Moving towards Gel for Fish Feeding: Focus on Functional Properties and Its Acceptance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
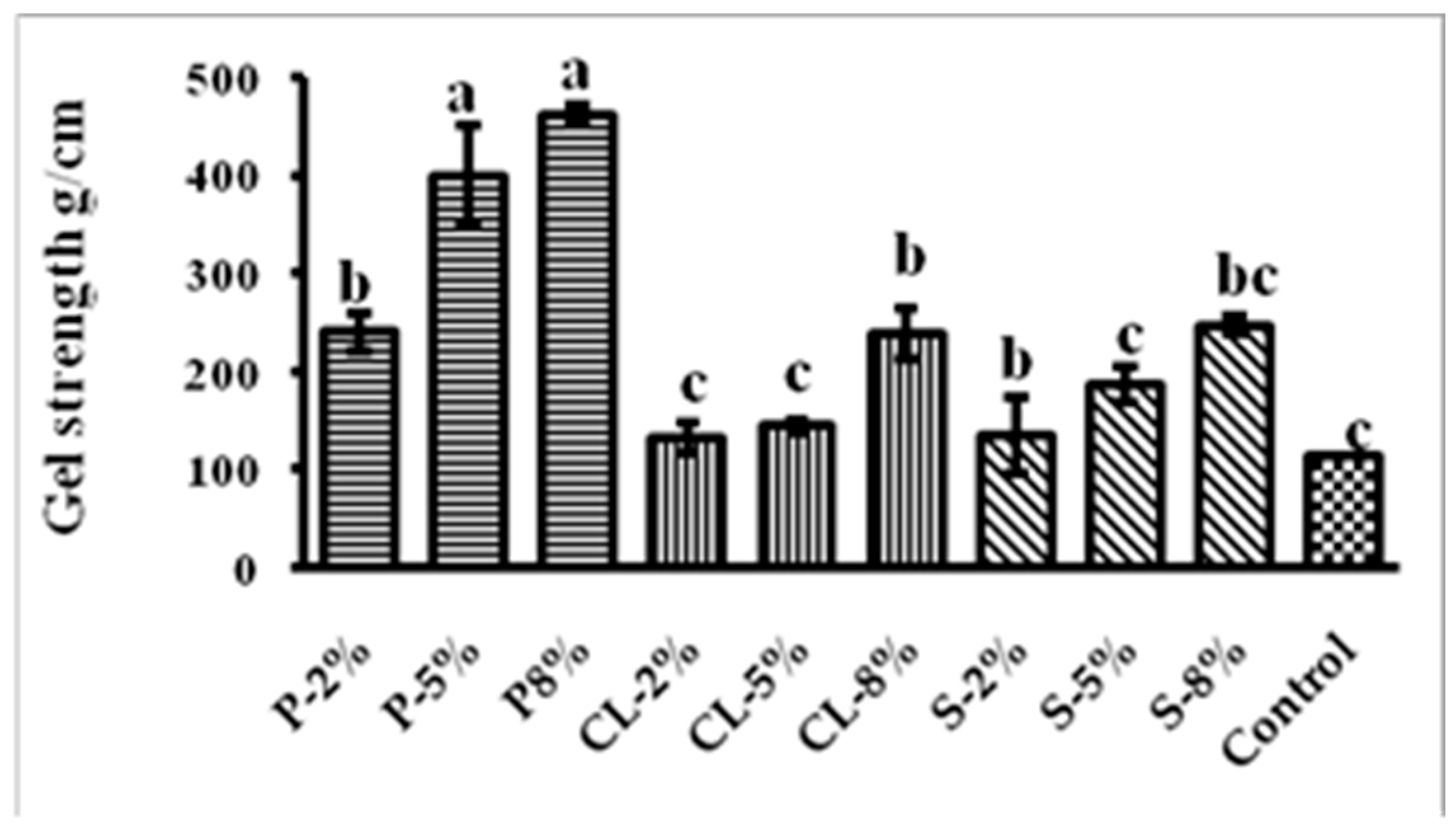
2.1. Gel Strength and Texture Profile Analysis of Gel Feed
2.2. Colour Characteristics of Gel Feed
2.3. Physical Characteristics of Gel Feed in the Water Column
2.4. Nutrient-Leaching Characteristics in the Water Column
2.5. Proximate Composition in Different Gel-Based Feeds
2.6. Gel Feed Acceptance by P. conchonius and Growth Performance
2.7. Water Quality Parameters
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ingredients of Gel Feed
4.2. Preparation of Gel Feed
4.3. Gel Strength and Texture Profile Analysis
4.4. Determination of Colour Characteristics of Gel Feed
4.5. Physical Properties of Gel Feed
4.5.1. Evaluation of the Gel Stability of Gel-Based Feed
4.5.2. Water Stability
4.5.3. Sinking Velocity (SV)
4.5.4. Water-Holding Capacity (WHC)
4.6. Nutrient Leaching (Protein and Lipids)
4.7. Proximate Analysis of Gel Feed
4.8. Feeding Acceptance Test of Gel Feed
4.8.1. Experimental Fish
4.8.2. Experimental Design and Tank Management
4.8.3. Growth Performance and Feeding Acceptance of Gel Feed
4.8.4. Management of Water Quality Parameters
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture (SOFIA); Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2020; p. 244. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, C.E.; McNevin, A.A.; Davis, R.P. The contribution of fisheries and aquaculture to the global protein supply. Food Secur. 2022, 14, 805–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouquet, P.; Harit, A.; Herve, V.; Moger, H.; Carrijo, T.; Donoso, D.A.; Eldridge, D.; da Cunha, H.F.; Choosai, C.; Janeau, J.L.; et al. The impact of termites on soil sheeting properties is by their feeding and biulding strategies. Geoderma 2022, 412, 115706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriherwanto, C.; Rahmanisa, H.; Yunita, E.; Suja’I, I.; Nadaviana, A. Altering Physical Characteristics of Sinking Fish-Feed through Sub-Optimal Fermentation Using Tempeh Mould without Mechanical Extrusion. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. IOP Publ. 2021, 1751, 012047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballester-Moltó, M.; Sanchez-Jerez, P.; Cerezo-Valverde, J.; Aguado-Giménez, F. Particulate waste outflow from fish-farming cages. How much is uneaten feed? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 119, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilfart, A.; Dusart, L.; Méda, B.; Gac, A.; Espagnol, S.; Morin, L.; Dronne, Y.; Garcia-Launay, F. Réduire les impacts environnementaux des aliments pour les animaux d’élevage. INRA Prod. Anim. 2018, 31, 289–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacon, A.G.; Metian, M. Feed matters: Satisfying the feed demand of aquaculture. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2015, 23, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnaneswari, M.D.; Narala, V.R.; Subramani, P.A. Components of Aquaculture as Sources of Environmental Pollution and Available Remedial Measures. In Impact of COVID-19 on Emerging Contaminants; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 305–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, J.M. Gelation of Whey Proteins: Chemical and Rheological Changes during Phase Transition in Food. Food Technol. 1995, 49, 83–89. Available online: http://pascalfrancis.inist.fr/vibad/index.php?action=getRecordDetail&idt=3687552 (accessed on 5 January 2023).
