Synthesis and Characterization of Acrylamide/Acrylic Acid Co-Polymers and Glutaraldehyde Crosslinked pH-Sensitive Hydrogels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis Hydrogel
2.2. Solubility Study
2.3. FTIR
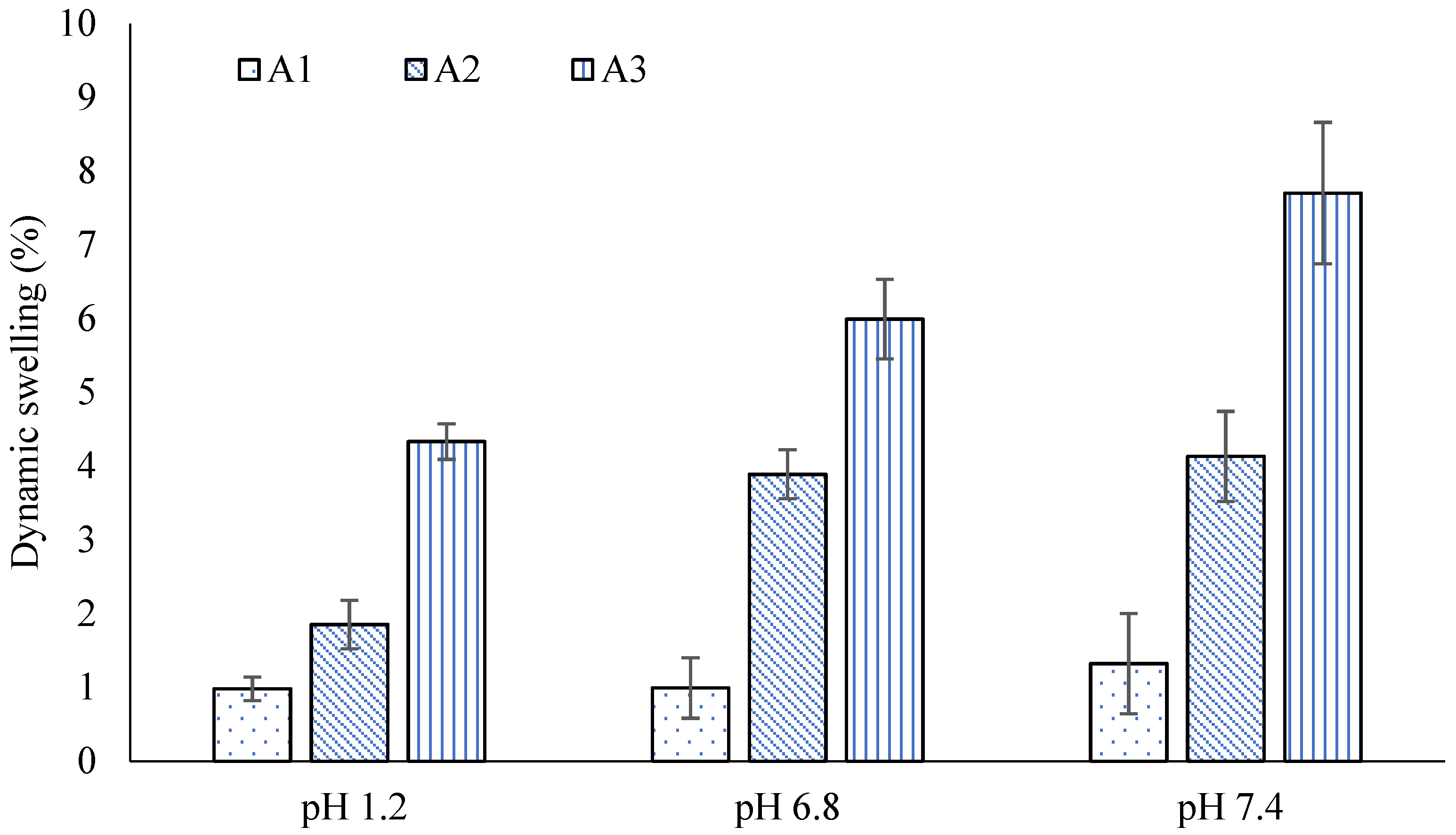
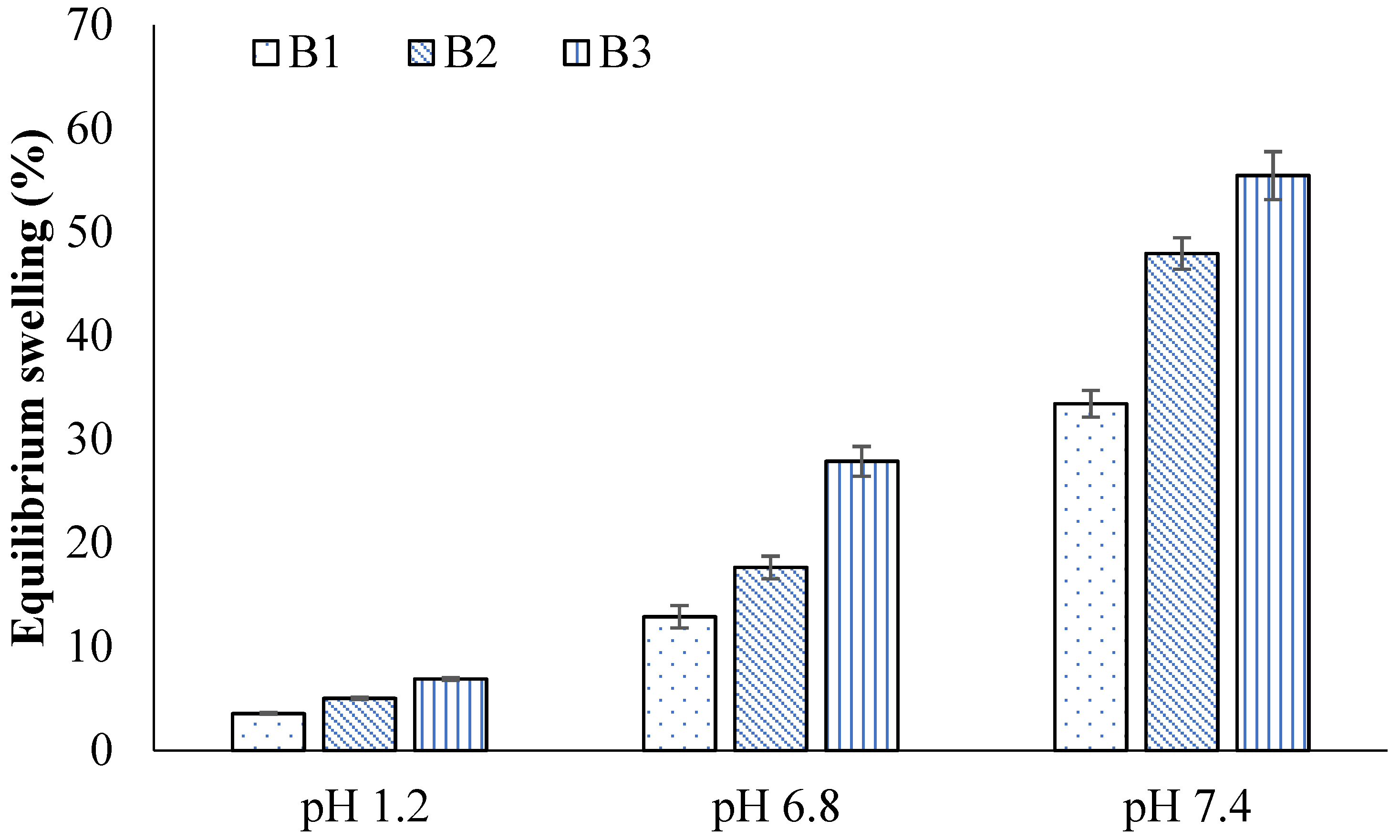
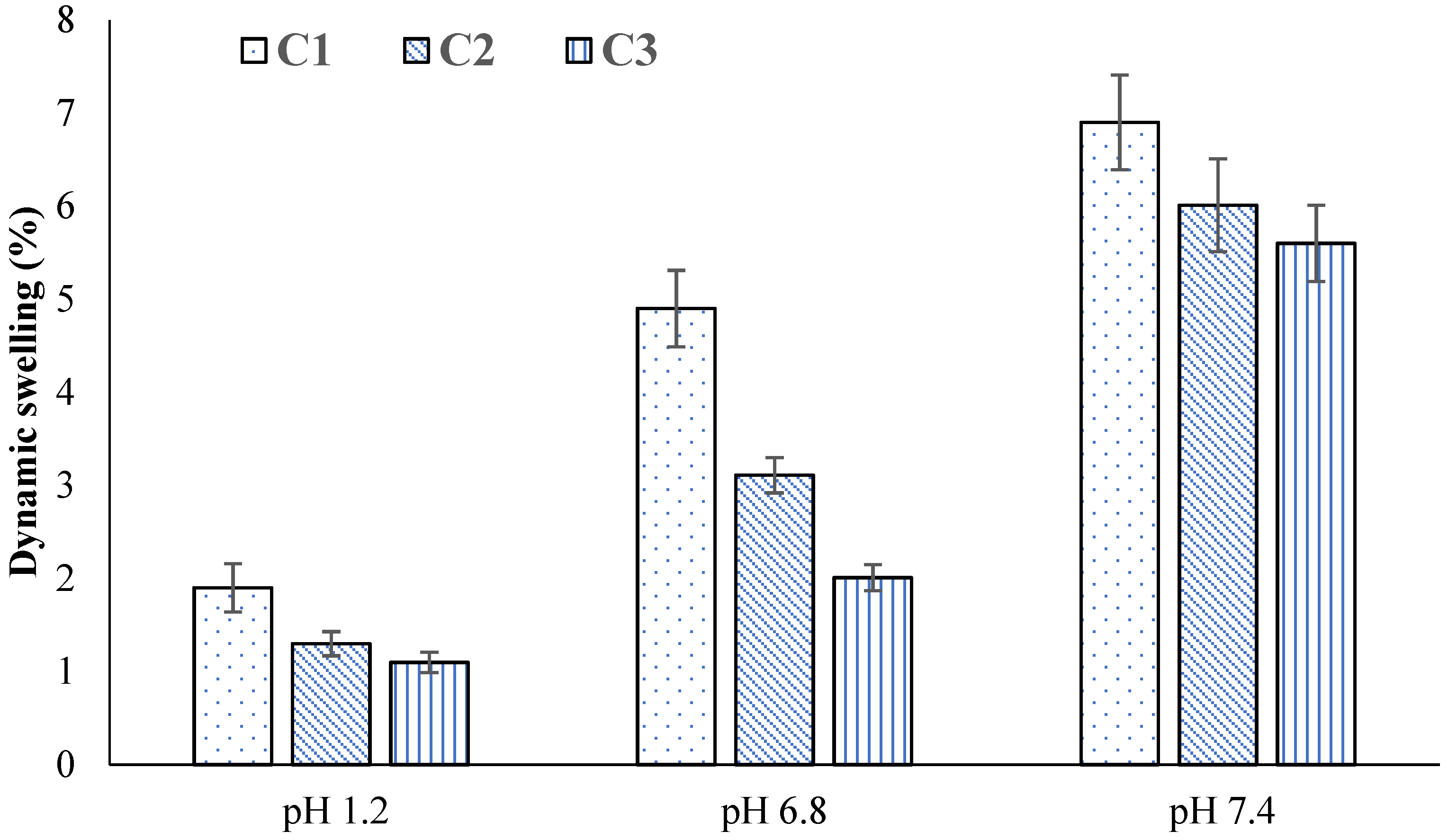
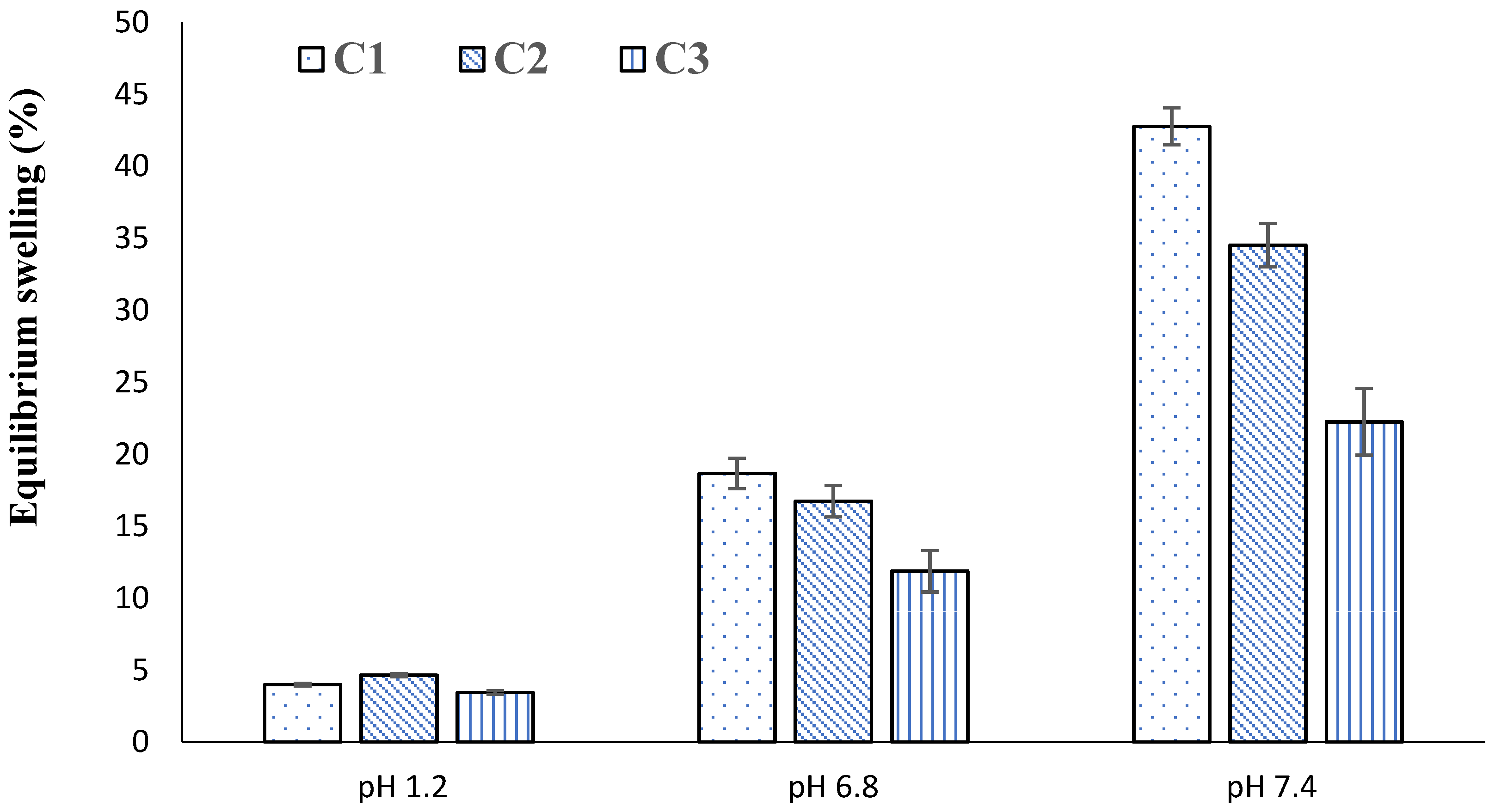
2.4. Swelling Studies
2.5. Effect of AM
2.6. Effect of AA
2.7. Effect of GA
2.8. Porosity Measurement
2.9. Gel Fraction
2.10. Drug Loading
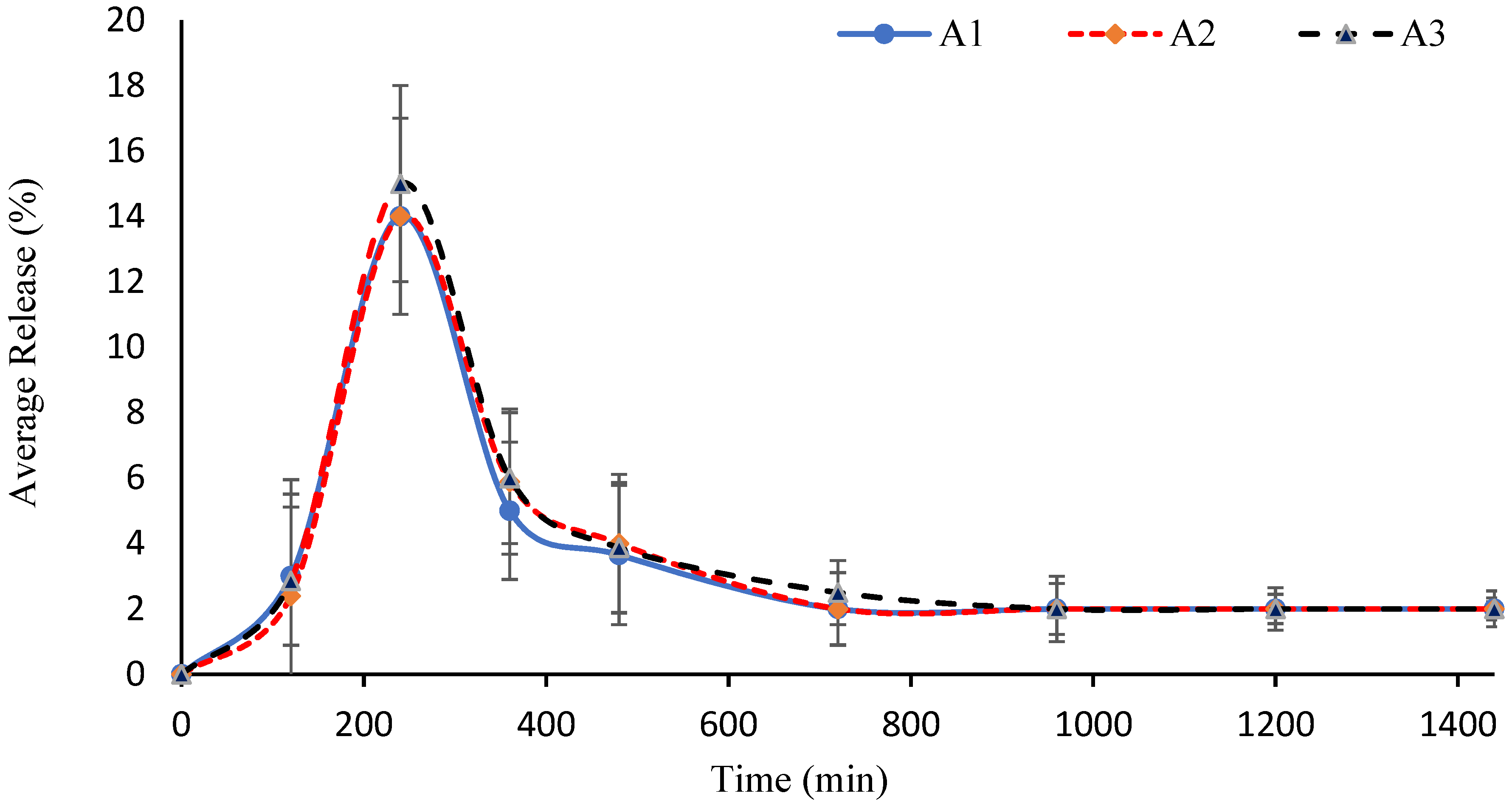
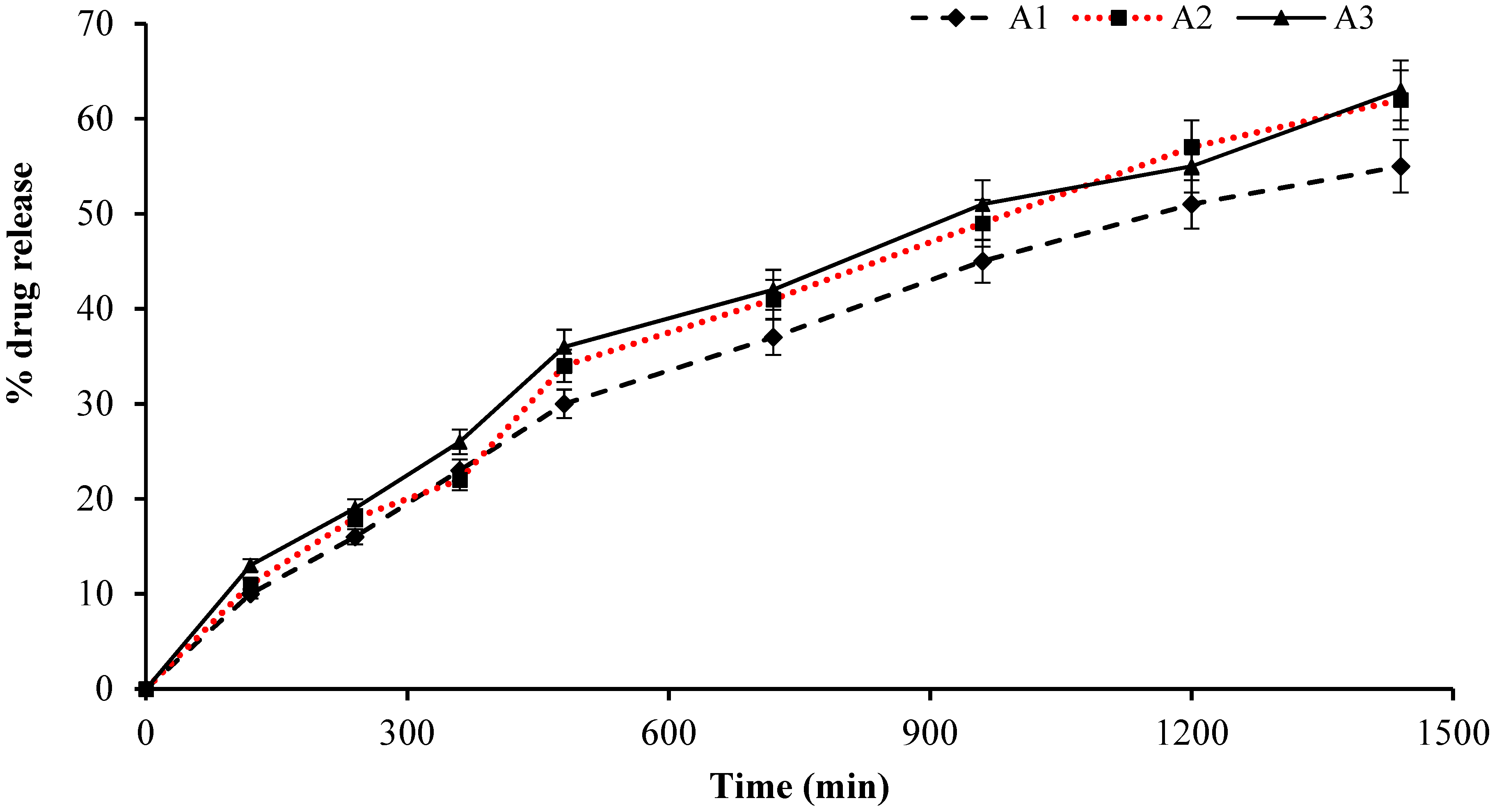
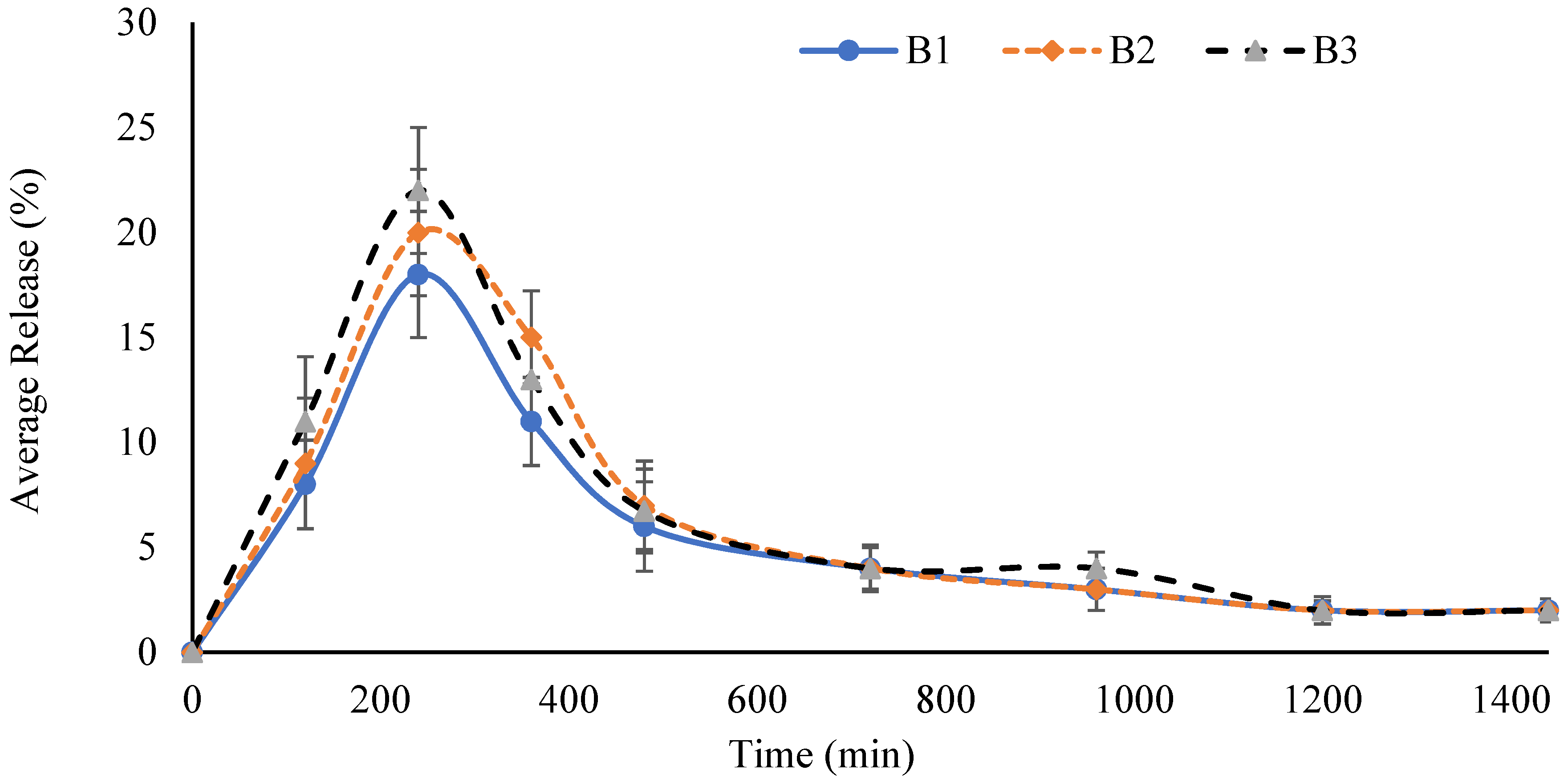
2.11. Cumulative Drug Release Measurement
2.12. Effect of AM
2.13. Effect of AA
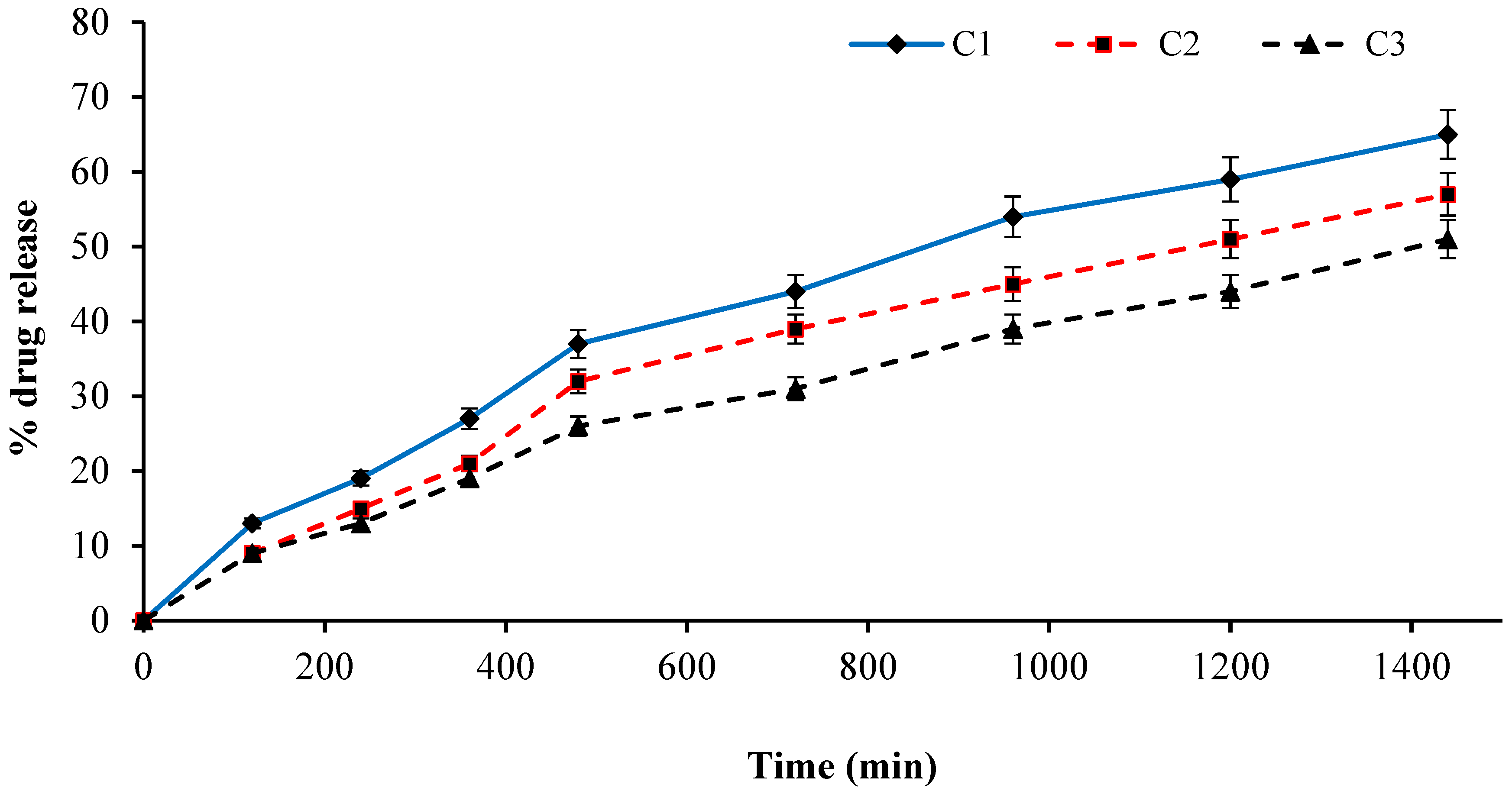
2.14. Effect of GA
2.15. Release Kinetics
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Pre-Formulation Studies and Standard Curve
4.3. Solubility Study of Drug
4.4. Preparation of 5-FULH
4.5. Hydrogel’s Characterizations
4.5.1. ATR-FTIR
4.5.2. Dynamic Swelling Study
4.5.3. Equilibrium Swelling Study
4.5.4. Diffusion Coefficient (DC)
4.5.5. Sol Gel Fraction Analysis
4.5.6. Porosity Measurement
4.5.7. Drug Loading
4.5.8. In Vitro Release Study
4.5.9. Release Kinetics
| First order kinetics | ln (1 − F) = K1t |
| Zero order kinetics | Mo − Mt = Kot |
| Higuchi model | Q = K2t1/2 |
| Korsmyer Peppas Model | Mt/Mœ = Ktn |
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olga, H.; Maryam, A.S.B.; Karim, S.S.; Brigitta, L.; Alf, L.; Claus-Michael, L. Drug delivery to the inflamed intestinal mucosa-targeting technologies and human cell culture models for better therapies of IBD. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 175, 113828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajitkumar, B.N.; Kumar, L. Treating colon cancers with a non-conventional yet strategic approach: An overview of various nanoparticulate systems. J. Control. Release 2021, 336, 16–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patole, V.C.; Pandit, A.P. Mesalamine-loaded alginate microspheres filled in enteric coated HPMC capsules for local treatment of ulcerative colitis: In vitro and in vivo characterization. J. Pharm. Investig. 2018, 48, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hani, U.; Honnavalli, Y.K.; Begum, M.Y.; Yasmin, S.; Osmani, R.A.M.; Ansari, M.Y. Colorectal cancer: A comprehensive review based on the novel drug delivery systems approach and its management. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 63, 102532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, S.; Marks, E.; Schneider, J.J.; Keely, S. Advances in oral nano-delivery systems for colon targeted drug delivery in inflammatory bowel disease: Selective targeting to diseased versus healthy tissue. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2015, 11, 1117–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Bajracharya, R.; Min, J.Y.; Han, J.-W.; Park, B.J.; Han, H.-K. Strategic Approaches for Colon Targeted Drug Delivery: An Overview of Recent Advancements. