Biomedical Trends in Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels with Emphasis on Chitosan-Based Formulations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
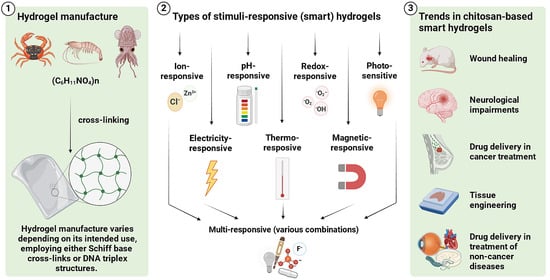
2. Manufacture, Structure, and Administration of Hydrogels
2.1. Manufacturing Hydrogels
2.2. Structure of Chitosan and the Process of Obtaining Hydrogels
2.3. Routes of Administering Hydrogels
2.4. Advantages of Chitosan-Based Hydrogels
3. Selected Types of Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels
3.1. Ion-Responsive Hydrogels
3.2. pH-Responsive Hydrogels
3.3. Redox-Responsive Hydrogels
3.4. Photo-Sensitive Hydrogels
3.5. Electricity-Responsive Hydrogels
3.6. Thermo-Responsive Hydrogels
3.7. Magnetic-Responsive Hydrogels
3.8. Multi-Responsive Hydrogels
4. Current Trends in the Biomedical Application of Stimuli-Responsive Chitosan-Based Hydrogels
4.1. Wound Healing
4.2. Neurological Impairments
4.3. Tissue Engineering
4.4. Drug Delivery in Cancer Treatment
4.5. Drug Delivery in the Treatment of Non-Cancer Diseases
5. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vallet-Regí, M. Evolution of Biomaterials. Front. Mater. 2022, 9, 864016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshangiti, D.M.; El-Damhougy, T.K.; Zaher, A.; Madani, M.; Mohamady Ghobashy, M. Revolutionizing biomedicine: Advancements, applications, and prospects of nanocomposite macromolecular carbohydrate-based hydrogel biomaterials: A review. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 35251–35291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, A.M.; Frazar, E.M.; Klaus, M.V.X.; Paul, P.; Hilt, J.Z. Hydrogels and Hydrogel Nanocomposites: Enhancing Healthcare through Human and Environmental Treatment. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 11, e2101820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, J.L.; Yu, A.C.; Agmon, G.; Appel, E.A. Supramolecular polymeric biomaterials. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 6, 10–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Liu, L.; He, G.; Zhang, T.; Yang, M.; Cai, J.; Fan, L.; Tao, S. Preparation and properties of carboxymethyl chitosan/oxidized hydroxyethyl cellulose hydrogel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 1692–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klosinski, K.K.; Wach, R.A.; Girek-Bak, M.K.; Rokita, B.; Kolat, D.; Kaluzinska-Kolat, Z.; Klosinska, B.; Duda, L.; Pasieka, Z.W. Biocompatibility and Mechanical Properties of Carboxymethyl Chitosan Hydrogels. Polymers 2022, 15, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aswathy, S.H.; Narendrakumar, U.; Manjubala, I. Commercial hydrogels for biomedical applications. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, S.A.; Rangappa, S.M.; Siengchin, S.; Parameswaranpillai, J. Natural polymers and the hydrogels prepared from them. In Hydrogels Based on Natural Polymers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 17–47. [Google Scholar]
- Contessotto, P.; Orbanic, D.; Da Costa, M.; Jin, C.; Owens, P.; Chantepie, S.; Chinello, C.; Newell, J.; Magni, F.; Papy-Garcia, D.; et al. Elastin-like recombinamers-based hydrogel modulates post-ischemic remodeling in a non-transmural myocardial infarction in sheep. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eaaz5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitura, S.; Sionkowska, A.; Jaiswal, A. Biopolymers for hydrogels in cosmetics: Review. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2020, 31, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, N.; Hoque, M.; Taharat, S.F. Recent advances in extraction of chitin and chitosan. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 39, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherng, J.H.; Lin, C.J.; Liu, C.C.; Yeh, J.Z.; Fan, G.Y.; Tsai, H.D.; Chung, C.F.; Hsu, S.D. Hemostasis and Anti-Inflammatory Abilities of AuNPs-Coated Chitosan Dressing for Burn Wounds. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.H.; Cherng, J.H.; Liu, C.C.; Fang, T.J.; Hong, Z.J.; Chang, S.J.; Fan, G.Y.; Hsu, S.D. Procoagulant and Antimicrobial Effects of Chitosan in Wound Healing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, P.; Zeng, Y.; Zaldivar-Silva, D.; Aguero, L.; Wang, S. Chitosan-Based Hemostatic Hydrogels: The Concept, Mechanism, Application, and Prospects. Molecules 2023, 28, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Song, R.; Johnson, M.; A, S.; Shen, P.; Zhang, N.; Lara-Saez, I.; Xu, Q.; Wang, W. Chitosan-Based Hydrogels for Infected Wound Treatment. Macromol. Biosci. 2023, 23, e2300094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, N.H.N.; Truong, Q.T.; Le, P.K.; Ha, A.C. Recent developments in chitosan hydrogels carrying natural bioactive compounds. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 294, 119726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Shang, Y.; Nuri Ertas, Y.; Orive, G. Chitosan-functionalized bioplatforms and hydrogels in breast cancer: Immunotherapy, phototherapy and clinical perspectives. Drug Discov. Today 2024, 29, 103851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, B.M. Current Advances in Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels as Smart Drug Delivery Carriers. Gels 2023, 9, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoque, J.; Sangaj, N.; Varghese, S. Stimuli-Responsive Supramolecular Hydrogels and Their Applications in Regenerative Medicine. Macromol. Biosci. 2019, 19, e1800259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Li, X.; Han, L. Recent developments in stimuli-responsive hydrogels for biomedical applications. Biosurf. Biotribol. 2022, 8, 290–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirupathi, K.; Raorane, C.J.; Ramkumar, V.; Ulagesan, S.; Santhamoorthy, M.; Raj, V.; Krishnakumar, G.S.; Phan, T.T.V.; Kim, S.C. Update on Chitosan-Based Hydrogels: Preparation, Characterization, and Its Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Applications. Gels 2022, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.C.; Chang, C.C.; Chan, H.P.; Chung, T.W.; Shu, C.W.; Chuang, K.P.; Duh, T.H.; Yang, M.H.; Tyan, Y.C. Hydrogels: Properties and Applications in Biomedicine. Molecules 2022, 27, 2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aminabhavi, T.M.; Dharupaneedi, S.P. Production of chitosan-based hydrogels for biomedical applications. In Chitosan Based Biomaterials Volume 1; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2017; pp. 295–319. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, N.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Xie, T. Dynamic Covalent Polymer Networks: A Molecular Platform for Designing Functions beyond Chemical Recycling and Self-Healing. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 1716–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, J.; Ponsford, D.; Dreiss, C.A.; Lee, T.C.; Loh, X.J. Supramolecular Hydrogels: Design Strategies and Contemporary Biomedical Applications. Chem. Asian J. 2022, 17, e202200081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.S.; Ji, S.M.; Park, M.J.; Suneetha, M.; Uthappa, U.T. Pectin Based Hydrogels for Drug Delivery Applications: A Mini Review. Gels 2022, 8, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maric, I.; Yang, L.; Li, X.; Santiago, G.M.; Pappas, C.G.; Qiu, X.; Dijksman, J.A.; Mikhailov, K.; van Rijn, P.; Otto, S. Tailorable and Biocompatible Supramolecular-Based Hydrogels Featuring two Dynamic Covalent Chemistries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2023, 62, e202216475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Yi, S.; Chen, X. Visible-light/temperature dual-responsive hydrogel constructed by alpha-cyclodextrin and an azobenzene linked surfactant. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 6490–6498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Liu, Y.Y.; Li, Y.J.; Wang, W.; Song, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tian, H. High-Preservation Single-Cell Operation through a Photo-responsive Hydrogel-Nanopipette System. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2021, 60, 5157–5161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Qin, Z.; Yu, X.; Li, J.; Lv, H.; Yang, X. On-demand removable hydrogels based on photolabile cross-linkings as wound dressing materials. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 5669–5676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabb, C.P.; O’Bryan, C.S.; Deng, C.C.; Angelini, T.E.; Sumerlin, B.S. Photoreversible Covalent Hydrogels for Soft-Matter Additive Manufacturing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 16793–16801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; An, N.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, K.; Hu, X.; Wu, Y.; Wu, F.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, H.; et al. Sustained-release of PDGF from PLGA microsphere embedded thermo-sensitive hydrogel promoting wound healing by inhibiting autophagy. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 101405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, S.L.; Huynh, T.H.; Poschko, P.; Fruergaard, A.S.; Jarlstad Olesen, M.T.; Chen, Y.; Birkedal, H.; Subbiahdoss, G.; Reimhult, E.; Thogersen, J.; et al. Remotely Triggered Liquefaction of Hydrogel Materials. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 9145–9155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, M.; Niu, W.; Winston, D.D.; Cheng, W.; Lei, B. Injectable biodegradation-visual self-healing citrate hydrogel with high tissue penetration for microenvironment-responsive degradation and local tumor therapy. Biomaterials 2020, 261, 120301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, J.S.; Hu, Y.; Willner, I. Stimuli-Responsive DNA-Based Hydrogels: From Basic Principles to Applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 680–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Khan, I.; Chen, J.; Akhtar, K.; Bakhsh, E.M.; Khan, S.B. Emerging Fabrication Strategies of Hydrogels and Its Applications. Gels 2022, 8, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Jung, Y.; Lee, N.; Lee, I.; Lee, J.H. Nature-Derived Polysaccharide-Based Composite Hydrogels for Promoting Wound Healing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantha, S.; Pillai, S.; Khayambashi, P.; Upadhyay, A.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, O.; Pham, H.M.; Tran, S.D. Smart Hydrogels in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. Materials 2019, 12, 3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Meng, Q.; Li, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhou, M.; Jin, Z.; Zhao, K. Chitosan Derivatives and Their Application in Biomedicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelu, M.; Musuc, A.M.; Popa, M.; Calderon Moreno, J.M. Chitosan Hydrogels for Water Purification Applications. Gels 2023, 9, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psarrou, M.; Mitraki, A.; Vamvakaki, M.; Kokotidou, C. Stimuli-Responsive Polysaccharide Hydrogels and Their Composites for Wound Healing Applications. Polymers 2023, 15, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.C.; Shukla, S.; Skoog, S.A.; Boehm, R.D.; Narayan, R.J. Current Advancements in Transdermal Biosensing and Targeted Drug Delivery. Sensors 2019, 19, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, D.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, J.; Li, X.; Zhuang, W.; Yang, X. Intra-articular Injection of Chitosan-Based Supramolecular Hydrogel for Osteoarthritis Treatment. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2021, 18, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, F.; Zeng, F.; Yu, X.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, M.; Ding, N.; Tian, J.; Li, C. Oral hydrogel nanoemulsion co-delivery system treats inflammatory bowel disease via anti-inflammatory and promoting intestinal mucosa repair. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, J.; Hu, W.; Tian, R.; Zhang, H.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L. Optimization and evaluation of a thermoresponsive ophthalmic in situ gel containing curcumin-loaded albumin nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 2517–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedford, J.G.; Caminschi, I.; Wakim, L.M. Intranasal Delivery of a Chitosan-Hydrogel Vaccine Generates Nasal Tissue Resident Memory CD8(+) T Cells That Are Protective against Influenza Virus Infection. Vaccines 2020, 8, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosecka, M.; Gosecki, M. Antimicrobial Polymer-Based Hydrogels for the Intravaginal Therapies-Engineering Considerations. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathi, R.; Sanshita; Kumar, A.; Vishvakarma, V.; Huanbutta, K.; Singh, I.; Sangnim, T. Advancements in Rectal Drug Delivery Systems: Clinical Trials, and Patents Perspective. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taokaew, S.; Kaewkong, W.; Kriangkrai, W. Recent Development of Functional Chitosan-Based Hydrogels for Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications. Gels 2023, 9, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shariatinia, Z.; Jalali, A.M. Chitosan-based hydrogels: Preparation, properties and applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 115, 194–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egorov, A.R.; Kirichuk, A.A.; Rubanik, V.V.; Rubanik, V.V., Jr.; Tskhovrebov, A.G.; Kritchenkov, A.S. Chitosan and Its Derivatives: Preparation and Antibacterial Properties. Materials 2023, 16, 6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, F.; Oveisi, Z.; Samani, S.M.; Amoozgar, Z. Chitosan based hydrogels: Characteristics and pharmaceutical applications. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zavyalova, O.; Gajewska, S.; Dąbrowska-Wisłocka, D.; Sionkowska, A. Characteristics of physicochemical and rheological properties of chitosan hydrogels based on selected hydroxy acids. Eng. Biomater. 2021, 24, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, B.B.; Saibi, S.; Haroune, L.; Rios, N.S.; Goncalves, L.R.B.; Cabana, H. Genipin and glutaraldehyde based laccase two-layers immobilization with improved properties: New biocatalysts with high potential for enzymatic removal of trace organic contaminants. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2023, 169, 110261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedzierska, M.; Jamrozy, M.; Drabczyk, A.; Kudlacik-Kramarczyk, S.; Bankosz, M.; Gruca, M.; Potemski, P.; Tyliszczak, B. Analysis of the Influence of Both the Average Molecular Weight and the Content of Crosslinking Agent on Physicochemical Properties of PVP-Based Hydrogels Developed as Innovative Dressings. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drabczyk, A.; Kudlacik-Kramarczyk, S.; Glab, M.; Kedzierska, M.; Jaromin, A.; Mierzwinski, D.; Tyliszczak, B. Physicochemical Investigations of Chitosan-Based Hydrogels Containing Aloe Vera Designed for Biomedical Use. Materials 2020, 13, 3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farasati Far, B.; Omrani, M.; Naimi Jamal, M.R.; Javanshir, S. Multi-responsive chitosan-based hydrogels for controlled release of vincristine. Commun. Chem. 2023, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, S.; Kim, I.; Jeong, Y.J.; Kim, Y.; Chung, J.J.; Kim, S.W. Comparative Analysis of Antibacterial and Wound Healing Activities of Chitosan and Povidone-Iodine-Based Hydrogels. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2024, 92, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyliszczak, B.; Drabczyk, A.; Kudlacik, S. Comparison of Hydrogels Based on Commercial Chitosan and Beetosan® Containing Nanosilver. Molecules 2016, 22, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjbar, R.; Yousefi, A. Effects of Aloe Vera and Chitosan Nanoparticle Thin-Film Membranes on Wound Healing in Full Thickness Infected Wounds with Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Bull. Emerg. Trauma. 