Nanowire-Enhanced Fully Transparent and Flexible Indium Gallium Zinc Oxide Transistors with Chitosan Hydrogel Gate Dielectric: A Pathway to Improved Synaptic Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
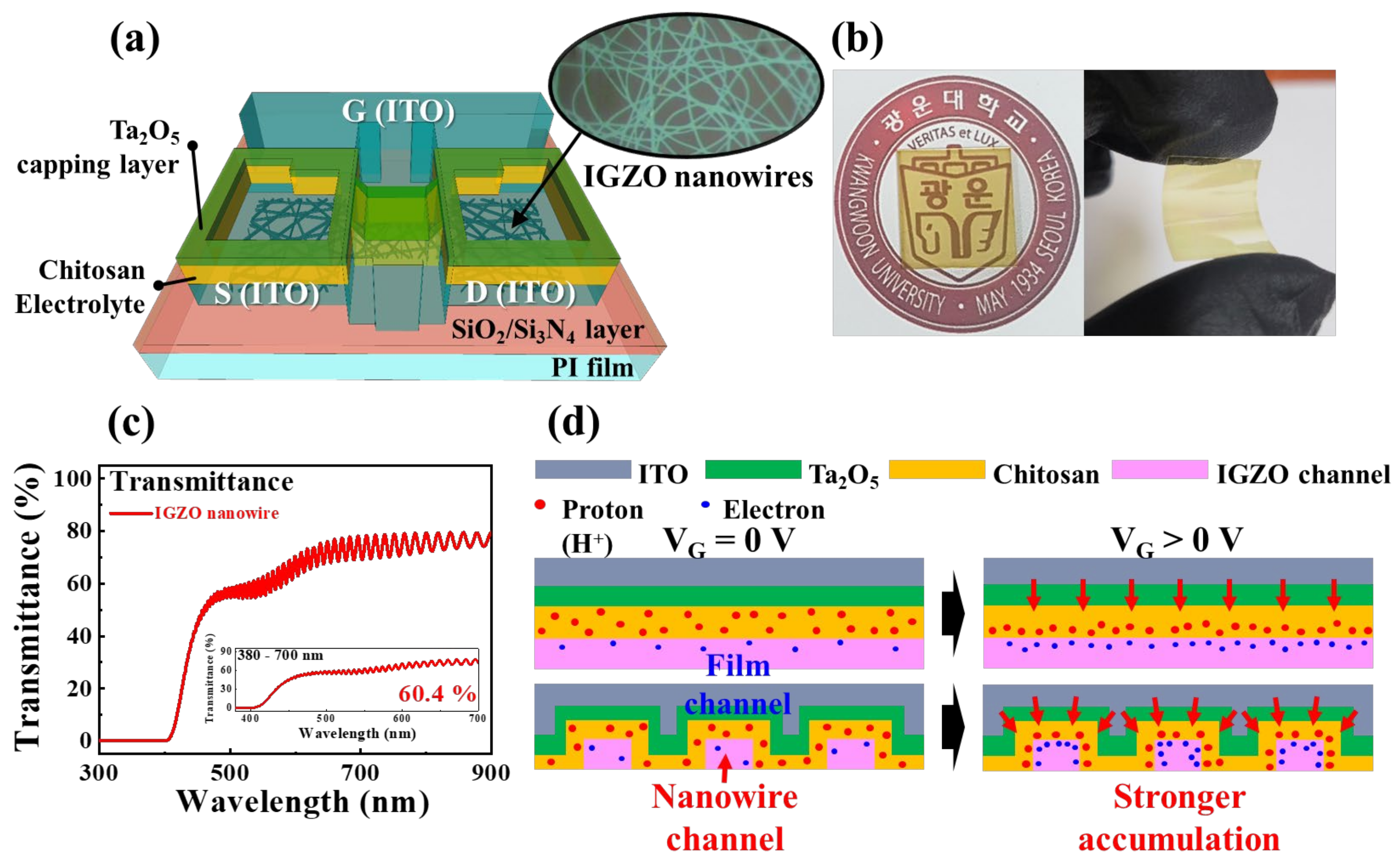
2.1. Electrical Characteristics of Transparent and Flexible IGZO NW Synaptic Transistors
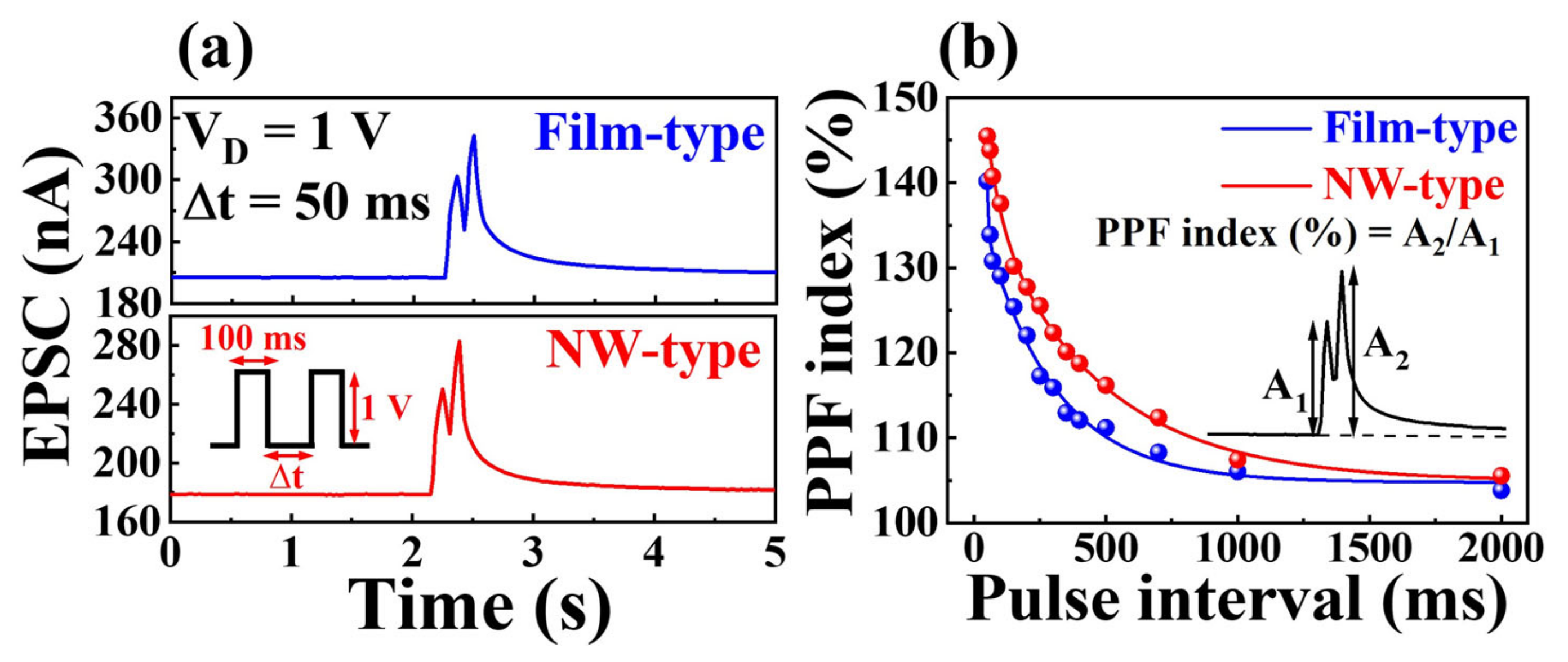
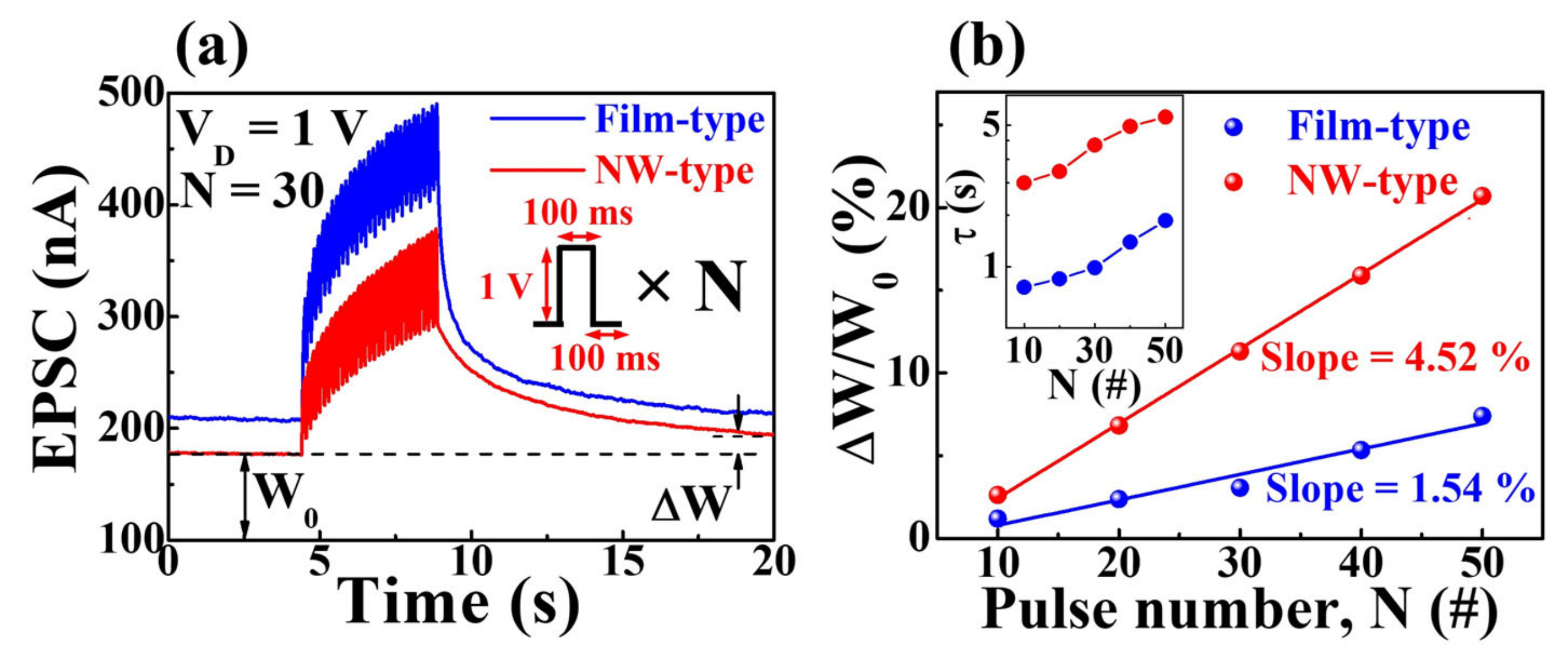
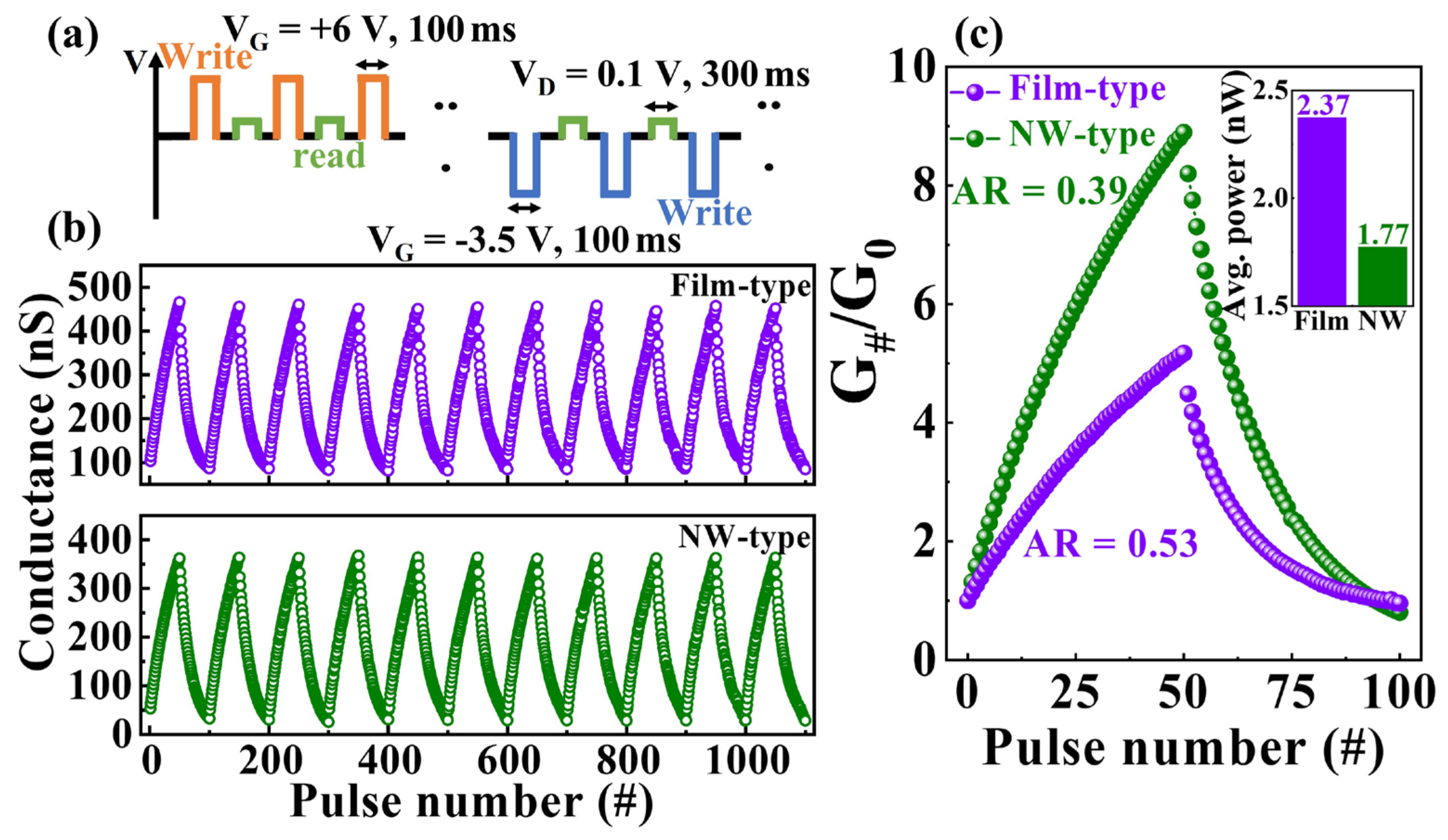
2.2. Synaptic Characteristics of Transparent and Flexible IGZO NW Synaptic Transistors
2.3. MNIST ANN Recognition Simulations
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Method
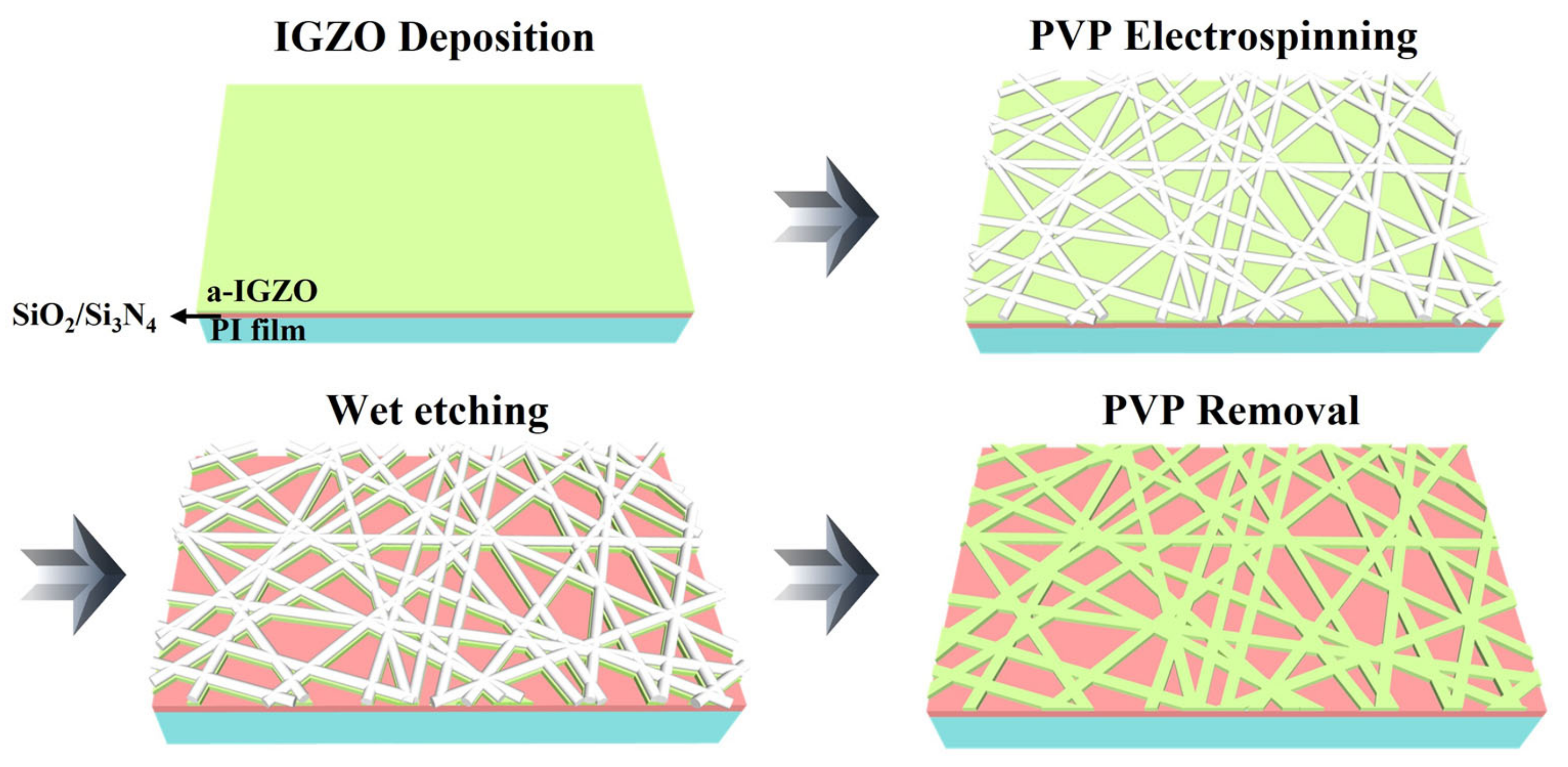
4.1. Formation Process of IGZO NWs
4.2. Preparation of Chitosan Solution
4.3. Fabrication of Transparent and Flexible IGZO NW Synaptic Transistors
4.4. Characterizations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, Y.; Oh, S.; Qian, C.; Park, J.H.; Cho, J.H. Vertical organic synapse expandable to 3D crossbar array. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, H.; Goh, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.; Ling, H.; Xie, L.; Liu, X. Stimuli-Responsive Memristive Materials for Artificial Synapses and Neuromorphic Computing. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2006469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Heo, K.; Lee, S.; Seo, S.; Kim, H.; Cho, J.; Lee, H.; Lee, K.B.; Park, J.H. Ferroelectric polymer-based artificial synapse for neuromorphic computing. Nanoscale Horiz. 2021, 6, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Zhao, J.; Liu, S.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Q.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.Y. Memristor with Ag-cluster-doped TiO2 films as artificial synapse for neuroinspired computing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1705320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, W.; Drabek, D.; Okba, N.M.; van Haperen, R.; Osterhaus, A.D.