- Hermans, P.H. Gels. In Colloid Science, 1st ed.; Kruyt, H.R., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1949; pp. 483–650. [Google Scholar]
- Lanter, K.J.; Waterloo, I.L.; Gonzalez, C.R.A.; Laurel, M.D. Animal Feed Gel. U.S. Patent US6171632B1, 9 January 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, E. Gelling Fish, Food Composition. U.S. Patent US3591389A, 6 July 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Dhanukar, N. Pethiaconchonius, the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015. Available online: http://www.iucnredlist.org/details/full/166646/0 (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- Pethiyagoda, R.; Meegaskumbura, M.; Maduwage, K. A synopsis of the South Asian fishes referred to Puntius (Pisces: Cyprinidae). Ichthyol. Explor. Freshw. 2012, 23, 69. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, N.K.; Chouksey, M.K.; Balange, A.K.; Tripathi, G.; Nayak, B.B. Physicochemical and gel properties of myofibrillar protein from sin croaker (Johnius dussumieri) fish during ice storage. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2017, 26, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buda, U.; Priyadarshini, M.B.; Majumdar, R.K.; Mahanand, S.S.; Patel, A.B.; Mehta, N.K. Quality characteristics of fortified silver carp surimi with soluble dietary fiber: Effect of apple pectin and konjac glucomannan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 175, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camou, J.P.; Sebranek, J.G.; Olson, D.G. Effect of heating rate and protein concentration on gel strength and water loss of muscle protein gels. J. Food Sci. 1989, 54, 850–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, J.I.; Lozano, J.E.; Genovese, D.B. Effect of formulation variables on rheology, texture, colour, and acceptability of apple jelly: Modelling and optimization. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 62, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamedi, F.; Mohebbi, M.; Shahidi, F.; Azarpazhooh, E. Ultrasound-assisted osmotic treatment of model food impregnated with pomegranate peel phenolic compounds: Mass transfer, texture, and phenolic evaluations. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2018, 11, 1061–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, C.; Tontul, S.A.; Erbas, M. Production of a minimally processed jelly candy for children using honey instead of sugar. LWT 2018, 93, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreungngern, D.; Chaikham, P. Rheological, physical and sensory attributes of Chao Kuay jelly added with gelling agents. Int. Food. Res. J. 2016, 23, 1474–1478. [Google Scholar]
