Hydrogel Adsorbents for the Removal of Hazardous Pollutants—Requirements and Available Functions as Adsorbent
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Basic Requirements for Adsorbents
3. Gel Adsorbents
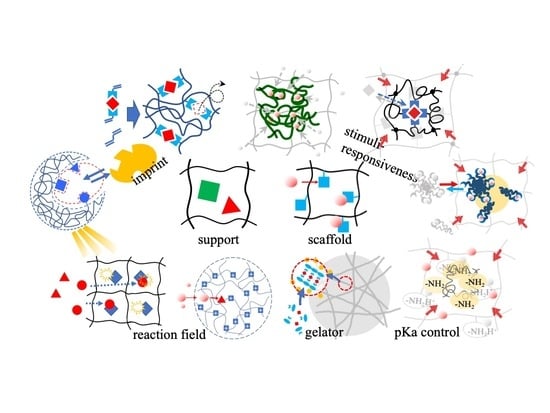
4. Classification of Hydrogels Based on the Roles or Functions of the Polymer Networks
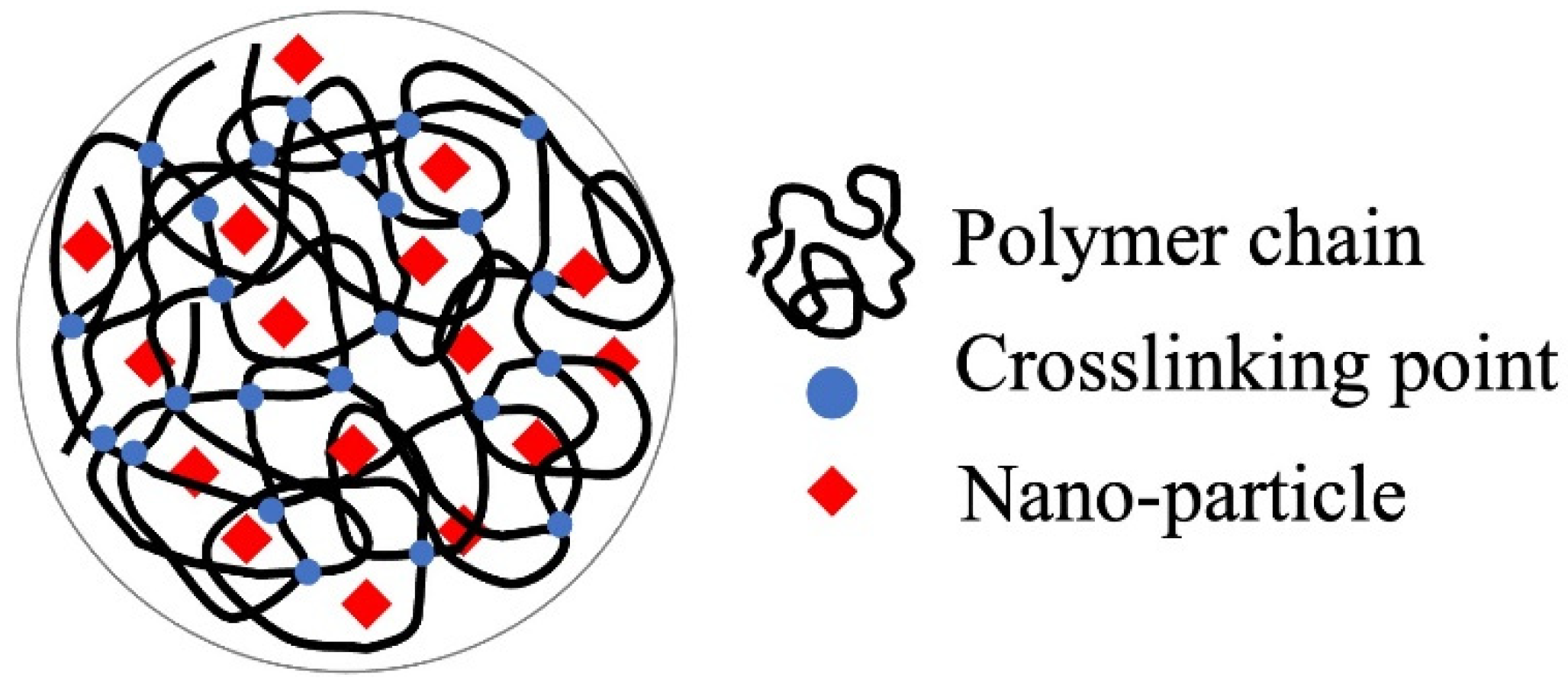
4.1. Matrix for Immobilization
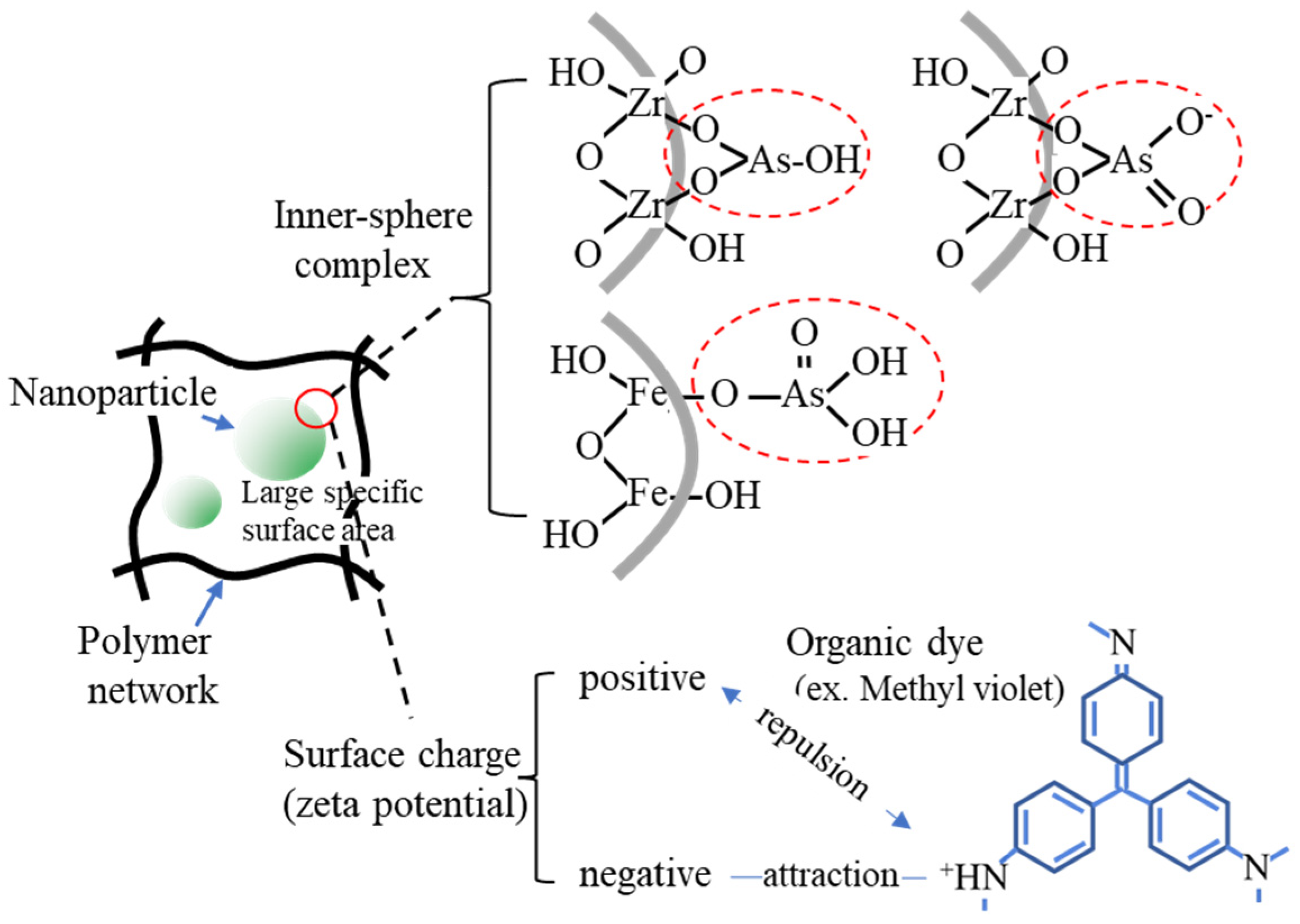
4.2. Scaffold Fixing Functional Groups
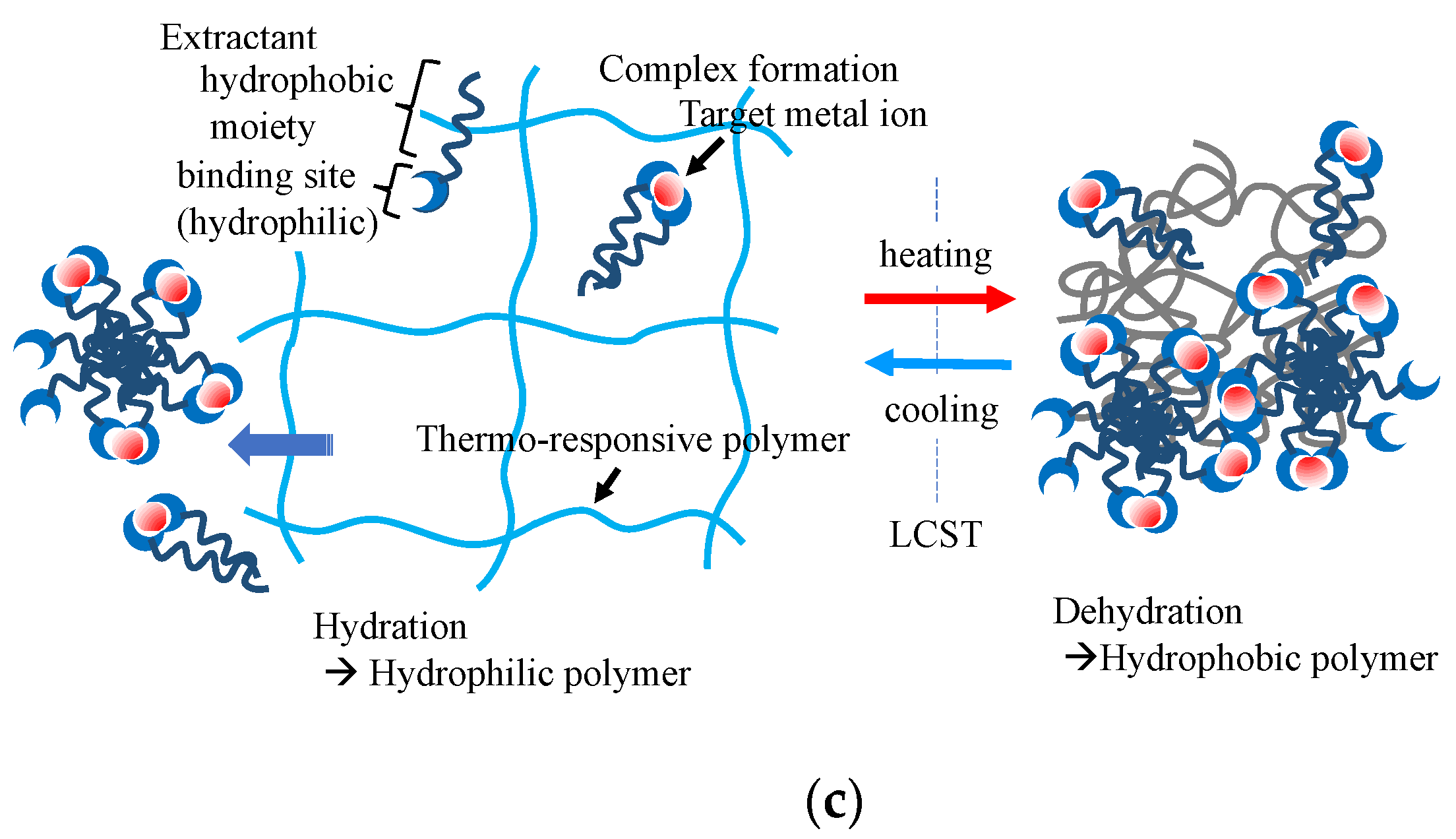
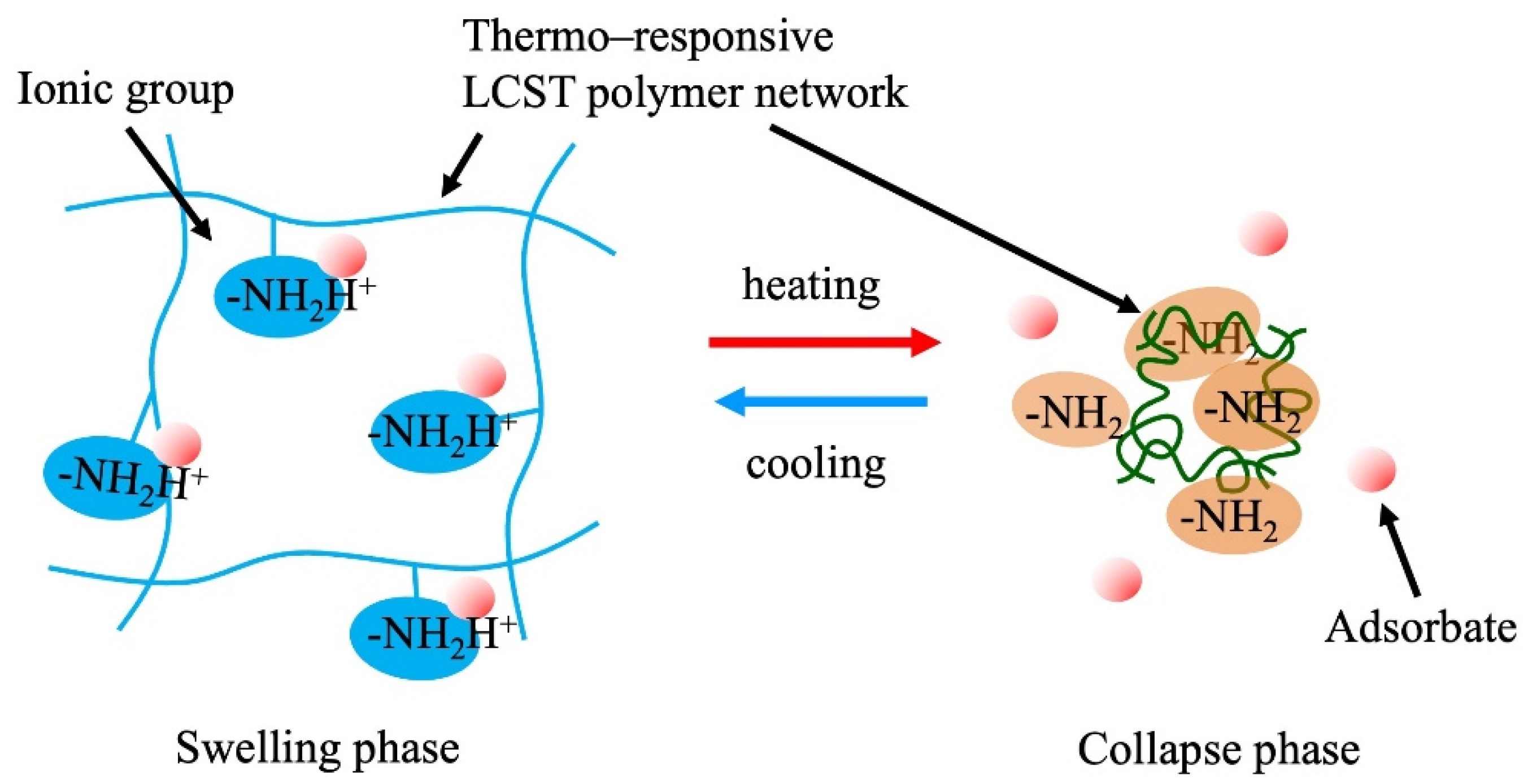
4.3. Stimuli-Responsive Network
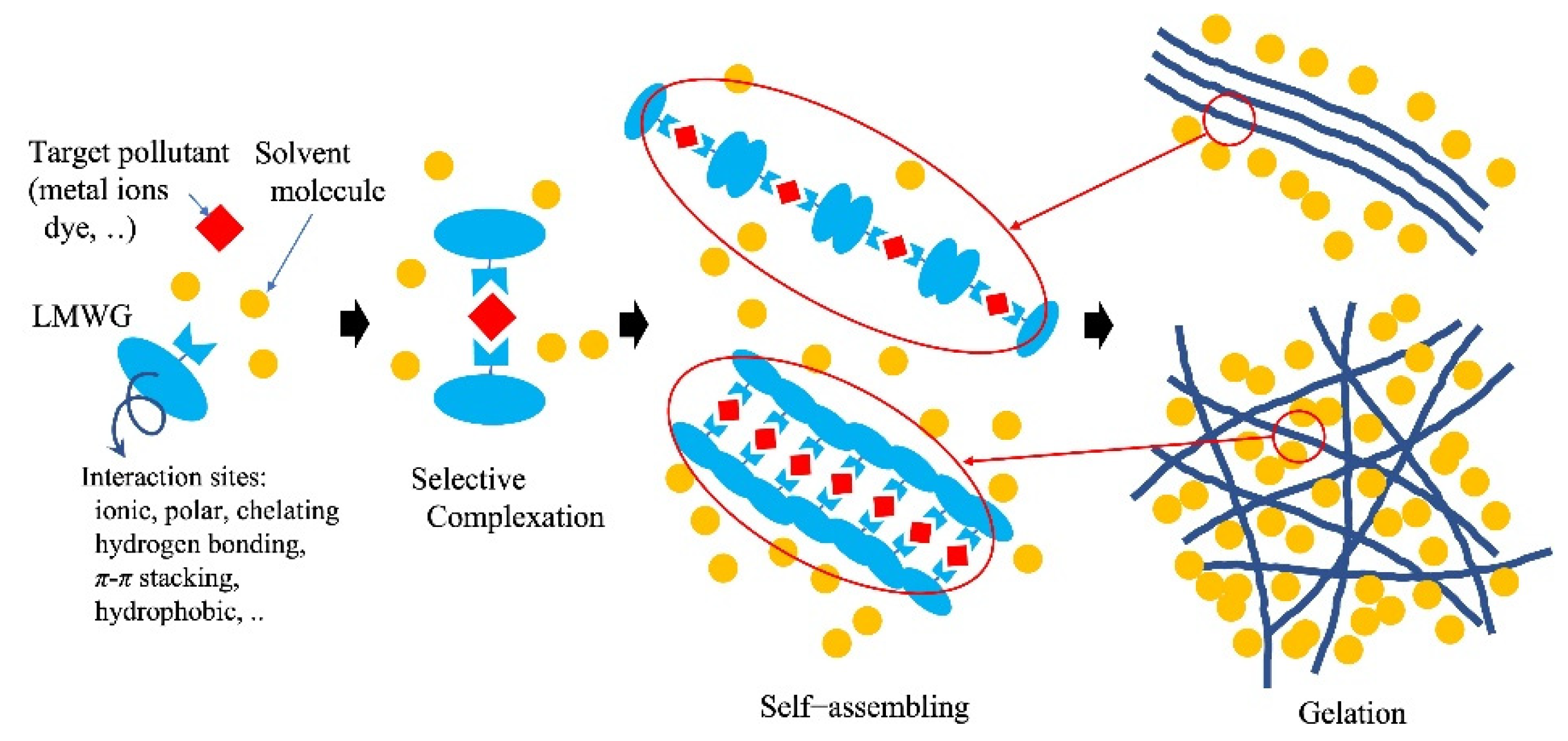
4.4. Contaminant Uptake with Self-Assembling and Gelation
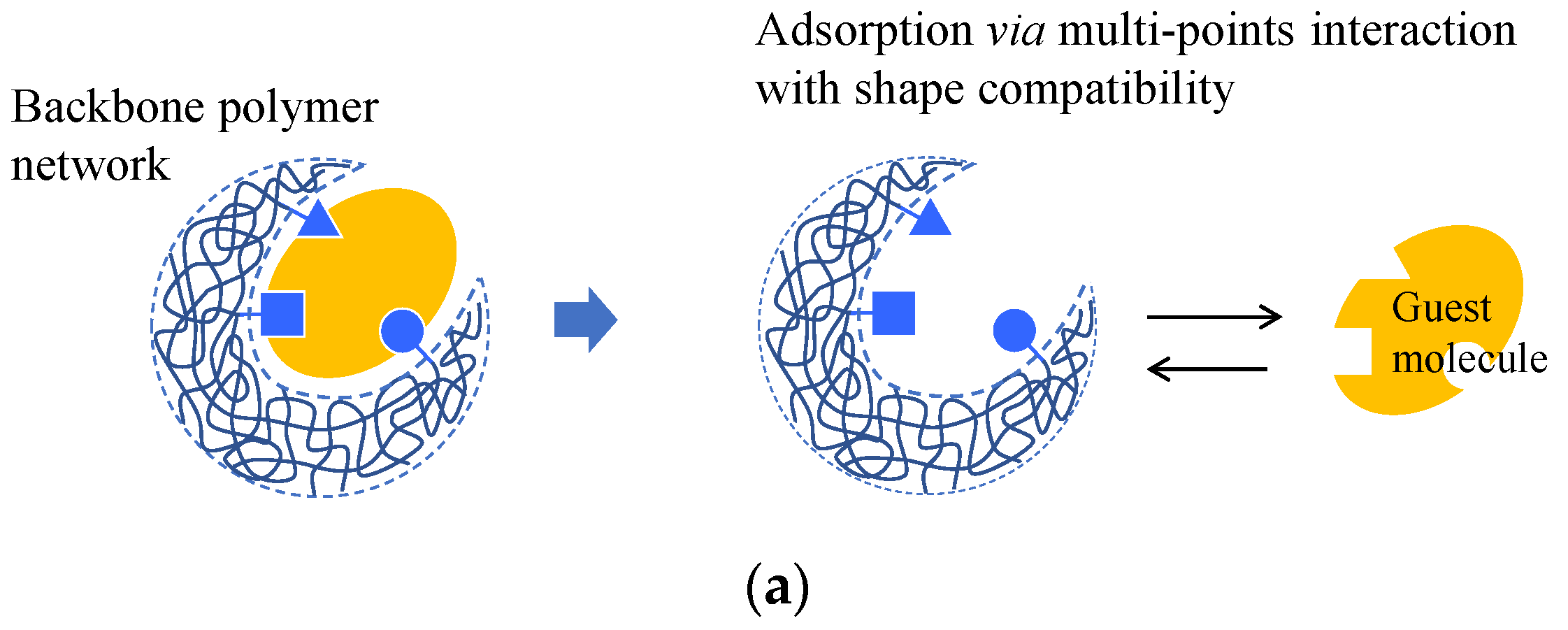
4.5. Molecular and Ion Imprint Networks
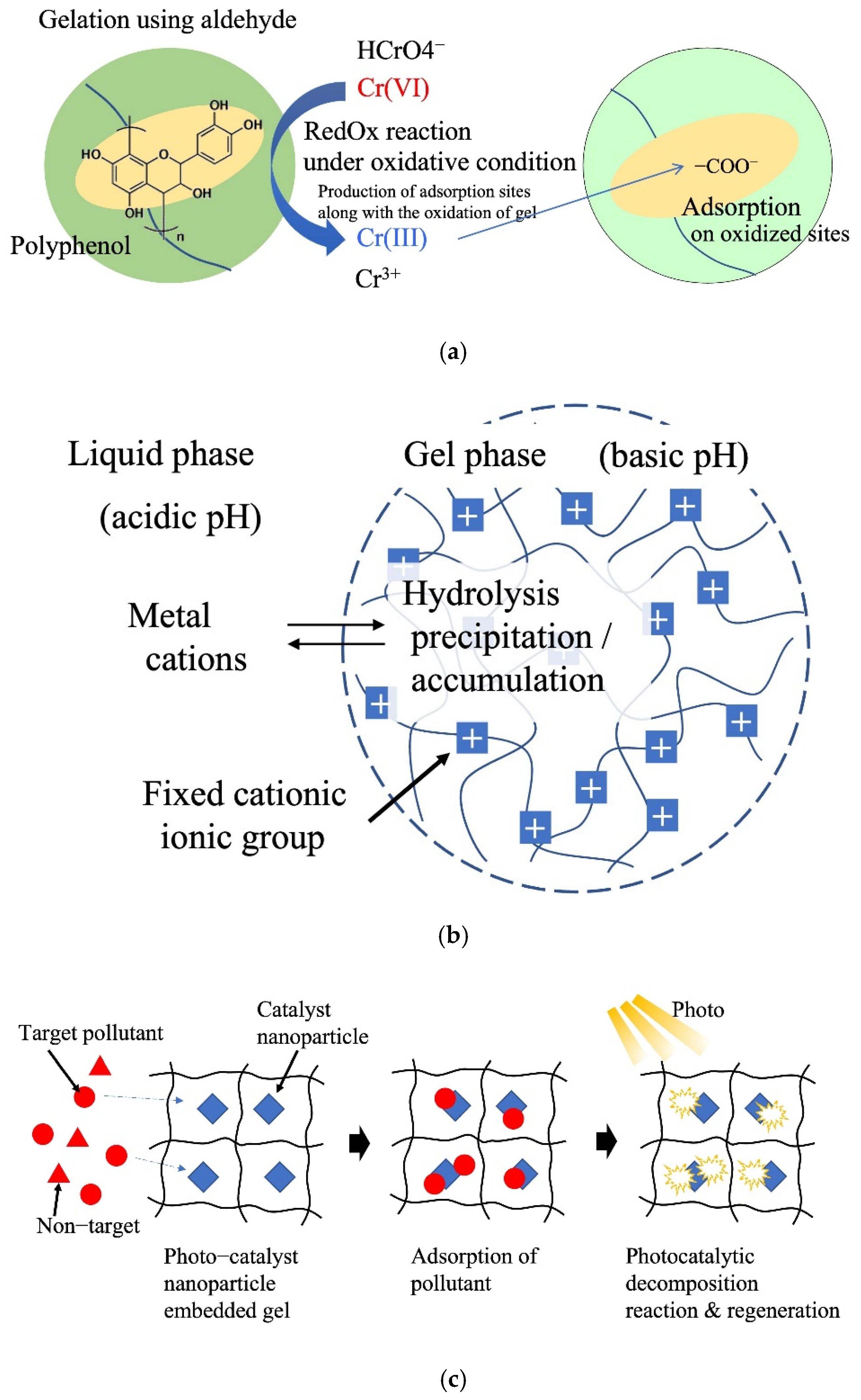
4.6. Reaction Field
4.7. Dissociation Control of Functional Groups in the Polymer Network
4.8. Diversification of the Application
5. Perspective
6. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, F.-C.; Tseng, R.-L.; Juang, R.-S. A review and experimental verification of using chitosan and its derivatives as adsorbents for selected heavy metals. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshaid, A.; Hamid, A.; Muhammad, N.; Naseer, A.; Ghauri, M.; Iqbal, J.; Rafiq, S.; Shah, N.S. Cellulose-based Materials for the Removal of Heavy Metals from Wastewater—An Overview. ChemBioEng Rev. 2017, 4, 240–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Tran, V.; Park, D.; Lee, Y.-C. Hydrogel applications for adsorption of contaminants in water and wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 24569–24599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalla, A.H.; Bhat, M.A.; Yaseen, Z. Hydrogels for removal of recalcitrant organic dyes: A conceptual overview. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5938–5949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaddar, P.; Kumar, S.; Kim, K.-H. Polymer Hydrogels and Their Applications Toward Sorptive Removal of Potential Aqueous Pollutants. Polym. Rev. 2019, 59, 418–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, K.; Farooqi, Z.H.; Rehman, M.A.U.; Ghufran, M. Microgels as efficient adsorbents for the removal of pollutants from aqueous medium. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2018, 35, 285–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhmetzhan, A.; Myrzakhmetova, N.; Amangeldi, N.; Kuanyshova, Z.; Akimbayeva, N.; Dosmaganbetova, S.; Toktarbay, Z.; Longinos, S.N. A Short Review on the N,N-Dimethylacrylamide-Based Hydrogels. Gels 2021, 7, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruthven, D.M. Principles of Adsorption and Adsorption Process; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: NewYork, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, M. Adsorption Engineering; Chemical Engineering Monographs; Elsevier Science: Tokyo, Japan, 1990; 306p. [Google Scholar]
- Amid, H.; Mazé, B.; Flickinger, M.C.; Pourdeyhimi, B. Hybrid adsorbent nonwoven structures: A review of current technologies. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 4173–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Lou, H.; Xu, X.; Xu, W.; Yang, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y. Preparation of PP non-woven fabric with good heavy metal adsorption performance via plasma modification and graft polymerization. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 539, 148195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakita, T.; Seida, Y.; Murota, A.; Fujiki, J.; Furuya, E. Applicability of theKFavmodel in the prediction of fixed bed breakthrough curve. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2016, 35, 178–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakita, T.; Fan, H.-J.; Seida, Y.; Kinoshita, T.; Furuya, E. A simple method for the determination of adsorption kinetic parameters using circulating-type shallow bed reactor (CSBR). Desalination Water Treat. 2017, 92, 1944–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakita, T.; Fan, H.-J.; Seida, Y.; Fujiki, J.; Furuya, E. A simplified technique to determine intraparticle diffusivity of macro-reticular resins. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2016, 26, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonetaka, N.; Seida, Y.; Nakano, T.; Furuya, E. Determination of intraparticle diffusivity and fluid-to-solid mass transfer coefficient from single concentration history curve in circulated-type fixed-bed reactor. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2018, 36, 571–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amsden, B. Solute Diffusion within Hydrogels. Mechanisms and Models. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 8382–8395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaro, L.; Zhu, X. Physical models of diffusion for polymer solutions, gels and solids. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1999, 24, 731–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagel, V.; Haraszti, T.; Boehm, H. Diffusion and interaction in PEG-DA hydrogels. Biointerphases 2013, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjiev, N.A.; Amsden, B.G. An assessment of the ability of the obstruction-scaling model to estimate solute diffusion coefficients in hydrogels. J. Control. Release 2015, 199, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puguan, J.M.C.; Yu, X.; Kim, H. Diffusion characteristics of different molecular weight solutes in Ca–alginate gel beads. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 469, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, T.; Kaji, M.; Nagatsu, Y.; Tokuyama, H. Propagating Precipitation Waves in Disordered Media. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 8027–8032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosecki, M.; Kazmierski, S.; Gosecka, M. Diffusion-Controllable Biomineralization Conducted In Situ in Hydrogels Based on Reversibly Cross-Linked Hyperbranched Polyglycidol. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 3418–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, D.; Zhang, E.; Ji, F.; Qin, Z.; Yang, J.; Yao, F. Establishment of a Physical Model for Solute Diffusion in Hydrogel: Understanding the Diffusion of Proteins in Poly(sulfobetaine methacrylate) Hydrogel. J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 121, 800–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokuyama, H.; Nakahata, Y.; Ban, T. Diffusion coefficient of solute in heterogeneous and macroporous hydrogels and its correlation with the effective crosslinking density. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 595, 117533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyama, H. Polymeric Monolith—New Fabrication Methods and Applications. Kobunshi Ronbunshu 2010, 67, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nischang, I. Porous polymer monoliths: Morphology, porous properties, polymer nanoscale gel structure and their impact on chromatographic performance. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1287, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosoda, N.; Tsujimoto, T.; Uyama, H. Plant oil-based green composite using porous poly(3-hydroxybutyrate). Polym. J. 2014, 46, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuyama, H.; Kanehara, A. Novel Synthesis of Macroporous Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Hydrogels Using Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Langmuir 2007, 23, 11246–11251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokuyama, H.; Sumida, H.; Kanehara, A.; Nii, S. Effect of surfactants on the porous structure of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels prepared by an emulsion templating method. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2009, 287, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverstein, M.S. Emulsion-templated porous polymers: A retrospective perspective. Polymer 2014, 55, 304–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Fan, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, J. Synthesis of Emulsion-Templated Magnetic Porous Hydrogel Beads and Their Application for Catalyst of Fenton Reaction. Langmuir 2018, 34, 3669–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlačík, T.; Nonoyama, T.; Guo, H.; Kiyama, R.; Nakajima, T.; Takeda, Y.; Kurokawa, T.; Gong, J.P. Preparation of Tough Double- and Triple-Network Supermacroporous Hydrogels through Repeated Cryogelation. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 8576–8586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teodosiu, C.; Wenkert, R.; Tofan, L.; Paduraru, C. Advances in preconcentration/removal of environmentally relevant heavy metal ions from water and wastewater by sorbents based on polyurethane foam. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2014, 30, 403–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Chen, X.; Yuan, B.; Fu, M.