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bignotti, F.; Baldi, F.; Grassi, M.; Abrami, M.; Spagnoli, G. Hydrophobically-Modified PEG Hydrogels with Controllable Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Balance. Polymers 2021, 13, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Q.; Jiao, Y.; Yu, X. Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications: Their Characteristics and the Mechanisms behind Them. Gels 2017, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudassir, J.; Ranjha, N.M. Dynamic and equilibrium swelling studies: Crosslinked pH sensitive methyl methacrylate-co-itaconic acid (MMA-co-IA) hydrogels. J. Polym. Res. 2008, 15, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.E.; Macdonald, M.; Nie, J.; Bowman, C.N. Structure and swelling of poly (acrylic acid) hydrogels: Effect of pH, ionic strength, and dilution on the crosslinked polymer structure. Polymer 2004, 45, 1503–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjha, N.M.; Ayub, G.; Naseem, S.; Ansari, M.T. Preparation and characterization of hybrid pH-sensitive hydrogels of chitosan-coacrylic acid for controlled release of verapamil. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 2805–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhlaq, M.; Azad, A.K.; Ullah, I.; Nawaz, A.; Safdar, M.; Bhattacharya, T.; Uddin, A.B.; Abbas, S.A.; Mathews, A.; Kundu, S.K.; et al. Methotrexate-loaded gelatin and polyvinyl alcohol (Gel/PVA) hydrogel as a pH-sensitive matrix. Polymers 2021, 13, 2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malviya, R.; Sundram, S.; Fuloria, S.; Subramaniyan, V.; Sathasivam, K.V.; Azad, A.K.; Sekar, M.; Kumar, D.H.; Chakravarthi, S.; Porwal, O.; et al. Evaluation and Characterization of Tamarind Gum Polysaccharide: The Biopolymer. Polymers 2021, 13, 3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, Y.L.; Hsu, C.Y.; Lin, H.R. pH-andthermo-sensitivepluronic/poly(acrylic acid) in situ hydrogels for sustained release of an anticancer drug. J. Drug Target. 2013, 21, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajpai, A.K.; Kankane, S. Evaluation of water sorption property and in vitro blood compatibility of poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) (PHEMA) based semi interpenetrating polymer networks (IPNs). J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008, 19, 1921–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheirandish, S.; Jabbari, E. Effect of surface polarity on wettability and friction coefficient of silicone rubber/poly(acrylic acid) hydrogel composite. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2006, 284, 1411–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, M.; Yahya, R.; Hassan, A.; Yar, M.; Azzahari, A.D.; Selvanathan, V.; Sonsudin, F.; Abouloula, C.N. pH Sensitive Hydrogels in Drug Delivery: Brief History, Properties, Swelling, and Release Mechanism, Material Selection and Applications. Polymers 2017, 9, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhakar, K.; Fuloria, S.; Subramaniyan, V.; Sathasivam, K.V.; Azad, A.K.; Swain, S.S.; Sekar, M.; Karupiah, S.; Porwal, O.; Sahoo, A.; et al. Ultraflexible Liposome Nanocargo as a Dermal and Transdermal Drug Delivery System. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Brazel, C.S. Modifying the release of proxyphylline from PVA hydrogels using surface crosslinking. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 349, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlovskaya, V.; Kharlampieva, E.; Sukhishvili, S.A. 1.124-Polymer Films Using LbL Self-Assembly. Compr. Biomater. 2011, 1, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-J.; Lee, S.-B.; Han, N.-W. Kinetics of crosslinking reaction of PVA membrane with glutaraldehyde. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 1994, 11, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, K.; Urabe, I.; Yamada, Y.; Okada, H. Reaction of glutaraldehyde with amino and thiol compounds. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 1991, 71, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.A.; Azad, A.K.; Fuloria, S.; Nawaz, A.; Subramaniyan, V.; Akhlaq, M.; Safdar, M.; Sathasivam, K.V.; Sekar, M.; Porwal, O.; et al. Chitosan-Coated 5-Fluorouracil Incorporated Emulsions as Transdermal Drug Delivery Matrices. Polymers 2021, 13, 3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandran, S.P.; Natarajan, S.B.; Chandraseharan, S.; Mohd Shahimi, M.S.B. Nano drug delivery strategy of 5-fluorouracil for the treatment of colorectal cancer. J. Cancer Res. Pract. 2017, 4, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamy, B.Y.; Chang, J.H.; Ahn, H.; Lee, W.-K.; Chung, I. Thermoresponsive N-vinyl caprolactam grafted sodium alginate hydrogel beads for the controlled release of an anticancer drug. Cellulose 2013, 20, 1261–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anirudhan, T.S.; Mohan, A.M. Novel pH switchable gelatin-based hydrogel for the controlled delivery of the anticancer drug 5-fluorouracil. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 12109–12118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eswaramma, S.; Rao, K.S.V.K.; Rao, K.M. Diffusion and Controlled Release Characteristics of Ph-Sensitive Poly(2-(Dimethyl Amino)ethyl Methacrylate-co-2-hydroxyethylacrylate) Hydrogels. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2016, 65, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Y.; Li, D.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Q.; Tan, Y.; Yue, Q.; Meng, F. Physically crosslinked pH-responsive chitosan-based hydrogels with enhanced mechanical performance for controlled drug delivery. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 106035–106045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Ma, R.; Wang, X.; Gao, J.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, Z. Enzyme and pH responsive 5-flurouracil (5-FU) loaded hydrogels based on olsalazine derivatives for colon-specific drug delivery. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 118, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, M.S.; Azad, A.K.; Nawaz, A.; Rashid, S.A.; Rahman, M.; Al Omar, S.Y.; Bungau, S.G.; Aleya, L.; Abdel-Daim, M.M. Ethyl Cellulose and Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose Blended Methotrexate-Loaded Transdermal Patches: In Vitro and Ex Vivo. Polymers 2021, 13, 3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Y.; Wang, Y.P.; Yu, Y.T.; Wang, Y.M.; Ni, J.H. Glutaraldehyde-Cross-Linked Poly(acrylic acid-co-acrylamide)/Poly(vinyl alcohol) Superabsorbent Membranes. Mater. Sci. Forum 2014, 789, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhail, M.; Fang, C.W.; Khan, A.; Minhas, M.U.; Wu, P.C. Fabrication and In Vitro Evaluation of pH-Sensitive Polymeric Hydrogels as Controlled Release Carriers. Gels 2021, 7, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, M.F.; Ranjha, N.M.; Hanif, M. Effect of ethylene glycol dimethacrylate on swelling and on metformin hydrochloride release behavior of chemically crosslinked pH–sensitive acrylic acid–polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 23, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Tabakha, M.M.; Khan, S.A.; Ashames, A.; Ullah, H.; Ullah, K.; Murtaza, G.; Hassan, N. Synthesis, Characterization and Safety Evaluation of Sericin-Based Hydrogels for Controlled Delivery of Acyclovir. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugwu, O.B.; Barminas, J.T.; Nkafamiya, I.I.; Akinterinwa, A. Synthesis and Characterization of Crosslinked Hydrogel of Konkoli (Maesopsis eminii) Grafted Polymethylacrylamide for a Preliminary Study as an Insulin Delivery System. J. Biosci. Med. 2016, 4, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cavalcante, L.A.; Batista, B.S.; Fonseca, A.P.G.; Balteiro, A.J.D.; Amaral, F.M.B.; Mendes, F.; Macêdo, A.A.M. Effect of pH on Swelling Profile of Glutaraldehyde Crosslinked Adenanthera pavonina L. Galactomannan. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Architecture, Materials and Construction (ICAMC 2019), Lisbon, Portugal, 2–4 December 2019; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020; Volume 809, p. 012023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunjiappan, S.; Theivendran, P.; Baskararaj, S.; Sankaranarayanan, B.; Palanisamy, P.; Saravanan, G.; Arunachalam, S.; Sankaranarayanan, M.; Natarajan, J.; Somasundaram, B.; et al. Modeling a pH-sensitive Zein-co-acrylic acid hybrid hydrogels loaded 5-fluorouracil and rutin for enhanced anticancer efficacy by oral delivery. 3 Biotech 2019, 9, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.K.; Azad, A.K.; Nawaz, A.; Ullah, S.; Latif, M.S.; Rahman, H.; Alsharif, K.F.; Alzahrani, K.J.; El-Kott, A.F.; Albrakati, A.; et al. Formulation Development, Characterization and Antifungal Evaluation of Chitosan NPs for Topical Delivery of Voriconazole In Vitro and Ex Vivo. Polymers 2022, 14, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, L.; Ahmad, M.; Usman, M. Evaluation of crosslinked hydroxypropyl methylcellulose graft-methacrylic acid copolymer as extended-release oral drug carrier. Cell. Chem. Technol. 2015, 49, 143–151. [Google Scholar]