2018, 6, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudko, M.; Urbaniak, T.; Musial, W. Recent Developments in Ion-Sensitive Systems for Pharmaceutical Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, I.R.; Gamble, G.D.; Bolland, M.J. Circulating calcium concentrations, vascular disease and mortality: A systematic review. J. Intern. Med. 2016, 279, 524–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portbury, S.D.; Adlard, P.A. Zinc Signal in Brain Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardhan, K.H.; Kumar, P.S.; Panda, R.C. A review on heavy metal pollution, toxicity and remedial measures: Current trends and future perspectives. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 290, 111197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diacon, A.; Albota, F.; Mocanu, A.; Brincoveanu, O.; Podaru, A.I.; Rotariu, T.; Ahmad, A.A.; Rusen, E.; Toader, G. Dual-Responsive Hydrogels for Mercury Ion Detection and Removal from Wastewater. Gels 2024, 10, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Cui, W.; Li, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y. Supramolecular self-assembly of two-component systems comprising aromatic amides/Schiff base and tartaric acid. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2020, 14, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Sun, R.; Zheng, R.; Huang, Y. Anions-responsive supramolecular gels: A review. Mater. Des. 2021, 205, 109759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, N.S.; Ahmad, M.; Alqahtani, M.S.; Mahmood, A.; Barkat, K.; Khan, M.T.; Tulain, U.R.; Rashid, A. beta-cyclodextrin chitosan-based hydrogels with tunable pH-responsive properties for controlled release of acyclovir: Design, characterization, safety, and pharmacokinetic evaluation. Drug Deliv. 2021, 28, 1093–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.; Liu, S.; Zhu, W.; Li, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y. Synthesis, Characterization, Properties, and Biomedical Application of Chitosan-Based Hydrogels. Polymers 2023, 15, 2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Yang, C.; Jian, Y.; Deng, H.; Du, Y.; Shi, X. Ion-responsive chitosan hydrogel actuator inspired by carrotwood seed pod. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 276, 118759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vegad, U.; Patel, M.; Khunt, D.; Zupancic, O.; Chauhan, S.; Paudel, A. pH stimuli-responsive hydrogels from non-cellulosic biopolymers for drug delivery. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1270364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhail, M.; Ullah, H.; Vu, Q.L.; Khan, A.; Tsai, M.J.; Wu, P.C. Preparation of pH-Responsive Hydrogels Based on Chondroitin Sulfate/Alginate for Oral Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, A.; Paschew, G.; Klatt, S.; Lienig, J.; Arndt, K.F.; Adler, H.P. Review on Hydrogel-based pH Sensors and Microsensors. Sensors 2008, 8, 561–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizwan, M.; Yahya, R.; Hassan, A.; Yar, M.; Azzahari, A.D.; Selvanathan, V.; Sonsudin, F.; Abouloula, C.N. pH Sensitive Hydrogels in Drug Delivery: Brief History, Properties, Swelling, and Release Mechanism, Material Selection and Applications. Polymers 2017, 9, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofridam, F.; Tarhini, M.; Lebaz, N.; Gagnière, É.; Mangin, D.; Elaissari, A. pH-sensitive polymers: Classification and some fine potential applications. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2021, 32, 1455–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woraphatphadung, T.; Sajomsang, W.; Rojanarata, T.; Ngawhirunpat, T.; Tonglairoum, P.; Opanasopit, P. Development of Chitosan-Based pH-Sensitive Polymeric Micelles Containing Curcumin for Colon-Targeted Drug Delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 991–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ata, S.; Rasool, A.; Islam, A.; Bibi, I.; Rizwan, M.; Azeem, M.K.; Qureshi, A.U.R.; Iqbal, M. Loading of Cefixime to pH sensitive chitosan based hydrogel and investigation of controlled release kinetics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 1236–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Mahrouk, G.M.; Aboul-Einien, M.H.; Makhlouf, A.I. Design, Optimization, and Evaluation of a Novel Metronidazole-Loaded Gastro-Retentive pH-Sensitive Hydrogel. AAPS PharmSciTech 2016, 17, 1285–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezati, P.; Rhim, J.-W. pH-responsive chitosan-based film incorporated with alizarin for intelligent packaging applications. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 102, 105629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauler Riera, P.; Volterrani, M.; Iellamo, F.; Fallo, F.; Ermolao, A.; Kraemer, W.J.; Ratamess, N.A.; Faigenbaum, A.; Philp, A.; Baar, K. Redox Status. In Encyclopedia of Exercise Medicine in Health and Disease; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 751–753. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, W.; Liu, Y. Redox-responsive hydrogels. In Biopolymer-Based Composites; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2017; pp. 31–60. [Google Scholar]
- Abed, H.F.; Abuwatfa, W.H.; Husseini, G.A. Redox-Responsive Drug Delivery Systems: A Chemical Perspective. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, C.; Zhang, S.; Wei, C.; Xu, Y.; Lu, W. ROS-responsive selenium-containing polyphosphoester nanogels for activated anticancer drug release. Mater. Today Chem. 2018, 9, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Peng, F.; Cai, J.; Yang, D.; Zhang, P. Redox dual-stimuli responsive drug delivery systems for improving tumor-targeting ability and reducing adverse side effects. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 15, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Duan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhang, K. Current hydrogel advances in physicochemical and biological response-driven biomedical application diversity. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, T.T.; Yadav, S.; Reddy, O.S.; Jo, S.H.; Joo, S.B.; Kim, B.K.; Park, E.J.; Park, S.H.; Lim, K.T. Reduction-Responsive Chitosan-Based Injectable Hydrogels for Enhanced Anticancer Therapy. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, P.; Dai, C.; Cao, P.; Sun, D.; Ouyang, R.; Miao, Y. The role of reactive oxygen species in tumor treatment. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 7740–7750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, M.; Yuan, J.; Tao, L.; Wei, Y. Redox-responsive polymers for drug delivery: From molecular design to applications. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 1519–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wu, S.; Zhang, X.; Feng, T.; Wu, L. Chitosan-Based Hydrogels for Bioelectronic Sensing: Recent Advances and Applications in Biomedicine and Food Safety. Biosensors 2023, 13, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, F.; Roca-Melendres, M.M.; Duran-Lara, E.F.; Rafael, D.; Schwartz, S., Jr. Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels for Cancer Treatment: The Role of pH, Light, Ionic Strength and Magnetic Field. Cancers 2021, 13, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.; Zeng, B.; Yang, W. Light responsive hydrogels for controlled drug delivery. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1075670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomatsu, I.; Peng, K.; Kros, A. Photoresponsive hydrogels for biomedical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 1257–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Liu, H.; Tang, D.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, F. Bioactuators based on stimulus-responsive hydrogels and their emerging biomedical applications. NPG Asia Mater. 2019, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Duan, L.; Kong, M.; Wen, X.; Guan, F.; Ma, S. Applications and Mechanisms of Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels in Traumatic Brain Injury. Gels 2022, 8, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, P.; Svirskis, D.; Rees, S.W.P.; Barker, D.