The Influence of Gamma Radiation on Different Gelatin Nanofibers and Gelatins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
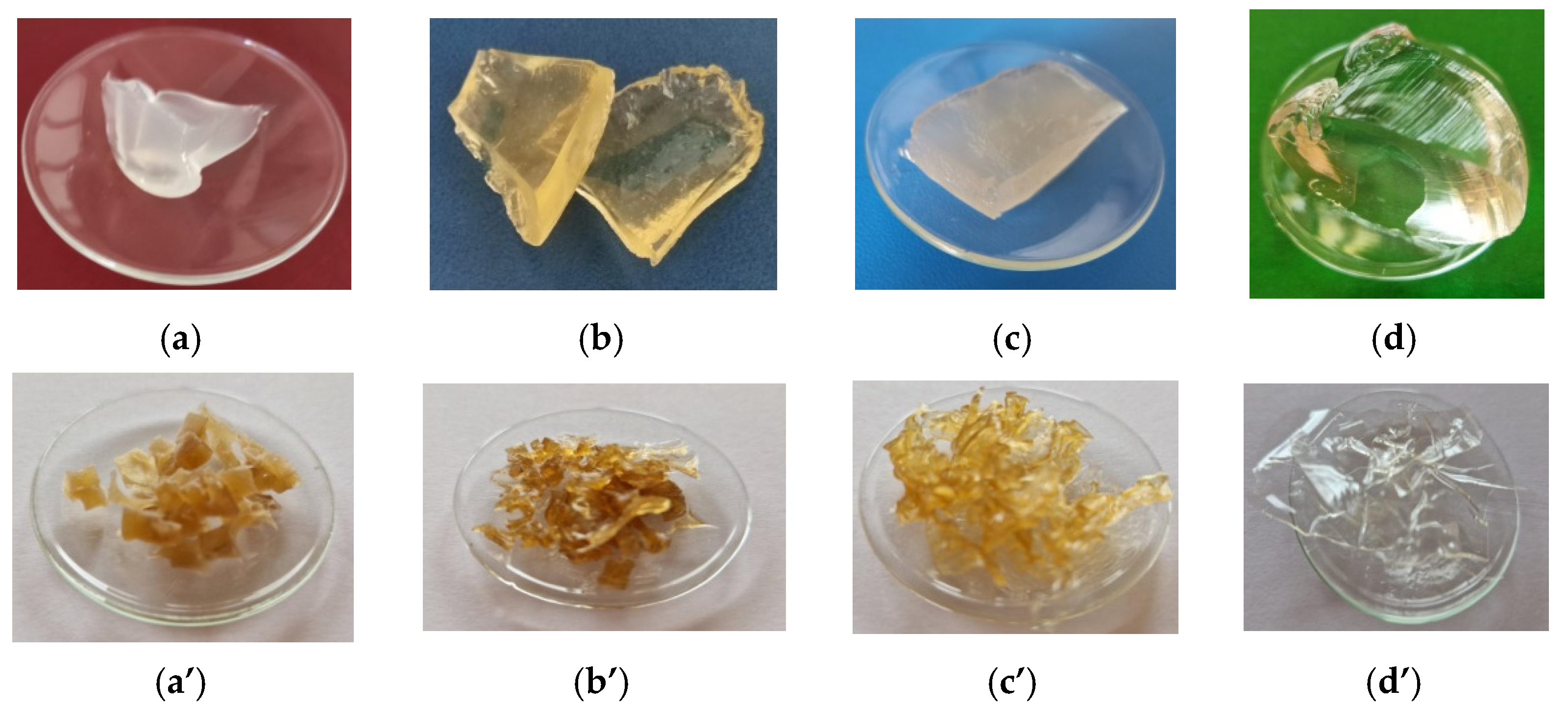
2.1. Gelatin Characterization
2.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
2.3. The Efficacy of Antimicrobial Preservation
2.4. Chemiluminescence Spectroscopy
2.5. EPR Spectroscopy
2.6. ATR-FTIR
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Nanofibers (NF) Preparation
4.3. Gelatin Nanofibers and Gelatin Treatment through Gamma Irradiation
4.4. Characterisation Methods
4.4.1. Physicochemical and Spectroscopic Characterization of Gelatins and Gelatin Nanofibers
4.4.2. Determination of Microbial Contamination
4.5. Statistical Data
5. Patents
- P1.