- Dergunov, S.A.; Nam, I.K.; Mun, G.A.; Nurkeeva, Z.S.; Shaikhutdinov, E.M. Radiation synthesis and characterization of stimuli-sensitive chitosan–polyvinyl pyrrolidone hydrogels. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2005, 72, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundargi, R.C.; Rangaswamy, V.; Aminabhavi, T.M. A novel method to prepare 5-fluorouracil, an anti-cancer drug, loaded microspheres from poly (N-vinyl caprolactam-co-acrylamide) and controlled release studies. Des. Monomers Polym. 2010, 13, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.R.; Soppimath, K.S.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; Dave, A.M.; Mehta, M.H. Glutaraldehyde crosslinked sodium alginate beads containing liquid pesticide for soil application. J. Control. Release 2000, 63, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, K.; Khan, I.U.; Shahzad, Y.; Hussain, T.; Ranjha, N.M. pH-sensitive polyvinylpyrrolidone-acrylic acid hydrogels: Impact of material parameters on swelling and drug release. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 50, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özbaş, Z.; Gürdağ, G. Synthesis and Characterization of 5-Fluorouracil-Loaded Glutaraldehyde Crosslinked Chitosan Hydrogels. Süleyman Demirel Üniv. Fen Bilim. Enst. Derg. 2016, 20, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ju, H.K.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, Y.M. pH/temperature-responsive behaviors of semi-IPN and comb-type graft hydrogels composed of alginate and poly (N-isopropylacrylamide). Polymer 2001, 42, 6851–6857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.-H.; Huynh, L.-H.; Kasim, N.S.; Guo, T.-J.; Wang, J.-H.; Fazary, A.E. Analysis of soluble and insoluble fractions of alkali and subcritical water treated sugarcane bagasse. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, S.; Teo, Y.Y.; Naeem, S.; Ramesh, S.; Ramesh, K. pH responsive N-succinyl chitosan/Poly (acrylamide-co-acrylic acid) hydrogels and in vitro release of 5-fluorouracil. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179250. [Google Scholar]
- Bashir, S.; Teo, Y.Y.; Ramesh, S.; Ramesh, K. Synthesis, characterization, properties of N-succinyl chitosan-g-poly (methacrylic acid) hydrogels and in vitro release of theophylline. Polymer 2016, 92, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, A.M. Swelling behaviors of polyelectrolyte hydrogels containing sulfonate groups. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2002, 13, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.E.-H. Removal of heavy metals from model wastewater by using carboxymehyl cellulose/2-acrylamido-2-methyl propane sulfonic acid hydrogels. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 123, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.V.; Shivakumar, H.G. Investigation of swelling behavior and mechanical properties of a pH-sensitive superporous hydrogel composite. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2012, 11, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bukhari, S.M.H.; Khan, S.; Rehanullah, M.; Ranjha, N.M. Synthesis and Characterization of Chemically Cross-Linked Acrylic Acid/Gelatin Hydrogels: Effect of pH and Composition on Swelling and Drug Release. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2015, 2015, 187961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, A.K.; Al-Mahmood, S.M.A.; Chatterjee, B.; Wan Sulaiman, W.M.A.; Elsayed, T.M.; Doolaanea, A.A. Encapsulation of black seed oil in alginate beads as a pH-sensitive carrier for intestine-targeted drug delivery: In vitro, in vivo and ex vivo study. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, B.E.; Ramazani, S.A.A.; Shafiee, M.; Danaei, M. Studies on glutaraldehyde crosslinked chitosan hydrogel properties for drug delivery systems. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2013, 62, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhail, M.; Hsieh, Y.-H.; Khan, A.; Minhas, M.U.; Wu, P.-C. Preparation and In Vitro Evaluation of Aspartic/Alginic Acid Based Semi-Interpenetrating Network Hydrogels for Controlled Release of Ibuprofen. Gels 2021, 7, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhail, M.; Khan, A.; Rosenholm, J.M.; Minhas, M.U.; Wu, P.-C. Fabrication and Characterization of Diclofenac Sodium Loaded Hydrogels of Sodium Alginate as Sustained Release Carrier. Gels 2021, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhlaq, M.; Azad, A.K.; Fuloria, S.; Meenakshi, D.U.; Raza, S.; Safdar, M.; Nawaz, A.; Subramaniyan, V.; Sekar, M.; Sathasivam, K.V.; et al. Fabrication of Tizanidine Loaded Patches Using Flaxseed Oil and Coriander Oil as a Penetration Enhancer for Transdermal Delivery. Polymers 2021, 13, 4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azad, A.K.; Doolaanea, A.A.; Al-Mahmood, S.M.A.; Kennedy, J.F.; Chatterjee, B.; Bera, H. Electro-hydrodynamic assisted synthesis of lecithin-stabilized peppermint oil-loaded alginate microbeads for intestinal drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 185, 861–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhlaq, M.; Idrees, N.; Nawaz, A.; Jalil, A.; Zafar, N.; Adeel, M.; Afridi, H.H. HPMC-coacrylic acid dexibuprofen once-daily oral hydrogels. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A 2020, 57, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, U.; Sohail, M.; Ahmad, M.; Minhas, M.U.; Khan, S.; Hussain, Z.; Kousar, M.; Mohsin, S.; Abbasi, M.; Shah, S.A.; et al. Chitosan based thermosensitive injectable hydrogels for controlled delivery of loxoprofen: Development, characterization and in-vivo evaluation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 129, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjha, N.M.; Qureshi, U.F. Preparation and characterization of crosslinked acrylic acid/hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose hydrogels for drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 6, 400–410. [Google Scholar]
