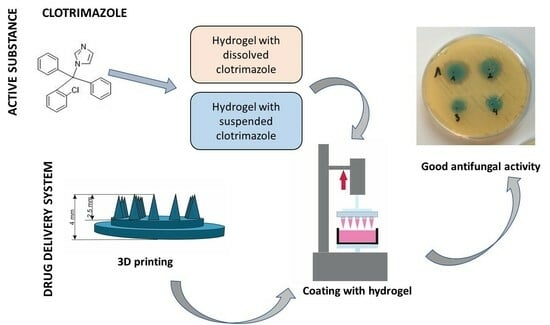
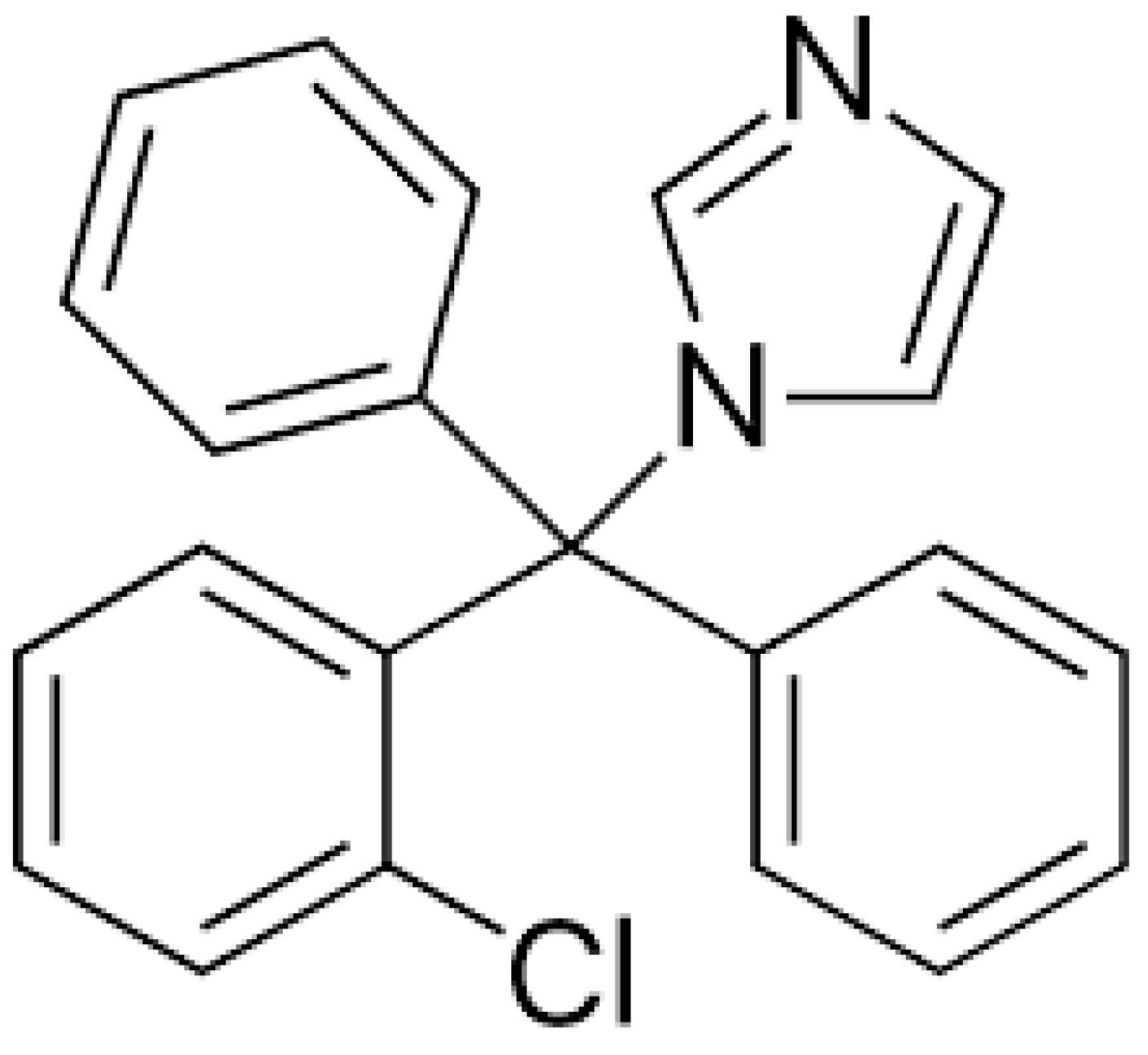
Coated Microneedle System for Delivery of Clotrimazole in Deep-Skin Mycoses
Abstract
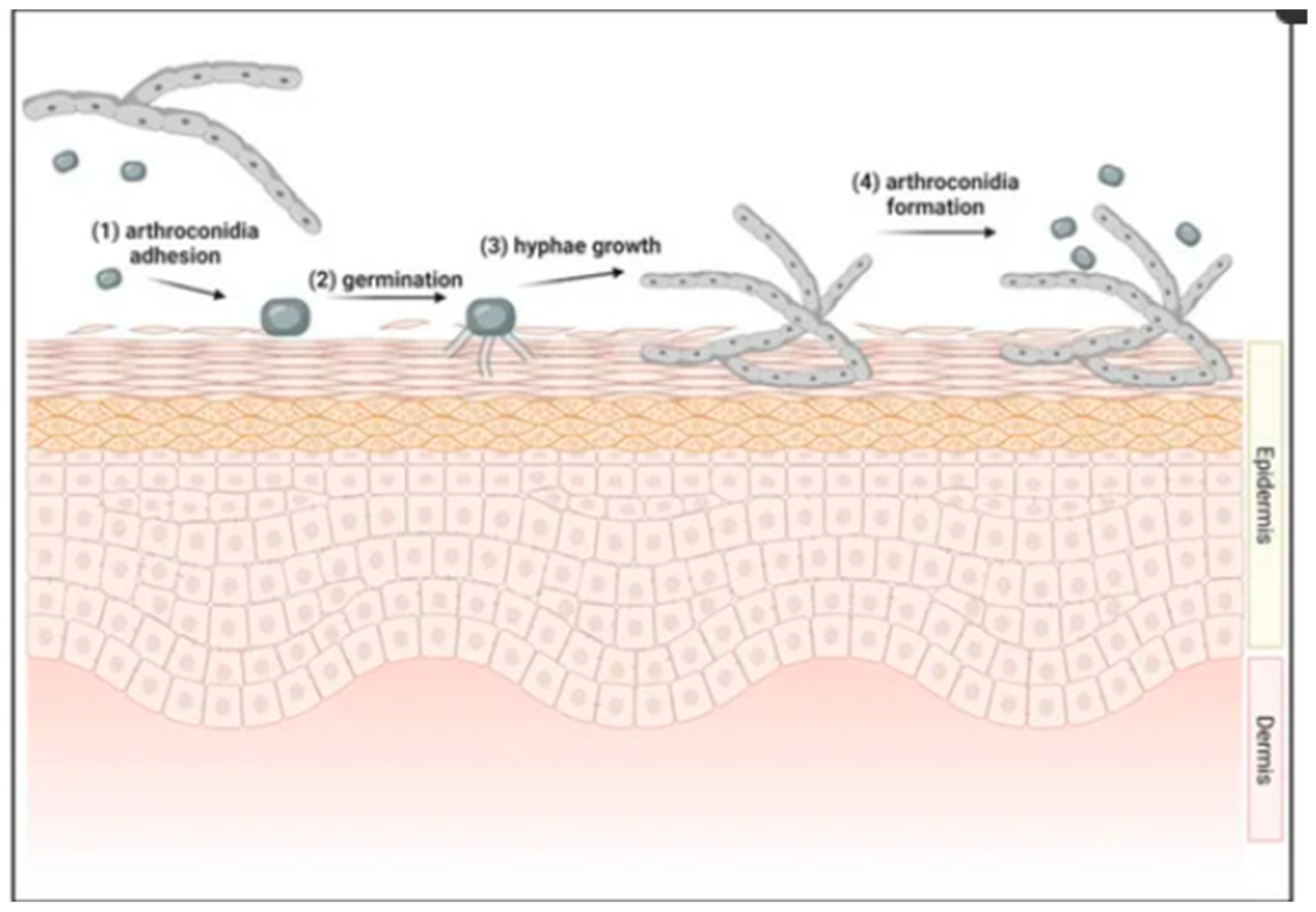
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
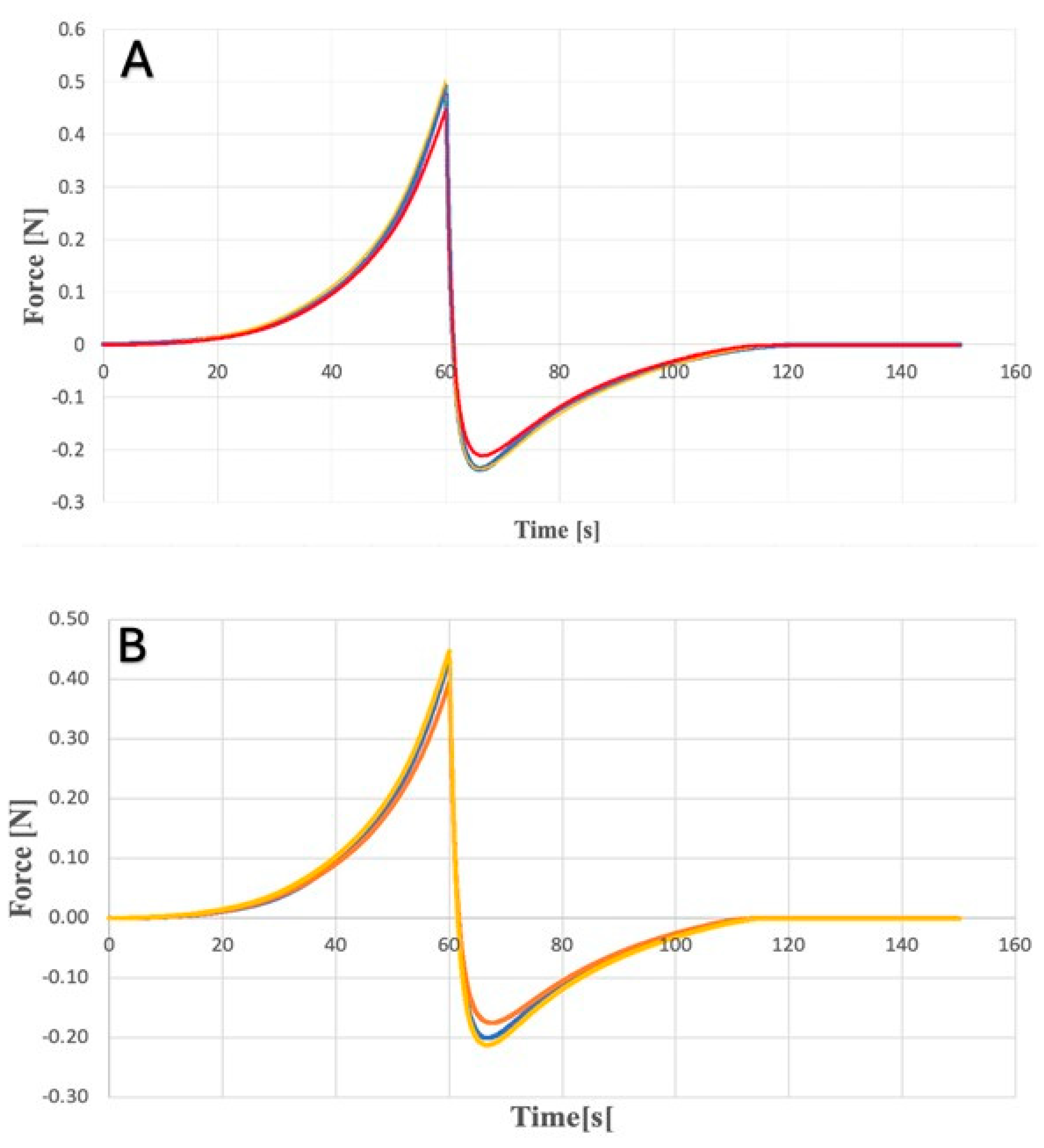
2.1. Texture Analysis of Hydrogels
2.2. Spreadability Analysis of Hydrogels
2.3. Dissolution Study
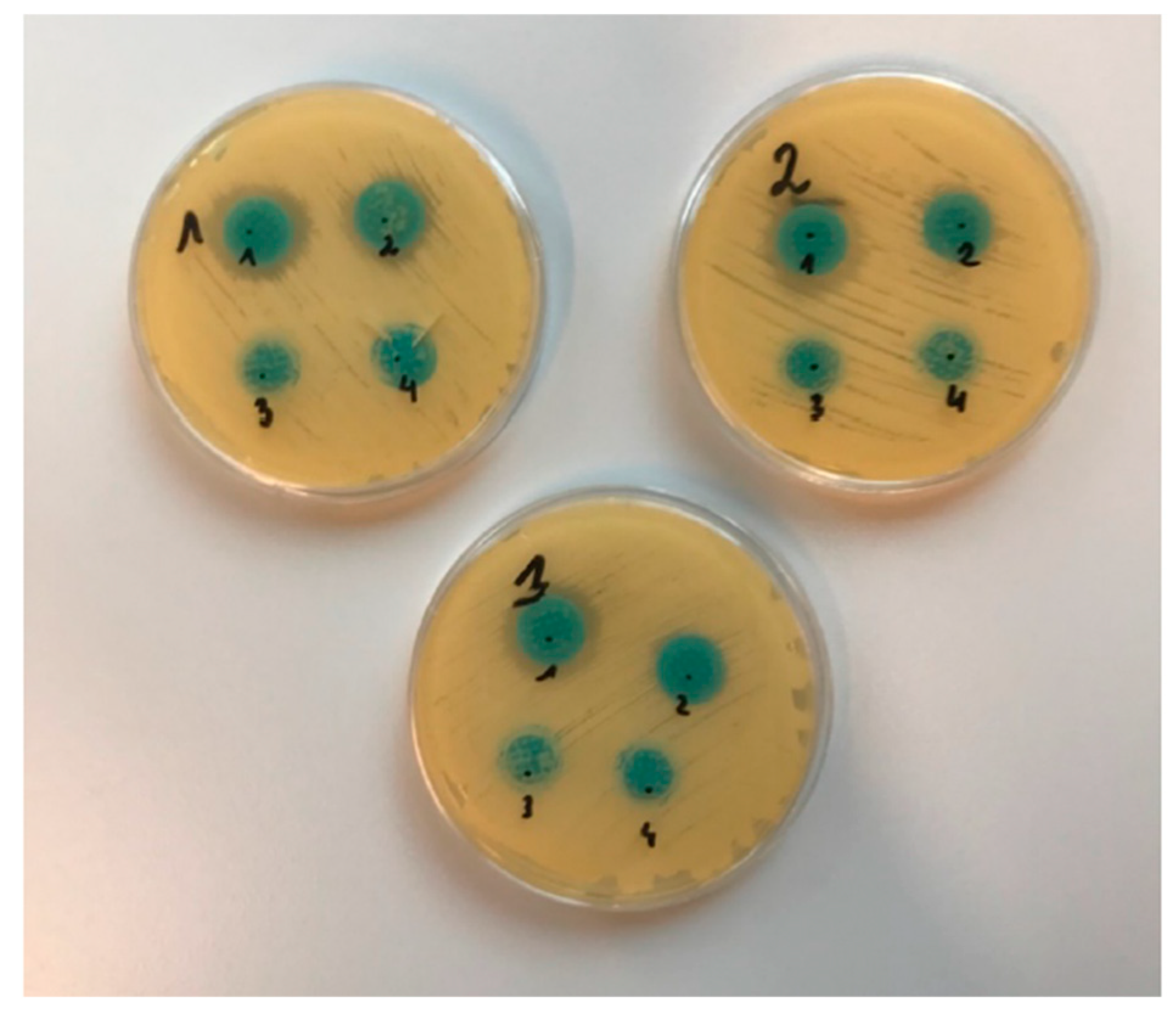
2.4. Analysis of Antifungal Activity
2.4.1. Diffusion Method
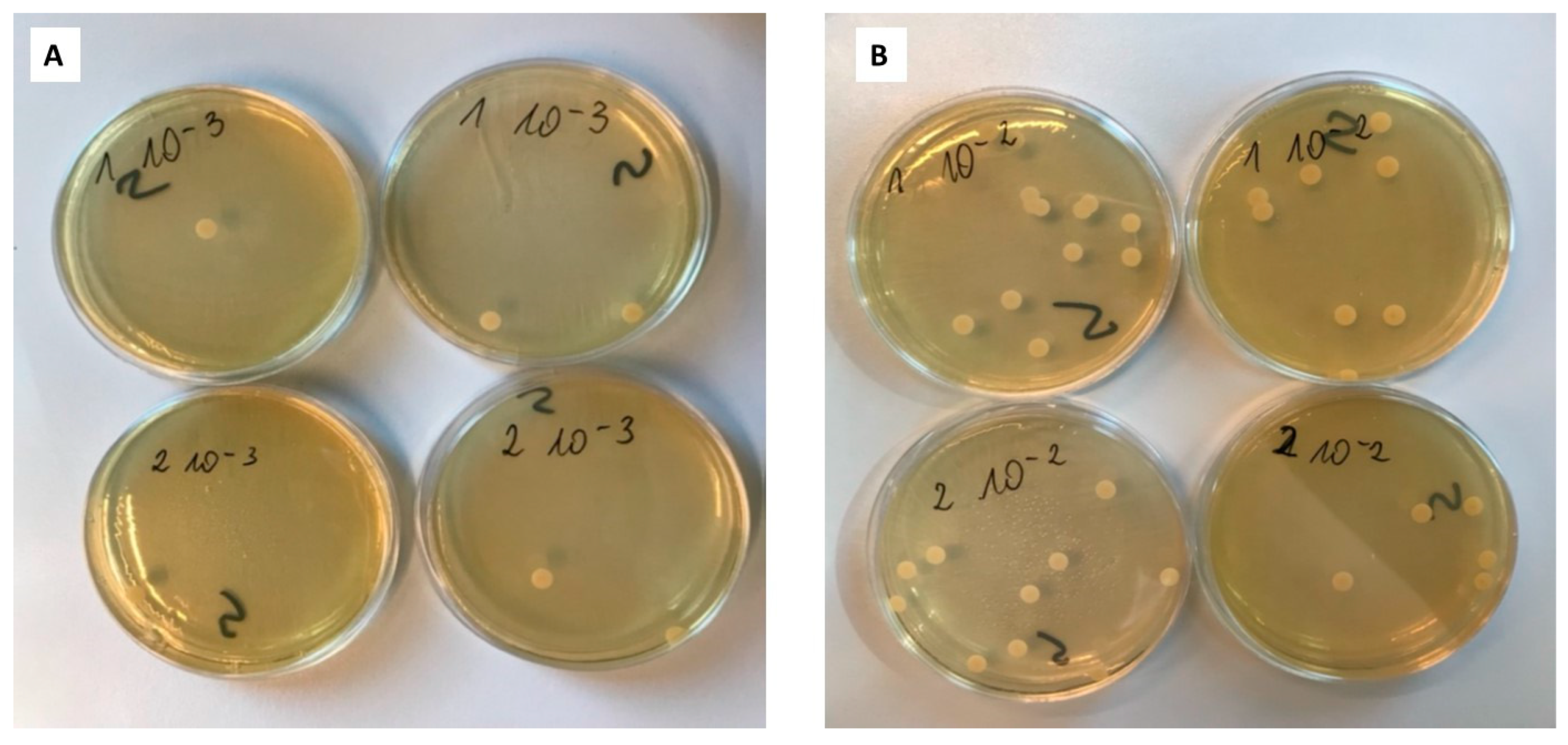
2.4.2. Suspension-Plate Method
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
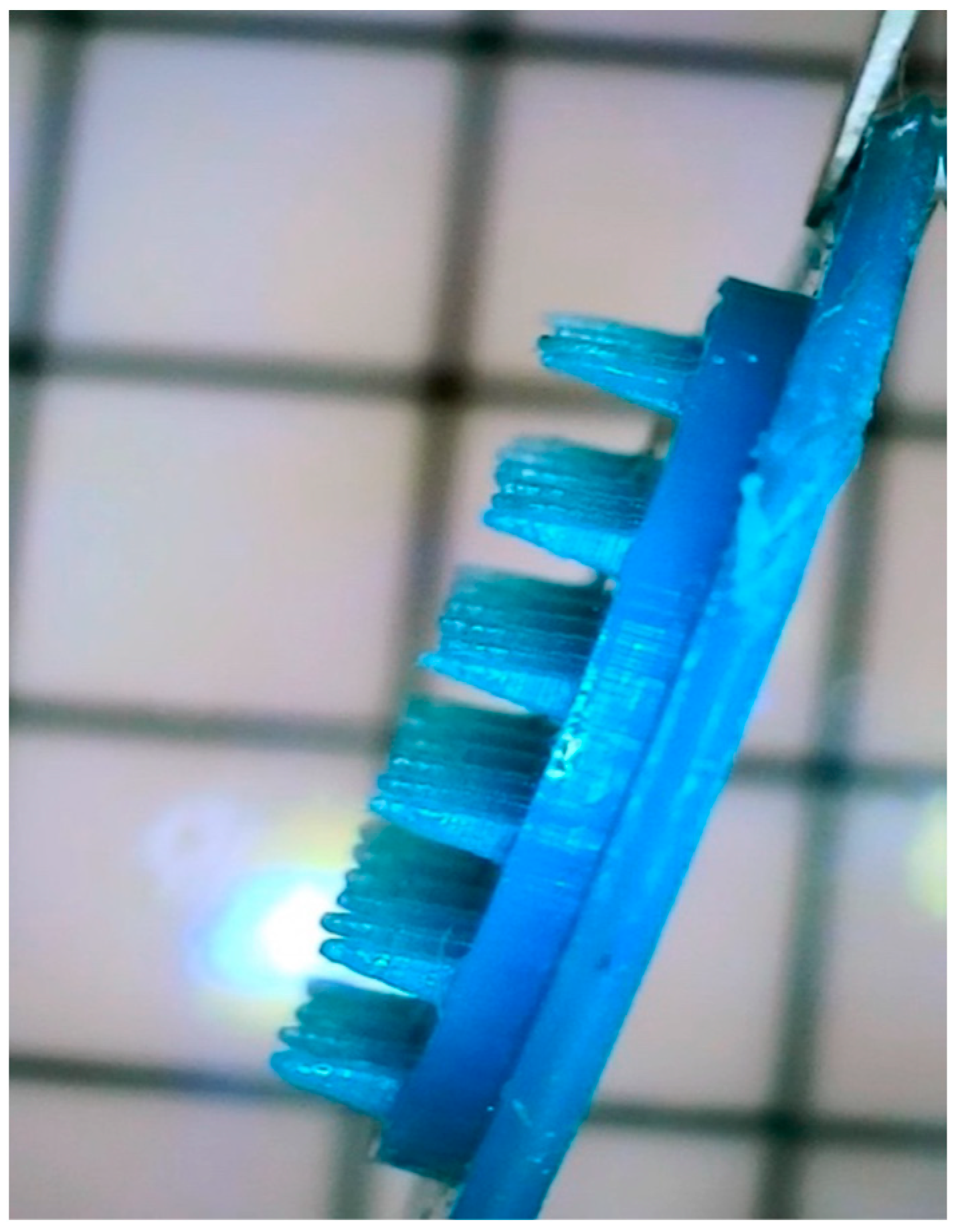
4.2. Preparation of Microneedles
4.3. Preparation of the Hydrogels
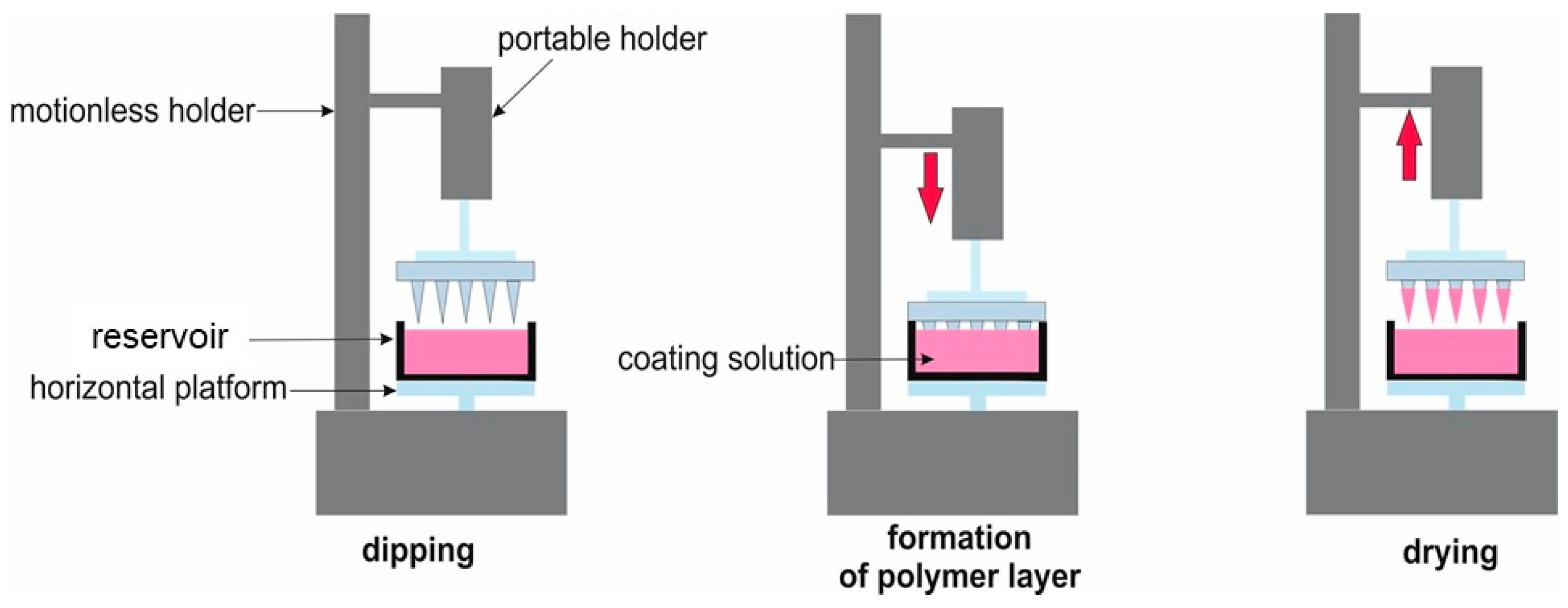
4.4. Coating of Microneedles
4.5. Characterization of Prepared Hydrogels and Microneedles
4.5.1. Texturometric Profile of Hydrogels
4.5.2. Spreadability Analysis
4.5.3. Dissolution Study of Clotrimazole for Hydrogels
4.5.4. Analysis of Antifungal Activity
4.5.5. HPLC Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Havlickova, B.; Czaika, V.A.; Friedrich, M. Epidemiological trends in skin mycoses worldwide. Mycoses 2008, 51 (Suppl. S4), 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellabib, M.S.; Khalifa, Z.; Kavanagh, K. Dermatophytes and other fungi associated with skin mycoses in