- Calvarro, J.; Perez-Palacios, T.; Ruiz, J. Modification of gelatin functionality for culinary applications by using transglutaminase. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2016, 5, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nickum, J.G. Intensive culture of walleyes: The state of the art. Am. Fish Soc. Spec. Publ. 1978, 11, 187–194. [Google Scholar]
- Masterson, M.F.; Garling, D.L. Effect of feed color on feed acceptance and growth of walleye fingerlings. Prog. Fish Cult. 1986, 48, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banan, A.; Kalbassi, M.R.; Bahmani, M.; Sadati, M.Y. Effects of colored light and tank color on growth indices and some physiological parameters of juvenile beluga (Huso huso). J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2011, 27, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, A.F.; El-Ghobashy, A.E. Effects of tank colour and feed colour on growth and feed utilization of thinlip mullet (Liza ramada) larvae. Aquac. Res. 2011, 42, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, Å.; Alanärä, A.; Staffan, F.; Magnhagen, C. Effects of tank colour and light intensity on feed intake, growth rate and energy expenditure of juvenile Eurasian perch, Percafluviatilis L. Aquaculture 2007, 272, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastings, W.H.; Meyers, S.P.; Butler, D.P. A commercial process for water stable fish feeds. Feedstuffs 1971, 43, 38. [Google Scholar]
- Farmanfarmaian, A.; Lauterion, T.; Ibe, M. Improvement of the stability of commercial feed pellets for the giant shrimp (Macrobrachium rosenbergii). Aquaculture 1982, 27, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.G.; Ataguba, G.A.; Abeje, A. Water stability and floatation test of fish pellets using local starch sources and yeast (Saccahromyces cerevisae). Int. J. Latest Trends Agric. Food Sci. 2011, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ighwela, K.A.; Ahmad, A.B.; Abol-Munafi, A.B. Water stability and nutrient leaching of different levels of maltose formulated fish pellets. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haetami, K.; Junianto, J.; Iskandar, I.; Rostika, R.; Abun, A. Durability and water stability of pellet fish supplementation results pairing coconut oils and hazlenut oil. Int. J. Environ. Agric. Biotechnol. 2017, 2, 238800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohrer, B.M. An investigation of the formulation and nutritional composition of modern meat analogue products. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2019, 8, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriegha, O.J.; Ekokotu, P.A. Factors affecting feed intake in cultured fish species: A review. Anim. Res. Int. 2017, 14, 2697–2709. [Google Scholar]
- Barbut, S. Determining Water and Fat Holding. In Methods of Testing Protein Functionality; Hall, G.M., Ed.; Blackie Academie & Professional, an Imprint of Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, A.; Getty, K.J.; Park, J.W. Roles of starch in surimi seafood: A review. Food Rev. Int. 2009, 25, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.M.; Wu, M.M.; Okada, M. Ingredient and formulation technology for surimi-based products. In Surimi Technology; Lanier, T.C., Lee, C.M., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 273–302. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, F.F.; Zhang, H.C.; Hao, B.X.; Sun, T.; Kong, L.; Li, Y.; Hou, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, A. Controllable transformation from sensitive and reversible heat-set organogel to stable gel induced by sodium acetate. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 410, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yu, X.; Tang, W.; Wan, C.; Lu, Y.; Dong, N.; Chen, Z.; Lei, Z.; Ren, T.; Wang, Z.; et al. Characterization of food gels prepared from the water extract of fish (Cyprinuscarpio L.) scales: From molecular components to sensory attributes. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 112, 106263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, S.; Willhite, G.P.; Green, D.W.; McCool, C.S. The effect of fluid leakoff on gel placement and gel stability in fractures. SPE J. 2002, 7, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanter, K.; de Rodas, B.; Miller, B.L.; Fitzner, G.E. Gel Based Livestock Feed, Method of Manufacture and Use. WIPO Patent WO2007011330A1, 25 January 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hamre, K. Nutrition in cod (Gadusmorhua) larvae and juveniles. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2006, 63, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aaqillah-Amr, M.A.; Hidir, A.; David, M.; Ahmad-Ideris, A.R.; Muhammad-Zulhilmi, R.; Julius, Y.F.; Noordiyana, M.N.; Abualreesh, M.H.; Peng, T.H.; Ma, H.; et al. Development of semi-moist formulated feed for female orange mud crabs, Scylla olivacea (Herbst, 1796) broodstocks with graded lipid levels. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2022, 290, 115365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.A. Food for Benthic Feeding Aquatic Animals. UK Patent GB2175486A, 3 December 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Folke, C. The role of ecosystems for a sustainable development of aquaculture. Ambio 1989, 18, 234–243. [Google Scholar]
- Lanter, K.; de Rodas, B.; Miller, B.L.; Fitzner, G.E. Gel Based Livestock Feed, Method of Manufacture and Use. U.S. Patent US8092853B2, 10 January 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Aaqillah-Amr, M.A.; Hidir, A.; Noordiyana, M.N.; Ikhwanuddin, M. Morphological, biochemical and histological analysis of mud crab ovary and hepatopancreas at different stages of development. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2018, 195, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghittino, P. Formulation and technology of moist feed. In Finfish Nutrition and Fish Feed Technology; Halver, J.E., Tiews, K., Eds.; Heinemann: Berlin, Germany, 1979; pp. 37–40. [Google Scholar]
- Parvathi, K.; Jayaprakash, S.; Jeyakumar, P.; Kalaimani, C.; Sivakumar, P.; Kalaimani, S.; Venkatachalam, T. A Study on the Effect of Commercial Probiotics on Physico-Chemical Parameters of Ornamental fish (Puntius conchonius) culture water. Int. J. Curr. Res. 2017, 3, 1305–1310. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, F.A. Ornamental fish culture, freshwater. In Encyclopedia of Aquacult; Stickney, R.R., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 602–610. [Google Scholar]