-L. A facile foaming-polymerization strategy to prepare 3D MnO2 modified biochar-based porous hydrogels for efficient removal of Cd(II) and Pb(II). Chemosphere 2020, 239, 124745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seida, Y.; Nakano, Y.; Ichida, H. Surface Properties of Temperature-Sensitive N-isopropylacrylamide-Copolymer Gels. Kagaku Kogaku Ronbunshu 1992, 18, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yue, Y.; Wang, X.; Han, J.; Yu, L.; Chen, J.; Wu, Q.; Jiang, J. Effects of nanocellulose on sodium alginate/polyacrylamide hydrogel: Mechanical properties and adsorption-desorption capacities. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 206, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossen, M.J.; Sarkar, S.D.; Uddin, M.M.; Roy, C.K.; Azam, M.S. Mussel-Inspired Adhesive Nano-Filler for Strengthening Polyacrylamide Hydrogel. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 8906–8914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, H.; Tsunemitsu, K.; Onoe, H.; Obata, K.; Sugioka, K.; Terakawa, M. Microfabrication of cellulose nanofiber-reinforced hydrogel by multiphoton polymerization. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Liu, Y.; Ali, O.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, T.; Liu, C.; Luo, S. Fast adsorption of heavy metal ions by waste cotton fabrics based double network hydrogel and influencing factors insight. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Li, T.; Liu, Y.; Cai, T.; Wei, Y.; Dong, W.; Chen, H. Rice husk derived double network hydrogel as efficient adsorbent for Pb(II), Cu(II) and Cd(II) removal in individual and multicomponent systems. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 290, 121793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Yang, J.; Lin, L.; Peng, K.; Chen, Y.; Jin, S.; Yao, W. Construction of physically crosslinked chitosan/sodium alginate/calcium ion double-network hydrogel and its application to heavy metal ions removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 393, 124728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Lu, X.; Li, X. Selective removals of heavy metals (Pb2+, Cu2+, and Cd2+) from wastewater by gelation with alginate for effective metal recovery. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 308, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, Y.; Wang, S.; Vincent, T.; Desbrieres, J.; Faur, C.; Guibal, E. New highly-percolating alginate-PEI membranes for efficient recovery of chromium from aqueous solutions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 225, 115177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwakeel, K.Z. Environmental Application of Chitosan Resins for the Treatment of Water and Wastewater: A Review. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2010, 31, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemrabat, E.; Jaafari, K.; Benkhouja, K.; Touaiher, M. Removal of heavy-metal ion by adsorption on chitosan gel beads. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 2013, 15, 1298–1302. [Google Scholar]
- Francis, A.O.; Zaini, M.A.A.; Muhammad, I.M.; Abdulsalam, S.; El-Nafaty, U.A. Physicochemical modification of chitosan adsorbent: A perspective. Biomass-Convers. Biorefinery 2021, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godiya, C.B.; Cheng, X.; Deng, G.; Li, D.; Lu, X. Silk fibroin/polyethylenimine functional hydrogel for metal ion adsorption and upcycling utilization. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musarurwa, H.; Tavengwa, N.T. Application of carboxymethyl polysaccharides as bio-sorbents for the sequestration of heavy metals in aquatic environments. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 237, 116142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhre, N.A.; Ibrahim, B.M. The use of new chemically modified cellulose for heavy metal ion adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 343, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, S.M.; Zulkifli, M.Z.A.; Nordin, D.; Teow, Y.H. Synthesis of Cellulose/Nano-hydroxyapatite Composite Hydrogel Absorbent for Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Palm Oil Mill Effluents. J. Polym. Environ. 2021, 29, 4106–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, Y.; Takeshita, K.; Tsutsumi, T. Adsorption mechanism of hexavalent chromium by redox within condensed-tannin gel. Water Res. 2000, 35, 496–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisada, S.; Kim, Y.