Tripoli, Libya. Mycoses 2002, 45, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lekkas, D.; Lacarrubba, F.; Verzì, A.E.; Micali, G. Mycoses. In Dermoscopy in General Dermatology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, D.Z.; Schwartz, I.S. Emerging Fungal Infections: New Patients, New Patterns, and New Pathogens. J. Fungi 2019, 5, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskaluk, A.E.; VandeWoude, S. Current Topics in Dermatophyte Classification and Clinical Diagnosis. Pathogens 2022, 11, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Li, D.; Wang, S.; Pang, Z.; Chen, L.; Li, R.; Shi, D. Correlation between Drug Resistance and Virulence of Candida Isolates from Patients with Candidiasis. Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, 15, 7459–7473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.K.; Talukder, M.; Venkataraman, M. Review of the alternative therapies for onychomycosis and superficial fungal infections: Posaconazole, fosravuconazole, voriconazole, oteseconazole. Int. J. Dermatol. 2022, 61, 1431–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scorzoni, L.; de Paula ESilva, A.C.; Marcos, C.M.; Assato, P.A.; de Melo, W.C.; de Oliveira, H.C.; Costa-Orlandi, C.B.; Mendes-Giannini, M.J.; Fusco-Almeida, A.M. Antifungal Therapy: New Advances in the Understanding and Treatment of Mycosis. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 36. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/microbiology/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2017.00036/full (accessed on 13 March 2024). [CrossRef]
