Injectable and In Situ Phospholipid-Based Phase Separation Gel for Sustained Delivery of Altrenogest
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
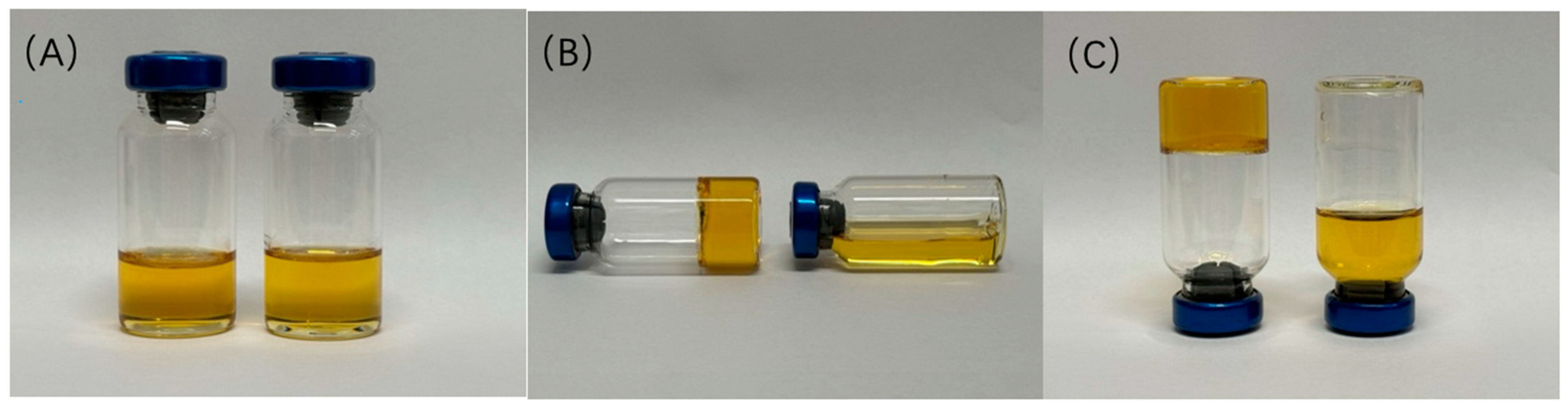
2.1. Characterization and Viscosity of Blank Gel
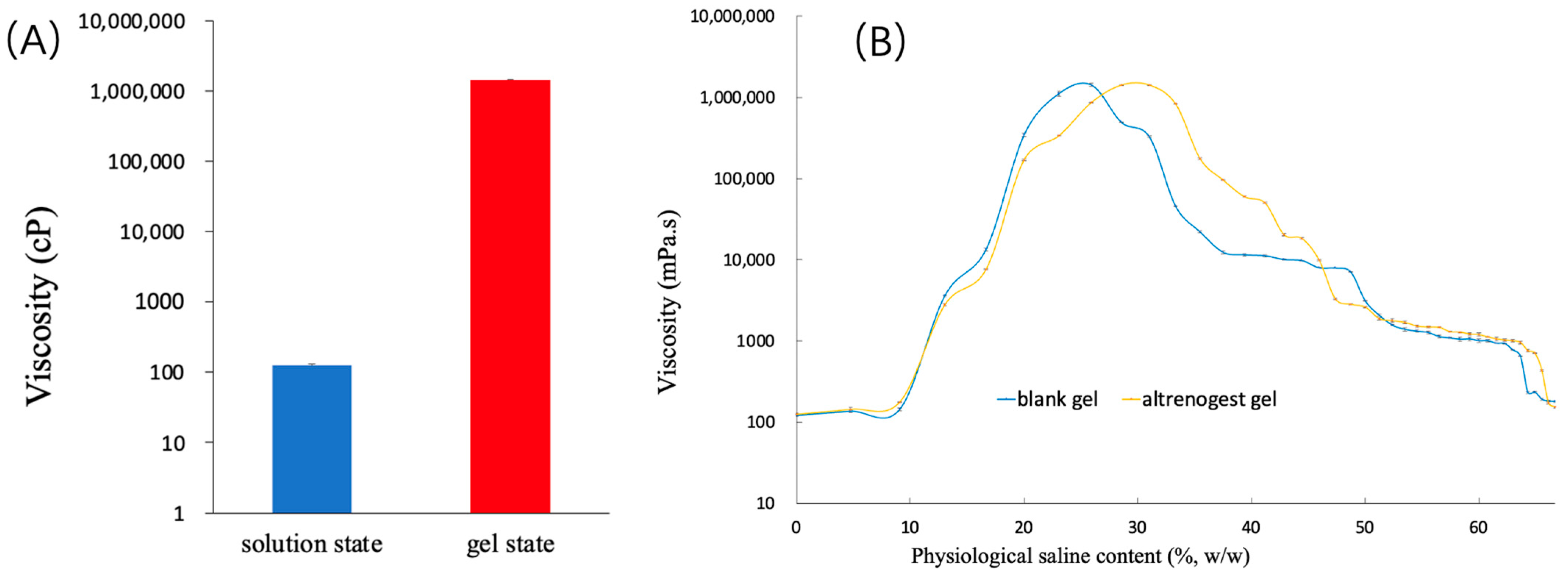
2.2. Effect of Physiological Saline on the Viscosity of Blank Gel
2.3. Characterization of Altrenogest Gel
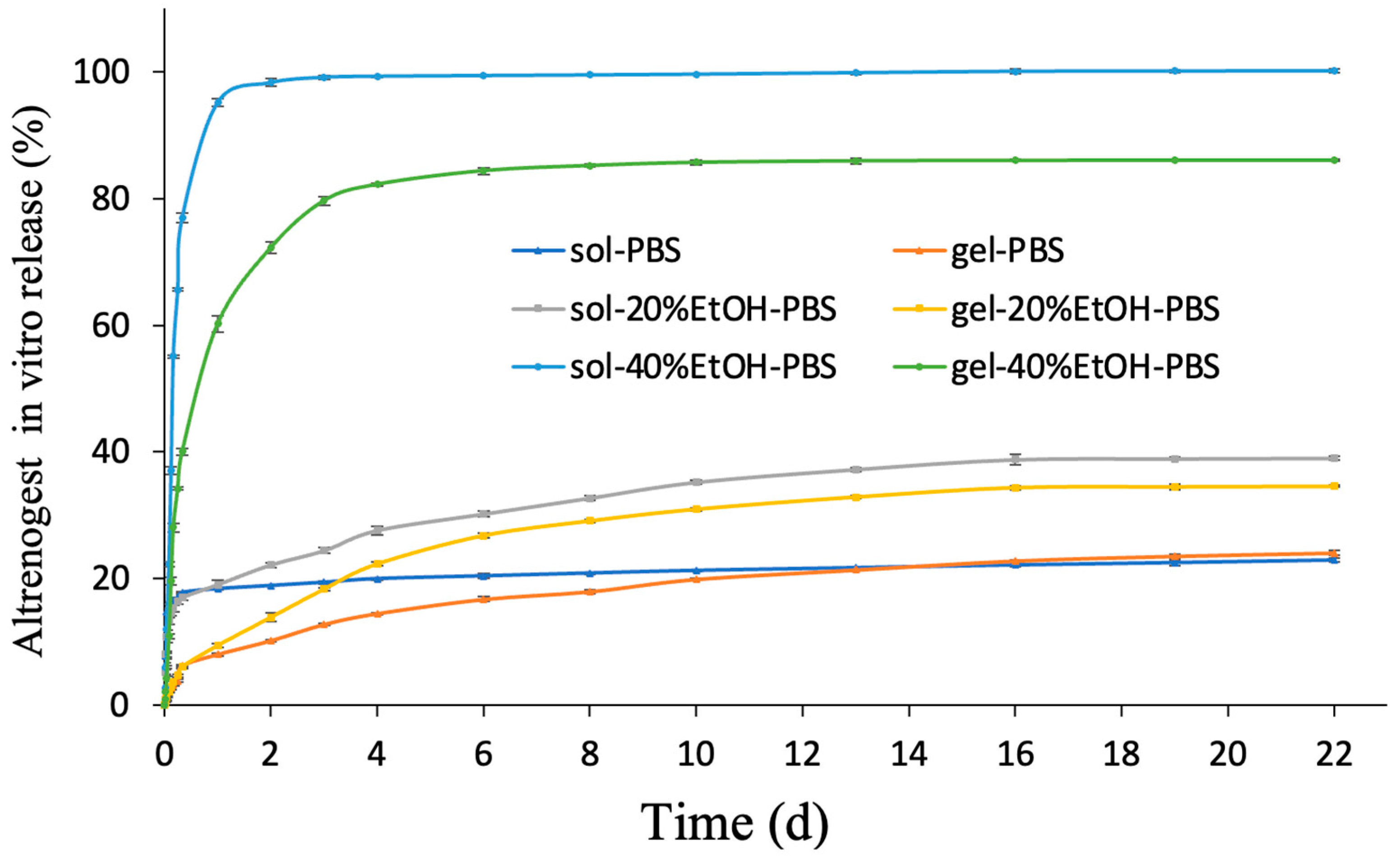
2.4. In Vitro Release Study
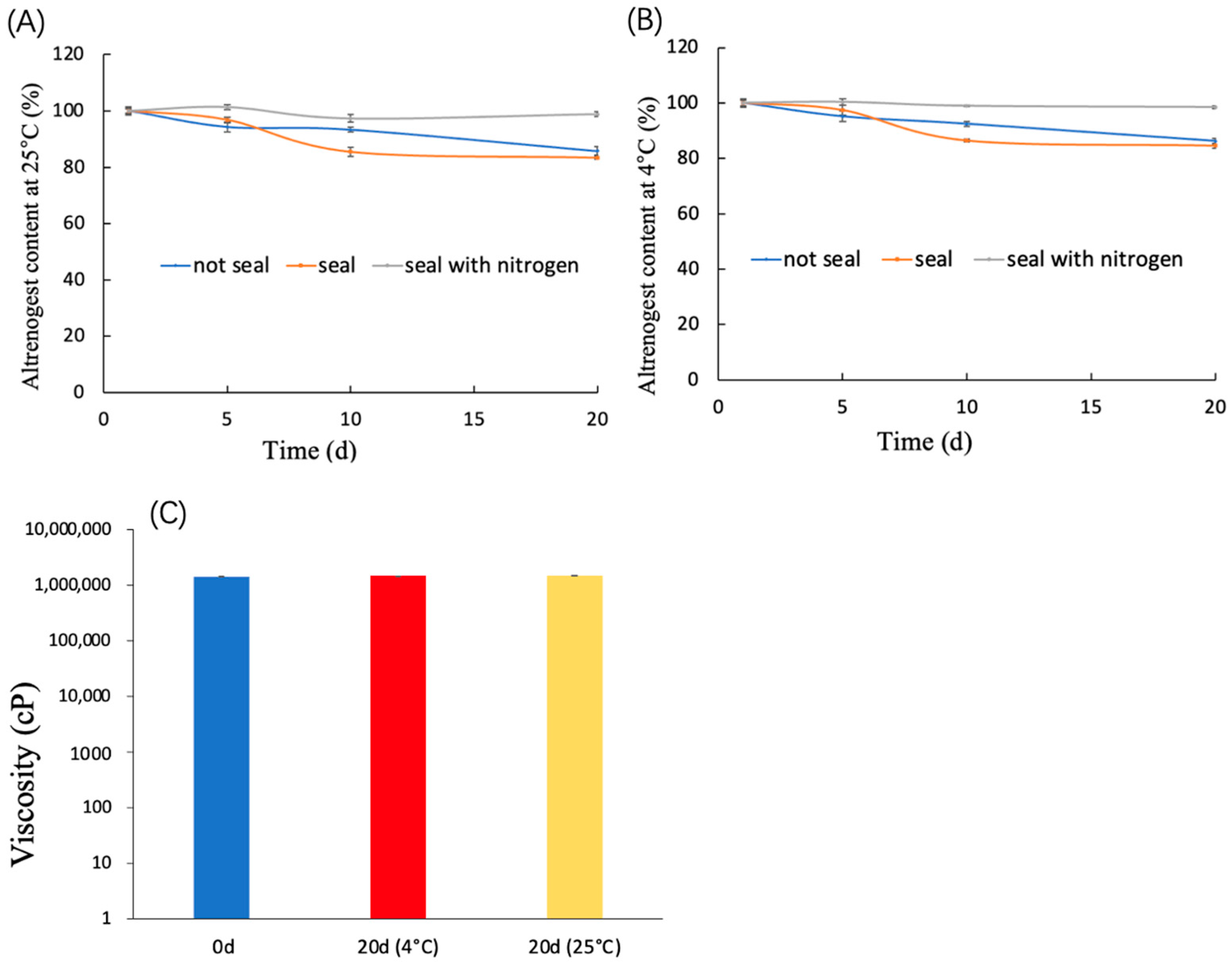
2.5. Storage Stability
2.6. Pharmacokinetic Study
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of Blank Gel and Altrenogest Gel
4.3. Viscosity Measurement
4.4. Effect of Physiological Saline on Viscosity of Gel
4.5. Phase Transition of Altrenogest Gel
4.6. Sustained Drug Release Behavior
4.7. Storage Stability Study of Altrenogest Gel
4.8. In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Study
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, K.; Xu, X.; Song, Y.; Xiao, L.; Wen, J.; Ding, H.; Zhao, S.; Qiao, D.; Zhang, B.; Niu, A.; et al. Effect of altrenogest treatment before weaning on reproductive performance and production efficiency in primiparous and multiparous sows. Porc. Health Manag. 2024, 10, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muro, B.B.D.; Oliveira, A.C.R.; Carnevale, R.F.; Leal, D.F.; Monteiro, M.S.; Poor, A.P.; Pereira, F.A.; de Souza, L.J.; Ferreira, J.B.; Almond, G.W.; et al. Altrenogest Supplementation During Early Pregnancy Improves Reproductive Outcome in Pigs. Animals 2022, 12, 1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaggini, T.; Perin, J.; Arend, L.; Bernardi, M.; Wentz, I.; Bortolozzo, F. Altrenogest treatment associated with a farrowing induction protocol to avoid early parturition in sows. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2013, 48, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaeoket, K. Study on the oestrous synchronization in gilts by using progestin altrenogest and hCG: Its effect on the follicular development, ovulation time and subsequent reproductive performance. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2008, 43, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taechamaeteekul, P.; Dumniem, N.; Sang-Gassanee, K.; Tummaruk, P. Control of parturition in hyperprolific sows by using altrenogest and double administrations of PGF2α. Theriogenology 2022, 181, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muro, B.B.D.; Leal, D.F.; Carnevale, R.F.; Torres, M.A.; Mendonça, M.V.; Nakasone, D.H.; Martinez, C.H.G.; Ravagnani, G.M.; Monteiro, M.S.; Poor, A.P.; et al. Altrenogest during early pregnancy modulates uterine glandular epithelium and endometrial growth factor expression at the time implantation in pigs. Anim. Reprod. 2021, 18, e20200431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yu, F.; Zhu, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhang, L.; Pan, J. The effect of fixed-time artificial insemination protocol initiated at different stages of the estrous cycle on follicle development and ovulation in gilts. J. Reprod. Dev. 2021, 67, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianluppi, R.D.F.; Lucca, M.S.; Quirino, M.; Mellagi, A.P.G.; Ulguim, R.d.R.; Bortolozzo, F.P. Altrenogest treatment during the last week of lactation on ovarian traits and subsequent reproductive performance of primiparous and multiparous sows. Theriogenology 2021, 176, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romoser, M.R.; Bidne, K.L.; Baumgard, L.H.; Keating, A.F.; Ross, J.W. Effects of increased ambient temperature and supplemental altrenogest prior to pregnancy establishment in gilts. J. Anim. Sci. 2022, 100, skac007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, H.; Qiu, S.; Wang, S.; Xia, L.; Bu, S. Investigations on residual elimination of altrenogest oral solution in pigs and the withdrawal time. Anim. Biotechnol. 2019, 32, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Ling, L.; Lan, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Ran, L.; Jiang, J.; Huang, X. Preparation of altrenogest soft capsules and their bioequivalence in gilts. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1468615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zheng, X.; Lao, W.; Wang, H.; Chen, S.; Liu, C.; Chen, Z.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhan, X.; et al. Enhancement of the solubility and oral bioavailability of altrenogest through complexation with hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 194, 106691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Gao, J.; Xu, X.; Zhao, H.; Xue, R.; Zhou, J.; Hong, W.; Qiu, H. Fabrication of thermal sensitive folic acid based supramolecular hybrid gels for injectable drug release gels. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 75, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Lee, H.J.; Jeong, B. Hyaluronic acid-g-PPG and PEG-PPG-PEG hybrid thermogel for prolonged gel stability and sustained drug release. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 291, 119559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, M.; Tang, P.; Jiang, D. Chitosan/Sodium Alginate Hydrogel for the Release of Berberine as an Algae Suppressant: RSM Optimization and Analysis of Sustained Release Characteristics. Gels 2024, 10, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafarbeglou, M.; Meimandi-Parizi, A.; Derakhshandeh, A.; Khodakaram-Tafti, A.; Bigham-Sadegh, A.; Arkan, P.; Jafarbeglou, M. Silk fibroin/chitosan thiourea hydrogel scaffold with vancomycin and quercetin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles for treating chronic MRSA osteomyelitis in rats. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 666, 124826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mistretta, K.S.; Tiche, J.; Chiu, B.; Coburn, J.M. Local Sustained Dinutuximab Delivery and Release from Methacrylated Chondroitin Sulfate. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalessi, M.; Moghaddam, Y.T.; Khanmohammadi, M.; Hassanzadeh, S.; Azad, Z.; Farhadi, M. Sustained co-release of ciprofloxacin and dexamethasone in rabbit maxillary sinus using polyvinyl alcohol-based hydrogel microparticle. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2024, 35, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Luo, S.; Peng, X.; Zhao, T.; He, Q.; Wu, M.; Zhang, W.; Gong, T.; Zhang, Z. An intra-articular injectable phospholipids-based gel for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 18, 100777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Chen, D.; Gong, T.; He, Q.; Guo, C.; Zhang, P.; Song, X.; Ruan, J.; Gong, T. Chlorogenic acid sustained-release gel for treatment of glioma and hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2021, 166, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Guidoin, R.; Li, Y.; Brochu, G.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, L. Soybean-derived phospholipids complexed poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanofibrous scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Mater. Des. 2021, 205, 109737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Yi, X.; Liu, Z.; Dong, X.; Xia, G.; Zhang, X.; Shen, X. Comparative Study on Curcumin Loaded in Golden Pompano (Trachinotus blochii) Head Phospholipid and Soybean Lecithin Liposomes: Preparation, Characteristics and Anti-Inflammatory Properties. Molecules 2021, 26, 2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chang, C.; Zhai, J.; Yang, Y.; Yu, H. Ascorbyl palmitate effects on the stability of curcumin-loaded soybean phosphatidylcholine liposomes. Food Biosci. 2021, 41, 100923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Cao, X.; Chu, Y. Ginkgolides-loaded soybean phospholipid-stabilized nanosuspension with improved storage stability and in vivo bioavailability. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 181, 910–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, K.; Zhao, D.; Shi, X.; Lu, X. Use of caprylic/capric triglyceride in the encapsulation of dementholized peppermint fragrance leading to smaller and better distributed nanocapsules. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 84119–84126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, D.; Kang, H.; Gu, X.; Chen, F.; Liu, C. Robust, self-lubricating and injectable dECM-loaded hydrogels based on rapid photo-crosslinking for articular cartilage regeneration. Appl. Mater. Today 2024, 41, 102462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Luo, J.; Peng, Q.; Dong, J.; Wang, Y.; Gong, T.; Zhang, Z. Injectable and biodegradable phospholipid-based phase separation gel for sustained delivery of insulin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 176, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, L.; Mei, Q.; Dong, W.; Wu, S. Redox-responsive self-assembled peptide hydrogel for mitochondrial-targeted anticancer drug delivery. Appl. Mater. Today 2024, 41, 102471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Peng, Q.; San, F.-Y.; Luo, J.-W.; Wang, M.-X.; Wu, W.-Q.; Gong, T.; Zhang, Z.-R. A high-efficiency, low-toxicity, phospholipids-based phase separation gel for long-term delivery of peptides. Biomaterials 2015, 45, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.; Tang, L.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, T.; He, H.; Gou, J.; Yuan, Y.; Tang, X. Progesterone Phospholipid Gel for Intramuscular Administration Prepared by In Situ-Phase Separation. AAPS PharmSciTech 2022, 23, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visan, A.I.; Negut, I. Development and Applications of PLGA Hydrogels for Sustained Delivery of Therapeutic Agents. Gels 2024, 10, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hemelryck, S.; Wens, R.; van Poppel, H.; Luijks, M.; Shahidi, K.; Marczak, M.; Kahnt, A.; Holm, R.; Mannaert, E.; Langguth, P. In Vitro Evaluation of Poly(lactide-co-glycolide) In Situ Forming Gels for Bedaquiline Fumarate Salt and Pharmacokinetics Following Subcutaneous Injection in Rats. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorogy, H.M.E.; Fayez, S.M.; Khalil, I.A.; Jaleel, G.A.A.; Fayez, A.M.; Eliwa, H.A.; Teba, H.E. Microporation-Mediated Transdermal Delivery of In Situ Gel Incorporating Etodolac-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles for Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, S.; Roh, S.; Shim, J.; Yu, J.W.; Jung, Y.; Jang, W.Y.; Seo, B.; Won, Y.