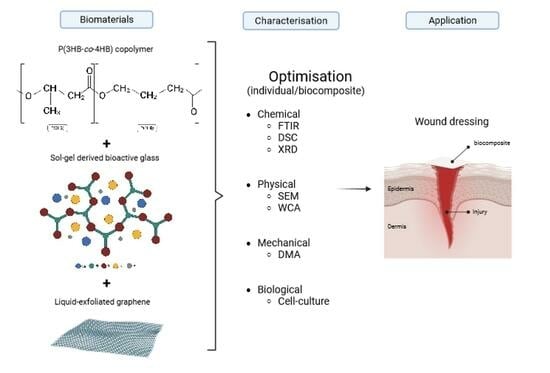
The Development and Characterisation of a P(3HB-co-4HB)–Bioactive Glass–Graphene Hydrogel as a Potential Formulation for Biomedical and Therapeutical Translation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Optimisation and Characterisation of P(3HB-co-4HB) Copolymer Biosynthesis
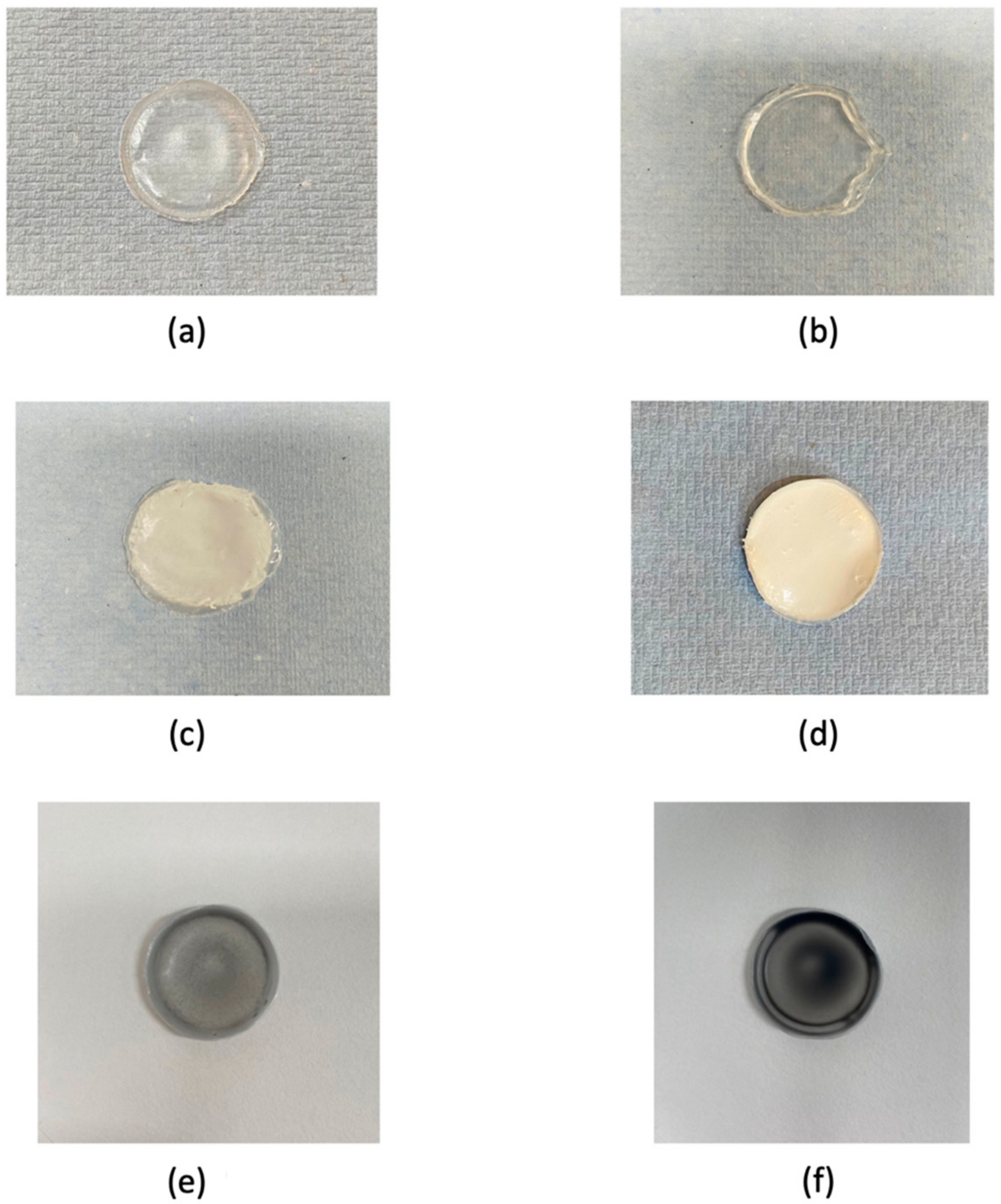
2.2. Composite Casting of the Copolymer
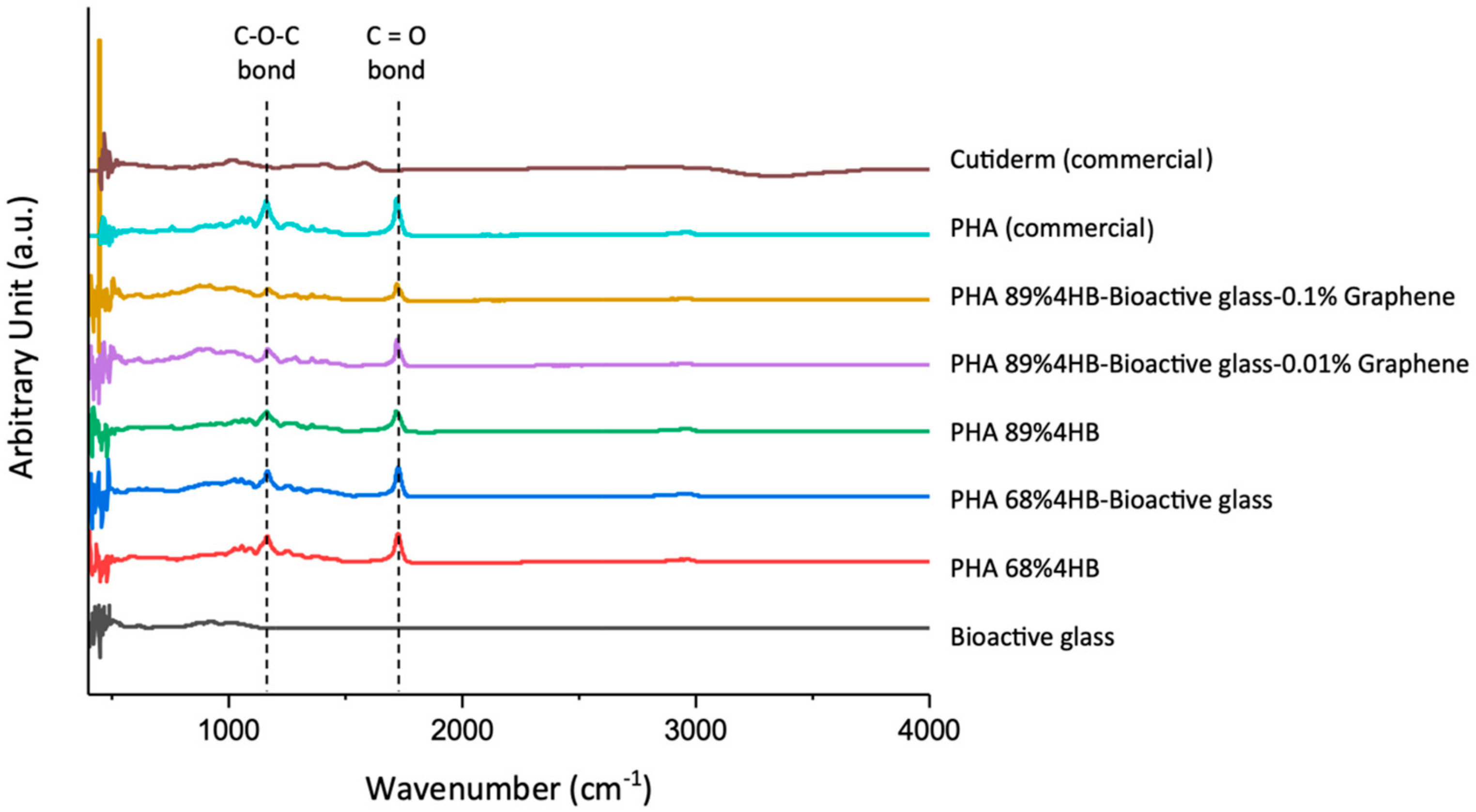
2.3. ATR-FTIR
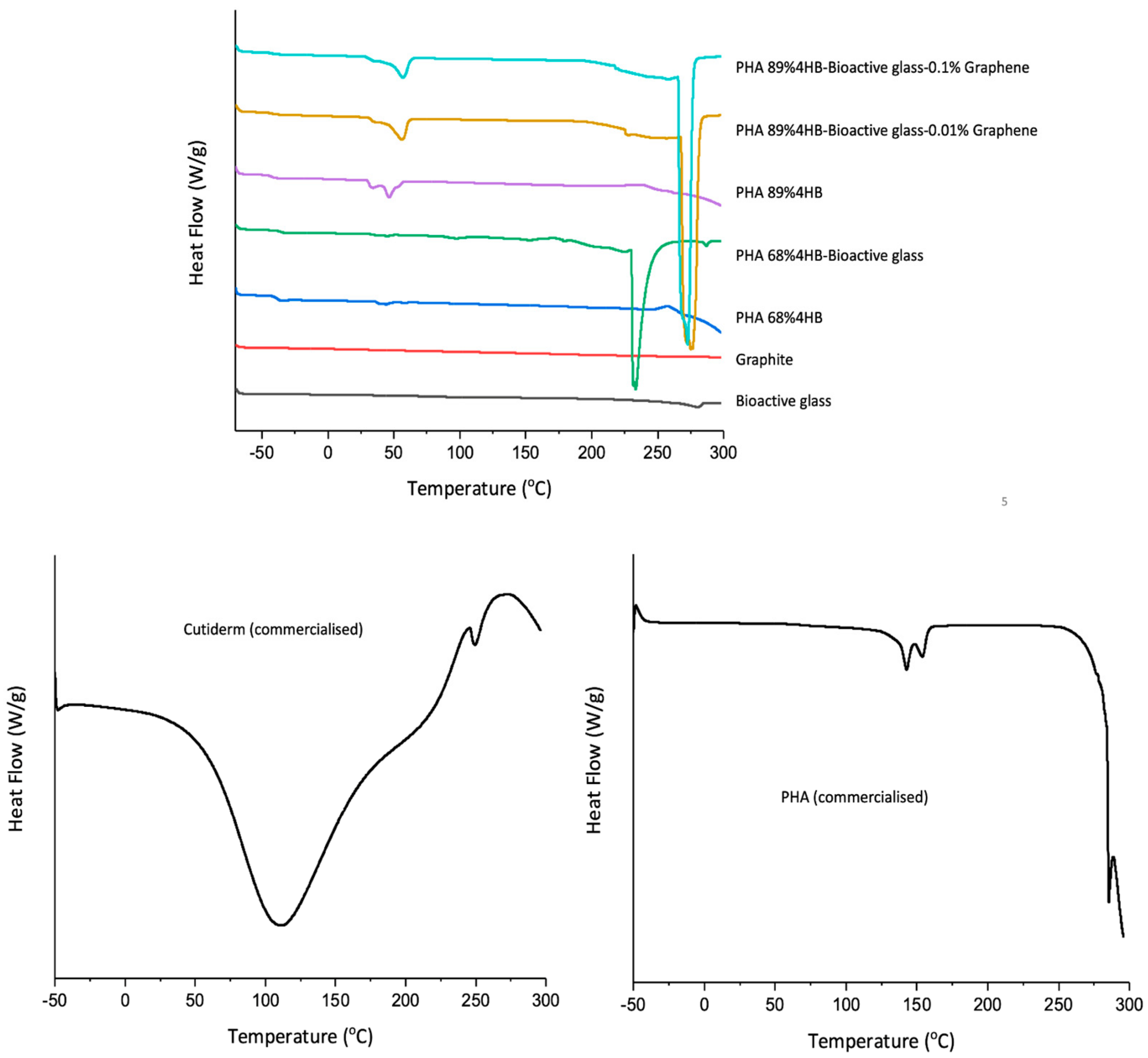
2.4. DSC
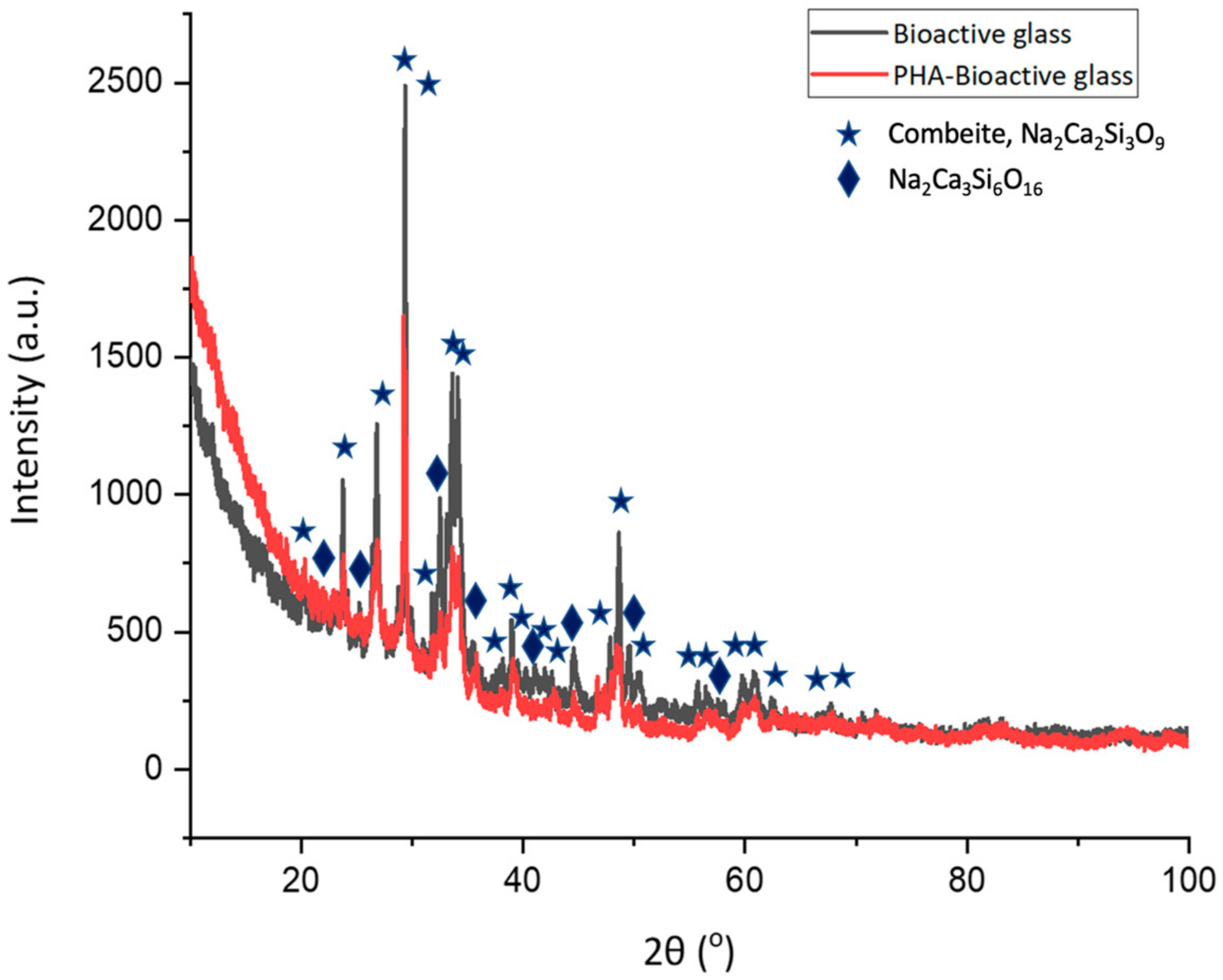
2.5. XRD
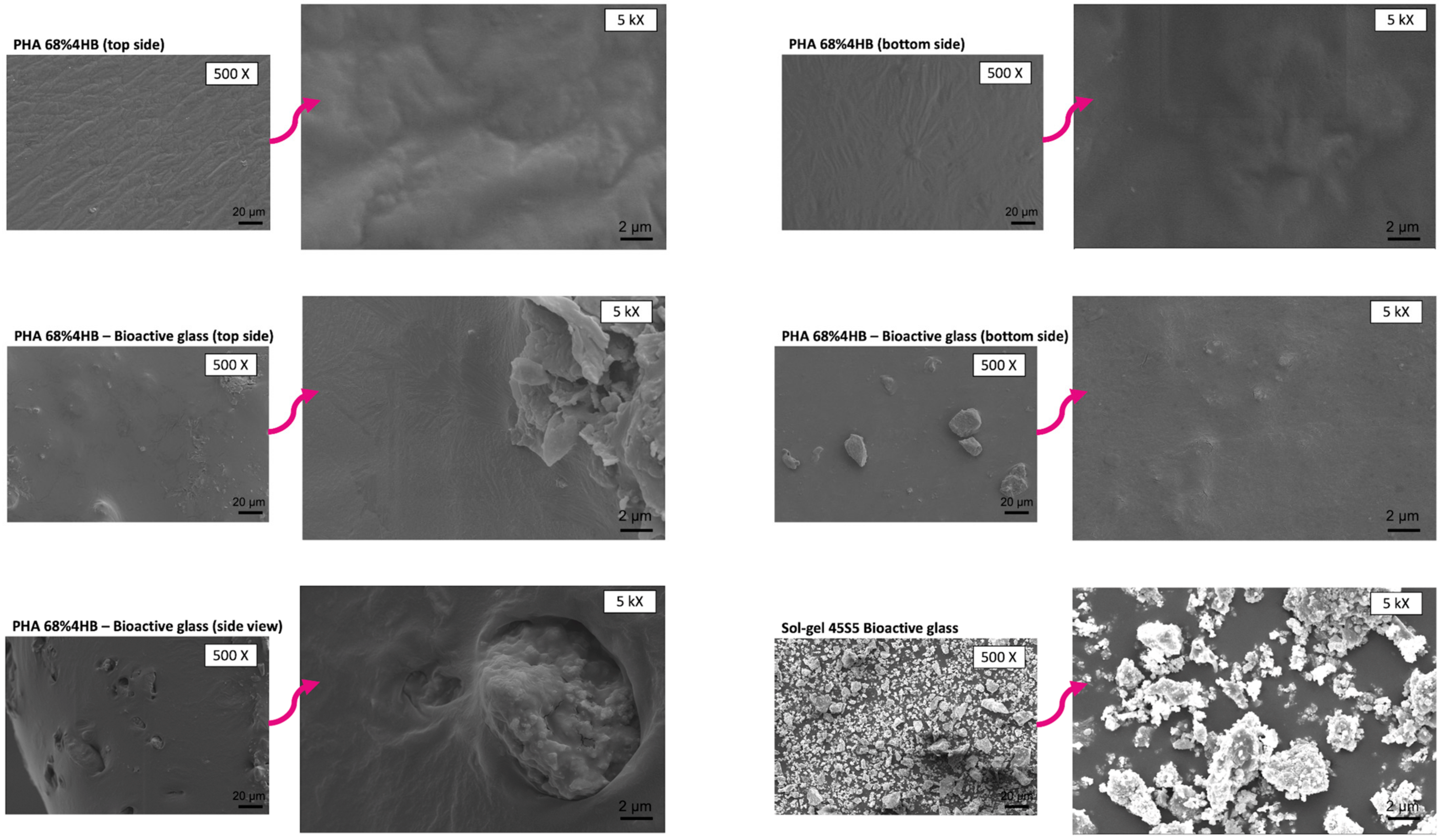
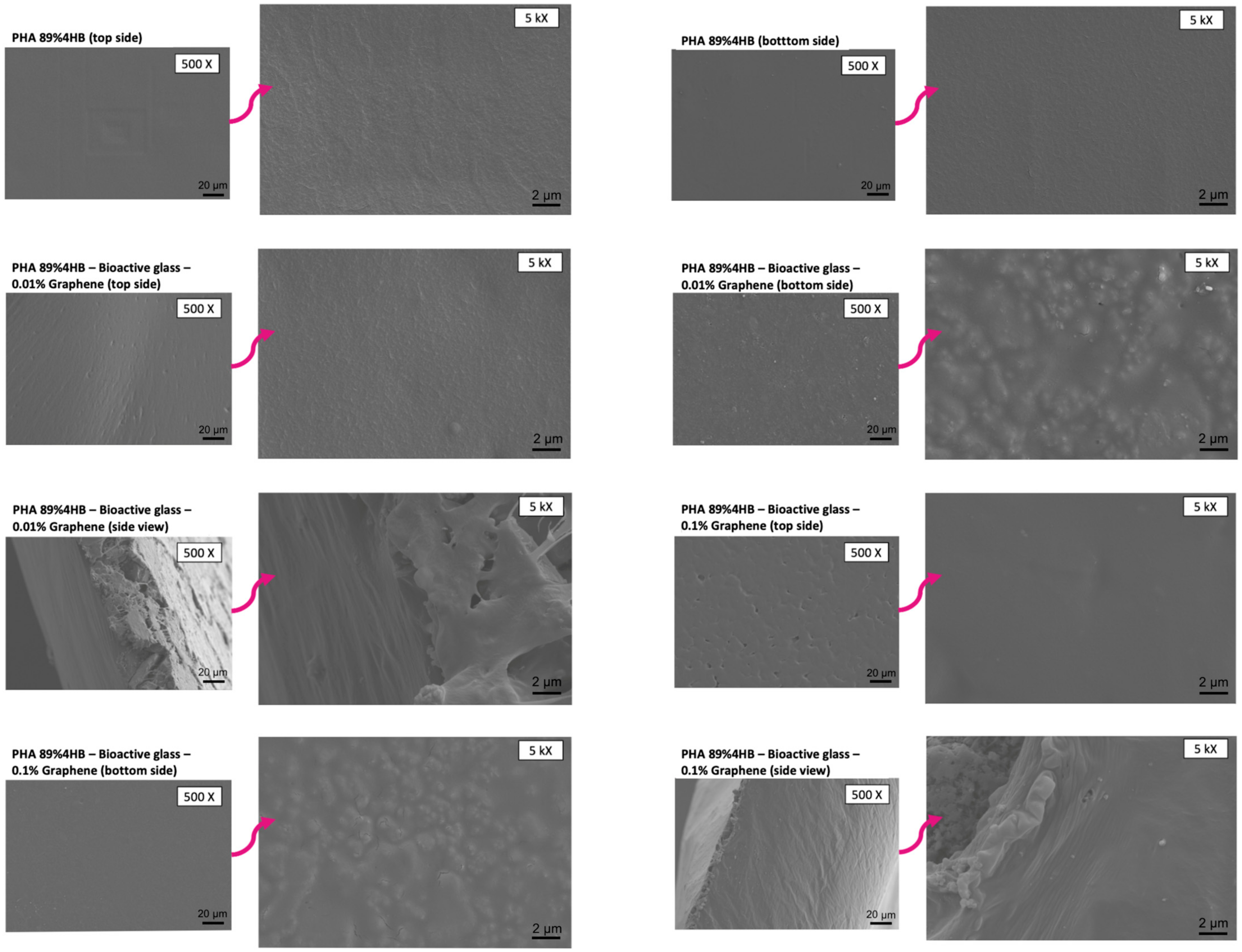
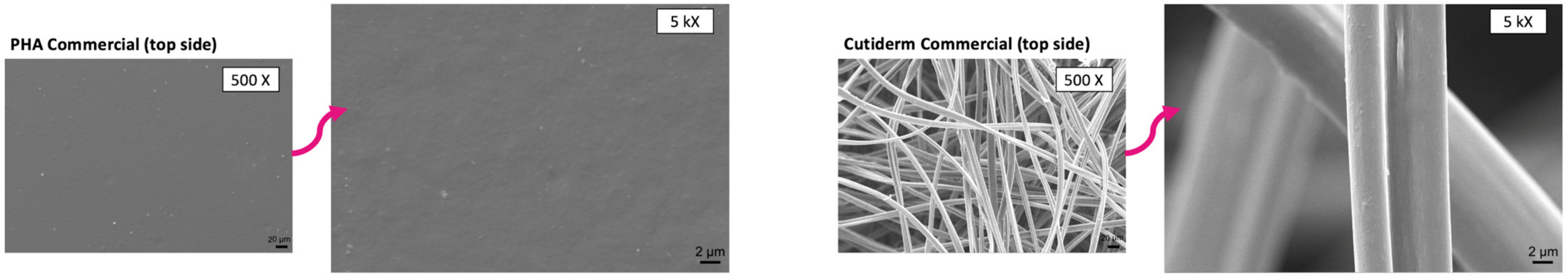
2.6. SEM
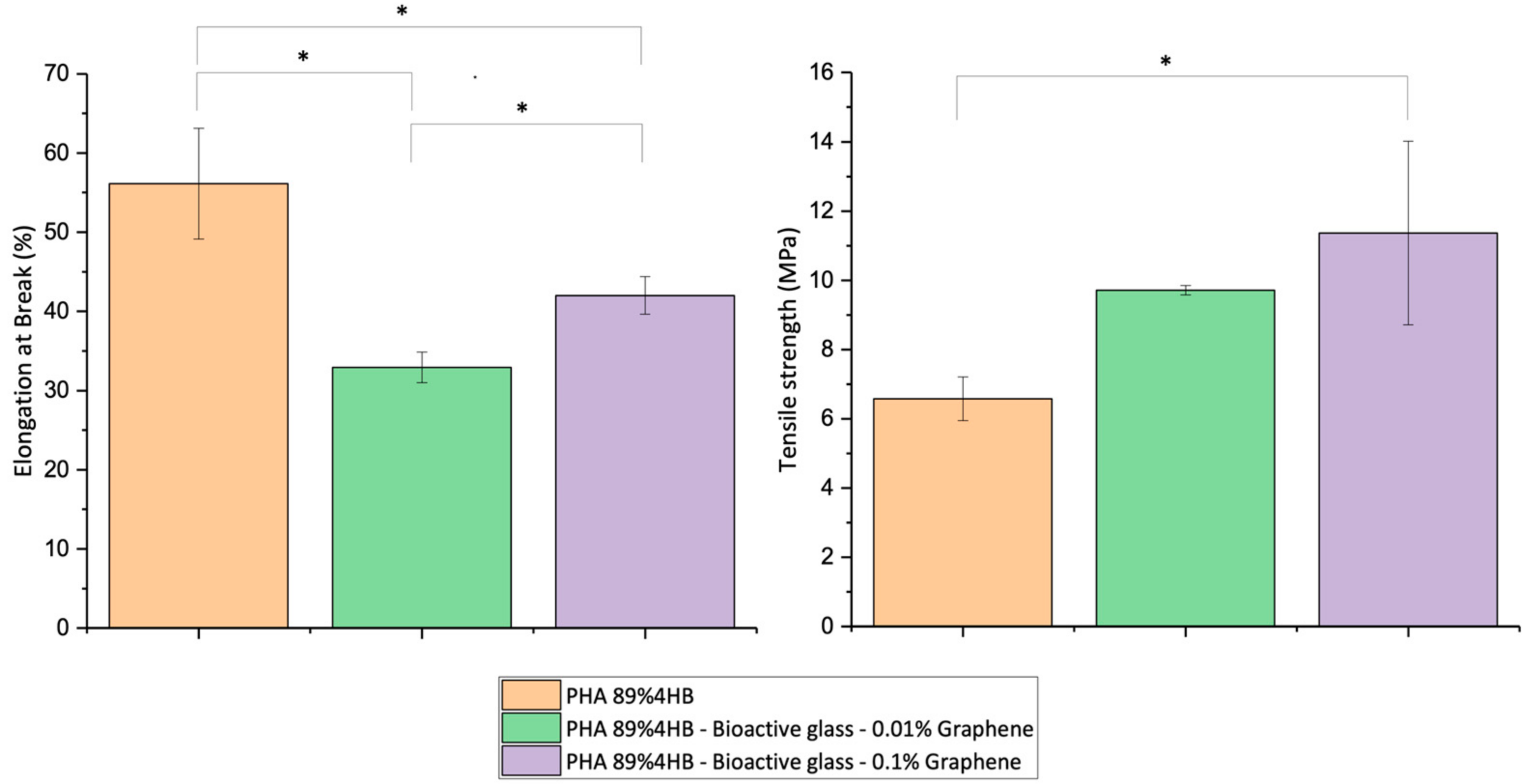
2.7. DMA
2.8. Water Contact Angle
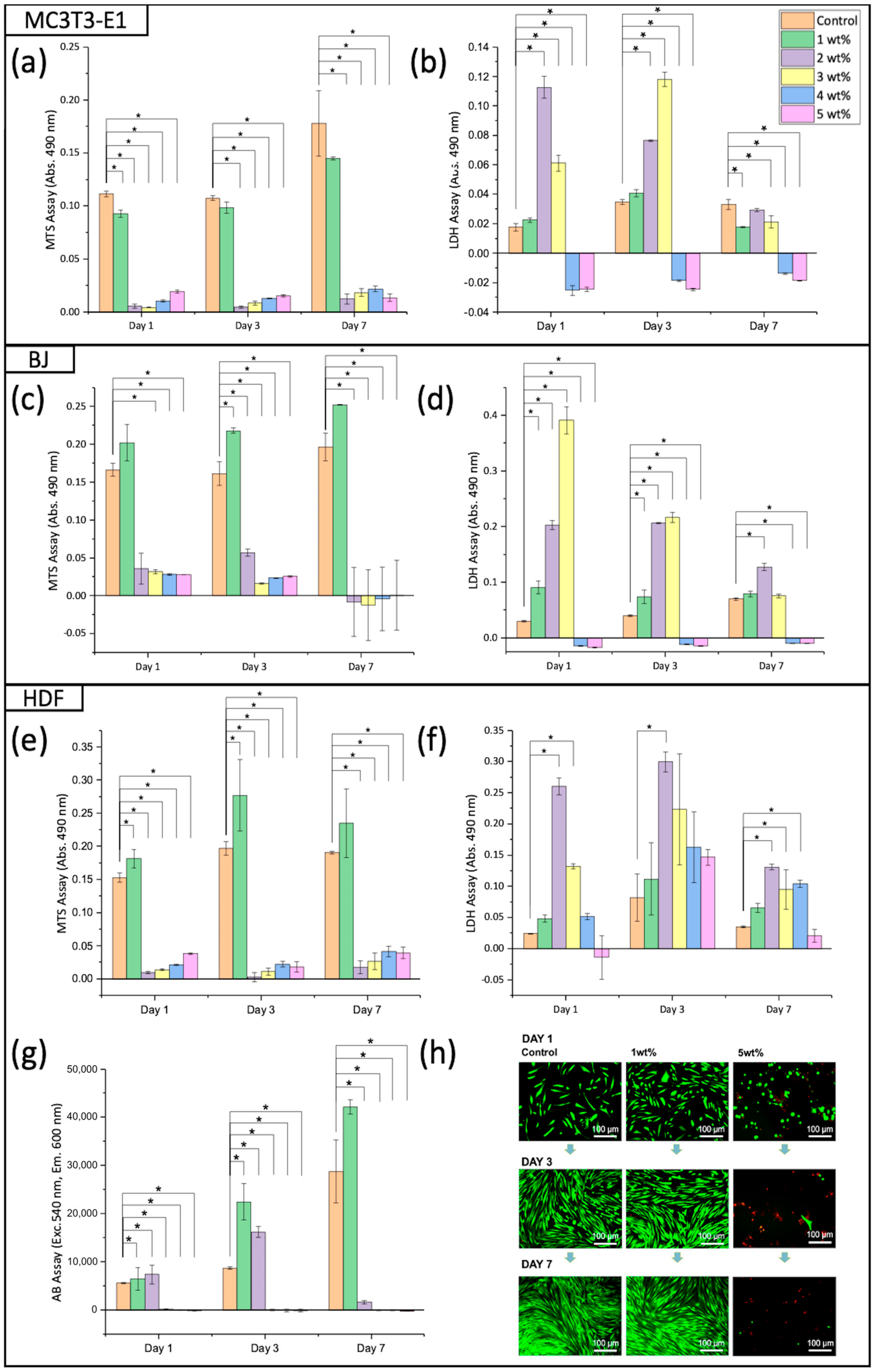
2.9. Viability of Cells
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Preparation of the Inoculum
4.2.2. Biosynthesis of the P(3HB-co-4HB) Copolymer
Fermentation in the Shake Flask
Fermentation in the Bioreactor
4.2.3. Extraction and Recovery of the P(3HB-co-4HB) Copolymer
4.2.4. Endotoxin Removal from the Copolymer
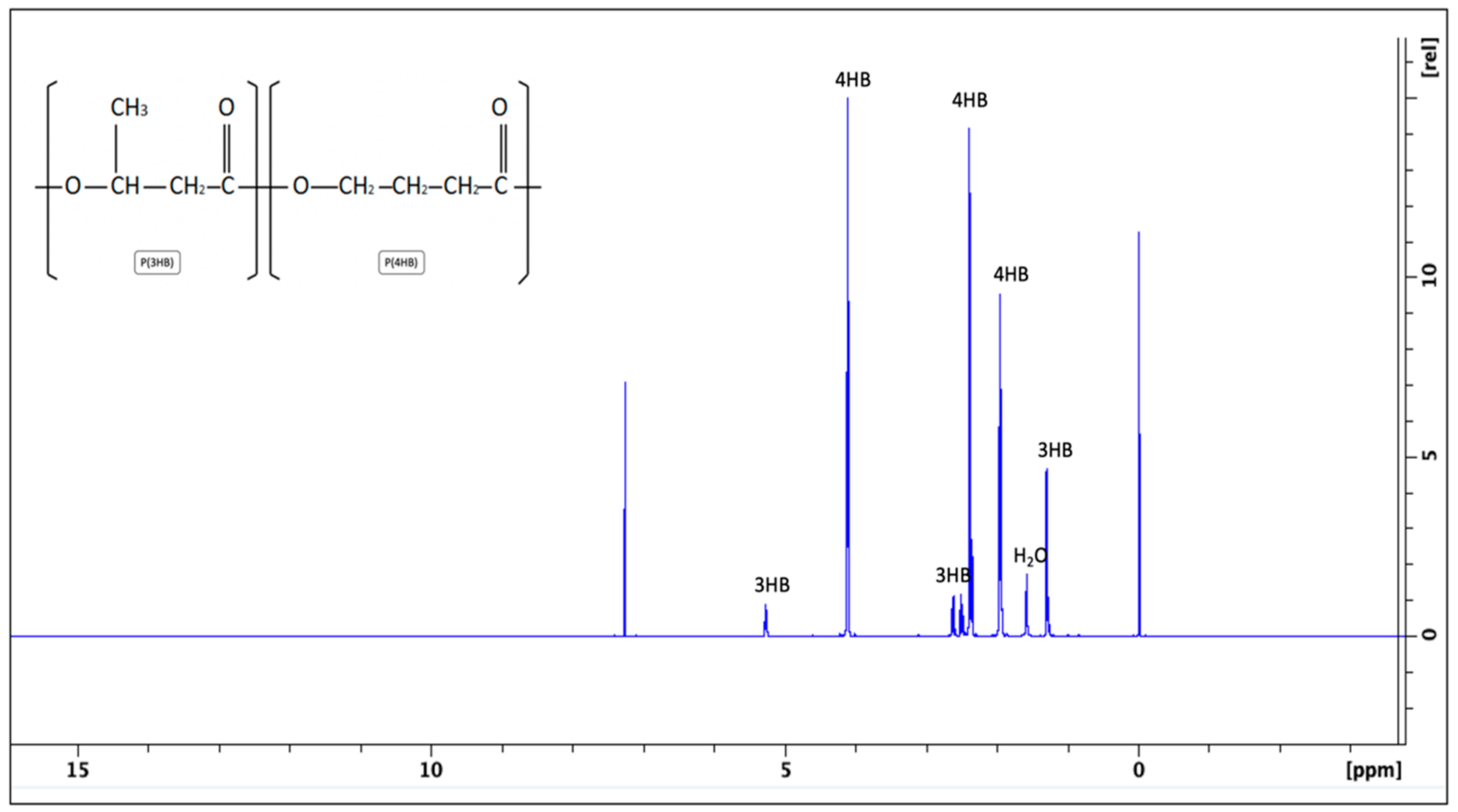
4.2.5. Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (1H-NMR) Spectroscopy
4.2.6. Preparation of the Sol-Gel-Derived Bioactive Glass
4.2.7. Preparation of the Liquid Exfoliated Graphene
4.2.8. Casting of the P(3HB-co-4HB) Composite
4.3. Characterisation Techniques
4.3.1. Attenuated Total Reflectance—Fourier-Transform Infrared (ATR-FTIR)
4.3.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
