Fabrication Technology of Self-Dissolving Sodium Hyaluronate Gels Ultrafine Microneedles for Medical Applications with UV-Curing Gas-Permeable Mold
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
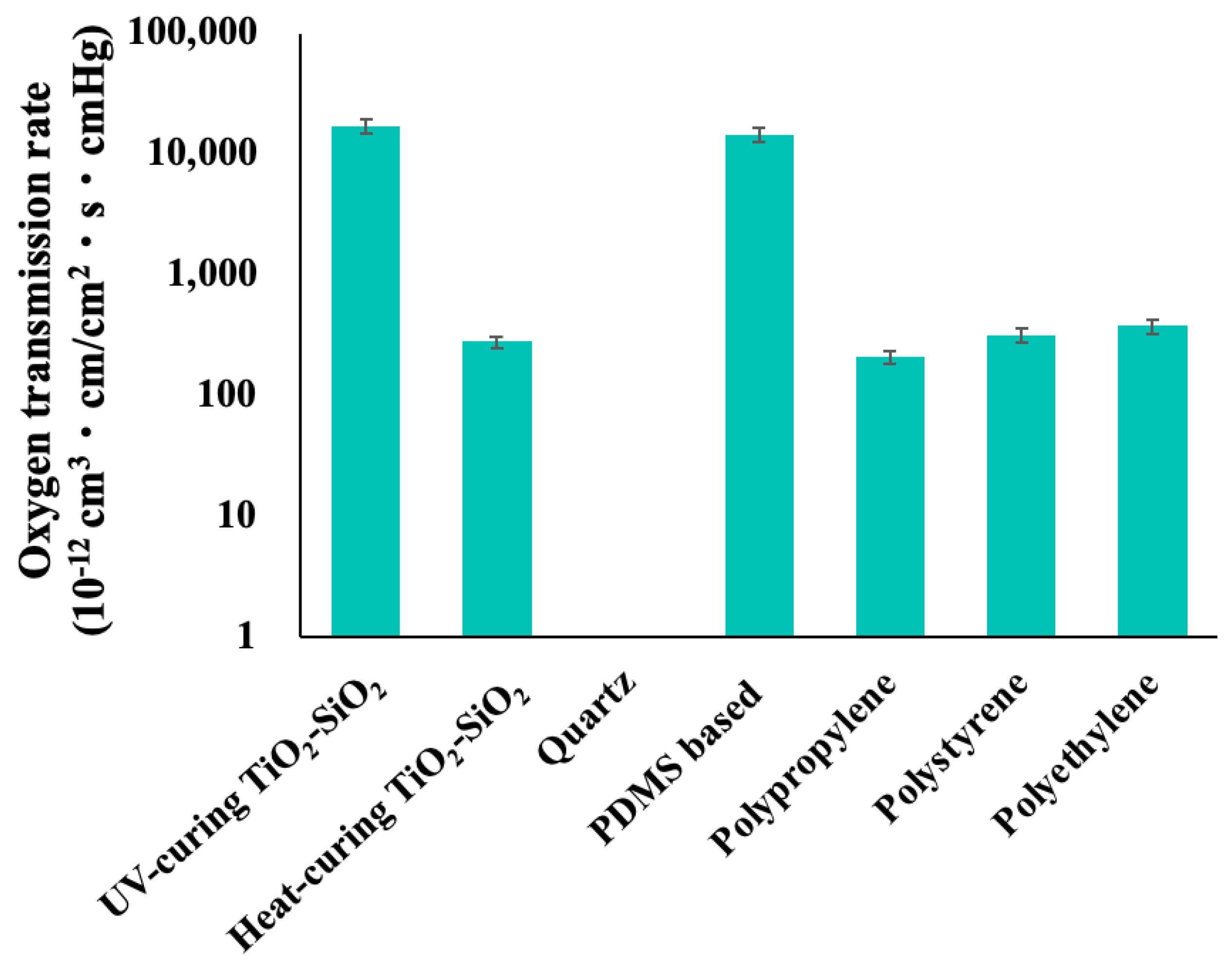
2.1. Oxygen Gas Permeability Measurement Test
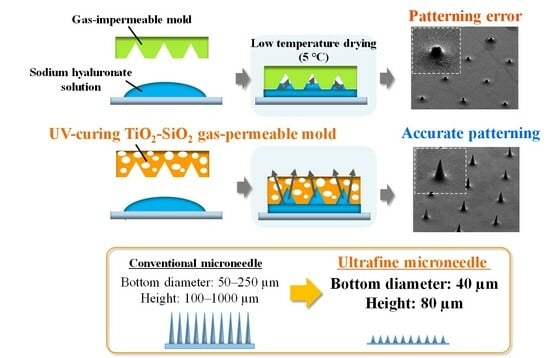
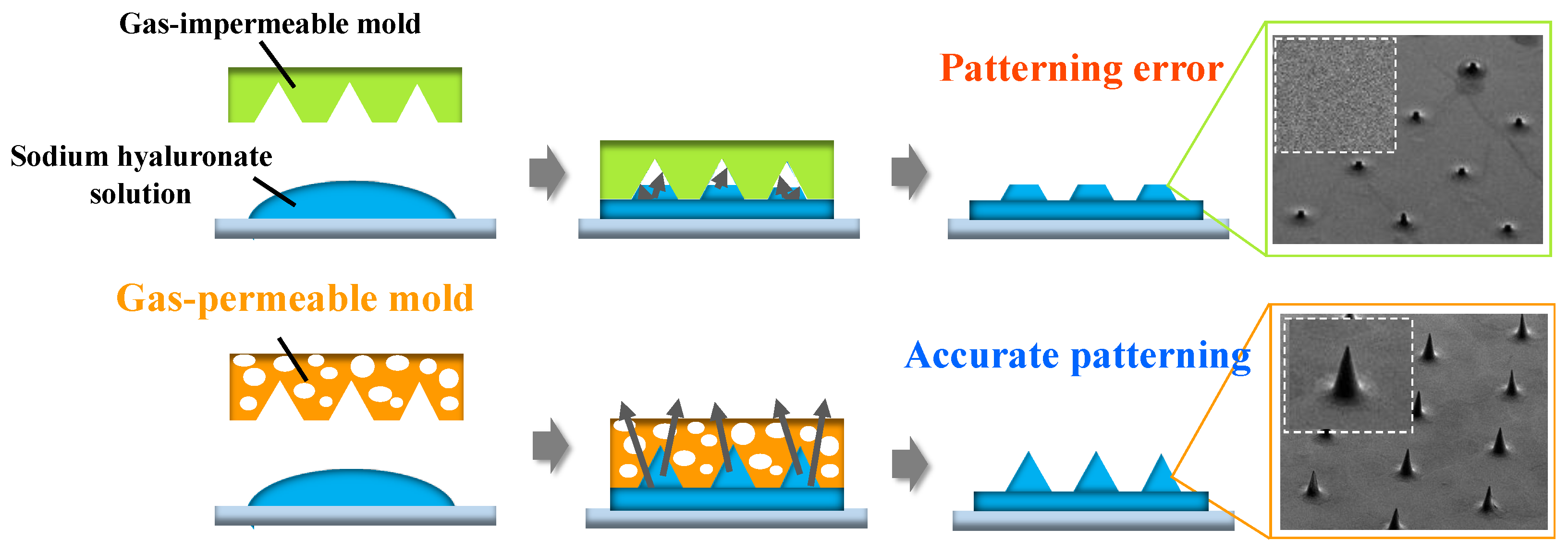
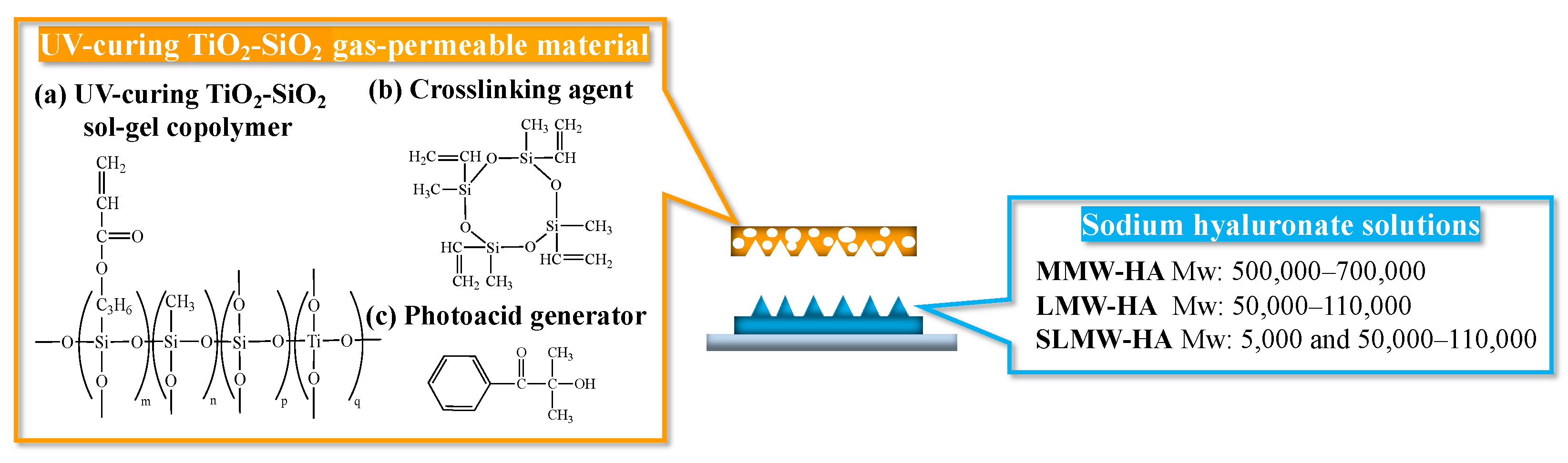
2.2. Patterning of Sodium Hyaluronate Ultrafine Microneedles Using UV-Curing TiO2-SiO2 Gas-Permeable Mold
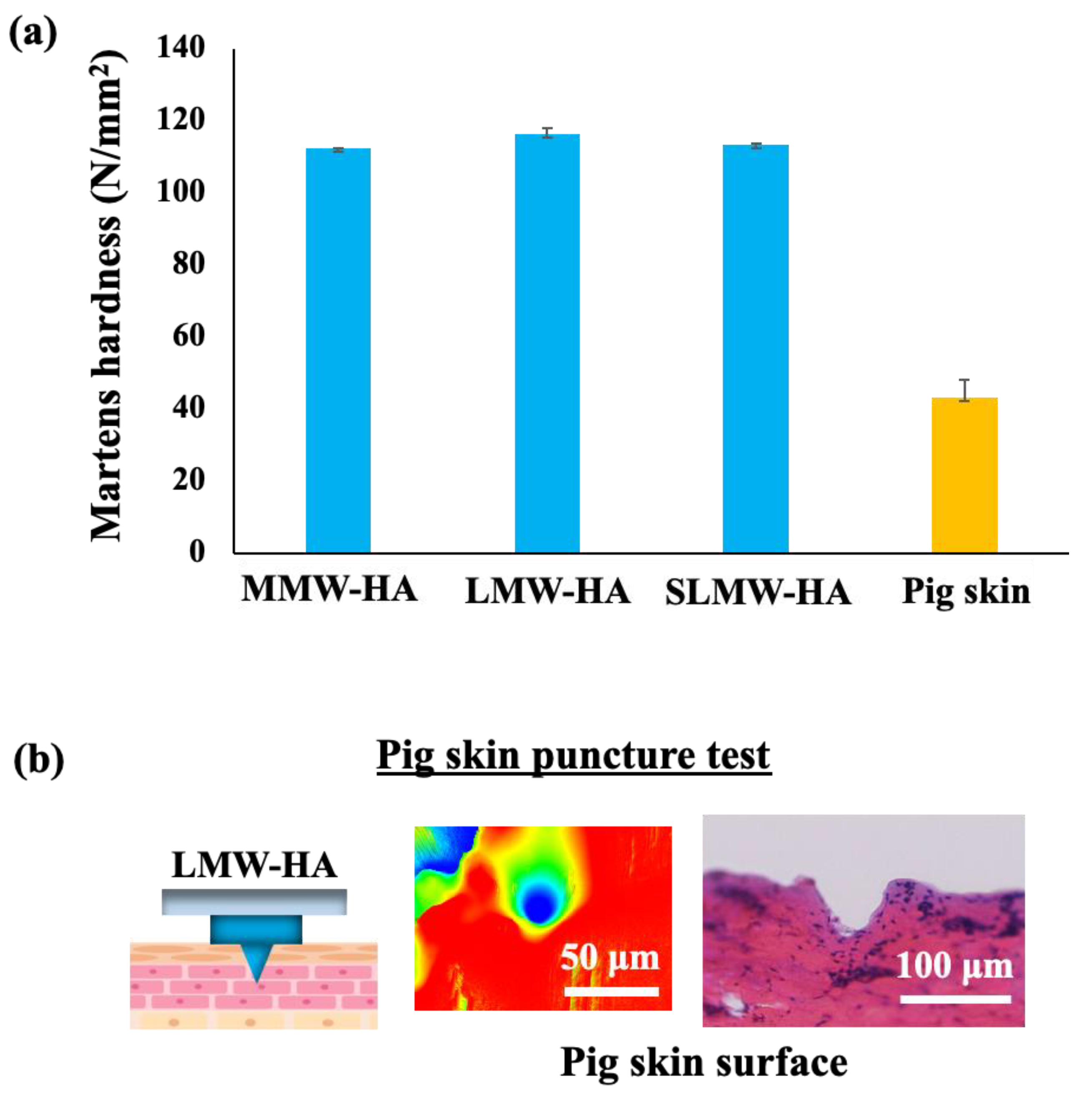
2.3. Mechanical Strength Measurement Test
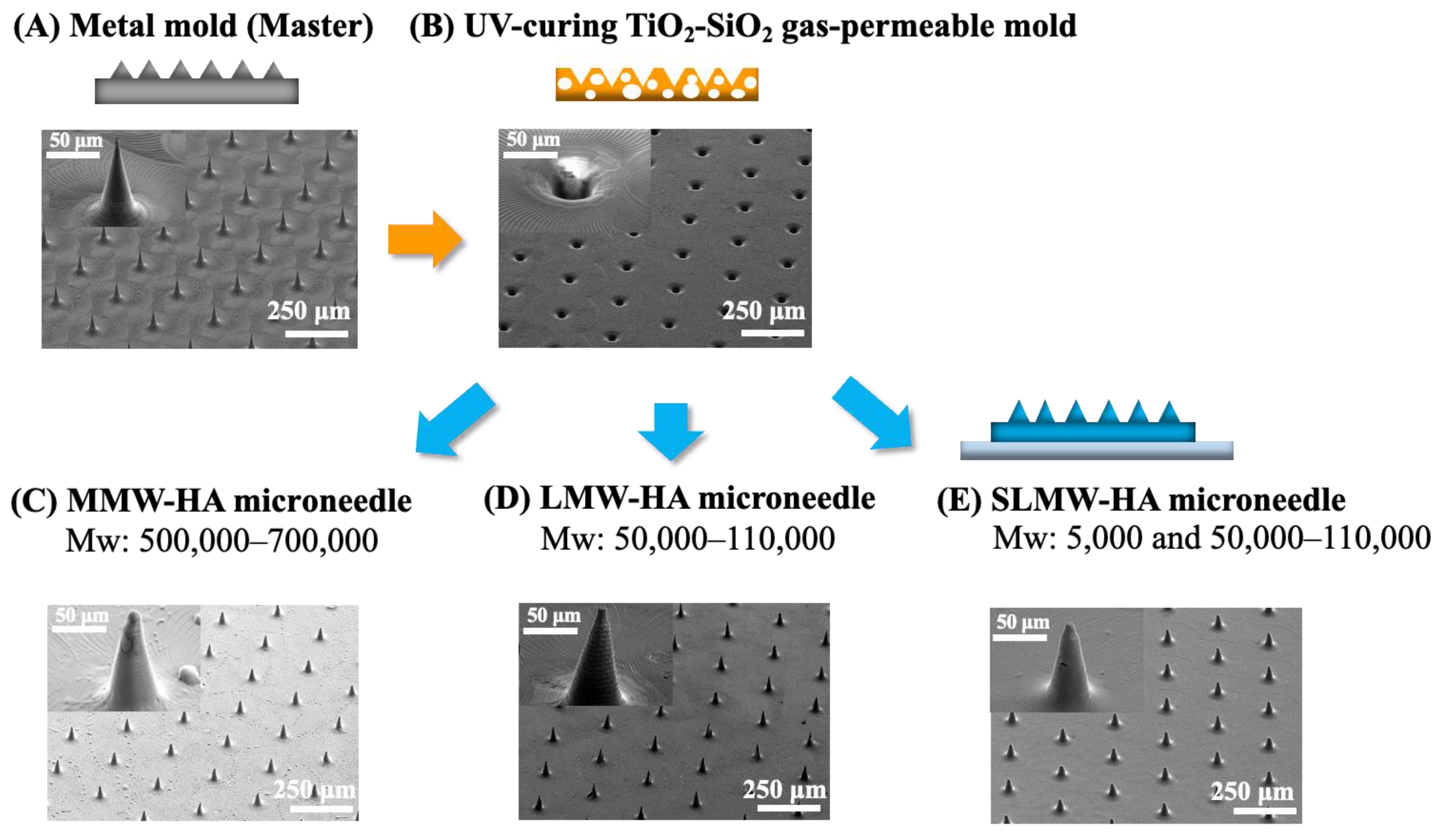
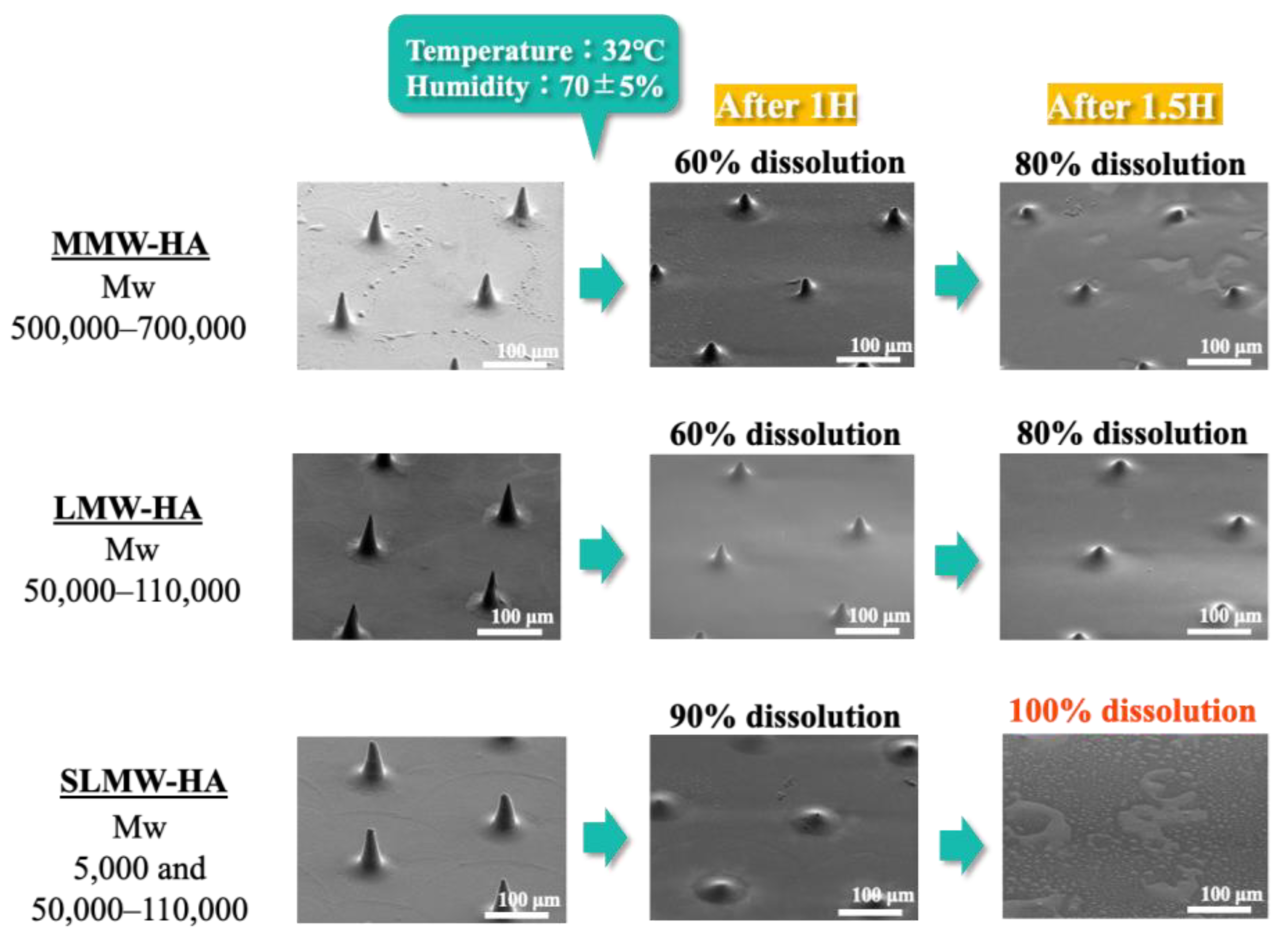
2.4. Dissolution Behavior of Sodium Hyaluronate Ultrafine Microneedles with Different Molecular Weights
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.1.1. Materials for UV-Curing TiO2-SiO2 Gas-Permeable Mold
4.1.2. Selection of Sodium Hyaluronate for Ultrafine Microneedles
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Oxygen Gas Permeability Measurement Test
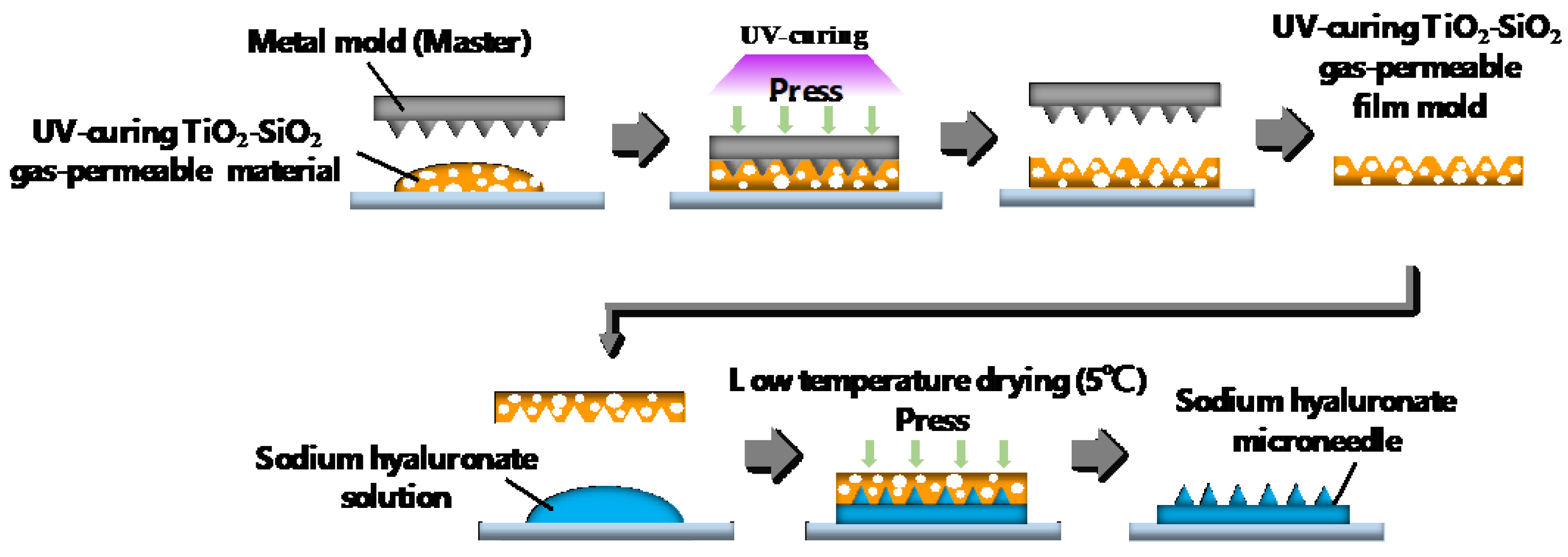
4.2.2. Two-Step Nanoimprinting Process for Fabricating UV-Curing TiO2-SiO2 Gas-Permeable Mold and Sodium Hyaluronate Ultrafine Microneedles
4.2.3. Mechanical Strength Measurement Test
4.2.4. Pig Skin Puncture Test
4.2.5. Dissolution Behavior of Sodium Hyaluronate Ultrafine Microneedles with Different Molecular Weights
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, S.; Tang, Y.; Lin, C.; Liu, X.Y.; Lin, Y. Recent advances in patterning natural polymers: From nanofabrication techniques to applications. Small Methods 2021, 5, 2001060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, M.; Baek, S.; Kang, G.; Yang, H.; Kim, S.; Jung, H. Dissolving microneedle with high molecular weight hyaluronic acid to improve skin wrinkles, dermal density and elasticity. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2020, 42, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yu, H.; Wang, L.; Shen, D.; Ni, Z.; Ren, S.; Lu, Y.; Chen, X.; Yang, J.; Hong, Y. Research progress on cosmetic microneedle systems: Preparation, property and application. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 163, 110942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadziński, P.; Froelich, A.; Wojtyłko, M.; Białek, A.; Krysztofiak, J.; Osmałek, T. Microneedle-based ocular drug delivery systems–recent advances and challenges. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2022, 13, 1167–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Hasan, A.; Babadaei, M.M.N.; Kani, P.H.; Talaei, A.J.; Sharifi, M.; Cai, T.; Falahati, M.; Cai, Y. Polymeric-based microneedle arrays as potential platforms in the development of drugs delivery systems. J. Adv. Res. 2020, 26, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saifullah, K.M.; Faraji Rad, Z. Sampling Dermal Interstitial Fluid Using Microneedles: A Review of Recent Developments in Sampling Methods and Microneedle-Based Biosensors. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 10, 2201763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Li, J.; Pei, L.; Feng, N.; Zhang, Y. Microneedle-based interstitial fluid extraction for drug analysis: Advances, challenges, and prospects. J. Pharm. Anal. 2023, 13, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, H.; Poly, T.S.; Tisha, Z.T.; Rahman, S.; Naveed, A.I.J.; Ahmed, A.; Ahmed, S.N.; Hassan, J.; Uddin, M.D.; Das, D.B. 3D Printed Hollow Microneedles for Treating Skin Wrinkles Using Different Anti-Wrinkle Agents: A Possible Futuristic Approach. Cosmetics 2023, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.H.; Kathuria, H.; Amir, M.H.B.; Zhang, X.; Duong, H.T.; Ho, P.C.L.; Kang, L. High resolution photopolymer for 3D printing of personalised microneedle for transdermal delivery of anti-wrinkle small peptide. J. Control. Release 2021, 329, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, H.L.; Bonham, L.; Hughes, C.M.; Donnelly, R.F. Design of a dissolving microneedle platform for transdermal delivery of a fixed-dose combination of cardiovascular drugs. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 3490–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, C.