The Effect of Crosslinking Degree of Hydrogels on Hydrogel Adhesion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. The Effect of The Crosslinking Degree of PVA Hydrogels on Hydrogel Adhesion, and Mechanical and Swelling Properties
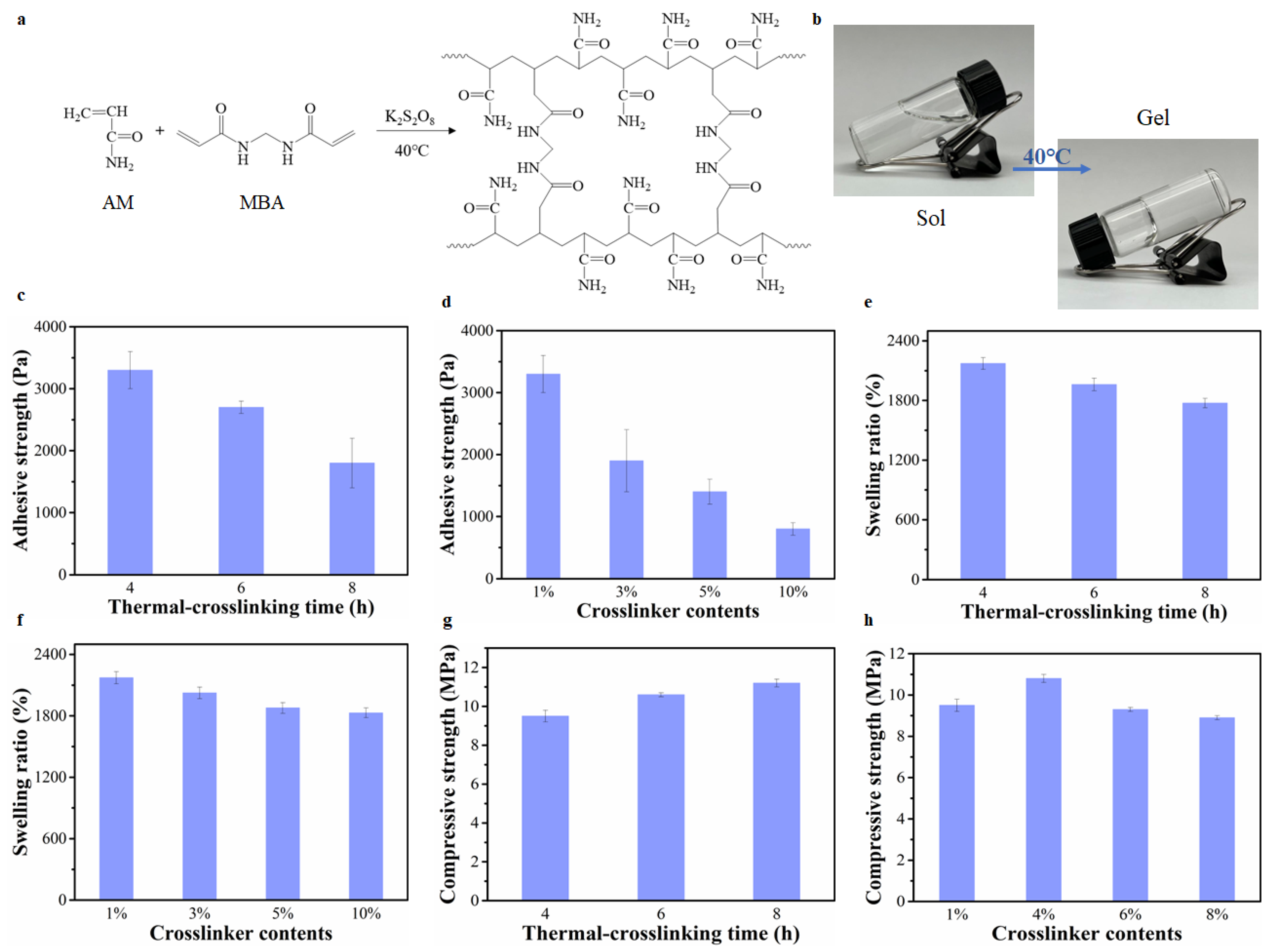
2.2. The Effect of The Crosslinking Degree of PAM Hydrogels on Hydrogel Adhesion, and Mechanical and Swelling Properties
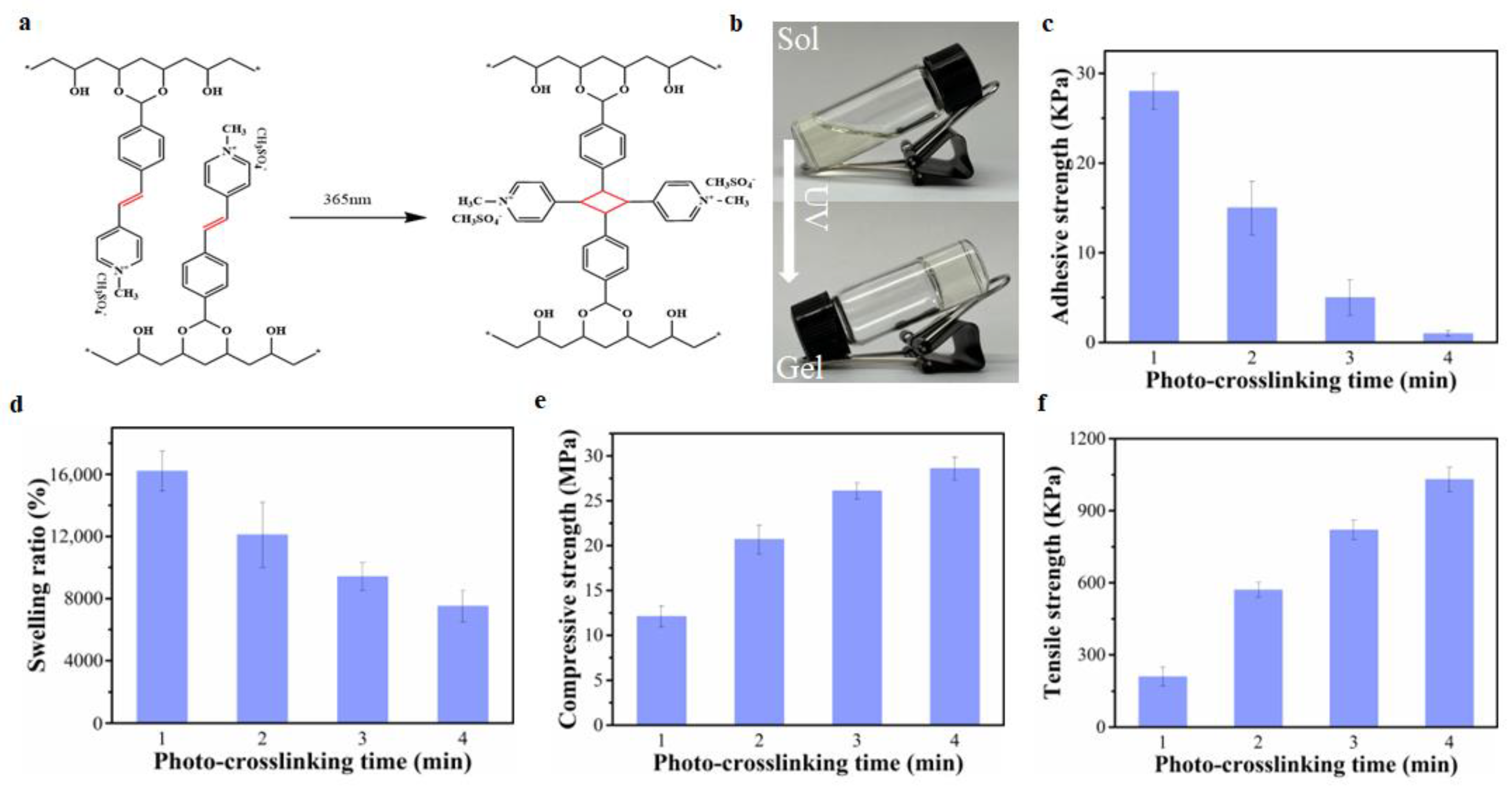
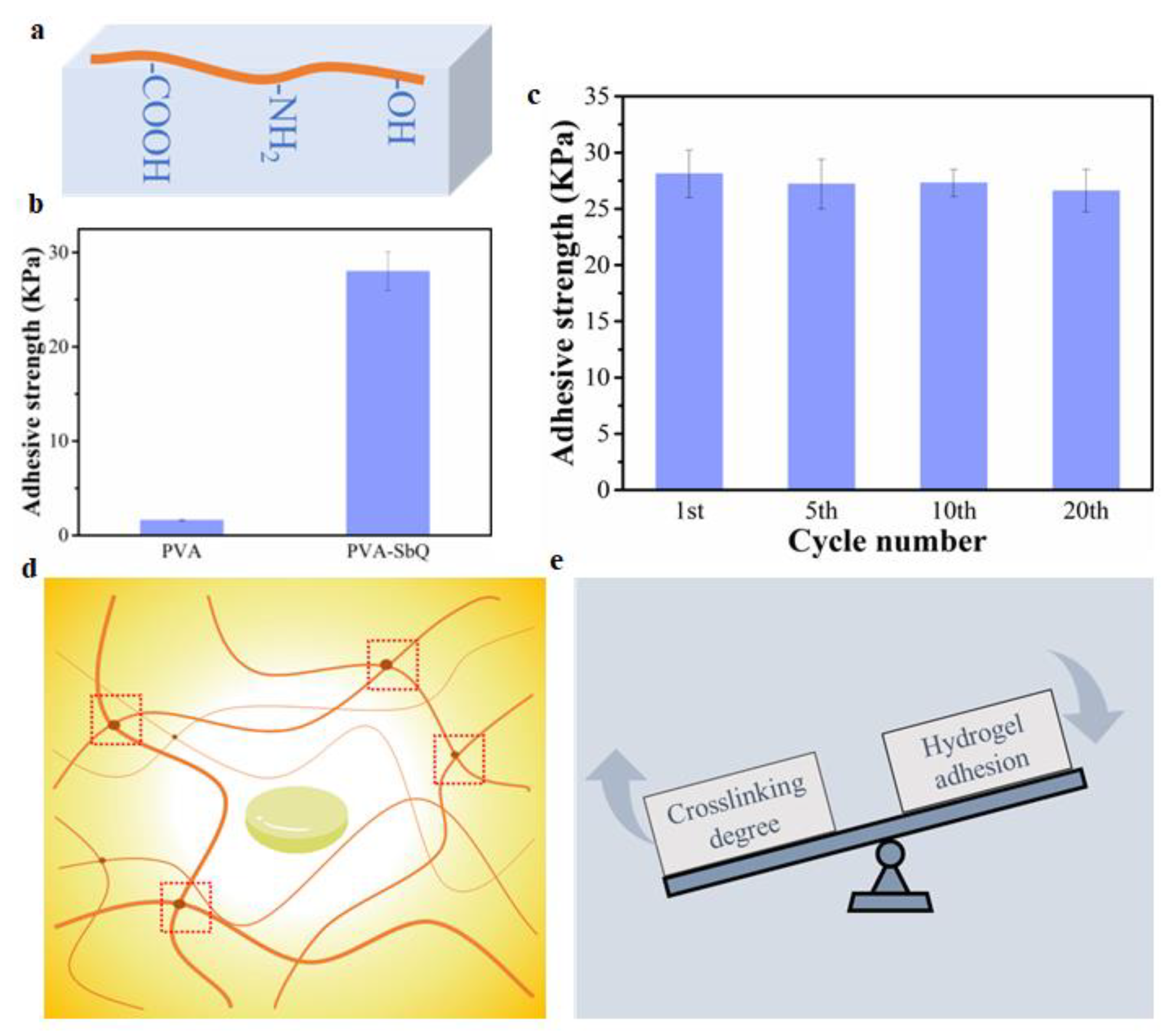
2.3. The Effect of The Crosslinking Degree of PVA-SbQ Hydrogels on Hydrogel Adhesion, and Mechanical and Swelling Properties
2.4. The Strategies for Constructing Strong Hydrogel Adhesion
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. The Preparation of PVA Hydrogel
4.3. The Preparation of PVA/CNC Hydrogels
4.4. The Preparation of PAM Hydrogels
4.5. The Preparation of PVA-SbQ Hydrogels
4.6. Characterization
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, J.; Bai, R.; Chen, B.; Suo, Z. Hydrogel adhesion: A supramolecular synergy of chemistry, topology, and mechanics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1901693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, R.; Sun, Z.M.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, T.; Cholewinski, A.; Yang, F.; Zhao, B.; Pinnaratip, R.; et al. Catechol-functionalized hydrogels: Biomimetic design, adhesion mechanism, and biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 433–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamoun, E.A.; Kenawy, E.-R.S.; Chen, X. A review on polymeric hydrogel membranes for wound dressing applications: PVA-based hydrogel dressings. J. Adv. Res. 2017, 8, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; He, J.; Guo, B. Functional hydrogels as wound dressing to enhance wound healing. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 12687–12722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovone, G.; Dudaryeva, O.Y.; Marco-Dufort, B.; Tibbitt, M.W. Engineering hydrogel adhesion for biomedical applications via chemical design of the junction. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 4048–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caló, E.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Biomedical applications of hydrogels: A review of patents and commercial products. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 65, 252–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Wang, D.; Bai, H.; Zhang, S.; Ma, P.; Dong, W. Photo-crosslinking strategy constructs adhesive, superabsorbent, and tough PVA-based hydrogel through controlling the balance of cohesion and adhesion. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2020, 305, 1900623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, M.; Xu, T.; Zhang, X. Multifunctional hydrogel as wound dressing for intelligent wound monitoring. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 433, 134625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Steck, J.; Bai, R.; Suo, Z. Topological adhesion II. Stretchable adhesion. Extreme Mech. Lett. 2020, 40, 100891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steck, J.; Kim, J.; Yang, J.; Hassan, S.; Suo, Z. Topological adhesion. I. Rapid and strong topohesives. Extreme Mech. Lett. 2020, 39, 100803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wang, W.; Dong, W. Interpenetrating polymer networks in polyvinyl alcohol/cellulose nanocrystals hydrogels to develop absorbent materials. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 200, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Bai, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, W.; Ma, P.; Dong, W. DN strategy constructed photo-crosslinked PVA/CNC/P(NIPPAm-co-AA) hydrogels with temperature-sensitive and pH-sensitive properties. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 13453–13460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; He, X.; Yang, B.; Lai, L.; Chen, N.; Hu, J.; Lu, Q. Dual physically cross-linked hydrogels incorporating hydrophobic interactions with promising repairability and ultrahigh elongation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2008187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodero, A.; Pianella, L.; Vicini, S.; Alloisio, M.; Ottonelli, M.; Castellano, M. Alginate-based hydrogels prepared via ionic gelation: An experimental design approach to predict the crosslinking degree. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 118, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Duan, L.; Gao, G. Bioinspired nucleobase-driven nonswellable adhesive and tough gel with excellent underwater adhesion. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 6644–6651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, Z.; Hou, R.; Gao, G. Bioinspired adhesive hydrogel driven by adenine and thymine. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 17645–17652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Lu, J.; Ding, M.; Chen, Y. Synthesis and properties of poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogels with high strength and toughness. Polym. Test. 2022, 108, 107516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Su, C.; Chen, Y.; Tian, S.; Lu, C.; Huang, W.; Lv, Q. Current understanding of the applications of photocrosslinked hydrogels in biomedical engineering. Gels 2022, 8, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Liu, S.; Feng, W. PVA hydrogel properties for biomedical application. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2011, 4, 1228–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Hua, M.; Alsaid, Y.; Du, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Lo, C.; Wang, C.; Wu, D.; Yao, B.; et al. Poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogels with broad-range tunable mechanical properties via the hofmeister effect. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2007829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, C.M.; Peppas, N.A. Cellular PVA hydrogels produced by freeze/thawing. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2000, 76, 2075–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xia, H.; Zhao, Y. Poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogel can autonomously self-heal. ACS Macro Lett. 2012, 1, 1233–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, C.M.; Peppas, N.A. Structure and morphology of freeze/thawed PVA hydrogels. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 2472–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Yu, C.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, S.; Ma, P.; Dong, W. Mussel-inspired cellulose-based adhesive with underwater adhesion ability. Cellulose 2021, 29, 893–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.; Sun, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Ding, Y.; Cheng, J.; Guo, M. Mechanical, microstructural, and rheological characterization of gelatin-dialdehyde starch hydrogels constructed by dual dynamic crosslinking. LWT 2022, 161, 113374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Zhao, X.; Xu, C.; Wang, L.; Xia, Y. Progress in the mechanical enhancement of hydrogels: Fabrication strategies and underlying mechanisms. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 60, 2525–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Bai, J.; Shao, K.; Tang, W.; Zhao, X.; Lin, D.; Huang, S.; Chen, C.; Ding, Z.; Ye, J. Poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogels: The old and new functional materials. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2021, 2021, 2225426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sennakesavan, G.; Mostakhdemin, M.; Dkhar, L.K.; Seyfoddin, A.; Fatihhi, S. Acrylic acid/acrylamide based hydrogels and its properties—A review. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2020, 180, 109308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gombert, Y.; Roncoroni, F.; Sánchez-Ferrer, A.; Spencer, N.D. The hierarchical bulk molecular structure of poly (acrylamide) hydrogels: Beyond the fishing net. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 9789–9798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-García, J.M.; Liras, M.; Garrido, I.Q.; Gallardo, A.; París, R. Swelling control in thermo-responsive hydrogels based on 2-(2-methoxyethoxy) ethyl methacrylate by crosslinking and copolymerization with N-isopropylacrylamide. Polym. J. 2011, 43, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Barney, C.W.; Erk, K.A. Effect of ionic crosslinking on the swelling and mechanical response of model superabsorbent polymer hydrogels for internally cured concrete. Mater. Struct. Constr. 