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.; Haagmans, B.L.; Grosveld, F.; Bosch, B.J. A human monoclonal antibody blocking SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, S.Y.; Cho, W.J. Modulation of excitatory behavior by organic-inorganic hybrid electric-double-layers in polysilicon synaptic transistors. IEEE Electron. Dev. Lett. 2020, 42, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fang, L.; Jin, S.; Shao, Y.; Huang, J. Recent advances in transistor-based artificial synapses. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1903700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Baek, J.H.; Ren, F.; Pearton, S.J.; Lee, G.H.; Kim, J. Artificial neuron and synapse devices based on 2D materials. Small 2021, 17, 2100640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, J.; Xu, W.; Jiang, C.; Zhong, N.; Tian, B.; Lin, H.; Luo, C.; Travas-sejdic, J.; Peng, H.; Duan, C.G. An air-stable artificial synapse based on a lead-free double perovskite Cs 2 AgBiBr 6 film for neuromorphic computing. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 5706–5712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhong, J.; Li, E.; Yang, H.; Wang, X.; Lai, D.; Chen, H.; Guo, T. Self-powered artificial synapses actuated by triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2019, 60, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yang, Y.; Nie, S.; Liu, R.; Wan, Q. Electric-double-layer transistors for synaptic devices and neuromorphic systems. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 5336–5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.I.; Jeon, J.B.