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Han, X.; Wang, J.; Ye, X.; Prausnitz, M.R.; et al. Microneedle patches loaded with nanovesicles for glucose transporter-mediated insulin delivery. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 18223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodgers, A.M.; Cordeiro, A.S.; Donnelly, R.F. Technology update: Dissolvable microneedle patches for vaccine delivery. Med. Devices Evid. Res. 2019, 12, 379–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, R.K.; Goud, K.Y.; Li, Z.; Moonla, C.; Mohamed, M.A.; Tehrani, F.; Teymourian, H.; Wang, J. Continuous opioid monitoring along with nerve agents on a wearable microneedle sensor array. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 5991–5995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Cao, Y.; Mariappan, D.; Bono, M.S., Jr.; Hart, A.J.; Marelli, B. A microneedle technology for sampling and sensing bacteria in the food supply chain. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2005370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillot, A.J.; Cordeiro, A.S.; Donnelly, R.F.; Montesinos, M.C.; Garrigues, T.M.; Melero, A. Microneedle-based delivery: An overview of current applications and trends. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parhi, R. Recent advances in microneedle designs and their applications in drug and cosmeceutical delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 75, 103639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.X.; Nguyen, C.N. Microneedle-mediated transdermal delivery of biopharmaceuticals. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiri, F.; Kommineni, N.; Ebhodaghe, S.O.; Bulusu, R.; Jyothi, V.G.S.; Sayed, A.A.; Awaji, A.A.; Germoush, M.O.; Al-Malky, H.S.; Nasrullah, M.Z.; et al. Microneedle-based natural polysaccharide for drug delivery systems (DDS): Progress and challenges. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, F.; Sabri, A.H.; Heppel, M.; Fonseca, I.; Chowdhury, F.; Cheung, K.; Willmor, S.; Rawson, F.; Marlow, M. The clinical and translational prospects of microneedle devices, with a focus on insulin therapy for diabetes mellitus as a case study. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 628, 122234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, B.Z.; Wang, Q.L.; Jin, X.; Guo, X.D. Fabrication of coated polymer microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2017, 265, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, M.; Ling, G.; Zhang, P. Research progress of microneedles in the treatment of melanoma. J. Control. Release 2022, 348, 631–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansoor, I.; Eassa, H.A.; Mohammed, K.H.; Abd El-Fattah, M.A.; Abdo, M.H.; Rashad, E.; Eassa, H.A.; Saleh, A.; Amin, O.M.; Nounou, M.I.; et al. Microneedle-based vaccine delivery: Review of an emerging technology. AAPS PharmSciTech 2022, 23, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.; Zuo, Z.; Lin, R.; Yao, M.; Han, Y.; Han, J. The most promising microneedle device: Present and future of hyaluronic acid microneedle patch. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 3087–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Zhao, J.; Fan, D. The Progress in the Application of Dissolving Microneedles in Biomedicine. Polymers 2023, 15, 4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, J.; Rao, F.; Wu, D.; Huang, Y.; Xu, H.; Gao, W.; Zhang, J.; Sun, J. Study on the fabrication and characterization of tip-loaded dissolving microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 157, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabri, A.H.; Kim, Y.; Marlow, M.; Scurr, D.J.; Segal, J.; Banga, A.K.; Kagan, L.; Lee, J.B. Intradermal and transdermal drug delivery using microneedles–Fabrication, performance evaluation and application to lymphatic delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 153, 195–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Japairai, K.A.S.; Mahmood, S.; Almurisi, S.H.; Venugopal, J.R.; Hilles, A.R.; Azmana, M.; Raman, S. Current trends in polymer microneedle for transdermal drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 