4.3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4.3.4. X-ray Diffractometry (XRD)
4.3.5. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA)
4.3.6. Water Contact Angle
4.3.7. Cell Metabolic Assays
Metabolic Activity Using MTS and AB
LDH Assay
Live and Dead Cell Imaging
4.4. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marques, R.; Lopes, M.; Ramos, P.; Neves Amado, J.; Alves, P. Prognostic Factors for Delayed Healing of Complex Wounds in Adults: A Scoping Review Protocol. Nurs. Rep. 2022, 12, 904–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faisalina, A.F.; Sonvico, F.; Colombo, P.; Amirul, A.A.; Wahab, H.A.; Majid, M.I.A. Docetaxel-Loaded Poly(3hb-Co-4hb) Biodegradable Nanoparticles: Impact of Copolymer Composition. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimada, K.; Ojima, Y.; Ida, Y.; Matsumura, H. Efficacy of Versajet Hydrosurgery System in Chronic Wounds: A Systematic Review. Int. Wound J. 2021, 18, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aramwit, P. Introduction to Biomaterials for Wound Healing; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirhaj, M.; Labbaf, S.; Tavakoli, M.; Seifalian, A.M. Emerging Treatment Strategies in Wound Care. Int. Wound J. 2022, 19, 1934–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norhafini, H.; Thinagaran, L.; Shantini, K.; Huong, K.H.; Syafiq, I.M.; Bhubalan, K.; Amirul, A.A. Synthesis of Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate-Co-4-Hydroxybutyrate) with High 4HB Composition and PHA Content Using 1,4-Butanediol and 1,6-Hexanediol for Medical Application. J. Polym. Res. 2017, 24, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huong, K.H.; Azuraini, M.J.; Aziz, N.A.; Amirul, A.A.A. Pilot Scale Production of Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate-Co-4-Hydroxybutyrate) Biopolymers with High Molecular Weight and Elastomeric Properties. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2017, 124, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muneer, F.; Rasul, I.; Azeem, F.; Siddique, M.H.; Zubair, M.; Nadeem, H. Microbial Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs): Efficient Replacement of Synthetic Polymers. J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 28, 2301–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syafiq, I.M.; Huong, K.H.; Shantini, K.; Vigneswari, S.; Aziz, N.A.; Amirul, A.A.A.; Bhubalan, K. Synthesis of High 4-Hydroxybutyrate Copolymer by Cupriavidus Sp. Transformants Using One-Stage Cultivation and Mixed Precursor Substrates Strategy. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2017, 98, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, K.; Zahid, S.; Batool, M.; Chaudhry, A.A.; Jamal, A.; Iqbal, F.; Nawaz, M.H.; Goerke, O.; Gurlo, A.; Shah, A.T.; et al. In-Vitro Investigation of Graphene Oxide Reinforced Bioactive Glass Ceramics Composites. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2019, 505, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Guo, B. Antibacterial Biomaterials for Skin Wound Dressing. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 17, 353–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramlee, S.N.L.; Sharifulden, N.S.A.N.; Mohamad, H.; Noor, S.N.F.M. Sol-Gel Derived Bioactive Glass Scaffolds Incorporated with Polyvinyl-Alcohol and Pluronic P123 Polymers Using Sponge Replication Technique. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 17, 966–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Li, W.; Müller, T.; Schubert, D.W.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Yao, Q.; Roether, J.A. Electrospun Polyhydroxybutyrate/Poly(ϵ-Caprolactone)/58S Sol-Gel Bioactive Glass Hybrid Scaffolds with Highly Improved Osteogenic Potential for Bone Tissue Engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 17098–17108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Cao, H.; Xue, Y.; Li, B.; Cai, W. Liquid-Phase Exfoliation of Graphene: An Overview on Exfoliation Media, Techniques, and Challenges. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noroozi, M.; Zakaria, A.; Radiman, S.; Wahab, Z.A. Environmental Synthesis of Few Layers Graphene Sheets Using Ultrasonic Exfoliation with Enhanced Electrical and Thermal Properties. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.C.; Deokar, A.R.; Liao, J.H.; Shih, P.Y.; Ling, Y.C. Graphene-Based Photothermal Agent for Rapid and Effective Killing of Bacteria. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 1281–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vacacela Gomez, C.; Guevara, M.; Tene, T.; Villamagua, L.; Usca, G.T.; Maldonado, F.; Tapia, C.; Cataldo, A.; Bellucci, S.; Caputi, L.S. The Liquid Exfoliation of Graphene in Polar Solvents. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 546, 149046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, K.