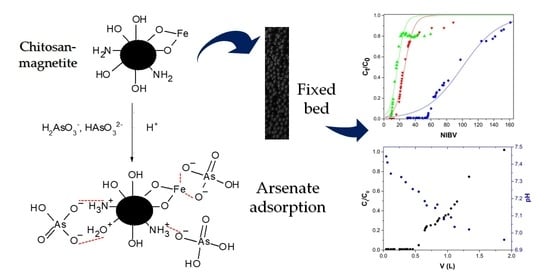
Removal of Arsenate by Fixed-Bed Columns Using Chitosan-Magnetite Hydrogel Beads and Chitosan Hydrogel Beads: Effect of the Operating Conditions on Column Efficiency
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of the Hydrogel Beads
2.1.1. Hydrogel Beads Composition
2.1.2. Average Diameter of the Hydrogel Beads
2.1.3. Characterization of the ChM Hydrogel Beads
2.1.4. Potentiometric Titration
2.1.5. Interaction of Ch and Magnetite Determined by FTIR
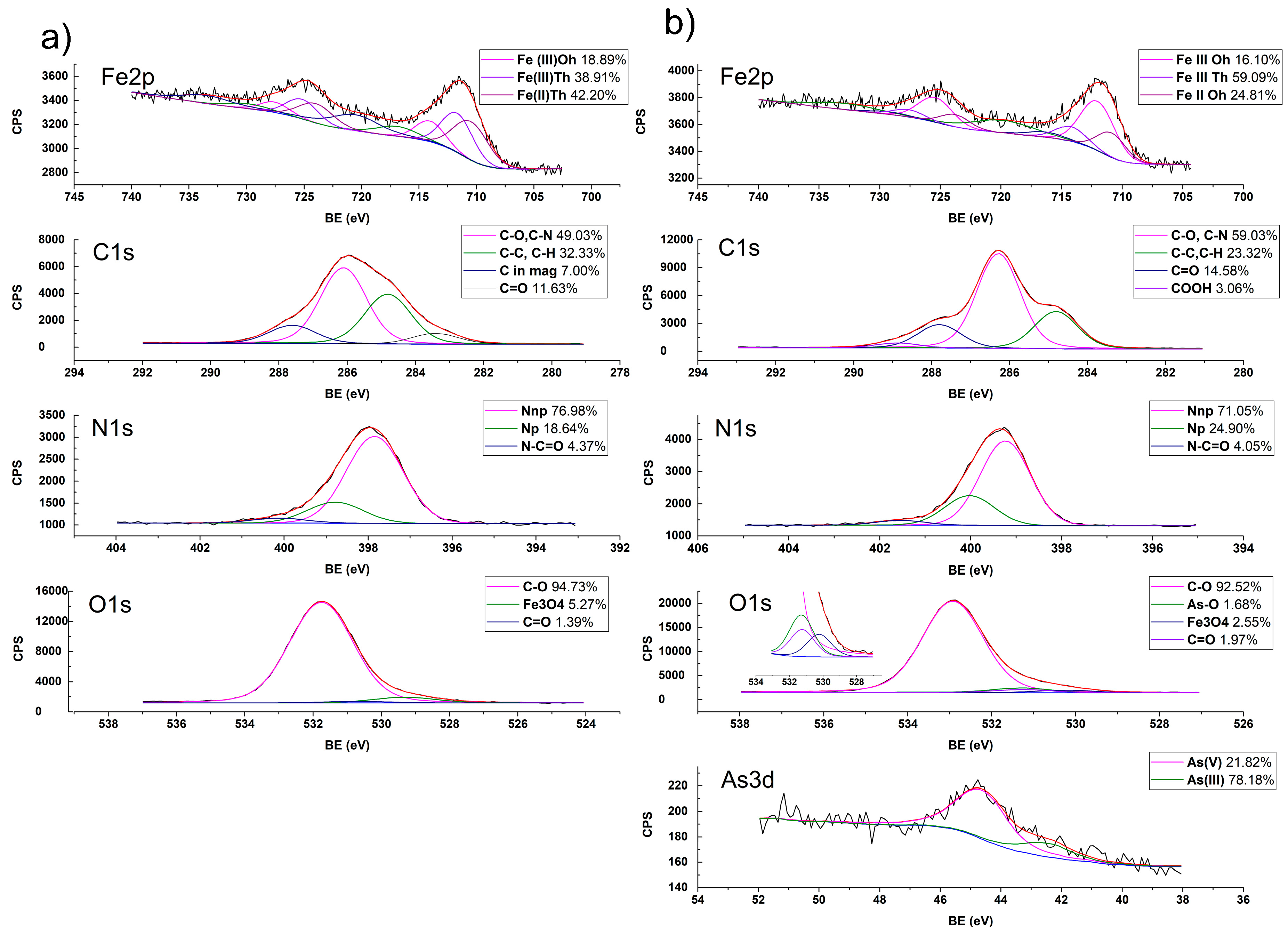
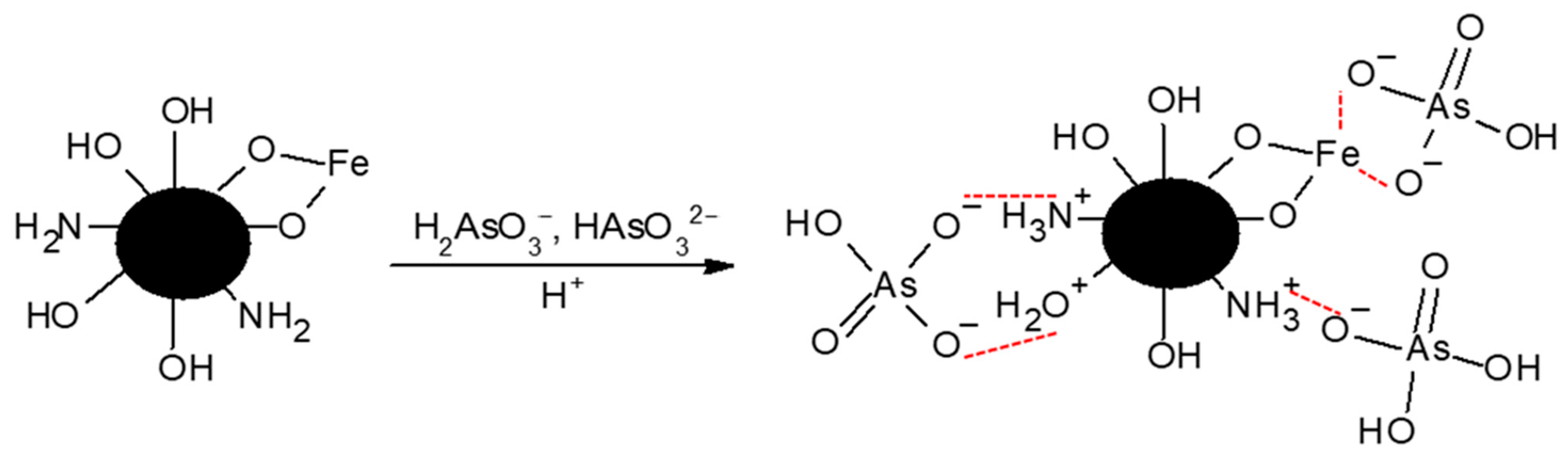
2.1.6. Interaction of ChM and Arsenate Determined by XPS
2.2. Arsenate Adsorption Studies in Fixed-Bed Columns
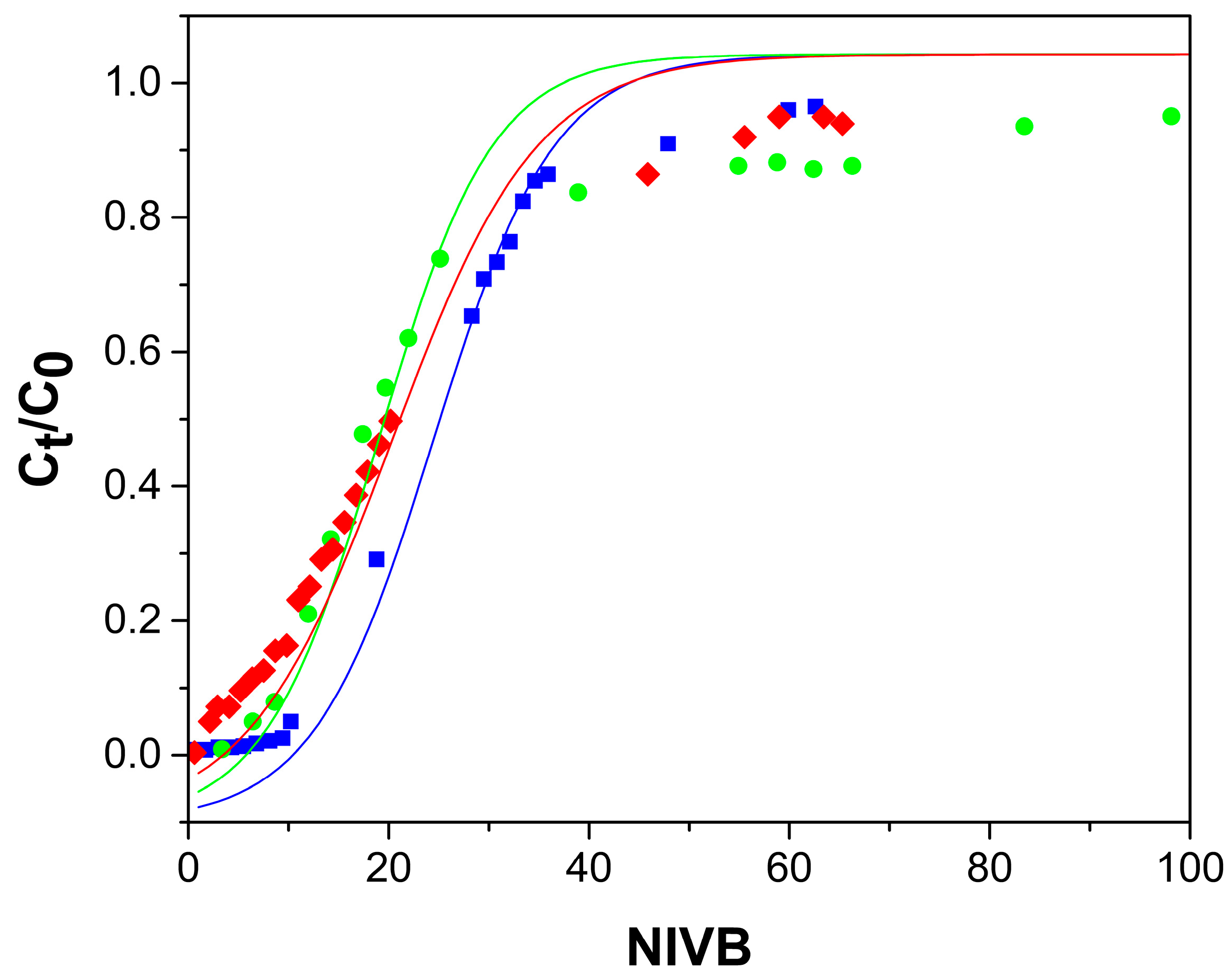
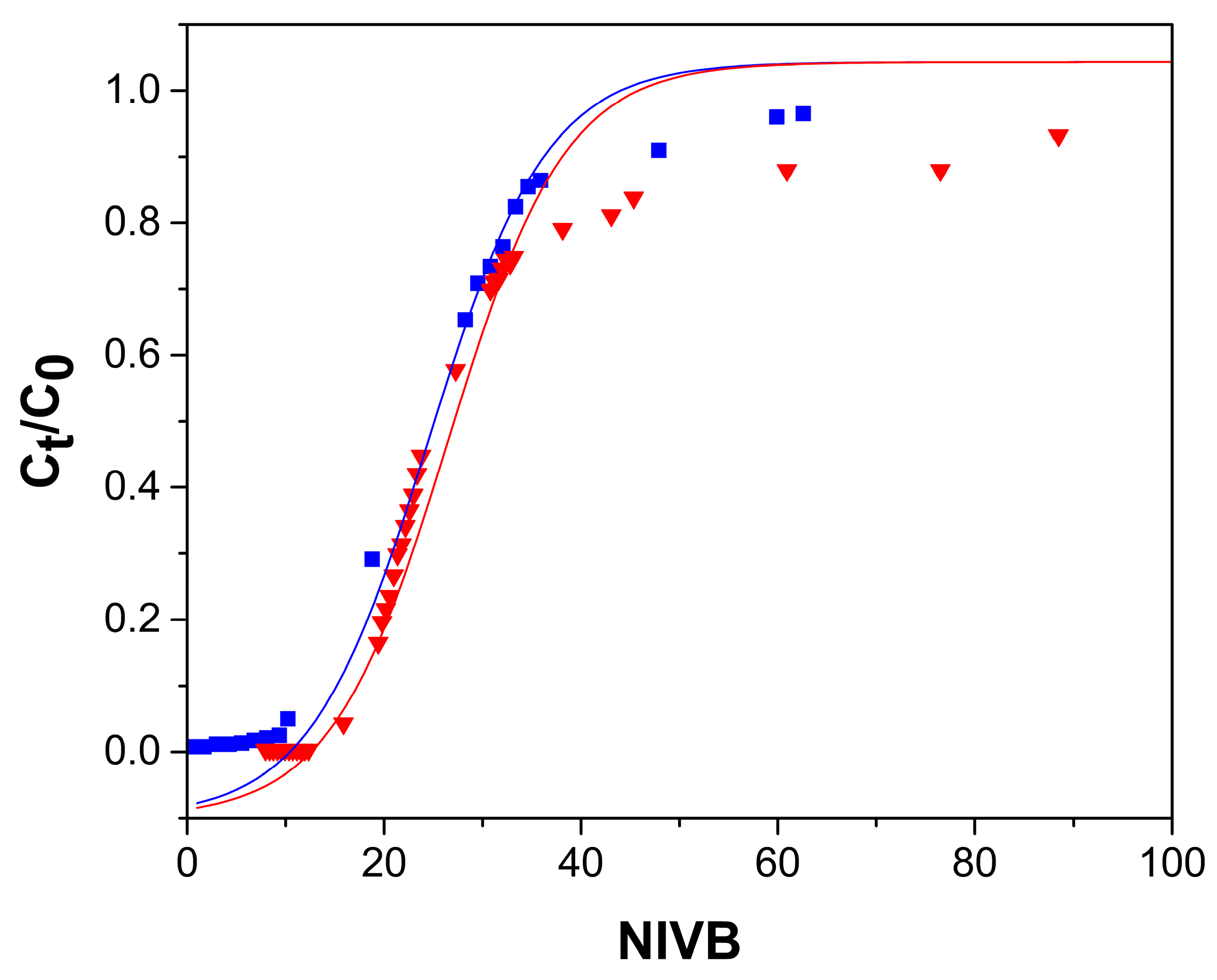
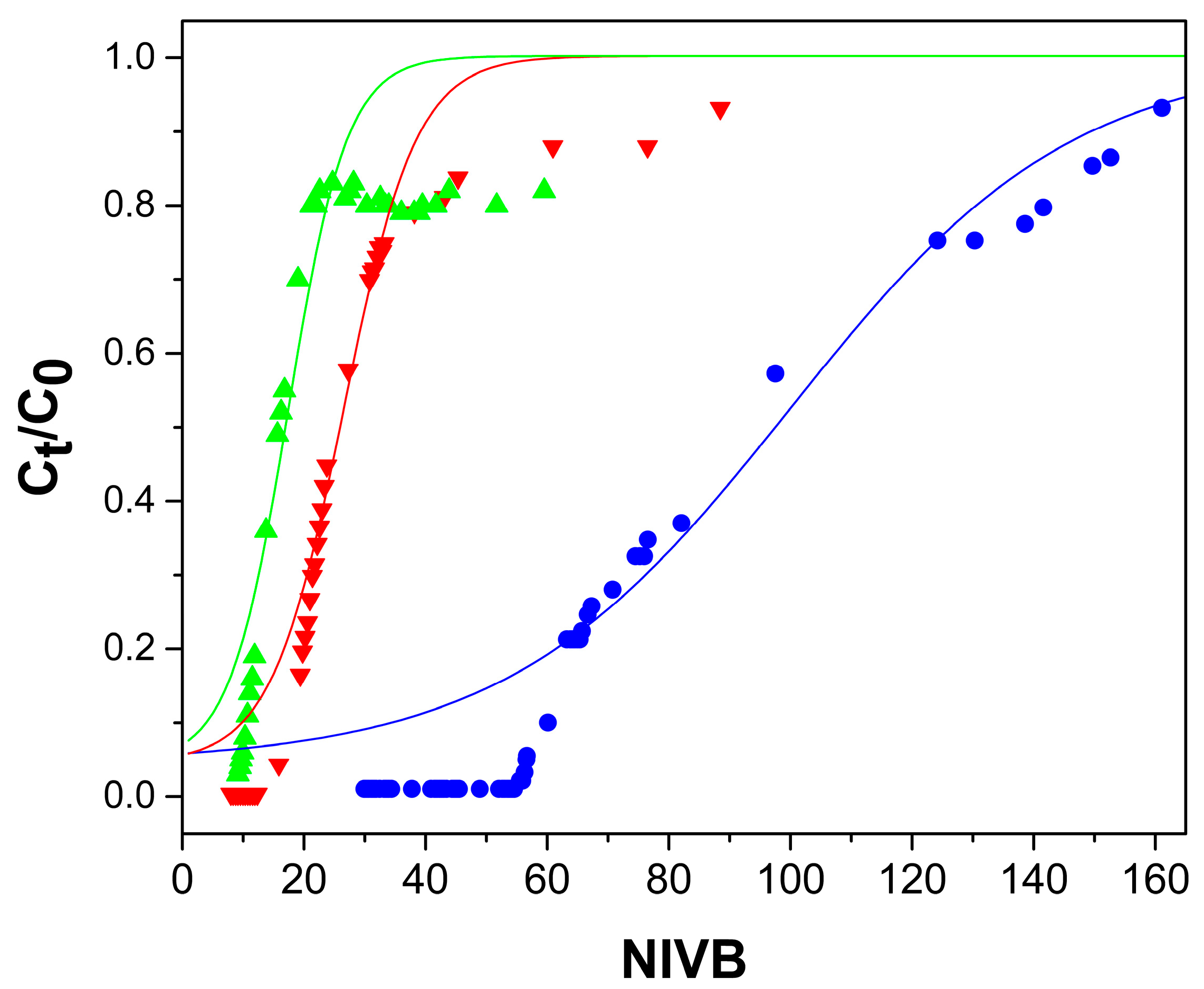
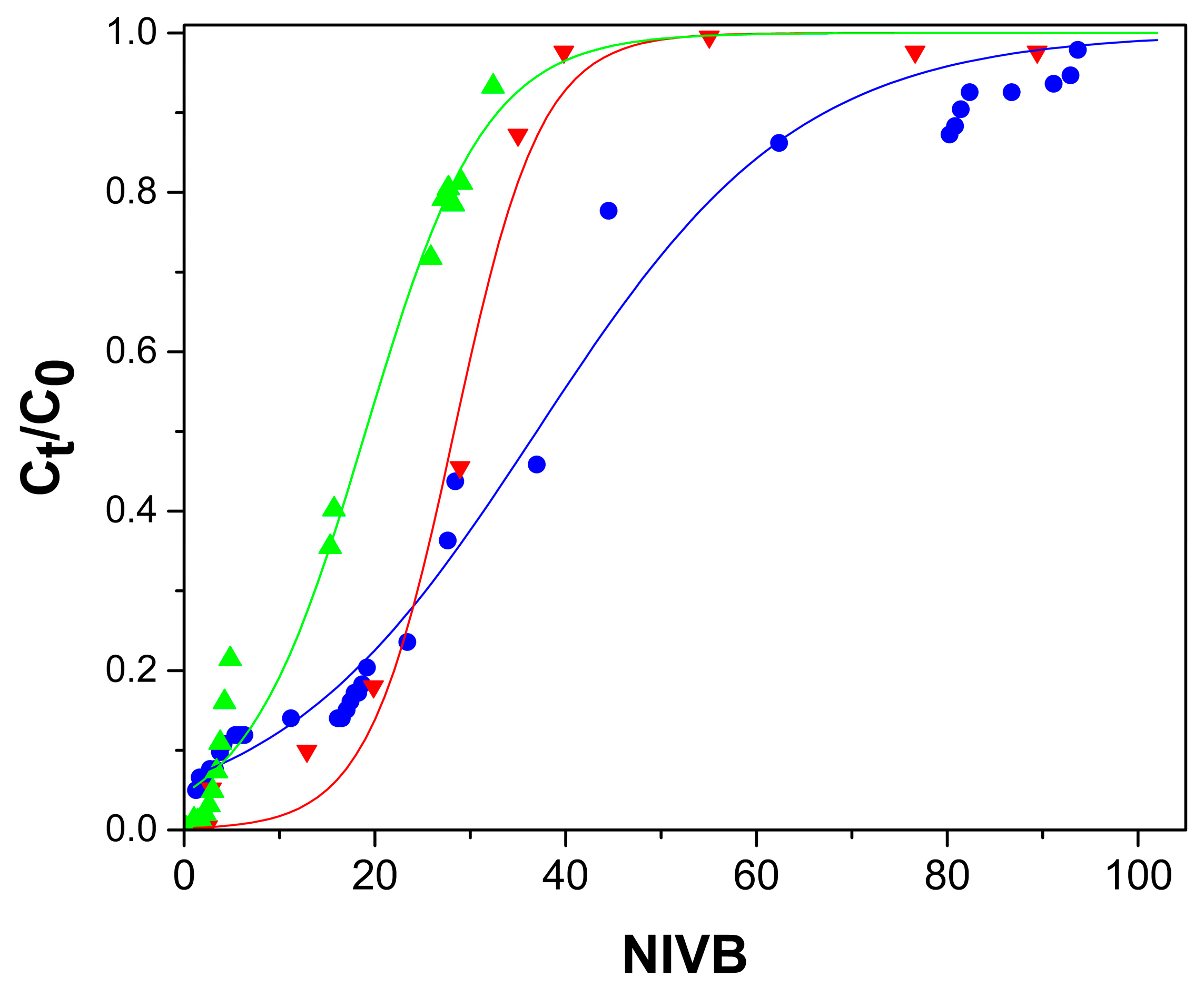
2.2.1. Effect of Flow Rate
2.2.2. Bed Height Effect
2.2.3. As(V) Concentration Effect
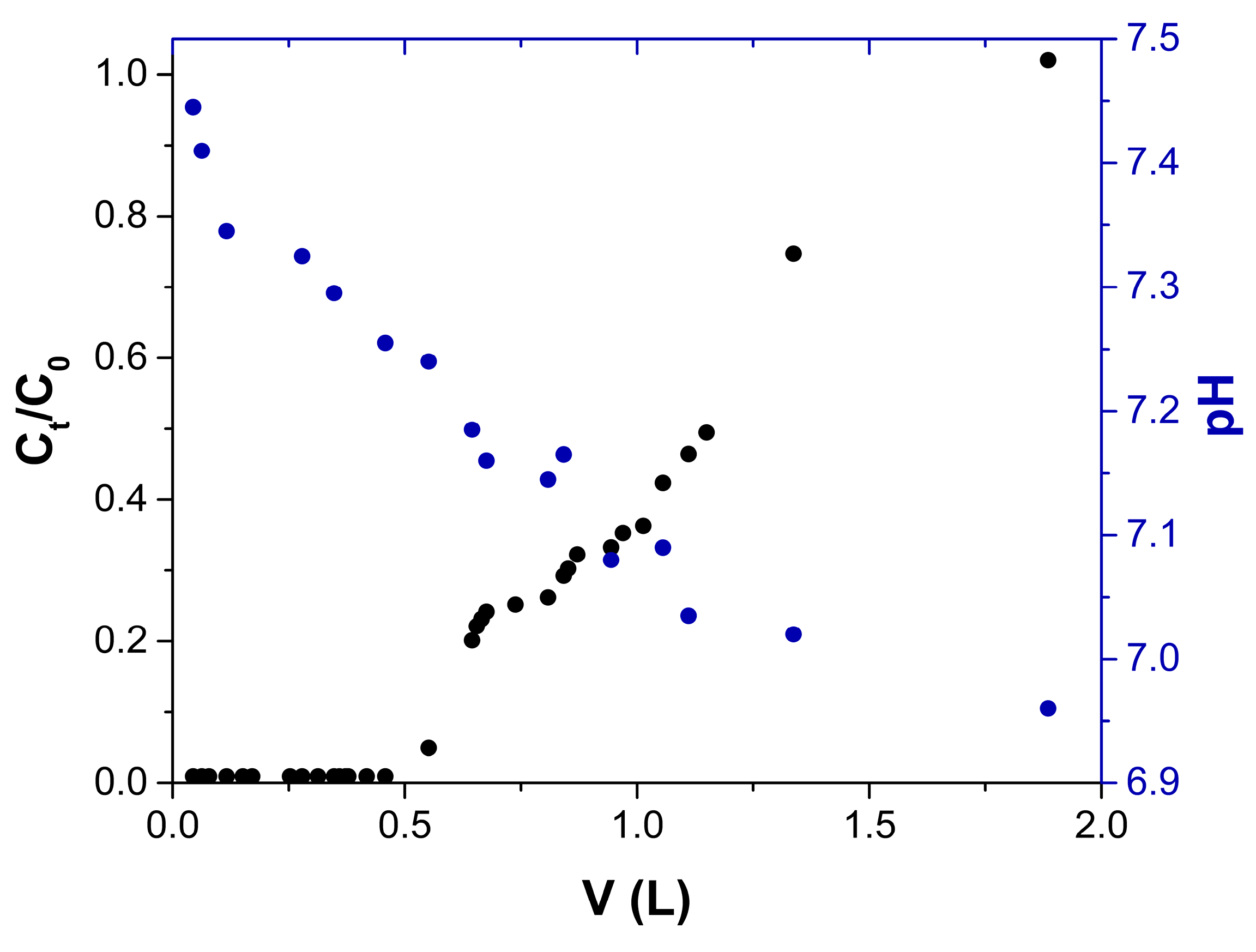
2.2.4. pH Effect
2.3. Modelling of the Behavior of the Fixed-Bed Column
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of ChM Hydrogel Beads
4.3. Characterization of Hydrogel Beads
4.3.1. Hydrogel Beads Composition
4.3.2. Average Diameter of Hydrogel Beads
4.3.3. Morphology and Surface Characterization of the Hydrogel Beads
4.3.4. Potentiometric Titration of ChM
4.3.5. FTIR Characterization of ChM
4.3.6. ChM-Arsenate Interactions Characterization
4.4. Fixed Bed Column Studies on Arsenate Iones Adsorption from Aqueous Solution
4.5. Fixed Bed Column Data Analysis
4.6. Fixed Bed Models
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bujňáková, Z.; Baláž, P.; Zorkovská, A.; Sayagués, M.J.; Kováč, J.; Timko, M. Arsenic sorption by nanocrystalline magnetite: An example of environmentally promising interface with geosphere. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 262, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alchouron, J.; Navarathna, C.; Rodrigo, P.M.; Snyder, A.; Chludil, H.D.; Vega, A.S.; Bosi, G.; Perez, F.; Mohan, D.; Pittman, C.U.; et al. Household arsenic contaminated water treatment employing iron oxide/bamboo biochar composite: An approach to technology transfer. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 587, 767–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Rubio, P.; Roberge, J.; Arendell, L.; Harris, R.B.; O’Rourke, M.K.; Chen, Z.; Cantu-Soto, E.; Meza-Montenegro, M.M.; Billheimer, D.; Lu, Z.; et al. Association between body mass index and arsenic methylation efficiency in adult women from southwest U.S. and northwest Mexico. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2011, 252, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruíz-Huerta, E.A.; de la Garza Varela, A.; Gómez-Bernal, J.M.; Castillo, F.; Avalos-Borja, M.; SenGupta, B.; Martínez-Villegas, N. Arsenic contamination in irrigation water, agricultural soil and maize crop from an abandoned smelter site in Matehuala, Mexico. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 339, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, A.T.; López-Carrillo, L.; Gamboa-Loira, B.; Cebrián, M.E. Standards for arsenic in drinking water: Implications for policy in Mexico. J. Public Health Policy 2017, 38, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osuna-Martínez, C.C.; Armienta, M.A.; Bergés-Tiznado, M.E.; Páez-Osuna, F. Arsenic in waters, soils, sediments, and biota from Mexico: An environmental review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 142062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, K.C.M.; Koong, L.F.; Chen, G.; McKay, G. Mechanism of arsenic removal using chitosan and nanochitosan. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 416, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flora, S.J.S. Arsenic: Chemistry, Occurrence, and Exposure. In Handbook of Arsenic Toxicology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 1–49. ISBN 9780124199552. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, A.; Paul, B. The global menace of arsenic and its conventional remediation—A critical review. Chemosphere 2016, 158, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, P.H. Chemistry of natural waters—I. Water Res. 1971, 5, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, J.W.; Fortner, J.; Work, S.; Avendano, C.; Gonzalez-Pech, N.I.; Zárate Araiza, R.; Li, Q.; Álvarez, P.J.J.; Colvin, V.; Kan, A.; et al. Arsenic Removal by Nanoscale Magnetite in Guanajuato, Mexico. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2014, 31, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, S.; Surianarayanan, M.; Ranganathan, V.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Mandal, A.B. Choline-based ionic liquids-enhanced biodegradation of azo dyes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 4902–4908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Badot, P.M. Application of chitosan, a natural aminopolysaccharide, for dye removal from aqueous solutions by adsorption processes using batch studies: A review of recent literature. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 399–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccin, J.S.; Sant’Anna Cadaval, T.R.J.; Almeida de Pinto, L.A.; Dotto, G.L. Adsorption Isotherms in Liquid Phase: Experimental, Modeling and Interpretations. In Adsorption Processes for Water Treatment and Purification; Bonilla-Petricolet, A., Mendoza-Castillo, D.I., Reynel-Ávila, H.E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 19–48. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M. Applications of chitin- and chitosan-derivatives for the detoxification of water and wastewater—A short review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 152, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H. Fixed-bed column adsorption study: A comprehensive review. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouf, S.; Nagapadma, M. Modeling of Fixed Bed Column Studies for Adsorption of Azo Dye on Chitosan Impregnated with a Cationic Surfactant. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2015, 6, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cussler, E.L. Adsorption. In Diffusion; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009; pp. 375–403. [Google Scholar]