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Wu, Z. Photosensitive drug delivery systems for cancer therapy: Mechanisms and applications. J. Control Release 2021, 338, 446–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasinski, A.; Zielinska-Pisklak, M.; Oledzka, E.; Sobczak, M. Smart Hydrogels-Synthetic Stimuli-Responsive Antitumor Drug Release Systems. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 4541–4572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Scheiger, J.M.; Levkin, P.A. Design and Applications of Photoresponsive Hydrogels. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1807333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azagarsamy, M.A.; McKinnon, D.D.; Alge, D.L.; Anseth, K.S. Coumarin-Based Photodegradable Hydrogel: Design, Synthesis, Gelation, and Degradation Kinetics. ACS Macro Lett. 2014, 3, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.R.; Yong, K.W.; Choi, J.Y.; Cowie, A.C. Recent advances in photo-crosslinkable hydrogels for biomedical applications. Biotechniques 2019, 66, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, W.; Wu, Q.; Han, X.; Zhang, W.; Wei, W.; Chen, L.; Li, L.; Huang, W. Photosensitive hydrogels: From structure, mechanisms, design to bioapplications. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 1813–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, F.; Qiu, P.; Wang, Y.; Ren, P.; Liu, J.; Zhao, J.; Gou, D. Chitosan-based hydrogels: From preparation to applications, a review. Food Chem. X 2024, 21, 101095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Shao, Z.; Chen, X. Chitosan-based electroactive hydrogel. Polymer 2008, 49, 5520–5525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, B.; Zarrintaj, P.; Surwase, S.S.; Baheiraei, N.; Saeb, M.R.; Mozafari, M.; Kim, Y.C.; Park, O.O. Self-gelling electroactive hydrogels based on chitosan-aniline oligomers/agarose for neural tissue engineering with on-demand drug release. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 184, 110549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, J.H.; Lim, J.H.; Lee, J.M.; Chung, B.G. Electro-Responsive Conductive Blended Hydrogel Patch. Polymers 2023, 15, 2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Zhao, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Gu, X.; Ding, J.; Lv, Z.; Liu, G.; Liu, X.; Xu, W. Advances in preparation, design strategy and application of electroactive hydrogels. J. Power Sources 2023, 581, 233485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peers, S.; Montembault, A.; Ladaviere, C. Chitosan hydrogels for sustained drug delivery. J. Control Release 2020, 326, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Valle, L.J.; Diaz, A.; Puiggali, J. Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications: Cellulose, Chitosan, and Protein/Peptide Derivatives. Gels 2017, 3, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiz-Fernandez, S.; Perez-Alvarez, L.; Silvan, U.; Vilas-Vilela, J.L.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. pH-Induced 3D Printable Chitosan Hydrogels for Soft Actuation. Polymers 2022, 14, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Xue, K.; Loh, X.J. Thermo-Responsive Hydrogels: From Recent Progress to Biomedical Applications. Gels 2021, 7, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Song, S.; Zheng, A. Thermosensitive Hydrogels and Advances in Their Application in Disease Therapy. Polymers 2022, 14, 2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazar, E.M.; Shah, R.A.; Dziubla, T.D.; Hilt, J.Z. Multifunctional temperature-responsive polymers as advanced biomaterials and beyond. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Qi, X.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Z. Thermo-sensitive hydrogels for delivering biotherapeutic molecules: A review. Saudi Pharm. J. 2019, 27, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liang, H.; Chen, X.; Tan, H. Natural Polymer-Based Hydrogels: From Polymer to Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.J.; Tomlins, P.; Sahota, T.S. Thermoresponsive Gels. Gels 2017, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellotti, E.; Schilling, A.L.; Little, S.R.; Decuzzi, P. Injectable thermoresponsive hydrogels as drug delivery system for the treatment of central nervous system disorders: A review. J. Control Release 2021, 329, 16–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Zhu, C.; Li, B.; Wang, T.; Wan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J.; Yang, D.; Shen, Y. Improving the Anti-Ovarian Cancer Activity of Docetaxel by Self-Assemble Micelles and Thermosensitive Hydrogel Drug Delivery System. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2020, 16, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, A.; Farooq, M.A.; Parveen, A. Thermosensitive Chitosan-Based Injectable Hydrogel as an Efficient Anticancer Drug Carrier. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 20450–20460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Husseiny, H.M.; Mady, E.A.; El-Dakroury, W.A.; Doghish, A.S.; Tanaka, R. Stimuli-responsive hydrogels: Smart state of-the-art platforms for cardiac tissue engineering. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1174075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Han, W.J.; Jang, H.S.; Choi, H.J. Highly Tough, Biocompatible, and Magneto-Responsive Fe3O4/Laponite/PDMAAm Nanocomposite Hydrogels. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, C.; Cheng, Y. Magnetic-responsive hydrogels: From strategic design to biomedical applications. J. Control Release 2021, 335, 541–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yin, H.; Chu, J.; Eglin, D.; Serra, T.; Docheva, D. An anisotropic nanocomposite hydrogel guides aligned orientation and enhances tenogenesis of human tendon stem/progenitor cells. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Liang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zhao, P.; Liang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Duan, L.; Liu, W.; Zhu, F.; Bian, L.; et al. Magnetic Enhancement of Chondrogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 2200–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antman-Passig, M.; Shefi, O. Remote Magnetic Orientation of 3D Collagen Hydrogels for Directed Neuronal Regeneration. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 2567–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, C.; Xu, K.; Niu, Z.; Zou, S.; Zhang, D.; Qian, Z.; Liao, J.; Xie, J. Hydrogel platform with tunable stiffness based on magnetic nanoparticles cross-linked GelMA for cartilage regeneration and its intrinsic biomechanism. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 25, 615–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, T.; Iwanaga, A.; Shirosaki, Y.; Kawashita, M. In situ synthesis of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in chitosan hydrogels as a reaction field: Effect of cross-linking density. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 179, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadban, A.; Ahmed, A.S.; Ping, Y.; Ramos, R.; Arfin, N.; Cantaert, B.; Ramanujan, R.V.; Miserez, A. Bioinspired pH and magnetic responsive catechol-functionalized chitosan hydrogels with tunable elastic properties. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 697–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Hosta-Rigau, L.; Chandrawati, R.; Cui, J. Multi-Stimuli-Responsive Polymer Particles, Films, and Hydrogels for Drug Delivery. Chem 2018, 4, 2084–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.Q.; Wang, G.J. Multi-Stimuli-Responsive Polymer Materials: Particles, Films, and Bulk Gels. Chem. Rec. 2016, 16, 1398–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Yuan, P.; Wu, B.; Liu, Y.; Hu, C. Advances in the Research and Application of Smart-Responsive Hydrogels in Disease Treatment. Gels 2023, 9, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourjavadi, A.; Heydarpour, R.; Tehrani, Z.M. Multi-stimuli-responsive hydrogels and their medical applications. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 15705–15717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xu, W.; Liu, H. Fabrication of chitosan functionalized dual stimuli-responsive injectable nanogel to control delivery of doxorubicin. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2023, 301, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Husseiny, H.M.; Mady, E.A.; Doghish, A.S.; Zewail, M.B.; Abdelfatah, A.M.; Noshy, M.; Mohammed, O.A.; El-Dakroury, W.A. Smart/stimuli-responsive chitosan/gelatin and other polymeric macromolecules natural hydrogels vs. synthetic hydrogels systems for brain tissue engineering: A state-of-the-art review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 260, 129323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavari Maroufi, L.; Ghorbani, M. Injectable chitosan-quince seed gum hydrogels encapsulated with curcumin loaded-halloysite nanotubes designed for tissue engineering application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 177, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, P.C.; Zhang, Y.; Abebe, F. Recent Applications of Dual-Stimuli Responsive Chitosan Hydrogel Nanocomposites as Drug Delivery Tools. Molecules 2021, 26, 4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garshasbi, H.; Salehi, S.; Naghib, S.M.; Ghorbanzadeh, S.; Zhang, W. Stimuli-responsive injectable chitosan-based hydrogels for controlled drug delivery systems. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1126774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madivoli, E.S.; Schwarte, J.V.; Kareru, P.G.; Gachanja, A.N.; Fromm, K.M. Stimuli-Responsive and Antibacterial Cellulose-Chitosan Hydrogels Containing Polydiacetylene Nanosheets. Polymers 2023, 15, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Hua, D.; Xiong, R.; Huang, C. Bio-based stimuli-responsive materials for biomedical applications. Mater. Adv. 2023, 4, 458–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Sharma, A.; Puri, V.; Aggarwal, G.; Maman, P.; Huanbutta, K.; Nagpal, M.; Sangnim, T. Chitosan-Based Polymer Blends for Drug Delivery Systems. Polymers 2023, 15, 2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubbs, H.; Manna, B. Wound Physiology; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Pazyar, N.; Houshmand, G.; Yaghoobi, R.; Hemmati, A.A.; Zeineli, Z.; Ghorbanzadeh, B. Wound healing effects of topical Vitamin K: A randomized controlled trial. Indian. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 51, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarbrink, K.; Ni, G.; Sonnergren, H.; Schmidtchen, A.; Pang, C.; Bajpai, R.; Car, J. Prevalence and incidence of chronic wounds and related complications: A protocol for a systematic review. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, X.; Zhao, T.; Hu, J.; Yang, K.; Ma, N.; Li, A.; Sun, Q.; Ding, C.; Ding, Q. Application of Chitosan-Based Hydrogel in Promoting Wound Healing: A Review. Polymers 2024, 16, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, P.; Luo, Y.; Ke, C.; Qiu, H.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Hou, R.; Xu, L.; Wu, S. Chitosan-Based Functional Materials for Skin Wound Repair: Mechanisms and Applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 650598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliakbar Ahovan, Z.; Esmaeili, Z.; Eftekhari, B.S.; Khosravimelal, S.; Alehosseini, M.; Orive, G.; Dolatshahi-Pirouz, A.; Pal Singh Chauhan, N.; Janmey, P.A.; Hashemi, A.; et al. Antibacterial smart hydrogels: New hope for infectious wound management. Mater. Today Bio 2022, 17, 100499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klosinski, K.K.; Wach, R.A.; Kruczkowska, W.; Duda, L.; Kolat, D.; Kaluzinska-Kolat, Z.; Arkuszewski, P.T.; Pasieka, Z.W. Carboxymethyl Chitosan Hydrogels for Effective Wound Healing-An Animal Study. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Li, C.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, F.; Li, Z.; Wang, J. A functional chitosan-based hydrogel as a wound dressing and drug delivery system in the treatment of wound healing. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 7533–7549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Yan, Y.; Huang, J.; Liang, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, B.; Ma, B.; Bianco, A.; Ge, S.; Shao, J. A multifunctional chitosan-based hydrogel with self-healing, antibacterial, and immunomodulatory effects as wound dressing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 231, 123149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Hao, Y.; Francesco, S.; Mao, X.; Huang, W.C. A chitosan-based antibacterial hydrogel with injectable and self-healing capabilities. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2024, 6, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Chen, C.; Yang, K.; Wang, H.; Xia, H.; Zhao, Y.; Teng, Y.; Feng, G.; Chen, Y.M. Hyaluronic acid and chitosan-based injectable and self-healing hydrogel with inherent antibacterial and antioxidant bioactivities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 227, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatarusanu, S.M.; Sava, A.; Profire, B.S.; Pinteala, T.; Jitareanu, A.; Iacob, A.T.; Lupascu, F.; Simionescu, N.; Rosca, I.; Profire, L. New Smart Bioactive and Biomimetic Chitosan-Based Hydrogels for Wounds Care Management. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Bratlie, K.M. pH sensitive methacrylated chitosan hydrogels with tunable physical and chemical properties. Biochem. Eng. J. 2018, 132, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, E.; Machado, S.; Soares, G. Smart Hydrogel for the pH-Selective Drug Delivery of Antimicrobial Compounds. Macromol. Symp. 2019, 385, 1800182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Mu, L.; Zhao, X.; Han, Y.; Guo, B. Bacterial Growth-Induced Tobramycin Smart Release Self-Healing Hydrogel for Pseudomonas aeruginosa-Infected Burn Wound Healing. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 13022–13036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.U.A.; Iqbal, I.; Ansari, M.N.M.; Razak, S.I.A.; Raza, M.A.; Sajjad, A.; Jabeen, F.; Riduan Mohamad, M.; Jusoh, N. Development of Antibacterial, Degradable and pH-Responsive Chitosan/Guar Gum/Polyvinyl Alcohol Blended Hydrogels for Wound Dressing. Molecules 2021, 26, 5937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, A.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, Z.; Cheng, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wu, X.; Chen, K.; Ning, X. A photoactive self-healing carboxymethyl chitosan-based hydrogel for accelerated infected wound healing through simultaneously modulating multiple critical tissue repair factors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 124631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, B.; Jia, M.; Liu, S.; Sheng, Z.; Li, M.; Gao, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, P. Smart Hydrogel-Based DVDMS/bFGF Nanohybrids for Antibacterial Phototherapy with Multiple Damaging Sites and Accelerated Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 10156–10169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.H.M.; Abueva, C.; Ho, H.V.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, B.T. In vitro and in vivo acute response towards injectable thermosensitive chitosan/TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofiber hydrogel. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 180, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Zhong, Y.; Jiang, X. An injectable photothermally active antibacterial composite hydroxypropyl chitin hydrogel for promoting the wound healing process through photobiomodulation. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 4567–4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, M.A.; Khatoon, F. In Vitro Study of Temperature and pH-Responsive Gentamycin Sulphate-Loaded Chitosan-Based Hydrogel Films for Wound Dressing Applications. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Eng. 2014, 54, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiSabato, D.J.; Quan, N.; Godbout, J.P. Neuroinflammation: The devil is in the details. J. Neurochem. 