2015, 48, 2261–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahkam, M.; Doostie, L. The relation between swelling properties and cross-linking of hydrogels designed for colon-specific drug delivery. Drug Deliv. J. Deliv. Target. Ther. Agents 2005, 12, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avramescu, A.; Noguer, T.; Avramescu, M.; Marty, J.-L. Screen-printed biosensors for the control of wine quality based on lactate and acetaldehyde determination. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 458, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldatkin, A.P.; Montoriol, J.; Sant, W.; Martelet, C.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Development of potentiometric creatinine-sensitive biosensor based on ISFET and creatinine deiminase immobilised in PVA/SbQ photopolymeric membrane. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2002, 21, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Yu, C.; Kumar, H.; He, X.; Lu, Q.; Bai, H.; Kim, K.; Hu, J. The Effect of Crosslinking Degree of Hydrogels on Hydrogel Adhesion. Gels 2022, 8, 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8100682
Li Z, Yu C, Kumar H, He X, Lu Q, Bai H, Kim K, Hu J. The Effect of Crosslinking Degree of Hydrogels on Hydrogel Adhesion. Gels. 2022; 8(10):682. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8100682
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhangkang, Cheng Yu, Hitendra Kumar, Xiao He, Qingye Lu, Huiyu Bai, Keekyoung Kim, and Jinguang Hu. 2022. "The Effect of Crosslinking Degree of Hydrogels on Hydrogel Adhesion" Gels 8, no. 10: 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8100682
APA StyleLi, Z., Yu, C., Kumar, H., He, X., Lu, Q., Bai, H., Kim, K., & Hu, J. (2022). The Effect of Crosslinking Degree of Hydrogels on Hydrogel Adhesion. Gels, 8(10), 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8100682










