Mechanically Strong, Low Thermal Conductivity and Improved Thermal Stability Polyvinyl Alcohol–Graphene–Nanocellulose Aerogel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Microstructure and Chemical Characterization
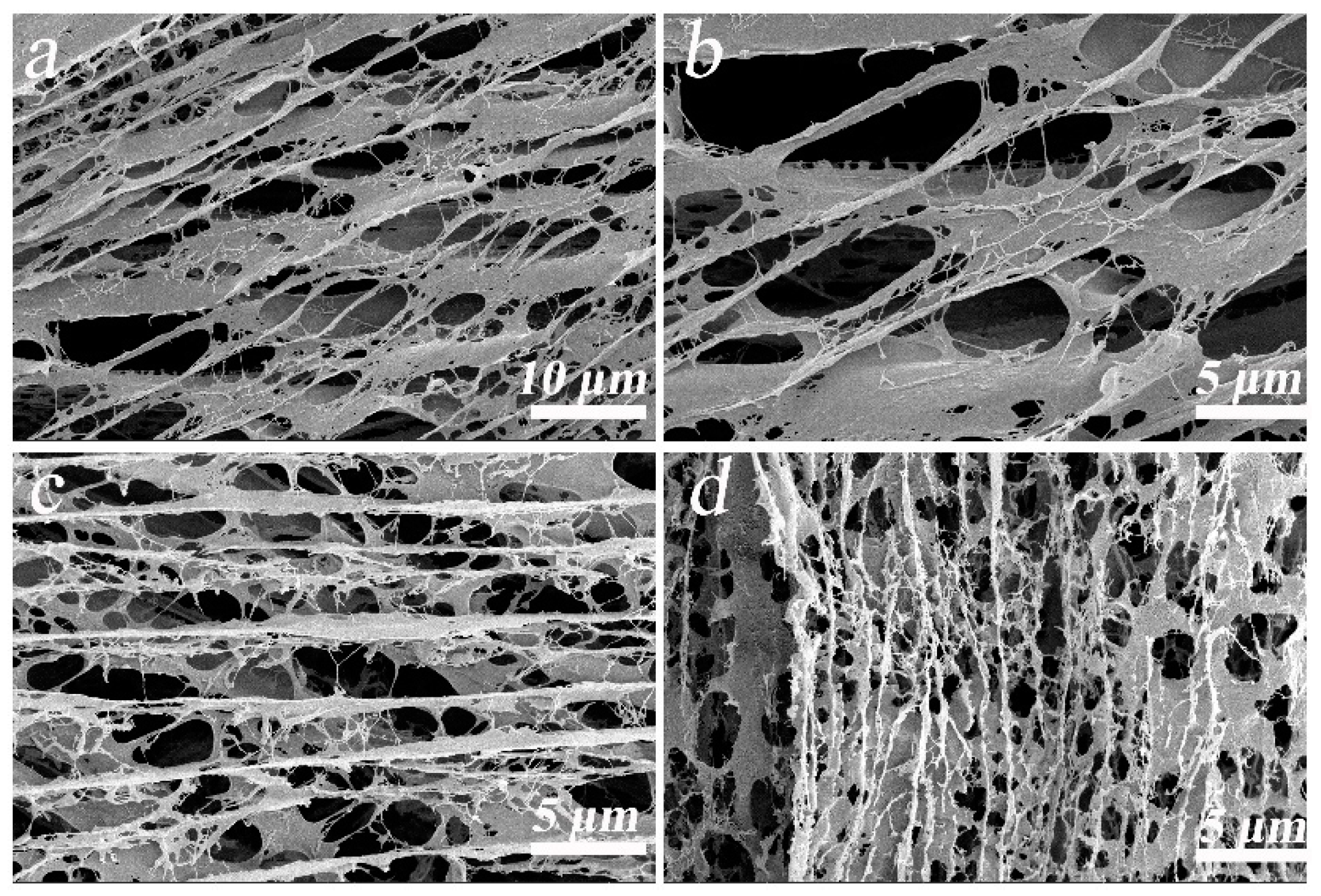
2.1.1. SEM
2.1.2. FTIR
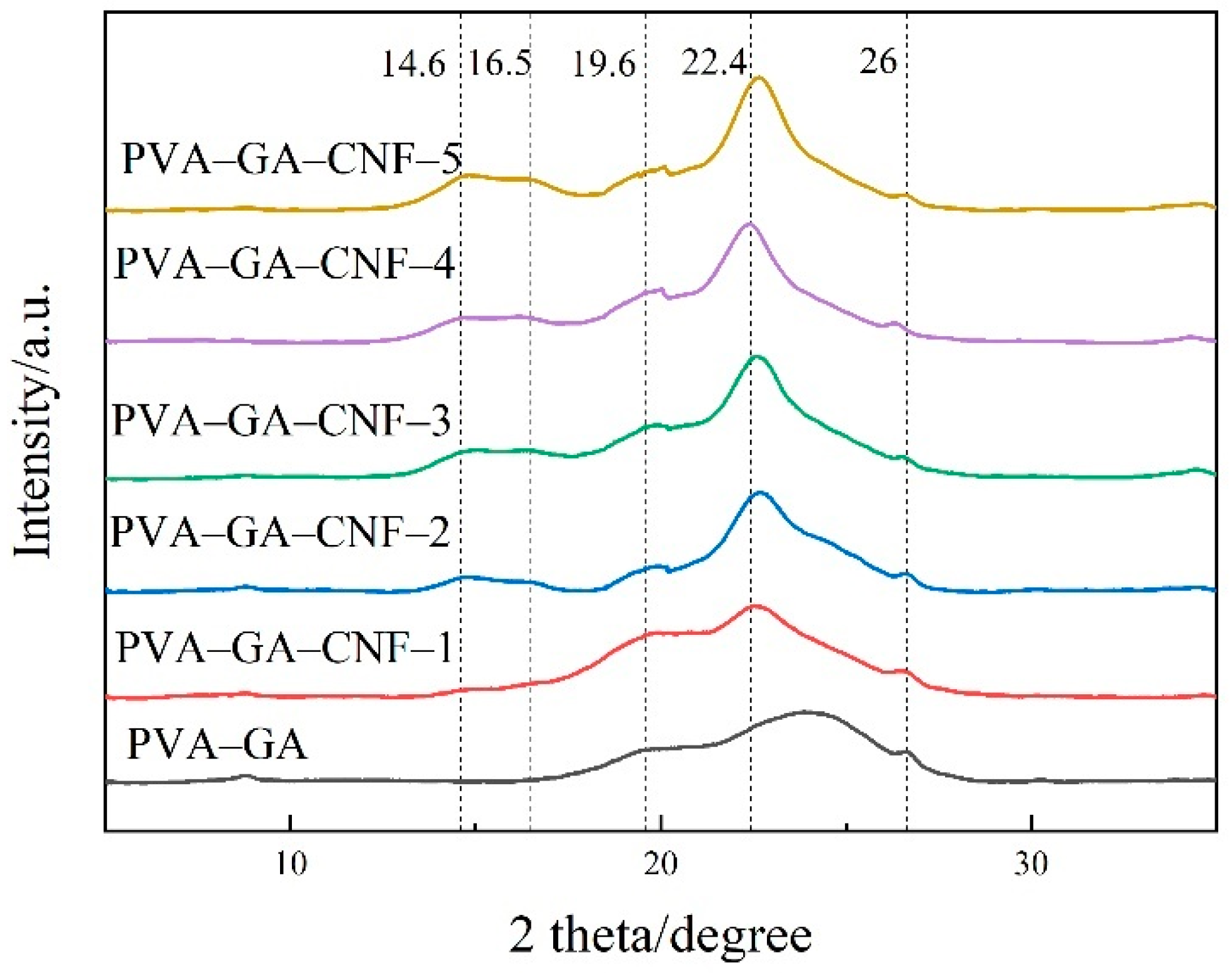
2.1.3. XRD
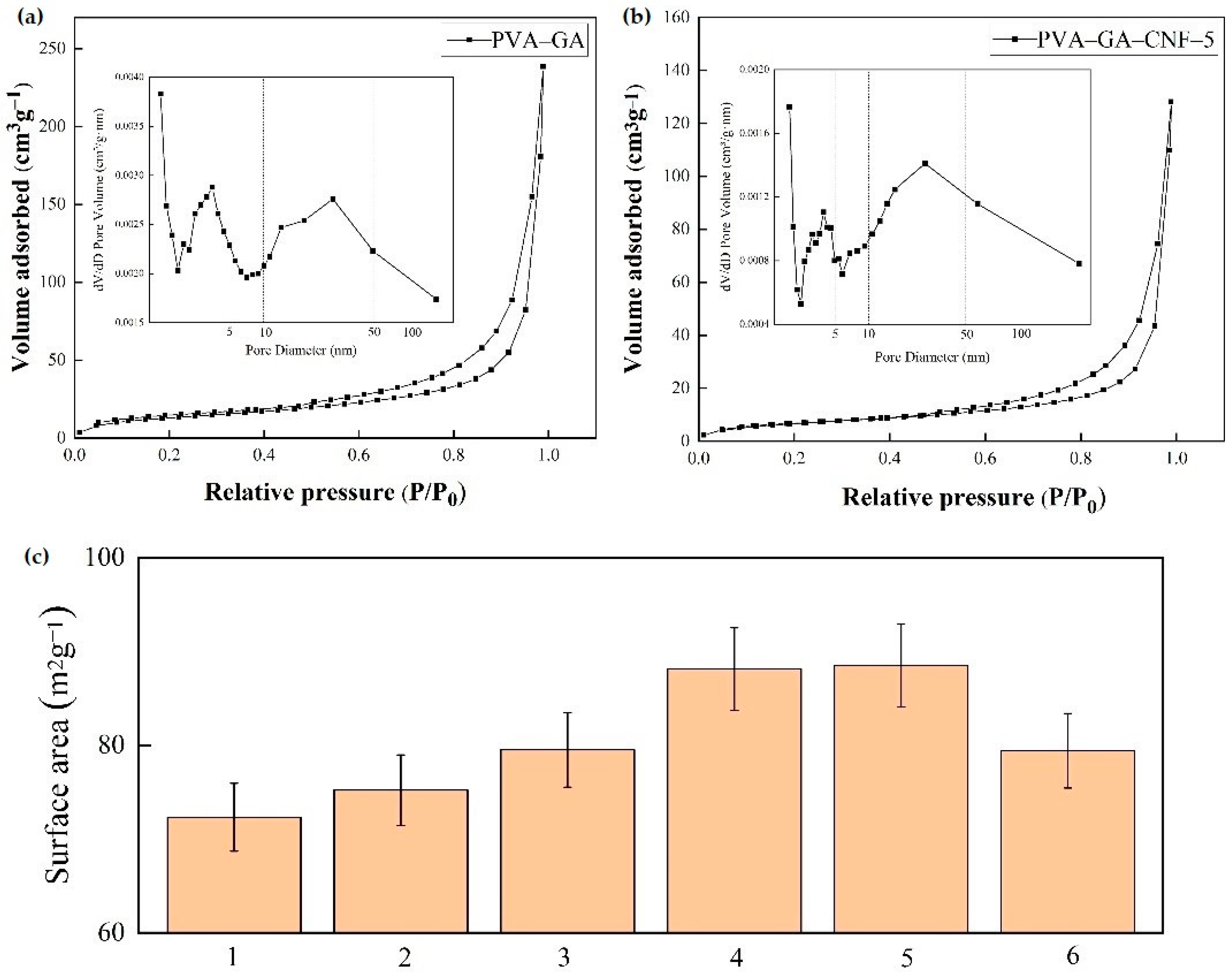
2.1.4. BET
2.2. Mechanical Property
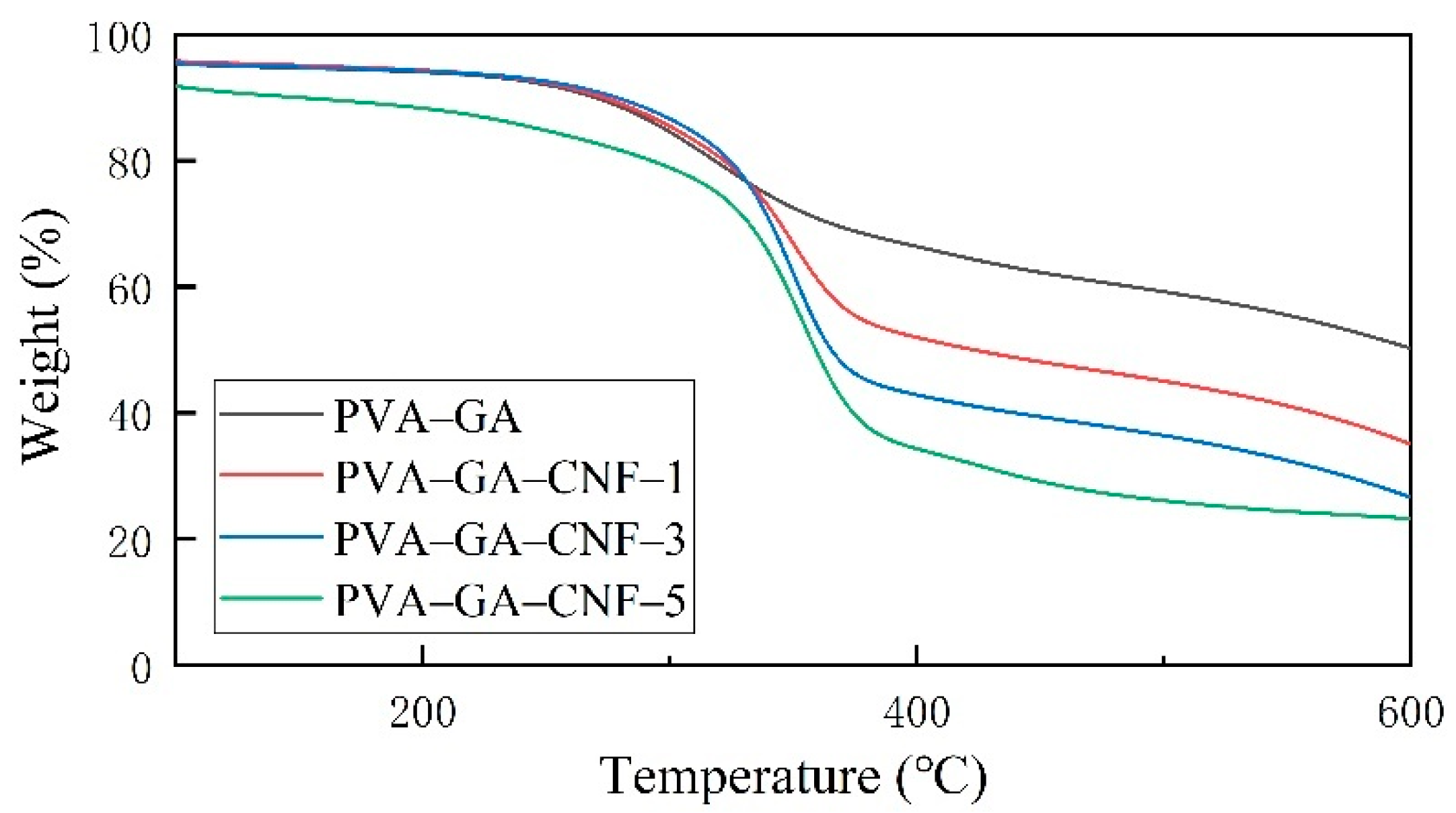
2.3. Thermal Properties
| Composite Aerogels | Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| graphene aerogel | 0.0667 | [57] |
| cellulose aerogel | 0.174 | [58] |
| polyvinyl alcohol-cellulose acetate aerogel | 0.049 | [60] |
| tetradecanoyl-graphene aerogel | 0.498 | [61] |
| graphene-carbon nanotube aerogel | 0.76 | [62] |
| nanocellulose aerogel | 0.105 | [63] |
| cellulose nanofibers aerogel | 0.12 | [64] |
| polyvinyl alcohol-cellulose nanofibers-gelatin aerogel | 0.047 | [41] |
| waste tissue paper-polyvinyl alcohol-carbon aerogel | 0.087 | [65] |
| attapulgite-polyvinyl alcohol-cotton cellulose nanowhisker-melamine aerogel | 0.045 | [66] |
3. Conclusions
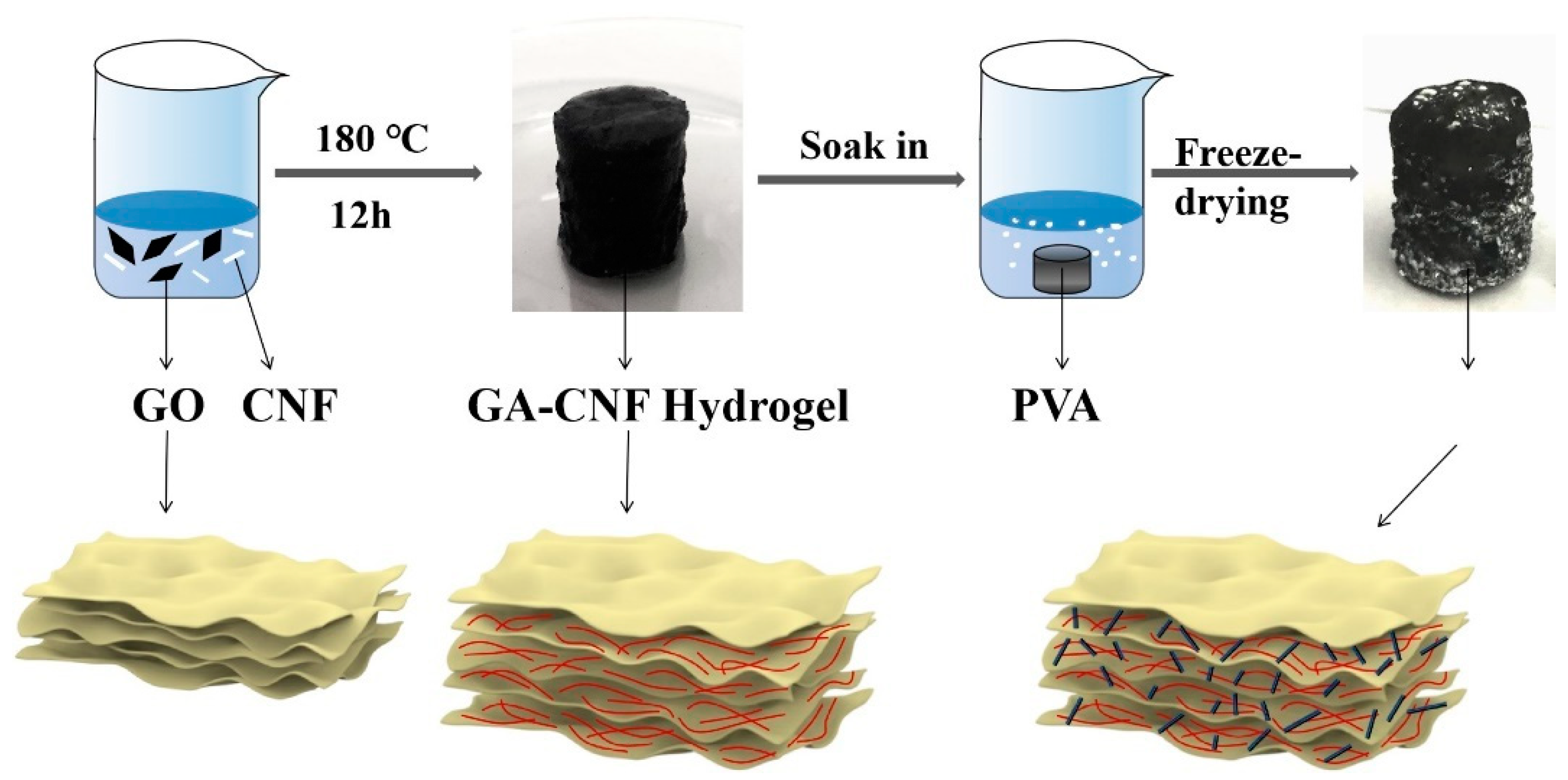
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Chemicals
4.2. Graphene Oxide (GO) Preparation
4.3. Nanocellulose (CNF) Preparation
4.4. PVA–GA–CNF Aerogel Preparation
4.5. Characterization
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Hu, H.; Zhao, Z.B.; Wan, W.B.; Gogotsi, Y.; Qiu, J.S. Ultralight and Highly Compressible Graphene Aerogels. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2219–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korhonen, J.T.; Kettunen, M.; Ras, R.H.A.; Ikkala, O. Hydrophobic nanocellulose aerogels as floating, sustainable, reusable, and recyclable oil absorbents. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 1813–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baetens, R.; Jelle, B.P.; Gustavsen, A. Aerogel insulation for building applications: A state-of-the-art review. Energy Build. 2011, 43, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cuce, E.; Cuce, P.M.; Wood, C.J.; Riffat, S.B. Toward aerogel based thermal superinsulation in buildings: A comprehensive review. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2014, 34, 273–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.X.; Lu, R.; Ren, S.S.; Chen, C.T.; Chen, Z.J.; Yang, X.Y. Three dimensional reduced graphene oxide/ZIF-67 aerogel: Effective removal cationic and anionic dyes from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 348, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, A.