- Pailan, G.H.; Sinha, A.; Kumar, M. Rose petals meal as natural carotenoid source in pigmentation and growth of rosy Barb (Puntius conchonius). Indian J. Anim. Nutr. 2012, 29, 291–296. [Google Scholar]
- Brahman, L.K.; Chandra, R. A comparative study on survival and growth of larvivorous fish, Rasboradaniconius, Puntiusticto, and Puntius conchonius. Int. J. Life Sci. 2014, 8, 180–183. [Google Scholar]
- Jagadeesh, T.D.; Murthy, H.S.; Surendranath, S.V.; Panikkar, P.; Manjappa, N.; Mahesh, V. Effects of supplementation of marigold (Tageteserecta) oleoresin on growth, survival and pigmentation of rosy barb, Puntius conchonius (hamilton). Int. Q. J. Life Sci. 2015, 10, 1431–1435. [Google Scholar]
- Santhosh, B.; Singh, N.P. Guidelines for Water Quality Management for Fish Culture in Tripura, ICAR Research Complex for NEH Region, Tripura Centre, Publication No. 29; New Manikya Press: Agartala, India, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Chandravanshi, S.K.; Dhar, B.; Majumdar, R.K.; Saha, A. Biochemical, textural and sensory analysis of paneer developed from mince of Pangasianodon hypophthalmus (Sauvage, 1878). Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2018, 6, 2071–2077. [Google Scholar]
- Lanier, T.C.; Hart, K.; Martin, R.E. Manual of Standard Methods for Measuring and Specifying the Properties of Surimi; National Fisheries Institute: Arlington, VA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Das, H.K.; Hattula, M.T.; Myllymäki, O.M.; Mälkki, Y. Effects of formulation and processing variables on dry fish feed pellets containing fish waste. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1993, 61, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, S.; Kamarudin, M.S.; Ramezani-Fard, E. Physical properties of extruded aquafeed with a combination of sago and tapioca starches at different moisture contents. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2013, 183, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barrera, A.M.; Ramırez, J.A.; González-Cabriales, J.J.; Vázquez, M. Effect of pectins on the gelling properties of surimi from silver carp. Food Hydrocoll. 2002, 16, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists International, 16th ed.; Cunnif, P.A., Ed.; AOAC Int.: Arlington, VA, USA, 1995; Volume 1, pp. 31–65. [Google Scholar]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Water Works Association: Denver, CO, USA; American Public Works Association: Kansas City, MO, USA; Water Environment Federation: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]




| Parameters | Concentration | Hardness (N) | Adhesiveness | Springiness | Cohesiveness | Gumminess (N) | Chewiness (N) | Resilience |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pectin | 2% | 28.9 ± 4 ab | −21.3 ± 13.9 | 0.7 ± 0.1 b | 0.3 ± 0.1 f | 8.4 ± 0.9 cd | 5.9 ± 0.7 b | 0.09 ± 0.02 cd |
| 5% | 19.4 ± 1.8 de | −22.1 ± 1.4 | 0.5 ± 0.01 b | 0.3 ± 0.1 f | 6.3 ± 1.6 d | 3.4 ± 0.9 b | 0.08 ± 0.01 d | |
| 8% | 15.5 ± 0.8 e | −6.6 ± 3.7 | 0.61 ± 0.02 b | 0.34 ± 0.02 ef | 5.3 ± 0.3 d | 3.3 ± 0.2 b | 0.12 ± 0.0 bcd | |
| Calcium lactate | 2% | 21.2 ± 2.5 cde | −10.8 ± 5.2 | 0.7 ± 0.03 b | 0.4 ± 0.01 def | 7.8 ± 0.7 cd | 5.5 ± 0.5 b | 0.10 ± 0.01 cd |