2016, 139 (Suppl. S2), 136–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danon, J.J.; Reekie, T.A.; Kassiou, M. Challenges and Opportunities in Central Nervous System Drug Discovery. Trends Chem. 2019, 1, 612–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achar, A.; Myers, R.; Ghosh, C. Drug Delivery Challenges in Brain Disorders across the Blood-Brain Barrier: Novel Methods and Future Considerations for Improved Therapy. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, H.; Cheng, S.; Pozzoli, M.; Messerotti, E.; Traini, D.; Young, P.; Kourmatzis, A.; Ong, H.X. Smart thermosensitive chitosan hydrogel for nasal delivery of ibuprofen to treat neurological disorders. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatzitaki, A.T.; Jesus, S.; Karavasili, C.; Andreadis, D.; Fatouros, D.G.; Borges, O. Chitosan-coated PLGA nanoparticles for the nasal delivery of ropinirole hydrochloride: In vitro and ex vivo evaluation of efficacy and safety. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 589, 119776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Patil, K.; Bobade, N.; Yeole, P.; Gaikwad, R. Formulation of intranasal mucoadhesive temperature-mediated in situ gel containing ropinirole and evaluation of brain targeting efficiency in rats. J. Drug Target. 2010, 18, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hsu, Y.H.; Huang, A.P.; Hsu, S.H. Semi-Interpenetrating Polymer Network of Hyaluronan and Chitosan Self-Healing Hydrogels for Central Nervous System Repair. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 40108–40120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almuhayawi, M.S.; Ramadan, W.S.; Harakeh, S.; Al Jaouni, S.K.; Bharali, D.J.; Mousa, S.A.; Almuhayawi, S.M. The potential role of pomegranate and its nano-formulations on cerebral neurons in aluminum chloride induced Alzheimer rat model. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 1710–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, G.; Li, Z.; Mei, J. Resveratrol-loaded selenium/chitosan nano-flowers alleviate glucolipid metabolism disorder-associated cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 239, 124316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, B.; Samanta, M.K.; Santhi, K.; Kumar, K.P.; Ramasamy, M.; Suresh, B. Chitosan nanoparticles as a new delivery system for the anti-Alzheimer drug tacrine. Nanomedicine 2010, 6, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, A.; Yoyen-Ermis, D.; Caban-Toktas, S.; Horzum, U.; Aktas, Y.; Couvreur, P.; Esendagli, G.; Capan, Y. Evaluation of brain-targeted chitosan nanoparticles through blood-brain barrier cerebral microvessel endothelial cells. J. Microencapsul. 2017, 34, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajamanickam, G.; Manju, S.L. Formulation and characterization of chitosan nanoparticles loaded with neuroprotective flavonoid from Phyllanthus niruri Linn. Macromol. Res. 2023, 31, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, M.; Elangovan, A.; Sennimalai, R.; Babu, H.W.S.; Thiruvenkataswamy, S.; Krishnan, J.; Yadav, M.K.; Gopalakrishnan, A.V.; Narayanasamy, A.; Vellingiri, B. Chitosan—An alternative drug delivery approach for neurodegenerative diseases. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2024, 7, 100460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Dawson, C.; Lamb, M.; Mueller, E.; Stefanek, E.; Akbari, M.; Hoare, T. Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering: Addressing Key Design Needs Toward Clinical Translation. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 849831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahranavard, M.; Zamanian, A.; Ghorbani, F.; Shahrezaee, M.H. A critical review on three dimensional-printed chitosan hydrogels for development of tissue engineering. Bioprinting 2020, 17, e00063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, S.; Chakraborty, E. Hydrogel based tissue engineering and its future applications in personalized disease modeling and regenerative therapy. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2022, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, B.P.; Leong, K.W. Scaffolding in tissue engineering: General approaches and tissue-specific considerations. Eur. Spine J. 2008, 17 (Suppl. S4), 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaharwar, A.K.; Singh, I.; Khademhosseini, A. Engineered biomaterials for in situ tissue regeneration. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020, 5, 686–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburaci, S.; Tihminlioglu, F. Development of Si doped nano hydroxyapatite reinforced bilayer chitosan nanocomposite barrier membranes for guided bone regeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2021, 128, 112298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehghani Nazhvani, F.; Mohammadi Amirabad, L.; Azari, A.; Namazi, H.; Hosseinzadeh, S.; Samanipour, R.; Khojasteh, A.; Golchin, A.; Hashemi, S. Effects of in vitro low oxygen tension preconditioning of buccal fat pad stem cells on in Vivo articular cartilage tissue repair. Life Sci. 2021, 280, 119728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Nada, A.A.; Valmikinathan, C.M.; Lee, P.; Liang, D.; Yu, X.; Kumbar, S.G. In situ gelling polysaccharide-based hydrogel for cell and drug delivery in tissue engineering. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 131, 39934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.Z.; Wang, H.F.; Guan, J.; Fu, J.N.; Yang, M.; Zhang, J.Y.; Chen, Y.R.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.K. Fabrication of Injectable Chitosan-Chondroitin Sulfate Hydrogel Embedding Kartogenin-Loaded Microspheres as an Ultrasound-Triggered Drug Delivery System for Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Yang, J.; Xu, J. Structural and biological investigation of chitosan/hyaluronic acid with silanized-hydroxypropyl methylcellulose as an injectable reinforced interpenetrating network hydrogel for cartilage tissue engineering. Drug Deliv. 2021, 28, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.Z.; Ji, Y.R.; Kang, Z.W.; Li, F.; Ge, S.F.; Yang, D.P.; Ruan, J.; Fan, X.Q. Integrating eggshell-derived CaCO3/MgO nanocomposites and chitosan into a biomimetic scaffold for bone regeneration. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 395, 125098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavanya, K.; Chandran, S.V.; Balagangadharan, K.; Selvamurugan, N. Temperature- and pH-responsive chitosan-based injectable hydrogels for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 111, 110862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Qazvini, N.T.; Sadati, M.; Zeng, Z.; Huang, S.; De La Lastra, A.L.; Zhang, L.; Feng, Y.; Liu, W.; Huang, B.; et al. A pH-Triggered, Self-Assembled, and Bioprintable Hybrid Hydrogel Scaffold for Mesenchymal Stem Cell Based Bone Tissue Engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 8749–8762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niranjan, R.; Koushik, C.; Saravanan, S.; Moorthi, A.; Vairamani, M.; Selvamurugan, N. A novel injectable temperature-sensitive zinc doped chitosan/beta-glycerophosphate hydrogel for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 54, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi-Aghdam, F.; Jahed, V.; Dehghan-Niri, M.; Ganji, F.; Vasheghani-Farahani, E. Injectable chitosan hydrogel embedding modified halloysite nanotubes for bone tissue engineering. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 269, 118311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanzadeh, E.; Seifalian, A.; Mellati, A.; Saremi, J.; Asadpour, S.; Enderami, S.E.; Nekounam, H.; Mahmoodi, N. Injectable hydrogels in central nervous system: Unique and novel platforms for promoting extracellular matrix remodeling and tissue engineering. Mater. Today Bio 2023, 20, 100614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, N.; Bhardwaj, A.; Mehta, S.; Mehta, A. Stimuli-responsive hydrogels in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 758–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Fan, Z.; Liu, Z.; Xie, X.; Guan, J. Regulating myogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells using thermosensitive hydrogels. Acta Biomater. 