Time Dependence of Gel Formation in Lyotropic Nematic Liquid Crystals: From Hours to Weeks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
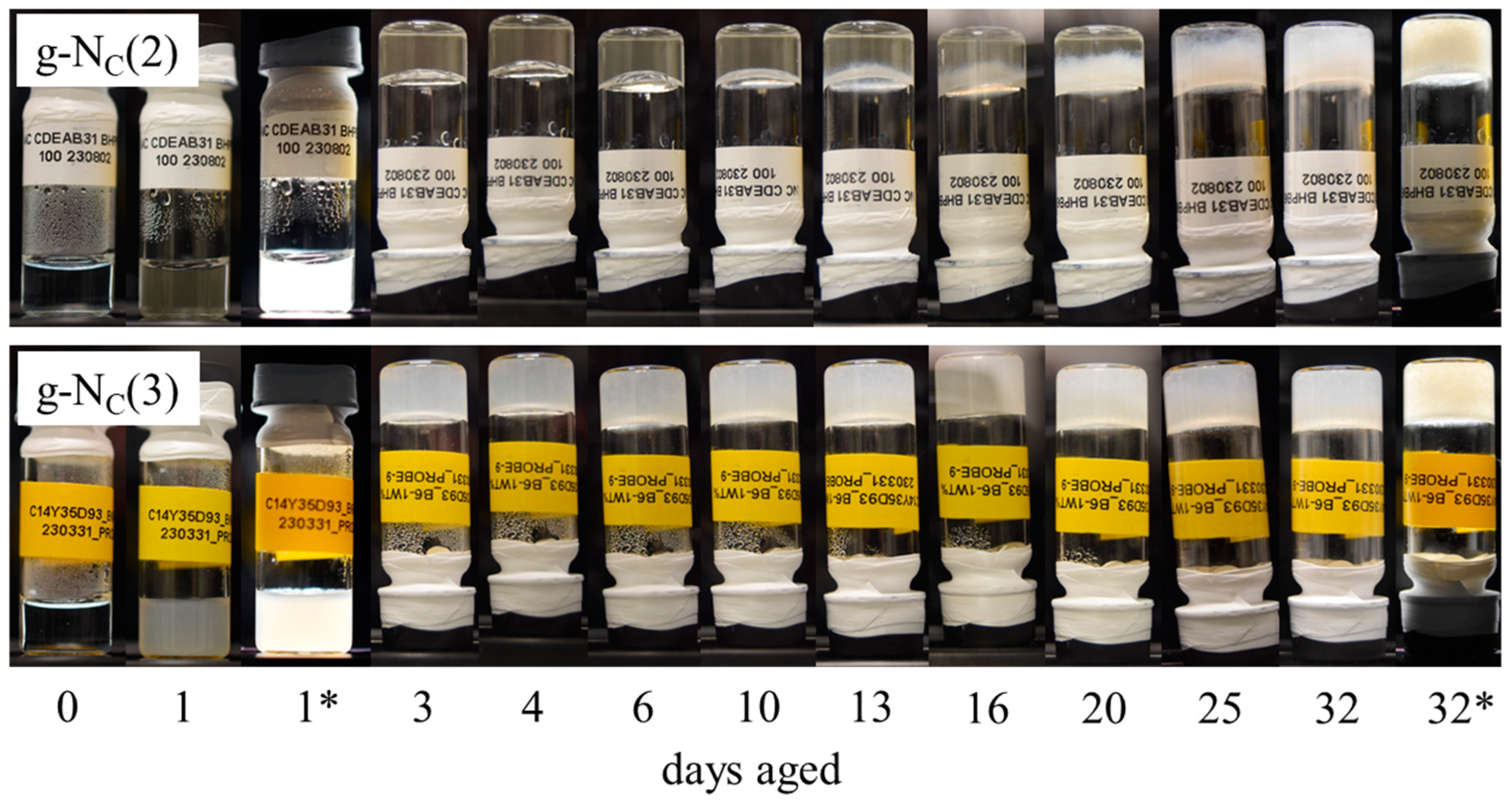
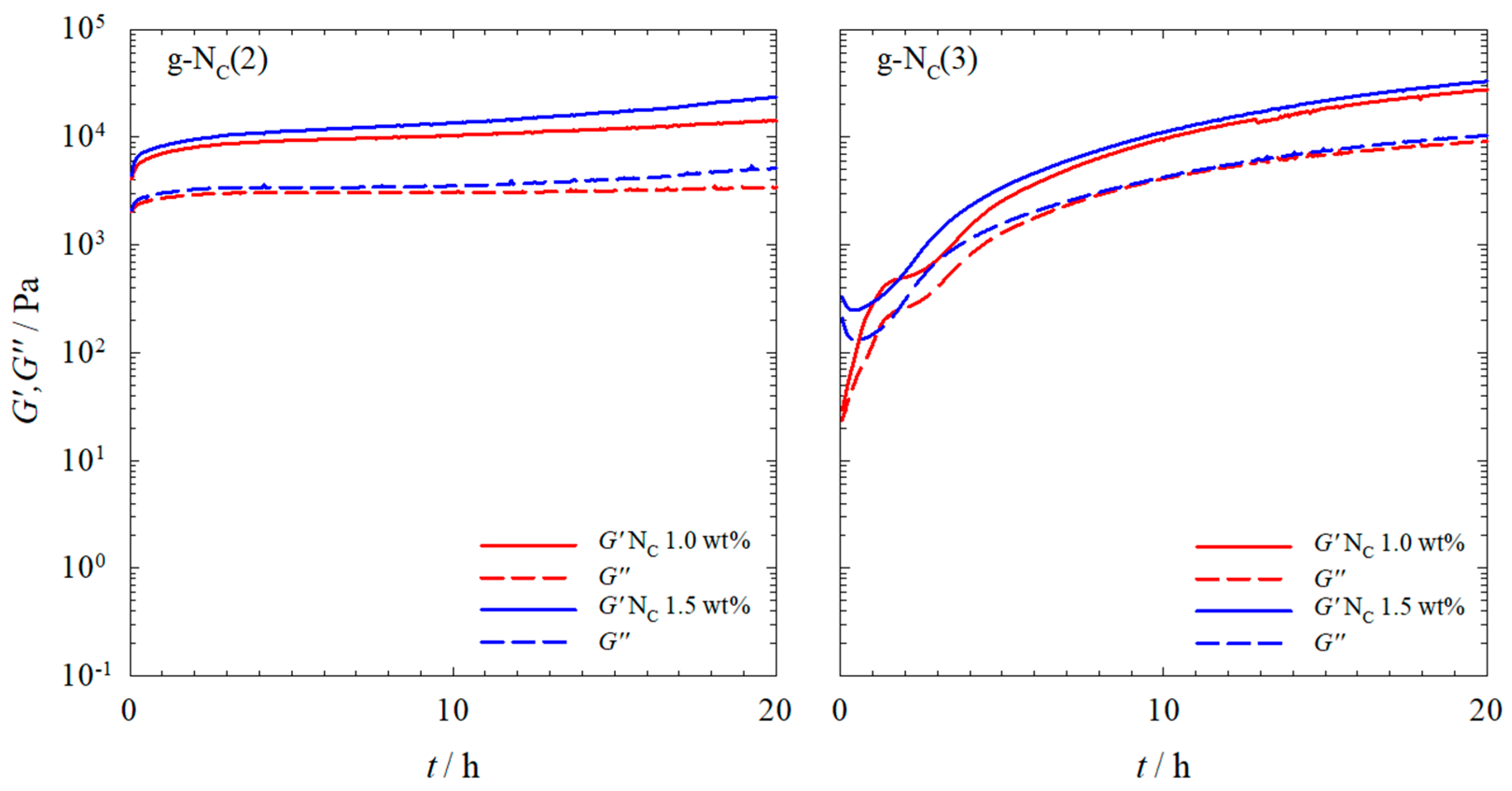
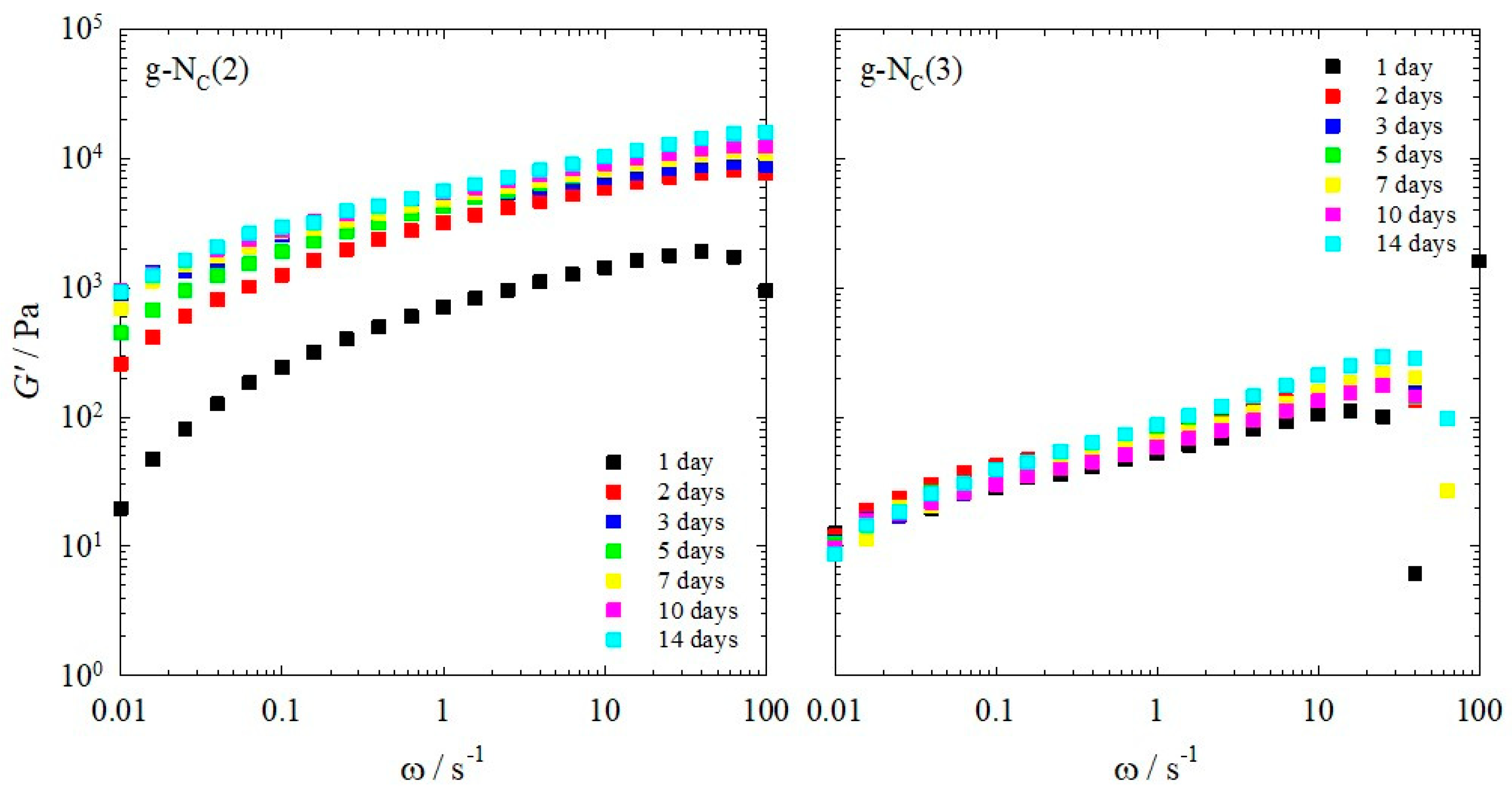
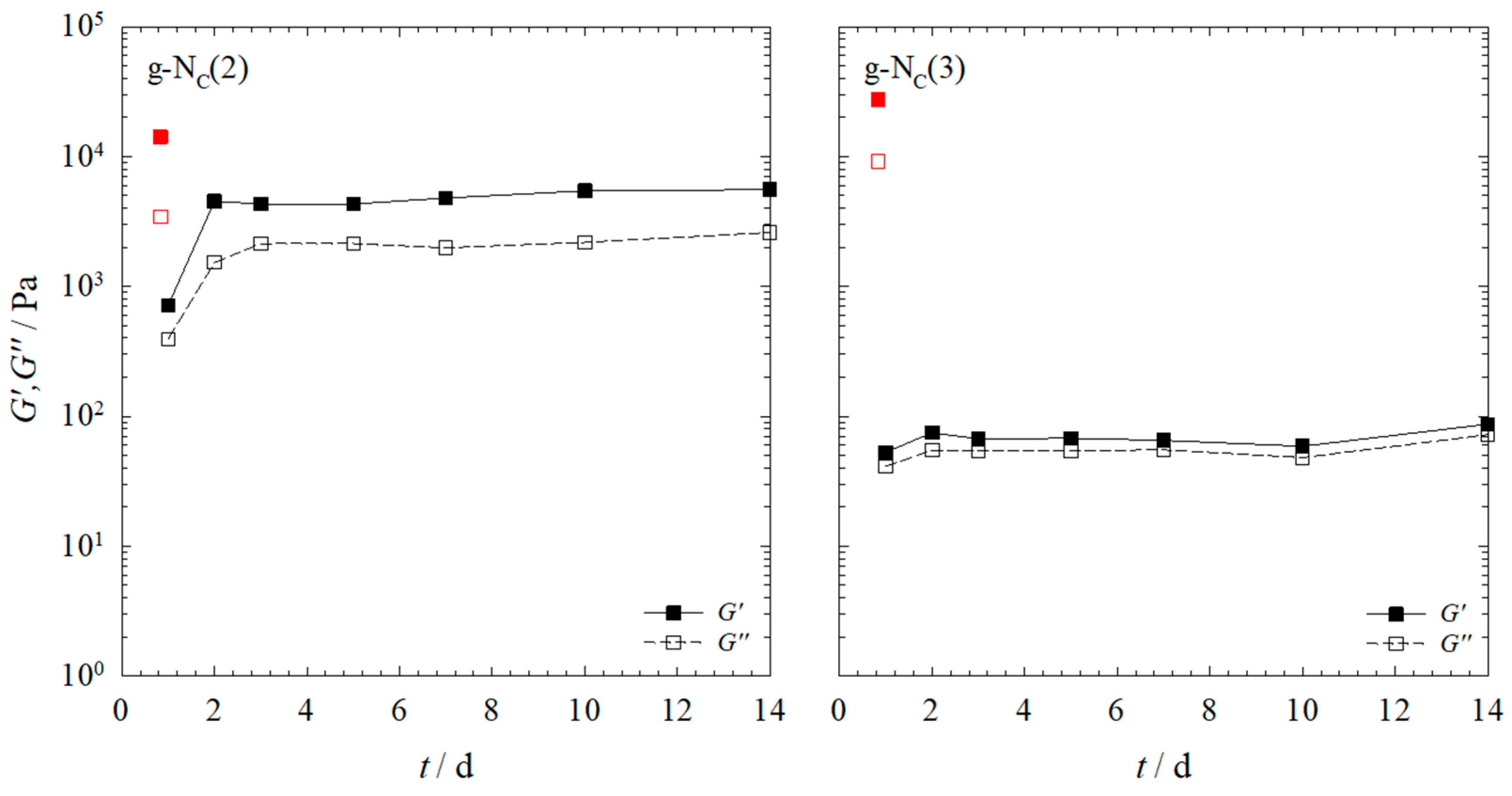
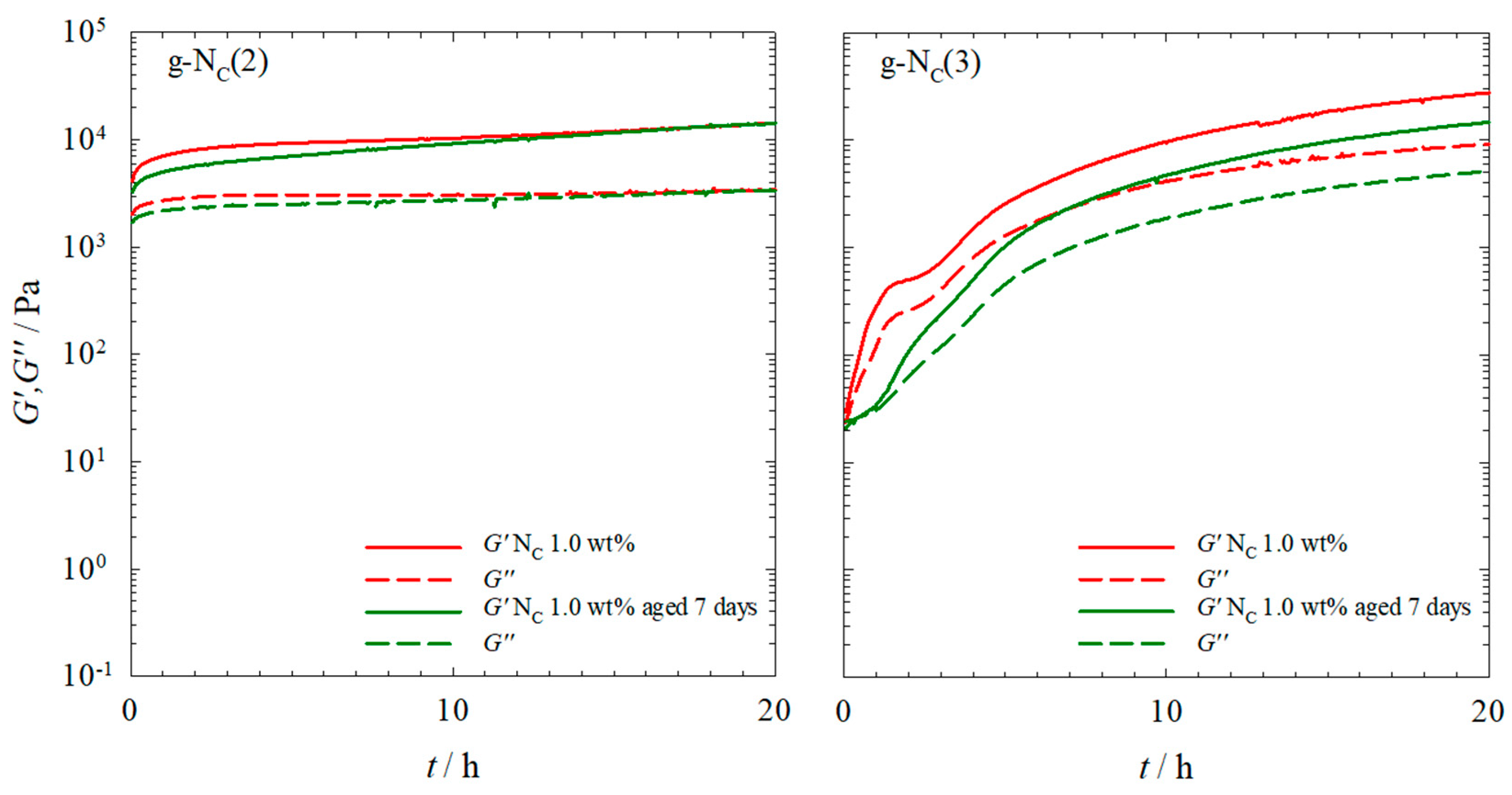
2.1. Rheology
2.2. Freeze Fracture Electron Microscopy of the Gelled NC Phases
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Sample Preparation
4.2. Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Figueiredo Neto, A.M.; Salinas, S.R.A. The Physics of Lyotropic Liquid Crystals: Phase Transitions and Structural Properties; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Hendrikx, Y.; Charvolin, J.; Rawiso, M. Segregation of Two Amphiphilic Molecules within Nonspherical Micelles: A Neutron Scattering Study. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1984, 100, 597–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montecinos, R.; Ahumada, H.; Araya-Maturana, R.; Olea, A.F.; Weiss-López, B.E. Counterion and composition effects on discotic nematic lyotropic liquid crystals I. Size and order. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 316, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, R.G.; Terech, P. Molecular Gels Materials with Self-Assembled Fibrillar Networks; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, R.G. The Past, Present, and Future of Molecular Gels. What Is the Status of the Field, and Where Is It