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Jeong, W.; Kim, J.; Kim, G.; Kim, K.M.; Park, S.H.K. Synaptic transistors with human brain-like fJ energy consumption via double oxide semiconductor engineering for neuromorphic electronics. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 10243–10253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshita, S.; Yoda, S. Chitosan aerogels: Transparent, flexible thermal insulators. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 7569–7572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Jiang, J.; Guo, J.; Sun, J.; Yang, J. Chitosan-gated low-voltage transparent indium-free aluminum-doped zinc oxide thin-film transistors. Org. Electron. 2016, 33, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, Y.; Shi, Y.; Wan, Q. Solution-processed chitosan-gated IZO-based transistors for mimicking synaptic plasticity. IEEE Electron. Dev. Lett. 2014, 35, 280–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Zhu, L.Q.; Feng, P.; Shi, Y.; Wan, Q. Freestanding artificial synapses based on laterally proton-coupled transistors on chitosan membranes. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 5599–5604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Jiang, S.; Chen, C.; Wan, C.; Shi, Y.; Wan, Q. Electrolyte-gated neuromorphic transistors for brain-like dynamic computing. J. Appl. Phys. 2021, 130, 190904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, H.; Sim, K.; Ershad, F.; Yang, P.; Thukral, A.; Rao, Z.; Kim, H.J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Gu, G.; et al. Stretchable elastic synaptic transistors for neurologically integrated soft engineering systems. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax4961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.L.; Lee, Y.; Kim, N.; Seo, D.G.; Go, G.T.; Lee, T.W. Flexible neuromorphic electronics for computing, soft robotics, and neuroprosthetics. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1903558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.G.; Go, G.T.; Park, H.L.; Lee, T.W. Organic synaptic transistors for flexible and stretchable artificial sensory nerves. MRS Bull. 2021, 46, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.X.; Liu, W.H.; Li, X.; Guo, X.; Wan, J.; Zhang, G.H.; Wang, X.L.; Lin, Q. An artificial synapse based on graphene field-effect transistor with silver gel/polarized-aptamer gate. Org. Electron. 2021, 92, 106118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tao, R.; He, W.; Chang, C.; Zou, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Fan, Z.; Zhou, G.; et al. Realization of tunable artificial synapse through ambipolar charge trapping in organic transistor with pentacene/poly (α-methylstyrene) architecture. J. Appl. Phys. 2021, 129, 074903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Hong, M.C.; Sahoo, M.; Ong, B.L.; Tok, E.S.; Di, M.; Ho, Y.P.; Liang, H.; Bow, J.S.; Liu, Z.; et al. A fluorographene-based synaptic transistor. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1900422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Gu, J.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, Y. COD capture: A feasible option towards energy self-sufficient domestic wastewater treatment. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.K.; Cho, W.J. Ultra-high sensitivity pH-sensors using silicon nanowire channel dual-gate field-effect transistors fabricated by electrospun polyvinylpyrrolidone nanofibers pattern template transfer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 326, 128835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Zha, C.; Zhang, X.; Yan, X.; Ren, X. Synaptic devices based on gate-all-around InAs nanowire field effect transistor. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2370, 012015. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.; Cong, H.; Zhou, R.; Zhang, W.; Qin, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, F. Enhanced artificial synaptic properties enabled by arrays of electrolyte-gated electrospun InZnO nanowires. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2022, 4, 2570–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukoma, P.; Jooste, B.R.; Vosloo, H.C.M. Synthesis and characterization of cross-linked chitosan membranes for application as alternative proton exchange membrane materials in fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2004, 136, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wan, C.; Zhu, L.; Shi, Y.; Wan, Q. Synaptic behaviors mimicked in flexible oxide-based transistors on plastic substrates. IEEE Electron. Dev. Lett. 2013, 34, 1433–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, J.; Cai, W.; Wang, H.; Wilson, J.; Wang, Q.; Xin, Q.; Song, A. A sputtered silicon oxide electrolyte for high-performance thin-film transistors. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.T.; Chen, Y.H.; Ho, Y.J.; Huang, S.W.; Chang, Y.R.; Watanabe, K.; Taniguchi, T.; Chiu, H.C.; Liang, C.T.; Sankar, R.; et al. High-performance InSe transistors with ohmic contact enabled by nonrectifying barrier-type indium electrodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 33450–33456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonomano, D.V. Decoding temporal information: A model based on short-term synaptic plasticity. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 1129–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, S.; Wu, X.; Liu, D.; Chu, Y.; Wang, K.; Yang, B.; Huang, J. Light-stimulated synaptic devices utilizing interfacial effect of organic field-effect transistors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 21472–21480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.H.; Li, J.