AfuPmV-1-Infected Aspergillus fumigatus Is More Susceptible to Stress Than Virus-Free Fungus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Agar Plates
2.3. Strains and Isolates
2.4. Measuring Growth from A. fumigatus Conidia-Based Cultures on Agar, Visualized in Figure 1
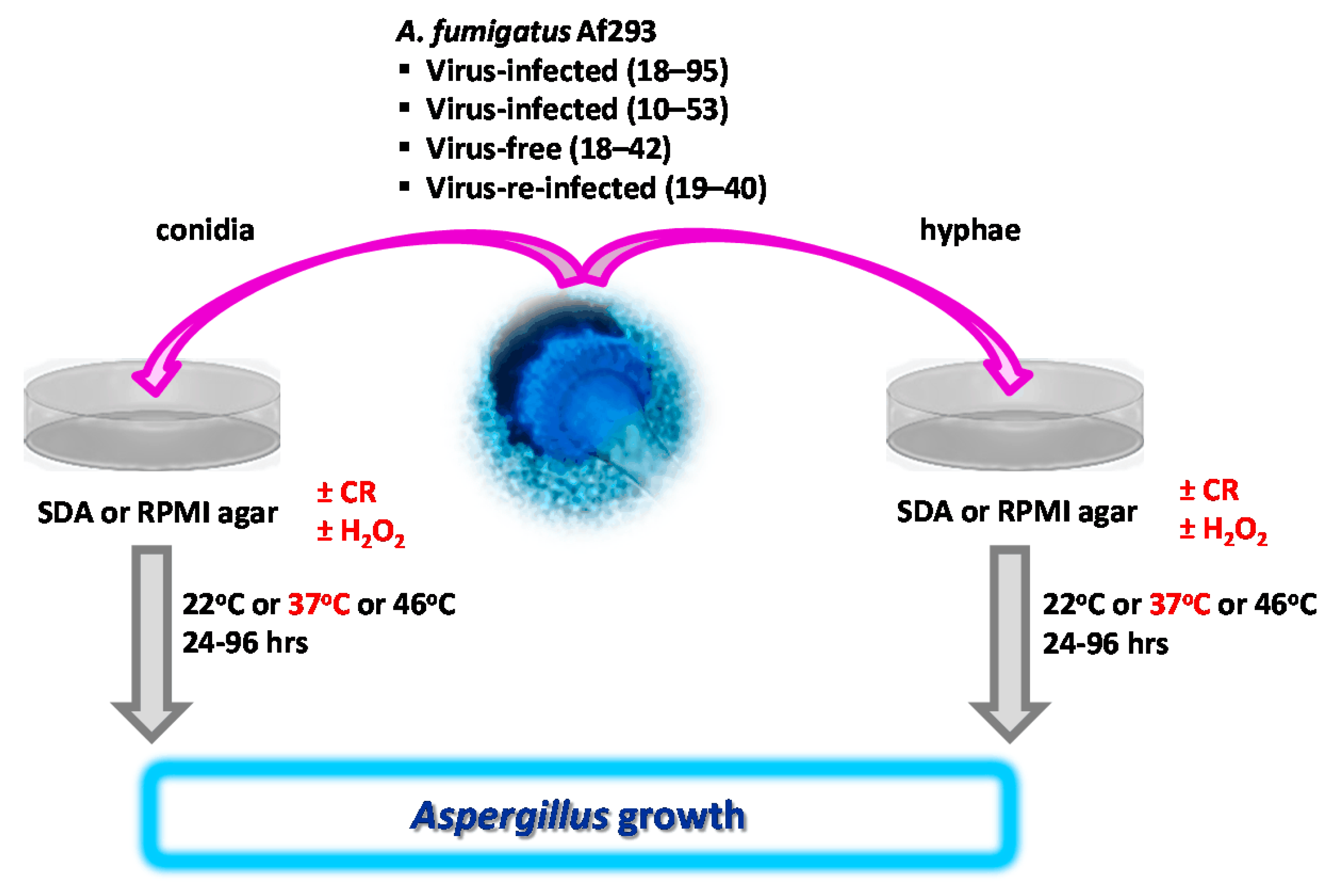
2.5. Measuring Growth from A. fumigatus Hyphae-Based Cultures on Agar, Visualized in Figure 1
2.6. Temperature Treatment of Conidia
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Virus-Free A. fumigatus Af293 Grows Faster Than AfuPmV-1-Infected Fungus at 37 °C
3.2. Effect of Heat Stress: Early Growth Advantage of Virus-Free A. fumigatus Af293 Compared to AfuPmV-1-Infected Fungus at 46 °C
3.3. At Room Temperature (22 °C), Virus-Free A. fumigatus Af293 Has No Growth Advantage over AfuPmV-1-Infected Fungus
3.4. Heating or Freezing of Conidia Does Not Differentially Affect Fungal Growth
3.5. Congo Red (CR) Inhibits Fungal Growth, with Virus-Free A. fumigatus Af293 Less Susceptible to CR Than AfuPmV-1-Infected Fungus
3.6. Virus-Free Af293 Is Less Susceptible to Hydrogen Peroxide Than AfuPmV-1-Infected Af293 on SDA and RPMI Agar
3.7. Agar Content as a Stress Factor
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nierman, W.C.; Pain, A.; Anderson, M.J.; Wortman, J.R.; Kim, H.S.; Arroyo, J.; Berriman, M.; Abe, K.; Archer, D.B.; Bermejo, C.; et al. Genomic sequence of the pathogenic and allergenic filamentous fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. Nature 2005, 438, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotta-Loizou, I.; Coutts, R.H.A. Mycoviruses in Aspergilli: A comprehensive review. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kanhayuwa, L.; Kotta-Loizou, I.; Özkan, S.; Gunning, A.P.; Coutts, R.H.A. A novel mycovirus from Aspergillus fumigatus contains four unique dsRNAs as its genome and is infectious as dsRNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 9100–9105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatti, M.F.; Jamal, A.; Bignell, E.M.; Petrou, M.A.; Coutts, R.H. Incidence of dsRNA mycoviruses in a collection of Aspergillus fumigatus isolates. Mycopathologia 2012, 174, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Refos, J.M.; Vonk, A.G.; Eadie, K.; Lo-Ten-Foe, J.R.; Verbrugh, H.A.; van Diepeningen, A.D.; van de Sande, W.W.J. Double-stranded RNA mycovirus infection of Aspergillus fumigatus is not dependent on the genetic make-up of the host. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zoll, J.; Verweij, P.E.; Melchers, W.J.G. Discovery and characterization of novel Aspergillus fumigatus mycoviruses. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi-Nakaguchi, A.; Shishido, E.; Yahara, M.; Urayama, S.-I.; Ninomiya, A.; Chiba, Y.; Sakai, K.; Hagiwara, D.; Chibana, H.; Moriyama, H.; et al. Phenotypic and molecular biological analysis of Polymycovirus AfuPmV-1M from Aspergillus fumigatus: Reduced fungal virulence in a mouse infection model. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 607795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazik, H.; Kotta-Loizou, I.; Sass, G.; Coutts, R.H.A.; Stevens, D.A. Virus infection of Aspergillus fumigatus compromises the fungus in intermicrobial competition. Viruses 2021, 13, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, R.H.; Kotta-Loizou, I.; Palyzová, A.; Pluháček, T.; Coutts, R.H.A.; Stevens, D.A.; Havlíček, V. Freeing Aspergillus fumigatus of Polymycovirus infection renders it more resistant to competition with Pseudomonas aeruginosa due to altered iron-acquiring tactics. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazik, H.; Sass, G.; Déziel, E.; Stevens, D.A. Aspergillus is inhibited by Pseudomonas aeruginosa volatiles. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, D.A.; Kotta-Loizou, I.; Martinez, M.; Coutts, R.H.A.; Sass, G. Virus infection impairs fungal response to stress: Effect of salt. Viruses 2023, 15, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sass, G.; Kotta-Loizou, I.; Martinez, M.; Larwood, D.J.; Stevens, D.A. Polymycovirus infection sensitizes Aspergillus fumigatus for antifungal effects of Nikkomycin Z. Viruses 2023, 15, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi-Nakaguchi, A.; Shishido, E.; Yahara, M.; Urayama, S.-I.; Sakai, K.; Chibana, H.; Kamei, K.; Moriyama, H.; Gonoi, T. Analysis of an intrinsic mycovirus associated with reduced virulence of the human pathogenic fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Yang, B.; Liu, X.; Tian, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, W.; Qi, X.; Jiang, Y.; et al. A Satellite dsRNA attenuates the induction of helper virus-mediated symptoms in Aspergillus flavus. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 895844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhabhra, R.; Askew, D.S. Thermotolerance and virulence of Aspergillus fumigatus: Role of the fungal nucleolus. Med. Mycol. 2005, 43 (Suppl. 1), S87–S93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ji, D.; Chen, T.; Li, B.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, G.; Tian, S. Production, signaling, and scavenging mechanisms of reactive oxygen species in fruit-pathogen interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreno-Loshuertos, R.; Marco-Brualla, J.; Meade, P.; Soler-Agesta, R.; Enriquez, J.A.; Fernández-Silva, P. How hot can mitochondria be? Incubation at temperatures above 43 °C induces the degradation of respiratory complexes and supercomplexes in intact cells and isolated mitochondria. Mitochondrion 2023, 69, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.-W.; Cui, Z.-G.; Jin, Y.-J.; Sun, L.; Li, M.-L.; Zakki, S.A.; Zhou, D.-J.; Inadera, H. Protective effect of dihydromyricetin on hyperthermia-induced apoptosis in human myelomonocytic lymphoma cells. Apoptosis 2019, 24, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roti Roti, J.L. Cellular responses to hyperthermia (40–46 degrees C): Cell killing and molecular events. Int. J. Hyperth. 2008, 24, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabri, J.H.T.M.; Rocha, M.C.; Fernandes, C.M.; Persinoti, G.F.; Ries, L.N.A.; da Cunha, A.F.; Goldman, G.H.; Del Poeta, M.; Malavazi, I. The heat shock transcription factor HsfA is essential for thermotolerance and regulates cell wall integrity in Aspergillus fumigatus. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 656548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Yang, F.; Ma, D.; Zhang, J.; Wan, Z.; Liu, W.; Li, R. HOG-MAPK signaling regulates the adaptive responses of Aspergillus fumigatus to thermal stress and other related stress. Mycopathologia 2012, 174, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oiki, S.; Nasuno, R.; Urayama, S.I.; Takagi, H.; Hagiwara, D. Intracellular production of reactive oxygen species and a DAF-FM-related compound in Aspergillus fumigatus in response to antifungal agent exposure. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuskern, L.; Tkalec, M.; Ježić, M.; Katanić, Z.; Krstin, L.; Ćurković-Perica, M. Cryphonectria hypovirus 1-induced changes of stress enzyme activity in transfected phytopathogenic fungus Cryphonectria parasitica. Microb. Ecol. 2017, 74, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Raj, S.; van Rhijn, N.; Fraczek, M.; Michel, J.P.; Sismeiro, O.; Legendre, R.; Varet, H.; Fontaine, T.; Bromley, M.; et al. Functional genomic and biochemical analysis reveals pleiotropic effect of Congo red on Aspergillus fumigatus. mBio 2021, 12, e00863-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herth, W. Calcofluor white and Congo red inhibit chitin microfibril assembly of Poteriochromonas: Evidence for a gap between polymerization and microfibril formation. J. Cell Biol. 1980, 87, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabib, E.; Bowers, B. Timing and function of chitin synthesis in yeast. J. Bacteriol. 1975, 124, 1586–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Staehelin, L.A.; Giddings, T.H. Developmental Order: Its Origin and Regulation. Membrane-Mediated Control of Cell Wall Microfibrillar Order; Subtenly, S., Ed.; Alan R. Liss, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1982; pp. 133–147. [Google Scholar]
- Vannini, G.L.; Poli, F.; Donini, A.; Pancaldi, S. Effects of Congo red on wall synthesis and morphogenesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Plant Sci. Lett. 1983, 31, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncero, C.; Durán, A. Effect of Calcofluor white and Congo red on fungal cell wall morphogenesis: In vivo activation of chitin polymerization. J. Bacteriol. 1985, 163, 1180–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stevens, D.A. Drug interaction studies of a glucan synthase inhibitor (LY 303366) and a chitin synthase inhibitor (Nikkomycin Z) for inhibition and killing of fungal pathogens. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 2547–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jadhav, S.B.; Surwase, S.N.; Kalyani, D.C.; Gurav, R.G.; Jadhav, J.P. Biodecolorization of azo dye Remazol orange by Pseudomonas aeruginosa BCH and toxicity (oxidative stress) reduction in Allium cepa root cells. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 168, 1319–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; An, Y.; Jiang, L.; Geng, C.; Cao, J.; Jiang, L.; Zhong, L. The role of oxidative stress in Sudan IV-induced DNA damage in human liver-derived HepG2 cells. Environ. Toxicol. 2011, 26, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Xu, Y.; Lv, X.; Chang, X.; Ma, X.; Tian, X.; Shi, X.; Li, X.; Kong, X. Impacts of an azo food dye tartrazine uptake on intestinal barrier, oxidative stress, inflammatory response and intestinal microbiome in crucian carp (Carassius auratus). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 223, 112551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu-Denoncourt, J.; Martyniuk, C.J.; de Solla, S.R.; Balakrishnan, V.K.; Langlois, V.S. Sediment contaminated with the azo dye disperse yellow 7 alters cellular stress- and androgen-related transcription in Silurana tropicalis larvae. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 2952–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Methneni, N.; Ezdini, K.; Ben Abdeljelil, N.; Van Loco, J.; Van den Houwe, K.; Jabeur, R.; Fekih Sallem, O.; Jaziri, A.; Fernandez-Serrano, M.; Khdary, N.H.; et al. Occurrence of textile dyes and metals in tunisian textile dyeing effluent: Effects on oxidative stress status and histological changes in Balb/c Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharwani, A.A.; Narayanan, K.B.; Khan, M.E.; Han, S.S. Photocatalytic degradation activity of goji berry extract synthesized silver-loaded mesoporous zinc oxide (Ag@ZnO) nanocomposites under simulated solar light irradiation. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakupova, E.I.; Bobyleva, L.G.; Vikhlyantsev, I.M.; Bobylev, A.G. Congo Red and amyloids: History and relationship. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20181415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frid, P.; Anisimov, S.V.; Popovic, N. Congo red and protein aggregation in neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res. Rev. 2007, 53, 135–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shekhova, E.; Kniemeyer, O.; Brakhage, A.A. Induction of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production by itraconazole, terbinafine, and amphotericin B as a mode of action against Aspergillus fumigatus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e00978-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stevens, D.A.; Hope, W. Polyene antifungals. In Principles and Practice of Infectious Disease, 10th ed.; Blaser, M.J., Cohen, J.I., Holland, S.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, in press.
- Ghabrial, S.A.; Castón, J.R.; Jiang, D.; Nibert, M.L.; Suzuki, N. 50-plus years of fungal viruses. Virology 2015, 479–480, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kortright, K.E.; Chan, B.K.; Koff, J.L.; Turner, P.E. Phage Therapy: A renewed approach to combat antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 25, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nikolich, M.P.; Filippov, A.A. Bacteriophage Therapy: Developments and directions. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]









Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sass, G.; Martinez, M.; Kotta-Loizou, I.; Stevens, D. AfuPmV-1-Infected Aspergillus fumigatus Is More Susceptible to Stress Than Virus-Free Fungus. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 750. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9070750
Sass G, Martinez M, Kotta-Loizou I, Stevens D. AfuPmV-1-Infected Aspergillus fumigatus Is More Susceptible to Stress Than Virus-Free Fungus. Journal of Fungi. 2023; 9(7):750. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9070750
Chicago/Turabian StyleSass, Gabriele, Marife Martinez, Ioly Kotta-Loizou, and David Stevens. 2023. "AfuPmV-1-Infected Aspergillus fumigatus Is More Susceptible to Stress Than Virus-Free Fungus" Journal of Fungi 9, no. 7: 750. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9070750
APA StyleSass, G., Martinez, M., Kotta-Loizou, I., & Stevens, D. (2023). AfuPmV-1-Infected Aspergillus fumigatus Is More Susceptible to Stress Than Virus-Free Fungus. Journal of Fungi, 9(7), 750. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9070750







