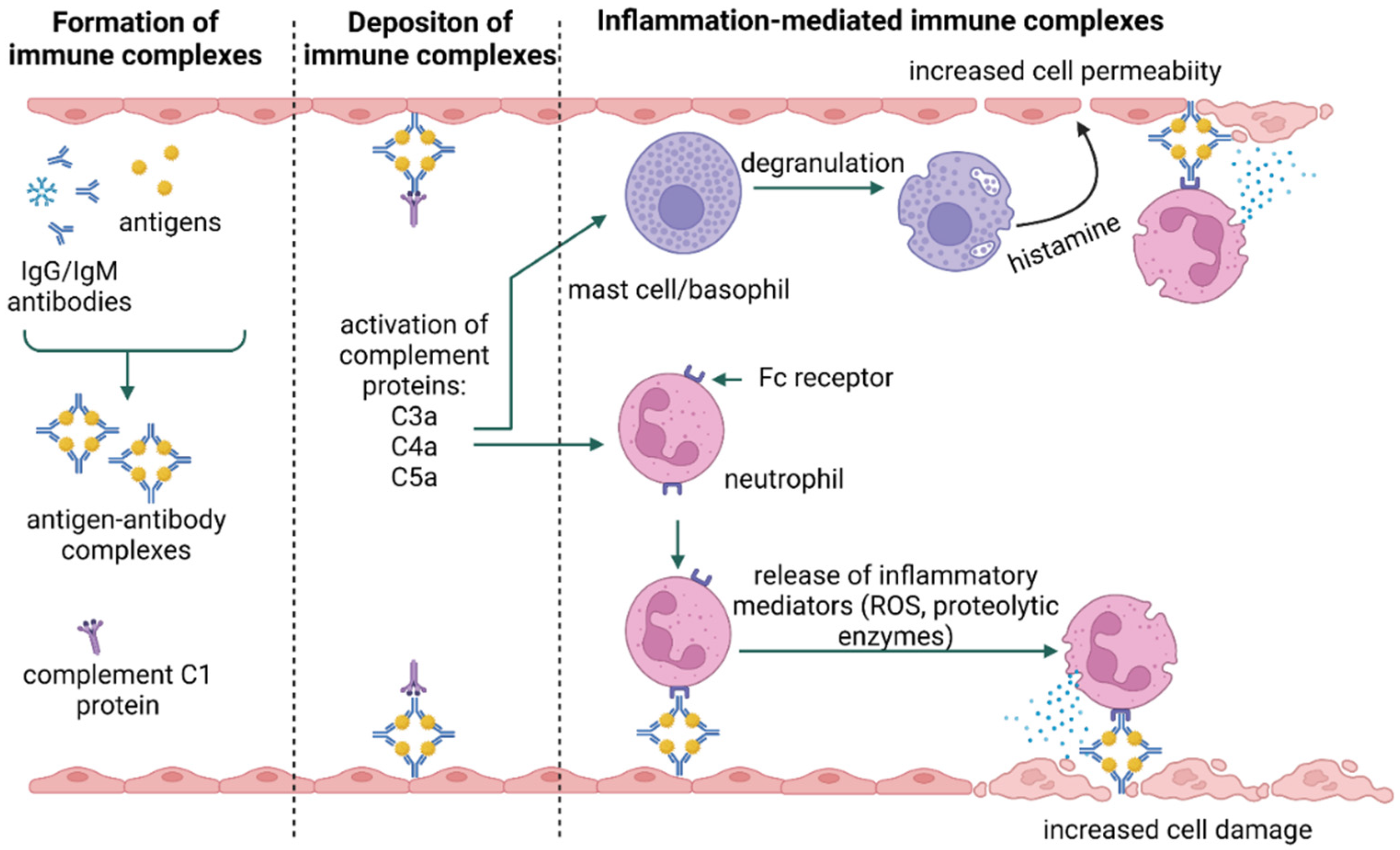
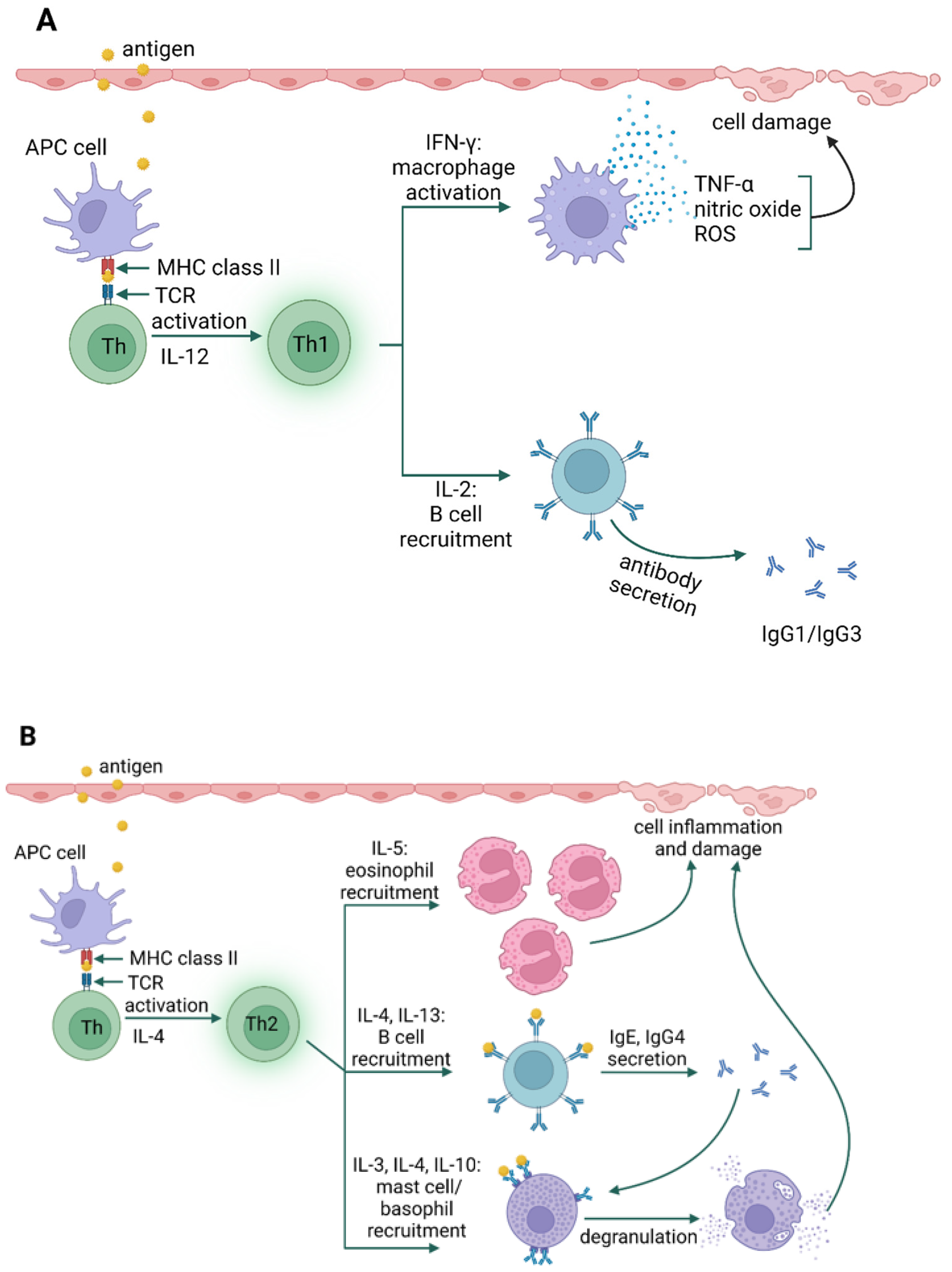
3. Types of Hypersensitivity Reactions
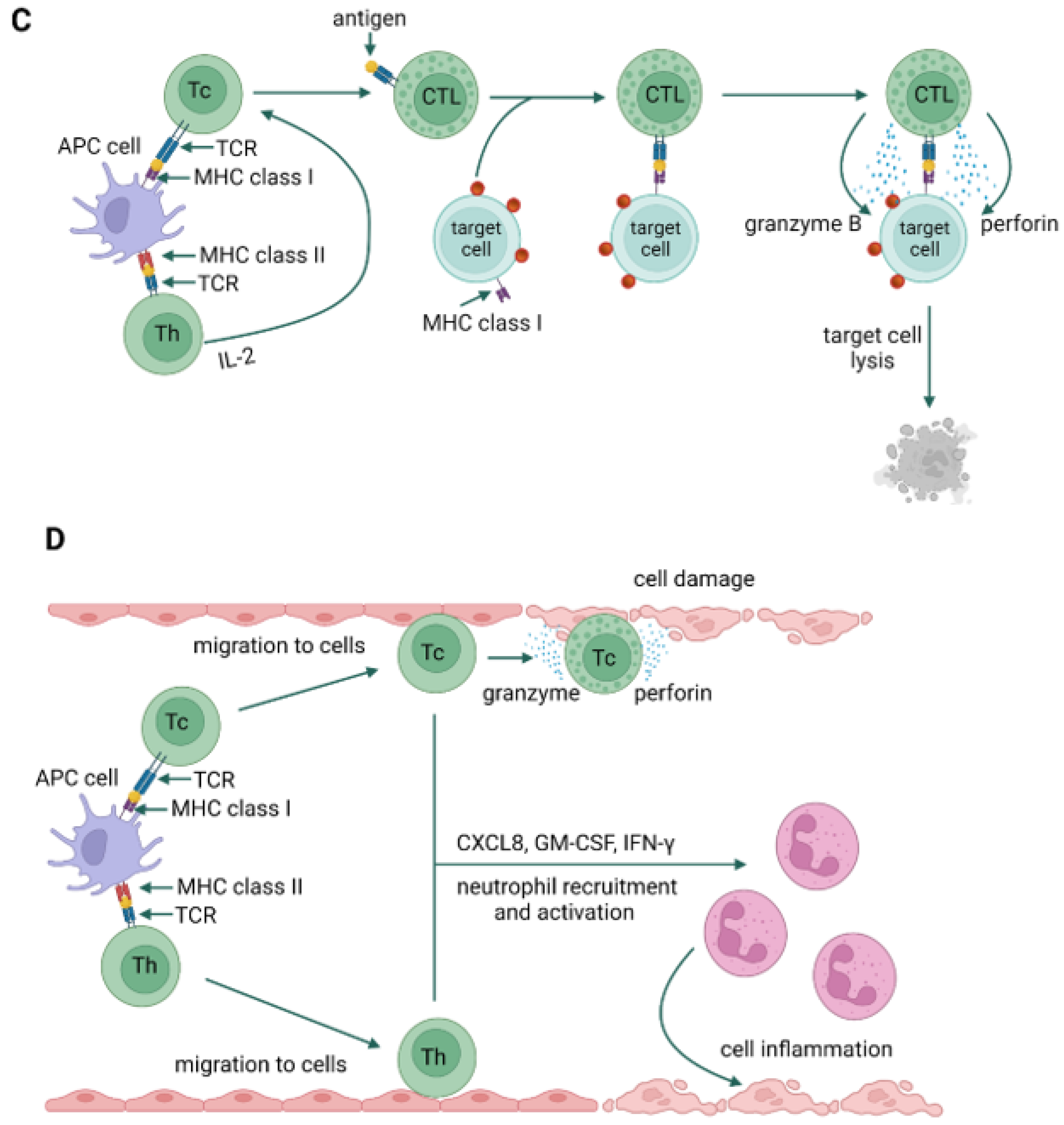
4. Allergy Mechanism
5. Fungal Aeroallergens
6. Clinical Manifestations of Fungal Hypersensitivity
6.1. Allergic Rhinitis (AR)
6.2. Allergic Fungal Rhinosinusitis (AFSR)
6.3. Allergic Bronchopulmonary Mycosis (ABPM)
6.4. Allergic Asthma
6.5. Severe Asthma with Fungal Sensitization (SAFS)
7. Impact of Climate Change on Fungal Aeroallergens
Fungal Plant Parasites as a Source of New Allergens—Impact of Climate Change
- −
- plant parasites are commonly found in the human environment;
- −
- large numbers of spores are produced on the surface of infected plant organs and in the air. In favorable environmental conditions, spores are released into the air in enormous numbers. Estimates indicate that the number of fungal spores on the surface of infected plant organs and in the air is comparable to the amount of vascular plant pollen [168];
- −
- microfungal spores and fruiting bodies are microscopic, readily carried by air currents, and can be inhaled into the human respiratory tract. The dimensions of conidia, urediniospores and teliospores of microfungi are within the limits of 16–63 × 12–25 µm [169,170]. The fruiting bodies are more extensive, with a diameter of 105–270 µm. However, such sizes do not exclude their penetration into the respiratory tract of humans and animals;
- −
- the presence of chitin in the cell wall (in species from the kingdom Fungi) can induce severe allergic reactions [50];
- −
- representatives of the kingdom Chromista can cause an allergic response in humans [171]. Our preliminary studies have indicated that Peronospora lamii produces large amounts of arachidonic acid, which is responsible for development of human inflammation (unpublished data).