- Rapa, M.; Gaidau, C.; Matei, E.; Berechet, M.D.; Pantilimon, M.C.; Predescu, A.M.; Predescu, C. Composition of Nanowires Based on Collagen Using Rabbit Glue and Antimicrobial Agents and Process for Obtaining Them. RO 133873A0. Available online: http://pub.osim.ro/publication-server/pdf-document?PN=RO133873%20RO%20133873&iDocId=12868&iepatch=.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- P2.
- Rapa, M.; Gaidau, C.C.; Matei, E.; Stanca, M.; Berechet, M.D. Nanofibers from Donkey Hide Collagen and Process for Obtaining Therefore. OSIM A00770 from 28.11.2022 and Published in 2023. pg. 23. Available online: https://www.osim.ro/images/Publicatii/Inventii/2023/inv_03_2023.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- P3.
- Gaidau, C.; Rapa, M.; Predescu, C.; Stanca, M.; Alexe, C.A. Nanofibers from Fish Scale Collagen and Process to Obtaining Therefore, OSIM A00782 from 29.11.2022, Published in 2023. pg. 23. Available online: https://www.osim.ro/images/Publicatii/Inventii/2023/inv_03_2023.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2024).
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eskilson, O.; Zattarin, E.; Berglund, L.; Oksman, K.; Hanna, K.; Rakar, J.; Sivler, P.; Skog, M.; Rinklake, I.; Shamasha, R.; et al. Nanocellulose composite wound dressings for real-time pH wound monitoring. Mater. Today Bio 2023, 19, 100574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haug, I.J.; Draget, K.I. Gelatin. In Handbook of Food Proteins; Woodhead Publishing Series in Food Science; Technology and Nutrition: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 92–115. [Google Scholar]
- Ishaqa, A.; Rahman, U.; Sahar, A.; Perveena, R.; Deering, A.; Khalilf, A.A.; Aadil, R.M.; Hafeez, M.A.; Khaliqg, A.; Siddique, U. Potentiality of analytical approaches to determine gelatin authenticity in food systems: A review. LWT 2020, 121, 108968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipal, J.; Pu’ad, N.A.S.M.; Lee, T.C.; Nayan, N.H.M.; Sahari, N.; Basri, H.; Idris, M.I.; Abdullah, H.Z. A review of gelatin: Properties, sources, process, applications, and commercialization. Mater. Today 2021, 42, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Zi, Y.; Peng, J.; Shi, C.; Zhen, Y.; Zhong, J. Gelatin as a bioactive nanodelivery system for functional food applications. Food Chem. 2023, 423, 136265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, M.I.A.; Barroso Rodríguez, L.G.; Sánchez, M.L. Collagen: A review on its sources and potential cosmetic applications. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2017, 17, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitura, S.; Sionkowska, A.; Jaiswal, A. Biopolymers for hydrogels in cosmetics: Review. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2020, 31, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmandari, F.; Swastawati, F.; Kurniasih, R.A. Quality Characteristics of Body Cream with the Addition of Gelatin from Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Scales as an Emulsifier. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 750, 012008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, M.; Cao, Y.; Yin, J.; Zhou, H.; Yu, W.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Huang, C.; Ma, P.; et al. Hydrogel sunscreen based on yeast/gelatin demonstrates excellent UV-shielding and skin protection performance. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 205, 111885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siahaan, E.A.; Agusman; Pangestuti, R.; Shin, K.-H.; Kim, S.-K. Potential Cosmetic Active Ingredients Derived from Marine By-Products. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumerka, E.T.A. Chapter 21—Sustainable utilization of gelatin from animal-based agri–food waste for the food industry and pharmacology. In Valorization of Agri-Food Wastes and By-Products; Recent Trends, Innovations and Sustainability Challenges; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 425–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Dong, L.; Noh, H.M.; Park, S.-G.; Kim, S.-H.; Jo, E.H.; Lee, D.