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, Z.H.; Shen, J.A. Special Material or a New State of Matter: A Review and Reconsideration of the Aerogel. Metals 2013, 6, 941–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akimov, Y.K. Fields of application of aerogels (Review). Instrum. Exp. Tech. 2003, 46, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.M. Aerogel: Space exploration applications. J. Solgel. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F. Starch based aerogels: Production, properties and applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 89, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.P.; Ren, W.C.; Gao, L.B.; Liu, B.L.; Pei, S.F.; Cheng, H.M. Three-dimensional flexible and conductive interconnected graphene networks grown by chemical vapour deposition. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, H.P.; Ren, X.C.; Wang, P.; Yu, S.H. Macroscopic Multifunctional Graphene-Based Hydrogels and Aerogels by a Metal Ion Induced Self-Assembly Process. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 2693–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, P.G.; Gao, C. Strong, Conductive, Lightweight, Neat Graphene Aerogel Fibers with Aligned Pores. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 7103–7113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, C.; Shi, G.Q. Graphene Materials for Electrochemical Capacitors. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 1244–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.Y.; Wan, K.; Xie, P.B.; Miao, Y.Y.; Liu, Z.B. Ultralight, High Capacitance, Mechanically Strong Graphene-Cellulose Aerogels. Molecules 2021, 6, 4891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Han, T.Y.J.; Duoss, E.B.; Golobic, A.M.; Kuntz, J.D.; Spadaccini, C.M.; Worsley, M.A. Highly compressible 3D periodic graphene aerogel microlattices. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, X.H.; Yin, Z.Y.; Zhang, H. Three-dimensional graphene materials: Preparation, structures and application in supercapacitors. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 1850–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhou, W.; Li, G.; Liang, X.; Guo, J.; Tang, S. Low temperature reduction of graphene oxide film by ammonia solution and its application for high-performance supercapacitors. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2017, 28, 10098–10105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Miao, Y.; Zhai, X.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jian, Z.; Wang, X.; Sun, L.; Liu, Z. Preparation of and research on bioinspired graphene oxide/nanocellulose/polydopamine ternary artificial nacre. Mater. Des. 2019, 181, 107961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, X.; Zhao, R.; Miao, Y.; Liu, Z. A novel graphene-based micro/nano architecture with high strength and conductivity inspired by multiple creatures. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Li, D.G. Flexible and foldable supercapacitor electrodes from the porous 3D network of cellulose nanofibers, carbon nanotubes and polyaniline. Mater. Lett. 2015, 155, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, D.T.; Yang, L.L.; Fan, L.; Zhang, C.F.; Xiao, X.; Gogotsi, Y.; Yang, S. Foldable supercapacitors from triple networks of macroporous cellulose fibers, single-walled carbon nanotubes and polyaniline nanoribbons. Nano Energy 2015, 11, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.Q.; Nie, S.X.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, S.F.; Qin, C.R. Efficient extraction of bagasse hemicelluloses and characterization of solid remainder. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 185, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, R.; Kim, H.S.; Zhang, L.J.; Korolovych, V.F.; Zhang, S.D.; Yingling, Y.G.; Tsukruk, V.V. Wrapping Nanocellulose Nets around Graphene Oxide Sheets. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 8508–8513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Liu, P.; Duan, Y.X.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, J.M. Graphene/cellulose nanocrystals hybrid aerogel with tunable mechanical strength and hydrophilicity fabricated by ambient pressure drying technique. RSC Adv. 2017, 27, 16467–16473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yue, C.W.; Feng, J.; Feng, J.Z.; Jiang, Y.G. Thermal conductivity of aerogel composites with oriented nitrogen-doped graphene. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 146, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Rodriguez, R.; Espinosa-Andrews, H.; Velasquillo-Martinez, C.; Garcia-Carvajal, Z.Y. Composite hydrogels based on gelatin, chitosan and polyvinyl alcohol to biomedical applications: A review. Int. J. Polym. Mater. 