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, Y.H.; Zhu, W.Q.; Zhang, J.H. Double-gate InZnO synaptic transistor with aqueous-solution-processed wheat flour electrolyte. Org. Electron. 2020, 77, 105518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Ni, Z.; Tan, H.; Wang, Y.; Jin, H.; Nie, T.; Xu, M.; Pi, X.; Yang, D. Electroluminescent synaptic devices with logic functions. Nano Energy 2018, 54, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Wan, Q.; Wan, C.; Zhu, L.; Shi, Y. Short-term memory to long-term memory transition mimicked in IZO homojunction synaptic transistors. IEEE Electron. Dev. Lett. 2013, 34, 1581–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Q.; Yang, B.; Zhang, J.; Liu, D.; Chen, T.; Wang, X.; Hao, D.; Lu, Y.; Huang, J. Degradable photonic synaptic transistors based on natural biomaterials and carbon nanotubes. Small 2021, 17, 2007241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; He, Z.; Zhu, H.; Chen, L.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, D.W. Laterally coupled 2D MoS2 synaptic transistor with ion gating. IEEE Electron. Dev. Lett. 2020, 41, 1424–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Yang, Y.; Jia, R.; Liang, Z.; Zhu, W.; Rehman, Z.U.; Bao, L.; Zhang, X.; Cai, Y.; Song, L.; et al. Ion gated synaptic transistors based on 2D van der Waals crystals with tunable diffusive dynamics. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1800195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wen, J.; Guo, L.; Wan, X.; Du, P.; Feng, P.; Shi, Y.; Wan, Q. Long-term synaptic plasticity emulated in modified graphene oxide electrolyte gated IZO-based thin-film transistors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 30281–30286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.; Jo, S.H.; Lu, W. Short-term memory to long-term memory transition in a nanoscale memristor. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 7669–7676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Wang, W.; Wang, P.; Iqbal, M.Z.; Annabi, N.; Amin, N. Realization of tunable artificial synapse and memory based on amorphous oxide semiconductor transistor. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Jung, S.; Ali, M.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.; Park, J.H. Highly stable artificial synapse consisting of low-surface defect van der Waals and self-assembled materials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 38299–38305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Fu, M.; Liu, Y.; Lin, Z.; Ling, H.; Gkoupidenis, P.; Yi, M.; et al. Thin-film transistors for emerging neuromorphic electronics: Fundamentals, materials, and pattern recognition. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 11464–11483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.W.; Park, S.; Burr, G.W.; Hwang, H.; Jeong, Y.H. Optimization of conductance change in Pr1–xCaxMnO3-based synaptic devices for neuromorphic systems. IEEE Electron. Dev. Lett. 2015, 36, 457–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Xiao, W.; Liu, F.; Liu, Y.; Han, G.; Yang, N.; Zhong, N.; Duan, C.; Liu, C.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Non-volatile field-effect transistors enabled by oxygen vacancy-related dipoles for memory and synapse applications. IEEE Trans. Electron. Dev. 2020, 67, 3632–3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Wang, D.; Yu, T.; Xing, R.; Wu, Z.; Yan, S.; Wei, L.; Chen, Y.; Ren, H.; Yu, C.; et al. Solid-state electrolyte gated synaptic transistor based on SrFeO2. 