-Y. Definitions for Hydrophilicity, Hydrophobicity, and Superhydrophobicity: Getting the Basics Right. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 686–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piarali, S.; Marlinghaus, L.; Viebahn, R.; Lewis, H.; Ryadnov, M.G.; Groll, J.; Salber, J.; Roy, I. Activated Polyhydroxyalkanoate Meshes Prevent Bacterial Adhesion and Biofilm Development in Regenerative Medicine Applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsner, J.J.; Kraitzer, A.; Grinberg, O.; Zilberman, M. Highly Porous Drug-Eluting Structures: From Wound Dressings to Stents and Scaffolds for Tissue Regeneration. Biomatter 2012, 2, 239–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugnicourt, E.; Cinelli, P.; Lazzeri, A.; Alvarez, V. Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA): Review of Synthesis, Characteristics, Processing and Potential Applications in Packaging. Express Polym. Lett. 2014, 8, 791–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, Q.; de Pablos-Martín, A.; Martins de Souza e Silva, J.; Hurle, K.; Jaimes, A.T.C.; Brauer, D.S.; Boccaccini, A.R. New Insights into the Crystallization Process of Sol-Gel–Derived 45S5 Bioactive Glass. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 103, 4234–4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayari, S.; Severcan, F. FTIR Study of Biodegradable Biopolymers: P(3HB), P(3HB-Co-4HB) and P(3HB-Co-3HV). J. Mol. Struct. 2005, 744–747, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansiz, K.; Billman-Jacobe, H.; McNaughton, D. Quantitative Determination of the Biodegradable Polymer Poly(β-Hydroxybutyrate) in a Recombinant Escherichia Coli Strain by Use of Mid-Infrared Spectroscopy and Multivariative Statistics. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 3415–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagiah, N.; Madhavi, L.; Anitha, R.; Srinivasan, N.T.; Sivagnanam, U.T. Electrospinning of Poly (3-Hydroxybutyric Acid) and Gelatin Blended Thin Films: Fabrication, Characterization, and Application in Skin Regeneration. Polym. Bull. 2013, 70, 2337–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothfuss, N.E.; Petters, M.D. Influence of Functional Groups on the Viscosity of Organic Aerosol. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliaa, N.S.N.S.; Fazliah, M.N.S.N.; Fatimah, S.S.; Syazana, A.N. Synthesis and Characterization of PLA-PEG Biocomposite Incorporated with Sol-Gel Derived 45S5 Bioactive Glass. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 17, 982–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, J.; Drevet, R.; Lemelle, A.; Ben Jaber, N.; Tara, A.; El Btaouri, H.; Benhayoune, H. A New Sol-Gel Synthesis of 45S5 Bioactive Glass Using an Organic Acid as Catalyst. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 47, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daemi, H.; Barikani, M. Synthesis and Characterization of Calcium Alginate Nanoparticles, Sodium Homopolymannuronate Salt and Its Calcium Nanoparticles. Sci. Iran. 2012, 19, 2023–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.P.; Williams, S.F. Medical Applications of Poly-4-Hydroxybutyrate: A Strong Flexible Absorbable Biomaterial. Biochem. Eng. J. 2003, 16, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sombatmankhong, K.; Suwantong, O.; Waleetorncheepsawat, S.; Supphol, P. Electrospun Fiber Mats of Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate), Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate-Co-3-Hydroxyvalerate), and Their Blends. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2006, 44, 2923–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza Santos, C.L.; Dias, M.L.; da Silva, M.H.P. Polyoxymethylene/Graphene Nanocomposites: Thermal, Crystallization, Melting and Rheological Behavior. J. Compos. Mater. 2021, 55, 1485–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.R.; Ashok Kumar, S.; Bhuvana, K.P. Preparation and Evaluation of Bioactivity of Porous Bioglass Tablets for Bone Tissue Regeneration. SciMed. J. 2019, 1, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifulden, N.S.A.N.; Noor, S.N.F.M.; Samsurrijal, S.F.; Ramlee, S.N.L.; Azizan, N.S. Investigation of PLA-PEG-45S5 Bioactive Glass Composite Enhancement on Bioactivity. Key Eng. Mater. 2020, 833, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneswari, S.; Abdul Khalil, H.P.S.; Amirul, A.A. Designing of Collagen Based Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate-Co-4-Hydroxybutyrate) Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2015, 2015, 731690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girvan, L. Preparing Samples for the Electron Microscope. Science Learning Hub—Pokapū Akoranga Pūtaiao. 2014. Available online: https://www.sciencelearn.org.nz/resources/500-preparing-samples-for-the-electron-microscope (accessed on 8 August 2023).