-S.; Park, M.C. Inhibitory Effects of Donkey Hide Gelatin on DNCB-Induced Atopic Dermatitis in NC/Nga Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 896450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaib, S.; Shah, H.S.; Usman, F.; Shahzadi, K.; Asjad, H.M.; Khan, R.; Dera, A.A.; Pashameah, R.A.; Alzahrani, E.; Farouk, A.; et al. Green Synthesis of Gelatin-Lipid Nanocarriers Incorporating Berberis aristata Extract for Cancer Therapy; Physical Characterization, Pharmacological and Molecular Modeling Analysis. ChemistrySelect 2022, 7, e202203430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacero, B.A.; Deogil, K.; Dohyun, K.; Hansoo, P.; Soo-Hong, L. Engineering and Functionalization of Gelatin Biomaterials: From Cell Culture to Medical Applications. Tissue Engineering Part B: Reviews. Tissue Eng. 2020, 26, 164–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Wolf, F.A. Collagen and Gelatin, Progress in Biotechnology; Elsevier Science B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; Volume 23, pp. 133–218. [Google Scholar]
- Lukin, I.; Erezuma, I.; Maeso, L.; Zarate, J.; Desimone, M.F.; Al-Tel, T.H.; Dolatshahi-Pirouz, A.; Orive, G. Progress in Gelatin as Biomaterial for Tissue Engineering. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Seedi, H.R.; Said, N.S.; Yosri, N.; Hawash, H.B.; El-Sherif, D.M.; Abouzid, M.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Yaseen, M.; Omar, H.; Shou, Q.; et al. Gelatin nanofibers: Recent insights in synthesis, bio-medical applications and limitations. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultana, S.; Motalib Hossain, M.A.; Zaidul, I.S.M.; Ali, M.E. Multiplex PCR to discriminate bovine, porcine, and fish DNA in gelatin and confectionery products. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 92, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkach, S.R.; Kuchina, Y.A.; Kolotova, D.S.; Boronko, N.G. Polyelectrolyte Polysaccharide–Gelatin Complexes: Rheology and Structure. Polymers 2020, 12, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Zhang, H.; Chitrakar, B.; Adhikari, B.; Yang, C. Effects of nanoemulsion-based chicken bone gelatin-chitosan coatings with cinnamon essential oil and rosemary extract on the storage quality of ready-to-eat chicken patties. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 34, 100933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafabadi, A.P.; Pourmadadi, M.; Yazdian, F.; Rashedi, H.; Rahdar, A.; Díez-Pascual, A.M. pH-sensitive ameliorated quercetin delivery using graphene oxide nanocarriers coated with potential anticancer gelatin-polyvinylpyrrolidone nanoemulsion with bitter almond oil. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 8, 2104339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erahimi, A.; Hamishehkar, H.; Amjadi, S. Development of gelatin-coated nanoliposomes loaded with β-cyclodextrin/vitamin D3 inclusion complex for nutritional therapy. Food Chem. 2023, 424, 136346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohandoss, S.; Palanisamy, S.; You, S.G.; Shim, J.-J.; Lee, Y.R. Supramolecular nanogels based on gelatin–cyclodextrin-stabilized silver nanocomposites with antibacterial and anticancer properties. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2022, 33, 689–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etxabide, A.; Akbarinejad, A.; Chan, E.W.C.; Guerrero, P.; de la Caba, K.; Travas-Sejdic, J.; Kilmartin, P.A. Effect of gelatin concentration, ribose and glycerol additions on the electrospinning process and physicochemical properties of gelatin nanofibers. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 180, 111597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffari, A.; Mirjalili, M.; Gashti, M.P.; Parsania, M. Effect of tannic acid on properties of electrospun gelatin nanofibers. Indian J. Fibre Text. Res. 2020, 45, 153–163. [Google Scholar]