2015, 26, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zeng, X.; Ma, C.; Yi, H.; Ali, Z.; Mou, X.; Li, S.; Deng, Y.; He, N. Injectable hydrogels for cartilage and bone tissue engineering. Bone Res. 2017, 5, 17014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Cui, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Tang, P. Recent Advances on Magnetic Sensitive Hydrogels in Tissue Engineering. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaudo, M.A.; Krishnakumar, G.S.; Giusto, E.; Furlani, F.; Bassi, G.; Rossi, A.; Molinari, F.; Lista, F.; Montesi, M.; Panseri, S. Bioactive injectable hydrogels for on demand molecule/cell delivery and for tissue regeneration in the central nervous system. Acta Biomater. 2022, 140, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Kaufman, L.J. Flow and magnetic field induced collagen alignment. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, Y.P.; Moses, J.C.; Bhardwaj, N.; Mandal, B.B. Injectable hydrogels: A new paradigm for osteochondral tissue engineering. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 5499–5529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaing, Z.Z.; Ehsanipour, A.; Hofstetter, C.P.; Seidlits, S.K. Injectable Hydrogels for Spinal Cord Repair: A Focus on Swelling and Intraspinal Pressure. Cells Tissues Organs 2016, 202, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.D.; Duan, H.M.; Hao, F.; Zhao, W.; Gao, Y.D.; Hao, P.; Yang, Z.Y.; Li, X.G. Biomimetic chitosan scaffolds with long-term controlled release of nerve growth factor repairs 20-mm-long sciatic nerve defects in rats. Neural Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 1146–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, M.; Li, X.; Tong, A.; Guo, G. Multi-functional chitosan-based smart hydrogels mediated biomedical application. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeya, H.; Itai, S.; Kimura, H.; Kurashina, Y.; Amemiya, T.; Nagoshi, N.; Iwamoto, T.; Sato, K.; Shibata, S.; Matsumoto, M.; et al. Schwann cell-encapsulated chitosan-collagen hydrogel nerve conduit promotes peripheral nerve regeneration in rodent sciatic nerve defect models. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Liu, C.; Hai, B.; Ma, T.; Zhang, W.; Tan, J.; Fu, X.; Wang, H.; Xu, Y.; Song, C. Chitosan conduits filled with simvastatin/Pluronic F-127 hydrogel promote peripheral nerve regeneration in rats. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2018, 106, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Soury, M.; Garcia-Garcia, O.D.; Tarulli, I.; Chato-Astrain, J.; Perroteau, I.; Geuna, S.; Raimondo, S.; Gambarotta, G.; Carriel, V. Chitosan conduits enriched with fibrin-collagen hydrogel with or without adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells for the repair of 15-mm-long sciatic nerve defect. Neural Regen. Res. 2023, 18, 1378–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boido, M.; Ghibaudi, M.; Gentile, P.; Favaro, E.; Fusaro, R.; Tonda-Turo, C. Chitosan-based hydrogel to support the paracrine activity of mesenchymal stem cells in spinal cord injury treatment. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanzione, A.; Polini, A.; La Pesa, V.; Quattrini, A.; Romano, A.; Gigli, G.; Moroni, L.; Gervaso, F. Thermosensitive chitosan-based hydrogels supporting motor neuron-like NSC-34 cell differentiation. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 7492–7503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, G.; Tiwari, R.; Sriwastawa, B.; Bhati, L.; Pandey, S.; Pandey, P.; Bannerjee, S.K. Drug delivery systems: An updated review. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2012, 2, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Karp, J.M.; Langer, R.; Joshi, N. The Future of Drug Delivery. Chem. Mater. 2023, 35, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chehelgerdi, M.; Chehelgerdi, M.; Allela, O.Q.B.; Pecho, R.D.C.; Jayasankar, N.; Rao, D.P.; Thamaraikani, T.; Vasanthan, M.; Viktor, P.; Lakshmaiya, N.; et al. Progressing nanotechnology to improve targeted cancer treatment: Overcoming hurdles in its clinical implementation. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Akhtar, N.; Minhas, M.U.; Badshah, S.F. pH/Thermo-Dual Responsive Tunable In Situ Cross-Linkable Depot Injectable Hydrogels Based on Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide)/Carboxymethyl Chitosan with Potential of Controlled Localized and Systemic Drug Delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalabi-Dchar, M.; Fenouil, T.; Machon, C.; Vincent, A.; Catez, F.; Marcel, V.; Mertani, H.C.; Saurin, J.C.; Bouvet, P.; Guitton, J.; et al. A novel view on an old drug, 5-fluorouracil: An unexpected RNA modifier with intriguing impact on cancer cell fate. NAR Cancer 2021, 3, zcab032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sritharan, S.; Sivalingam, N. A comprehensive review on time-tested anticancer drug doxorubicin. Life Sci. 2021, 278, 119527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Z.; Zhao, N.; Wang, C.; Yuan, W. Injectable self-healing polysaccharide hydrogel loading CuS and pH-responsive DOX@ZIF-8 nanoparticles for synergistic photothermal-photodynamic-chemo therapy of cancer. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 127, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.; LoGiudice, K.; Mays, G.; Schorr, A.; Rowey, R.; Yang, H.; Trivedi, S.; Srivastava, V. Increasing Chemotherapeutic Efficacy Using pH-Modulating and Doxorubicin-Releasing Injectable Chitosan-Poly(ethylene glycol) Hydrogels. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 45626–45639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Zhao, X.; Ma, P.X.; Guo, B. pH-responsive self-healing injectable hydrogel based on N-carboxyethyl chitosan for hepatocellular carcinoma therapy. Acta Biomater. 2017, 58, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zheng, H.; Zhou, L.; Cheng, F.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q. Injectable redox and light responsive MnO2 hybrid hydrogel for simultaneous melanoma therapy and multidrug-resistant bacteria-infected wound healing. Biomaterials 2020, 260, 120314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Guo, L.; Shi, D.; Sun, X.; Shang, M.; Zhou, X.; Li, J. Charge-conversion and ultrasound-responsive O-carboxymethyl chitosan nanodroplets for controlled drug delivery. Nanomedicine 2019, 14, 2549–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekinci, E.; Rohondia, S.; Khan, R.; Dou, Q.P. Repurposing Disulfiram as An Anti-Cancer Agent: Updated Review on Literature and Patents. Recent Pat. Anti-Cancer Drug Discov. 2019, 14, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzazzadeh, A.; Dizaji, B.F.; Kianinejad, N.; Nouri, A.; Irani, M. Fabrication of poly(acrylic acid) grafted-chitosan/polyurethane/magnetic MIL-53 metal organic framework composite core-shell nanofibers for co-delivery of temozolomide and paclitaxel against glioblastoma cancer cells. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 587, 119674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heragh, B.K.; Taherinezhad, H.; Mahdavinia, G.R.; Javanshir, S.; Labib, P.; Ghasemsolb, S. pH-responsive co-delivery of doxorubicin and saffron via cross-linked chitosan/laponite RD nanoparticles for enhanced-chemotherapy. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 34, 104956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabourian, P.; Ji, J.; Lotocki, V.; Moquin, A.; Hanna, R.; Frounchi, M.; Maysinger, D.; Kakkar, A. Facile design of autogenous stimuli-responsive chitosan/hyaluronic acid nanoparticles for efficient small molecules to protein delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 7275–7287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Lin, J.