- Verduzco-Navarro, I.P.; Rios-Donato, N.; Jasso-Gastinel, C.F.; Martínez-Gómez, Á. de J.; Mendizábal, E. Removal of Cu(II) by Fixed-Bed Columns Using Alg-Ch and Alg-ChS Hydrogel Beads: Effect of Operating Conditions on the Mass Transfer Zone. Polymers 2020, 12, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerente, C.; Lee, V.K.C.; Cloirec, P.L.; McKay, G. Application of Chitosan for the Removal of Metals From Wastewaters by Adsorption—Mechanisms and Models Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 37, 41–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargar, V.; Asghari, M.; Dashti, A. A Review on Chitin and Chitosan Polymers: Structure, Chemistry, Solubility, Derivatives, and Applications. ChemBioEng Rev. 2015, 2, 204–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Bai, R. Recent advances in chitosan and its derivatives as adsorbents for removal of pollutants from water and wastewater. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2014, 4, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan Ngah, W.S.; Teong, L.C.; Hanafiah, M.A.K.M. Adsorption of dyes and heavy metal ions by chitosan composites: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 1446–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, D.D.; Deng, B.; Lin, L.S. As(III) removal using an iron-impregnated chitosan sorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 182, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, M.L.G.; Esquerdo, V.M.; Nobre, L.R.; Dotto, G.L.; Pinto, L.A.A. Glass beads coated with chitosan for the food azo dyes adsorption in a fixed bed column. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 3387–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, N.R.; Deb, M.; Chattopadhyay, P.K. Chitin and chitosan-based blends and composites. In Biodegradable Polymers, Blends and Composites; Rangappa, S.M., Parameswaranpillai, J., Siengchin, S., Ramesh, M., Eds.; Elsevier Ltd: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 123–203. ISBN 9780128237915. [Google Scholar]
- Carneiro, M.A.; Pintor, A.M.A.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Botelho, C.M.S. Efficient removal of arsenic from aqueous solution by continuous adsorption onto iron-coated cork granulates. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 432, 128657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamaddoni Moghaddam, S.; Ghasemi, H.; Hussein, F.B.; Abu-Zahra, N. Effect of reaction parameters on Arsenic removal capacity from aqueous solutions using modified magnetic PU foam nanocomposite. Results Mater. 2023, 17, 100373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontoni, L.; Fabbricino, M. Use of chitosan and chitosan-derivatives to remove arsenic from aqueous solutions—A mini review. Carbohydr. Res. 2012, 356, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Chauhan, V.S.; Sankararamakrishnan, N. Preparation and evaluation of iron-chitosan composites for removal of As(III) and As(V) from arsenic contaminated real life groundwater. Water Res. 2009, 43, 3862–3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, W.; Chen, L.; Huang, X.; Liu, J. Preparation and evaluation of magnetic nanoparticles impregnated chitosan beads for arsenic removal from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 251, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayub, A.; Raza, Z.A.; Majeed, M.I.; Tariq, M.R.; Irfan, A. Development of sustainable magnetic chitosan biosorbent beads for kinetic remediation of arsenic contaminated water. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 603–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verduzco Navarro, I.P.; Mendizábal, E.; Rivera Mayorga, J.A.; Rentería-Urquiza, M.; Gonzalez-Alvarez, A.; Rios-Donato, N. Arsenate Removal from Aqueous Media Using Chitosan-Magnetite Hydrogel by Batch and Fixed-Bed Columns. Gels 2022, 8, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios-Donato, N.; Navarro, R.; Avila-Rodriguez, M.; Mendizábal, E. Coagulation-flocculation of colloidal suspensions of kaolinite, bentonite, and alumina by chitosan sulfate. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 123, 2003–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maachou, H.; Genet, M.J.; Aliouche, D.; Dupont-Gillain, C.C.; Rouxhet, P.G. XPS analysis of chitosan-hydroxyapatite biomaterials: From elements to compounds. Surf. Interface Anal. 2013, 45, 1088–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieroba, B.; Sroka-Bartnicka, A.; Kazimierczak, P.; Kalisz, G.; Lewalska-Graczyk, A.; Vivcharenko, V.; Nowakowski, R.; Pieta, I.S.; Przekora, A. Spectroscopic studies on the temperature-dependent molecular arrangements in hybrid chitosan/1,3-β-D-glucan polymeric matrices. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 159, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, S.; Barbera, V.; Vitale, A.; Bongiovanni, R.; Serafini, A.; Conzatti, L.; Brambilla, L.; Galimberti, M. Edge functionalized graphene layers for (ultra) high exfoliation in carbon papers and aerogels in the presence of chitosan. Materials 2020, 13, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesiak, B.; Rangam, N.; Jiricek, P.; Gordeev, I.; Tóth, J.; Kövér, L.; Mohai, M.; Borowicz, P. Surface Study of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Functionalized With Biocompatible Adsorbed Molecules. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goretzki, H.; Rosenstiel, P.V.; Mandziej, S. Standard Reference Data. Fresenius’ Zeitschrift für Anal. Chemie 1989, 333, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.R.; Yanful, E.K.; Pratt, A.R. Arsenic removal from aqueous solutions by mixed magnetite-maghemite nanoparticles. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 64, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.H.; Chuang, Y.H.; Chen, T.Y.; Tian, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, M.K.; Zhang, W. Mechanism of Arsenic Adsorption on Magnetite Nanoparticles from Water: Thermodynamic and Spectroscopic Studies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 7726–7734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naja, G.; Volesky, B. Behavior of the mass transfer zone in a biosorption column. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 3996–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wankat, P.C. Ingeniería de procesos de separación, 2nd ed.; Pearson: Mexico City, Mexico, 2008; ISBN 9789702612810. [Google Scholar]