- Hay, R. Therapy of Skin, Hair and Nail Fungal Infections. J. Fungi 2018, 4, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolton, M.J.; Perera, V.; Pont, L.G.; McLachlan, A.J. Terbinafine in Combination with Other Antifungal Agents for Treatment of Resistant or Refractory Mycoses: Investigating Optimal Dosing Regimens Using a Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piérard, G.; Arrese, J.; Piérard-Franchimont, C. Itraconazole. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2000, 1, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Daigle, D.; Paquet, M.; Gandhi, B.; Simpson, F.; Villanueva, E.; Verreault, M.; Lyons, D. Topical treatments for athlete’s foot. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 2018, CD010863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, T.; Tsuboi, R.; Iozumi, K.; Ishizaki, S.; Ushigami, T.; Ogawa, Y.; Kaneko, T.; Kawai, M.; Kitami, Y.; Kusuhara, M.; et al. Guidelines for the management of dermatomycosis (2019). J. Dermatol. 2020, 47, 1343–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, R.; Targhotra, M.; Kumar, B.; Sahoo, P.; Chauhan, M. Treatment and management strategies of onychomycosis. J. Med. Mycol. 2020, 30, 100949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finch, J.J.; Warshaw, E.M. Toenail onychomycosis: Current and future treatment options. Dermatol. Ther. 2007, 20, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arastehfar, A.; Lass-Flörl, C.; Garcia-Rubio, R.; Daneshnia, F.F.; Ilkit, M.; Boekhout, T.; Gabaldon, T.; Perlin, D.S. The Quiet and Underappreciated Rise of Drug-Resistant Invasive Fungal Pathogens. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, R.; Bell-Syer, S.E.M.; Crawford, F.; Torgerson, D.J.; Young, P.; Russell, I. Systematic review of topical treatments for fungal infections of the skin and nails of the feet. BMJ 1999, 319, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bseiso, E.; Nasr, M.; El Gawad, N.A.; Sammour, O. Recent advances in topical formulation carriers of antifungal agents. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2015, 81, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, Z.M.; Ricci-Júnior, E.; Benvindo, C.S.; Volpato, N.M. Development and Characterization of Ketoconazole Cream To Treat Superficial Mycoses: In Vitro Permeation and In Vivo Retention Studies. Lat. Am. J. Pharm. 2015, 34, 1304–1310. [Google Scholar]