- Peppas, N.A.; Hilt, J.Z.; Khademhosseini, A.; Langer, R. Hydrogels in Biology and Medicine: From Molecular Principles to Bionanotechnology. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 1345–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, N.A.; Bures, P.; Leobandung, W.; Ichikawa, H. Hydrogels in pharmaceutical formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2006, 50, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, N.A.; Mikos, A.G. Preparation methods and structure of hydrogels. In Hydrogels in Medicine and Pharmacy; Peppas, N.A., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1986; Volume 1, pp. 2–23. [Google Scholar]
- Amini-Fazl, M.S.; Mohammadi, R.; Kheiri, K. 5-Fluorouracil loaded chitosan/polyacrylic acid/Fe3O4 magnetic nanocomposite hydrogel as a potential anticancer drug delivery system. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 132, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjha, N.M.; Mudassir, J.; Akhtar, N. Methyl methacrylate-co-itaconic acid (MMA-co-IA) hydrogels for controlled drug delivery. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2008, 47, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.R.S.; Rao, K.S.V.K.; Rao, K.M.; Reddy, N.S. Synthesis of Novel Hydrogels based Poly(4-Hydroxyphenylazo-3-N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)maleimide) for Specific Colon Delivery of Chemotherapeutic Agent. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 5, 021–028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Yang, H.; Dong, X.; Lei, H.; Chen, D. pH-sensitive polymeric particles as smart carriers for rebar inhibitors delivery in alkaline condition. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 45886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
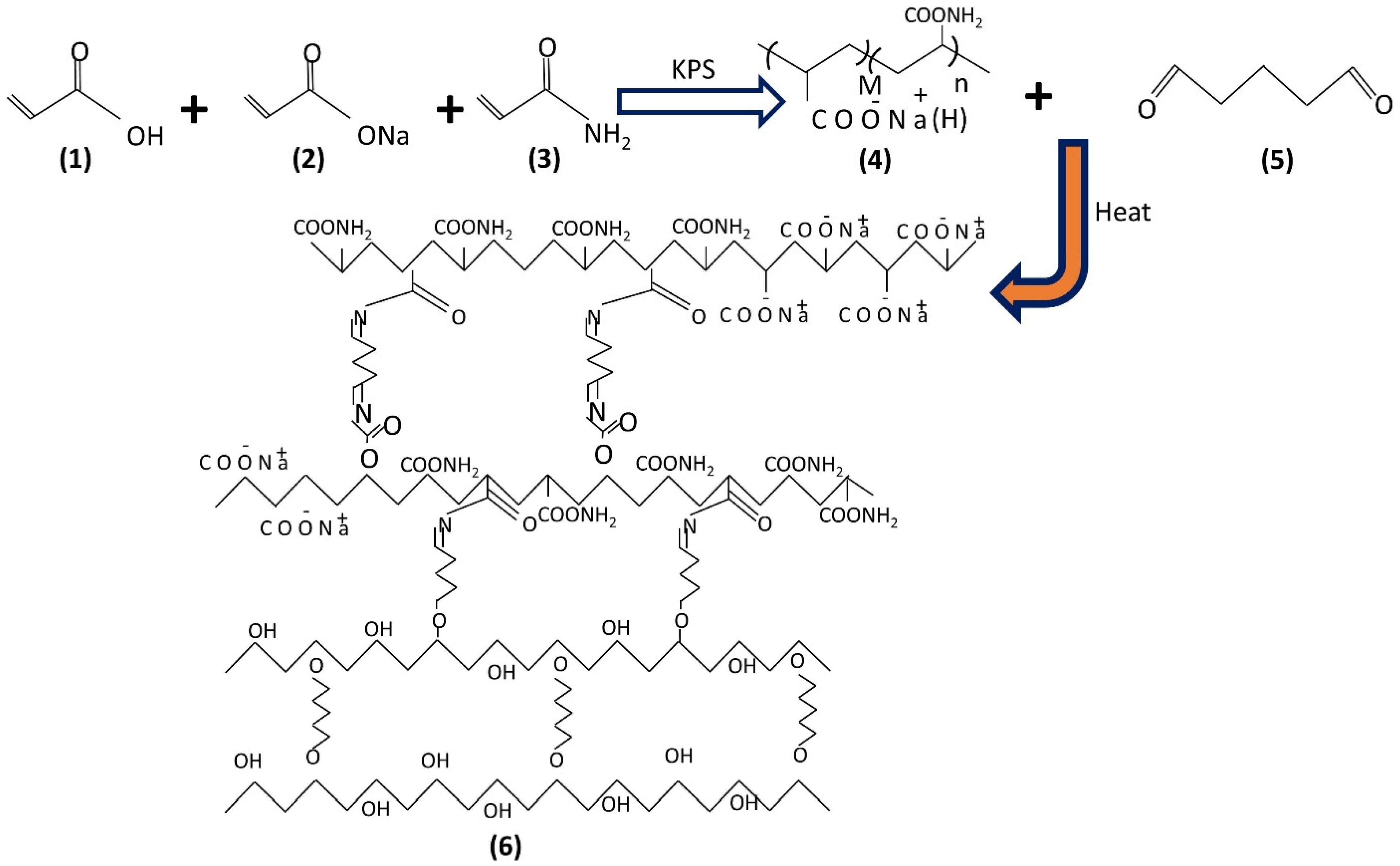





| S.No | Solvent | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Distilled Water | Soluble |
| 2 | Phosphate buffer pH 7.4 | Soluble |
| 3 | Acidic media pH 1.2 | Sparingly soluble |
| F. Code | pH 1.2 | pH 6.8 | pH 7.4 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dynamic Swelling | Equilibrium Swelling | Dynamic Swelling | Equilibrium Swelling | Dynamic Swelling | Equilibrium Swelling | |
| A1 | 0.98 ± 0.04 | 1.65 ± 0.01 | 1.85 ± 0.01 | 10.12 ± 0.02 | 4.33 ± 0.04 | 29.67 ± 0.05 |
| A2 | 0.99 ± 0.03 | 2.98 ± 0.03 | 3.89 ± 0.03 | 16.27 ± 0.03 | 5.99 ± 0.03 | 39.68 ± 0.03 |
| A3 | 1.32 ± 0.01 | 4.11 ± 0.05 | 4.13 ± 0.05 | 28.15 ± 0.01 | 7.71 ± 0.03 | 47.98 ± 0.02 |
| B1 | 0.99 ± 0.02 | 3.55 ± 0.02 | 3.35 ± 0.02 | 12.89 ± 0.04 | 5.77 ± 0.02 | 33.46 ± 0.07 |
| B2 | 1.21 ± 0.04 | 5.02 ± 0.01 | 5.02 ± 0.01 | 17.65 ± 0.05 | 7.44 ± 0.03 | 47.96 ± 0.05 |
| B3 | 1.43 ± 0.02 | 6.88 ± 0.03 | 6.68 ± 0.03 | 27.89 ± 0.03 | 10.21 ± 0.01 | 55.48 ± 0.04 |
| C1 | 1.90 ± 0.03 | 3.99 ± 0.01 | 4.99 ± 0.01 | 18.67 ± 0.02 | 6.88 ± 0.02 | 42.78 ± 0.06 |
| C2 | 1.33 ± 0.01 | 4.64 ± 0.02 | 3.14 ± 0.02 | 16.74 ± 0.01 | 6.10 ± 0.03 | 34.53 ± 0.05 |
| C3 | 1.10 ± 0.01 | 3.45 ± 0.04 | 2.05 ± 0.04 | 11.87 ± 0.04 | 5.66 ± 0.02 | 22.25 ± 0.03 |
| F. Code | DC (cm2/s) | Porosity % | Gel Fraction % | Sol Fraction % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 0.19 ± 0.02 | 34 ± 0.03 | 74 ± 0.4 | 24 ± 0.1 |