2020, 69, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondeson, D.; Mathew, A.; Oksman, K. Optimization of the isolation of nanocrystals from microcrystalline cellulose by acid hydrolysis. Cellulose 2006, 13, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapisarda, M.; Fierro, G.P.M.; Meo, M. Ultralight graphene oxide/polyvinyl alcohol aerogel for broadband and tuneable acoustic properties. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.Q.; Shen, Y.T.; Yoshino, K.; Feng, W. A mechanically strong, flexible and conductive film based on bacterial cellulose/graphene nanocomposite. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 644–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Lee, K.S.; Bozoklu, G.; Cai, W.; Nguyen, S.T.; Ruoff, R.S. Graphene oxide papers modified by divalent ions—Enhancing mechanical properties via chemical cross-linking. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meador, M.A.B.; Fabrizio, E.F.; Ilhan, F.; Dass, A.; Zhang, G.H.; Vassilaras, P.; Johnston, J.C.; Leventis, N. Cross-linking amine-modified silica aerogels with epoxies: Mechanically strong lightweight porous materials. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 1085–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banhart, F.; Kotakoski, J.; Krasheninnikov, A.V. Structural Defects in Graphene. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Wu, X.Y.; Yang, F.; Xu, L.; Sun, M. Study on the Preparation and Adsorption Property of Polyvinyl Alcohol/Cellulose Nanocrystal/Graphene Composite Aerogels (PCGAs). J. Renew. Mater. 2019, 7, 1181–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.G.; Sun, X.; Tian, H.F.; Maiti, S.; Ma, Z.S. Effects of cellulose nanofibrils on the structure and properties on PVA nanocomposites. Cellulose 2013, 20, 2981–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.M.; Xiao, G.Y.; Chen, C.B.; Li, R.; Mai, Y.Y.; Sun, G.M.; Yan, D.Y. Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic graphene aerogel prepared by facile chemical reduction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 7498–7504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.Y.; Sun, Y.Y.; Shi, J.J.; Ning, W.S.; Hou, Z.Y. Selective glycerol oxidation using platinum nanoparticles supported on multi-walled carbon nanotubes and nitrogen-doped graphene hybrid. Chin. J. Catal. 