- Subedi, L.; Song, S.-Y.; Jha, S.K.; Lee, S.-H.; Pangeni, R.; Koo, K.-T.; Kim, B.J.; Cho, S.-S.; Park, J.W. Preparation of Topical Itraconazole with Enhanced Skin/Nail Permeability and In Vivo Antifungal Efficacy against Superficial Mycosis. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, P.; Than, A.; Duong, P.K.; Song, J.; Xu, C.; Chen, P. Antimicrobial Microneedle Patch for Treating Deep Cutaneous Fungal Infection. Adv. Ther. 2019, 2, 1900064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Vora, L.K.; Tekko, I.A.; Permana, A.D.; Domínguez-Robles, J.; Ramadon, D.; Chambers, P.; McCarthy, H.O.; Larrañeta, E.; Donnelly, R.F. Dissolving microneedle patches loaded with amphotericin B microparticles for localised and sustained intradermal delivery: Potential for enhanced treatment of cutaneous fungal infections. J. Control. Release 2021, 339, 361–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, M.; Kan, S.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Tan, J.; Yang, L. Dissolving microneedle to improve transdermal delivery of terbinafine for treatment of onychomycosis. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 95, 105537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waghule, T.; Singhvi, G.; Dubey, S.K.; Pandey, M.M.; Gupta, G.; Singh, M.; Dua, K. Microneedles: A smart approach and increasing potential for transdermal drug delivery system. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 109, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, R.F.; Singh, T.R.R.; Woolfson, A.D. Microneedle-based drug delivery systems: Microfabrication, drug delivery, and safety. Drug Deliv. 