-Y.; Yoo, J. Modulating the Thermoresponsive Characteristics of PLGA-PEG-PLGA Hydrogels via Manipulation of PLGA Monomer Sequences. Biomacromolecules 2024, 25, 5374–5386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, M.; Wei, G.; Jia, M.; Gong, T.; Liu, J. An injectable in situ lipid phase transition system for sustained delivery of dabigatran etexilate with low burst release. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 56594–56601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Qin, X.-Y.; Cao, X.; Li, W.-H.; Gong, T.; Zhang, Z.-R. Thymopentin-loaded phospholipid-based phase separation gel with long-lasting immunomodulatory effects: In vitro and in vivo studies. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2019, 40, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Fan, L.; Yan, X.; Li, J. Stability and lipid oxidation of oil-in-water emulsion stabilized by Maillard conjugates of soybean phosphatidylethanolamine with different polysaccharides. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 156, 110343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, K.E.; Council-Troche, R.M.; Dollen, K.V.; Beachler, T.M.; Bailey, C.S.; Davis, J.L.; Lyle, S.K. Pharmacokinetics of intra-rectal altrenogest in horses. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2018, 72, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, H.; Xia, L.; Wang, S.; Bu, S. Comparative pharmacokinetic study of two kinds of altrenogest oral solutions for sows. Anim. Biotechnol. 2020, 32, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Sun, P.; Sun, F.; Qiu, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Lin, Y.; Gong, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; et al. Pharmacokinetics of altrenogest in gilts. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 42, 660–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
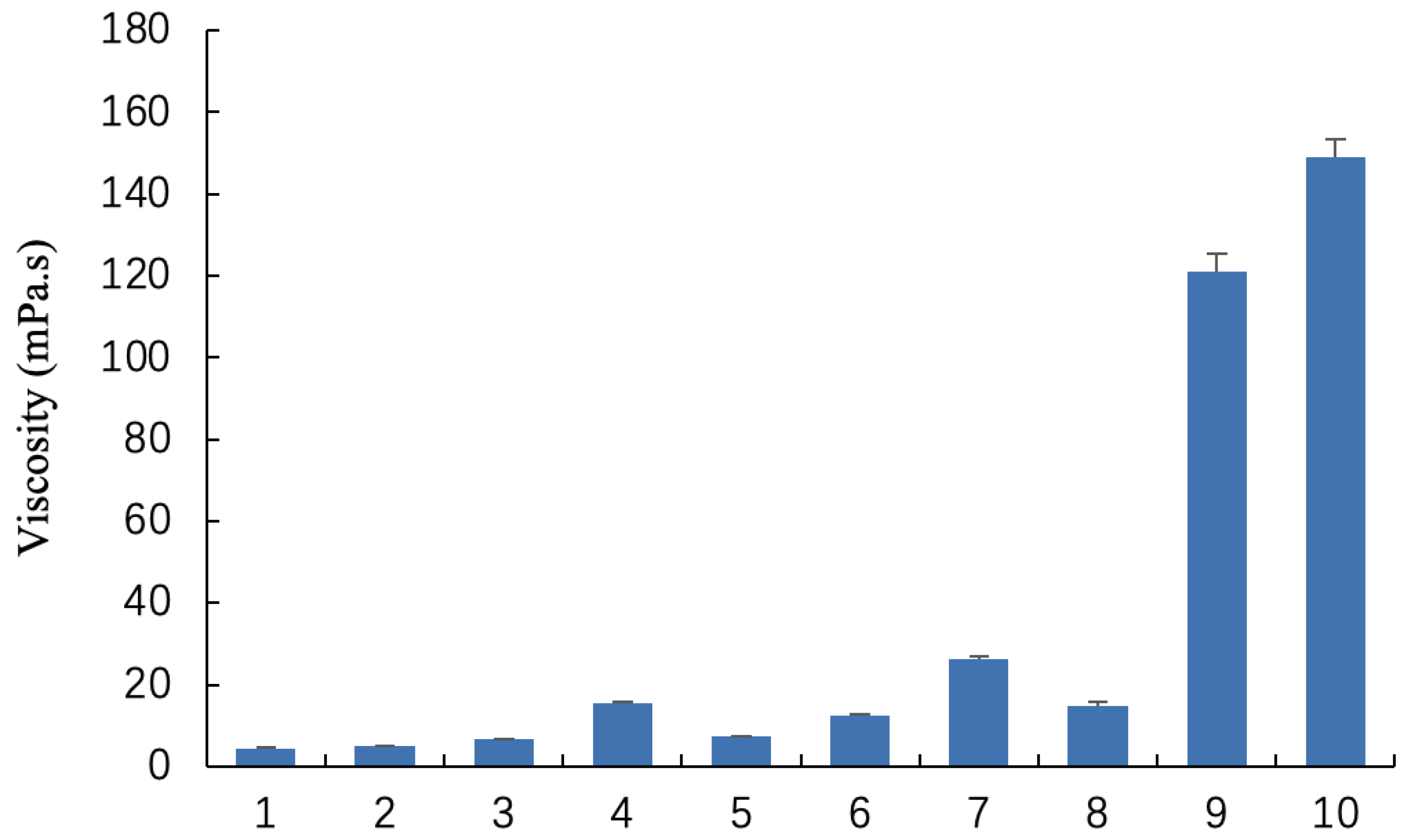