| 5% | 28.5 ± 2.3 ab | −14 ± 1.4 | 0.8 ± 0.01 b | 0.4 ± 0.0 de | 11.3 ± 1 bc | 9.4 ± 0.8 b | 0.09 ± 0.0 cd | |
| 8% | 31.1 ± 7.7 a | −7.8 ± 2.9 | 1.8 ± 1.6 a | 0.6 ± 0.06 ab | 17.8 ± 6.1 a | 32.7 ± 32.4 a | 0.2 ± 0.04 a | |
| Starch | 2% | 27.8 ± 5.2 abc | −35.6 ± 47.7 | 0.8 ± 0.04 b | 0.4 ± 0.03 cd | 12.3 ± 2.7 bc | 9.6 ± 2.4 b | 0.02 ± 0.02 b |
| 5% | 24.5 ± 4.2 abcd | −24.2 ± 7.6 | 0.78 ± 0.1 b | 0.5 ± 0.02 c | 11.6 ± 1.8 bc | 9.2 ± 2.5 b | 0.02 ± 0.02 bc | |
| 8% | 22.8 ± 1 bcde | −9.5 ± 2.1 | 0.9 ± 0.1 b | 0.6 ± 0.04 a | 13.6 ± 1.4 b | 11.9 ± 1.4 b | 0.03 ± 0.03 a | |
| Control | 0% | 17.5 ± 3.6 de | −8.8 ± 6.1 | 0.8 ± 0 b | 0.5 ± 0.03 bc | 8.8 ± 1.4 cd | 6.9 ± 1 b | 0.02 ± 0.02 b |
| p-value | Gelling | 0.018 | 0.296 | 0.164 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.079 | <0.001 |
| Conc. | 0.305 | 0.148 | 0.258 | <0.001 | 0.042 | 0.141 | <0.001 | |
| G × C 1 | <0.001 | 0.790 | 0.333 | 0.031 | <0.05 | 0.130 | 0.031 |
| Parameters | Concentration | L* (Lightness) | a* (Redness/ Greenness) | b* (Yellowness/ Blueness) | Whiteness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pectin | 2% | 63.7 ± 0.2 a | 24.6 ± 0.1 e | 33.5 ± 0.2 ef | 44.8 ± 0.3 b |
| 5% | 61.8 ± 0.3 c | 24.9 ± 0.1 d | 33.7 ± 0.5 e | 43.3 ± 0.2 c | |
| 8% | 61.9 ± 0.4 c | 25.02 ± 0.2 d | 33.5 ± 0.7 ef | 43.4 ± 0.3 c | |
| Calcium lactate | 2% | 62.6 ± 0.3 b | 21.9 ± 0.2 f | 31 ± 0.2 g | 46.7 ± 0.3 a |
| 5% | 56.4 ± 0.2 f | 34.8 ± 0.2 a | 39.5 ± 0.2 a | 31.7 ± 0.1 g | |
| 8% | 60.2 ± 0.2 d | 28.3 ± 0.2 c | 36.8 ± 0.2 c | 38.9 ± 0.1 f | |
| Starch | 2% | 59.6 ± 0.4 e | 28.09 ± 0.1 c | 35.5 ± 0.6 d | 39.3 ± 0.2 e |
| 5% | 56.01 ± 0.3 f | 24.8 ± 0.4 de | 32.9 ± 0.3 f | 39.7 ± 0.1 d | |
| 8% | 53.6 ± 0.2 g | 33.6 ± 0.2 b | 38.7 ± 0.3 b | 30.8 ± 0.1 h | |
| Control | 0% | 62.5 ± 0.2 b | 21.6 ± 0.2 f | 30.9 ± 0.1 g | 46.8 ± 0.02 a |
| p-value | Gelling | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Conc. | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| G × C 1 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Parameters | Concentration | Protein | Lipid | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 h | 12 h | 18 h | 24 h | 6 h | 12 h | 18 h | 24 h | ||
| Pectin | 2% | 0.4 ± 0.09 ab | 0.6 ± 0.2 ab | 0.9 ± 0.3 abcd | 1.4 ± 0.06 ab | 6 h | 12 h | 18 h | 24 h |
| 5% | 0.2 ± 0.07 abc | 0.5 ± 0.03 ab | 0.7 ± 0.2 bcde | 1.06 ± 0.4 abcd | 13.3 ± 11.5 | 13.3 ± 11.5 | 21.7 ± 2.9 | 28.3 ± 10.4 ab | |
| 8% | 0.1 ± 0.1 bc | 0.4 ± 0.1 b | 0.6 ± 0.3 cde | 0.8 ± 0.4 bcd | 4.2 ± 7.2 | 4.2 ± 7.2 | 13.09 ± 12.5 | 22.8 ± 12.8 b | |
| Calcium lactate | 2% | 0.4 ± 0.2 ab | 0.8 ± 0.4 a | 1.2 ± 0.2 a | 1.5 ± 0.2 a | 4.8 ± 8.2 | 4.8 ± 8.2 | 9.5 ± 8.2 | 14.3 ± 14.3 b |
| 5% | 0.2 ± 0.1 bc | 0.3 ± 0.02 b | 0.5 ± 0.06 e | 0.6 ± 0.1 d | 6.7 ± 11.5 | 6.7 ± 11.5 | 24.4 ± 21.4 | 24.4 ± 21.4 b | |
| 8% | 0.1 ± 0.1 c | 0.3 ± 0.1 b | 0.5 ± 0.1 de | 0.7 ± 0.2 cd | 5.5 ± 9.6 | 11.1 ± 9.6 | 16.7 ± 16.7 | 16.7 ± 16.7 b | |
| Starch | 2% | 0.4 ± 0.2 ab | 0.8 ± 0.06 a | 1.02 ± 0.1 abc | 1.2 ± 0.07 abc | 4.8 ± 8.2 | 4.8 ± 8.2 | 9.5 ± 16.5 | 24.5 ± 4.3 b |
| 5% | 0.2 ± 0.03 bc | 0.3 ± 0.05 b | 0.4 ± 0.2 e | 0.6 ± 0.2 d | 13.9 ± 12.7 | 13.9 ± 12.7 | 33.3 ± 14.4 | 36.1 ± 12.7 ab | |
