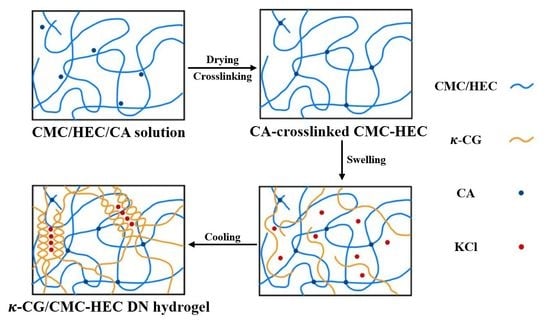
Double-Network Hydrogel Films Based on Cellulose Derivatives and κ-Carrageenan with Enhanced Mechanical Strength and Superabsorbent Properties
Abstract
Share and Cite
Kang, J.; Yun, S.I. Double-Network Hydrogel Films Based on Cellulose Derivatives and κ-Carrageenan with Enhanced Mechanical Strength and Superabsorbent Properties. Gels 2023, 9, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9010020
Kang J, Yun SI. Double-Network Hydrogel Films Based on Cellulose Derivatives and κ-Carrageenan with Enhanced Mechanical Strength and Superabsorbent Properties. Gels. 2023; 9(1):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9010020
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Jiseon, and Seok Il Yun. 2023. "Double-Network Hydrogel Films Based on Cellulose Derivatives and κ-Carrageenan with Enhanced Mechanical Strength and Superabsorbent Properties" Gels 9, no. 1: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9010020
APA StyleKang, J., & Yun, S. I. (2023). Double-Network Hydrogel Films Based on Cellulose Derivatives and κ-Carrageenan with Enhanced Mechanical Strength and Superabsorbent Properties. Gels, 9(1), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9010020