2010, 17, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avcil, M.; Çelik, A. Microneedles in Drug Delivery: Progress and Challenges. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Carrier, A.; Chen, Y.; Lin, S.; Wang, J.; Cui, S.; Zhang, X. Polymeric microneedles for controlled transdermal drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2019, 315, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.; Mehta, P.; Arshad, M.S.; Kucuk, I.; Chang, M.-W.; Ahmad, Z. Transdermal Microneedles—A Materials Perspective. Aaps Pharmscitech 2019, 21, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, L.; Park, J.; Bonfante, G.; Kim, B. Recent advances in porous microneedles: Materials, fabrication, and transdermal applications. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2022, 12, 395–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rzhevskiy, A.S.; Singh, T.R.R.; Donnelly, R.F.; Anissimov, Y.G. Microneedles as the technique of drug delivery enhancement in diverse organs and tissues. J. Control. Release 2018, 270, 184–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldawood, F.K.; Andar, A.; Desai, S. A Comprehensive Review of Microneedles: Types, Materials, Processes, Characterizations and Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, W.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Qin, L.; Lai, Y. Recent Advances of Microneedles and Their Application in Disease Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Li, J.; Hong, Y.; Ruan, H.; Long, M.; Feng, N.; Zhang, Y. Advances and Prospects for Hydrogel-Forming Microneedles in Transdermal Drug Delivery. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharadhar, S.; Majumdar, A.; Dhoble, S.; Patravale, V. Microneedles for transdermal drug delivery: A systematic review. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2019, 45, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detamornrat, U.; McAlister, E.; Hutton, A.R.J.; Larrañeta, E.; Donnelly, R.F. The Role of 3D Printing Technology in Microengineering of Microneedles. Small 2022, 18, e2106392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahpour, N.; Pahlevanzadeh, F.; Kharaziha, M.; Bakhsheshi-Rad, H.R.; Ramakrishna, S.; Berto, F. 3D printed microneedles for transdermal drug delivery: A brief review of two decades. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 597, 120301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoogerheide, J.G.; Wyka, B.E. Clotrimazole. In Analytical Profiles of Drug Substances; Florey, K., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1982; pp. 225–255. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0099542808602658 (accessed on 13 March 2024).