-H.; Ogata, T.; Marutani, Y.; Nakano, Y. Improved Adsorption Behaviors of Amine-Modified Tannin Gel for Palladium and Platinum Ions in Acidic Chloride Solutions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 1875–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacelo, H.A.M.; Santos, S.C.R.; Botelho, C.M.S. Tannin-based biosorbents for environmental applications—A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 303, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.; Parajuli, D.; Ghimire, K.N.; Biswas, B.K.; Kawakita, H.; Oshima, T.; Ohto, K. Biosorbents for Removing Hazardous Metals and Metalloids. Materials 2017, 10, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, S.; Chaudhary, J.; Kumar, V.; Thakur, V.K. Progress in pectin based hydrogels for water purification: Trends and challenges. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 238, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demey, H.; Vincent, T.; Guibal, E. A novel algal-based sorbent for heavy metal removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 332, 582–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Tsafrakidou, P.; Triantafyllidis, K.S.; Kornaros, M.; Anastopoulos, I. Aloe vera waste biomass-based adsorbents for the removal of aquatic pollutants: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 227, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikder, M.T.; Rahman, M.M.; Jakariya, M.; Hosokawa, T.; Kurasaki, M.; Saito, T. Remediation of water pollution with native cyclodextrins and modified cyclodextrins: A comparative overview and perspectives. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 355, 920–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Gao, Z.; Wu, D.; Jiang, J.; Sun, Y.; Luo, C. Efficient Pb(II) removal using sodium alginate–carboxymethyl cellulose gel beads: Preparation, characterization, and adsorption mechanism. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 137, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godiya, C.; Liang, M.; Sayed, S.M.; Li, D.; Lu, X. Novel alginate/polyethyleneimine hydrogel adsorbent for cascaded removal and utilization of Cu2+ and Pb2+ ions. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 232, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Liu, Y.; Ju, B.; Tian, Y. Preparation of thermoresponsive alginate/starch ether composite hydrogel and its application to the removal of Cu(II) from aqueous solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 294, 122192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuyan, M.M.; Adala, O.B.; Okabe, H.; Hidaka, Y.; Hara, K. Selective adsorption of trivalent metal ions from multielement solution by using gamma radiation-induced pectin-acrylamide-(2-Acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propanesulfonic acid) hydrogel. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Yang, Y.; Liang, Z.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, A. Preparation of Chitosan/Calcium Alginate/Bentonite Composite Hydrogel and Its Heavy Metal Ions Adsorption Properties. Polymers 2021, 13, 1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Tong, X.; Pan, W.; Zeng, Q.; You, S.; Shen, J. Recent advances in polysaccharide-based adsorbents for wastewater treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 315, 128221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.Y.C.; Goh, S.S.; Liow, S.S.; Xue, K.; Loh, X.J. Molecular gel sorbent materials for environmental remediation and wastewater treatment. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 18759–18791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hande, P.E.; Samui, A.B.; Kulkarni, P.S. Highly selective monitoring of metals by using ion-imprinted polymers. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 7375–7404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samiey, B.; Cheng, C.-H.; Wu, J. Organic-Inorganic Hybrid Polymers as Adsorbents for Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Solutions: A Review. Materials 2014, 7, 673–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claverie, M.; Garcia, J.; Prevost, T.; Brendlé, J.; Limousy, L. Inorganic and Hybrid (Organic–Inorganic) Lamellar Materials for Heavy metals and Radionuclides Capture in Energy Wastes Management-A Review. Materials 2019, 12, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maleki, H. Recent advances in aerogels for environmental remediation applications: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 300, 98–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, C.; Yuan, B. Polymer-based Electrochemical Sensing Platform for Heavy Metal Ions Detection—A Critical Review. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2019, 14, 8760–8771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajmal, M.; Siddiq, M.; Aktas, N.; Sahiner, N. Magnetic Co–Fe bimetallic nanoparticle containing modifiable microgels for the removal of heavy metal ions, organic dyes and herbicides from aqueous media. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 43873–43884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Dai, Y.; Wu, Y.; Lu, G.; Cao, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, K.; Yang, H.; Xia, Y.; Wen, X.; et al. Facile preparation of polyacrylamide/chitosan/Fe3O4 composite hydrogels for effective removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 234, 115882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z. Heavy metals removal using hydrogel-supported nanosized hydrous ferric oxide: Synthesis, characterization, and mechanism. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 776–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokuyama, H.; Kitamura, E.; Seida, Y. Development of zirconia nanoparticle-loaded hydrogel for arsenic adsorption and sensing. React. Funct. Polym. 2020, 146, 104427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safi, S.R.; Gotoh, T.; Iizawa, T.; Nakai, S. Development and regeneration of composite of cationic gel and iron hydroxide for adsorbing arsenic from ground water. Chemosphere 2019, 217, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.-M.; Zou, S.-W.; Nanayakkara, K.N.; Matsuura, T.; Chen, J.P. Adsorptive removal of arsenic from aqueous solution by a PVDF/zirconia blend flat sheet membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 374, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.-M.; Yu, L.; Chen, J.P. Removal of methylated arsenic using a nanostructured zirconia-based sorbent: Process performance and adsorption chemistry. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 367, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, G.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, S.; Naushad, M.; Dwivedi, R.P.; ALOthman, Z.A.; Mola, G.T. Novel development of na-noparticles to bimetallic nanoparticles and their composites: A review. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2019, 31, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harikumar, P.S.; Hridya, T.K. Application of CuNi bimetallic nanoparticle as an adsorbent for the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 101, 869–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuyama, H.; Yoshida, T.; He, L. Preparation of Novel Emulsion Gel Adsorbents and Their Adsorption Properties for Heavy-Metal Ions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 10270–10277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuyama, H.; Yoshida, T. Emulsion gel beads prepared by sedimentation polymerization using two-fluid atomization and their Pd(II) ion adsorption properties. React. Funct. Polym. 2013, 73, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Xi, X.; Dai, L.; Tong, S.; Chen, Z. Hydrogel as a Superwetting Surface Design Material for Oil/Water Separation: A Review. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 8, 2002030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mier, A.; Nestora, S.; Rangel, P.X.M.; Rossez, Y.; Haupt, K.; Bui, B.T.S. Cytocompatibility of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Deodorants: Evaluation on Human Keratinocytes and Axillary-Hosted Bacteria. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 3439–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasapollo, G.; Del Sole, R.; Mergola, L.; Lazzoi, M.R.; Scardino, A.; Scorrano, S.; Mele, G.; Vasapollo, G.; Del Sole, R.; Mergola, L.; et al. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: Present and Future Prospective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 5908–5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Royal Society of Chemistry. The Merck Index Online; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2022; Available online: https://www.rsc.org/Merck-Index/searchresults?searchterm=acrylamide (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- Sunaga, S.; Kokado, K.; Sada, K. Lipophilic polyelectrolyte gel derived from phosphonium borate can absorb a wide range of organic solvents. Soft Matter 2017, 14, 581–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prathap, A.; Sureshan, K.M. Organogelator-Cellulose Composite for Practical and Eco-Friendly Marine Oil-Spill Recovery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 9405–9409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seida, Y.; Imai, T.; Murata, K.; Nakano, Y. Thermo-responsivity of the polyacrylate-adsorbed metal cation and its hydration structure. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2008, 26, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuyama, H.; Yanagawa, K.; Sakohara, S. Temperature swing adsorption of heavy metals on novel phosphate-type adsorbents using thermosensitive gels and/or polymers. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 50, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuyama, H.; Iwama, T. Temperature-Swing Solid-Phase Extraction of Heavy Metals on a Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Hydrogel. Langmuir 2007, 23, 13104–13108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuyama, H.; Iwama, T. Solid-phase extraction of indium(III) ions onto thermosensitive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide). Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 68, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuyama, H.; Hisaeda, J.; Nii, S.; Sakohara, S. Removal of heavy metal ions and humic acid from aqueous solutions by co-adsorption onto thermosensitive polymers. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 71, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Bai, Y.; Li, W.; Gao, Z.; Chen, S.; Qiu, N.; Satoh, T.; Kakuchi, T.; Duanb, Q. Synthesis and characterization of Eu(III) com-plexes of modified D-glucosamine and poly(N-isopropylacrylamide). Mat. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 78, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokuyama, H.; Kanehara, A. Temperature swing adsorption of gold(III) ions on poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) gel. React. Funct. Polym. 2007, 67, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Jacques, A.L.; Lujan-Montelongo, J.A.; Silva-Cuevas, C.; Cortez-Valadez, M.; Estevez, M.; Hernandez-Martínez, A.R. Lead (II) removal by poly(N,N-dimethylacrylamide-co-2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate). Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 101, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleyman, R.; Pourjavadi, A.; Monfared, A.; Khorasani, Z. Novel salep-based chelating hydrogel for heavy metal removal from aqueous solutions. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2016, 27, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Chiang, C.L.; Chen, C.R. Removal of heavy metal ions by a chelating resin containing glycine as chelating groups. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 54, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.G.; Saleh, A.S.; Elsharma, E.M.; Metwally, E.; Siyam, T. Gamma radiation-induced preparation of poly(1-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone-co-sodium acrylate) for effective removal of Co(II), Ni(II), and Cu(II). Polym. Bull. 2019, 76, 303–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omondi, B.A.; Okabe, H.; Hidaka, Y.; Hara, K. Poly (1,4-diazocane-5,8-dione) macrocyclic-functionalized hydrogel for high selectivity transition metal ion adsorption. React. Funct. Polym. 2018, 125, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omondi, B.A.; Okabe, H.; Hidaka, Y.; Hara, K. Fabrication of poly (1,4-dioxa-7,12-diazacyclotetradecane-8,11-dione) macrocyclic functionalized hydrogel for high selective adsorption of Cr, Cu and Ni. React. Funct. Polym. 2018, 130, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Rozhina, E.; Konnova, S.; Kryuchkova, M.; Khaertdinov, N.; Fakhrullin, R. Organic-nanoclay composite materials as removal agents for environmental decontamination. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 40553–40564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, H.; Saha, S.; Kailasa, S.K.; Singhal, R.K. Present status of hybrid materials for potable water decontamination: A review. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2020, 6, 3214–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanazawa, H.; Matsushima, Y.; Okano, T. Temperature-responsive chromatography. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 1998, 17, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seida, Y.; Nakano, Y. Concept to control the phase behavior of stimulisensitive polymer gel. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 1995, 28, 425–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tokuyama, H.; Kanazawa, R.; Sakohara, S. Equilibrium and kinetics for temperature swing adsorption of a target metal on molecular imprinted thermosensitive gel adsorbents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 44, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, R.G. Molecular Gels: Structure and Dynamics (Monographs in Supramolecular Chemistry) (GLD); The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Vibhute, A.M.; Muvvala, V.; Sureshan, K.M. A Sugar-Based Gelator for Marine Oil-Spill Recovery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 7782–7785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, K.N.; McNeil, A.J. Streamlined approach to a new gelator: Inspiration from solid-state interactions for a mercury-induced gelation. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 3511–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, T.; Häring, M.; Haldar, D.; Díaz, D.D. Phenylalanine and derivatives as versatile low-molecular-weight gelators: Design, structure and tailored function. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 6, 38–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patwa, A.; Labille, J.; Bottero, J.-Y.; Thiéry, A.; Barthélémy, P. Decontamination of nanoparticles from aqueous samples using supramolecular gels. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 2547–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Llansola, F.; Escuder, B.; Miravet, J.F.; Hermida-Merino, D.; Hamley, I.W.; Cardin, C.J.; Hayes, W. Selective and highly efficient dye scavenging by a pH-responsive molecular hydrogelator. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 7960–7962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanazawa, R.; Yoshida, T.; Gotoh, T.; Sakohara, S. Preparation of Molecular Imprinted Thermosensitive Gel Adsorbents and Adsorption/Desorption Properties of Heavy Metal Ions by Temperature Swing. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2004, 37, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, T. Focusing Review, Development and Applications of Fragment Imprinting Technique. Chromatography 2008, 29, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, I.; Siddiqi, W.A.; Qadir, S.; Ahmad, T. Synthesis and characterization of molecular imprinted nanomaterials for the removal of heavy metals from water. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2018, 7, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, Y.; Kubo, T.; Kaya, K.; Hosoya, K. Effective Recognition on the Surface of a Polymer Prepared by Molecular Imprinting Using Ionic Complex. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 2911–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, T. Development of Application Techniques Based on Molecular Imprinting for Molecular Selective Pretreatments. Bunseki Kagaku 2012, 61, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, D.; Shi, Z.; Ma, S. Mercury nano-trap for effective and efficient removal of mercury(II) from aqueous solution. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, T.; Ma, R.; Ke, K.; Zhang, D.; Qi, D.; Zhao, H. Synthesis of gallic acid functionalized magnetic hydrogel beads for enhanced synergistic reductio and adsorption of aqueous chromium. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 408, 127327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, Y.; Seida, Y.; Uchida, M.; Yamamoto, S. Behavior of ions within hydrogel and its swelling properties. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 1990, 23, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gotoh, T.; Ogawa, A.; Nakata, D.; Iizawa, T.; Nakai, S. Metal Hydroxide Formation in DMAPAA Hydrogel and Novel Metal Ion Removal Method. Kagaku Kogaku Ronbunshu 2017, 43, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Li, Z.; Zhu, H. Adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of sulfamethoxazole by a novel composite hydrogel with visible light irradiation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 217, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Gotoh, T.; Nakai, S.; Tsunoji, N.; Sadakane, M. Poly(triethylene glycol methyl ether methacrylate) hydrogel as a carrier of phosphotungstic acid for acid catalytic reaction in water. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 3556–3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuyama, H.; Hamaguchi, R. TiO2 Nanoparticle-Loaded Poly(NIPA-co-NMA) Fiber Web for the Adsorption and Photocatalytic Degradation of 4-Isopropylphenol. Gels 2022, 8, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotoh, T.; Tanaka, K.; Arase, T.; Sakohara, S. A Novel Thermosensitive Gel Adsorbent for Phosphate Ions. Macromol. Symp. 2010, 295, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, R.; Hamasaki, A.; Miura, Y.; Hoshino, Y. Thermoresponsive CO2 absorbent for various CO2 concentrations: Tuning the pKa of ammonium ions for effective carbon capture. Polym. J. 2020, 53, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasawa, Y.; Seida, Y.; Gotoh, T.; Furuya, E. Influence of Hydrophobicity of Backbone Polymer in Thermo-Responsive Hydrogel with Immobilized Amine on Cycle Capacity for Absorption and Recovery of CO2. Polymers 2019, 11, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, S.U.; Siddiq, M.; Al-Lohedan, H.; Aktas, N.; Sahiner, M.; Demirci, S.; Sahiner, N. Fast removal of high quantities of toxic arsenate via cationic p(APTMACl) microgels. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 166, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Jiang, X.; Zhou, H.; Li, J. Preparation of magnetic hydrophobic polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)–cellulose nanofiber (CNF) aerogels as effective oil absorbents. Cellulose 2017, 25, 1217–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Fan, J.; Li, L.; Xu, T.; Yuan, W. Solar thermal energy storage based on sodium acetate trihydrate phase change hydrogels with excellent light-to-thermal conversion performance. Energy 2018, 165, 1240–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhivya, S.; Padma, V.V.; Santhini, E. Wound dressings—A review. BioMedicine 2015, 5(4), 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madden, B. Gels in Conservation of Art; Angelova, L.V., Ormsby, B., Townsend, J.H., Wolbers, R., Eds.; Archetype Publications: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa, N.; Fujii, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; Sano, C. On-site Surface Cleaning of Japanese Architecture Using Gels Incorporating Organic Solvents. Stud. Conserv. 2020, 65, P139–P141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirakawa, Y. Practical Use of Gels. In Seminor on Restoration Treatments for Cultural Property; Tokyo National Research Institute for Cultural Properties: Tokyo, Japan, 2021; pp. 25–31. Available online: http://id.nii.ac.jp/1440/00008990/ (accessed on 26 March 2022).
- He, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, S.; Feng, M.; Xu, G.; Zhu, H.; Ji, P.; Mao, H.; He, Y.; et al. A double-network polysaccharide-based composite hydrogel for skin wound healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 261, 117870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Synthetic Monomer/Polymer [84,85] | Natural Polymer [48,53,54,64] |
|---|---|
| vinyl derivatives: | carrageenan (−OSO3−, −OH) |
| acrylamide (−NH2, >C=O) | alginic acid (−COOH, −OH) |
| derivatives: | pectin (−COOH, −OH) |
| methylpropane sulfonic acid (−SO3−) | gellan gum (−COO−, −OH) |
| dimethyl aminopropyl (−N(CH3)2 | |
| trimethyl ammonium (−N(CH3)3+ ) | cellulose (−OH) |
| vinyl alcohol (−OH) | cyclodextrin (−OH) |
| acrylic acid (−COOH) | dextran (−OH) |
| styrene derivatives: −(C6H6) | |
| sulfonic acid (−SO3−) | chitin (>C=O, −NH, −OH) |
| poly(ethylene imine) (−N(CH3)3+) | chitosan (−NH2, −OH) |
| poly(ethylene glycol) (−O−) | |
| poly(aniline) (−N=, −(NH)−, −(C6H6)) | biomass (polyphenol, −OH) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seida, Y.; Tokuyama, H. Hydrogel Adsorbents for the Removal of Hazardous Pollutants—Requirements and Available Functions as Adsorbent. Gels 2022, 8, 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8040220
Seida Y, Tokuyama H. Hydrogel Adsorbents for the Removal of Hazardous Pollutants—Requirements and Available Functions as Adsorbent. Gels. 2022; 8(4):220. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8040220
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeida, Yoshimi, and Hideaki Tokuyama. 2022. "Hydrogel Adsorbents for the Removal of Hazardous Pollutants—Requirements and Available Functions as Adsorbent" Gels 8, no. 4: 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8040220
APA StyleSeida, Y., & Tokuyama, H. (2022). Hydrogel Adsorbents for the Removal of Hazardous Pollutants—Requirements and Available Functions as Adsorbent. Gels, 8(4), 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8040220