Going? J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 7519–7530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draper, E.R.; Adams, D.J. Low-Molecular-Weight Gels: The State of the Art. Chem 2017, 3, 390–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.K. Supramolecular gels—A panorama of low-molecular-weight gelators from ancient origins to next-generation technologies. Soft Matter 2024, 20, 10–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Zhou, J.; Shi, J.; Xu, B. Supramolecular Hydrogelators and Hydrogels: From Soft Matter to Molecular Biomaterials. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 13165–13307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estroff, L.A.; Hamilton, A.D. Water Gelation by Small Organic Molecules. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 1201–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terech, P.; Weiss, R.G. Low Molecular Mass Gelators of Organic Liquids and the Properties of Their Gels. Chem. Rev. 1997, 97, 3133–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.J. Dipeptide and Tripeptide Conjugates as Low-Molecular-Weight Hydrogelators. Macromol. Biosci. 2011, 11, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieterich, S.; Sottmann, T.; Giesselmann, F. Gelation of Lyotropic Liquid-Crystal Phases–The Interplay between Liquid Crystalline Order and Physical Gel Formation. Langmuir 2019, 35, 16793–16802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieterich, S.; Prévost, S.; Dargel, C.; Sottmann, T.; Giesselmann, F. Synergistic structures in lyotropic lamellar gels. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 10268–10279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koitani, S.; Dieterich, S.; Preisig, N.; Aramaki, K.; Stubenrauch, C. Gelling Lamellar Phases of the Binary System Water–Didodecyldimethylammonium Bromide with an Organogelator. Langmuir 2017, 33, 12171–12179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steck, K.; Schmidt, C.; Stubenrauch, C. The Twofold Role of 12-Hydroxyoctadecanoic Acid (12-HOA) in a Ternary Water—Surfactant—12-HOA System: Gelator and Co-Surfactant. Gels 2018, 4, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steck, K.; Stubenrauch, C. Gelling Lyotropic Liquid Crystals with the Organogelator 1,3:2,4-Dibenzylidene-D-sorbitol Part I: Phase Studies and Sol–Gel Transitions. Langmuir 2019, 35, 17132–17141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steck, K.; Preisig, N.; Stubenrauch, C. Gelling Lyotropic Liquid Crystals with the Organogelator 1,3:2,4-Dibenzylidene-D-sorbitol Part II: Microstructure. Langmuir 2019, 35, 17142–17149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steck, K.; van Esch, J.H.; Smith, D.K.; Stubenrauch, C. Tuning gelled lyotropic liquid crystals (LLCs)—Probing the influence of different low molecular weight gelators on the phase diagram of the system H2O/NaCl–Genapol LA070. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 3111–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steck, K.; Dieterich, S.; Stubenrauch, C.; Giesselmann, F. Surfactant-based lyotropic liquid crystal gels—The interplay between anisotropic order and gel formation. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 5335–5348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubenrauch, C.; Giesselmann, F. Gelled Complex Fluids: Combining Unique Structures with Mechanical Stability. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 3268–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Laupheimer, M.; Preisig, N.; Sottmann, T.; Schmidt, C.; Stubenrauch, C. Gelled Lyotropic Liquid Crystals. Langmuir 2015, 31, 8589–8598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieterich, S.; Stemmler, F.; Preisig, N.; Giesselmann, F. Micellar Lyotropic Nematic Gels. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2007340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, M.; Dombrowski, M.O.; Preisig, N.; Dieterich, S.; Giesselmann, F.; Mésini, P.; Stubenrauch, C. Gelled lyotropic nematic liquid crystals. Liq. Cryst. 2023, 50, 1090–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brizard, A.; Stuart, M.; van Bommel, K.; Friggeri, A.; de Jong, M.; van Esch, J. Preparation of Nanostructures by Orthogonal Self-Assembly of Hydrogelators and Surfactants. Angew. Chem. 2008, 120, 2093–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeres, A.; van der Pol, C.; Stuart, M.; Friggeri, A.; Feringa, B.L.; van Esch, J. Orthogonal Self-Assembly of Low Molecular Weight Hydrogelators and Surfactants. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 14252–14253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, F.X.