| Blank Gels | Soybean Phospholipid | Caprylic/Capric Triglyceride | Ethanol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Formulation 1 | 40 | 0 | 60 |
| Formulation 2 | 40 | 15 | 45 |
| Formulation 3 | 40 | 30 | 30 |
| Formulation 4 | 40 | 45 | 15 |
| Formulation 5 | 55 | 0 | 45 |
| Formulation 6 | 55 | 15 | 30 |
| Formulation 7 | 55 | 30 | 15 |
| Formulation 8 | 70 | 0 | 30 |
| Formulation 9 | 70 | 15 | 15 |
| Formulation 10 | 85 | 0 | 15 |
| Group | AUC (0–∞) (μg/L·h) | MRT (0–∞) (h) | t1/2 (h) | Tmax (h) | Cmax (μg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Altrenogest sol | 14,963.70 ± 1891.01 | 8.43 ± 1.69 | 8.51 ± 2.38 | 2.00 ± 1.22 | 1626.46 ± 421.81 |
| Altrenogest gel | 26,560.91 ± 6013.48 * | 40.92 ± 7.21 * | 80.03 ± 20.79 * | 5.33 ± 2.00 * | 1433.49 ± 416.41 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Abbas, A.; Li, N.; Li, C.; Ai, X.; Chen, L.; Dai, D.; Shu, G.; Lin, J.; Zhang, W.; et al. Injectable and In Situ Phospholipid-Based Phase Separation Gel for Sustained Delivery of Altrenogest. Gels 2024, 10, 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10120847
Li D, Abbas A, Li N, Li C, Ai X, Chen L, Dai D, Shu G, Lin J, Zhang W, et al. Injectable and In Situ Phospholipid-Based Phase Separation Gel for Sustained Delivery of Altrenogest. Gels. 2024; 10(12):847. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10120847
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Dongbo, Awn Abbas, Nanxin Li, Chao Li, Xiaoyang Ai, Lian Chen, Dongmei Dai, Gang Shu, Juchun Lin, Wei Zhang, and et al. 2024. "Injectable and In Situ Phospholipid-Based Phase Separation Gel for Sustained Delivery of Altrenogest" Gels 10, no. 12: 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10120847
APA StyleLi, D., Abbas, A., Li, N., Li, C., Ai, X., Chen, L., Dai, D., Shu, G., Lin, J., Zhang, W., Peng, G., Li, H., Xu, F., & Fu, H. (2024). Injectable and In Situ Phospholipid-Based Phase Separation Gel for Sustained Delivery of Altrenogest. Gels, 10(12), 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10120847