2017, 38, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervin, N.T.; Aulin, C.; Larsson, P.T.; Wagberg, L. Ultra porous nanocellulose aerogels as separation medium for mixtures of oil/water liquids. Cellulose 2012, 19, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.Y.; Zhou, H.; Tan, S.C.; Jiang, X.D.; Wu, W.B.; Shi, J.T.; Chen, P. Ultralight super-hydrophobic carbon aerogels based on cellulose nanofibers/poly (vinyl alcohol)/graphene oxide (CNFs/PVA/GO) for highly effective oil-water separation. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 508–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mi, H.Y.; Jing, X.; Politowicz, A.L.; Chen, E.; Huang, H.X.; Turng, L.S. Highly compressible ultra-light anisotropic cellulose/graphene aerogel fabricated by bidirectional freeze drying for selective oil absorption. Carbon 2018, 132, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.M.; Chen, Z.L.; Lyu, S.Y.; Fu, F.; Wang, S.Q. Highly flexible cross-linked cellulose nanofibril sponge-like aerogels with improved mechanical property and enhanced flame retardancy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 179, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Cheng, X.D.; Pan, Y.L.; Li, C.C.; Gong, L.L. Mechanical performance and thermal stability of polyvinyl alcohol-cellulose aerogels by freeze drying. Cellulose 2019, 26, 1747–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadi, A.; Zheng, Q.F.; Payen, F.; Javadi, A.; Altin, Y.; Cai, Z.Y.; Sabo, R.; Gong, S.Q. Polyvinyl Alcohol-Cellulose Nanofibrils-Graphene Oxide Hybrid Organic Aerogels. ACS Appl. Mater 2013, 5, 5969–5975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.Z.; Liu, J.; Gan, L.H.; Huang, N.Z.; Long, M.N. Green Synthesis of Fe3O4/Cellulose/Polyvinyl Alcohol Hybride Aerogel and Its Application for Dye Removal. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 2234–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, G.; Tesfaye, R.M.; Won, Y.; Yoon, H.H. NiO-Fe2O3 based graphene aerogel as urea electrooxidation catalyst. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 237, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Zhu, W.H.; Ma, J.; Yang, Y.Z.; Tang, B. Carbon fibers assisted 3D N-doped graphene aerogel on excellent adsorption capacity and mechanical property. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 608, 125602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.T.; Zhang, H.; He, X.H.; Chen, T.T.; Jiang, T.Y.; Liu, W.Y.; Zhang, M.Y. Preparation of porous conductive cellulose nanofibril based composite aerogels and performance comparison with films. React. Funct. Polym. 