5 film channel. Mater. Des. 2021, 210, 110022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Chen, J.; Yu, R.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Q.; Li, E.; Chen, Q.; Chen, H.; Guo, T. Tuning the synaptic behaviors of biocompatible synaptic transistor through ion-doping. Org. Electron. 2021, 89, 106019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, S.Y.; Cho, W.J. CMOS-compatible synaptic transistor gated by chitosan electrolyte-Ta2O5 hybrid electric double layer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, D.-H.; Park, H.; Cho, W.-J. Nanowire-Enhanced Fully Transparent and Flexible Indium Gallium Zinc Oxide Transistors with Chitosan Hydrogel Gate Dielectric: A Pathway to Improved Synaptic Properties. Gels 2023, 9, 931. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9120931
Lee D-H, Park H, Cho W-J. Nanowire-Enhanced Fully Transparent and Flexible Indium Gallium Zinc Oxide Transistors with Chitosan Hydrogel Gate Dielectric: A Pathway to Improved Synaptic Properties. Gels. 2023; 9(12):931. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9120931
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Dong-Hee, Hamin Park, and Won-Ju Cho. 2023. "Nanowire-Enhanced Fully Transparent and Flexible Indium Gallium Zinc Oxide Transistors with Chitosan Hydrogel Gate Dielectric: A Pathway to Improved Synaptic Properties" Gels 9, no. 12: 931. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9120931
APA StyleLee, D.-H., Park, H., & Cho, W.-J. (2023). Nanowire-Enhanced Fully Transparent and Flexible Indium Gallium Zinc Oxide Transistors with Chitosan Hydrogel Gate Dielectric: A Pathway to Improved Synaptic Properties. Gels, 9(12), 931. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9120931