| A2 | 0.09 ± 0.03 | 42 ± 0.04 | 86 ± 0.3 | 22 ± 0.2 |
| A3 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 55 ± 0.02 | 90 ± 0.4 | 15 ± 0.1 |
| B1 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 41 ± 0.03 | 85 ± 0.5 | 17 ± 0.3 |
| B2 | 0.07 ± 0.03 | 43 ± 0.04 | 91 ± 0.3 | 11 ± 0.2 |
| B3 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 62 ± 0.06 | 94 ± 0.2 | 09 ± 0.3 |
| C1 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 39 ± 0.05 | 83 ± 0.4 | 16 ± 0.4 |
| C2 | 0.09 ± 0.03 | 39 ± 0.04 | 89 ± 0.4 | 11 ± 0.4 |
| C3 | 0.07 ± 0.02 | 47 ± 0.03 | 93 ± 0.3 | 09 ± 0.3 |
| F. Code | Amount of 5-FU Loaded (g/g of Dry Gel) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| By Swelling | By Extraction | By Weight | |
| A1 | 0.0394 | 0.0373 | 0.0347 |
| A2 | 0.0402 | 0.0392 | 0.0369 |
| A3 | 0.0416 | 0.0423 | 0.0391 |
| B1 | 0.0372 | 0.0393 | 0.0357 |
| B2 | 0.0349 | 0.0385 | 0.0341 |
| B3 | 0.0331 | 0.0377 | 0.0328 |
| F. Code | AM | AA | GA | TEMED | APS | D/Water |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 4.08 g | 0.48 g | 23 µL | 235 µL | 0.20 g | 13 mL |
| A2 | 5.88 g | 0.48 g | 23 µL | 235 µL | 0.20 g | 13 mL |
| A3 | 7.5 g | 0.48 g | 23 µL | 235 µL | 0.20 g | 13 mL |
| B1 | 4.08 g | 0.96 g | 23 µL | 235 µL | 0.20 g | 13 mL |
| B2 | 4.08 g | 1.5 g | 23 µL | 235 µL | 0.20 g | 13 mL |
| B3 | 4.08 g | 2 g | 23 µL | 235 µL | 0.20 g | 13 mL |
| C1 | 4.08 g | 0.48 g | 19 µL | 235 µL | 0.20 g | 13 mL |
| C2 | 4.08 g | 0.48 g | 13 µL | 235 µL | 0.20 g | 13 mL |
| C3 | 4.08 g | 0.48 g | 7 µL | 235 µL | 0.20 g | 13 mL |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, M.A.; Azad, A.K.; Safdar, M.; Nawaz, A.; Akhlaq, M.; Paul, P.; Hossain, M.K.; Rahman, M.H.; Baty, R.S.; El-kott, A.F.; et al. Synthesis and Characterization of Acrylamide/Acrylic Acid Co-Polymers and Glutaraldehyde Crosslinked pH-Sensitive Hydrogels. Gels 2022, 8, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8010047
Khan MA, Azad AK, Safdar M, Nawaz A, Akhlaq M, Paul P, Hossain MK, Rahman MH, Baty RS, El-kott AF, et al. Synthesis and Characterization of Acrylamide/Acrylic Acid Co-Polymers and Glutaraldehyde Crosslinked pH-Sensitive Hydrogels. Gels. 2022; 8(1):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8010047
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Munir Ahmad, Abul Kalam Azad, Muhammad Safdar, Asif Nawaz, Muhammad Akhlaq, Pijush Paul, Md. Kamal Hossain, Md. Habibur Rahman, Roua S. Baty, Attalla F. El-kott, and et al. 2022. "Synthesis and Characterization of Acrylamide/Acrylic Acid Co-Polymers and Glutaraldehyde Crosslinked pH-Sensitive Hydrogels" Gels 8, no. 1: 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8010047
APA StyleKhan, M. A., Azad, A. K., Safdar, M., Nawaz, A., Akhlaq, M., Paul, P., Hossain, M. K., Rahman, M. H., Baty, R. S., El-kott, A. F., Kamel, M., Bungau, S. G., & Abdel-Daim, M. M. (2022). Synthesis and Characterization of Acrylamide/Acrylic Acid Co-Polymers and Glutaraldehyde Crosslinked pH-Sensitive Hydrogels. Gels, 8(1), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8010047