2020, 157, 104748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.M.; Zhai, T.L.; Turng, L.S. Aerogel microspheres based on cellulose nanofibrils as potential cell culture scaffolds. Cellulose 2017, 24, 2791–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, K.Y.; Chia, C.H.; Zakaria, S.; Sajab, M.S.; Chook, S.W.; Khiew, P.S. CaCO3-decorated cellulose aerogel for removal of Congo Red from aqueous solution. Cellulose 2015, 22, 2683–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yuan, D.S.; Guo, Q.; Qiu, F.X.; Yang, D.Y.; Ou, Z.P. Preparation of a renewable biomass carbon aerogel reinforced with sisal for oil spillage clean-up: Inspired by green leaves to green Tofu. Food Bioproc. Tech. 2019, 114, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.J.; Zhou, T.; He, S.; Xiao, H.; Dai, H.M.; Yuan, B.H.; Chen, X.F.; Yang, X.B. Flame-retardant polyvinyl alcohol/cellulose nanofibers hybrid carbon aerogel by freeze drying with ultra-low phosphorus. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, E.W.; Li, X.F.; Zhang, Y.T.; Qu, J.; Yu, Z.Z. Cellulose/graphene aerogel supported phase change composites with high thermal conductivity and good shape stability for thermal energy storage. Carbon 2016, 98, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.J.; Zhou, M.; Huang, F.Q.; Lin, T.Q.; Wan, D.Y. Effect of graphene aerogel on thermal behavior of phase change materials for thermal management. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2013, 113, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.L.; Xie, T. Advances of thermal conductivity models of nanoscale silica aerogel insulation material. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2015, 81, 28–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Fang, X.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Y.; Xiao, Y.-Q.; Yu, Z.-T.; Xu, X.; Hu, Y.-C.; Cen, K.-F. Effects of various carbon nanofillers on the thermal conductivity and energy storage properties of paraffin-based nanocomposite phase change materials. Appl. Energy 2013, 110, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrali, M.; Latibari, S.T.; Mehrali, M.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Metselaar, H.S.C. Preparation and properties of highly conductive palmitic acid/graphene oxide composites as thermal energy storage materials. Energy 2013, 58, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandi, S.; Schiraldi, D.A. Glass transition behavior of clay aerogel/poly (vinyl alcohol) composites. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 6537–6545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhou, S.; Hu, P.; Zhao, G.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Han, W. Enhanced mechanical, thermal, and electric properties of graphene aerogels via supercritical ethanol drying and high-temperature thermal reduction. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Xiong, Y.; Fan, B.; Yao, Q.; Wang, H.; Jin, C.; Sun, Q. Cellulose as an adhesion agent for the synthesis of lignin aerogel with strong mechanical performance, Sound-absorption and thermal Insulation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, T.; He, Y.-L.; Hu, Z.-J. Theoretical study on thermal conductivities of silica aerogel composite insulating material. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 58, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoc, D.Q.C.; Tram, T.N.N.; Huong, L.X.D.; Nga, H.N.D.; Tran, V.T.; Nguyen, S.T.; Le, P.K. Advanced Fabrication and Applications of Cellulose Acetate Aerogels from Cigarette Butts. Mater. Trans. 2020, 61, 1550–1554. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, B.Y.; Li, M. Fabrication and thermal properties of tetradecanol/graphene aerogel form-stable composite phase change materials. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Q.; He, F.; Li, Y.; He, Z.; Fan, J.; Wang, R.; Hu, W.; Zhang, K.; Yang, W. Graphene-carbon nanotube hybrid aerogel/polyethylene glycol phase change composite for thermal management. Fuller. Nanotub. Carbon Nanostructures 2020, 28, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liao, T.; Gao, L.; Wang, M.; Xu, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, H. Boron nitride-nanosheet enhanced cellulose nanofiber aerogel with excellent thermal management properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 241, 116425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.W.; Chen, C.J.; Yang, Z.; Kuang, Y.D.; Li, T.; Li, Y.J.; Huang, H.; Kierzewski, I.; Liu, B.Y.; He, S.M.; et al. Highly Compressible, Anisotropic Aerogel with Aligned Cellulose Nanofibers. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazhayal, L.; Wilson, P.; Prabhakaran, K. Waste to wealth: Lightweight, mechanically strong and conductive carbon aerogels from waste tissue paper for electromagnetic shielding and CO2 adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 381, 122628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.D.; Wang, R.; Wang, C.J.; Jia, J.; Sun, H.X.; Zhang, J.L.; Yang, Y.Y.