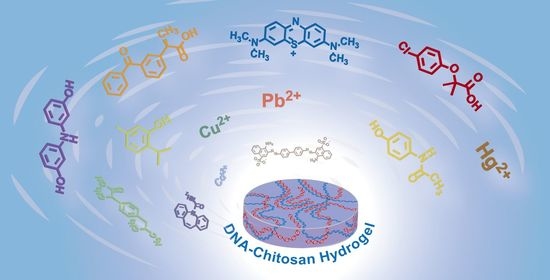
Adsorptive Removal of Heavy Metal Ions, Organic Dyes, and Pharmaceuticals by DNA–Chitosan Hydrogels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Preparation of DNA–CS Hydrogel Adsorbent
2.2. Adsorption of Heavy Metal Ions by DNA–CS Hydrogel
2.3. Adsorption of Anionic and Cationic Dyes and Pharmaceuticals by DNA-CS Hydrogel
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Methods
4.3. Samples’ Preparation
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kwon, Y.W.; Lee, C.H.; Choi, D.H.; Jin, J.I. Materials science of DNA. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 1353–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaudo, M. Chitin and chitosan: Properties and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2006, 31, 603–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokkanen, S.; Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M. A review on modification methods to cellulose-based adsorbents to improve adsorption capacity. Water Res. 2016, 91, 156–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.L.; Zhuang, S.T. Removal of various pollutants from water and wastewater by modified chitosan adsorbents. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 47, 2331–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guibal, E. Interactions of metal ions with chitosan-based sorbents: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2004, 38, 43–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinu, M.V.; Humelnicu, D.; Lazar, M.M. Analysis of Copper(II), Cobalt(II) and Iron(III) Sorption in Binary and Ternary Systems by Chitosan-Based Composite Sponges Obtained by Ice-Segregation Approach. Gels 2021, 7, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaridis, N.K.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Vassiliou, A.A.; Bikiaris, D.N. Chitosan derivatives as biosorbents for basic dyes. Langmuir 2007, 23, 7634–7643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Kostoglou, M.; Lazaridis, N.K.; Lambropoulou, D.A.; Bikiaris, D.N. Environmental friendly technology for the removal of pharmaceutical contaminants from wastewaters using modified chitosan adsorbents. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 222, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernkop-Schnurch, A.; Dunnhaupt, S. Chitosan-based drug delivery systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 81, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafizadeh, M.; Ahmadi, Z.; Mohamadi, N.; Zarrabi, A.; Abasi, S.; Dehghannoudeh, G.; Tamaddondoust, R.N.; Khanbabaei, H.; Mohammadinejad, R.; Thakur, V.K. Chitosan-based advanced materials for docetaxel and paclitaxel delivery: Recent advances and future directions in cancer theranostics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 145, 282–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, K.; Subramanian, K.; Murugan, K.; Dinakaran, K. Sensitive fluorescence detection of mercury(II) in aqueous solution by the fluorescence quenching effect of MoS2 with DNA functionalized carbon dots. Analyst 2016, 141, 6344–6352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinchenko, A.A.; Sakai, H.; Matsuoka, S.; Murata, S. Application of DNA condensation for removal of mercury ions from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Kato, K.; Nomizu, M.; Haruki, M.; Ohkawa, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Nishi, N. UV-Irradiated DNA Matrix Selectively Accumulates Heavy Metal Ions. Bull. Chem. Soc. Japan 2002, 75, 1627–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orakdogen, N.; Karacan, P.; Okay, O. Macroporous, responsive DNA cryogel beads. React. Funct. Polym. 2011, 71, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.D.; Murayama, Y.; Matsunaga, M.; Nomizu, M.; Nishi, N. Preparation and characterization of DNA hydrogel bead as selective adsorbent of dioxins. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2005, 35, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Solis, C.; Kuroda, Y.; Zinchenko, A.; Murata, S. Uptake of aromatic compounds by DNA: Toward the environmental application of DNA for cleaning water. Colloid. Surface. B 2015, 129, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.R.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zeng, G.M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Feng, C.L. How to Construct DNA Hydrogels for Environmental Applications: Advanced Water Treatment and Environmental Analysis. Small 2018, 14, e1703305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo-Anaya, L.M.; Soltero, J.F.A.; Rinaudo, M. DNA/chitosan electrostatic complex. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 88, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo-Anaya, L.M.; Fernandez-Solis, K.G.; Rosselgong, J.; Nano-Rodriguez, J.L.E.; Carvajal, F.; Rinaudo, M. Chitosan-DNA polyelectrolyte complex: Influence of chitosan characteristics and mechanism of complex formation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 1037–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morikawa, K.; Masubuchi, Y.; Shchipunov, Y.; Zinchenko, A. DNA-Chitosan Hydrogels: Formation, Properties, and Functionalization with Catalytic Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 1823–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shchipunov, Y.; Sarin, S.; Kim, I.; Ha, C.-S. Hydrogels formed through regulated self-organization of gradually charging chitosan in solution of xanthan. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, S.P.; Danielsen, S.; Christensen, B.E.; Vårum, K.M. Influence of chitosan structure on the formation and stability of DNA− chitosan polyelectrolyte complexes. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 3357–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thünemann, A.F.; Müller, M.; Dautzenberg, H.; Joanny, J.