- Prelipcean, A.-M.; Iosageanu, A.; Gaspar-Pintiliescu, A.; Moldovan, L.; Craciunescu, O.; Negreanu-Pirjol, T.; Negreanu-Pirjol, B.; Mitran, R.-A.; Marin, M.; D’Amora, U. Marine and Agro-Industrial By-Products Valorization Intended for Topical Formulations in Wound Healing Applications. Materials 2022, 15, 3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffari, A.; Parvinzadeh Gashti, M.; Mirjalili, M.; Parsania, M. Argon and Argon–Oxygen Plasma Surface Modification of Gelatin Nanofibers for Tissue Engineering Applications. Membranes 2021, 11, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deaconu, M.; Prelipcean, A.-M.; Brezoiu, A.-M.; Mitran, R.-A.; Isopencu, G.; Matei, C.; Berger, D. Novel Collagen-Polyphenols-Loaded Silica Composites for Topical Application. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersanli, C.; Tzora, A.; Skoufos, I.; Voidarou, C.; Zeugolis, D.I. Recent Advances in Collagen Antimicrobial Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering Applications: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, M.B.; Barbul, A. General Principles of Wound Healing. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 1997, 77, 509–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanu, N.J.; Gupta, E.; Vates, U.K.; Singh, G.K. Electrospinning process parameters optimization for biofunctional curcumin/gelatin nanofibers. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 035022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulsun, T.; Inal, M.; Akdag, Y.; Izat, N.; Oner, L.; Sahin, S. The development and characterization of electrospun gelatin nanofibers containing indomethacin and curcumin for accelerated wound healing. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 76, 103000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berechet, M.D.; Gaidau, C.; Miletic, A.; Pilic, B.; Rapa, M.; Stanca, M.; Ditu, L.-M.; Constantinescu, R.; Lazea-Stoyanova, A. Bioactive properties of nanowires based on concentrated collagen hydrolysate loaded with thyme and oregano essential oils. Materials 2020, 13, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Râpa, M.; Gaidau, C.; Mititelu-Tartau, L.; Berechet, M.-D.; Berbecaru, A.C.; Rosca, I.; Chiriac, A.P.; Matei, E.; Predescu, A.-M.; Predescu, C. Bioactive Collagen Hydrolysate-Chitosan/Essential Oil Electrospun Nanofibers Designed for Medical Wound Dressings. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Sun, M.; Wu, S. State-of-the-Art Review of Electrospun Gelatin-Based Nanofiber Dressings for Wound Healing Applications. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matei, E.; Gaidau, C.; Râpă, M.; Stefan, L.M.; Ditu, L.-M.; Predescu, A.M.; Stanca, M.; Pantilimon, M.C.; Berechet, D.; Predescu, C.; et al. Sustainable Coated Nanostructures Based on Alginate and Electrospun Collagen Loaded with Antimicrobial Agents. Coatings 2021, 11, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Râpă, M.; Zaharescu, T.; Stefan, L.M.; Gaidău, C.; Stănculescu, I.; Constantinescu, R.R.; Stanca, M. Bioactivity and Thermal Stability of Collagen–Chitosan Containing Lemongrass Essential Oil for Potential Medical Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanca, M.; Gaidau, C.; Zaharescu, T.; Balan, G.-A.; Matei, I.; Precupas, A.; Leonties, A.R.; Ionita, G. Physico-Chemical Changes Induced by Gamma Irradiation on Some Structural Protein Extracts. Biomolecules 2023, 12, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaidau, C.; Stanculescu, I.R.; Stanca, M.; Cutrubinis, M.; Trandafir, L.; Alexandru, M.; Alexe, C.-A. Gamma irradiation a green alternative for hides and leather conservation. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2021, 182, 109369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.Q.; Leung, W.Q. Calorimetric study of extracellular tissue matrix degradation and instability after gamma irradiation. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouk, S.-S.; Lim, T.-M.; Teoh, S.-H.; Sun, W.Q. Alterations of Human Acellular Tissue Matrix by Gamma Irradiation: Histology, Biomechanical Property, Stability, In Vitro Cell Repopulation, and Remodeling. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2008, 84B, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinemann, C.; Buchner, F.; Lee, P.S.; Bernhardt, A.; Kruppke, B.; Wiesmann, H.-P.; Hintze, V. Effects of Gamma Irradiation and Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Sterilization on Methacrylated Gelatin/Hyaluronan Hydrogels. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, N.B.; Wolkers, W.F.; Morrissey, M.; Sun, W.Q.; Bischof, J.C. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Investigation of Native Tissue Matrix Modifications Using a Gamma Irradiation Process. Tissue Eng. Part C 2009, 15, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoffrey, P.J. A Review of the Effects of Gamma Radiation on Pharmaceutical Materials. J. Biomater. Appl. 1995, 10, 5–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoffrey, P.J. Irradiation of pharmaceuticals: A literature review. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2022, 190, 109795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalande, M.; Schwob, L.; Vizcaino, V.; Chirot, F.; Dugourd, P.; Schlathölter, T.; Poully, J.-C. Direct radiation effects on the structure and stability of collagen and other proteins. ChemBioChem 2019, 20, 2972–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fertala, J.; Wang, M.L.; Rivlin, M.; Beredjiklian, P.K.; Abboud, J.; Arnold, W.V.; Fertala, A. Extracellular Targets to Reduce Excessive Scarring in Response to Tissue Injury. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Râpă, M.; Gaidău, C.; Stefan, L.M.; Matei, E.; Niculescu, M.; Berechet, M.D.; Stanca, M.; Tablet, C.; Tudorache, M.; Gavrilă, R.; et al. New Nanofibers Based on Protein By-Products with Bioactive Potential for Tissue Engineering. Materials 2020, 13, 3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Wang, X.M.; Ma, L.; Li, H.J.; He, Z.F.; Zhang, Y.H. Preparation, characterisation and structure of rabbit (Hyla rabbit) skin gelatin. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinh, N.T.; Manh, V.Q.; Trung, V.Q.; Lam, T.D.; Huynh, M.D.; Tung, N.Q.; Trinh, N.D.; Hoang, T. Characterization of Collagen Derived from Tropical Freshwater Carp Fish Scale Wastes and Its Amino Acid Sequence. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2019, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berillis, P. Marine Collagen: Extraction and Applications Research Trends in Biochemistry, Molecular Biology and Microbiology; SM Group Open Access eBooks, 2015; pp. 1–13. Available online: www.smgebooks.com (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- European Pharmacopoeia 10.0 to 10.2, 10th ed.; EDQM: Strasbourg, France, 2020.
- ISO 11137-1:20026; Sterilization of Health Care Products—Radiation—Part 1: Requirements for Development, Validation and Routine Control of a Sterilization Process for Medical Devices. The International Standard: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/33952.html (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Matei, E.; Gaidau, C.; Rapa, M.; Constantinescu, R.; Savin, S.; Berechet, M.D.; Predescu, A.M.; Berbecaru, A.C.; Coman, G.; Predescu, C. Sustainable Rabbit Skin Glue to Produce Bioactive Nanofibers for Nonactive Wound Dressings. Materials 2020, 13, 5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, K.-F.; Jipa, S.; Krahl, F.; Steiner, G.; Zaharescu, T.; Zimmerer, C. Polymers, Application of Chemiluminescence in Polymer Research, Landolt-Börnstein New Series VIII/6A1; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; p. 187. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, A.M.; Marques, A.P.; Silva, T.H.; Reis, R.L. Evaluation of the potential of collagen from codfish skin as a biomaterial for biomedical applications. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaidau, C.; Stanca, M.; Niculescu, M.-D.; Alexe, C.-A.; Becheritu, M.; Horoias, R.; Cioineag, C.; Râpă, M.; Stanculescu, I.R. Wool Keratin Hydrolysates for Bioactive Additives Preparation. Materials 2021, 14, 4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanculescu, I.; Mandravel, C.; Landy, D.; Woisel, P.; Surpateanu, G. Complexation of tetrandrine with calcium ion probed by various spectroscopic methods and molecular modeling. J. Mol. Struct. 2003, 655, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lungu, I.B.; Miu, L.; Cutrubinis, M.; Stanculescu, I. Physical Chemical Investigation of Gamma-Irradiated Parchment for Preservation of Cultural Heritage. Polymers 2023, 15, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SR EN ISO 4684:2006; Leather-Chemical Tests-Determination of Volatile Matter. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. Available online: https://magazin.asro.ro/ro/standard/112366 (accessed on 20 November 2023).