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Li, A. Facile preparation of attapulgite-based aerogels with excellent flame retardancy and better thermal insulation properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47849. [Google Scholar]



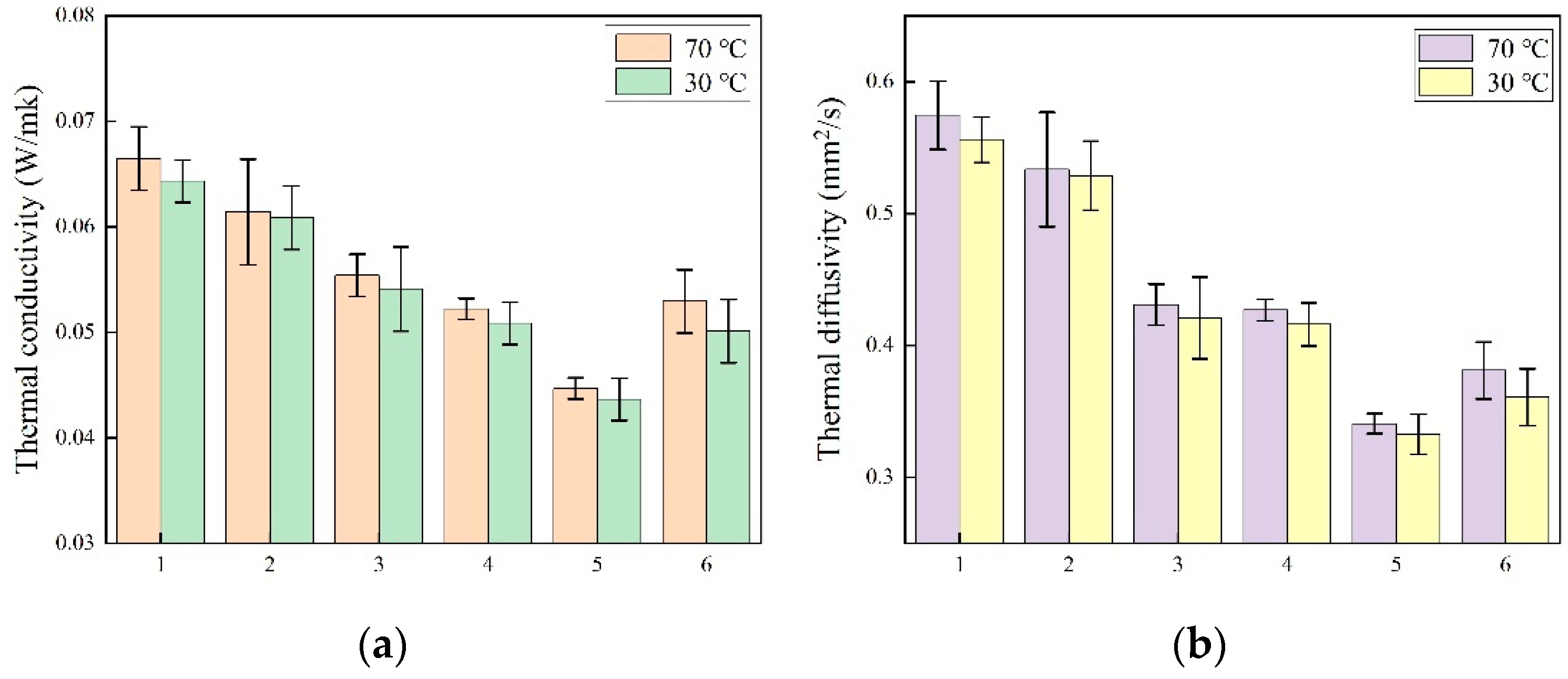
| Composite Aerogels | Maximum Allowable Pressure (kPa) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| cellulose-graphene aerogel | 7.4 | [39] |
| Graphemecellulose nanocrystalline aerogel | 6 | [24] |
| cellulose-graphene aerogel | 7.2 | [40] |
| polyvinyl alcohol–cellulose aerogel | 9.7 | [41] |
| polyvinyl alcohol-cellulose nanofibrils-graphene oxide hybrid aerogel | 4 | [42] |
| Fe3O4-cellulose-polyvinyl alcohol hybride aerogel | 6.5 | [43] |
| NiO-Fe2O3-reduced graphene oxide-polyvinyl alcohol aerogel | 9 | [44] |
| N-doped- reduced graphene oxide aerogel | 9.3 | [45] |
| cellulose nanofibrils-graphene nanosheets aerogel | 8.9 | [46] |
| polyvinyl alcohol-cellulose nanofibril hybrid aerogel | 7.2 | [47] |
| CaCO3-decorated cellulose aerogel | 4.5 | [48] |
| carbon-cellulose aerogel | 5.2 | [49] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Xie, P.; Wan, K.; Miao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, C. Mechanically Strong, Low Thermal Conductivity and Improved Thermal Stability Polyvinyl Alcohol–Graphene–Nanocellulose Aerogel. Gels 2021, 7, 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels7040170
Wang X, Xie P, Wan K, Miao Y, Liu Z, Li X, Wang C. Mechanically Strong, Low Thermal Conductivity and Improved Thermal Stability Polyvinyl Alcohol–Graphene–Nanocellulose Aerogel. Gels. 2021; 7(4):170. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels7040170
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiuya, Pengbo Xie, Ke Wan, Yuanyuan Miao, Zhenbo Liu, Xiaojun Li, and Chenxi Wang. 2021. "Mechanically Strong, Low Thermal Conductivity and Improved Thermal Stability Polyvinyl Alcohol–Graphene–Nanocellulose Aerogel" Gels 7, no. 4: 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels7040170
APA StyleWang, X., Xie, P., Wan, K., Miao, Y., Liu, Z., Li, X., & Wang, C. (2021). Mechanically Strong, Low Thermal Conductivity and Improved Thermal Stability Polyvinyl Alcohol–Graphene–Nanocellulose Aerogel. Gels, 7(4), 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels7040170