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Del Moral, M.G.; Martinez-Naves, E. The Role of Lipids in Development of Allergic Responses. Immune Netw. 2017, 17, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justiz Vaillant, A.A.; Vashisht, R.; Zito, P.M. Immediate Hypersensitivity Reactions; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Aldakheel, F.M. Allergic Diseases: A Comprehensive Review on Risk Factors, Immunological Mechanisms, Link with COVID-19, Potential Treatments, and Role of Allergen Bioinformatics. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohd Adnan, K. A review on Respiratory allergy caused by insects. Bioinformation 2018, 14, 540–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Liu, B.; Yang, W.; Snetselaar, L.G.; Chen, M.; Bao, W.; Strathearn, L. Association of Food Allergy, Respiratory Allergy, and Skin Allergy with Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder among Children. Nutrients 2022, 14, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Initiative for Asthma. Pocket Guide for Asthma Management and Prevention. 2022. Available online: https://kinderpneumologie.ch/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/gina-2022-pocket-guide-wms.pdf (accessed on 4 April 2023).
- (EAACI) Tackling the Allergy Crisis in Europe—Concerted Policy Action Needed 2015. Available online: https://www.veroval.info/-/media/diagnostics/files/knowledge/eaaci_advocacy_manifesto.pdf (accessed on 4 April 2023).
- Payandeh, P.; Fadaee, J.; Jabbari Azad, F.; Bakhshaii, M.; Sistani, S. Allergens Prevalence among Patients with Respiratory Allergies in Mashhad, Iran. Tanaffos 2019, 18, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mazur, M.; Czarnobilska, M.; Dyga, W.; Czarnobilska, E. Trends in the Epidemiology of Allergic Diseases of the Airways in Children Growing Up in an Urban Agglomeration. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AO White Book on Allergy 2013 Update. Available online: https://www.worldallergy.org/wao-white-book-on-allergy (accessed on 4 April 2023).
- Compalati, E.; Ridolo, E.; Passalacqua, G.; Braido, F.; Villa, E.; Canonica, G.W. The link between allergic rhinitis and asthma: The united airways disease. Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2010, 6, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nur Husna, S.M.; Tan, H.T.; Md Shukri, N.; Mohd Ashari, N.S.; Wong, K.K. Allergic Rhinitis: A Clinical and Pathophysiological Overview. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 874114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/facts-in-pictures/detail/asthma (accessed on 4 April 2023).
- 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/asthma (accessed on 4 April 2023).
- Lieberman, P.; Nicklas, R.A.; Randolph, C.; Oppenheimer, J.; Bernstein, D.; Bernstein, J.; Ellis, A.; Golden, D.B.; Greenberger, P.; Kemp, S.; et al. Anaphylaxis—A practice parameter update 2015. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2015, 115, 341–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 2023. Available online: https://www.efanet.org/inform/patient-evidence/rhinitis (accessed on 4 April 2023).
- Selroos, O.; Kupczyk, M.; Kuna, P.; Łacwik, P.; Bousquet, J.; Brennan, D.; Palkonen, S.; Contreras, J.; Fitzgerald, M.; Hedlin, G.; et al. National and regional asthma programmes in Europe. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2015, 24, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2019. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1296610/asthma-prevalence-in-the-eu/ (accessed on 4 April 2023).