- SR EN ISO 4047:2002; Finished Leathers. Determination of Total Sulfated Ash and Water-Insoluble Sulfated Ash. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002. Available online: https://magazin.asro.ro/ro/standard/8209 (accessed on 20 November 2023).
- SR EN 2788:1997; Water Quality. Determination of Electrical Conductivity. ASRO: Bucuresti, Romania, 1997. Available online: https://magazin.asro.ro/ro/standard/22665 (accessed on 20 November 2023).
- STAS 8619/3-90; Ph-Metry. Electrometric Determination of the pH of Aqueous Solutions. ASRO: Bucuresti, Romania, 1990. Available online: https://magazin.asro.ro/ro/standard/21072 (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- Duling, D.R. PEST Winsim, Version 0.96; National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences: Triangle Park, NC, USA, 1996.
- Duling, D.R. Simulation of multiple isotropic spin-trap EPR spectra. J. Magn. Reson. B 1994, 104, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Characteristics | Gelatin Extracted From | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bovine Hide | Donkey Hide | Rabbit Skin | Fish Scales | |
| Dry substance, % | 7.69 ± 0.35 | 11.80 ± 0.35 | 7.30 ± 0.35 | 4.82 ± 0.35 |
| Total ash *, % | 7.67 ± 0.24 | nd | 0.68 ± 0.24 | nd |
| pH (1:10), pH units | 6.60 ± 0.10 | 6.70 ± 0.10 | 6.60 ± 0.10 | 4.91 ± 0.10 |
| Bloom test, g | 215.30 | 321.00 | 657.40 | 362.10 |
| Relaxation, % | 38.30 | 21.50 | 51.54 | 14.30 |
| Viscosity, CP ** | 1.5 | 2.75 | 6.00 | 5.75 |
| Shear stress, dyne/cm2 | 2.79 | 5.12 | 11.16 | 10.70 |
| Conductivity, μS/cm | 419 ± 0.10 | 53 ± 0.10 | 32 ± 0.10 | 442 ± 0.10 |
| Samples | TAMC, CFU/g | TYMC, CFU/g | Staphylococcus aureus | Escherichia coli | Candida albicans |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nanofibers from bovine hide gelatin | 1060 ± 11.846 | 966.6 ± 29.143 | Positive | Positive | Positive |
| Nanofibers from bovine hide gelatin, irradiated at 10 kGy | 2.33 ± 0.577 | 0 | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Nanofibers from bovine hide gelatin, irradiated at 20 kGy | 0 | 0 | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Nanofibers from bovine hide gelatin, irradiated at 25 kGy | 0 | 0 | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Bovine hide gelatin | 0 | 0 | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Bovine hide gelatin, irradiated at 10 kGy | 0 | 0 | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Bovine hide gelatin, irradiated at 20 kGy | 0 | 0 | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Bovine hide gelatin, irradiated at 25 kGy | 0 | 0 | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Nanofibers from donkey hide gelatin | 1146 ± 4.509 | 986.6 ± 12.055 | Positive | Positive | Positive |
| Nanofibers from donkey hide gelatin, irradiated at 10 kGy | 0 | 0 | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Nanofibers from donkey hide gelatin, irradiated at 20 kGy | 0 | 0 | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Nanofibers from donkey hide gelatin, irradiated at 25 kGy | 0 | 0 | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Donkey hide gelatin | 0 | 0 | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Donkey hide gelatin, irradiated at 10 kGy | 0 | 0 | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Donkey hide gelatin, irradiated at 20 kGy | 0 | 0 | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Donkey hide gelatin, irradiated at 25 kGy | 0 | 0 | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Nanofibers from rabbit skin gelatin | 0 | 0 | Positive | Positive | Positive |