- Waugh, C.D. Clotrimazole. In xPharm: The Comprehensive Pharmacology Reference; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 1–4. Available online: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/B9780080552323614990 (accessed on 13 March 2024).
- Crowley, P.; Gallagher, H. Clotrimazole as a pharmaceutical: Past, present and future. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 117, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolla, P.K.; Meraz, C.A.; Rodriguez, V.A.; Deaguero, I.; Singh, M.; Yellepeddi, V.K.; Renukuntla, J. Clotrimazole Loaded Ufosomes for Topical Delivery: Formulation Development and In-Vitro Studies. Molecules 2019, 24, 3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visan, A.I.; Popescu-Pelin, G.; Gherasim, O.; Mihailescu, A.; Socol, M.; Zgura, I.; Chiritoiu, M.; Elena Sima, L.; Antohe, F.; Ivan, L.; et al. Long-Term Evaluation of Dip-Coated PCL-Blend-PEG Coatings in Simulated Conditions. Polymers 2020, 12, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, M.; Sanchez, R. Application of a factorial design to the study of the flow behavior, spreadability and transparency of a Carbopol ETD 2020 gel. Part II. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 234, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, B.Z.; Wang, Q.L.; Jin, X.; Guo, X.D. Fabrication of coated polymer microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2017, 265, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Type of Hydrogel | Adhesivness (mJ) | Cohesivness (-) | Hardnes (mN) | Gumminess (mN) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medium | SD | Medium | SD | Medium | SD | Medium | SD | |
| KLE | −0.40 | 7.09 × 10−5 | 0.90 | 0.11 | 93.54 | 0.003 | 84.39 | 0.007 |
| PLE | −0.39 | 1 × 10−5 | 0.91 | 0.01 | 104.33 | 0.002 | 94.66 | 0.002 |
| KLW | −0.68 | 4.16 × 10−5 | 0.88 | 0.44 | 193.19 | 0.005 | 169.80 | 0.006 |
| KLP | −0.66 | 5.5 × 10−5 | 0.86 | 0.033 | 185.72 | 0.009 | 159.78 | 0.010 |
| Type of Hydrogel | Adhesiveness (mJ) | Force of Adhesion (mN) | Firmness (mN) | Spreadability (mJ) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medium | SD | Medium | SD | Medium | SD | Medium | SD | |
| KLE | −0.72 | 0.0002 | −185.43 | 0.05 | 403.94 | 0.09 | 0.80 | 16.0 × 10−5 |
| PLE | −0.73 | 0.0001 | −196.48 | 0.02 | 425.36 | 0.03 | 0.85 | 6.0 × 10−5 |
| KLW | −1.20 | 0.0001 | −285.92 | 0.04 | 685.64 | 0.06 | 1.53 | 9.7 × 10−5 |
| PLW | −1.19 | 0.0001 | −272.12 | 0.01 | 646.40 | 0.02 | 1.43 | 7.5 × 10−5 |
| Type of Microneedles | Inhibition Growth Area (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| MN-KLE | 24 | 25 | 20 |
| MN-KLW | 19 | 17 | 17 |
| MN-PLE | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MN-PLW | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Type of Plate | Number of Counted Colonies | Number of CFU/mL | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dilution 10−2 | Dilution 10−3 | ||
| 1 | 13 | 1 | 1.1 × 104 |
| 1 | 8 | 2 | |
| 2 | 10 | 2 | 7.5 × 103 |
| 2 | 5 | 1 | |
| control | 5; 6 | 1; 0 | 5.5 × 103 |
| Type of Plate | Number of CFU/mL |
|---|---|
| k1 | 2.1 × 105 |
| control | 7.2 × 107 |
| Ingredient | KLE | PLE | KLW | PLW |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [g] | [g] | [g] | [g] | |
| Carbopol EZ-3 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Ethanol 96% | 25.17 | 25.17 | - | - |
| Glicerol | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 |
| Clotrimazol | 0.5 | 0 | 0.5 | 0 |
| Triizopropanolamine | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 |
| Water | 18.08 | 18.58 | 43.25 | 43.75 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jadach, B.; Nowak, A.; Długaszewska, J.; Kordyl, O.; Budnik, I.; Osmałek, T. Coated Microneedle System for Delivery of Clotrimazole in Deep-Skin Mycoses. Gels 2024, 10, 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10040264
Jadach B, Nowak A, Długaszewska J, Kordyl O, Budnik I, Osmałek T. Coated Microneedle System for Delivery of Clotrimazole in Deep-Skin Mycoses. Gels. 2024; 10(4):264. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10040264
Chicago/Turabian StyleJadach, Barbara, Agata Nowak, Jolanta Długaszewska, Oliwia Kordyl, Irena Budnik, and Tomasz Osmałek. 2024. "Coated Microneedle System for Delivery of Clotrimazole in Deep-Skin Mycoses" Gels 10, no. 4: 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10040264
APA StyleJadach, B., Nowak, A., Długaszewska, J., Kordyl, O., Budnik, I., & Osmałek, T. (2024). Coated Microneedle System for Delivery of Clotrimazole in Deep-Skin Mycoses. Gels, 10(4), 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10040264