- Celik, G.E.P.W.; Adkinson, N.F., Jr. Drug allergy. In Middleton’s Allergy: Principles and Practice; Adkinson, N.F., Jr., Bochner, B.S., Burks, A.W., Busse, W.W., Holgate, S.T., Lemanske, R.F., O’Hehir, R.E., Eds.; Elsevier Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chinen, J.F.T.; Shearer, W.T. The Immune system: An overview. In Middleton’s Allergy Principles & Practice; Szczeklik, A., Nizankowska-Mogilnicka, E., Sanak, M., Adkinson, N.F., Bochner, B.S., Busse, W.W., Holgate, S.T., Lemanske, R.F., Simons, F.E.R., Eds.; Mosby: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2009; pp. 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, M.; Moussa, M.; Akel, H. Type I Hypersensitivity Reaction; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- León, B.; Ballesteros-Tato, A. Modulating Th2 Cell Immunity for the Treatment of Asthma. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 637948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pritchard, D.I.; Falcone, F.H.; Mitchell, P.D. The evolution of IgE-mediated type I hypersensitivity and its immunological value. Allergy 2021, 76, 1024–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulsen, A.; Wedi, B.; Jappe, U. Hypersensitivity reactions to biologics (part I): Allergy as an important differential diagnosis in complex immune-derived adverse events. Allergo J. Int. 2020, 29, 97–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dispenza, M.C. Classification of hypersensitivity reactions. In Allergy & Asthma Proceedings; OceanSide Publications, Inc.: Cocoa Beach, FL, USA, 2019; Volume 40, pp. 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.J. Pathophysiology of allergic inflammation. Immunol. Rev. 2011, 242, 31–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzzaman, A.; Cho, S.H. Chapter 28: Classification of hypersensitivity reactions. In Allergy & Asthma Proceedings; OceanSide Publications, Inc.: Cocoa Beach, FL, USA, 2012; Volume 33, (Suppl. 1), pp. 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, T.F.; Saltoun, C.A. Chapter 21: Urticaria and angioedema. In Allergy & Asthma Proceedings; OceanSide Publications, Inc.: Cocoa Beach, FL, USA, 2012; Volume 33, (Suppl. 1), pp. 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van De Donk, N.W.C.J.; Moreau, P.; Plesner, T.; Palumbo, A.; Gay, F.; Laubach, J.P.; Malavasi, F.; Avet-Loiseau, H.; Mateos, M.-V.; Sonneveld, P.; et al. Clinical efficacy and management of monoclonal antibodies targeting CD38 and SLAMF7 in multiple myeloma. Blood 2016, 127, 681–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballanti, E.; Perricone, C.; Greco, E.; Ballanti, M.; Di Muzio, G.; Chimenti, M.S.; Perricone, R. Complement and autoimmunity. Immunol. Res. 2013, 56, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.K.L.A.; Pillai, S. (Eds.) Immediate hypersensitivity. In Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 6th ed.; Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007; pp. 441–461. [Google Scholar]
- Usman, N.; Annamaraju, P. Type III Hypersensitivity Reaction; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Marwa, K.; Kondamudi, N.P. Type IV Hypersensitivity Reaction; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, S.-Y.; Kim, J.; Ham, J.; Cho, S.-H.; Kang, H.-R.; Kim, H.Y. Altered T cell and monocyte subsets in prolonged immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome related with DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms). Asia Pac. Allergy 2020, 10, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichler, W.J. Delayed drug hypersensitivity reactions. Ann. Intern. Med. 2003, 139, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagnani, S. Th1/Th2 Cells. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 1999, 5, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ng, K.-Y.; Lillehei, K.O. Cell-Mediated Immunotherapy: A New Approach to the Treatment of Malignant Glioma. Cancer Control. 2003, 10, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldmeyer, L.; Heidemeyer, K.; Yawalkar, N. Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis: Pathogenesis, Genetic Background, Clinical Variants and Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, P.G.; Thomas, W.R. Sensitization to airborne environmental allergens: Unresolved issues. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 957–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzada, D.; Baos, S.; Cremades-Jimeno, L.; Cárdaba, B. Immunological Mechanisms in Allergic Diseases and Allergen Tolerance: The Role of Treg Cells. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 6012053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noertjojo, K.; Dimich-Ward, H.; Obata, H.; Manfreda, J.; Chan-Yeung, M. Exposure and sensitization to cat dander: Asthma and asthma-like symptoms among adults. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1999, 103 Pt 1, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pramod, S.N. Immunological basis for the development of allergic diseases-prevalence, diagnosis and treatment strategies. In Cell Interaction-Molecular and Immunological Basis for Disease Management; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Turcanu, V.; Stephens, A.C.; Chan, S.M.H.; Rancé, F.; Lack, G. IgE-mediated facilitated antigen presentation underlies higher immune responses in peanut allergy. Allergy 2010, 65, 1274–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, A.B. Allergy and allergic diseases. First of two parts. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathä, L.; Martinez-Gonzalez, I.; Steer, C.A.; Takei, F. The Fate of Activated Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 671966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howarth, P.H.; Salagean, M.; Dokic, D. Allergic rhinitis: Not purely a histamine-related disease. Allergy 2000, 55 (Suppl. 64), 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, A.N.; Hellings, P.W.; Rotiroti, G.; Scadding, G.K. Allergic rhinitis. Lancet 2011, 378, 2112–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canonica, G.W.; Bousquet, J.; Mullol, J.; Scadding, G.K.; Virchow, J.C. A survey of the burden of allergic rhinitis in Europe. Allergy 2007, 62 (Suppl. 85), 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horner, W.E.; Helbling, A.; Salvaggio, J.E.; Lehrer, S.B. Fungal allergens. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1995, 8, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Żukiewicz-Sobczak, W.A. The role of fungi in allergic diseases. Adv. Dermatol. Allergol. 2013, 30, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crameri, R.; Garbani, M.; Rhyner, C.; Huitema, C. Fungi: The neglected allergenic sources. Allergy 2014, 69, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon-Nobbe, B.; Denk, U.; Pöll, V.; Rid, R.; Breitenbach, M. The Spectrum of Fungal Allergy. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2008, 145, 58–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Gupta, D. Severe asthma and fungi: Current evidence. Med. Mycol. 2011, 49 (Suppl. 1), S150–S157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anees-Hill, S.; Douglas, P.; Pashley, C.H.; Hansell, A.; Marczylo, E.L. A systematic review of outdoor airborne fungal spore seasonality across Europe and the implications for health. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 818, 151716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolard, N.; Beguin, H.; Chasseur, C. Mold allergy: 25 years of indoor and outdoor studies in Belgium. Allerg. Immunol. 2001, 33, 101–102. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Liu, D.; Yao, J. Aerosolization of fungal spores in indoor environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 820, 153003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurup, V.P.; Shen, H.-D.; Banerjee, B. Respiratory fungal allergy. Microbes Infect. 2000, 2, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoabi, Y.; Levi-Schaffer, F.; Eliashar, R. Allergic Rhinitis: Pathophysiology and Treatment Focusing on Mast Cells. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokkens, W.; Lund, V.; Mullol, J. European Position Paper on R, Nasal Polyps g. European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2007. Rhinol. Suppl. 2007, 20, 1–136. [Google Scholar]
- Liva, G.A.; Karatzanis, A.D.; Prokopakis, E.P. Review of Rhinitis: Classification, Types, Pathophysiology. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousquet, J.; Anto, J.M.; Bachert, C.; Baiardini, I.; Bosnic-Anticevich, S.; Canonica, G.W.; Melén, E.; Palomares, O.; Scadding, G.K.; Togias, A.; et al. Allergic rhinitis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2020, 6, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smurthwaite, L.; Durham, S.R. Local ige synthesis in allergic rhinitis and asthma. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2002, 2, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, S.N.; Chew, F.T. Epidemiology of allergic rhinitis and associated risk factors in Asia. World Allergy Organ. J. 2018, 11, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, S.K.; Lin, S.Y.; Toskala, E.; Orlandi, R.R.; Akdis, C.A.; Alt, J.A.; Azar, A.; Baroody, F.M.; Bachert, C.; Canonica, G.W.; et al. International Consensus Statement on Allergy and Rhinology: Allergic Rhinitis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2018, 8, 108–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, W.; Zhang, X.; Lin, M.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Chen, A.; Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Yue, H.; et al. Allergic rhinitis, allergic contact dermatitis and disease comorbidity belong to separate entities with distinct composition of T-cell subsets, cytokines, immunoglobulins and autoantibodies. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2022, 18, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tohidinik, H.R.; Mallah, N.; Takkouche, B. History of allergic rhinitis and risk of asthma; a systematic review and meta-analysis. World Allergy Organ. J. 2019, 12, 100069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzner, P.; Malkusová, I.; Vachová, M.; Liska, M.; Brodská, P.; Růžičková, O.; Malý, M. Bronchial inflammation in seasonal allergic rhinitis with or without asthma in relation to natural exposure to pollen allergens. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2015, 43, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendtsen, P.; Grnbk, M.; Kjær, S.K.; Münk, C.; Linneberg, A.; Tolstrup, J.S. Alcohol consumption and the risk of self-reported perennial and seasonal allergic rhinitis in young adult women in a population-based cohort study. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2008, 38, 1179–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scadding, G.K.; Durham, S.R.; Mirakian, R.; Jones, N.S.; Leech, S.C.; Farooque, S.; Ryan, D.; Walker, S.M.; Clark, A.T.; Dixon, T.A.; et al. BSACI guidelines for the management of allergic and non-allergic rhinitis. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2008, 38, 19–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilos, D.L. Allergic Fungal Rhinitis and Rhinosinusitis. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2010, 7, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safirstein, B.H. Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis with Obstruction of the Upper Respiratory Tract. Chest 1976, 70, 788–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morpeth, J.F.; Bent, J.P.; Kuhn, F.A.; Rupp, N.T.; Dolen, W.K. Fungal Sinusitis: An Update. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1996, 76, 128–140; quiz 39–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykewicz, M.S.; Rodrigues, J.M.; Slavin, R.G. Allergic fungal rhinosinusitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 142, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meltzer, E.O.; Hamilos, D.L. Rhinosinusitis Diagnosis and Management for the Clinician: A Synopsis of Recent Consensus Guidelines. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2011, 86, 427–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, M.S. Allergic fungal sinusitis. Clin. Allergy Immunol. 2007, 20, 263–271. [Google Scholar]
- Hoyt, A.E.; Borish, L.; Gurrola, J.; Payne, S. Allergic Fungal Rhinosinusitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2016, 4, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, N.; Marr, K.A. Impact of Aspergillus fumigatus in allergic airway diseases. Clin. Transl. Allergy 2011, 1, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Hoselton, S.A.; Schuh, J.M. Allergic Inflammation in Aspergillus fumigatus-Induced Fungal Asthma. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2015, 15, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denning, D.W.; Pleuvry, A.; Cole, D.C. Global burden of allergic brochopulmonary aspergillosis with asthma and its complication chronic pulmonary aspergillosis in adults. Med. Mycol. 2013, 51, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crameri, R.; Hemmann, S.; Mayer, C.; Appenzeller, U.; Blaser, K. Molecular aspects and diagnostic value of fungal allergens. Mycoses 1998, 41 (Suppl. 1), 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denning, D.W.; Pashley, C.; Hartl, D.; Wardlaw, A.; Godet, C.; Del Giacco, S.; Delhaes, L.; Sergejeva, S. Fungal allergy in asthma–state of the art and research needs. Clin. Transl. Allergy 2014, 4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-C.; Chuang, J.-G.; Su, Y.-Y.; Chiang, B.-L.; Lin, Y.S.; Chow, L.-P. The Protease Allergen Pen c 13 Induces Allergic Airway Inflammation and Changes in Epithelial Barrier Integrity and Function in a Murine Model. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 26667–26679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberger, P.A.; Patterson, R. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis and the evaluation of the patient with asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1988, 81, 646–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowley, J.; Namvar, S.; Gago, S.; Labram, B.; Bowyer, P.; Richardson, M.D.; Herrick, S.E. Differential Proinflammatory Responses to Aspergillus fumigatus by Airway Epithelial Cells In Vitro Are Protease Dependent. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurup, V.P. Fungal Allergy. In Handbook of Fungal Biotechnology; Arora, N., Ed.; Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 515–525. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, R.; Chakrabarti, A.; Shah, A.; Gupta, D.; Meis, J.F.; Guleria, R.; Moss, R.; Denning, D.W.; ABPA complicating asthma ISHAM working group. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis: Review of literature and proposal of new diagnostic and classification criteria. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2013, 43, 850–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arruda, L.K.; Platts-Mills, T.A.; Fox, J.W.; Chapman, M. Aspergillus fumigatus allergen I, a major IgE-binding protein, is a member of the mitogillin family of cytotoxins. J. Exp. Med. 1990, 172, 1529–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holgate, S.T. A look at the pathogenesis of asthma: The need for a change in direction. Discov. Med. 2010, 9, 439–447. [Google Scholar]
- Sinyor, B.; Concepcion Perez, L. Pathophysiology of Asthma; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, A.Y.; Sur, S.; Grant, J.A.; Tripple, J.W. Interleukin-4/interleukin-13 versus interleukin-5: A comparison of molecular targets in biologic therapy for the treatment of severe asthma. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 19, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laing, K.J.; Secombes, C.J. Chemokines. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2004, 28, 443–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, D.; Brightling, C. Cytokine and anti-cytokine therapy in asthma: Ready for the clinic? Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2009, 158, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wills-Karp, M.; Karp, C.L. Biomedicine. Eosinophils in asthma: Remodeling a tangled tale. Science 2004, 305, 1726–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, P.J. The cytokine network in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 3546–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parulekar, A.D.; Kao, C.C.; Diamant, Z.; Hanania, N.A. Targeting the interleukin-4 and interleukin-13 pathways in severe asthma: Current knowledge and future needs. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2018, 24, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambrecht, B.N.; Hammad, H.; Fahy, J.V. The Cytokines of Asthma. Immunity 2019, 50, 975–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, F.; Ghaemmaghami, A.M. Allergen recognition by innate immune cells: Critical role of dendritic and epithelial cells. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morianos, I.; Semitekolou, M. Dendritic Cells: Critical Regulators of Allergic Asthma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendez-Enriquez, E.; Hallgren, J. Mast Cells and Their Progenitors in Allergic Asthma. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartemes, K.R.; Kita, H. Dynamic role of epithelium-derived cytokines in asthma. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 143, 222–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bai, C.; Li, K.; Adler, K.B.; Wang, X. Role of airway epithelial cells in development of asthma and allergic rhinitis. Respir. Med. 2008, 102, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, P.J. Immunology of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelaia, C.; Heffler, E.; Crimi, C.; Maglio, A.; Vatrella, A.; Pelaia, G.; Canonica, G.W. Interleukins 4 and 13 in Asthma: Key Pathophysiologic Cytokines and Druggable Molecular Targets. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 851940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaia, C.; Paoletti, G.; Puggioni, F.; Racca, F.; Pelaia, G.; Canonica, G.W.; Heffler, E. Interleukin-5 in the Pathophysiology of Severe Asthma. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenfeder, S.; Umland, S.P.; Cuss, F.M.; Chapman, R.W.; Egan, R.W. Th2 cytokines and asthma. The role of interleukin-5 in allergic eosinophilic disease. Respir. Res. 2001, 2, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hove, C.L.; Maes, T.; Joos, G.F.; Tournoy, K.G. Chronic inflammation in asthma: A contest of persistence vs resolution. Allergy 2008, 63, 1095–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobs, S.P.; Pohlmeier, L.; Li, F.; Kayhan, M.; Becher, B.; Kopf, M. GM-CSF instigates a dendritic cell-T-cell inflammatory circuit that drives chronic asthma development. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 2118–2133.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, S.E.; Wang, L.; Pirozzi, G. Dupilumab in persistent asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, N.; Kohrogi, H.; Iwagoe, H.; Goto, E.; Hamamoto, J.; Fujii, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Kawano, O.; Ando, M. Allergen Exposure Induces the Expression of Endothelial Adhesion Molecules in Passively Sensitized Human Bronchus: Time Course and the Role of Cytokines. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 1998, 18, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Qiu, C. Research advances in airway remodeling in asthma: A narrative review. Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukacs, N.W. Role of chemokines in the pathogenesis of asthma. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2001, 1, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Zhu, X. Role of Chemokines and Inflammatory Cells in Respiratory Allergy. J. Asthma Allergy 2022, 15, 1805–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, H.; Fang, Q.H.; Ma, Y.M.; Wang, X.Y. Analysis of growth factors in serum and induced sputum from patients with asthma. Exp. Ther. Med. 2014, 8, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badewa, A.P.; Hudson, C.E.; Heiman, A.S. Regulatory effects of eotaxin, eotaxin-2, and eotaxin-3 on eosinophil degranulation and superoxide anion generation. Exp. Biol. Med. 2002, 227, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampen, G.T.; Stafford, S.; Adachi, T.; Jinquan, T.; Quan, S.; Grant, J.A.; Skov, P.S.; Poulsen, L.K.; Alam, R. Eotaxin induces degranulation and chemotaxis of eosinophils through the activation of ERK2 and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases. Blood 2000, 95, 1911–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berghi, N.O.; Dumitru, M.; Vrinceanu, D.; Ciuluvica, R.C.; Simioniuc-Petrescu, A.; Caragheorgheopol, R.; Tucureanu, C.; Cornateanu, R.S.; Giurcaneanu, C. Relationship between chemokines and T lymphocytes in the context of respiratory allergies (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 2352–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardas, G.; Daszynska-Kardas, A.; Marynowski, M.; Brzakalska, O.; Kuna, P.; Panek, M. Role of Platelet-Derived Growth Factor (PDGF) in Asthma as an Immunoregulatory Factor Mediating Airway Remodeling and Possible Pharmacological Target. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, T.; Broide, D. Cytokines and growth factors in airway remodeling in asthma. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2007, 19, 676–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.Y.; Yan, Q.; Chen, W.; Forno, E.; Celedon, J.C. Serum insulin-like growth factor-1, asthma, and lung function among British adults. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021, 126, 284–291.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Puddicombe, S.M.; Field, S.; Haywood, J.; Broughton-Head, V.; Puxeddu, I.; Haitchi, H.M.; Vernon-Wilson, E.; Sammut, D.; Bedke, N.; et al. Defective epithelial barrier function in asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 128, 549–556.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gon, Y.; Hashimoto, S. Role of airway epithelial barrier dysfunction in pathogenesis of asthma. Allergol. Int. 2018, 67, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, H.; Lambrecht, B.N. The basic immunology of asthma. Cell 2021, 184, 1469–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calven, J.; Ax, E.; Radinger, M. The Airway Epithelium-A Central Player in Asthma Pathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackett, T.-L.; Singhera, G.K.; Shaheen, F.; Hayden, P.; Jackson, G.R.; Hegele, R.G.; Van Eeden, S.; Bai, T.R.; Dorscheid, D.R.; Knight, D.A. Intrinsic Phenotypic Differences of Asthmatic Epithelium and Its Inflammatory Responses to Respiratory Syncytial Virus and Air Pollution. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2011, 45, 1090–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heijink, I.H.; Kuchibhotla, V.N.S.; Roffel, M.P.; Maes, T.; Knight, D.A.; Sayers, I.; Nawijn, M.C. Epithelial cell dysfunction, a major driver of asthma development. Allergy 2020, 75, 1902–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Song, H.J.; Park, C.S. Role of inflammasome activation in development and exacerbation of asthma. Asia Pac. Allergy 2014, 4, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawijn, M.C.; Hackett, T.L.; Postma, D.S.; van Oosterhout, A.J.; Heijink, I.H. E-cadherin: Gatekeeper of airway mucosa and allergic sensitization. Trends Immunol. 2011, 32, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergeron, C.; Tulic, M.K.; Hamid, Q. Airway remodelling in asthma: From benchside to clinical practice. Can. Respir. J. 2010, 17, e85–e93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartsock, A.; Nelson, W.J. Adherens and tight junctions: Structure, function and connections to the actin cytoskeleton. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1778, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehrenbach, H.; Wagner, C.; Wegmann, M. Airway remodeling in asthma: What really matters. Cell Tissue Res. 2017, 367, 551–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.G.; Ma, B.; Takyar, S.; Ahangari, F.; DeLaCruz, C.; He, C.H.; Elias, J.A. Studies of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2011, 8, 512–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, W.I.; Sharma, H.S.; Baelemans, S.M.; Hoogsteden, H.C.; Lambrecht, B.N.; Braunstahl, G.J. Altered expression of epithelial junctional proteins in atopic asthma: Possible role in inflammation. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2008, 86, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackett, T.-L.; de Bruin, H.G.; Shaheen, F.; Berge, M.V.D.; van Oosterhout, A.J.; Postma, D.S.; Heijink, I.H. Caveolin-1 Controls Airway Epithelial Barrier Function. Implications for Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 49, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunggal, J.A.; Helfrich, I.; Schmitz, A.; Schwarz, H.; Günzel, D.; Fromm, M.; Kemler, R.; Krieg, T.; Niessen, C.M. E-cadherin is essential for in vivo epidermal barrier function by regulating tight junctions. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 1146–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heijink, I.H.; Brandenburg, S.M.; Noordhoek, J.A.; Postma, D.S.; Slebos, D.J.; van Oosterhout, A.J. Characterisation of cell adhesion in airway epithelial cell types using electric cell-substrate impedance sensing. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 35, 894–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, S.; Heijink, I.H.; Hesse, L.; Koo, H.K.; Shaheen, F.; Fouadi, M.; Kuchibhotla, V.N.S.; Lambrecht, B.N.; Van Oosterhout, A.J.M.; Hackett, T.L.; et al. Characterization of a lung epithelium specific E-cadherin knock-out model: Implications for obstructive lung pathology. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceteci, F.; Ceteci, S.; Zanucco, E.; Thakur, C.; Becker, M.; El-Nikhely, N.; Fink, L.; Seeger, W.; Savai, R.; Rapp, U.R. E-cadherin Controls Bronchiolar Progenitor Cells and Onset of Preneoplastic Lesions in Mice. Neoplasia 2012, 14, 1164–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackett, T.L. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in the pathophysiology of airway remodelling in asthma. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 12, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.J. Targeting cytokines to treat asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 454–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauserud, H.; Heegaard, E.; Halvorsen, R.; Boddy, L.; Hoiland, K.; Stenseth, N.C. Mushroom’s spore size and time of fruiting are strongly related: Is moisture important? Biol. Lett. 2011, 7, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, R.; Kazmi, S.A.; Kacker, R.; Gupta, N. Severe asthma with fungal sensitization. Indian J. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021, 35, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.; Plattner, G.K.; Knutti, R.; Friedlingstein, P. Irreversible climate change due to carbon dioxide emissions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1704–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsey, R. Climate Change: Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide 2023. Available online: https://www.climate.gov/news-features/understanding-climate/climate-change-atmospheric-carbon-dioxide (accessed on 2 April 2023).