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Díaz, N.; Schmutz, M.; Demé, B.; Jestin, J.; Combet, J.; Mésini, P.J. Self-assembling properties of a series of homologous ester-diamides—From ribbons to nanotubes. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 8483–8493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbert, K.M.; Fowler, H.E.; McCracken, J.M.; Schlafmann, K.R.; Koch, J.A.; White, T.J. Synthesis and alignment of liquid crystalline elastomers. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2022, 7, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.J.; Broer, D.J. Programmable and adaptive mechanics with liquid crystal polymer networks and elastomers. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 1087–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wermter, H.; Finkelmann, H. Liquid crystalline elastomers as artificial muscles. e-Polymers 2001, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Zhang, R. Liquid crystal elastomers, networks and gels: Advanced smart materials. J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 2529–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohm, C.; Kapernaum, N.; Nonnenmacher, D.; Giesselmann, F.; Serra, C.; Zentel, R. Microfluidic Synthesis of Highly Shape-Anisotropic Particles from Liquid Crystalline Elastomers with Defined Director Field Configurations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 5305–5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-H.; Keller, P. Artificial muscles based on liquid crystal elastomers. Philos. Trans. R Soc. A 2006, 364, 2763–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Ikeda, T. Soft Actuators Based on Liquid-Crystalline Elastomers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 5416–5418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kularatne, R.S.; Kim, H.; Boothby, J.M.; Ware, T.H. Liquid Crystal Elastomer Actuators: Synthesis, Alignment, and Applications. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2017, 55, 395–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper, E.R.; McDonald, T.M.; Adams, D.J. A low molecular weight hydrogel with unusual gel aging. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 6595–6597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gayen, K.; Nandi, N.; Das, K.S.; Hermida-Merino, D.; Hamley, I.W.; Banerjee, A. The aging effect on the enhancement of thermal stability, mechanical stiffness and fluorescence properties of histidine-appended naphthalenediimide based two-component hydrogels. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 10106–10114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Llansola, F.; Miravet, J.F.; Escuder, B. Supramolecular gel formation and self-correction induced by aggregation-driven conformational changes. Chem. Commun. 2009, 209–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, N.; Simon, F.X.; Schmutz, M.; Rawiso, M.; Decher, G.; Jestin, J.; Mésini, P.J. Self-assembled diamide nanotubes in organic solvents. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 3260–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Sample | BHPB-6/mg | CDEAB/mg | C14TAB/mg | H2O/mg | n-decanol/mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binary NC | - | 330.0 | - | 670.0 | - |