| 8% | 0.2 ± 0.09 abc | 0.4 ± 0.2 b | 0.7 ± 0.4 bcde | 0.7 ± 0.5 cd | 6.7 ± 11.5 | 6.7 ± 11.5 | 15 ± 13.2 | 32.8 ± 7.5 ab | |
| Control | 0% | 0.4 ± 0.09 a | 0.8 ± 0.2 a | 1.1 ± 0.3 ab | 1.7 ± 0.6 a | 12.2 ± 10.7 | 12.2 ± 10.7 | 18.9 ± 1.9 | 37.8 ± 3.8 ab |
| p-value | Gelling | 0.791 | 0.957 | 0.931 | 0.907 | 0.528 | 0.697 | 0.337 | 0.018 |
| Conc. | 0.004 | <0.001 | <0.05 | 0.122 | 0.454 | 0.617 | 0.286 | 0.946 | |
| G × C 1 | 0.899 | 0.389 | 0.660 | 0.401 | 0.921 | 0.710 | 0.755 | 0.512 | |
| Parameters | Concentration | Moisture | Protein | Lipid | Ash |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pectin | 2% | 71.6 ± 1.5 ab | 36.8 ± 0.4 b | 4.7 ± 0.6 bc | 10.9 ± 0.2 d |
| 5% | 70.8 ± 1.7 ab | 33.8 ± 0.6 cd | 7 ± 1 a | 8.9 ± 1.4 e | |
| 8% | 72.4 ± 7.6 ab | 34 ± 0.7 cd | 6.3 ± 1.2 ab | 9 ± 0.5 e | |
| Calcium lactate | 2% | 74.5 ± 1.8 a | 38.8 ± 0.5 a | 4 ± 1 c | 12.8 ± 0.03 c |
| 5% | 71.2 ± 1.6 ab | 39.9 ± 0.9 a | 5.7 ± 0.6 abc | 15.9 ± 0.9 a | |
| 8% | 67.3 ± 6.1 b | 39.6 ± 0.9 a | 5.3 ± 1.5 abc | 14.4 ± 0.1 b | |
| Starch | 2% | 75.3 ± 2.6 a | 34.5 ± 1.5 c | 4.7 ± 1.2 bc | 12.7 ± 0.8 c |
| 5% | 72.1 ± 0.1 ab | 37.1 ± 0.8 b | 4 ± 1 c | 7.8 ± 0.04 f | |
| 8% | 72.1 ± 0.8 ab | 35.9 ± 0.6 b | 5.3 ± 0.6 abc | 8.4 ± 0.2 ef | |
| Control | 0% | 75.4 ± 0.5 a | 32.5 ± 0.9 d | 4.7 ± 1.2 bc | 10.2 ± 0.4 d |
| p-value | Gelling | 0.400 | <0.001 | 0.030 | <0.001 |
| Conc. | 0.130 | 0.602 | 0.035 | <0.001 | |
| G × C 1 | 0.355 | <0.001 | 0.153 | <0.001 |
| Feed Composition | (%) | P-2% | P-5% | P-8% | CL-2% | CL-5% | CL-8% | S-2% | S-5% | S-8% | C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fish muscle (g) | 100 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 |
| Corn flour (g) | 12.5% | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Yeast (g) | 0.5% | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| Vitamin–mineral premix (g) | 1.25% | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Gelling agent (g) | - | 1.6 | 4 | 6.4 | 1.6 | 4 | 6.4 | 1.6 | 4 | 6.4 | 0 |
| Salt (g) | 2.5% | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lal, J.; Biswas, P.; Singh, S.K.; Debbarma, R.; Mehta, N.K.; Deb, S.; Sharma, S.; Waikhom, G.; Patel, A.B. Moving towards Gel for Fish Feeding: Focus on Functional Properties and Its Acceptance. Gels 2023, 9, 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9040305
Lal J, Biswas P, Singh SK, Debbarma R, Mehta NK, Deb S, Sharma S, Waikhom G, Patel AB. Moving towards Gel for Fish Feeding: Focus on Functional Properties and Its Acceptance. Gels. 2023; 9(4):305. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9040305
Chicago/Turabian StyleLal, Jham, Pradyut Biswas, Soibam Khogen Singh, Reshmi Debbarma, Naresh Kumar Mehta, Suparna Deb, Sanjeev Sharma, Gusheinzed Waikhom, and Arun Bhai Patel. 2023. "Moving towards Gel for Fish Feeding: Focus on Functional Properties and Its Acceptance" Gels 9, no. 4: 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9040305
APA StyleLal, J., Biswas, P., Singh, S. K., Debbarma, R., Mehta, N. K., Deb, S., Sharma, S., Waikhom, G., & Patel, A. B. (2023). Moving towards Gel for Fish Feeding: Focus on Functional Properties and Its Acceptance. Gels, 9(4), 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9040305