- Reid, C.E.; Gamble, J.L. Aeroallergens, allergic disease, and climate change: Impacts and adaptation. Ecohealth 2009, 6, 458–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauserud, H.; Stige, L.C.; Vik, J.O.; Okland, R.H.; Hoiland, K.; Stenseth, N.C. Mushroom fruiting and climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 3811–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wills-Karp, M. Allergen-specific pattern recognition receptor pathways. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2010, 22, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzyk, I.; Kaszewski, B.M.; Weryszko-Chmielewska, E.; Nowak, M.; Sulborska, A.; Kaczmarek, J.; Szymanska, A.; Haratym, W.; Jedryczka, M. Warm and dry weather accelerates and elongates Cladosporium spore seasons in Poland. Aerobiologia 2016, 32, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amato, G.; Cecchi, L.; Liccardi, G. Thunderstorm-related asthma: Not only grass pollen and spores. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 121, 537–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nnadi, N.E.; Carter, D.A. Climate change and the emergence of fungal pathogens. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbeau, D.N.; Grimsley, L.F.; White, L.E.; El-Dahr, J.M.; Lichtveld, M. Mold exposure and health effects following hurricanes Katrina and Rita. Annu. Rev. Public. Health 2010, 31, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchi, L.; D’amato, G.; Ayres, J.G.; Galan, C.; Forastiere, F.; Forsberg, B.; Gerritsen, J.; Nunes, C.; Behrendt, H.; Akdis, C.; et al. Projections of the effects of climate change on allergic asthma: The contribution of aerobiology. Allergy 2010, 65, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulimood, T.B.; Corden, J.M.; Bryden, C.; Sharples, L.; Nasser, S.M. Epidemic asthma and the role of the fungal mold Alternaria alternata. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 120, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dales, R.E.; Cakmak, S.; Judek, S.; Dann, T.; Coates, F.; Brook, J.R.; Burnett, R.T. The Role of Fungal Spores in Thunderstorm Asthma. Chest 2003, 123, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celenza, A.; Fothergill, J.; Kupek, E.; Shaw, R.J. Thunderstorm associated asthma: A detailed analysis of environmental factors. BMJ 1996, 312, 604–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packe, G.E.; Ayres, J.G. Asthma outbreak during a thunderstorm. Lancet 1985, 2, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kevat, A. Thunderstorm Asthma: Looking Back and Looking Forward. J. Asthma Allergy 2020, 13, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyamvada, H.; Singh, R.K.; Akila, M.; Ravikrishna, R.; Verma, R.S.; Gunthe, S.S. Seasonal variation of the dominant allergenic fungal aerosols—One year study from southern Indian region. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang-Yona, N.; Shuster-Meiseles, T.; Mazar, Y.; Yarden, O.; Rudich, Y. Impact of urban air pollution on the allergenicity of Aspergillus fumigatus conidia: Outdoor exposure study supported by laboratory experiments. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, C.; Varela, A.; Leclercq, C.C.; Núñez, O.; Větrovský, T.; Renaut, J.; Baldrian, P.; Pereira, C.S. Specialisation events of fungal metacommunities exposed to a persistent organic pollutant are suggestive of augmented pathogenic potential. Microbiome 2018, 6, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, H.C.Y.; Jarvis, D.; Fuertes, E. Interactive effects of allergens and air pollution on respiratory health: A systematic review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 143924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossman, A.Y. A Special Issue on Global Movement of Invasive Plants and Fungi. BioScience 2001, 51, 93–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.; Ale-Agha, N.; Brassmann, M. Survey of microfungi in the Kleinwalsertal (Austrian alps). Commun. Agric. Appl. Biol. Sci. 2008, 73, 135–145. [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch, G.; Braun, U. Communities of parasitic microfungi. In Fungi in Vegetation Science Handbook of Vegetation Science; Winterhoff, W., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Mułenko, W.P.M.; Wołczańska, A.; Kozłowska, M.; Ruszkiewicz-Michalska, M. Plant parasitic fungi introduced to Poland in modern times. Alien and invasive species. Biol. Invasions Pol. 2010, 1, 49–71. [Google Scholar]
- Wołczańska, A. First report of Erysiphe carpinicola (perfect state) in Poland. Plant. Pathol. 2007, 56, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wołczańska, A. First report of Puccinia bornmuelleri causing rust disease of lovage in Poland. Plant Pathol. 2010, 59, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wołczańska, A. Puccinia lojkaiana: A rust fungus new for Poland. Pol. Bot. J. 2012, 57, 479–482. [Google Scholar]
- Lacey, J. Spore dispersal—Its role in ecology and disease: The British contribution to fungal aerobiology. Mycol. Res. 1996, 100, 641–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochman, J. Flora Polska. In Grzyby (Mycota) 4. Glonowce (Phycomycetes), Wroślikowe (Peronosporales); PWN: Kraków, Poland; Warszawa, Poland, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Majewski, T. Flora Polska. In Grzyby (Mycota) 9: Basidiomycetes, Uredinales; PWN: Kraków, Poland; Warszawa, Poland, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Rossin, G.; Villalta, D.; Martelli, P.; Cecconi, D.; Polverari, A.; Zoccatelli, G. Grapevine Downy Mildew Plasmopara viticola Infection Elicits the Expression of Allergenic Pathogenesis-Related Proteins. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2015, 168, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poland, T.M.; Patel-Weynand, T.; Finch, D.M.; Miniat, C.F.; Hayes, D.C.; Lopez, V.M. Effects of climate change on invasive species. In Invasive Species in Forests and Rangelands of the United States; Poland, T.M., Patel-Weynand, T., Finch, D.M., Miniat, C.F., Hayes, D.C., Lopez, V.M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sztandera-Tymoczek, M.; Szuster-Ciesielska, A. Fungal Aeroallergens—The Impact of Climate Change. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 544. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9050544
Sztandera-Tymoczek M, Szuster-Ciesielska A. Fungal Aeroallergens—The Impact of Climate Change. Journal of Fungi. 2023; 9(5):544. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9050544
Chicago/Turabian StyleSztandera-Tymoczek, Monika, and Agnieszka Szuster-Ciesielska. 2023. "Fungal Aeroallergens—The Impact of Climate Change" Journal of Fungi 9, no. 5: 544. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9050544