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Li, R.; Wang, C.; Zhao, C.; Lu, L.; Zhou, C.; Tian, J.; et al. Temperature- and pH-responsive injectable chitosan hydrogels loaded with doxorubicin and curcumin as long-lasting release platforms for the treatment of solid tumors. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1043939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baghbani, F.; Chegeni, M.; Moztarzadeh, F.; Hadian-Ghazvini, S.; Raz, M. Novel ultrasound-responsive chitosan/perfluorohexane nanodroplets for image-guided smart delivery of an anticancer agent: Curcumin. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 74, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aycan, D.; Alemdar, N. Development of pH-responsive chitosan-based hydrogel modified with bone ash for controlled release of amoxicillin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 184, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.H.; Chang, C.H.; Wu, Y.S.; Hsu, Y.M.; Chiou, S.F.; Chen, Y.J. Development of pH-responsive chitosan/heparin nanoparticles for stomach-specific anti-Helicobacter pylori therapy. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 3332–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brutzkus, J.C.; Shahrokhi, M.; Varacallo, M. Naproxen; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, K.; Zhou, X.; He, T. The synthesis of bacterial cellulose-chitosan zwitterionic hydrogels with pH responsiveness for drug release mechanism of the naproxen. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 209, 814–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Bao, Y. Nanodelivery of natural isothiocyanates as a cancer therapeutic. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 167, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Cao, L.; Zhang, Q.; Song, Q.; Meng, Z.; Wu, X.; Xu, K. Inhibition of autophagy potentiates the anti-metastasis effect of phenethyl isothiocyanate through JAK2/STAT3 pathway in lung cancer cells. Mol. Carcinog. 2018, 57, 522–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haloi, P.; Chawla, S.; Konkimalla, V.B. Thermosensitive smart hydrogel of PEITC ameliorates the therapeutic efficacy in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 181, 106367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fea, A.M.; Novarese, C.; Caselgrandi, P.; Boscia, G. Glaucoma Treatment and Hydrogel: Current Insights and State of the Art. Gels 2022, 8, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storgaard, L.; Tran, T.L.; Freiberg, J.C.; Hauser, A.S.; Kolko, M. Glaucoma Clinical Research: Trends in Treatment Strategies and Drug Development. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 733080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prum, B.E., Jr.; Rosenberg, L.F.; Gedde, S.J.; Mansberger, S.L.; Stein, J.D.; Moroi, S.E.; Herndon, L.W., Jr.; Lim, M.C.; Williams, R.D. Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma Preferred Practice Pattern® Guidelines. Ophthalmology 2016, 123, P41–P111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belhassen, M.; Laforest, L.; Licaj, I.; Van Ganse, E. Early adherence to anti-glaucoma therapy: An observational study. Therapie 2016, 71, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Saha, D.; Majumdar, S.; Giri, L. Imaging Methods for the Assessment of a Complex Hydrogel as an Ocular Drug Delivery System for Glaucoma Treatment: Opportunities and Challenges in Preclinical Evaluation. Mol. Pharm. 2022, 19, 733–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, K.S.; Rajpurohit, R.; Sharma, S. Glaucoma: Current treatment and impact of advanced drug delivery systems. Life Sci. 2019, 221, 362–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.H.; Tsai, T.H.; Jhan, Y.Y.; Chiu, A.W.; Tsai, K.L.; Chien, C.S.; Chiou, S.H.; Liu, C.J. Thermosensitive chitosan-based hydrogel as a topical ocular drug delivery system of latanoprost for glaucoma treatment. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 144, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakzad, Y.; Fathi, M.; Omidi, Y.; Mozafari, M.; Zamanian, A. Synthesis and characterization of timolol maleate-loaded quaternized chitosan-based thermosensitive hydrogel: A transparent topical ocular delivery system for the treatment of glaucoma. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 159, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalla, N.; Jolly, P.; Formisano, N.; Estrela, P. Introduction to biosensors. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jeerapan, I.; Imani, S.; Cho, T.N.; Bandodkar, A.; Cinti, S.; Mercier, P.P.; Wang, J. Noninvasive Alcohol Monitoring Using a Wearable Tattoo-Based Iontophoretic-Biosensing System. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Song, S.; Jia, F.; Gao, G. A flexible, adhesive and self-healable hydrogel-based wearable strain sensor for human motion and physiological signal monitoring. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 4638–4648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ding, Q.; Wang, H.; Wu, Z.; Gui, X.; Li, C.; Hu, N.; Tao, K.; Wu, J. Engineering Smart Composite Hydrogels for Wearable Disease Monitoring. Nanomicro Lett. 2023, 15, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpa, R.; Remizovschi, A.; Culda, C.A.; Butiuc-Keul, A.L. Inherent and Composite Hydrogels as Promising Materials to Limit Antimicrobial Resistance. Gels 2022, 8, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kancı Bozoğlan, B.; Duman, O.; Tunç, S. Smart antifungal thermosensitive chitosan/carboxymethylcellulose/scleroglucan/montmorillonite nanocomposite hydrogels for onychomycosis treatment. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 610, 125600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmingsen, L.M.; Julin, K.; Ahsan, L.; Basnet, P.; Johannessen, M.; Skalko-Basnet, N. Chitosomes-In-Chitosan Hydrogel for Acute Skin Injuries: Prevention and Infection Control. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frade, M.L.; de Annunzio, S.R.; Calixto, G.M.F.; Victorelli, F.D.; Chorilli, M.; Fontana, C.R. Assessment of Chitosan-Based Hydrogel and Photodynamic Inactivation against Propionibacterium acnes. Molecules 2018, 23, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodor, G.S. Biochemical Markers of Myocardial Damage. EJIFCC 2016, 27, 95–111. [Google Scholar]
- Tohidi, H.; Maleki-Jirsaraei, N.; Simchi, A.; Mohandes, F.; Emami, Z.; Fassina, L.; Naro, F.; Conti, B.; Barbagallo, F. An Electroconductive, Thermosensitive, and Injectable Chitosan/Pluronic/Gold-Decorated Cellulose Nanofiber Hydrogel as an Efficient Carrier for Regeneration of Cardiac Tissue. Materials 2022, 15, 5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kruczkowska, W.; Gałęziewska, J.; Grabowska, K.; Liese, G.; Buczek, P.; Kłosiński, K.K.; Kciuk, M.; Pasieka, Z.; Kałuzińska-Kołat, Ż.; Kołat, D. Biomedical Trends in Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels with Emphasis on Chitosan-Based Formulations. Gels 2024, 10, 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10050295
Kruczkowska W, Gałęziewska J, Grabowska K, Liese G, Buczek P, Kłosiński KK, Kciuk M, Pasieka Z, Kałuzińska-Kołat Ż, Kołat D. Biomedical Trends in Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels with Emphasis on Chitosan-Based Formulations. Gels. 2024; 10(5):295. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10050295
Chicago/Turabian StyleKruczkowska, Weronika, Julia Gałęziewska, Katarzyna Grabowska, Gabriela Liese, Paulina Buczek, Karol Kamil Kłosiński, Mateusz Kciuk, Zbigniew Pasieka, Żaneta Kałuzińska-Kołat, and Damian Kołat. 2024. "Biomedical Trends in Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels with Emphasis on Chitosan-Based Formulations" Gels 10, no. 5: 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10050295
APA StyleKruczkowska, W., Gałęziewska, J., Grabowska, K., Liese, G., Buczek, P., Kłosiński, K. K., Kciuk, M., Pasieka, Z., Kałuzińska-Kołat, Ż., & Kołat, D. (2024). Biomedical Trends in Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels with Emphasis on Chitosan-Based Formulations. Gels, 10(5), 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10050295