- Barros, M.A.S.D.; Arroyo, P.A.; Silva, E.A. General Aspects of Aqueous Sorption Process in Fixed Beds. In Mass Transfer—Advances in Sustainable Energy and Environment Oriented Numerical Modeling; Nakajima, H., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2013; pp. 361–386. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, S.; Mishra, U. Continuous Fixed-Bed Column Study and Adsorption Modeling: Removal of Lead Ion from Aqueous Solution by Charcoal Originated from Chemical Carbonization of Rubber Wood Sawdust. J. Chem. 2015, 2015, 907379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotto, G.L.; Gonçalves Salau, N.P.; Piccin, J.S.; Sant’Anna Cadaval, T.R.J.; Almeida de Pinto, L.A. Adsorption Kinetics in Liquid Phase: Modeling for Discontinuous and Continuous Systems. In Adsorption Processes for Water Treatment and Purification; Bonilla-Petricolet, A., Mendoza-Castillo, D.I., Reynel-Ávila, H.E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 53–74. [Google Scholar]
- Futalan, C.M.; Kan, C.C.; Dalida, M.L.; Pascua, C.; Wan, M.W. Fixed-bed column studies on the removal of copper using chitosan immobilized on bentonite. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, B.; Biswas, M.; Bandyopadhyay, K.; Misra, A.K. Fixed Bed Column Adsorption Studies Using Fly Ash for Removal of Cadmium from Aqueous Solution. J. Inst. Eng. Ser. A 2014, 94, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouboulis, A.I.; Katsoyiannis, I.A. Arsenic removal using iron oxide loaded alginate beads. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2002, 41, 6149–6155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Singh, S.K.; Bajpai, J.; Bajpai, A.K.; Shrivastava, R.B. Iron crosslinked alginate as novel nanosorbents for removal of arsenic ions and bacteriological contamination from water. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2014, 3, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seawood, G.M.; Dixit, S.; Mishra, G.; Gupta, S.K. Selective As(v) capture by a novel magnetic green Fe-biochar composite in a packed column: An application of central composite design. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2021, 7, 2129–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Nguyen, A.T.; Loganathan, P.; Nguyen, T.V.; Vigneswaran, S.; Nguyen, T.H.H.; Tran, H.N. Low-cost laterite-laden household filters for removing arsenic from groundwater in Vietnam and waste management. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 152, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, L.; Singh, J. Removal of As(III) and As(V) from aqueous solution using engineered biochar: Batch and fixed-bed column study. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 1961–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalini, S.; Geethamalika, G.; Prasanthrajan, M.; Poornima, R.; John, J.E.; Davamani, V.; Rajkishore, S.K.; Jayabalakrishnan, R.M.; Boomiraj, K. Arsenic removal from aqueous water using pectin stabilised nano zero valent iron particles/neem bark supported (P-NZVI/NBP) treatment system. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te, B.; Wichitsathian, B.; Yossapol, C.; Wonglertarak, W. Investigation of Arsenic Removal from Water by Iron-Mixed Mesoporous Pellet in a Continuous Fixed-Bed Column. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, J. Removal of Arsenic Using Hydrated Mixed Trivalent Iron-Aluminum Oxide Adsorbent: Prediction of Column Performance. Orient. J. Chem. 2020, 36, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoob, S.; Gupta, A.K.; Bhakat, P.B. Analysis of breakthrough developments and modeling of fixed bed adsorption system for As(V) removal from water by modified calcined bauxite (MCB). Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 52, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dambies, L.; Vincent, T.; Guibal, E. Treatment of arsenic-containing solutions using chitosan derivatives: Uptake mechanism and sorption performances. Water Res. 2002, 36, 3699–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, K.C.M.; Koong, L.F.; Al Ansari, T.; McKay, G. Adsorption/desorption of arsenite and arsenate on chitosan and nanochitosan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 14734–14742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, K.F.H.; Dong, Y.; Xue, T.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Han, L.; Zhang, N.; Mawignon, F.J.; Kolani, K.; Wang, W. Fixed-bed column method for removing arsenate from groundwater using aluminium-modified kapok fibres. J. Porous Mater. 2023, 30, 1221–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Wei, S.; Liu, C.; Chen, T.; Tang, Y.; Ma, J.; Yin, K.; Luo, S. Efficient removal of arsenic from groundwater using iron oxide nanoneedle array-decorated biochar fibers with high Fe utilization and fast adsorption kinetics. Water Res. 2019, 167, 115107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boddu, V.M.; Abburi, K.; Talbott, J.L.; Smith, E.D.; Haasch, R. Removal of arsenic (III) and arsenic (V) from aqueous medium using chitosan-coated biosorbent. Water Res. 2008, 42, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhoble, R.M.; Maddigapu, P.R.; Rayalu, S.S.; Bhole, A.G.; Dhoble, A.S.; Dhoble, S.R. Removal of arsenic(III) from water by magnetic binary oxide particles (MBOP): Experimental studies on fixed bed column. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 322, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.; Riley, J.P. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 1962, 27, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geankoplis, C.; Hersel, A.; Lepek, D. Transport Processes and Separation Process Principles; Pearson: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, H.; Vashi, R.T. Fixed-Bed Column Studies of Dyeing Mill Wastewater Treatment Using Naturally Prepared Adsorbents. In Characterization and Treatment of Textile Wastewater; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Nederlands, 2015; pp. 127–145. ISBN 9780128023266. [Google Scholar]
- Kopsidas, O. Scale up of Adsorption inFixed-Bed Column Systems; University of Piraeus: Pireas, Greece, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bonilla-Petricolet, A.; Mendoza-Castillo, D.I.; Reynel-Ávila, H.E. Introduction. In Adsorption Processes for Water Treatment and Purification; Bonilla-Petricolet, A., Mendoza-Castillo, D.I., Reynel-Ávila, H.E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- González-López, M.E.; Laureano-Anzaldo, C.M.; Pérez-Fonseca, A.A.; Arellano, M.; Robledo-Ortíz, J.R. A discussion on linear and non-linear forms of Thomas equation for fixed-bed adsorption column modeling. Rev. Mex. Ing. Química 2021, 20, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, V.; Kamal, B.; V, M.H.M.; Mannarthippusulthan, M.A.M. Removal of dyes and metals using natural adsorbents. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2015, 7, 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Cai, J.; Pan, B. Mathematically modeling fixed-bed adsorption in aqueous systems. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 2013, 14, 155–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Mondal, S.; De, S. Design and scaling up of fixed bed adsorption columns for lead removal by treated laterite. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 177, 760–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leudjo Taka, A.; Klink, M.J.; Yangkou Mbianda, X.; Naidoo, E.B. Chitosan nanocomposites for water treatment by fixed-bed continuous flow column adsorption: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 255, 117398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, Y.H.; Nelson, J.H. Application of Gas Adsorption Kinetics I. A Theoretical Model for Respirator Cartridge Service Life. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 1984, 45, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.J.; Hameed, B.H. Removal of emerging pharmaceutical contaminants by adsorption in a fixed-bed column: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 149, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Cervantes, J.; Sánchez-Machado, D.I.; Sánchez-Duarte, R.G.; Correa-Murrieta, M.A. Study of a fixed-bed column in the adsorption of an azo dye from an aqueous medium using a chitosan–glutaraldehyde biosorbent. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2018, 36, 215–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Adsorbent | C0 (mg/L) | Q (mL/h) | H (cm) | HLUB (cm) | HL/HLUB | V (mL) at tb | NIVB at tb | NIVB at te | qb (mg/g) | qe (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ChM | 5 | 13 | 13 | 7.78 ± 0.26 | 0.67 ± 0.06 | 112.4 ± 4.3 | 10.4 ± 0.4 | 57.1 ± 1.2 | 0.48 ± 0.02 | 1.19 ± 0.10 |
| 5 | 20 | 13 | 9.54 ± 0.60 | 0.36 ± 0.08 | 70.2 ± 4.9 | 6.5 ± 0.5 | 68.9 ± 3.5 | 0.30 ± 0.02 | 1.15 ± 0.12 | |
| 5 | 25 | 13 | 9.75 ± 0.95 | 0.33 ± 0.19 | 73.3 ± 9.8 | 6.8 ± 1.0 | 59.0 ± 4.8 | 0.31 ± 0.07 | 1.12 ± 0.08 | |
| 2 | 13 | 33 | 6.60 ± 0.02 | 4.00 ± 0.01 | 1564.1 ± 43.3 | 57.1 ± 1.6 | 163.3 ± 8.0 | 2.70 ± 0.08 | 3.37 ± 0.10 | |
| 5 | 13 | 33 | 10.19 ± 0.46 | 2.24 ± 0.14 | 440.9 ± 8.2 | 16.1 ± 0.3 | 123.0 ± 0.0 | 2.18 ± 0.04 | 3.15 ± 0.00 | |
| 10 | 13 | 33 | 11.95 ± 0.08 | 2.12± 0.02 | 264.6 ± 9.0 | 9.7 ± 0.3 | 60.9 ± 3.4 | 2.61 ± 0.09 | 3.84 ± 0.12 | |
| Ch | 2 | 13 | 33 | 31.90 ± 0.03 | 0.03 ± 0.00 | 34.1 ± 3.8 | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 86.2 ± 13.2 | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 0.60 ± 0.08 |
| 5 | 13 | 33 | 29.57 ± 0.01 | 0.12 ± 0.00 | 78.6 ± 7.2 | 2.9 ± 0.3 | 90.4 ± 7.5 | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 0.95 ± 0.08 | |
| 10 | 13 | 33 | 27.45 ± 0.30 | 0.20 ± 0.01 | 82.6 ± 1.7 | 3.0 ± 0.1 | 32.4 ± 2.3 | 0.21 ± 0.00 | 1.24 ± 0.09 |
| Adsorbent | qe (mg As/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Iron oxide-coated alginate | 0.023 | [49] |
| Iron crosslinked alginate | 0.066 | [50] |
| Iron-impregnated Azadirachta indica biochar | 0.149 | [51] |
| Natural laterite | 0.20 | [52] |
| Iron-modified biochar | 0.303 | [53] |
