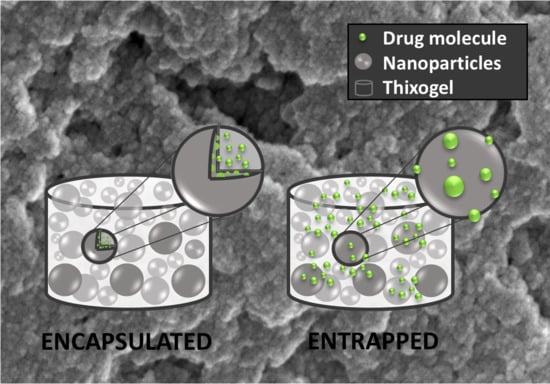
Tetraethyl Orthosilicate-Based Hydrogels for Drug Delivery—Effects of Their Nanoparticulate Structure on Release Properties
Abstract
Share and Cite
Serban, B.A.; Barrett-Catton, E.; Serban, M.A. Tetraethyl Orthosilicate-Based Hydrogels for Drug Delivery—Effects of Their Nanoparticulate Structure on Release Properties. Gels 2020, 6, 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels6040038
Serban BA, Barrett-Catton E, Serban MA. Tetraethyl Orthosilicate-Based Hydrogels for Drug Delivery—Effects of Their Nanoparticulate Structure on Release Properties. Gels. 2020; 6(4):38. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels6040038
Chicago/Turabian StyleSerban, Bogdan A., Emma Barrett-Catton, and Monica A. Serban. 2020. "Tetraethyl Orthosilicate-Based Hydrogels for Drug Delivery—Effects of Their Nanoparticulate Structure on Release Properties" Gels 6, no. 4: 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels6040038
APA StyleSerban, B. A., Barrett-Catton, E., & Serban, M. A. (2020). Tetraethyl Orthosilicate-Based Hydrogels for Drug Delivery—Effects of Their Nanoparticulate Structure on Release Properties. Gels, 6(4), 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels6040038