| Nanofibers from rabbit skin gelatin, irradiated at 10 kGy | 0 | 0 | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Nanofibers from rabbit skin gelatin, irradiated at 20 kGy | 0 | 0 | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Nanofibers from rabbit skin gelatin, irradiated at 25 kGy | 0 | 0 | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Rabbit skin gelatin | 0 | 0 | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Rabbit skin gelatin, irradiated at 10 kGy | 0 | 0 | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Rabbit skin gelatin, irradiated at 20 kGy | 0 | 0 | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Rabbit skin gelatin, irradiated at 25 kGy | 0 | 0 | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Nanofibers from fish scale gelatin | 86.00 ± 6.00 | 70.30 ± 1.528 | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Nanofibers from fish scale gelatin, irradiated at 10 kGy | 0 | 0 | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Nanofibers from fish scale gelatin, irradiated at 20 kGy | 0 | 0 | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Nanofibers from fish scale gelatin, irradiated at 25 kGy | 0 | 0 | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Fish scale gelatin | 0 | 0 | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Fish scale gelatin, irradiated at 10 kGy | 0 | 0 | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Fish scale gelatin, irradiated at 20 kGy | 0 | 0 | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Fish scale gelatin, irradiated at 25 kGy | 0 | 0 | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Material/ FTIR Bands | Nanofibers | Gelatins | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bovine | Donkey | Rabbit | Fish | Bovine | Donkey | Rabbit | Fish | |
| Amide A | 3285 | 3285 | 3287 | 3289 | 3283 | 3289 | 3279 | 3285 |
| Amide B | 2937 | 2940 | 2921 | 2937 | 2921 | 2936 | 2919 | 2939 |
| Amide I | 1640 | 1637 | 1640 | 1638 | 1638 | 1630 | 1620 | 1633 |
| Amide II | 1540 | 1538 | 1540 | 1538 | 1536 | 1543 | 1541 | 1532 |
| Amide III | 1242 | 1242 | 1243 | 1242 | 1241 | 1237 | 1241 | 1241 |
| Parameters | Bovine Gelatin NF | Donkey Gelatin NF | Rabbit Gelatin NF | Fish Scale Gelatin NF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flow rate, mL/h | 1 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 2 |
| Voltage supply, kV | 23.20 | 22.59 | 24.35 | 23.24 |
| Collector distance, mm | 130 | 130 | 90 | 130 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gaidau, C.; Râpă, M.; Ionita, G.; Stanculescu, I.R.; Zaharescu, T.; Constantinescu, R.-R.; Lazea-Stoyanova, A.; Stanca, M. The Influence of Gamma Radiation on Different Gelatin Nanofibers and Gelatins. Gels 2024, 10, 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10040226
Gaidau C, Râpă M, Ionita G, Stanculescu IR, Zaharescu T, Constantinescu R-R, Lazea-Stoyanova A, Stanca M. The Influence of Gamma Radiation on Different Gelatin Nanofibers and Gelatins. Gels. 2024; 10(4):226. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10040226
Chicago/Turabian StyleGaidau, Carmen, Maria Râpă, Gabriela Ionita, Ioana Rodica Stanculescu, Traian Zaharescu, Rodica-Roxana Constantinescu, Andrada Lazea-Stoyanova, and Maria Stanca. 2024. "The Influence of Gamma Radiation on Different Gelatin Nanofibers and Gelatins" Gels 10, no. 4: 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10040226
APA StyleGaidau, C., Râpă, M., Ionita, G., Stanculescu, I. R., Zaharescu, T., Constantinescu, R.-R., Lazea-Stoyanova, A., & Stanca, M. (2024). The Influence of Gamma Radiation on Different Gelatin Nanofibers and Gelatins. Gels, 10(4), 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10040226