| g-NC(2) 1.0 wt% BHPB-6 | 10 | 326.7 | - | 663.3 | - |
| g-NC(2) 1.5 wt% BHPB-6 | 15 | 325.0 | - | 660.0 | - |
| Ternary NC | - | - | 325.5 | 650.0 | 24.5 |
| g-NC(3) 1.0 wt% BHPB-6 | 10 | - | 322.2 | 643.5 | 24.3 |
| g-NC(3) 1.5 wt% BHPB-6 | 15 | - | 320.6 | 640.3 | 24.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dombrowski, M.; Herbst, M.; Preisig, N.; Giesselmann, F.; Stubenrauch, C. Time Dependence of Gel Formation in Lyotropic Nematic Liquid Crystals: From Hours to Weeks. Gels 2024, 10, 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10040261
Dombrowski M, Herbst M, Preisig N, Giesselmann F, Stubenrauch C. Time Dependence of Gel Formation in Lyotropic Nematic Liquid Crystals: From Hours to Weeks. Gels. 2024; 10(4):261. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10040261
Chicago/Turabian StyleDombrowski, Max, Michael Herbst, Natalie Preisig, Frank Giesselmann, and Cosima Stubenrauch. 2024. "Time Dependence of Gel Formation in Lyotropic Nematic Liquid Crystals: From Hours to Weeks" Gels 10, no. 4: 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10040261
APA StyleDombrowski, M., Herbst, M., Preisig, N., Giesselmann, F., & Stubenrauch, C. (2024). Time Dependence of Gel Formation in Lyotropic Nematic Liquid Crystals: From Hours to Weeks. Gels, 10(4), 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10040261