587, 119673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallacara, A.; Baldini, E.; Manfredini, S.; Vertuani, S. Hyaluronic acid in the third millennium. Polymers 2018, 10, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, A.; Matadh, V.A.; Suresh, S.; Shivakumar, H.N.; Murthy, S.N. Non-dermal applications of microneedle drug delivery systems. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2022, 12, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, S.; Fan, X.; Prausnitz, M.R. Microneedle patch designs to increase dose administered to human subjects. J. Control. Release 2021, 339, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Liu, P.; Zhu, J.; Lan, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, J.; Tao, J. Hyaluronic acid-based dissolving microneedle patch loaded with methotrexate for improved treatment of psoriasis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 43588–43598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.C.; Park, J.H.; Prausnitz, M.R. Microneedles for drug and vaccine delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 1547–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, H.S.; Prausnitz, M.R. Coating formulations for microneedles. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 1369–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagarkar, R.; Singh, M.; Nguyen, H.X.; Jonnalagadda, S. A review of recent advances in microneedle technology for transdermal drug delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 59, 101923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Jiang, G.; Aharodnikau, U.E.; Yunusov, K.; Sun, Y.; Liu, T.; Solomevich, S.O. Recent advances in polymer microneedles for drug transdermal delivery: Design strategies and applications. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2022, 43, 2200037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gera, A.K.; Burra, R.K. The rise of polymeric Microneedles: Recent developments, advances, challenges, and applications with regard to Transdermal drug delivery. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Economidou, S.N.; Pere, C.P.P.; Reid, A.; Uddin, M.J.; Windmill, J.F.; Lamprou, D.A.; Douroumis, D. 3D printed microneedle patches using stereolithography (SLA) for intradermal insulin delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 102, 743–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.R.; Caudill, C.L.; Tumbleston, J.R.; Bloomquist, C.J.; Moga, K.A.; Ermoshkin, A.; Shirvanyants, D.; Mecham, S.J.; Luft, J.C.; DeSimone, J.M. Single-step fabrication of computationally designed microneedles by continuous liquid interface production. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, C.; Katsumi, H.; Suzuki, T.; Quan, Y.S.; Kamiyama, F.; Sakane, T.; Yamamoto, A. Self-dissolving microneedle arrays for transdermal absorption enhancement of human parathyroid hormone (1-34). Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olowe, M.; Parupelli, S.K.; Desai, S. A review of 3D-printing of microneedles. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejad, H.R.; Sadeqi, A.; Kiaee, G.; Sonkusale, S. Low-cost and cleanroom-free fabrication of microneedles. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2018, 4, 17073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, M.G.; Vucen, S.; Vrdoljak, A.; Kelly, A.; O’Mahony, C.; Crean, A.M.; Moore, A. Production of dissolvable microneedles using an atomised spray process: Effect of microneedle composition on skin penetration. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 86, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, S.; Yamagishi, R.; Miyazaki, R.; Yasuda, K.; Kawano, Y.; Yokoyama, Y.; Sugino, N.; Kameda, T.; Takei, S. Fabrication of High-Resolution Fine Microneedles Derived from Hydrolyzed Hyaluronic Acid Gels in Vacuum Environment Imprinting Using Water Permeable Mold. Gels 2022, 8, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takei, S.; Hanabata, M. Ultraviolet nanoimprint lithography using cyclodextrin-based porous template for pattern failure reduction. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 141904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, S. Direct Nanoimprint Lithography of Polyethersulfone Using Cellulose-Based Mold. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2020, 305, 1900853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Xu, G.; Yao, X.; Zhou, H.; Lyu, B.; Pei, S.; Wen, P. Microneedle-based insulin transdermal delivery system: Current status and translation challenges. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2022, 12, 2403–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, B.; Xing, M.; Meng, F.; Zhang, S.; Yang, G.; Cheng, A.; Yan, C.; Xu, B.; Gao, Y. Thermal stability of exenatide encapsulated in stratified dissolving microneedles during storage. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 636, 122863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, F.; Suzuki, K.; Noriki, A.; Amano, T. Micromirror fabrication for co-packaged optics using 3D nanoimprint technology. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 2022, 40, 063203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Okada, M.; Minari, C.; Kanda, K.; Haruyama, Y.; Matsui, S. Room-temperature nanoimprinting using liquid-phase hydrogen silsesquioxane with hard poly (dimethylsiloxane) mold. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 49, 06GL13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagishi, R.; Miura, S.; Yasuda, K.; Sugino, N.; Kameda, T.; Kawano, Y.; Yokoyama, Y.; Takei, S. Thermal nanoimprint lithography of sodium hyaluronate solutions with gas permeable inorganic hybrid mold for cosmetic and pharmaceutical applications. Appl. Phys. Express 2022, 15, 046502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, M.; Yamagishi, R.; Miura, S.; Hachikubo, Y.; Murashita, T.; Sugino, N.; Kameda, T.; Yokoyama, Y.; Kawano, Y.; Yasuda, K.; et al. Surface nanopatterning of bioabsorbable materials using thermal imprinting technology. J. Photopolym. Sci. Technol. 2023, 36, 277–282. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, Y.; Huang, Y.; Kang, Y.; Dai, G.; Liu, Z.; Xu, K.; Zhong, W. The effects of molecular weight of hyaluronic acid on transdermal delivery efficiencies of dissolving microneedles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 168, 106075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, M.; Romeijn, S.; Slutter, B.; O’Mahony, C.; Kersten, G.; Bouwstra, J.A. Hyaluronan molecular weight: Effects on dissolution time of dissolving microneedles in the skin and on immunogenicity of antigen. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 146, 105269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, A.; Sun, W.; Xing, M.; Zhang, S.; Gao, Y. The hygroscopicity of polymer microneedles on the performance of dissolving behavior for transdermal delivery. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2022, 71, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yamagishi, R.; Miura, S.; Yabu, K.; Ando, M.; Hachikubo, Y.; Yokoyama, Y.; Yasuda, K.; Takei, S. Fabrication Technology of Self-Dissolving Sodium Hyaluronate Gels Ultrafine Microneedles for Medical Applications with UV-Curing Gas-Permeable Mold. Gels 2024, 10, 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10010065
Yamagishi R, Miura S, Yabu K, Ando M, Hachikubo Y, Yokoyama Y, Yasuda K, Takei S. Fabrication Technology of Self-Dissolving Sodium Hyaluronate Gels Ultrafine Microneedles for Medical Applications with UV-Curing Gas-Permeable Mold. Gels. 2024; 10(1):65. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10010065
Chicago/Turabian StyleYamagishi, Rio, Sayaka Miura, Kana Yabu, Mano Ando, Yuna Hachikubo, Yoshiyuki Yokoyama, Kaori Yasuda, and Satoshi Takei. 2024. "Fabrication Technology of Self-Dissolving Sodium Hyaluronate Gels Ultrafine Microneedles for Medical Applications with UV-Curing Gas-Permeable Mold" Gels 10, no. 1: 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10010065
APA StyleYamagishi, R., Miura, S., Yabu, K., Ando, M., Hachikubo, Y., Yokoyama, Y., Yasuda, K., & Takei, S. (2024). Fabrication Technology of Self-Dissolving Sodium Hyaluronate Gels Ultrafine Microneedles for Medical Applications with UV-Curing Gas-Permeable Mold. Gels, 10(1), 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10010065