-F.; Löwen, H. Polyelectrolyte Complexes. In Polyelectrolytes with Defined Molecular Architecture II; Schmidt, M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 113–171. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Gucht, J.; Spruijt, E.; Lemmers, M.; Stuart, M.A.C. Polyelectrolyte complexes: Bulk phases and colloidal systems. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 361, 407–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.M.; Mohamed, M.H.; Udoetok, I.A.; Steiger, B.G.K.; Wilson, L.D. Sequestration of Sulfate Anions from Groundwater by Biopolymer-Metal Composite Materials. Polymers 2020, 12, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udoetok, I.A.; Faye, O.; Wilson, L.D. Adsorption of Phosphate Dianions by Hybrid Inorganic–Biopolymer Polyelectrolyte Complexes: Experimental and Computational Studies. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, P.; Banu, H.A.T.; Meenakshi, S. Synthesis and characterization of metal loaded chitosan-alginate biopolymeric hybrid beads for the efficient removal of phosphate and nitrate ions from aqueous solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 130, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Jin, P.; Wang, M.; Wu, G.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, C.; Wu, A. Highly efficient removal of toxic Pb2+ from wastewater by an alginate–chitosan hybrid adsorbent. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 93, 2691–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Chen, H.; Wu, S.; Yang, C.; Cheng, J. Enhanced removal of bisphenol A from aqueous solution by aluminum-based MOF/sodium alginate-chitosan composite beads. Chemosphere 2019, 237, 124493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinchenko, A.A.; Maeda, N.; Pu, S.Y.; Murata, S. Entrapping of fullerenes, nanotubes, and inorganic nanoparticles by a DNA-chitosan complex: A method for nanomaterials removal. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 4489–4496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sissoeff, I.; Grisvard, J.; Guille, E. Studies on metal ions-DNA interactions: Specific behaviour of reiterative DNA sequences. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 1976, 31, 165–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanellis, V.G.; Dos Remedios, C.G. A review of heavy metal cation binding to deoxyribonucleic acids for the creation of chemical sensors. Biophys. Rev. 2018, 10, 1401–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juang, R.S.; Shao, H.J. Effect of pH on competitive adsorption of Cu(II), Ni(II), and Zn(II) from water onto chitosan beads. Adsorption 2002, 8, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhazi, M.; Desbrieres, J.; Tolaimate, A.; Rinaudo, M.; Vottero, P.; Alagui, A.; El Meray, M. Influence of the nature of the metal ions on the complexation with chitosan. Application to the treatment of liquid waste. Eur. Polym. J. 2002, 38, 1523–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajewska, B. Diffusion of metal ions through gel chitosan membranes. React. Funct. Polym. 2001, 47, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichhorn, G.L.; Shin, Y.A. Interaction of Metal Ions with Polynucleotides and Related Compounds.12. Relative Effect of Various Metal Ions on DNA Helicity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1968, 90, 7323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duguid, J.; Bloomfield, V.A.; Benevides, J.; Thomas, G.J. Raman Spectral Studies of Nucleic-Acids.44. Raman-Spectroscopy of DNA-Metal Complexes.1. Interactions and Conformational Effects of the Divalent-Cations—Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Mn, Co, Ni, Cu, Pd, and Cd. Biophys. J. 1993, 65, 1916–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zimmer, C.; Luck, G.; Fritzsche, H.; Triebel, H. DNA–copper(II) complex and the DNA conformation. Biopolymers 1971, 10, 441–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.; Kumar, G.S. DNA intercalation of methylene blue and quinacrine: New insights into base and sequence specificity from structural and thermodynamic studies with polynucleotides. Mol. Biosyst. 2009, 5, 1311–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Sanchez-Polo, M.; Ferro-Garcia, M.A.; Prados-Joya, G.; Ocampo-Perez, R. Pharmaceuticals as emerging contaminants and their removal from water. A review. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 1268–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Dye | qe, mg/g | qe,1 mmol/g |
|---|---|---|
| Congo Red (CR, anionic) | 12.6 | 0.014 |
| Methylene blue (MB, cationic) | 29.0 | 0.102 |
| Pharmaceuticals | logPo/w | Adsorption Capacity, mg/g |
|---|---|---|
| Paracetamol | 0.68 | <0.1 |
| Phenazone | 1.40 | 1.1 |
| 3,3’-Dihydroxydiphenylamine | 2.29 | 4.6 |
| Clofibric acid | 2.73 | 23.9 |
| Carbamazepine | 2.84 | 0.5 |
| Thymol | 3.34 | 4.6 |
| Ibuprofen | 3.46 | 39.7 |
| Ketoprofen | 3.59 | 23.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chan, K.; Morikawa, K.; Shibata, N.; Zinchenko, A. Adsorptive Removal of Heavy Metal Ions, Organic Dyes, and Pharmaceuticals by DNA–Chitosan Hydrogels. Gels 2021, 7, 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels7030112
Chan K, Morikawa K, Shibata N, Zinchenko A. Adsorptive Removal of Heavy Metal Ions, Organic Dyes, and Pharmaceuticals by DNA–Chitosan Hydrogels. Gels. 2021; 7(3):112. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels7030112
Chicago/Turabian StyleChan, Kayee, Kohki Morikawa, Nobuyuki Shibata, and Anatoly Zinchenko. 2021. "Adsorptive Removal of Heavy Metal Ions, Organic Dyes, and Pharmaceuticals by DNA–Chitosan Hydrogels" Gels 7, no. 3: 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels7030112
APA StyleChan, K., Morikawa, K., Shibata, N., & Zinchenko, A. (2021). Adsorptive Removal of Heavy Metal Ions, Organic Dyes, and Pharmaceuticals by DNA–Chitosan Hydrogels. Gels, 7(3), 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels7030112