- Baino, F.; Hamzehlou, S.; Kargozar, S. Bioactive Glasses: Where Are We and Where Are We Going? J. Funct. Biomater. 2018, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hench, L.L.; Jones, J.R. Bioactive Glasses: Frontiers and Challenges. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2015, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, V.; Lee, I.; Chun, H.H.; Park, H. Graphene Reinforced Biodegradable Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate-Co-4-Hydroxybutyrate) Nano-Composites. Express Polym. Lett. 2013, 7, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamjid, E.; Bagheri, R.; Vossoughi, M.; Simchi, A. Effect of Particle Size on the in Vitro Bioactivity, Hydrophilicity and Mechanical Properties of Bioactive Glass-Reinforced Polycaprolactone Composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2011, 31, 1526–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshaw, H.; Forbes, A.; Day, R.M. Release of Angiogenic Growth Factors from Cells Encapsulated in Alginate Beads with Bioactive Glass. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 4171–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zain, N.S.M.; Sharifulden, N.S.A.N.; Noor, S.N.F.M.; Zali, N.; Cugati, N.; Nordin, N.F. Dental Pulp Stem Cells Response to Chrysanthemum Flower Extract. Malaysian J. Med. Health Sci. 2019, 15, 80–87. [Google Scholar]
- Daya Gireesh, T.K.; Anzila, V.I.; Litha, T.T.; Nair, P.P. Synthesis of Graphene-Based Polymer Nanocomposites and Comparison of Properties. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 1248, 012012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Method of Inoculation | Optical Density Measurements to Monitor Bacterial Growth (A), by Trials | Initial Weight of Lyophilised Cells before Extraction 1 (g) | Final Weight of Extracted/Recovered Crude Copolymer 2 (g) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (Mean) | 2 (Mean) | 3 (Mean) | Mean of Three Trials ± SD | ||||
| Shake flask | 48 h | 0.667 | 0.649 | 0.625 | 0.647 ± 0.021 | 1.25 | 0.65 (51.72%) |
| Bioreactor | 48 h | 0.7 | 0.682 | 0.687 | 0.690 ± 0.019 | 1.25 | 0.69 (55.19%) |
| Samples (48 h Harvesting Timepoint) | Monomer Composition (3HB:4HB), via 1H-NMR |
|---|---|
| P(3HB-co-4HB): batch A | 16%:84% |
| 11%:89% | |
| P(3HB-co-4HB): batch B | 32%:68% |
| 31%:69% |
| Samples | Contact Angle of Water, θ (°) | |
|---|---|---|
| Side A | Side B | |
| PHA 68% 4HB | 106.2 | 103.1 |
| PHA 89% 4HB | 87.1 | 79.5 |
| PHA 89% 4HB—Bioactive glass—0.01% Graphene | 46.3 | 60.6 |
| PHA 89% 4HB—Bioactive glass—0.1% Graphene | 57.3 | 64.6 |
| Commercial PHA | 76.9 | 80.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sharifulden, N.S.A.N.; Barrios Silva, L.V.; Nair, S.P.; Abdullah, A.A.A.; Noor, S.N.F.M.; Sulu, M.; Nguyen, L.T.B.; Chau, D.Y.S. The Development and Characterisation of a P(3HB-co-4HB)–Bioactive Glass–Graphene Hydrogel as a Potential Formulation for Biomedical and Therapeutical Translation. Gels 2024, 10, 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10010085
Sharifulden NSAN, Barrios Silva LV, Nair SP, Abdullah AAA, Noor SNFM, Sulu M, Nguyen LTB, Chau DYS. The Development and Characterisation of a P(3HB-co-4HB)–Bioactive Glass–Graphene Hydrogel as a Potential Formulation for Biomedical and Therapeutical Translation. Gels. 2024; 10(1):85. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10010085
Chicago/Turabian StyleSharifulden, Nik S. A. N., Lady V. Barrios Silva, Sean P. Nair, Amirul A. A. Abdullah, Siti N. F. M. Noor, Michael Sulu, Linh T. B. Nguyen, and David Y. S. Chau. 2024. "The Development and Characterisation of a P(3HB-co-4HB)–Bioactive Glass–Graphene Hydrogel as a Potential Formulation for Biomedical and Therapeutical Translation" Gels 10, no. 1: 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10010085
APA StyleSharifulden, N. S. A. N., Barrios Silva, L. V., Nair, S. P., Abdullah, A. A. A., Noor, S. N. F. M., Sulu, M., Nguyen, L. T. B., & Chau, D. Y. S. (2024). The Development and Characterisation of a P(3HB-co-4HB)–Bioactive Glass–Graphene Hydrogel as a Potential Formulation for Biomedical and Therapeutical Translation. Gels, 10(1), 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10010085