| Pectin stabilized nano zero valent iron particles | 0.318 | [54] |
| Iron-mixed mesoporous pellet | 0.352 | [55] |
| Hydrated mixed trivalent iron-aluminum oxide | 0.569 | [56] |
| Iron-coated calcined bauxite | 0.606 | [57] |
| Iron-coated cork granulates | 2.0 | [27] |
| Chitosan-magnetite hydrogel beads | 3.84 | This study |
| Adsorbent | ChM | ChM | ChM | ChM | ChM | ChM | Ch | Ch | Ch |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | 13 | 13 | 13 | 33 | 33 | 33 | 33 | 33 | 33 |
| C0 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 2 | 5 | 10 | 2 | 5 | 10 |
| Q | 13 | 20 | 25 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 |
| Thomas | |||||||||
| kTh | 4.75 × 10−4 | 7.05 × 10−4 | 7.13 × 10−4 | 3.17 × 10−4 | 4.45 × 10−4 | 2.74 × 10−4 | 5.50 × 10−4 | 7.79 × 10−4 | 2.66 × 10−4 |
| qTh | 104.0 | 82.4 | 86.6 | 35.8 | 45.4 | 59.5 | 21.7 | 35.5 | 47.9 |
| R2 | 0.9956 | 0.9349 | 0.9851 | 0.9516 | 0.9440 | 0.7991 | 0.9829 | 0.9804 | 0.9830 |
| MAE | 0.0228 | 0.0683 | 0.0277 | 0.0502 | 0.0477 | 0.1174 | 0.0360 | 0.0388 | 0.0315 |
| Yoon–Nelson | |||||||||
| kYN | 3.54 × 10−3 | 5.35 × 10−3 | 5.30 × 10−3 | 3.32 × 10−4 | 1.33 × 10−3 | 1.63 × 10−3 | 6.40 × 10−4 | 1.96 × 10−3 | 1.40 × 10−3 |
| τ | 1152.5 | 627.7 | 531.5 | 7720.4 | 3340.2 | 2215.3 | 4196.5 | 3217.9 | 2160.2 |
| R2 | 0.9891 | 0.9349 | 0.9851 | 0.9516 | 0.9440 | 0.7991 | 0.9829 | 0.9804 | 0.9830 |
| MAE | 0.0196 | 0.0683 | 0.0277 | 0.0503 | 0.0477 | 0.1175 | 0.0360 | 0.0387 | 0.0315 |
| Adams–Bohart | |||||||||
| kBA | 8.49 × 10−5 | 7.01 × 10−5 | 2.40 × 10−4 | 7.52 × 10−5 | 6.71 × 10−6 | 1.56 × 10−5 | 9.53 × 10−5 | 7.28 × 10−5 | 7.85 × 10−5 |
| N0 | 105.8 | 173.2 | 114.4 | 83.7 | 593.2 | 215.5 | 71.0 | 85.3 | 113.0 |
| R2 | 0.5850 | 0.6120 | 0.8610 | 0.8769 | 0.6203 | 0.4773 | 89.5613 | 0.7471 | 0.9505 |
| MAE | 0.1382 | 0.1654 | 0.0902 | 0.1036 | 0.1094 | 0.1737 | 0.0875 | 1.1954 | 0.0607 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mendizabal, E.; Ríos-Donato, N.; Jasso-Gastinel, C.F.; Verduzco-Navarro, I.P. Removal of Arsenate by Fixed-Bed Columns Using Chitosan-Magnetite Hydrogel Beads and Chitosan Hydrogel Beads: Effect of the Operating Conditions on Column Efficiency. Gels 2023, 9, 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9100825
Mendizabal E, Ríos-Donato N, Jasso-Gastinel CF, Verduzco-Navarro IP. Removal of Arsenate by Fixed-Bed Columns Using Chitosan-Magnetite Hydrogel Beads and Chitosan Hydrogel Beads: Effect of the Operating Conditions on Column Efficiency. Gels. 2023; 9(10):825. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9100825
Chicago/Turabian StyleMendizabal, Eduardo, Nely Ríos-Donato, Carlos Federico Jasso-Gastinel, and Ilse Paulina Verduzco-Navarro. 2023. "Removal of Arsenate by Fixed-Bed Columns Using Chitosan-Magnetite Hydrogel Beads and Chitosan Hydrogel Beads: Effect of the Operating Conditions on Column Efficiency" Gels 9, no. 10: 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9100825
APA StyleMendizabal, E., Ríos-Donato, N., Jasso-Gastinel, C. F., & Verduzco-Navarro, I. P. (2023). Removal of Arsenate by Fixed-Bed Columns Using Chitosan-Magnetite Hydrogel Beads and Chitosan Hydrogel Beads: Effect of the Operating Conditions on Column Efficiency. Gels, 9(10), 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9100825